Abstract
Cassia fistula, a flowering plant in the family of Caesalpinaceae (Fabaceae), is used in traditional medicine for several indications. Nevertheless, too little is known about its effects on skin conditions and skin aging. Therefore, in this pioneering study, the extracts of oil-in-water macro-emulsions containing 5% C. fistula (L.) crude pods (i.e., phyto-active formulation) were optimally developed and compared to the placebo (i.e., emulsions without the crude extract) for assessment of their effects on human skin aging. Healthy adult male volunteers (n = 13) with a mean age of 31 ± 5.5 years (range: 24–47 years) were enrolled after informed written consent. For 12 consecutive weeks, the subjects were directed to use a patch containing the active emulsion on one of their forearms as well as a patch containing the placebo on their other forearm. Biometrological measurements of skin hydration (SH) and transepidermal water loss (TEWL) were performed on both sides of their respective cheeks at time 0 (baseline values), 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12th weeks. Surface evaluation of living skin (SELS) was taken at time 0 (baseline values) or after 1, 2 and 3 months. Topical application of C. fistula extracts showed a significant (p < 0.05) increase in stratum corneum hydration level, a significant enhancement in its water-holding function as well as in its barrier function. Further, significant (p < 0.005) ameliorations of skin aspects were observed (i.e., less roughness, less dryness, less wrinkles). Taken together, our results strongly suggest therapeutic and esthetic potential of C. fistula pod’s extracts to prevent or delay human skin aging.
1. Introduction
The constant search for bioactive plant extracts and the identification of their major bioactive phytochemicals, especially the more efficient and less toxic ones compared to conventional drugs, are undeniably valuable for both the traditional/folk and contemporary/alternative medicine. Indeed, many naturally-occurring pharmacological agents (e.g., polyphenols, triterpenes) play important roles as nutraceutics, cosmeceutics and preventive/therapeutic adjuvants for skin disorders/diseases such as melasma, melanoma, acne, dermatitis and premature skin aging [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10].
Recent advances in biotechnology have demonstrated the feasibility of incorporating plant extracts or derived-pure phytochemicals into various types of carriers (e.g., emulsions aka colloids or polymers in dispersed systems, other biocompatible and biodegradable polymers) in order to more specifically target the damaged tissue while enhancing their systemic bioavailability and reducing their cytotoxicity [11,12,13].
Further, the administration route represents an important parameter to take into consideration, and topical/local application of phyto-agents is rather suitable in skin aging prevention and skin therapy (e.g., ultraviolet (UV) protection and bio-damages repair) because this route allows reducing the efficacy dose and, subsequently, the overall systemic and organic toxicity [1,2,3,11,12,13].
Emulsions (including macro-, micro- and nano-) [6,7,14,15,16,17,18] are part of the colloids class, a two-phase system of matter, in which the liquid of the dispersed phase (e.g., oil) is put in contact, albeit normally immiscible (i.e., non-mixable or unblendable), with the liquid of the continuous phase (e.g., water). The droplets dispersed in the liquid matrix (aka “dispersion medium”) are usually assumed to be statistically distributed (Figure S1). Interestingly, emulsions are frequently employed to establish new pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations for either topical (e.g., skin applications), oral administration, or sometimes injection [6,7,14,15,16,19,20].
Skin aging is a complex, progressive and inevitable biological process that arises as a result of numerous intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Although it is primarily a physiological phenomenon (i.e., the so-called chronologic aging) involving our own genetic background, it also may become a pathological phenomenon (i.e., the so-called premature aging). Premature skin aging is manifested by accelerated induction of blemishes, wrinkling, scaling, roughness, dryness, laxity, as well as mottled pigment abnormalities including hypo-pigmentation and hyper-pigmentation, and can be caused by the detrimental effects of xenobiotics agents or environmental factors (e.g., chronic exposure to solar UV radiation (UVR)-induced oxidative stress aka photoaging, pollution, cigarette smoke, extreme temperature change) [1,3,21,22]. Over the past two decades, significant progress has been made in elucidating the molecular mechanisms of aging, including photoaging [23,24,25,26,27,28,29], an active but still challenging area for the development and promotion of effective healthy skin aging interventions [1,2,3,4,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,30,31,32]. For instance, it has been reported that one of the major features of aging skin is the progressive proteolytic degradation of cutaneous elastic fibers that cannot be adequately replaced or repaired by adult dermal fibroblasts [27]. Further, the impact of both chronological/physiological aging and premature/pathological on the skin appears particularly concerning when enhanced oxidative stress is involved (e.g., relative high lipid peroxides levels induced relative decay capacity of lipid membrane turnover, relative increased catalase levels) [33,34]. More recently, it was demonstrated by our team that the lowered moisture content of the skin is probably the prime factor in causing dry skin [6]. The factors that control the state of hydration of the stratum corneum (i.e., top most epidermal layer, also home to many above-cited skin imperfections, which mostly acts as a barrier between the outside world and the lower skin layers) are classified into three common categories [35]: (i) The rate at which water goes-out of the skin surface by evaporation; (ii) The ability of the stratum corneum to hold moisture; (iii) The rate at which water reaches the stratum corneum from layers beneath it. Overall, this means that the TEWL should be prevented and the skin moisture level (i.e., stratum corneum water content) should be restored. Interestingly, moisturizers protect the skin against external deleterious effects by making a thin film on the skin, which becomes then smoother while improving the stratum corneum moisture level [36]. Eventually, the in vivo measurement of SELS, via optical methods, remains the most reliable approach to measure skin surface roughness and wrinkling [37].
Plants are the source of important products with nutritional, cosmetic and therapeutic value, and have been used since ancient times for their relative health benefits. There is emerging evidence that topical application or oral intake of some plant extracts or phytochemicals can prettify the skin appearance and reduce a number of degenerative diseases and skin conditions such as skin inflammation, skin cancers and/or skin aging [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,32,34,38] Remarkably, botanical preparations have high potential for prevention against UVR damages (e.g., skin sunburns, premature skin aging and skin cancers), mainly due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities and nucleic acids repair potential [2,3,12,13,33,34,36].
Cassia fistula L. (Caesalpinaceae), known as the golden shower tree, represents a well-known yellow flowering plant in Asia, especially in the forests of India, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Pakistan, and displays numerous medicinal properties useful in the treatment of skin and inflammatory diseases [39,40]. Thereby, in Ayuverdic medicine, this ornamental plant is known as aragvadha, meaning “disease killer” [41]). Recently, we have shown that C. fistula extracts, which were rich in certain polyphenols (i.e., catechins), exhibited good potential to treat the skin of adult Asian patients with melasma (n = 50) compared to placebo (i.e., without the plant extract), due to its capacity to significantly decrease the tyrosine activity-mediated melanin level [5]. Also, the hydro-alcoholic extract from the fruit pulp of C. fistula displayed an in vitro antioxidant/radical scavenging activity (i.e., 2,2-Diphenyl-1-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)hydrazyl aka DPPH activity), certainly due to its relatively rich content of phenolic compounds, fatty acids, flavonoids, tannins and glycosides [42,43].
