Development of Emulsions Containing L-Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol Based on the Polysaccharide FucoPol: Stability Evaluation and Rheological and Texture Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of FucoPol-Based Emulsions
2.3. Preparation of FucoPol-Based Formulations
2.4. Formulations’ Characterization
2.5. Viscoelastic Properties
2.6. Texture Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
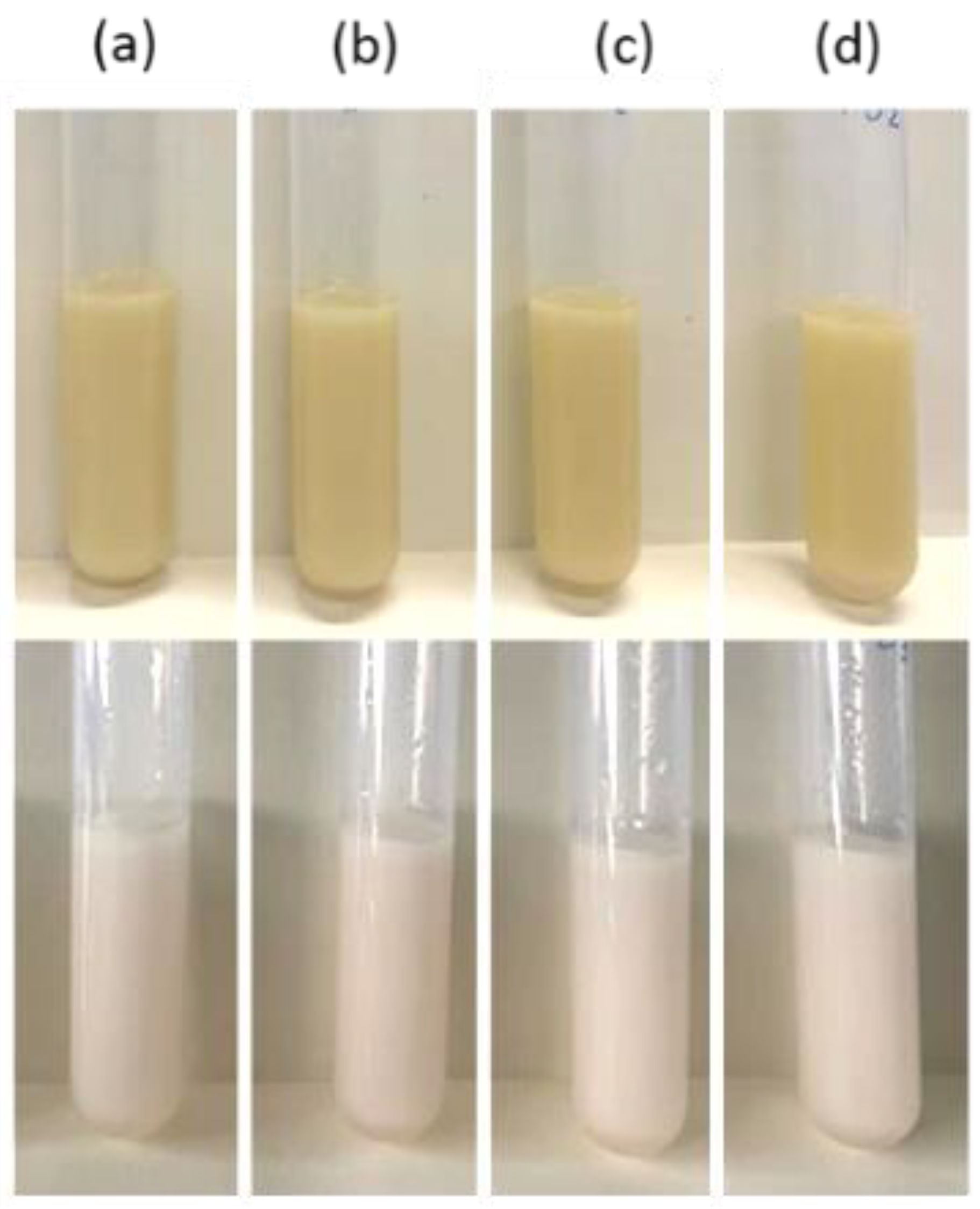
3.1. Defining L-Ascorbic Acid Concentration in the Emulsions’ Continuous Phase
