Abstract
The skin healing benefits of rice have been known for centuries. Rice (Oryza sativa) water is a food processing waste that can potentially be incorporated into cosmetic formulations. However, no scientific evidence supports their role in skincare products. The aim of this project is to design and develop a topical gel formulation containing rice water and to evaluate its biological properties, namely, the anti-aging and antioxidant rice water properties. Rice water was evaluated in terms of physico-chemical composition and in terms of in vitro biological antioxidant activity and elastase inhibitory effect. Rice water was incorporated into a hydrogel and the developed formulation was subjected to pharmacotechnical tests such as pH and viscosity. Biological and sensory effects were evaluated on a panel of 12 volunteers for 28 days. The safety evaluation study was performed on rice water gel, using the Human Repeat Insult Patch test protocol. Rice water presented in vitro biological antioxidant activity and elastase inhibitory effect. The gel formulation containing 96% rice water was biocompatible with the human skin and presented suitable cosmetic properties. Rice water should be thus considered as an anti-aging ingredient to be used as raw material for skincare applications.
1. Introduction
Rice (Oryza sativa) is a fundamental food for almost half of the world’s population, supplying nearly all the daily calories especially in Asia. Rice water retained after soaking or boiling rice is commonly consumed but, in general, rice water is discarded in many food preparation procedures worldwide.
Rice bran oil is well known for its contents of antioxidant-rich components such as ferulic acid, gamma-oryzanol and phytic acid and has been used in the cosmetic industry [1] and also in the management of skin diseases [2]. Rice bran oil and rice bran extracts have been used in the free form and nanoencapsulated for protection against UVB-radiation injuries [3,4], for skin disease treatment [5,6]. Additionally, rice bran bioactive compounds have been found to exert anti-aging activity [7,8] and to be efficient in the treatment of alopecia [9]. Nevertheless, rice water skin benefits are supported by scarce scientific studies and there is a lack of scientific literature unveiling the skin effects largely claimed by cosmetic manufacturers. The empiric use of rice water as a bath component, especially among Asian women, became a tradition with a lack of scientific evidence.
The major component in rice grains, starch, is recommended to be added to bath water for the treatment of atopic dermatitis or skin diseases associated with pruritus [10]. Starch is a biodegradable polymer with safe application in the pharmaceutical industry [11] and it was demonstrated that glucose and mannose residues from polysaccharides could reduce inflammatory activity in vivo [12]. In a recent study, a formulation composed of starch-based nanocapsules incorporating an anti-inflammatory agent was tested in a mouse model of cutaneous inflammation and it was possible to observe the synergistic action of starch on the anti-inflammatory activity of the formulation [13].
In the last years, the search for new bioactive compounds to prevent skin aging has increased. In parallel, there is an increasing concern regarding products from natural origin, if possible, from organic farming in cosmetic products. Rice water is a natural, economic and simple ingredient that can be incorporated into skincare products. It can be obtained from different types of rice present in the human diet and also from rice residues resulting from the rice industry, as a way to transform it into an added-value product.
The main aim of this study was thus to develop a semi-solid dosage form incorporating rice water and to test such formulation on human skin to evaluate its biological and sensory effects. To carry out this proposal, rice water was prepared, physico-chemically characterized and tested in vitro for antioxidant activity and anti-aging effects. In this study paddy rice, with peel, was used to produce the rice water, in order to maintain all the rice components. The rice water presenting the best antioxidant activity was incorporated in a hydrogel formulation with very few ingredients in order to incorporate almost 96% of the rice water in the composition. After the characterization of the hydrogel, biological and sensory effects and the safety of the formulation were evaluated in vivo, in human volunteers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Paddy rice, guadiagran variety, (batch n. 0539) was a gift from “Casa Agricola Quinta das Barracas da Rainha” (Coruche, Portugal). Purified water was obtained by reverse osmosis and electrodeionization (Millipore, Elix 3, Darmstadt, Germany) being afterwards filtered (pore 0.22 µm). LecigelTM (sodium acrylates copolymer and lecithin) and Dermosoft® OMP (methylpropanediol, caprylyl glycol and phenylpropanol) were obtained from Dr. Straetmans (Hamburg, Germany). Ascorbic acid and MTT (3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl- 2H-tetrazolium bromide) were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2-DCFDA) was obtained from Life Technologies (Paisley, UK). Spontaneously immortalized human keratinocyte cell lines HaCaT were from CLS (Eppelheim, Germany). Folin–Ciocalteu reagent was prepared according the requirements of Portuguese Pharmacopoeia 9.0. Human Neutrophil Elastase (HNE) was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). The conductivity standards (84, 147, 1413 and 12,880 µS/cm, 25 °C) were supplied by Reagecon (Shannon, Co. Clare, Ireland). The pH standards (pH 4, pH 7, pH 6 and pH 9) were supplied by Crison (Barcelona, Spain). All other reagents were of analytical grade and were used without further purification.
2.2. Rice Water Preparation by Three Different Procedures
Water prepared by the boiling process (RWB): 400 g of paddy rice whole grains were boiled in 1 L of deionized water for 30 min. Rice water was filtered through cotton gaze and frozen at −30 °C until used.
Water prepared with the intact grain (RWM): 400 g of paddy rice whole grains were mixed with 1 L of deionized and left to shake, at room temperature, for 24 h. Rice water was then filtered through cotton gaze and frozen at −30 °C until used.
Water prepared with the crushed grain (RWS): 400 g of paddy rice grains were grinded into smaller pieces using a kitchen robot, for 10 s, mixed with 1 L of deionized water and left to shake, at room temperature, for 24 h. Rice water was then filtered through cotton gaze and frozen at −30 °C until used.
2.3. Rice Water Characterization
2.3.1. Physical Characterization
The pH was determined using a combined glass electrode from Crison GLP 21 pH meter (Barcelona, Spain), with automatic temperature compensation. The conductivity was measured using the CyberScan CON 200 Conductivity meter (Eutech Instruments, Ayer Rajah Crescent, Singapore). The turbidimetry was determined using the TN 100 Infra-Red Turbidimeter (Eutech Instruments, Ayer Rajah Crescent, Singapore).
