Cosmetics for Sensitive Skin: Assessing Rheological Properties, Stability, and Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Emulsions
2.3. pH Determination
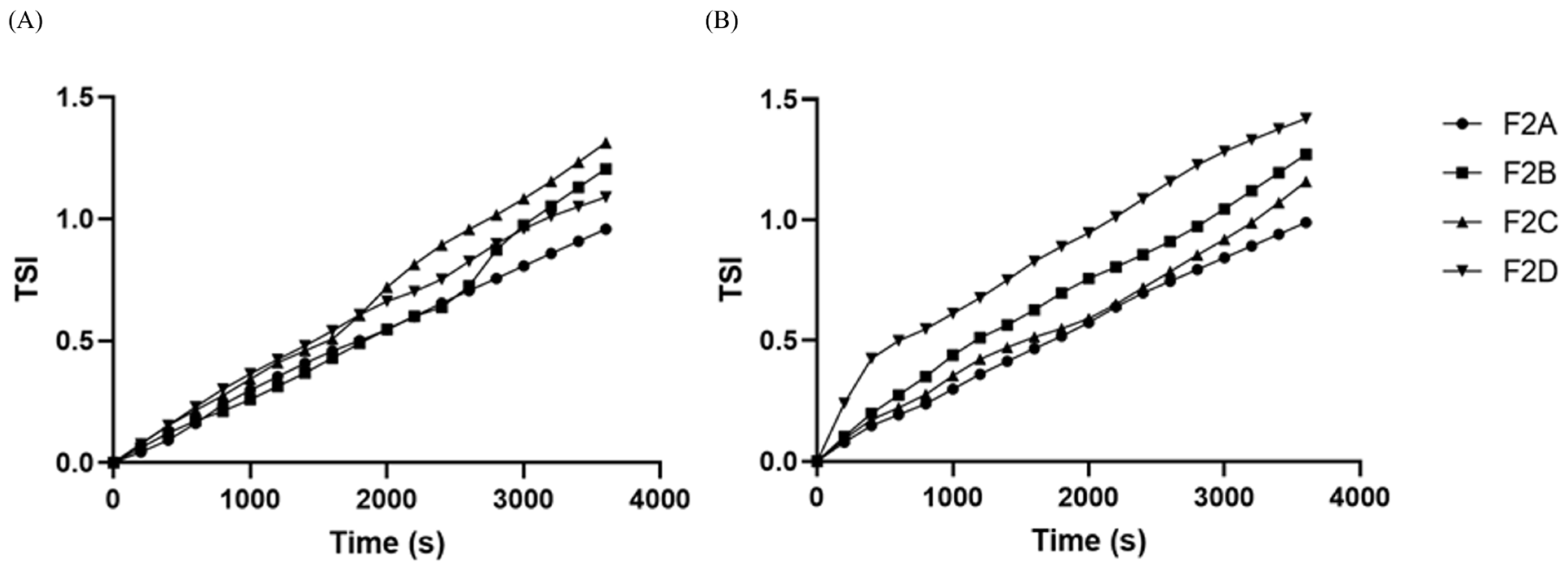
2.4. Stability Test
2.5. Rheological Studies
2.6. In Vivo Studies on Human Volunteers
2.6.1. Assessment of Skin Sensations
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
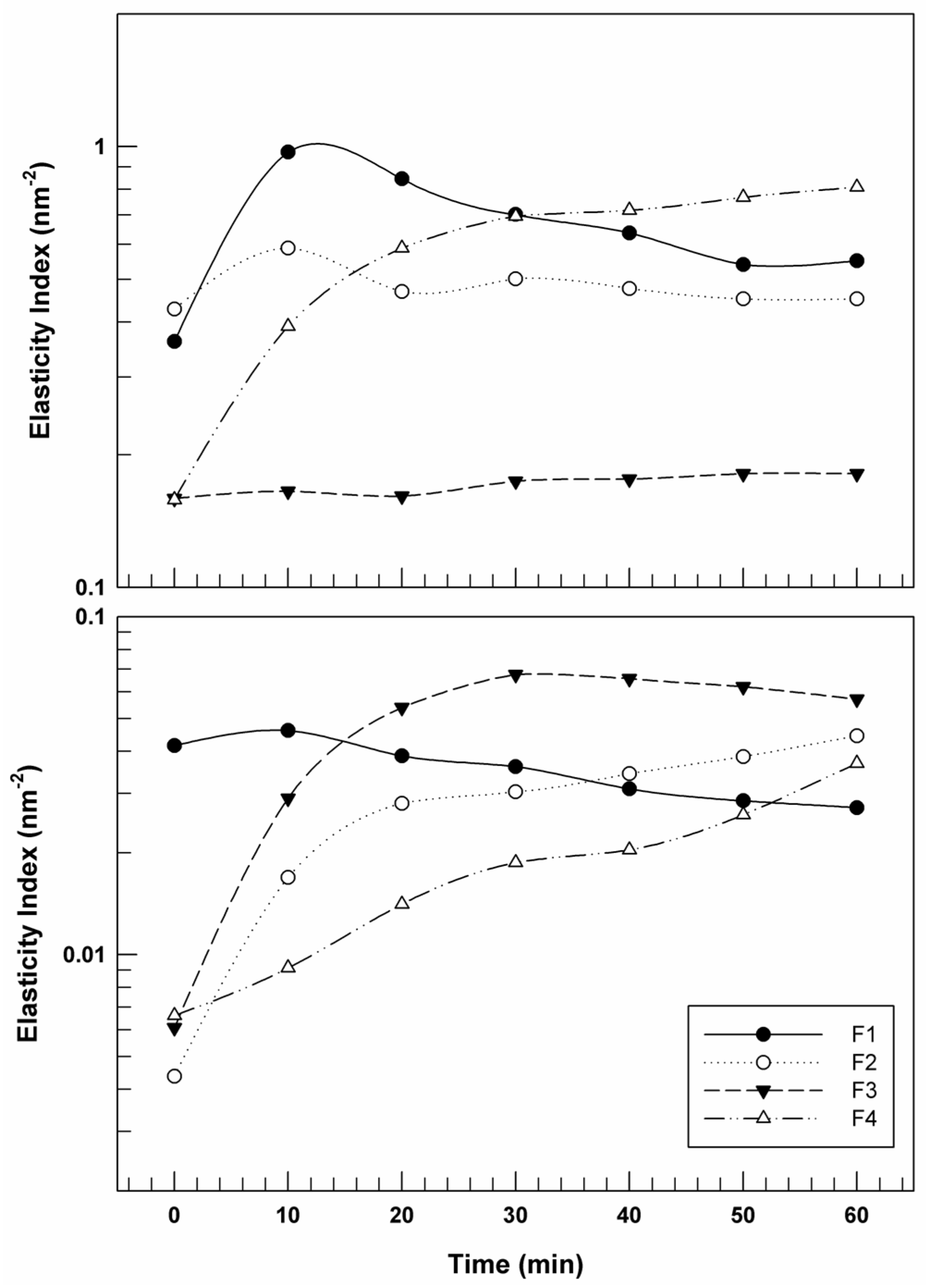
3.1. Characterization of Formulation Prototypes
3.2. Optimization and Further Characterization of Creams
3.3. Analysis of pH Values
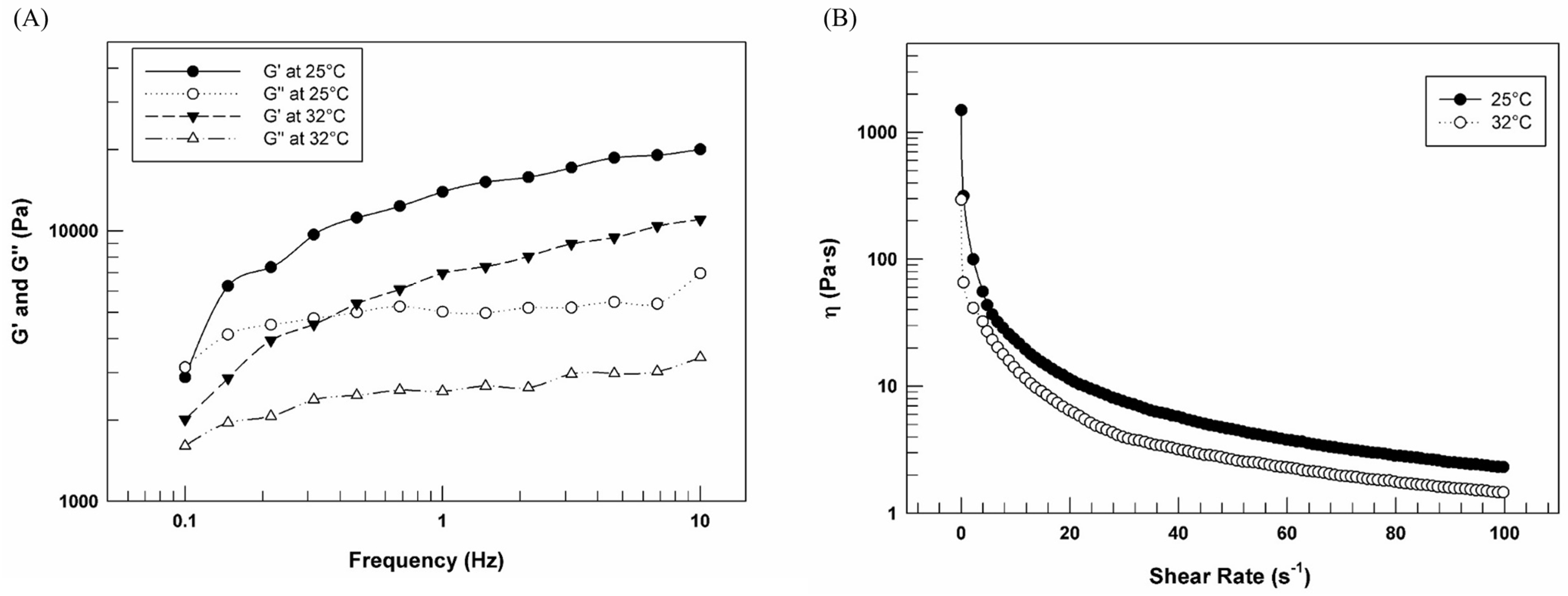
3.4. Assessment of Rheological Features of Optimized Formulations
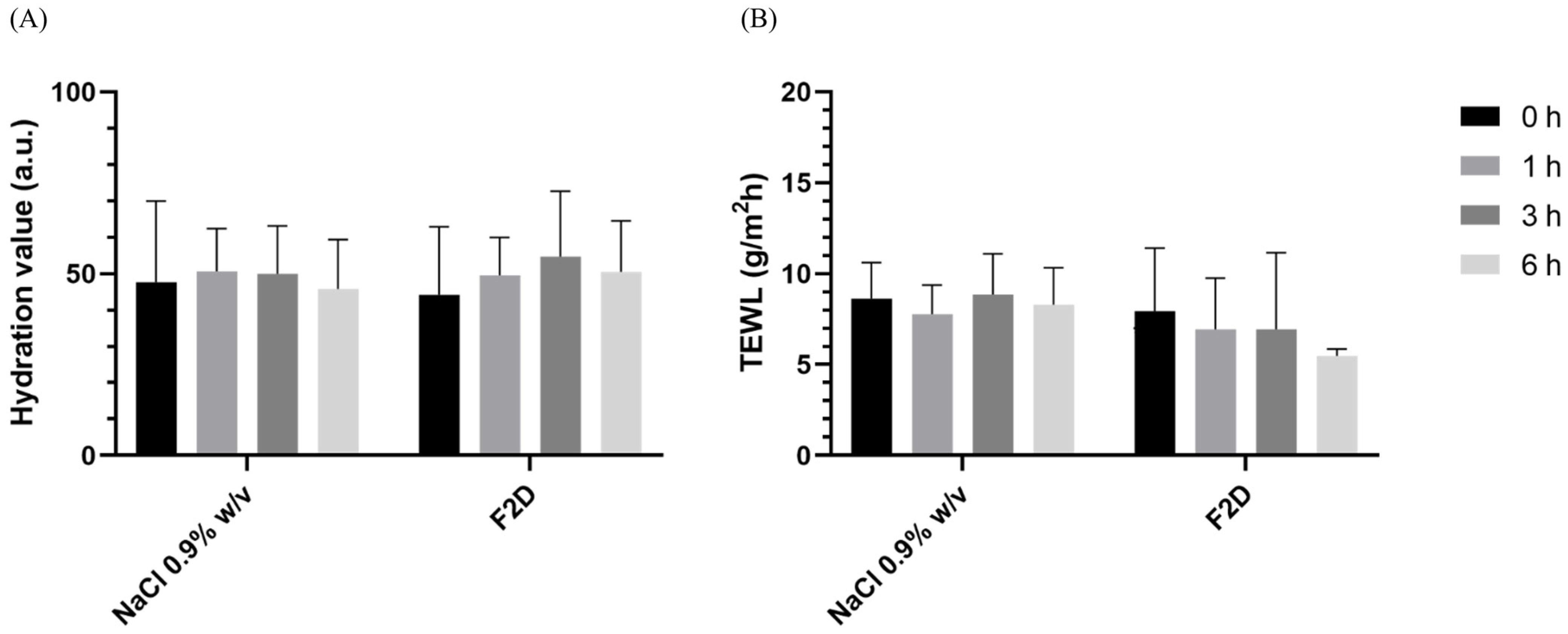
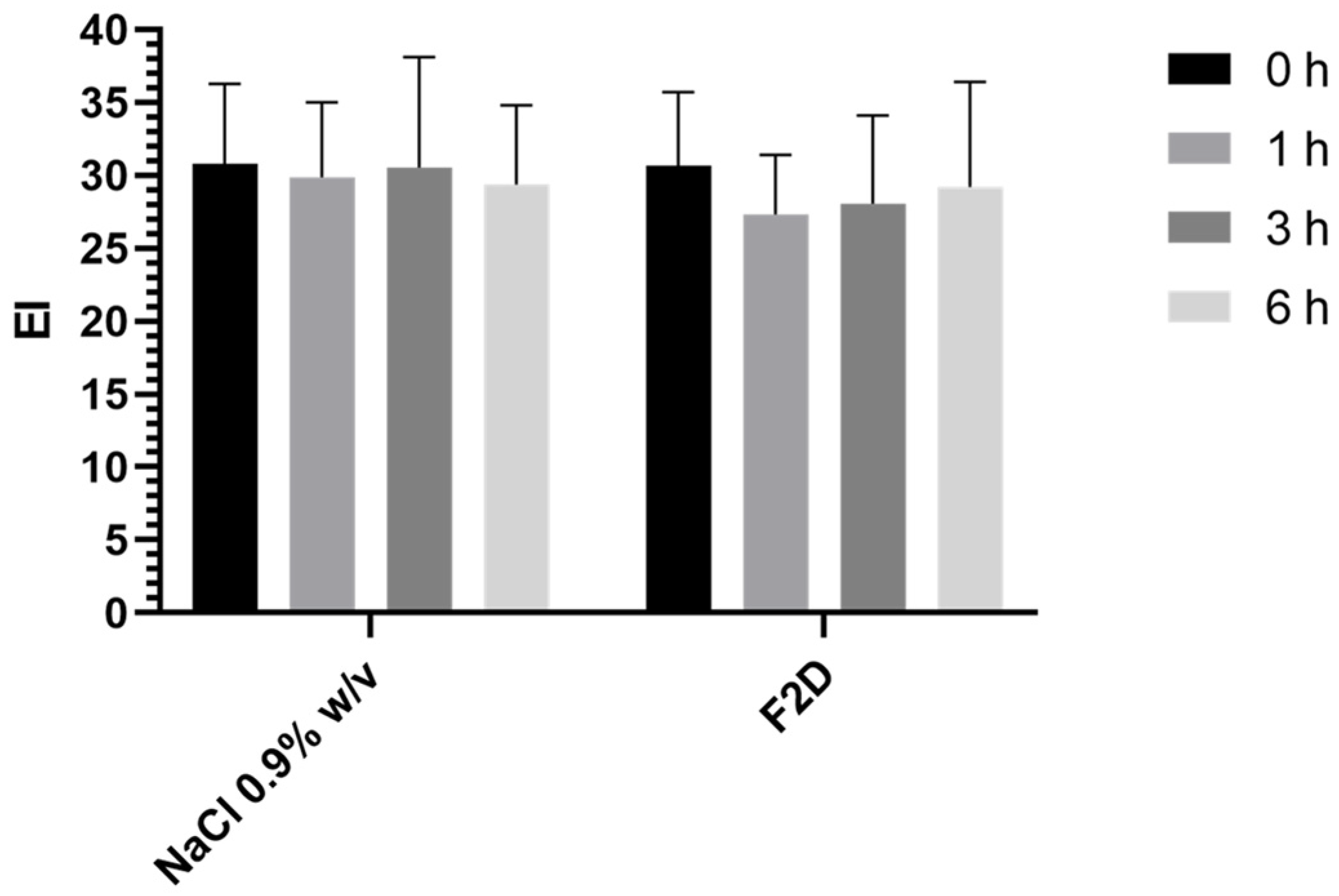
3.5. In Vivo Evaluation
3.5.1. Skin Feeling Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TSI | Turbiscan Stability Index |
| EI | Erythematous Index (EI) |
| TEWL | Transepidermal Water Loss |
| ΔBS | Delta Backscattering |
| ΔT | Delta Transmission |
References
- Farage, M.A. The prevalence of sensitive skin. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.O.; Um, J.Y.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Ko, E.; Chung, B.Y.; Park, C.W. Comprehensive Approaches to Diagnosis and Treatment of Sensitive Skin. Ann. Dermatol. 2025, 37, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, L.H.D.; Azizi, N.; Maibach, H. Sensitive skin syndrome: An update. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Guo, C.; Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Peng, S.; Huang, H.; Wu, W.; Nie, Y.; Pei, Y.; Sun, H. Sensitive skin syndrome: Research progress on mechanisms and applications. J. Dermatol. Sci. Cosmet. Technol. 2024, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenaut, E.; Barnetche, T.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Roudot, A.C.; Misery, L.; Ficheux, A.S. Triggering factors in sensitive skin from the worldwide patients’ point of view: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wangari-Olivero, J.; Zhen, Y. Compromised Skin Barrier and Sensitive Skin in Diverse Populations. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2021, 20, s17–s22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.S.; Ferreira, M.S.; Almeida, I.F.; Sousa, E. Occurrence of allergens in cosmetics for sensitive skin. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Pan, Y. Skin irritation potential of cosmetic preservatives: An exposure-relevant study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouaz, K.; Chiclana-Rodríguez, B.; Nardi-Ricart, A.; Suñé-Pou, M.; Mercadé-Frutos, D.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Pérez-Lozano, P.; García-Montoya, E. Excipients in the paediatric population: A review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monograph FN/2003/EX/005, Emulsion A/O (Cold-Cream), 2nd ed.; Ministerio de Sanidad y Consumo: Madrid, Spain, 2003.
- d’Avanzo, N.; Mancuso, A.; Mare, R.; Silletta, A.; Maurotti, S.; Parisi, O.I.; Cristiano, M.C.; Paolino, D. Olive leaves and citrus peels: From waste to potential resource for cosmetic products. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, M.; Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Körber, A.; Kerscher, M.; Itschert, G.; Dippel, M.; Staubach, P. Diagnosis and treatment of xerosis cutis–a position paper. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukić, M.; Pantelić, I.; Savić, S.D. Towards optimal ph of the skin and topical formulations: From the current state of the art to tailored products. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Cao, C.; Li, R.-Y.; Cao, L.-D.; Zhou, Z.-L.; Li, M.; Huang, Q.-L. Preparation and characterization of water-in-oil emulsions of isoprothiolane. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, A.; Cristiano, M.C.; d’Avanzo, N.; Panza, S.; Tarsitano, M.; Celia, C.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M. Assessing effectiveness of multistage nanomedicines for multidrug therapy of vitiligo. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 105, 106615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, A.; Tarsitano, M.; Cavaliere, R.; Fresta, M.; Cristiano, M.C.; Paolino, D. Gelled Liquid Crystal Nanocarriers for Improved Antioxidant Activity of Resveratrol. Gels 2023, 9, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Sun, J.; Ding, J. Thermogel loaded with low-dose paclitaxel as a facile coating to