Our present study aimed to develop a stable macro-emulsion loaded with 5% C. fistula pod extract which could serve as a novel carrier system to further improve C. fistula’s potential effects on skin aging.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Extracts
C. fistula pods were collected from Abbasia Campus, Islamia University Bahawalpur, Pakistan. The identification of the plant was performed at CIDS (Cholistan Institute of Desert Studies). The voucher specimens were preserved at the herbarium of Pharmacognosy Section, Faculty of Pharmacy, Islamia University Bahawalpur for future reference. The voucher number is CF-FT-03-11-27. Paraffin oil was obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Tween80™, Stearic acid, Span20™, Cetomacrogol™ and Bees wax were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Pods have been rigorously tested and selected among other parts of the C. fistula plant (i.e., flowers, bark, leaves) based on (i) their higher extractable concentration in methanol 70%, compared to other solvents (i.e., ethanol, n-Hexane, petroleum ether) and concentrations (e.g., 40% methanol) (data not shown but available); (ii) their easy extraction by simple maceration method, compared to percolation/Soxhlet method, which was found more appropriate for C. fistula’s leaves extract (data not shown). Five percent of C. fistula pod’s extract was found to be the optimal concentration, notably because of the highest noticed DPPH scavenging activity (over 80%) when compared to a large number of concentrations ranging from 0% to 5% (data not shown).
2.2. Instrumental Measurements
Corneometer® CM825, Tewameter® TM300 and Visioscans® VC 98 (Courage & Khazaka, Cologne, Germany) with non-invasive probes were used in this study for the assessment of SH level, TEWL and SELS, respectively. All the measurements were performed at 21 ± 1 °C and 40% ± 2% relative humidity conditions.
2.3. Creams Preparation, Composition and Characteristics
Oil-in-water (O/W) macro-emulsions were formulated in this study according to our established protocol, which was previously reported [6]. Briefly, aqueous and oily phase were heated at 75 °C and 70 °C, respectively. Aqueous phase was then added to the oily phase drop by drop, while the mechanical stirring speed was carried out at 1500 rpm and subsequent cooling agitation at 500 rpm. Methanolic extract was dried before dispersion in the aqueous phase/incorporation to the emulsion, and solvent was removed by rotary evaporator. Following the composition of the active formulation (i.e., with plant extract) and placebo (i.e., without plant extract) (Table 1), emulsion stability was checked in triplicate at different time intervals to ensure that there were no unexpected organoleptically and physical-chemical changes (data not shown) such as: (i) odor/smell; (ii) color; (iii) temperature; (iv) pH; (v) phase separation (centrifugation)/phase thaw cycles; (vi) electrical conductivity; (vii) rheological characteristics (i.e., flow index, % confidence of fit, rheograms, viscosity).

Table 1.
Composition of emulsions (% w/w).
| Phase | No. | Composition | Placebo | Active Formulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oily Phase | 01 | Liquid Paraffin | 24 | 24 |
| 02 | Stearic Acid | 5 | 5 | |
| 03 | Span 20 ™ | 2 | 2 | |
| 04 | Bees wax | 7 | 7 | |
| 05 | Cetomacrogol ™ | 5 | 5 | |
| Aqueous Phase | 01 | Tween 80 ™ | 6 | 6 |
| 02 | Plant Extract | Nil | 5 | |
| 03 | Preservative | 1 | 1 | |
| 04 | D/W | 50 | 45 |
2.4. Study Protocol
A one-sided, placebo controlled monocentric study was designed to compare the active C. fistula formulation with placebo. Thirteen healthy male volunteers (mean age 31 ± 5.5 years; range: 24–47 years) were recruited. Active formulation and placebo were provided to each volunteer.
Prior to sampling, a safety test that consisted in using surgical dressing (patch) was executed to find out any possible reactions of emulsions on forearms of each volunteer. A 5 cm × 4 cm area was marked on the inner forearms. The patch saturated with placebo emulsion was applied to the right forearm while the patch saturated with the active formulation was applied to the left forearm. Both types of patches were removed after 2 days to determine the presence or absence of erythema (i.e., kind of skin hypersensitivity) using a 4-point scale scoring (i.e., ranging from 0 to 3): 3 stands for severe erythema (post-exclusion criterion), 2 for moderate erythema, 1 for mild erythema, and 0 for absence of erythema. Each volunteer was requested to note the degree of itching/rash/irritation and allocate a score from the same scale. All volunteers were then directed to come for biometrological measurements (i.e., SH and TEWL) on time 0 (baseline values) and then on week 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12. SELS was also assessed at time 0 (baseline values) and then at month 1, 2 and 3.
2.5. Ethics Approval
The study was conducted according to the Helsinki Declaration, and written informed consent was obtained from each participant prior to the study. All subjects were selected from the population of Bahawalpur City in Pakistan. A clinical research coordinator (CRC) assigned them to receive active formulation and placebo treatment regularly. The study was approved by the Institutional ethical review board of Faculty of Pharmacy, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur (942/Acad/EC/IUB/2011), where the study was carried out.
2.6. Mathematical Analysis
The percentage changes in the values of SH, TEWL and SELS, at baseline and at different time intervals, were calculated by:
where:
% Change = [(Dx − D0)/D0] × 100
- D0 = Baseline values (time 0 value).
- Dx = Value obtained at week 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12 (for SH and TEWL) or at month 1, 2 and 3 (for SELS).
2.7. Statistical Analysis
There was no previous clinical trial to compare the C. fistula extract emulsion with placebo. Therefore, this study was designed as a pilot study to calculate the suitable sample size for future precise randomized clinical trials. We set a sample size at n = 13. To ensure accuracy, all data obtained from three sets of independent experiments were entered into a data sheet twice, and were independently reviewed by experts in the field. All statistical calculations were then performed using Graphpad prism for Windows software (version 5). Paired sample t-test was used for assessing the variation between the active formulation and placebo. ANOVA (Analysis of variance) with Dunnett Multiple comparisons post-test was used to find the correlation between baseline values and the different time intervals values. Significance level was established at 5% (p ≤ 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Cream Characterization
Active formulation and placebo-based macro-emulsions (Figure S1) were prepared following an optimized routine procedure recently published by our group [5,6]. The compositions of the active formulation (i.e., emulsion containing C. fistula’s pods extract) and placebo (i.e., emulsion without active ingredient) are respectively described in Table 1. The emulsions were environmentally and kinetically quite stable, and normal physical-chemical characteristics (e.g., aspect, odor/smelling, pH, temperature, electrical conductivity, rheology) were obtained as expected (Table 2).

Table 2.
Physico-chemical characteristics of the emulsions. O/W: oil/water emulsion; RH: relative humidity.