2.3.2. Dry Residue Assay
Five millilitres of sample were weighted to a porcelain capsule with 25 g of treated sea sand (granulometry: 0.25 a 0.35 mm). The capsule and its contents, including a small glass rod, were dried in the oven at 102 ± 2 °C for 2 h. Then the capsule and its contents were cooled in the desiccator to room temperature and weighted again. After drying the systems in the oven, for one more hour, it was cooled in the desiccator and weighted again. The process was carried out with successive dryings at the same temperature, followed by cooling in the desiccator, until two successive weighings did not differ more than 0.5 mg.
2.3.3. Carbohydrates Determination by Phenol Sulphuric Acid Method
Carbohydrates determination was performed according to the methods published elsewhere [14]. Concentrated sulphuric acid (5 mL) was rapidly added to a solution of 1 mL of sample/standard and 1 mL of 5% (w/v) phenol was then added. Because the reaction is exothermic, the test tubes were cooled to room temperature before spectrophometric readings. The change of the colour’s solution was measured in the region of the visible and it was proportional to the amount of sugars present in the sample. The absorbance was measured at 490 nm against purified water as reagent blank using a spectrophotometer HITACHI U-2000 (Tokyo, Japan). A calibration curve ranging from 6 mg/L to 60 mg/L of glucose was used.
2.3.4. Total Protein by Kjeldahl Method
Mineralization
An amount of 20 mL of rice water, the catalyst tablet (copper catalyst) and the antifoam agent (silicon) were introduced into a Kjeldahl digestion flask [15]. Twenty millilitres of concentrated sulfuric acid (ρ20 = 1.84 g/cm3, ≥98%) were carefully added. The Kjeldahl digestion flask was placed on the heating device (digestion apparatus, Selecta, Barcelona, Spain) and heated at 400 °C for 45 min until the liquid was completely clear (characteristic emerald green colour).
Distillation
The content of the Kjeldahl digestion flask was cooled to room temperature and 50 mL of purified water were added. The Kjeldahl flask was mixed and placed on the Kjeltec System 1002 Distilling unit (Tecator, Apeldoorn, Nederland). Eighty millilitres of 40% (w/v) sodium hydroxide solution were added to the Kjeldahl tube and the distillation started and took place until approximately 150 mL of the distillate were collected. The distillate was collected on 50 mL of 4% (w/v) boric acid solution with 4 drops of Kjeldahl indicator. The distillate was titrated with 0.1 N sulphuric acid. The end point was given by the passage from green to violet. Phenylalanine was used as a mineralization control.
2.3.5. Analysis of Fat by Rose Gottlieb Method
For this analysis, the Rose Gottlieb method was used [16]. An amount of 15 mL of rice water was placed into a decantation ampoule and weighted. An amount of 2 mL of ammonium hydroxide (25% (w/w) was added and mixed, then 10 mL of 96% (v/v) ethyl alcohol were added and mixed thoroughly. Twenty millilitres of ethyl ether were added and stirred vigorously for 1 min and 25 mL of petroleum ether were added and the mixture was stirred gently for 30 s. The mixture was left standing until clear separation of the ethereal from aqueous layers. Two further extractions of the aqueous phase were done as before but using only 15 mL of ethyl ether and 15 mL of petroleum ether and always keeping the ethereal phase in the same flask. The contents of the flask were evaporated on a rotary evaporator (60 °C) and the flask was dried in an oven at 105 °C for successive periods of 1 h until two successive weighings did not differ more than 0.5 mg.
2.3.6. Total Phenolic Compounds by Folin–Ciocalteu Method
Total phenolic compounds were measured in rice waters samples by the Folin–Ciocalteu method. Folin–Ciocalteu reagent was prepared according the requirements of Portuguese Pharmacopoeia 9.0. Folin–Ciocalteu reagent (1 mL) was added to an aliquot (3 mL) of the target rice water diluted to 25 mL. The solution was shaken vigorously and allowed to stand for three min. Sodium carbonate solution (4 mL) was added and the sample again was shaken and allowed to stand for thirty minutes. The absorbance was measured at 760 nm by UV/VIS Spectrophotometer (Hitachi U-2000, Tokyo, Japan). A blank was also performed. The pyrogallol was used as reference standard of phenolic content. The calibration curve for pyrogallol was found to be linear in the range of 0.5 to 8 mg/L. The coefficient of determination (r2) of 0.998 indicates the good linearity between the concentration and absorbance. The method was validated for precision and accuracy by duplicate determinations and standard controls.
2.3.7. In Vitro Studies
Cell Viability
The cytotoxicity of rice water was evaluated using general cell viability endpoint MTT reduction and it was performed according to a previous reported work [17]. Cell viability was assessed after 24 h of incubation of a spontaneously immortalized human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT (CLS, Eppelheim, Germany) with different dilutions (up to 1:100) of rice water. HaCaT cells were seeded in sterile flat-bottom 96-well tissue culture plates (Greiner, Kremsmünster, Austria), in RPMI 1640 culture medium (Life Technologies, Paisley, UK), supplemented with 10% Fetal serum bovine, 100 units of penicillin G (sodium salt) and 100 μg of streptomycin sulfate and 2 mM L-glutamine (Life Technologies, Paisley, UK), at a cell density of 2 × 105 cells/mL, 100 µL/well. Cells were incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Negative control was the culture medium and positive control sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) at 1 mg/mL. After the time of exposition, the MTT assay was performed. Medium was replaced by medium containing 0.25 mg/mL MTT. The cells were incubated again for 3 h. Afterwards, the medium was removed and the intracellular formazan crystals were solubilized and extracted with 100 μL dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). After 15 min in continuous stirring at room temperature, the absorbance was measured at 570 nm in FLUOstar Omega BMGLabtech Microplate Reader (FLUOstar BMGLabtech, Offenburg, Germany).
The relative cell viability (%) compared to control cells was calculated for the MTT assay using the following equation:
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production Measurement
The capacity of rice water to reduce the ROS production was evaluated through a fluorimeter technique that uses 2,7’ dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2-DCFDA) to quantify the intracellular ROS production, according to the method described elsewhere [17]. Briefly, for this measurement, HaCaT sub-confluent cells grown in 96-well plates, which were incubated for 30 min with 20 μM of H2-DCFDA in the dark, at 37 °C, were used. Later, the medium was removed and fresh medium was added to the cells before being exposed to different concentrations of extracts and ascorbic acid for 1 h. In the case of the hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) assay, H2O2 in a final concentration of 500 µM was added simultaneously with the samples in study and it was used as a positive control, once it induces the intracellular ROS production in cells. For the UV assay, three UV-B lamps (Sankyo Denki G8T5E, Kanagawa, Japan) with a peak emission at 312 nm were used as the UV-B source, and measured with a VLX 312 radiometer equipped with a UV-B sensor (Vilber Lourmat, Marne-la-Vallée France). The cells with the rice water were irradiated with a UV-B single dose of 26 mJ/cm2 for 15 min. In each assay, ROS levels were determined at 485 nm and 520 nm, as excitation and emission wavelengths, respectively, using a florescence microplate reader (FLUOstar BMGLabtech, Offenburg, Germany). Data collected from at least six replicates is expressed as percentage of reduction of ROS.
