Impact of Cosmetic Lotions on Nanoparticle Penetration through ex Vivo C57BL/6 Hairless Mouse and Human Skin: A Comparison Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Quantum Dot (QD) Functionalization
2.2. Skin Preparation
2.2.1. Mouse Skin
2.2.2. Human Skin
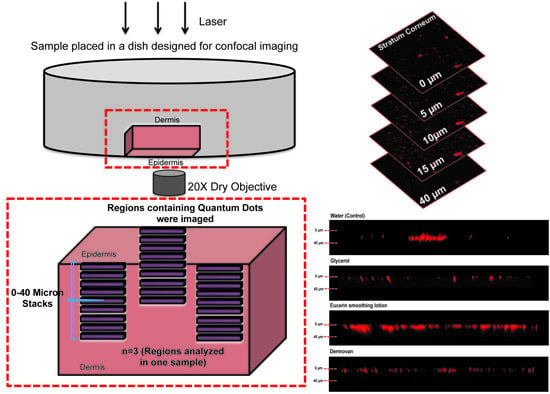
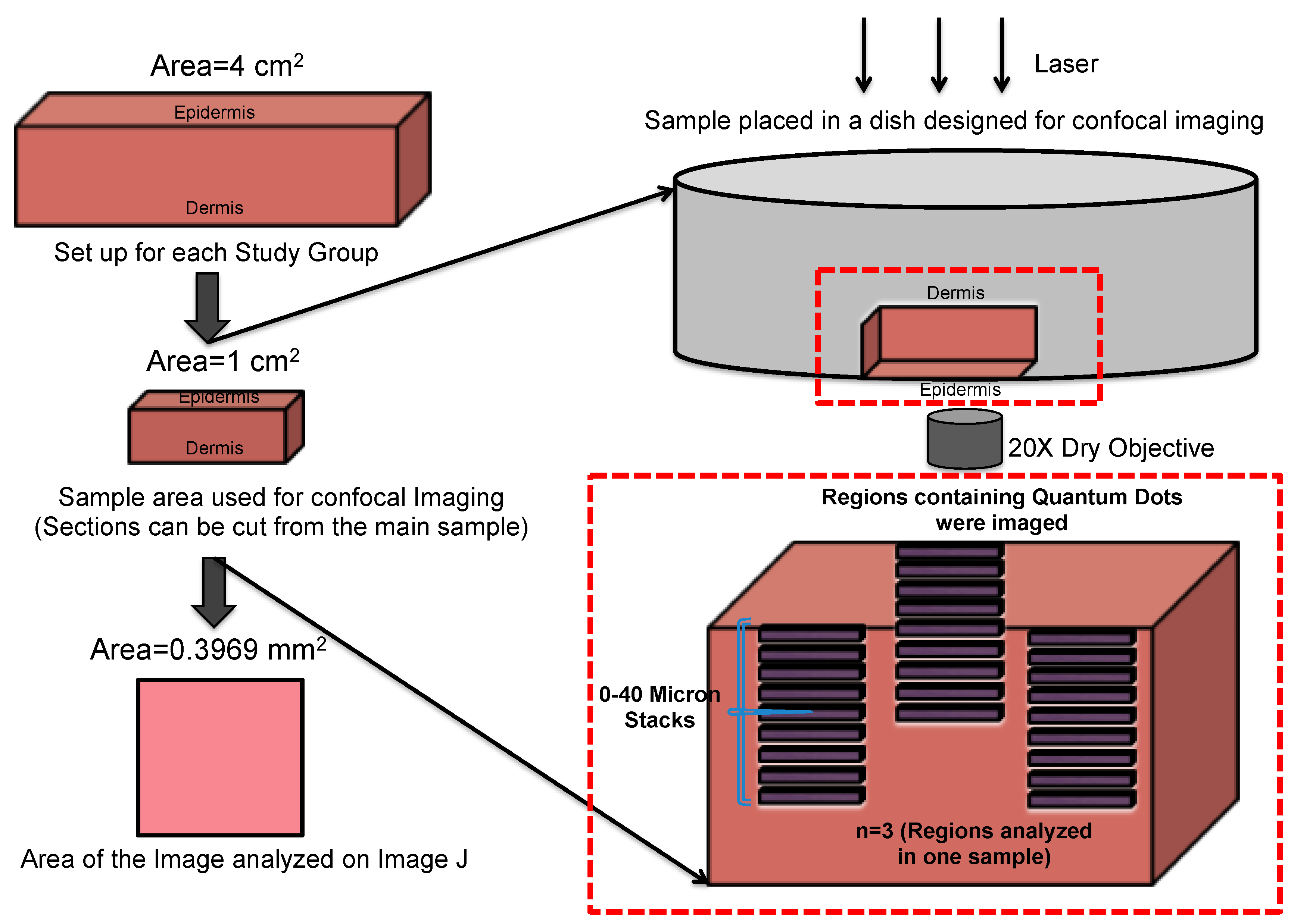
2.3. Ex Vivo Skin QD Exposure Experimental Protocol
2.4. Validation of the Imaging Technique: Diffusion and Injection of QDs in ex Vivo Human Skin
2.5. Confocal Microscopy and Image Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
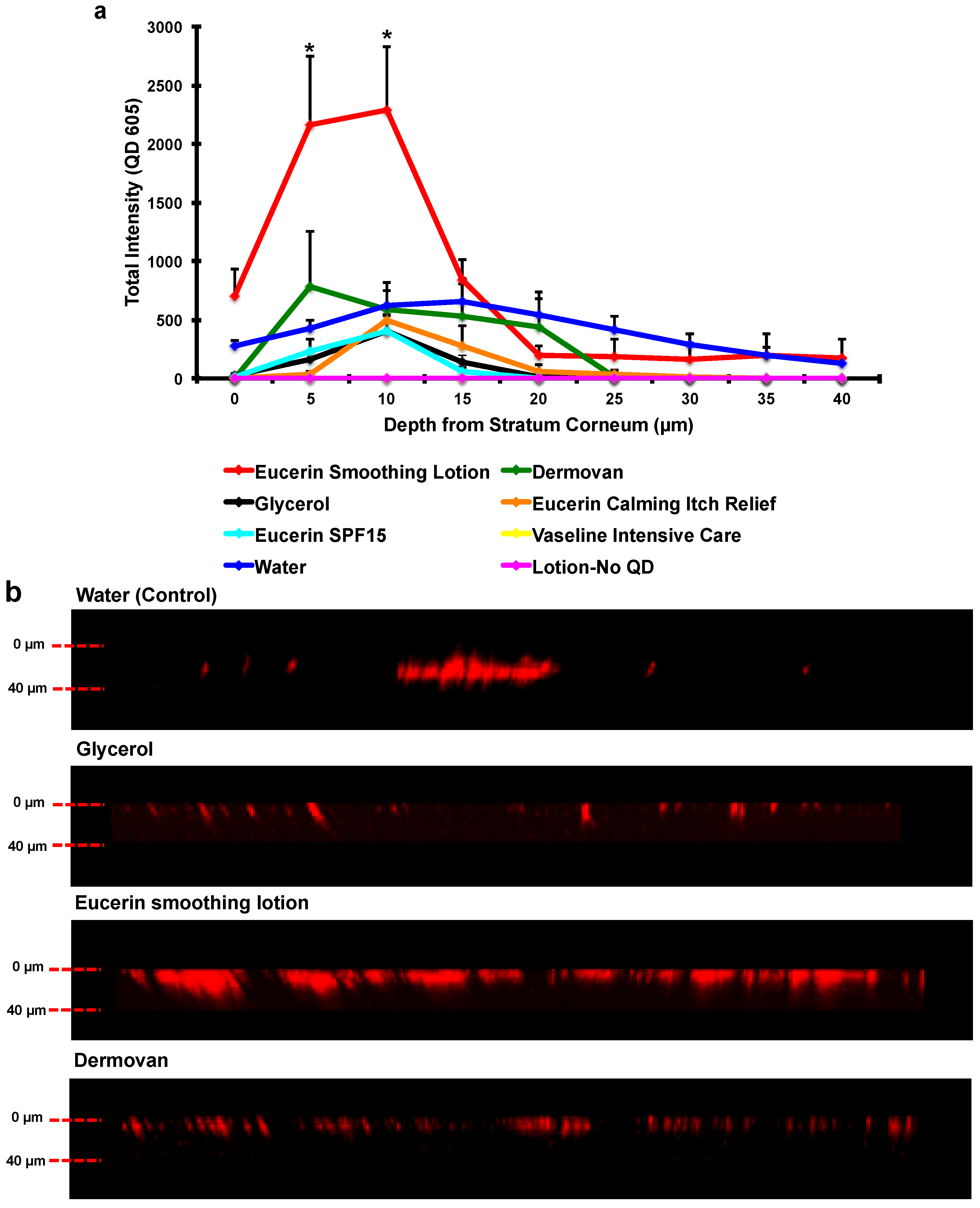
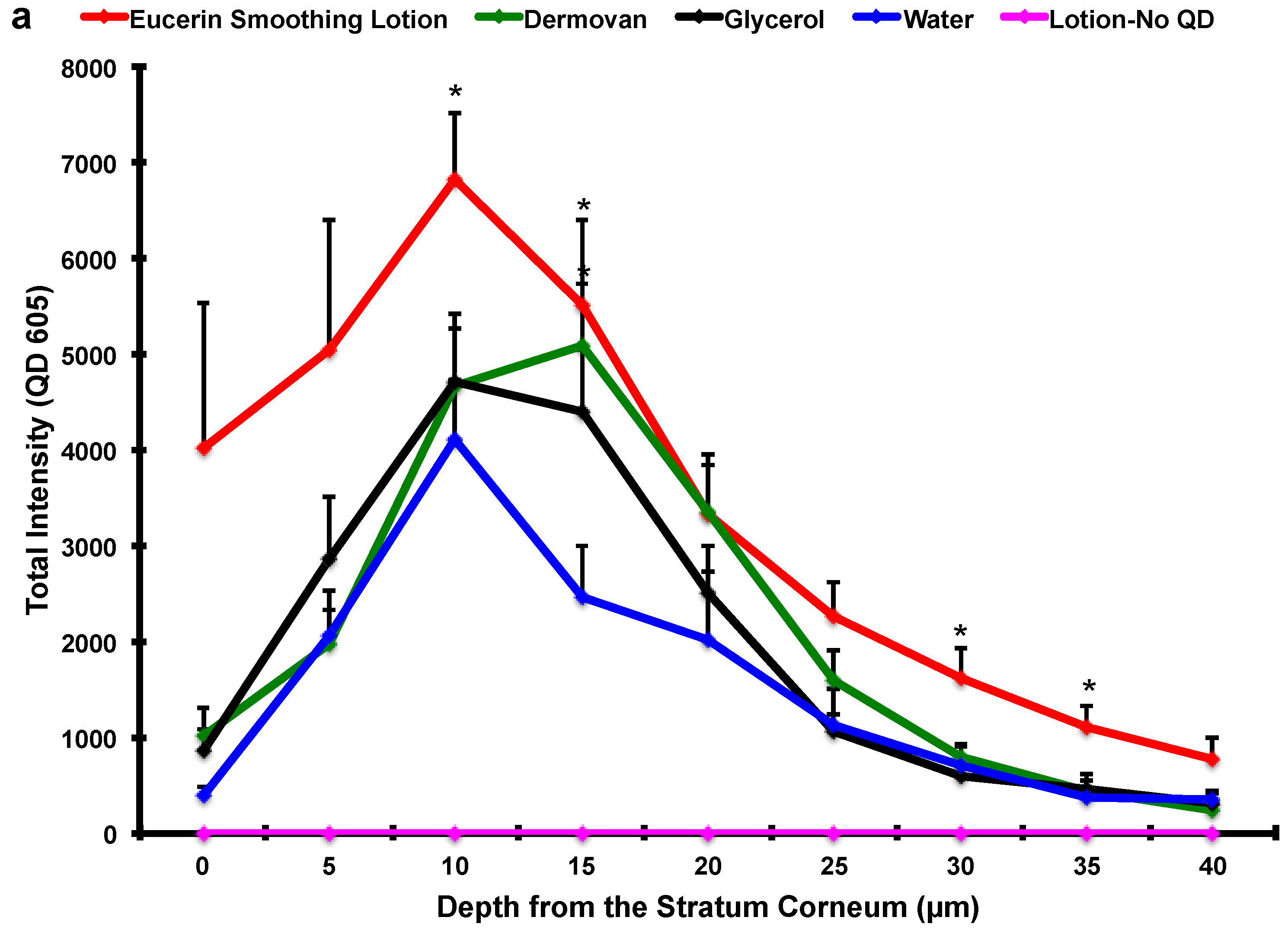
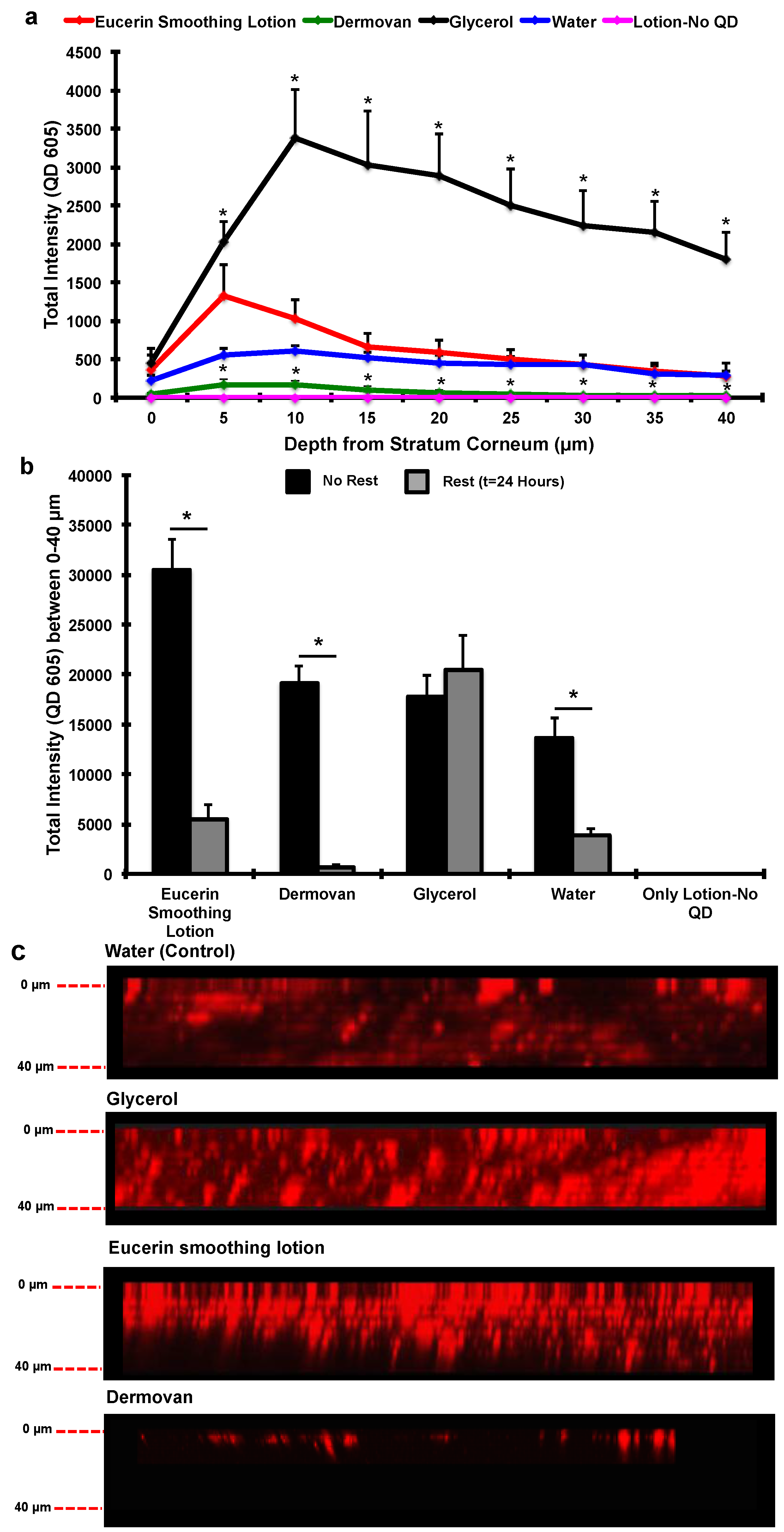
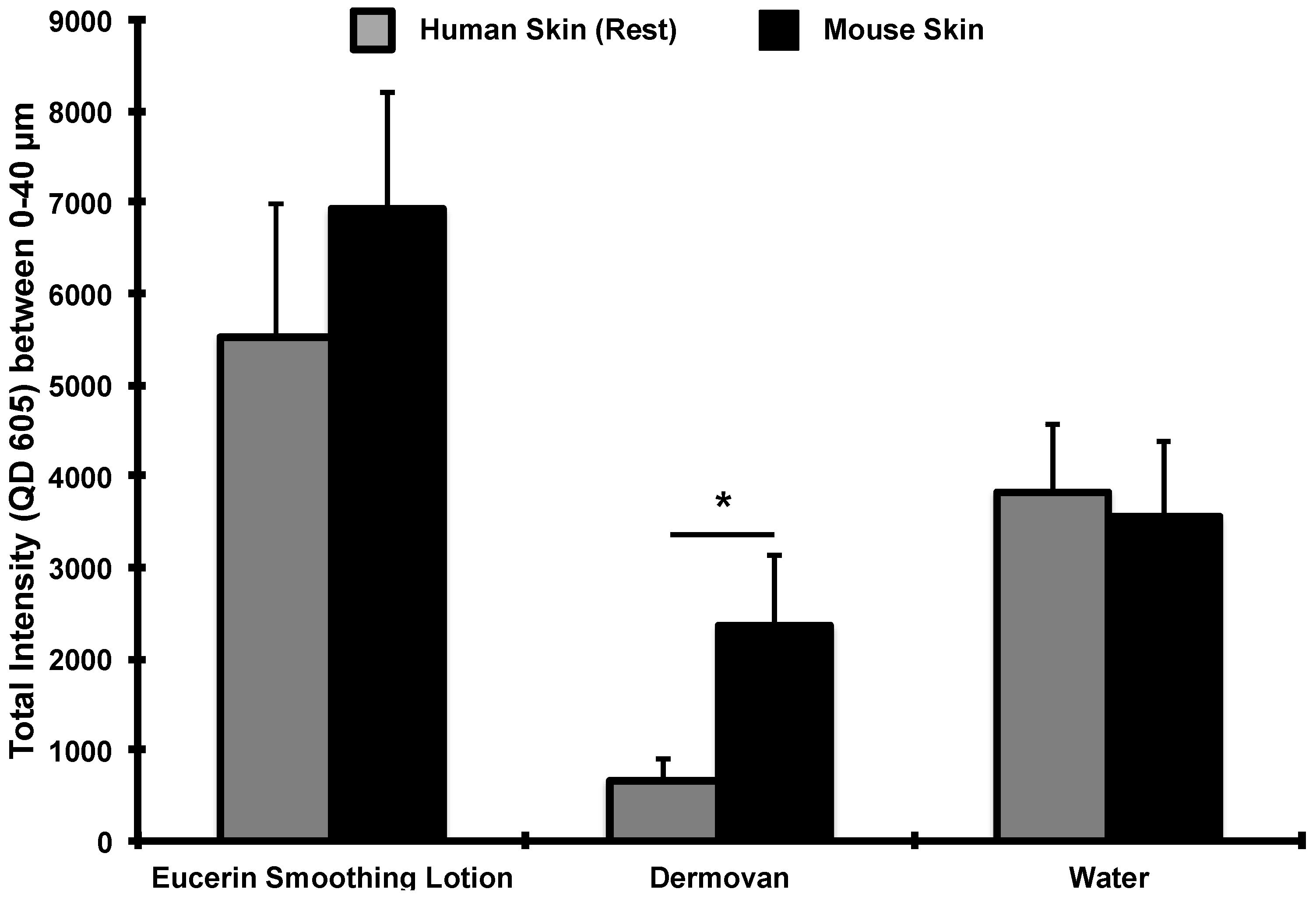
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Praetorius, A.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbuhler, K. Development of environmental fate models for engineered nanoparticles—A case study of TiO2 nanoparticles in the rhine river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6705–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jatana, S.; DeLouise, L.A. UVR and nanotechnology skin safety. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 6, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holsapple, M.P.; Farland, W.H.; Landry, T.D.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Carter, J.M.; Walker, N.J.; Thomas, K.V. Research strategies for safety evaluation of nanomaterials, part II: Toxicological and safety evaluation of nanomaterials, current challenges and data needs. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 88, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLouise, L.A. Applications of nanotechnology in dermatology. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Stracke, F.; Hansen, S.; Schaefer, U.F. Nanoparticles and their interactions with the dermal barrier. Dermatoendocrinol 2009, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prow, T.W.