| Parameters | Placebo | Active Formulation |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Macro-emulsion; O/W | Macro-emulsion; O/W |
| Appearance | Milky; Pale; Yellow | Milky; Pale; Yellow |
| Organoleptic property | Odorless | Odorless |
| Thermo-Stability | 8 °C or 40 °C, with 75% RH | 8 °C or 40 °C, with 75% RH |
| pH | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Electrical conductivity | 49 μS/cm | 55 μS/cm |
| Rheological stability | – | – |
| Flow index | 0.53 | 0.50 |
| % Confidence | 99.45 | 99.59 |
| Shear stress | 95–125 D/cm2 | 140–225 D/cm2 |
| Viscosity | 126.36 cP | 145.35 cP |
Indeed, the macro-emulsions were kinetically stabilized mixtures of two immiscible liquids (i.e., oil and water aka O/W type) where one of the liquids had droplets with a diameter greater than 0.1 μm. Optical micro-examination of the cream macro-emulsions mixed with amaranth red dye indicated red dispersed globules of the droplets and the ground colorless indicated that the cream was of O/W type. All the emulsions also appeared milky, which was in agreement with previous reports stating that macro-emulsions scatter light effectively since their droplets size are greater than a wavelength of light [44]. The active or placebo-based emulsions were normally odorless, pale yellow, stable at various temperatures (8 ± 0.1 °C, 25 ± 0.1 °C, or 40 ± 0.1 °C, with 75% relative humidity) during the whole process. They were also slightly acidic (i.e., pH: 5.5) independently of the used temperatures and conformed to the human skin pH. The electrical conductivity of the respective emulsions was normal (i.e., <5% changes noticed at the set temperatures) with a global mean value of 55 μS/cm for the active formulation and 49 μS/cm for the placebo. Their rheological characteristics, which contribute to determining creaming and liquefaction, did not significantly change at the different used temperatures and no significant difference was observed between the active and placebo-based emulsions. Indeed, the flow index had a global mean value of 0.50 for the active formulation and 0.53 for the placebo; the % confidence of fit had great global mean value of 99.59% for the active formulation and 99.45% for the placebo; The rheograms showed a shear stress varying from about 140 D/cm2 to 225 D/cm2 for the active formulation and from about 95 D/cm2 to 125 D/cm2 for the placebo when a shear rate of 200–380/s was applied; The viscosity had a global mean value of 145.35 cP for the active formulation and 126.36 cP for the placebo.
3.2. Patch Test (Skin Compatibility Test)
As shown in Table 3, severe (i.e., score 3) erythema did not occur in any of the volunteers (n = 13), which were pre-selected on the basis of their healthiness and age (mean age 31 ± 5.5 years; range: 24–47 years). Moderate (i.e., score 2) erythema occurred in one volunteer patched with the placebo and two independent volunteers patched with the active formulation. Mild (i.e., score 1) erythema occurred in four volunteers with the placebo and four volunteers with the active formulation. No (i.e., score 0) erythema occurred in the remaining eight volunteers patched with the placebo and the remaining seven volunteers patched with the active formulation.

Table 3.
Score allocated by volunteers (n = 13) to placebo and formulation on the basis of itching/irritation. Score 0 is attributed in absence of erythema; Score 1 stands for mild erythema; Score 2 stands for moderate erythema; Score 3 stands for severe erythema.
| Emulsion Type | Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| No. of Volunteers Indicating Itching/Irritation | ||||
| Placebo | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Active formulation | 7 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
3.3. Skin Hydratation (SH) and Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL)
The statistical analysis of percentage changes calculated for the values of SH and TEWL, after the application of the placebo and the active formulation for a period of 12 weeks, are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
In case of SH, the placebo produced initial increase in hydration level (i.e., mean of 2.6%) after the second week, and the effects were maintained until the 12th week (i.e., mean of 5.5%, maximum effect), compared to that baseline hydration level of the volunteers (n = 13). Interestingly, the active formulation showed an initial mean increase of 3.98% after the second week of treatment, and a mean increase of 9.83% after 12 weeks of treatment, while the maximum effect could be noticed after six weeks of treatment (i.e., mean of 13.36%), compared to that baseline hydration level of the volunteers (Figure 1). When analysis of variance ANOVA (Kruskal-Wallis test) was applied, a significant (p < 0.0001) difference was observed between the active formulation and the placebo, in favor of the active formulation (Figure 1). When Dunn’s multiple comparison tests between the active formulation and the placebo were applied, significant (p ˂ 0.05) results were obtained at the sixth, eighth, 10th and 12th week, in favor of the active formulation (Figure 1).
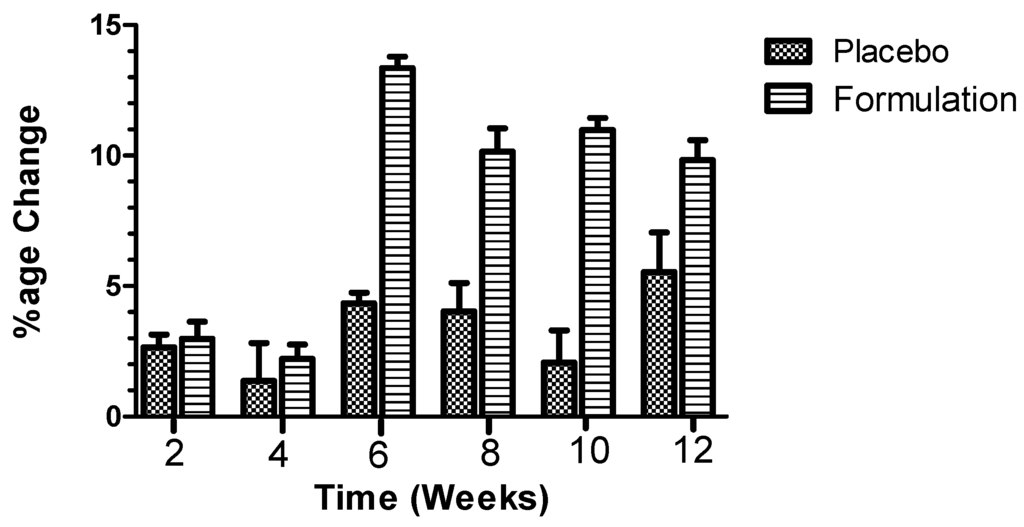
Figure 1.
Percentage of change produced in skin hydration (SH) values after application of placebo and active formulation in respective cheeks of volunteers (n = 13). Bars represent mean standard deviation (s.d.) of three independent experiments. Statistical significance (p ˂ 0.05) results were obtained at sixth, eighth, 10th and 12th week, in favor of the active formulation.
Figure 1.
Percentage of change produced in skin hydration (SH) values after application of placebo and active formulation in respective cheeks of volunteers (n = 13). Bars represent mean standard deviation (s.d.) of three independent experiments. Statistical significance (p ˂ 0.05) results were obtained at sixth, eighth, 10th and 12th week, in favor of the active formulation.