Enzymatic Inhibition Assay
Fluorometric assays for the HNE inhibition activity were carried out in 200 μL assay buffer (0.1 M HEPES pH 7.5 at 25 °C) containing 20 μL of 0.17 μM HNE (stock solution 1.7 μM in 0.05 M acetate buffer, pH 5.5), 155 μL of assay buffer and 5 μL of each concentration of tested inhibitors. After 30 min of incubation at 25 °C, the reaction was initiated by the addition of 20 μL of fluorogenic substrate to a final concentration of 200 μM (MeO-Suc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val-AMC, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). The Michaelis–Menten constant (Km) of this substrate of HNE was previously determined to be 185 μM (data not shown). For all assays, saturated substrate concentration was used throughout in order to obtain linear fluorescence curves. Controls were performed using enzyme alone, substrate alone, enzyme with DMSO and a positive control (Sivelestat sodium salt hydrate, Sigma Aldrich Quimica S.L., Lisbon, Portugal) [18].
2.3.8. Antimicrobial Activity
The antimicrobial activity was screened against Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Candida albicans ATCC 10231, Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 16404 and Escherichia coli ATCC 87394. The microorganism inoculum was prepared from 18 h broth culture and the suspension was adjusted to a turbidity of 0.5 McFarland (~1.5 × 108 colony-forming units (cfu/mL). Then, the Mueller–Hinton agar (MHA) (Thermo Scientific™ Oxoid™, Hampshire, UK) was poured into petri dishes and inoculated with 100 μL of the suspension containing ~1.5 × 108 cfu/mL of microorganisms. Sterile paper discs (6 mm; Thermo Scientific™ Oxoid™, Hampshire, UK) were loaded with 15 μL of rice waters. After incubation (37 °C, 24 or 48 h), the mean of the inhibition zone diameters were calculated. Each assay was performed in triplicate.
2.4. Rice Water Gel (RWG) Preparation
Based on the results obtained from several physico-chemical characterization assays, RWB was selected for the preparation of the rice water gel (RWG). The composition of the RWG and the control gel is presented in Table 1. DermosoftTM OMP (Evonik Dr. Straetmans GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) was firstly dispersed in the rice water and the gelling agent, Lecigel® (Lucas Meyer Cosmetics, Champlan, France), was added and mixed with vigorous stirring to allow for the formation of a hydrogel. A control gel containing deionized water instead of rice water was also prepared to compare the results of in vivo performed studies.

Table 1.
Qualitative and quantitative composition of the prepared rice water gel (RWG) and control hydrogel (HG).
2.5. Rice Water Gel Physico-Chemical Characterization
Macroscopic organoleptic characteristics of the gel (colour, odour and appearance) were analysed. The pH was determined using a 713 pH meter from Metrohm (Filderstadt, Germany), at a temperature of 20 °C. The rheological profiles of RWG and control gel were evaluated at room temperature using a Brookfield Rotation Viscosimeter®, RV DV-II, SSA with a spindle 07 (Brookfield Engineering Laboratories, Middleborough, Massachusetts, USA). The shear rate [1/s] versus shear stress [Pa] plots (flow curves) were obtained by submitting the samples to a shear rate sweep from 0.61 to 122/s up and down. This means that the angular velocities varied from 0.5 rpm to 100 rpm and each one was read after 30 s, and then reversed the velocity to the initial.
2.6. In Vivo Studies
2.6.1. Local Compatibility Tests on Human Skin (HRIPT)
The compatibility evaluation study was performed on RWG, using the Marzulli and Maibach method [19]. Human Repeat Insult Patch Test (HRIPT) protocol, as described in detail elsewhere [17], was performed to evaluate the RWG irritant capacity. This protocol was approved by the local Ethical Committee and respected the Helsinki Declaration and the French Agency for the Safety of Health Products regulations on performed HRIPT studies on cosmetic products. The study was conducted under the supervision of a dermatologist who participated in the evaluation of irritation/allergic reactions to the tested formulations.
2.6.2. Biological Effects of Rice Water Gel
Twelve healthy volunteers, aged between 21 and 46, were selected, and provided informed written consent. The protocol was approved by the local Ethical Committee (Lisbon, Portugal). Volunteers applied the RWG formulation on the forearm during 28 days and the results were compared with a defined control area (anatomically equivalent and without product). A placebo formulation (Control Hydrogel-HG) was applied for the same period on the other forearm of the volunteers. The products were applied in an amount of 2 mg/cm2.
The epidermal capacitance and skin surface lipids were evaluated with a Corneometer CM820 and a Sebumeter SM810 (C+K Electronics GmbH, Cologne, Germany), respectively, at day 0, 14 and 28. Measurements were performed under standardized conditions, at room temperature according to the Good Clinical Practices rules [20].
2.6.3. Rice Water Gel Sensory Analysis
A sensory analysis was conducted according to ISO 11136:2014, using a panel of 12 volunteers. The panel was questioned to scale characteristics of the RWG. Each volunteer answered a few questions about the RWG sensory attributes, such as texture (consistency and stickiness), skin feel during application (ease of application, spreadability and oiliness), skin feeling after application (hydration, softness of the skin and freshness). Responses were given on a scale from 1 to 5. Sensory parameters were evaluated by a small amount of each formulation applied between the fingertips and rubbed into the skin.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Each value is the average of three different experiments ± standard deviation, except when referred within the text. Statistical analysis was assessed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using the Sigma Plot 11.0 software® (Systat Software GmbH, 11.0, Erkrath, Germany). The differences were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Rice Water
In this work, we prepared and characterized a liquid generally named as Rice Water that could be obtained by different methods but always involves the contact of water with rice grains. The preparation is empirically obtained in different regions of the globe and with different health purposes. In order to investigate which method would lead to a rice water with higher capacity of reducing the ROS production, three types of rice water were prepared: one was obtained by boiling the whole rice grain, another one by stirring the water in contact with crushed rice grains, and another one by stirring the water in contact with intact rice grain. After preparing the rice water, we observed higher turbidity for water prepared by the boiling process (RWB) and with the crushed grain (RWS) than for the water prepared with the intact grain (RWM). On the other hand, the water obtained from the crushed rice was milkier than the rice water obtained by boiling the rice. These observations were proven by the conductivity and turbidimetry assays, which results are present in Table 2.