3.2. Emulsified Formulations with L-Ascorbic Acid
3.3. Characterization of FucoPol-Based Emulsified Formulations
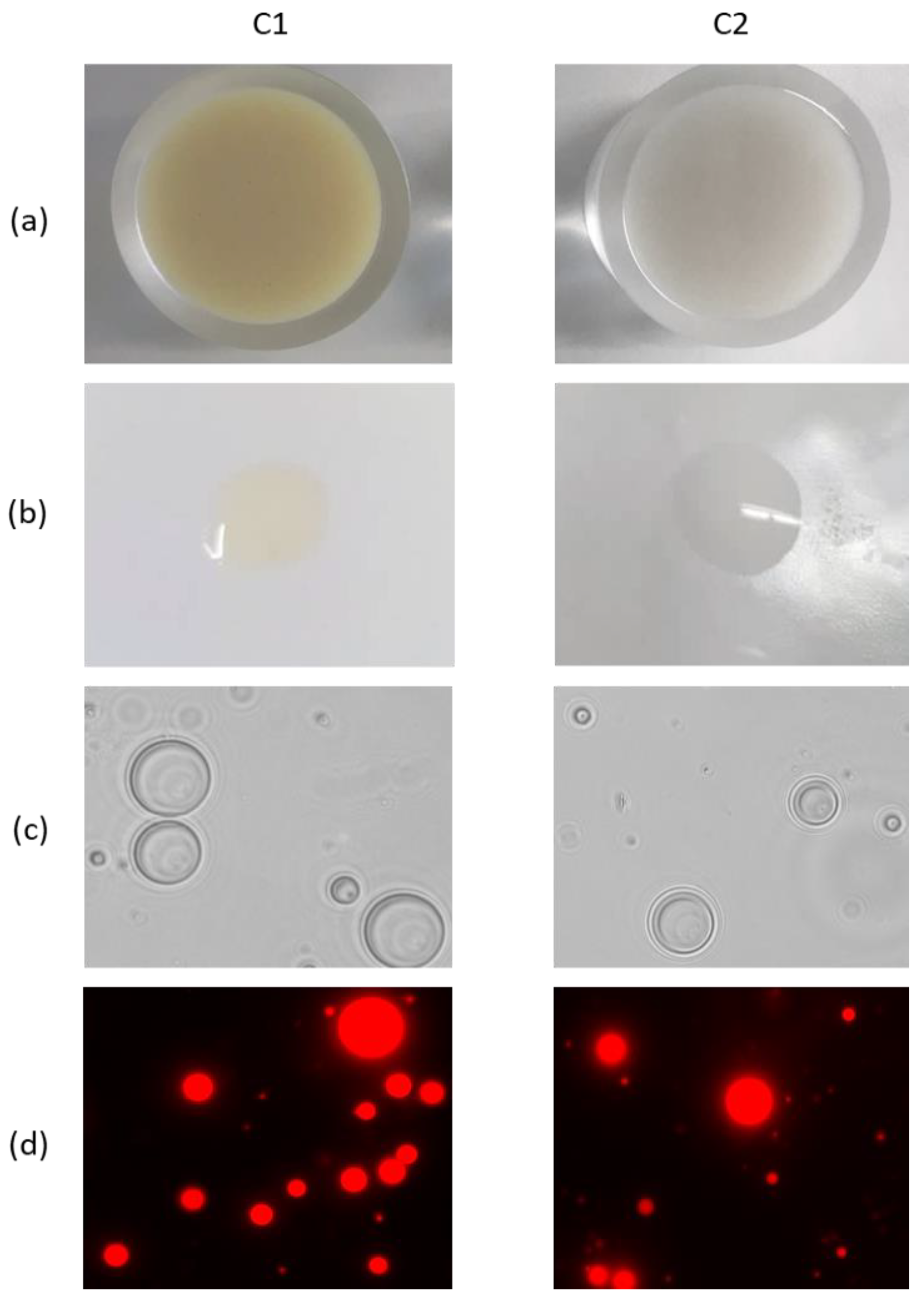
3.3.1. Organoleptic Characteristics and Physical Stability
3.3.2. Emulsion Type