alleviate periprosthetic fibrous capsule formation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30235–30246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidberger, M.; Nikolic, I.; Pantelic, I.; Lunter, D. Optimization of rheological behaviour and skin penetration of thermogelling emulsions with enhanced substantivity for potential application in treatment of chronic skin diseases. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, M.C.; Froiio, F.; Mancuso, A.; Iannone, M.; Fresta, M.; Fiorito, S.; Celia, C.; Paolino, D. In vitro and in vivo trans-epidermal water loss evaluation following topical drug delivery systems application for pharmaceutical analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 186, 113295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dan, Y.; Yang, J.; He, X.; Liu, J.; Yi, Y.; Chen, X.; Yin, X.; Song, W.; Niu, Y. Clinical Efficacy of a Salicylic Acid–Containing Gel on Acne Management and Skin Barrier Function: A 21-Day Prospective Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e70353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, Y.; Namjoshi, S.; Jung, N.; Windbergs, M.; Benson, H.; Grice, J.; Raney, S.; Roberts, M. Topical semisolid drug product critical quality attributes with relevance to cutaneous bioavailability and pharmacokinetics: Part I—Bioequivalence of acyclovir topical creams. Pharm. Res. 2024, 41, 1507–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seweryn, A. Interactions between surfactants and the skin–Theory and practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, H.; Deng, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wen, Y. Efficacy and safety of a panthenol-enriched mask for individuals with distinct impaired skin barrier subtypes. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, M.; Webber, G.; Louw, N. Relating rheological measurements to primary and secondary skin feeling when mineral-based and Fischer–Tropsch wax-based cosmetic emulsions and jellies are applied to the skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celleno, L. Topical urea in skincare: A review. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 31, e12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panin, G.; Strumia, R.; Ursini, F. Topical α-Tocopherol Acetate in the Bulk Phase: Eight Years of Experience in Skin Treatment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1031, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piquero-Casals, J.; Morgado-Carrasco, D.; Granger, C.; Trullàs, C.; Jesús-Silva, A.; Krutmann, J. Urea in dermatology: A review of its emollient, moisturizing, keratolytic, skin barrier enhancing and antimicrobial properties. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Weber, S.U.; Rimbach, G. Molecular aspects of α-tocotrienol antioxidant action and cell signalling. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 369S–373S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, G.; Xiao, J.; Cao, Y.; Sun, B. Influence of unadsorbed emulsifiers on the rheological properties and structure of heteroaggregate of whey protein isolate (WPI) coated droplets and flaxseed gum (FG) coated droplets. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Rousseau, D. Fat crystals and water-in-oil emulsion stability. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Xi, C.; Liu, Y. Exploration of the natural waxes-tuned crystallization behavior, droplet shape and rheology properties of O/W emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 587, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, D.E.; Negrão, C.O. Rheology of waxy oils: A critical review. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2025, 21, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Deac, A.; Zhang, G.G. Assessing physical stability of colloidal dispersions using a turbiscan optical analyzer. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calienni, M.N.; Prieto, M.J.; Couto, V.M.; de Paula, E.; Alonso, S.d.V.; Montanari, J. 5-Fluorouracil-Loaded Ultradeformable Liposomes for Skin Therapy; AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; p. 020024. [Google Scholar]