Table 2.
Physical characterization results of water prepared by the boiling process (RWB), water prepared with the crushed grain (RWS) and water prepared with the intact grain (RWM).
3.2. Evaluation of Rice Water In Vitro Anti-Aging Properties
The total phenol contents of the rice waters are 3.33 ± 0.36, 3.15 ± 0.41 and 0.23 ± 0.01 mg/L for RWS, RWB and RWM, respectively. The total polyphenol content of rice waters was higher for RWS and RWB than for RWM, due to the water production method used.
Rice has been extensively studied due to the great quantity of bioactive compounds, due to the beneficial effects of these compounds on human skin, namely their antioxidant and other biological activities, such as enzyme inhibition. According to literature, cooking processes reduce only the average content of total phenolics in the pigmented rice; on the other hand, in non-pigmented rice, total phenolics compounds were not significantly affected by cooking, which is our case [21].
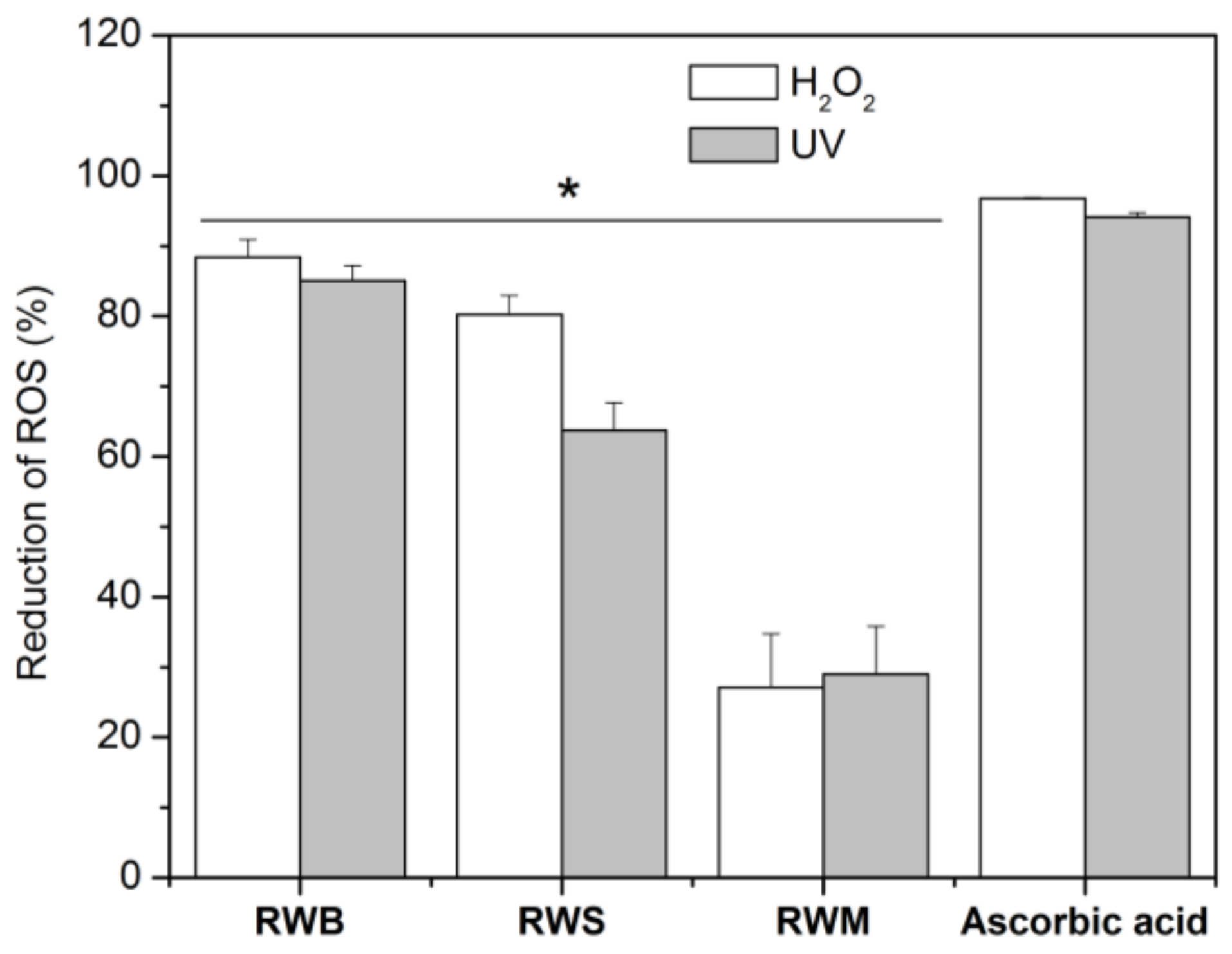
Phenolic compounds may act as antioxidants by different mechanisms, including free radical scavenging and inhibition of pro-oxidant enzymes, such as tyrosinase and elastase [7]. Thus, we further tested the rice water capacity of reducing intracellular generation of ROS induced both by a chemical compound (H2O2) or by UV light, assessed in vitro in human keratinocytes. The percentage of reduction of ROS by RWB is approximately 80% for both methods comparable to the values obtained for the positive control, ascorbic acid (Figure 1). All tested rice water samples presented a positive reduction, the RWM being the one presenting a lower effect.
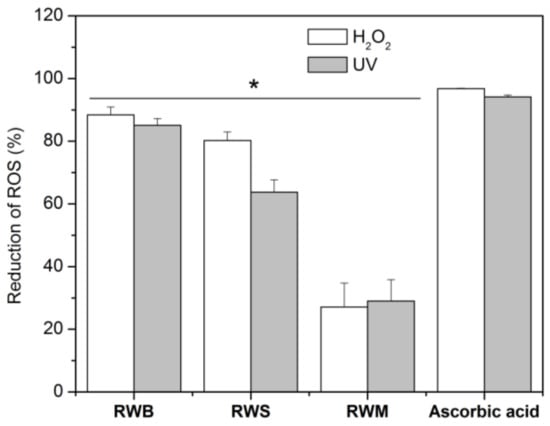
Figure 1.