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Inman, A.O.; Grice, J.E.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Sanchez, W.H.; Gierden, A.; Kendall, M.A.; Zvyagin, A.V.; et al. Quantum dot penetration into viable human skin. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosera, M.; Bovenzi, M.; Maina, G.; Adami, G.; Zanette, C.; Florio, C.; Filon Larese, F. Nanoparticle dermal absorption and toxicity: A review of the literature. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2009, 82, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.W.; Yu, W.W.; Colvin, V.L.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Biological interactions of quantum dot nanoparticles in skin and in human epidermal keratinocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 228, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, J.; Hohenberg, H.; Pflucker, F.; Gartner, E.; Will, T.; Pfeiffer, S.; Wepf, R.; Wendel, V.; Gers-Barlag, H.; Wittern, K.P. Distribution of sunscreens on skin. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54 (Suppl. 1), S157–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, M.E.; Wang, S.Q. Current sunscreen controversies: A critical review. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroli, B.; Ennas, M.G.; Loffredo, F.; Isola, M.; Pinna, R.; Lopez-Quintela, M.A. Penetration of metallic nanoparticles in human full-thickness skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroli, B. Penetration of nanoparticles and nanomaterials in the skin: Fiction or reality? J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopee, N.V.; Roberts, D.W.; Webb, P.; Cozart, C.R.; Siitonen, P.H.; Latendresse, J.R.; Warbitton, A.R.; Yu, W.W.; Colvin, V.L.; Walker, N.J.; et al. Quantitative determination of skin penetration of PEG-coated cdse quantum dots in dermabraded but not intact SKH-1 hairless mouse skin. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 111, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.; Patlolla, R.R.; Singh, M. Interaction of nanoparticles and cell-penetrating peptides with skin for transdermal drug delivery. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2010, 27, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labouta, H.I.; Hampel, M.; Thude, S.; Reutlinger, K.; Kostka, K.H.; Schneider, M. Depth profiling of gold nanoparticles and characterization of point spread functions in reconstructed and human skin using multiphoton microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2012, 5, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labouta, H.I.; El-Khordagui, L.K.; Kraus, T.; Schneider, M. Mechanism and determinants of nanoparticle penetration through human skin. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4989–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratieri, T.; Schaefer, U.F.; Jing, L.; Gao, M.; Kostka, K.H.; Lopez, R.F.; Schneider, M. Penetration of quantum dot particles through human skin. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, S.; Mortensen, L.J.; DeLouise, L.A. Quantification of human skin barrier function and susceptibility to quantum dot skin penetration. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, L.J.; Oberdorster, G.; Pentland, A.P.; Delouise, L.A. In vivo skin penetration of quantum dot nanoparticles in the murine model: The effect of UVR. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, L.J.; Jatana, S.; Gelein, R.; de Benedetto, A.; de Mesy Bentley, K.L.; Beck, L.A.; Elder, A.; Delouise, L.A. Quantification of quantum dot murine skin penetration with UVR barrier impairment. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviere, N.A.M.; Zhang, L.W. Assessment of quantum dot penetration into skin in different species under different mechanical actions. In Nanomaterials: Risks and Benefits; Springer Science + Business Media B.V.: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Price, G.J.; Guy, R.H. Disposition of nanoparticles and an associated lipophilic permeant following topical application to the skin. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Landfester, K.; Musyanovych, A.; Guy, R.H. Disposition of charged nanoparticles after their topical application to the skin. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 23, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.A.; Moulari, B.; Beduneau, A.; Pellequer, Y.; Lamprecht, A. Nanoparticles enhance therapeutic outcome in inflamed skin therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, W.C.; Richter, H.; Patzelt, A.; Sterry, W.; Lai, K.K.; Renneberg, R.; Lademann, J. Drug delivery into the skin by degradable particles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Meinke, M.C.; Lange-Asschenfeldt, B.; Antoniou, C.; Mak, W.C.; Renneberg, R.; Sterry, W.; Patzelt, A. Drug delivery with topically applied nanoparticles: Science fiction or reality? Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2013, 26, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzelt, A.; Lademann, J. Drug delivery to hair follicles. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowski, A.; Nordmeyer, D.; Boreham, A.; Brodwolf, R.; Mundhenk, L.; Fluhr, J.W.; Lademann, J.; Graf, C.; Ruhl, E.; Alexiev, U.; et al. Skin barrier disruptions in tape stripped and allergic dermatitis models have no effect on dermal penetration and systemic distribution of ahaps-functionalized silica nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganti, P.; Morganti, G. Chitin nanofibrils for advanced cosmeceuticals. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganti, P. Use and potential of nanotechnology in cosmetic dermatology. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 3, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Knorr, F.; Schafer, U.; Lehr, C.M.; Dahne, L.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Selective follicular targeting by modification of the particle sizes. J. Controll. Release 2011, 150, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Dahne, L.; Walden, P.; Wiesmuller, K.H.; Wank, U.