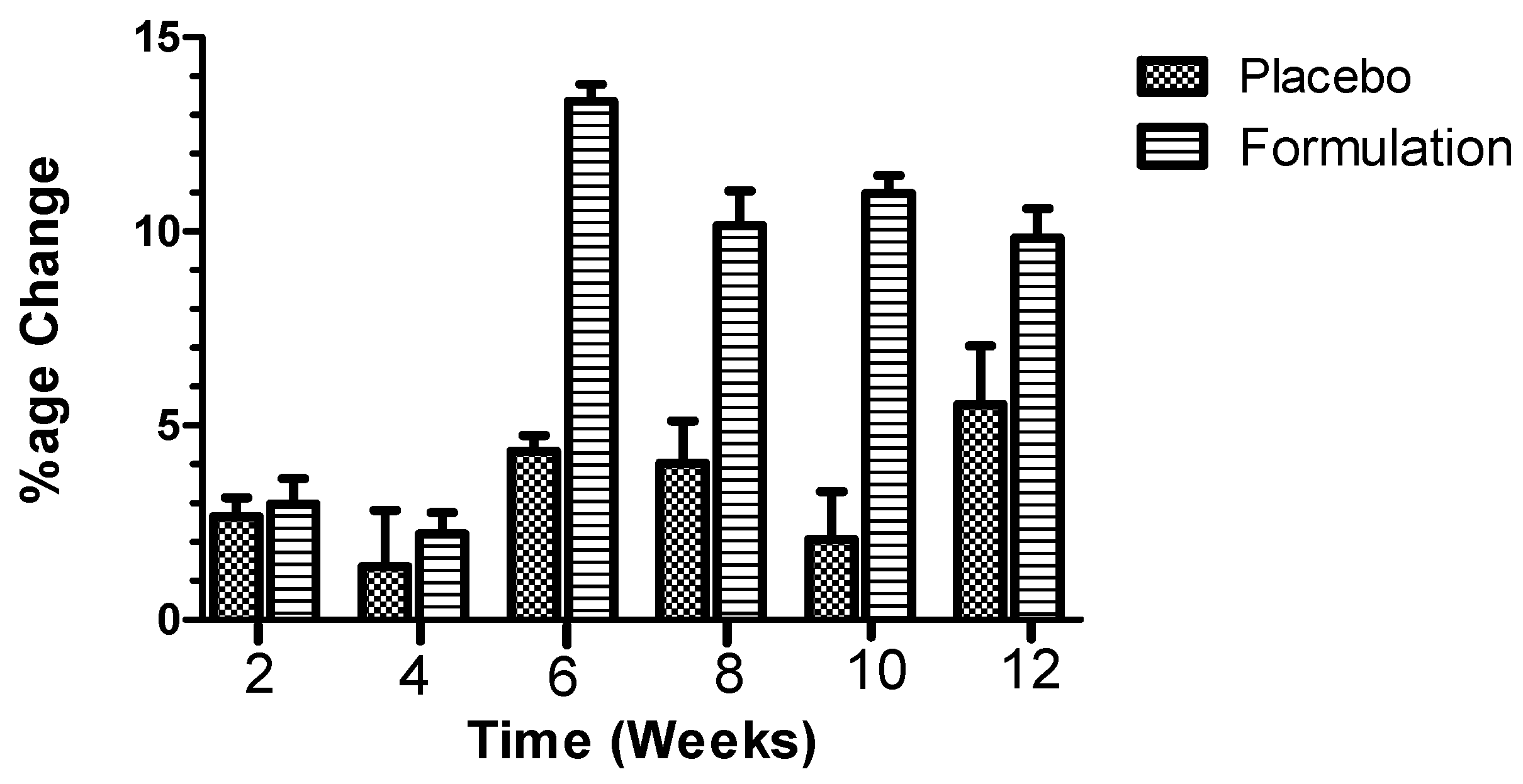
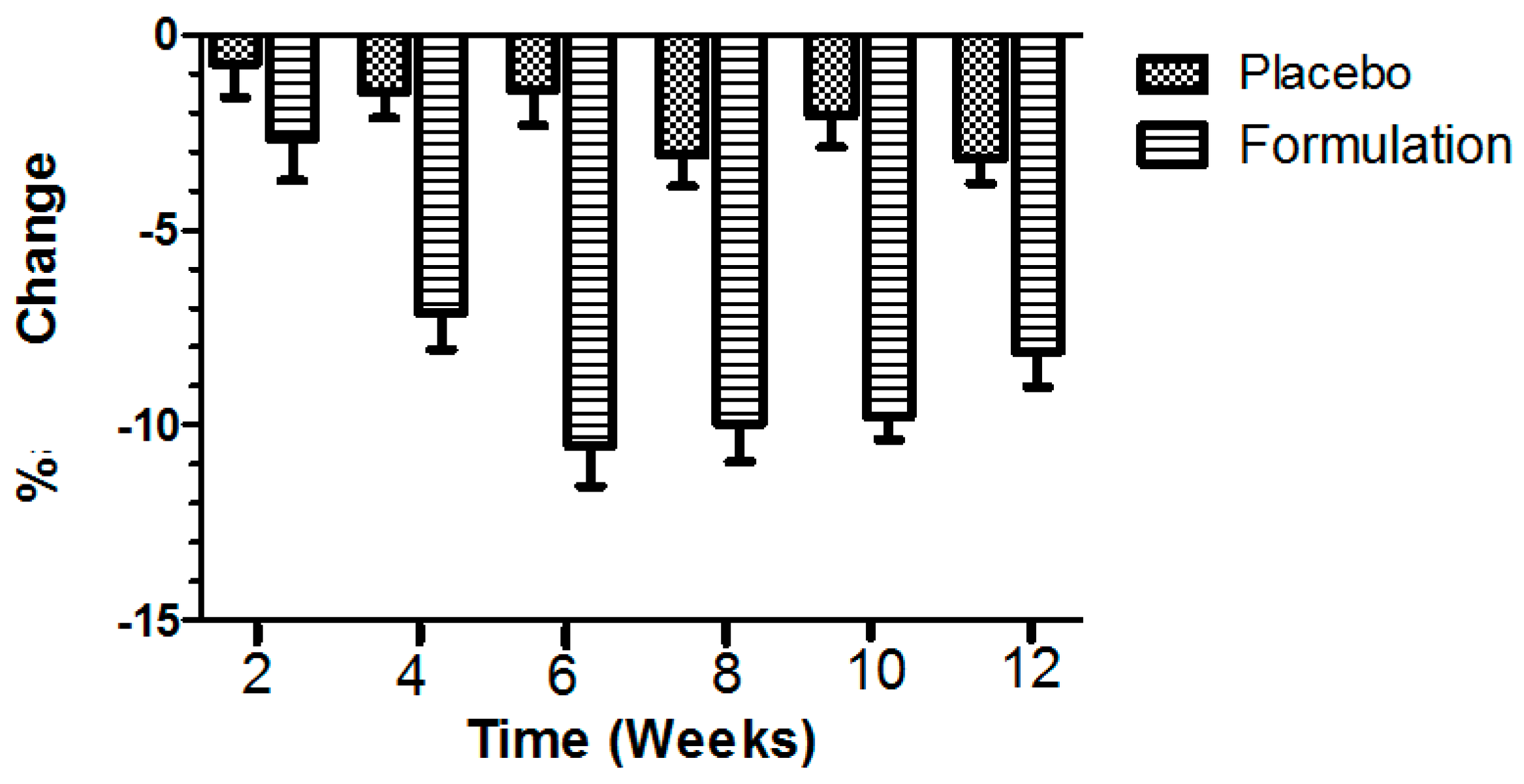
Compared to the baseline TEWL level of the volunteers (n = 13), the placebo exerted TEWL effects in an irregular pattern, with similar optimal decreased peaks at weeks 8 and 12 (i.e., about −3.0%), while the active formulation elicited a regular decrease in TEWL throughout the study period of 12 weeks, with an optimal decreased peak (i.e., about −11%) at week 6 (Figure 2). Indeed, in terms of the percentage TEWL changes during the study period, the placebo showed a mean initial decrease in TEWL after the second week (i.e., −0.728%), and the effect was greater until the 12th week (i.e., −3.187%) (Figure 2). The active formulation produced a mean initial reduction in TEWL after the second week treatment (i.e., −2.638%), and a mean reduction in TEWL after the 12 week study period (i.e., −8.102%). When ANOVA was applied, significant (p < 0.0001) differences were observed between the active formulation and the placebo, in favor of the active formulation. When Dunn’s multiple comparison tests were applied, significant (p ≤ 0.05) results were noticed between the second and 12th weeks, in favor of the active formulation.