Reactive Oxygen Species reduction after exposure to H2O2 and UVB radiation of HaCaT cells, containing rice water samples and ascorbic acid. The data are expressed as the mean of at least 6 replicate experiments ± standard deviation. Significance: (*) p < 0.05 versus positive control cells (ascorbic acid).
This antioxidant activity might be due to the transference to the water of several phenolic compounds identified in rice, tocopherols, tocotrienols and γ-oryzanol [22]. These results are also in accordance with the phenolic content in rice water samples obtained in this study.
Very high anti-elastase activities were exhibited by RWB and RWS, which inhibited over 89.0 and 57.9% of enzyme activity respectively. A relatively moderate anti-elastase activity was exhibited by RWM (24.2%).
In the MTT assay, the viable cells with active metabolism are capable of converting the MTT into a purple compound, the formazan, while the dead cells are incapable of converting it, which allows for the differentiation between the viable and dead cells. RWS, RWB and RWM showed a cell viability higher than 50%, while SDS showed 8.6% and the medium 100%. Hence, all rice waters can be considered as non-irritant. However, the HaCaT cell lines are more sensitive than skin, since skin has a functional barrier that prevents the total absorption of these compounds when applied to the skin. The rate-limiting barrier to the absorption of topical cosmetics is the stratum corneum, due to its length, which comprehends the number of cell layers, the thickness, the cell size and the difficulty of this pathway that the substances have to cross.
These assays were determinant for the selection of rice water to be further incorporated into a hydrogel. Considering the results, RWB was chosen to be the main ingredient of the gel composition.
The amount of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids were determined for RWB and the results obtained were 0.20%, 0.14% and 0.013%, respectively. These results may reflect the fact that we have used paddy rice for the rice water preparation as the rice pericarp prevents the release of the rice grain (white rice) components into the water. In addition, the content of insoluble phenolic compounds is significantly higher in brown rice than in white rice, a fact which also can prevent the release of rice components to the water [23].
We evaluated also the antimicrobial activity of rice waters prepared. None of them presented antibacterial or antifungal activity. However, according to other research studies, boiled rice water and soaked rice water showed antimicrobial and antifungal activity, due to zinc and selenium content present in these types of rice waters [24].
3.3. Preparation and Characterization of Rice Water Hydrogel
Semisolid dosage forms, such as a hydrogel, promote the consistency and the adhesiveness and could be more suitable for topical application than the liquid ones. The rice water presenting the best antioxidant and anti-elastase activity (RWB) was incorporated into a hydrogel formulation with very few ingredients in order to incorporate almost 96% of rice water into the composition.
After preparing the RWB hydrogel and the control hydrogel, both odour and transparency were consistent with the ingredients used. The hydrogel with rice water had a yellowish colour compared to the control hydrogel, whitish in colour.
The pH values of both formulations prepared ranged between 5.4 and 5.9, meaning they are all pH compatible with skin.
The hydrogel containing rice water also appeared to be more fluid than the control hydrogel. This might be due to the presence of phospholipids which results in low viscosity pastes and with lower transmittance power [25]. The hydrogel also had a homogeneous appearance and an appropriate consistency, but was easy to spread over a surface.
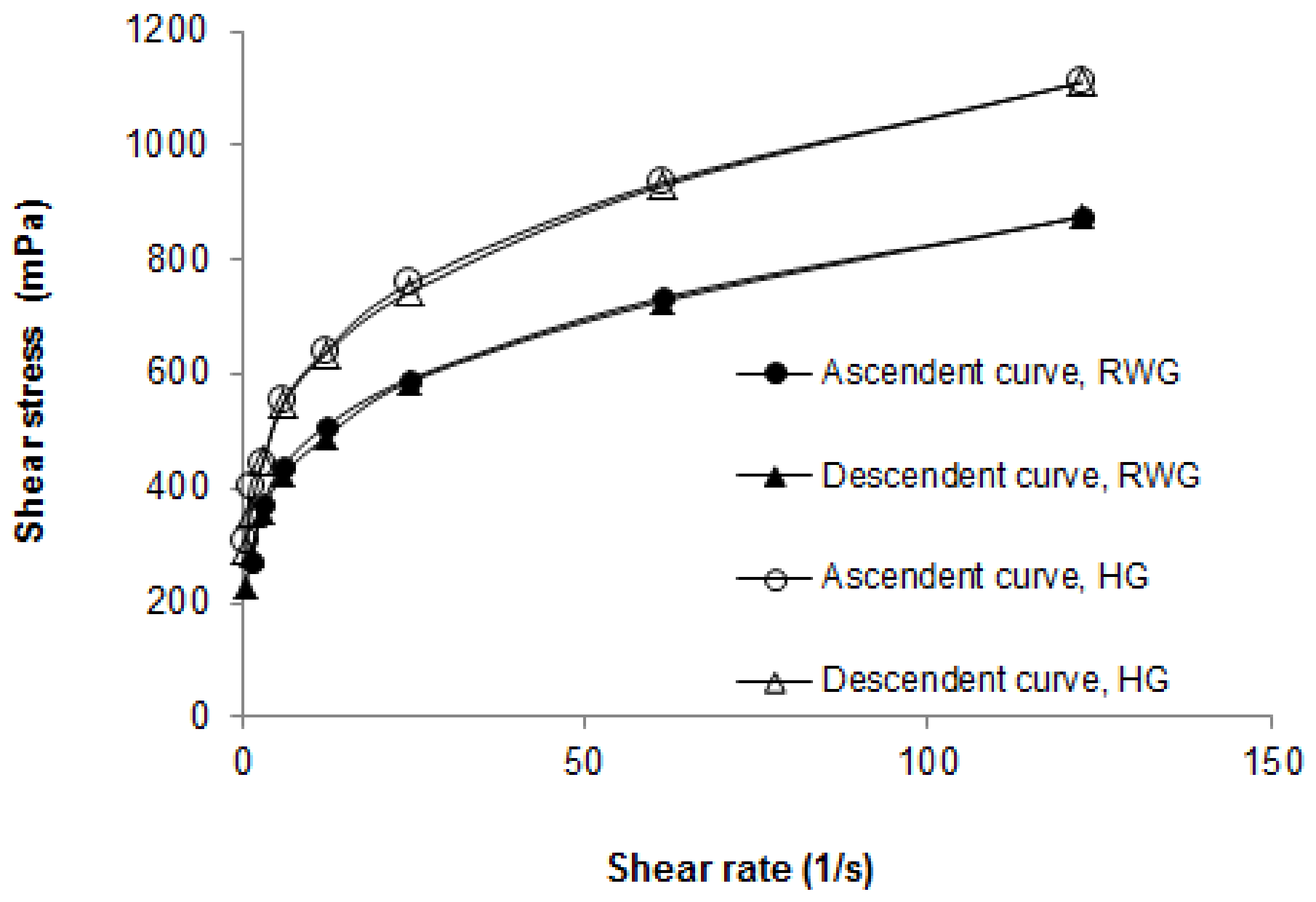
The rheology of the rice water hydrogel was studied since it is an important parameter in the development of a semisolid formulation for topical application as it determines the spreadability. The rice water hydrogel appeared to have pseudoplastic and thixotropic flow, as shown in Figure 2. In addition, the results presented in Figure 2 prove that the hydrogel containing rice water is less viscous than the control hydrogel, which is in agreement with that previously described. The results also indicate that the rice water hydrogel has a rheological profile adequate for topical application.