- Olejnik, A.; Kapuscinska, A.; Schroeder, G.; Nowak, I. Physico-chemical characterization of formulations containing endomorphin-2 derivatives. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1719–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Truong, T.; Chandrapala, J.; Cheong, L.-z.; Farahnaky, A. Multicomponent oleogels of ethylcellulose-binary waxes: Atomic force microscopy observation and synergistic effect analysis. Food Res. Int. 2025, 219, 117111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirow, R.; Blume, A.; Hellwig, N.; Herzler, M.; Huhse, B.; Hutzler, C.; Pfaff, K.; Thierse, H.-J.; Tralau, T.; Vieth, B. Mineral oil in food, cosmetic products, and in products regulated by other legislations. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2019, 49, 742–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Rego, L.; Martins, M.S.; Ferreira, M.S.; Cruz, M.T.; Sousa, E.; Almeida, I.F. How to promote skin repair? In-depth look at pharmaceutical and cosmetic strategies. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.S.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Almeida, I.F. Sensitive skin: Active ingredients on the spotlight. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2022, 44, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danby, S.G.; Andrew, P.V.; Taylor, R.N.; Kay, L.J.; Chittock, J.; Pinnock, A.; Ulhaq, I.; Fasth, A.; Carlander, K.; Holm, T. Different types of emollient cream exhibit diverse physiological effects on the skin barrier in adults with atopic dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 47, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiume, M.M.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W. Safety assessment of tocopherols and tocotrienols as used in cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2018, 37 (Suppl. S2), 61S–94S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dréno, B.; Zuberbier, T.; Gelmetti, C.; Gontijo, G.; Marinovich, M. Safety review of phenoxyethanol when used as a preservative in cosmetics. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E. pH in nature, humans and skin. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, V. Influence of hydroxyethyl and carboxymethyl celluloses on the rheology, water retention and surface tension of water-suspended microfibrillated cellulose. Cellulose 2022, 29, 7063–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhao, W.; Lin, B.