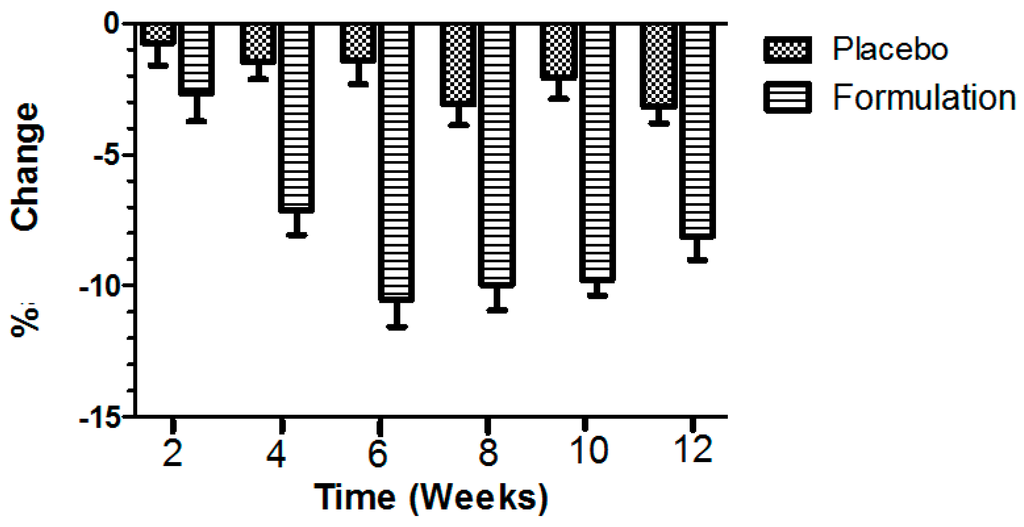
Figure 2.
Percentage of change produced in transepidermal water loss (TEWL) values after application of placebo and active formulation in respective cheeks of volunteers (n = 13). Bars represent mean standard deviation (s.d.) of three independent experiments. Statistical significance (p ≤ 0.05) results were obtained between the second and 12th weeks, in favor of the active formulation.
Figure 2.
Percentage of change produced in transepidermal water loss (TEWL) values after application of placebo and active formulation in respective cheeks of volunteers (n = 13). Bars represent mean standard deviation (s.d.) of three independent experiments. Statistical significance (p ≤ 0.05) results were obtained between the second and 12th weeks, in favor of the active formulation.
3.4. Surface Evaluation of Living Skin (SELS)
Four major SELS (SEr, SEsc, SEsm and SEw) parameters were measured. SEr represents the skin roughness parameter which calculates the proportion of dark pixels. SEsc is the index of skin scaliness which represents the level of dryness of the stratum corneum. SEsm denotes the index of skin smoothness, seems to be the opposite parameter to SEr, and is calculated from the average width and depth of the wrinkles. SEw identifies aging including wrinkles and is calculated from the proportion of horizontal and vertical wrinkles.
The measurements were taken by Visioscan® VC 98 at time 0 (baseline values) and at the first, second and third month of the study period. The percentage changes in the values obtained for the placebo or the active formulation applied to the volunteers (n = 13) were calculated in triplicate for each designed month for which a mean was calculated (Table S1). Since no significant (p > 0.05) difference was found among the values with respect to time (Table S1), values obtained for each SELS parameter from month 0 to month 3 were respectively pooled and a new mean was then obtained. These relative mean percentage changes are presented in the Figure 3. Applying one way ANOVA, a statistically significant (p < 0.005) difference was observed between the effects of the active formulation and the placebo, for each of the four SELS parameters (i.e., roughness, scaliness/dryness, smoothness and “wrinkleness”/aging). The highest differences (>2.5 fold), between the placebo and the active formulation, were noticed when evaluating the roughness (i.e., SEr) and smoothness (i.e., SEsm).
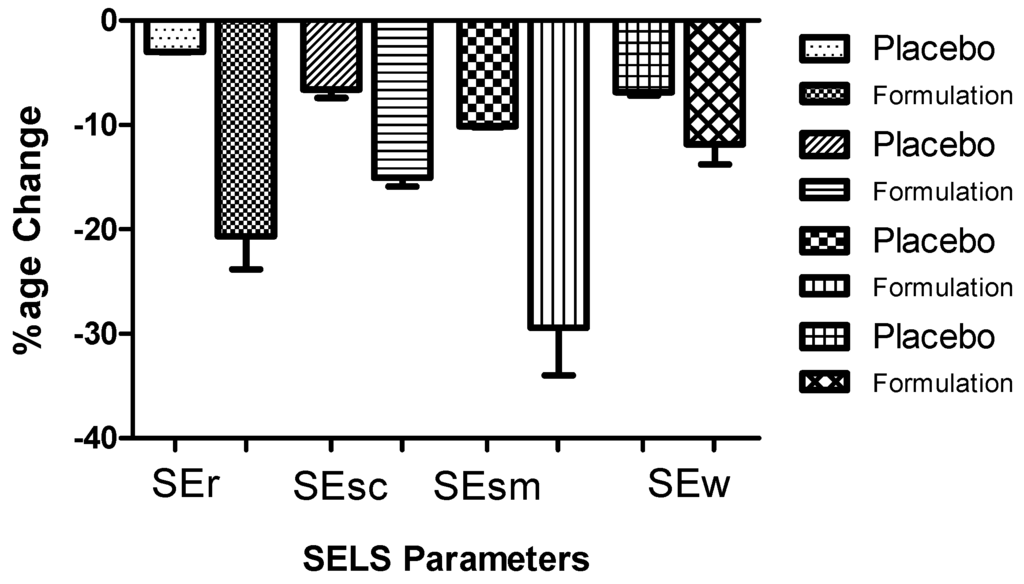
Figure 3.
Percentage of global changes in mean Visioscan® VC98 units of surface evaluation of living skin (SELS) parameters after application of formulation and placebo in respective cheeks of volunteers (n = 13) during three months. Bars represent mean standard deviation (s.d.) of three independent experiments. Statistically significant (p < 0.005) difference was observed between the effects of the active formulation and the placebo, for each of the four SELS parameters. SEr represents the index of skin roughness parameters; SEsc represents the index of skin scaliness/dryness; SEsm represents the index of skin smoothness; SEw represents the index of skin wrinkles/aging.
Figure 3.
Percentage of global changes in mean Visioscan® VC98 units of surface evaluation of living skin (SELS) parameters after application of formulation and placebo in respective cheeks of volunteers (n = 13) during three months. Bars represent mean standard deviation (s.d.) of three independent experiments. Statistically significant (p < 0.005) difference was observed between the effects of the active formulation and the placebo, for each of the four SELS parameters. SEr represents the index of skin roughness parameters; SEsc represents the index of skin scaliness/dryness; SEsm represents the index of skin smoothness; SEw represents the index of skin wrinkles/aging.
An example of typical 3D images obtained by Visioscan® VC 98 and processed by the SELS 2000 software of a volunteer’s facial skin, at baseline and after three months (i.e., 12 weeks) treatment, is shown in Figure 4. An improvement can be observed in facial wrinkle perfection after treatment (Figure 4).