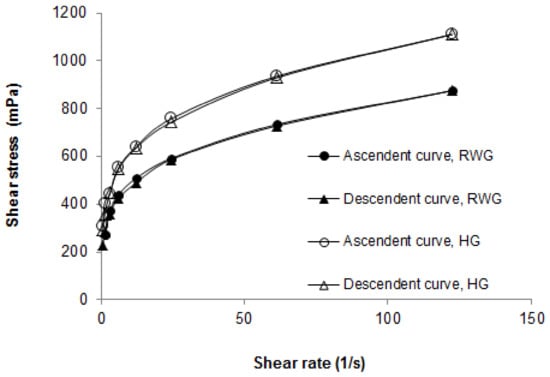
Figure 2.
Rheograms of the rice water hydrogel (RWG) and the control hydrogel (HG).
3.4. Biological Effects and Cosmetic Properties of Rice Water Hydrogel
During the HRIPT study, in the initial 3 weeks contact and even after the final challenge contact, no reactions or skin sensitization/irritation were observed. Therefore, the repeated application of the product did not induce any sensitization on the volunteers’ skin. The formulation presented very good skin compatibility and absence of allergenic potential.
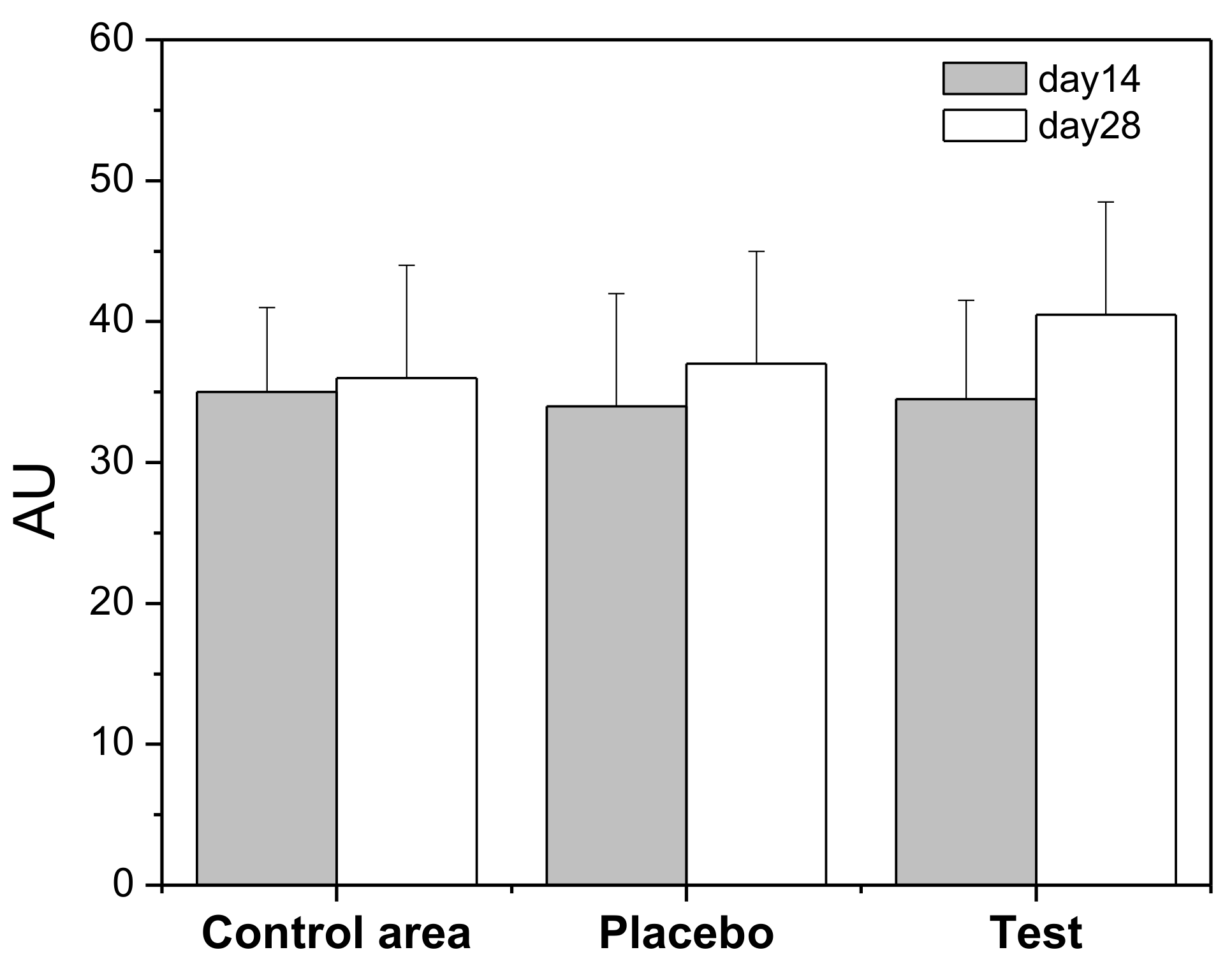
The skin is often exposed to physical and chemical agents which may affect the skin barrier. Corneometry is a technology that is used to measure the hydration of the outer layer of the epidermis (stratum corneum). Volunteers applied the Rice Water Gel (Test) formulation on the forearm during 28 days and the results were compared with a defined control area. A placebo formulation (HG) was applied for the same period on the other forearm of the volunteers. Results (Figure 3) showed, at day 28, a 10% increase of hydration in the area where the rice water hydrogel was applied, relative to day 14; however, there is no statistically significant difference between day 14 and day 28.