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Influence of the vehicle on the penetration of particles into hair follicles. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Giljohann, D.A.; Chen, D.L.; Massich, M.D.; Wang, X.Q.; Iordanov, H.; Mirkin, C.A.; Paller, A.S. Topical delivery of sirna-based spherical nucleic acid nanoparticle conjugates for gene regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11975–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Mohapatra, S.; Kong, X.; Li, X.; Lockey, R.F.; Mohapatra, S.S. Prevention of airway inflammation with topical cream containing imiquimod and small interfering RNA for natriuretic peptide receptor. Genet. Vaccines Ther. 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Wiench, K.; Landsiedel, R.; Schulte, S.; Inman, A.O.; Riviere, J.E. Safety evaluation of sunscreen formulations containing titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in UVB sunburned skin: An in vitro and in vivo study. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, K.A.; Roberts, M.S. Dermatological and Transdermal Formulations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; Volume 119, p. 574. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, K. Quantum dots go large. Nature 2009, 459, 760–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, T.; Bakhshi, R.; Petrova, D.; Pocock, R.; Imani, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4717–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.S.W.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Use of confocal microscopy for nanoparticle drug delivery through skin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Introduction to histological aspects of dermatotoxicology. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1997, 37, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Mortensen, L.J.; DeLouise, L.A. Thiol antioxidant-functionalized CdSe/ZnS quantum dots: Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentland, A.P.; Mahoney, M.; Jacobs, S.C.; Holtzman, M.J. Enhanced prostaglandin synthesis after ultraviolet injury is mediated by endogenous histamine stimulation. A mechanism for irradiation erythema. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluhr, J.W.; Darlenski, R.; Surber, C. Glycerol and the skin: Holistic approach to its origin and functions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, S.; Menon, G.K.; Mitragotri, S. Low-frequency sonophoresis: Ultrastructural basis for stratum corneum permeability assessed using quantum dots. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.A.; Moulari, B.; Beduneau, A.; Pellequer, Y.; Lamprecht, A. Surface-charge-dependent nanoparticles accumulation in inflamed skin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 4231–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batt, M.D.; Davis, W.B.; Fairhurst, E.; Gerrard, W.A.; Ridge, B.D. Changes in the physical-properties of the stratum-corneum following treatment with glycerol. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1988, 39, 367–381. [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi, C.; Rossi, S.; Bagnasco, M.; Lanata, L.; Sandri, G.; Bona, F.; Ferrari, F.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Caramella, C. Penetration and distribution of thiocolchicoside through human skin: Comparison between a commercial foam (miotens) and a drug solution. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kuijk-Meuwissen, M.E.; Junginger, H.E.; Bouwstra, J.A. Interactions between liposomes and human skin in vitro, a confocal laser scanning microscopy study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1371, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Kostka, K.H.; Lehr, C.M.; Schaefer, U.F. Human skin penetration of flufenamic acid: In vivo/in vitro correlation (deeper skin layers) for skin samples from the same subject. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelissen, J.A.; Arth, C.; Schrijvers, A.H.; Junginger, H.E.; Bodde, H.E. Validation of freeze-drying to visualize percutaneous 3h-estradiol transport: The influence of skin hydration on the efficacy of the method. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 1998, 11, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levintova, Y.; Plakogiannis, F.M.; Bellantone, R.A. An improved in vitro method for measuring skin permeability that controls excess hydration of skin using modified franz diffusion cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 419, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeling, M.E.K.; Bronaugh, R.L. In vitro percutaneous absorption of alpha hydroxy acids in human skin. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1997, 48, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, H.L.; Kraeling, M.E.K.; Robl, M.G.; Bronaugh, R.L. The effects of an alpha hydroxy acid (glycolic acid) on hairless guinea pig skin. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1997, 48, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copovi, A.; Diez-Sales, O.; Herraez-Dominguez, J.V.; Herraez-Dominguez, M. Enhancing effect of alpha-hydroxyacids on “in vitro” permeation across the human skin of compounds with different lipophilicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 314, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trommer, H.; Neubert, R.H. Overcoming the stratum corneum: The modulation of skin penetration. A review. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caussin, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. Ftir studies show lipophilic moisturizers to interact with stratum corneum lipids, rendering the more densely packed. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caussin, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Janssens, M.; Bouwstra, J.A. Lipid organization in human and porcine stratum corneum differs widely, while lipid mixtures with porcine ceramides model human stratum corneum lipid organization very closely. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larese, F.F.; D’Agostin, F.; Crosera, M.; Adami, G.; Renzi, N.; Bovenzi, M.; Maina, G. Human skin penetration of silver nanoparticles through intact and damaged skin. Toxicology 2009, 255, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.C.; Raphael, A.P.; Sundh, D.; Grice, J.E.; Soyer, H.P.; Roberts, M.S.; Prow, T.W. The human stratum corneum prevents small gold nanoparticle penetration and their potential toxic metabolic consequences. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filon, F.L.; Crosera, M.; Adami, G.; Bovenzi, M.; Rossi, F.; Maina, G. Human skin penetration of gold nanoparticles through intact and damaged skin. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Roman, R.; Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Fessi, H.; Guy, R.H. Visualization of skin penetration using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jatana, S.; Callahan, L.M.; Pentland, A.P.; DeLouise, L.A. Impact of Cosmetic Lotions on Nanoparticle Penetration through ex Vivo C57BL/6 Hairless Mouse and Human Skin: A Comparison Study. Cosmetics 2016, 3, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics3010006
Jatana S, Callahan LM, Pentland AP, DeLouise LA. Impact of Cosmetic Lotions on Nanoparticle Penetration through ex Vivo C57BL/6 Hairless Mouse and Human Skin: A Comparison Study. Cosmetics. 2016; 3(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics3010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleJatana, Samreen, Linda M. Callahan, Alice P. Pentland, and Lisa A. DeLouise. 2016. "Impact of Cosmetic Lotions on Nanoparticle Penetration through ex Vivo C57BL/6 Hairless Mouse and Human Skin: A Comparison Study" Cosmetics 3, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics3010006
APA StyleJatana, S., Callahan, L. M., Pentland, A. P., & DeLouise, L. A. (2016). Impact of Cosmetic Lotions on Nanoparticle Penetration through ex Vivo C57BL/6 Hairless Mouse and Human Skin: A Comparison Study. Cosmetics, 3(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics3010006