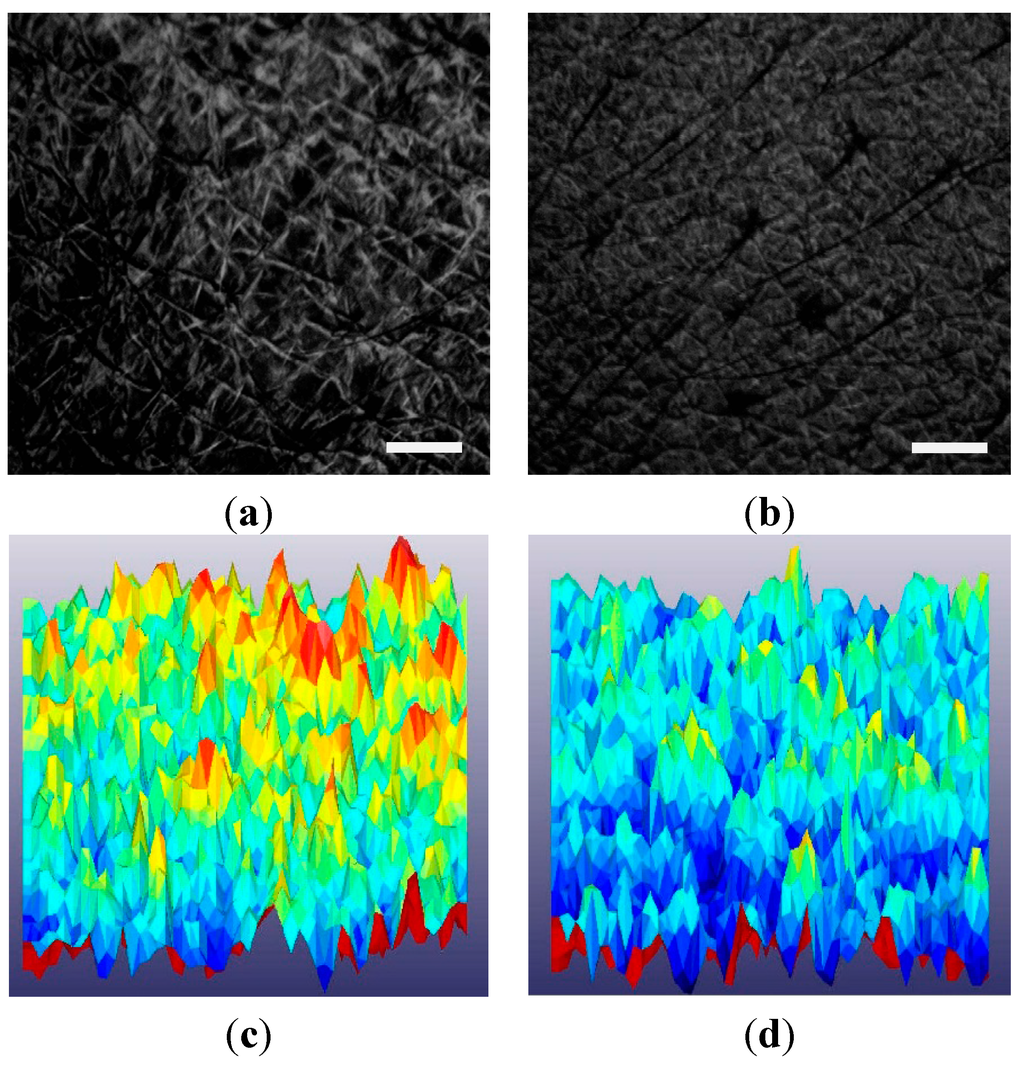
Figure 4.
Visioscan® VC98 UV camera images obtained (a) before any treatment; (b) after 90 days’ treatment with Cassia fistula extract emulsion; Scale bar: 1 mm for (a) and (b); (c) 3D image before any treatment; (d) 3D image after 90 days treatment. The yellow and red color in (c) indicate extensive roughness (SEr), scaliness (SEsc) and wrinkles (SEw) while light yellow color in (d) shows decrease roughness and improved skin smoothness (SEsm).
Figure 4.
Visioscan® VC98 UV camera images obtained (a) before any treatment; (b) after 90 days’ treatment with Cassia fistula extract emulsion; Scale bar: 1 mm for (a) and (b); (c) 3D image before any treatment; (d) 3D image after 90 days treatment. The yellow and red color in (c) indicate extensive roughness (SEr), scaliness (SEsc) and wrinkles (SEw) while light yellow color in (d) shows decrease roughness and improved skin smoothness (SEsm).
4. Discussion
The appearance of fine lines can be diminished through the application of moisturizers and/or herbal medicine [45]. Nowadays, plant extracts are usually incorporated into moisturizing formulations designed to achieve the above mentioned claims [46]. Moisturizers protect the skin against extrinsic damages by forming a thin film layer on the skin [47,48]. Plant extracts and purified plant-derived alkaloids are increasingly used in various (nano-) formulations for preserving and enhancing human skin because of their recognized valuable properties (e.g., sunscreen, anti-aging, moisturizing, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and/or anti-cellulite activities) [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,11,12,13,49].
For instance, it was shown that premature skin aging due to chronic or high sun exposure/UVR can be prevented by powerful purified phyto-antioxidants (e.g., polyphenols) and certain plant extracts [1,2,3,11,12,13,50]. Further, as compared to synthetic topical products, natural products are mild, biodegradable and display low toxicity [43].
Topical phyto-formulations for facial use are claimed to improve skin tone, glow and texture while decreasing skin wrinkling, subsequently providing important anti-aging benefits [1,2,3,4,5,6,11,12,13,32,49,51].
Moreover, compared to other administration routes, topical preventive and therapeutic formulations combine targeted non-invasiveness with low systemic toxicity, subsequently limiting unwanted, other adverse-effects on tissues while enhancing efficacy at lower doses [1,3,6,11,12,13,52].
In recent years, an increasing number of studies in cells and/or animal models have reported the therapeutic benefits of plants for alternative dermatology such as Cinnamomum cassia (L.) Presl extracts tested in mice as potential skin-whitening agents [53] and anti-atopic dermatitis [54], Cassia tora (L.) extracts tested in rats as a possible remedy against UVB-induced psoriasis [55], Cassia occidentalis (L.) pod’s extracts as a promising stimulant for skin repigmentation in vitiligo [56], and Cassia siamea (L.)-derived molecules emodin and cassiamin B tested in mice as potent inhibitors of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced skin carcinogenesis [57].
C. fistula L has been reported as a medicinal plant, notably in the treatment of skin and inflammatory diseases [40], particularly due to its relatively rich content of polyphenols and Vitamin C [5], which are known to highly contribute to anti-oxidant activity [43]. Interestingly, considering that the emulsion stability refers to the ability of an emulsion to resist change in its properties over time [58], no significant stability changes were observed during our study period of three months, when ANOVA statistical tests were respectively applied (data not shown). Further, for the first time, our results obtained from macro-emulsions made with crude extracts of C. fistula’s pods at the optimal concentration of 5% strongly suggest good potential for clinical skin application in order to: (i) increase SH; and (ii) enhance the stratum corneum water content. Both (i) and (ii) improvements could be explained by the high concentration of unsaturated fatty acids present in C. fistula [39]. The decline in TEWL could also be attributed to the emollient nature of mineral oil (paraffin oil) incorporated in the formulations and which is known to moisturize the skin and prevent dryness. Indeed, mineral oils primarily consist of lipids, filling the space between cells of stratum corneum, subsequently forming a film of lipids on skin surface which restores the barrier function of the skin. Water holding capacity of the stratum corneum is then enhanced by this film leading to reduced TEWL, which can then increase SH level [59]; (iii) improve SELS parameters, which may be explained by the strong anti-oxidant activity of C. fistula. Indeed, it has been described in the literature that plant extracts exhibiting significant DPPH radical scavenging activity display a stimulation index on normal human fibroblasts’ proliferation, and so, should be suggested or recommended for assessing new anti-aging formulations [60]. In our present study, skin surface was mainly explained by four different parameters that are: scaliness (SEsc), roughness (SEr), smoothness (SEsm) and wrinkling (SEw). SELS is used to evaluate qualitatively and quantitatively the skin surface [61]. SEsc evaluates stratum corneum hydration level: the smaller SEsc, the higher the hydration level with less scaliness [49]. A higher value of SEr indicates more roughness while a lower SEr value reflects more smoothness (SEsm) [49]. SEw is used as the marker of the number and width of skin wrinkles. A higher value reflects more wrinkles and wider wrinkles and vice-versa [62]. Our ongoing investigation is determining on each individual the safety aspects (i.e., eventual side-effects such as irritation, allergy; sensory values such as ease of application, spreadability, sense just after application and chronically, skin appearance, texture feeling) of the macro-emulsions post-skin applications (data not shown). Briefly, from the average response of volunteers, it was preliminary found that the active formulation and the placebo were both significantly comparable in terms of safety (i.e., no side-effects) and sensory point of view (i.e., pleasant feeling). Shine on skin was significantly more visible for the active formulation than the placebo, which was expected as C. fistula contains essential fatty acids.