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. Hydroxyethyl cellulose as a rheological additive for tuning the extrusion printability and scaffold properties. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 8, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, E.H.; Baik, J.H.; Park, J.D. The role of rheology in cosmetics research: A review. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2024, 36, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, R.; Godersky, S. Rheological studies to objectify sensations occurring when cosmetic emulsions are applied to the skin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 152, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.S.; da Silva, A.M.M.; Mendes, G.A.C.; Sato, A.C.K.; Cunha, R.L. Almond protein as Pickering emulsion stabilizer: Impact of microgel fabrication method and pH on emulsion stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsaros, G.; Tsoukala, M.; Giannoglou, M.; Taoukis, P. Effect of storage on the rheological and viscoelastic properties of mayonnaise emulsions of different oil droplet size. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manian, M.; Jain, P.; Vora, D.; Banga, A.K. Formulation and evaluation of the in vitro performance of topical dermatological products containing diclofenac sodium. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, D.; Temesvári, E.; Holló, P.; Pónyai, G. Preservative contact hypersensitivity among adult atopic dermatitis patients. Life 2022, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, H.; Brown, S.; Danby, S.; Flohr, C. Research techniques made simple: Transepidermal water loss measurement as a research tool. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2295–2300.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, B.C.K.; Dyer, E.B.; Feig, J.L.; Chien, A.L.; Del Bino, S. Research techniques made simple: Cutaneous colorimetry: A reliable technique for objective skin color measurement. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 3–12.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panico, A.; Serio, F.; Bagordo, F.; Grassi, T.; Idolo, A.; De Giorgi, M.; Guido, M.; Congedo, M.; De Donno, A. Skin safety and health prevention: An overview of chemicals in cosmetic products. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2019, 60, E50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Formulations | Composition (%) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cetyl Palmitate | Beeswax | Caprylic/Capric Triglyceride | Xanthan Gum | Tocopheryl Acetate | Sweet Almond Oil | Cetyl/Stearyl Alcohol | Isopropyl Myristate | Shea Butter | Jojoba Oil | Argania Spinosa Kernel Oil | Panthenol | Allantoin | Urea | Phenoxyethanol | Glycerol | Hydroxyethyl Cellulose | MilliQ Water | |
| F2A | 12.5 | 2.5 | / | / | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 0.8 | 3 | / | Q.s. to 100 |
| F2B | 6 | 1 | 6 | 0.1 | 4 | 3.5 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 4 | / | |||||||
| F2C | 4 | 6 | 0.3 | / | ||||||||||||||
| F2D | 3 | 6 | 0.3 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||
| Formulation | pH |
|---|---|
| F2A | 6.66 ± 0.12 |
| F2B | 7.14 ± 0.28 |
| F2C | 7.11 ± 0.31 |
| F2D | 6.72 ± 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mancuso, A.; Silletta, A.; Verdiglione, M.; d’Avanzo, N.; Barone, A.; Sacco, J.; Cristiano, M.C.; Paolino, D. Cosmetics for Sensitive Skin: Assessing Rheological Properties, Stability, and Safety. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060239
Mancuso A, Silletta A, Verdiglione M, d’Avanzo N, Barone A, Sacco J, Cristiano MC, Paolino D. Cosmetics for Sensitive Skin: Assessing Rheological Properties, Stability, and Safety. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(6):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060239
Chicago/Turabian StyleMancuso, Antonia, Antonio Silletta, Mario Verdiglione, Nicola d’Avanzo, Antonella Barone, Jolanda Sacco, Maria Chiara Cristiano, and Donatella Paolino. 2025. "Cosmetics for Sensitive Skin: Assessing Rheological Properties, Stability, and Safety" Cosmetics 12, no. 6: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060239
APA StyleMancuso, A., Silletta, A., Verdiglione, M., d’Avanzo, N., Barone, A., Sacco, J., Cristiano, M. C., & Paolino, D. (2025). Cosmetics for Sensitive Skin: Assessing Rheological Properties, Stability, and Safety. Cosmetics, 12(6), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060239