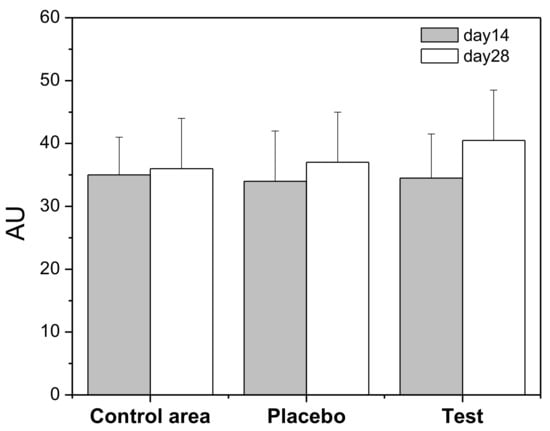
Figure 3.
Skin hydration values (Arbitrary Units, AU) in terms of capacitance during 28 days. Control area: forearm without any formulation application; Placebo: hydrogel; Test: Rice Water Gel (RWG).
Sebometry is a method employed for quantifying the fat content of the skin. Sebometry was measured in the same tested area and the results were zero at day 1, 14 and 28 for all volunteers, which means that rice water hydrogel did not significantly increase skin surface lipids compared to the control.
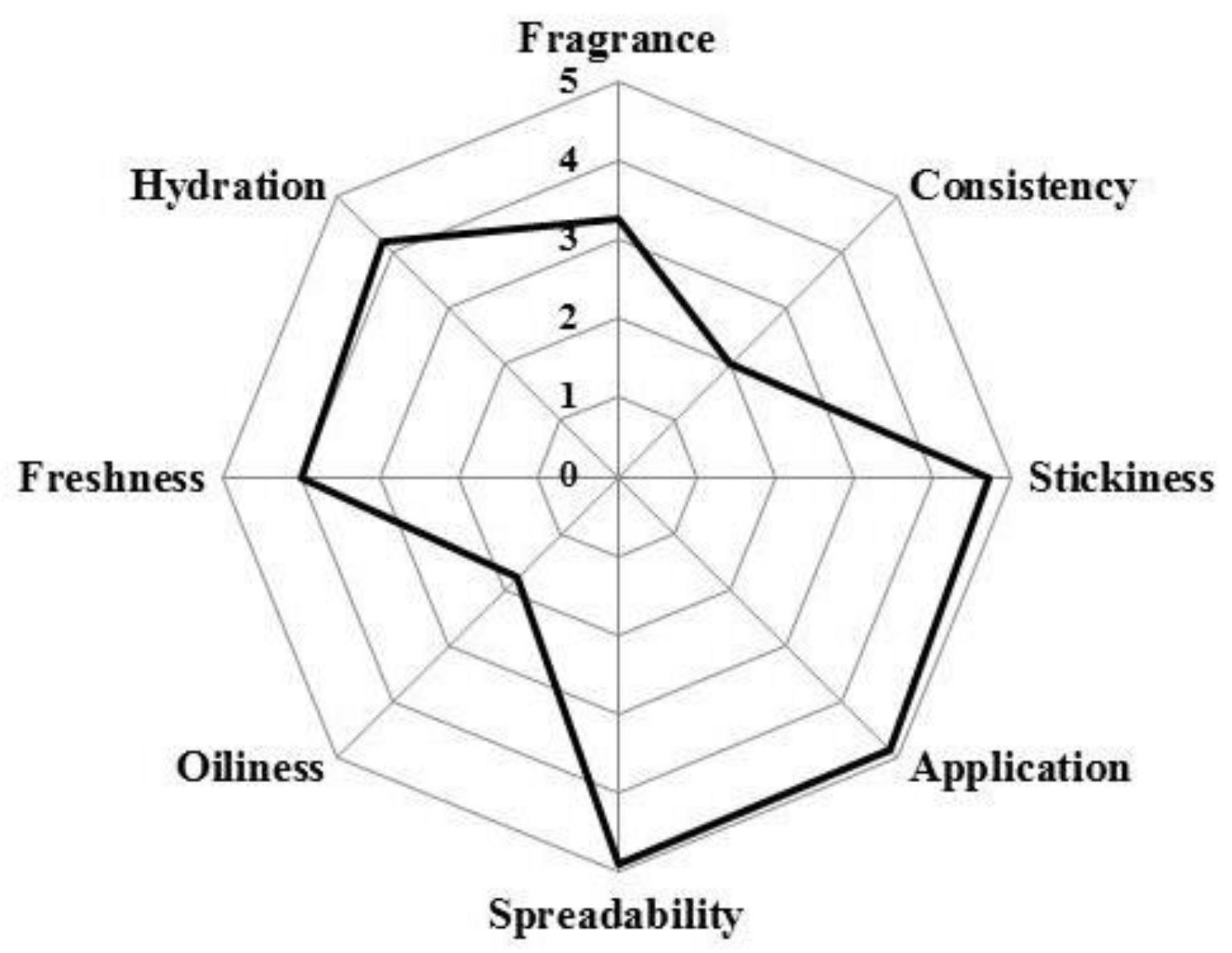
The cosmetic properties of the rice water hydrogel were assessed using a simple sensory survey, in which 12 volunteers participated. The questions focused on the basic characteristics evaluated by volunteers, during and after application (texture, skin feel, among others). Results showed that rice water hydrogel met consumer appeal and acceptance requirements (Figure 4). Rice water gel presents the highest score for spreadability, ease of application and stickiness, with a low score for the fragrance and oiliness. Hydration and freshness have also high scores. These observations are in agreement with the results obtained so far in corneometry and sebometry.