Eventually, in this pioneering study, we have successfully developed a 5% C. fistula-based macro-emulsion for topical application and used non-invasive probes to evaluate various skin surface parameters of living human skin. Our overall results strongly suggest application of the active formulation to significantly and safely improve the appearance and consistency of the human skin.
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Our one-sided placebo controlled monocentric study, involving a first set of individuals, was designed to compare the active C. fistula formulation with its placebo. A three month treatment with a 5% C. fistula extract-based emulsion has shown good potential to increase skin hydration, enhance stratum corneum water content, and improve human facial wrinkles. Interestingly, C. fistula extract-based emulsion significantly influenced skin parameters when compared with placebo. No safety issues were noted.
Further studies in larger numbers of subjects, for a longer period of time and with compromised skin conditions are required to determine whether C. fistula pod extract-based emulsions have everlasting beneficial effects in terms of efficacy and safety on human skin. Also, we aim to compare our data (obtained from macro-emulsions) with those that will result from micro-emulsion and nano-emulsion-based experiments assessed in several age groups, including the elderly. Eventually, we intend to identify and purify the active ingredients present in the crude extracts of C. fistula’s pods in order to unravel their molecular mechanisms and precisely determine their pharmaco-toxicological aspects, notably by employing our state-of-the art fluoro-carbon spectroscopy-derived tools and methods [63].
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the grant number: 074-0992-BM4-073 awarded by the Higher education commission (HEC) of Pakistan. The authors are grateful to HEC, to Mahmood Ahmad, Dean of the Pharmacy department, Islamia University of Bahawalpur, Pakistan, and to Bouzid Menaa, expert in chemical sciences and nanobiotechnology, Hymetec SA, Belgium.
Author Contributions
Barkat Ali Khan, Naveed Akhtar and Farid Menaa conceived and designed the experiments; Barkat Ali Khan and Naveed Akhtar performed the experiments; Barkat Ali Khan, Naveed Akhtar, Abder Menaa and Farid Menaa analyzed the data; Barkat Ali Khan and Farid Menaa wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acronyms
| C. fistula | Cassia fistula | SEw | surface evaluation of wrinkling |
| SH | skin hydratation | UV | ultraviolet |
| TEWL | transepidermal water loss | UVR | ultraviolet radiation |
| SELS | surface evaluation of living skin | DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)hydrazyl |
| SEsc | surface evaluation of scaliness | SEsm | surface evaluation of smoothness |
| SEr | surface evaluation of roughness |
References
- Menaa, F.; Menaa, A.; Tréton, J. Polyphenols against skin aging. In Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease, 1st ed.; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 819–829. [Google Scholar]
- Menaa, F.; Badole, S.L.; Menaa, B.; Menaa, A. Promising Plant Extracts with in Vivo Anti-Melanoma Potential. In Bioactive Dietary Factors and Plant Extracts in Dermatology, 1st ed.; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Humana Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Menaa, F.; Menaa, A. Skin Photoprotection by Polyphenols in Animal Models and Humans. In Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease, 1st ed.; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 831–838. [Google Scholar]
- Zanwar, A.A.; Badole, L.S.; Menaa, F. Curcuma Longa: Use for Skin Disease Care. In Bioactive Dietary Factors and Plant Extracts in Dermatology; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Humana Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, B.A.; Akhtar, N.; Hussain, I.; Abbas, K.A.; Rasul, A. Whitening efficacy of plant extracts including Hippophae rhamnoides and Cassia fistula extracts on the skin of Asian patients with melasma. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2013, 30, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.A.; Akhtar, N.; Braga, V.A. Anti-Aging Effects of Hippophae rhamnoides Emulsion on Human Skin. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, H.M.S.; Waseem, K.; Mahmood, T.; Rasul, A.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, H. Basics of pharmaceutical emulsions: A review. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar]
- Rasul, A.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, B.A.; Mahmood, T.; Zaman, S.U.; Ali, A.; Khan, H.M.S.; Parveen, R. Evaluation for antierythmic and depigmenting effects of a newly formulated emulsion containing basil extract. J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 6249–6253. [Google Scholar]
- Cuéllar, M.J.; Giner, R.M.; Recio, M.C.; Máñez, S.; Ríos, J.L. Topical anti-inflammatory activity of some Asian medicinal plants used in dermatological disorders. Fitoterapia 2001, 72, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali, H.; Perchellet, E.; Makkar, H.; Perchellet, J. Ability of tannins extracted from the leaves of various trees and shrubs to inhibit the biomarkers of tumor promotion in mouse skin in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 1996, 9, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menaa, F.; Menaa, B. Polyphenols nanoformulations for topical dermal delivery and skin tissue engineering. In Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Menaa, F.; Menaa, A.; Treton, J.; Menaa, B. Nanoencapsulations of Dietary Polyphenols for Oncology and Gerontology: Resveratrol as a Good Example—Resveratrol Nano-Formulations: Suitable for Cancer Patients and the Elderly? In Introduction to Functional Food Science; Martirosyan, D.M., Ed.; Food Science Publisher: Dallas, TX, USA, 2013; pp. 383–404. [Google Scholar]
- Menaa, F.; Menaa, A.; Tréton, J.; Menaa, B. Dietary Intake of (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate against Aging and Cancers: Nanoencapsulation of Multi-Rings Still Requires New Rounds! J. Nanomater. Mol. Nanotechnol. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, B.A.; Rasul, A.; Khan, H.M.S. Fabrication, physicochemical characterization and preliminary efficacy evaluation of a W/O/W multiple emulsion loaded with 5% green tea extract. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Hisham, J.; Khan, B.A.; Shoaib Khan, H.M.; Mahmood, T.; Rasul, A.; Iqbal, M.; Qayum, M. Cosmetic application of phenolic cream from mulberry bark extract. Asian J. Chem. 2012, 24, 1805–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, N.; Anwar, M.; Khan, B.A.; Mahmood, T.; Zaman, S.U. Formulation development and pharmaceutical evaluation of a w/o emulsion of Coleus extract. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2011, 45, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, T.G.; Wilking, J.N.; Meleson, K.; Chang, C.B.; Graves, S.M. Nanoemulsions: Formation, structure, and physical properties. J. Phys. Condens. Matt. 2006, 18, R635–R666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoar, T.P.; Schulman, J.H. Transparent water-in-oil dispersions: The oleopathic hydro-micelle. Nature 1943, 152, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulton, M.E. Aulton’s Pharmaceutics: The Design and Manufacture of Medicines; Aulton, M.E., Taylor, K.M.G., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Troy, D.A.; Remington, J.P.; Beringer, P. Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy. In University of the Sciences in Philadelphia, 21st ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 886–887. [Google Scholar]
- Ichihashi, M.; Ueda, M.; Budiyanto, A. UV-induced skin damage. Toxicology 2003, 189, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, H.; Elmets, C.A. Photocarcinogenesis: Mechanisms, models and human health implications. Photochem. Photobiol. 1996, 63, 355–447. [Google Scholar]
- Alic, N.; Partridge, L. Death and dessert: Nutrient signalling pathways and ageing. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C.J. The genetics of ageing. Nature 2010, 464, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigis, M.C.; Yankner, B.A. The aging stress response. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L.; Partridge, L.; Longo, V.D. Extending healthy life span-from yeast to humans. Science 2010, 328, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, F.; Mitts, T.F.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Hinek, A. Ellagic and tannic acids protect newly synthesized elastic fibers from premature enzymatic degradation in dermal fibroblast cultures. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, C.; Menaa, F.; Pinon-Lataillade, G.; Frobert, Y.; Chevillard, S.; Radicella, J.P.; Sarasin, A.; Angulo, J.F. Global genome repair is required to activate KIN17, a UVC-responsive gene involved in DNA replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masson, C.; Menaa, F.; Pinon-Lataillade, G.; Frobert, Y.; Radicella, J.P.; Angulo, J.F. Identification of KIN (KIN17), a human gene encoding a nuclear DNA-binding protein, as a novel component of the TP53-independent response to ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res. 2001, 156, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Guha, S.; Sun, X.; Cao, M.; Wang, X.; Zou, S. Nutraceutical interventions for promoting healthy aging in invertebrate models. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012, 2012, 718491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Parveen, R.; Khan, B.A.; Jamshaid, M.; Khan, H.M.S. Development of skin-friendly dermatological water-in-oil emulsion of pomegranate juice. Proc. Pakistan Acad. Sci. 2012, 49, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, N.; Mahmood, T.; Khan, B.A.; Khan, H.M.S.; Saeed, T. Depigmenting and anti-erythematic effects of 3% green tea emulsion. HealthMED 2011, 5, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Peres, P.S.; Terra, V.A.; Guarnier, F.A.; Cecchini, R.; Cecchini, A.L. Photoaging and chronological aging profile: Understanding oxidation of the skin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2011, 103, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.A.; Katiyar, S.K. Skin photoprotection by natural polyphenols: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and DNA repair mechanisms. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2010, 302, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, V.R.; Ian, R.S.; Clive, R.H.; Paul, A.B. Stratum Corneum Moisturization at the Molecular Level. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 103, 731–740. [Google Scholar]
- Korać, R.R.; Khambholja, K.M. Potential of herbs in skin protection from ultraviolet radiation. Pharmacogn Rev. 2011, 5, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottner, J.; Schario, M.; Bartels, N.G.; Pantchechnikova, E.; Hillmann, K.; Blume-Peytavi, U. Comparison of two in vivo measurements for skin surface topography. Skin Res. Technol. 2013, 19, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganceviciene, R.; Liakou, A.I.; Theodoridis, A.; Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Skin anti-aging strategies. Dermato-Endocrinol. 2012, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danish, M.; Singh, P.; Mishra, G.; Srivastava, S.; Jha, K.K.; Khosa, R.L. Cassia Fistula Linn. (Amulthus)—An Important Medicinal Plant: A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Properties. J. Nat. Prod. Plant Resour. 2011, 1, 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Bahorun, T.; Neergheen, V.S.; Aruoma, O.I. Phytochemical constituents of Cassia fistula. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, P. Ayurvedic Medicine: The Principles of Traditional Practice; Singing Dragon: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Manonmani, G.; Bhavapriya, V.; Kalpana, S.; Govindasamy, S.; Apparanantham, T. Antioxidant activity of Cassia fistula (Linn.) flowers in alloxan induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalodia, N.R.; Nariya, P.B.; Acharya, R.N.; Shukla, V.J. In vitro antioxidant activity of hydro alcoholic extract from the fruit pulp of Cassia fistula Linn. Ayu 2013, 34, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.O. Macro- and micro-emulsions: Theory and applications. In Proceedings of the 186th Meeting of the American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, USA, 28 August–2 September 1983.
- Chanchal, D.; Swarnlata, S. Novel approaches in herbal cosmetics. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2008, 7, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoe, D. The cosmeceutical realm. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 627–632. [Google Scholar]
- Zoe, D. The latest cosmeceutical approaches for anti-aging. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2007, 6, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ozgen, O. Anti-Aging Cosmeceutics for Facial Skin Care in Aging. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 29, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rasul, A.; Akhtar, N. Formulation and in vivo evaluation for anti-aging effects of an emulsion containing basil extract using non-invasive biophysical techniques. DARU 2011, 19, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Bae, E.Y.; Choi, G.; Hyun, J.W.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Chae, S. Protective effect of mango (Mangifera indica L.) against UVB-induced skin aging in hairless mice. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2013, 29, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahshawat, M.S.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Preparation and characterization of herbal creams for improvement of skin viscoelastic properties. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menaa, F. When Pharma Meets Nano or the Emerging Era of Nano-Pharmaceuticals. Pharmaceut. Anal. Acta 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.T.; Chang, W.L.; Chang, C.T.; Hsu, S.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Shih, Y. Cinnamomum cassia essential oil inhibits α-MSH-induced melanin production and oxidative stress in murine B16 melanoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19186–19201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Yoon, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Park, S.J.; Jeong, G.H.; Kim, H.K. Inhibitory effects of Cinnamomum cassia extract on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by mite antigen in NC/Nga mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, M.; Kansara, N. Cassia tora linn cream inhibits ultraviolet-B-induced psoriasis in rats. ISRN Dermatol. 2012, 2012, 346510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Babitha, S.; Shin, J.H.; Nguyen, D.H.; Park, S.J.; Reyes, G.A.; Caburian, A.; Kim, E.K. A stimulatory effect of Cassia occidentalis on melanoblast differentiation and migration. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, J.; Morita, I.; Tagahara, K.; Nobukuni, Y.; Mukainaka, T.; Kuchide, M.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H. Chemopreventive effects of emodin and cassiamin B in mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2002, 182, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions, Principles, Practices and Techniques, 2nd ed.; McClements, D.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Waqas, M.K.; Akhtar, N.; Ahmad, M.; Murtaza, G.; Khan, H.M.S.; Iqbal, M.; Rasul, A.; Bhatti, N.S. Formulation and characterization of a cream containing extract of fenugreek seeds. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2010, 67, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, R.N.; Akhtar, B.A.; Khan, T.M.; Uz Zaman, S.; Shoaib Khan, H.M. Formulation development of a cream containing fennel extract: In vivo evaluation for anti-aging effects. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 67, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, U.; Tronnier, H.; Stahl, W.; Béjot, M.; Maurette, J.M. Antioxidant supplements improve parameters related to skin structure in humans. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Sakamoto, W.; Odanaka, W.; Yoshida, K.; Urishibata, O. Clinical effects of dietary hyaluronic acid on dry, rough skin. Aesthetic. Dermatol. 2002, 12, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Menaa, F.; Menaa, B.; Sharts, O. Development of carbon-fluorine spectroscopy for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Faraday Discuss. 2011, 149, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