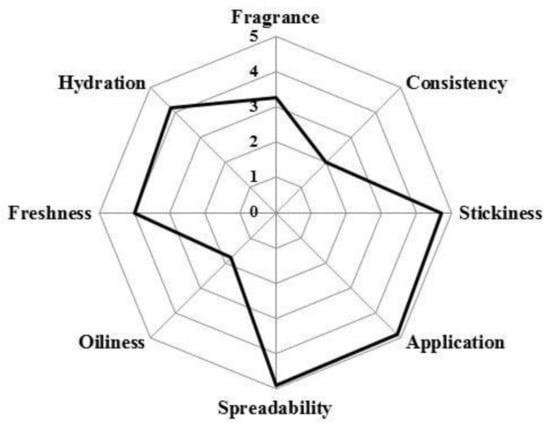
Figure 4.
Sensory analysis of the rice water hydrogel.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we produced rice water by different methods. The rice water obtained after boiling the rice presented in vitro biological antioxidant activity comparable to that of ascorbic acid and remarkable elastase inhibition activity. Its incorporation into a hydrogel formulation has led to the development of a semisolid dosage form suitable for topical application and with adequate cosmetic properties. It would be very important to identify the component or the class of compounds responsible for the antioxidant activity. Another important evaluation would be how such antioxidant activity could be used to supplement skin antioxidant capacity. Rice water should be thus considered as an anti-aging ingredient to be used in skincare products.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ana Neves and Casa Agricola Quinta das Barracas da Rainha for providing the paddy rice samples.
Author Contributions
Joana Marto and Sandra Simões conceived and designed the experiments; Joana Marto was responsible for the evaluation of antioxidant activity; Ângela Neves prepared rice water and made the sensory analysis evaluation; Lídia Maria Gonçalves evaluated elastase activity; Pedro Pinto was responsible for biological evaluation (HRIPT); Cristina Almeida performed physico-chemical characterization of rice water; Sandra Simões prepared rice water and rice water gel and was responsible for rice water characterization. All authors contributed to the manuscript preparation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the content of this article.
References
- Coppini, D.; Paganizzi, P.; Santi, P.; Ghirardini, A. Capacitá protettiva nei confronti delle radiazioni solari di derivati di origine vegetable. Cosm. News 2001, 136, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lerma-García, M.J.; Herrero-Martínez, J.M.; Simó-Alfonso, E.F.; Mendonça, C.R.B.; Ramis-Ramos, G. Composition industrial processing and applications of rice bran gamma-oryzanol. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.J.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Song, K.M.; Um, M.Y.; Cho, S.; Jung, S.K. Rice bran supplement prevents UVB-induced skin photoaging in vivo. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigo, L.A.; da Silva, C.R.; de Oliveira, S.M.; Cabreira, T.N.; de Bona da Silva, C.; Ferreira, J.; Beck, R.C. Nanoencapsulation of rice bran oil increases its protective effects against UVB radiation-induced skin injury in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, D.S.; Pereira, T.A.; Maciel, N.R.; Bortoloto, J.; Viera, G.S.; Oliveira, G.C.; Rocha-Filho, P.A. Formation and stability of oil-in-water nanoemulsions containing rice bran oil: In vitro and in vivo assessments. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, E.; Lee, C.H.; da Jeong, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, T.H.; Roh, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Rhee, M.H. Fermented rice bran prevents atopic dermatitis in DNCB-treated NC/Nga mice. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 30, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Lourith, N.; Chaikul, P. Jasmine rice panicle: A safe and efficient natural ingredient for skin aging treatments. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manosroi, A.; Chutoprapat, R.; Abe, M.; Manosroi, W.; Manosroi, J. Anti-aging efficacy of topical formulations containing niosomes entrapped with rice bran bioactive compounds. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Park, J.B.; Moon, W.S.; Moon, J.N.; Son, S.W.; Kim, M.R. Safety and efficacy of rice bran supercritical CO2 extract for hair growth in androgenic alopecia: A 16-week double-blind randomized controlled trial. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paepe, K.; Hachem, J.P.; Vanpee, E.; Roseeuw, D.; Rogiers, V. Effect of rice starch as a bath additive on the barrier function of healthy but SLS-damaged skin and skin of atopic patients. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2002, 82, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwunobi, A.P.; Emeje, M.O. Recent applications of natural polymers in nanodrug delivery. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, S4, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacki, N.; Gloaguen, V.; Damas, J.; Hoffmann, L.; Tits, M.; Angenot, L. Inhibition of croton oil-induced oedema in mice ear skin by capsular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 361, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marto, J.; Ruivo, E.; Lucas, S.D.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Simões, S.; Gouveia, L.F.; Felix, R.; Moreira, R.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Almeida, A.J. Starch nanocapsules containing a novel neutrophil elastase inhibitor with improved pharmaceutical performance. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.M.; Barbano, D.M. Kjeldahl nitrogen analysis as a reference method for protein determination in dairy products. JAOAC Int. 1999, 82, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, C. Use of the Rose-Gottlieb method for rapid gravimetric fat determination with the Heraeus apparatus. Deutsche Milchwirtschaft 1970, 21, 797–798. [Google Scholar]
- Marto, J.; Ascenso, A.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Gouveia, L.F.; Manteigas, P.; Pinto, P.; Oliveira, E.; Almeida, A.J.; Ribeiro, H.M. Melatonin-based pickering emulsion for skin’s photoprotection. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, S.D.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Carvalho, L.A.; Correia, H.F.; Da Costa, E.M.; Guedes, R.A.; Moreira, R.; Guedes, R.C. Optimization of O3-acyl kojic acid derivatives as potent and selective human neutrophil elastase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9802–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzulli, F.N.; Maibach, H.I. Contact allergy: Predictive testing in man. Contact Dermatitis 1976, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICHE6(R1). ICH harmonised tripartite guideline: Guideline for good clinical practice E6 (R1), in International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. 1996. Available online: https://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Efficacy/E6/E6_R1_Guideline.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- Massaretto, I.L.; Alves, M.F.; Mira, N.V.; Carmona, A.K.; Marquez, U.M. Phenolic compounds in raw and cooked rice (Oryza sativa L.) and their inhibitory effect on the activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 54, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.; Marchesan, E. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of rice. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Nakamura, K.; Kayahara, H. Analysis of phenolic compounds in white rice, brown rice, and germinated brown rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4808–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, S.; Das, A.; Bhattacharjee, C. Physico-chemical properties of different kind of rice water and their effect on diarrhoea causing bacteria and dandruff causing fungi. J. Phytol. 2011, 3, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Alcázar-Alay, S.; Almeida Meireles, M.A. Physicochemical properties, modifications and applications of starches from different botanical sources. Food Sci. Technol. Campinas 2015, 35, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).