3.3.3. pH and Conductivity
3.3.4. Droplet Size and Zeta Potential
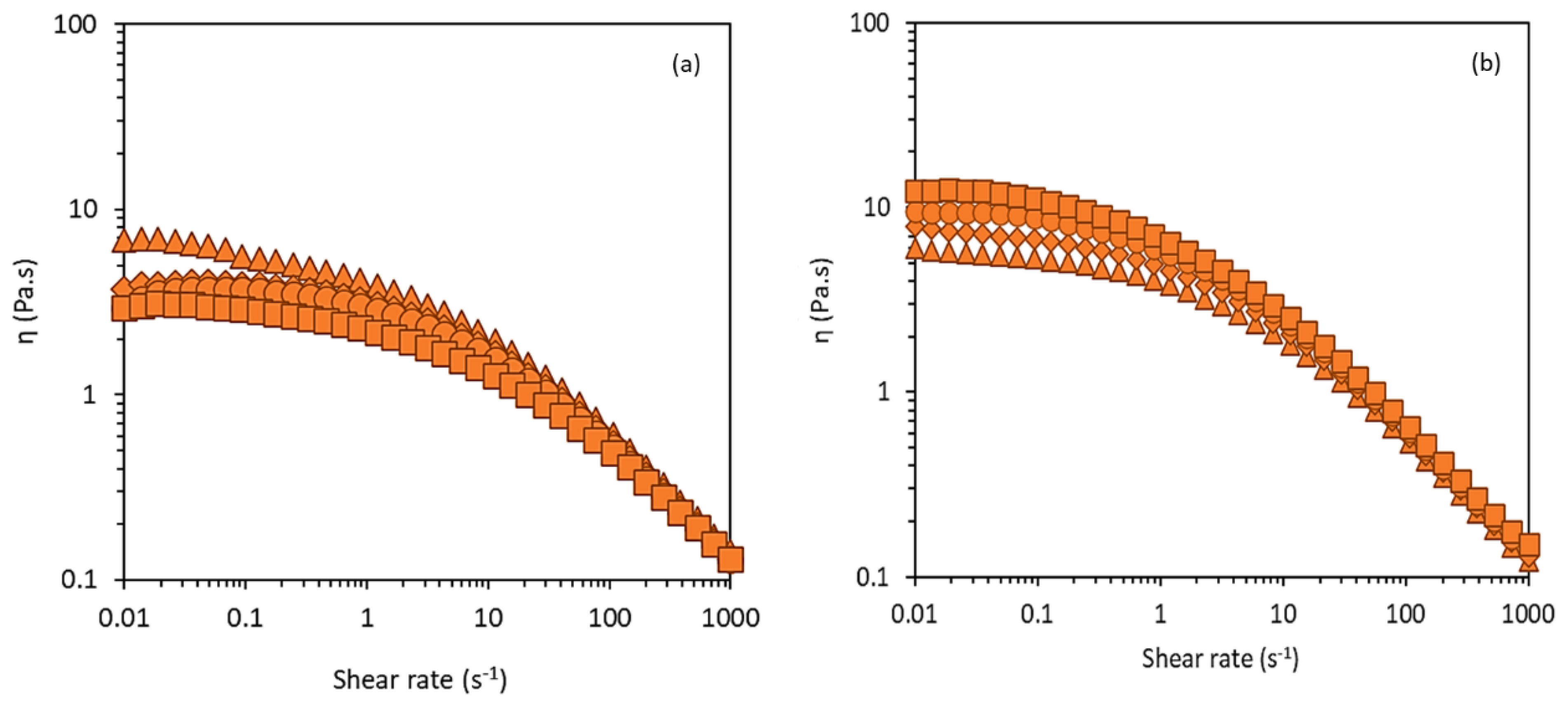
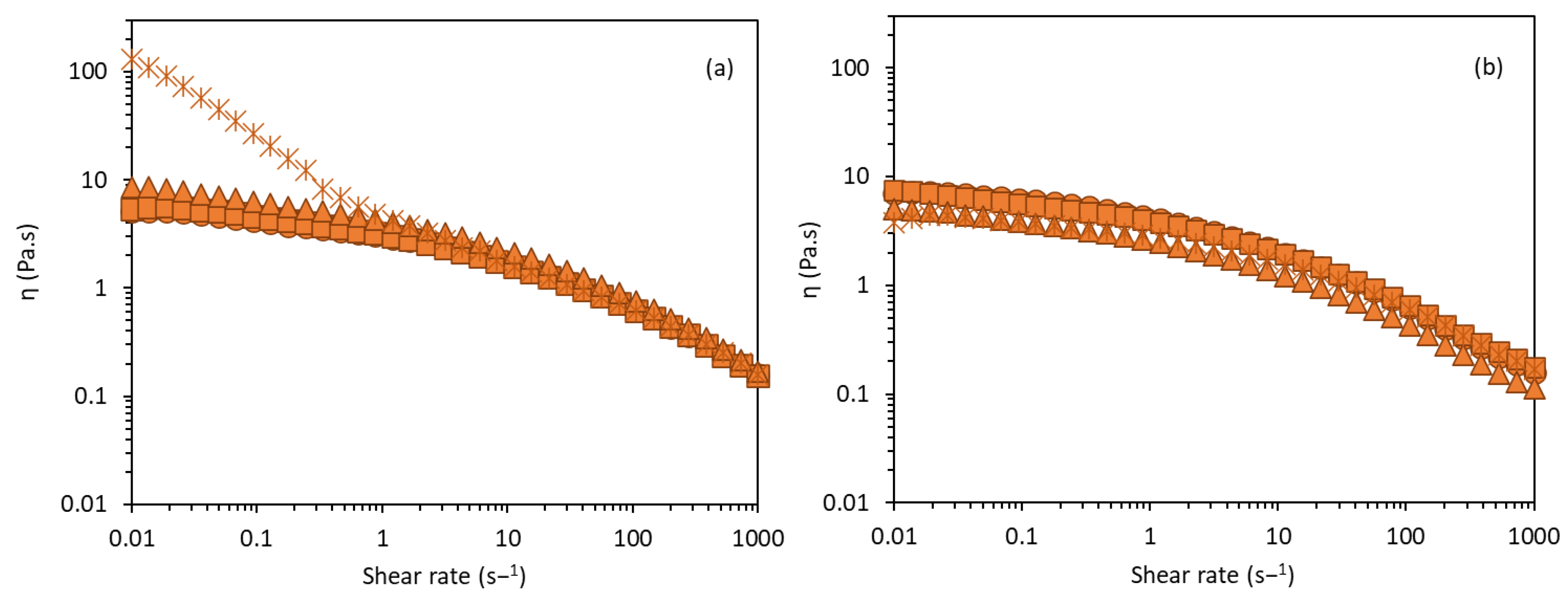
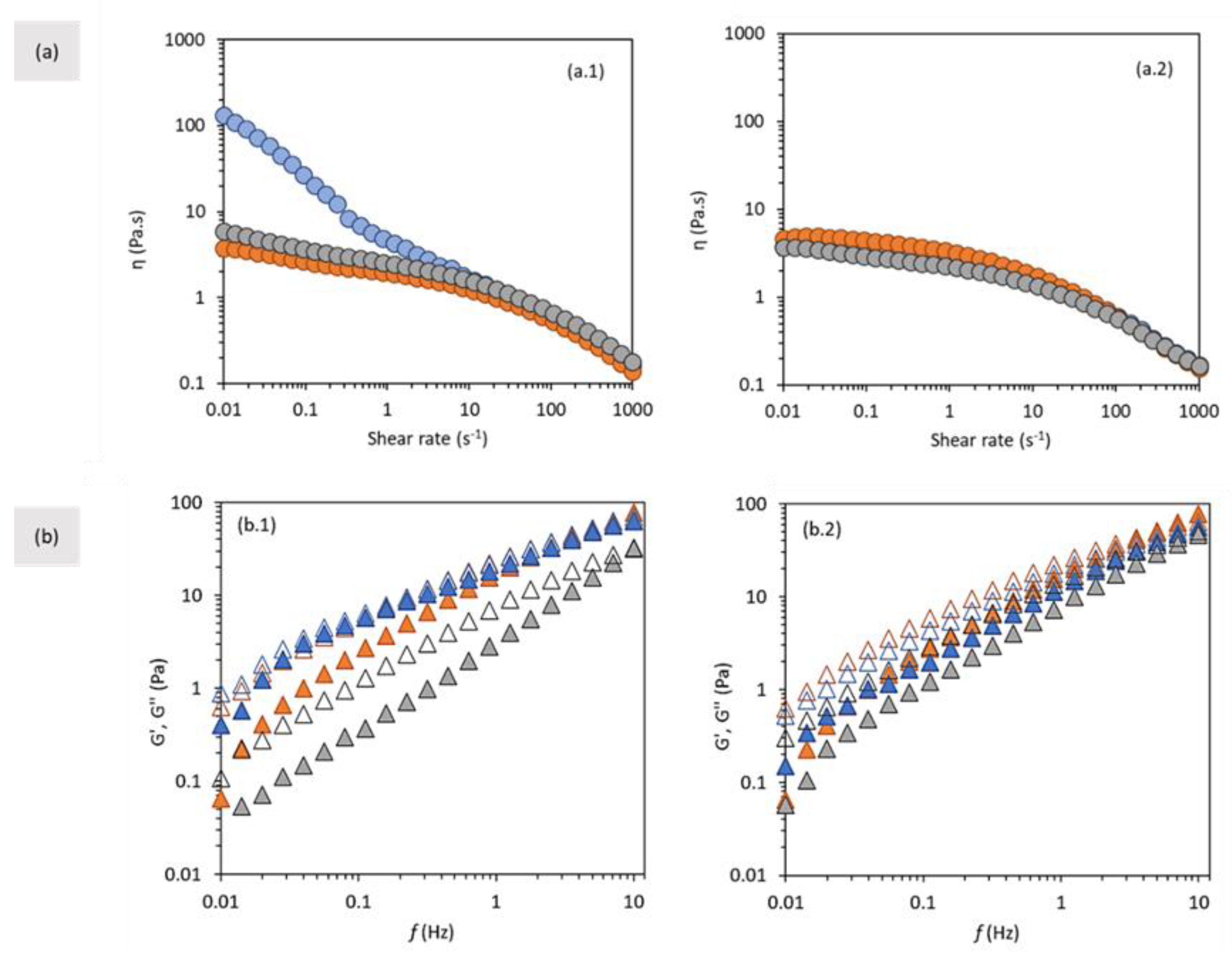
3.3.5. Apparent Viscosity and Viscoelastic Properties
3.3.6. Textural Assessment
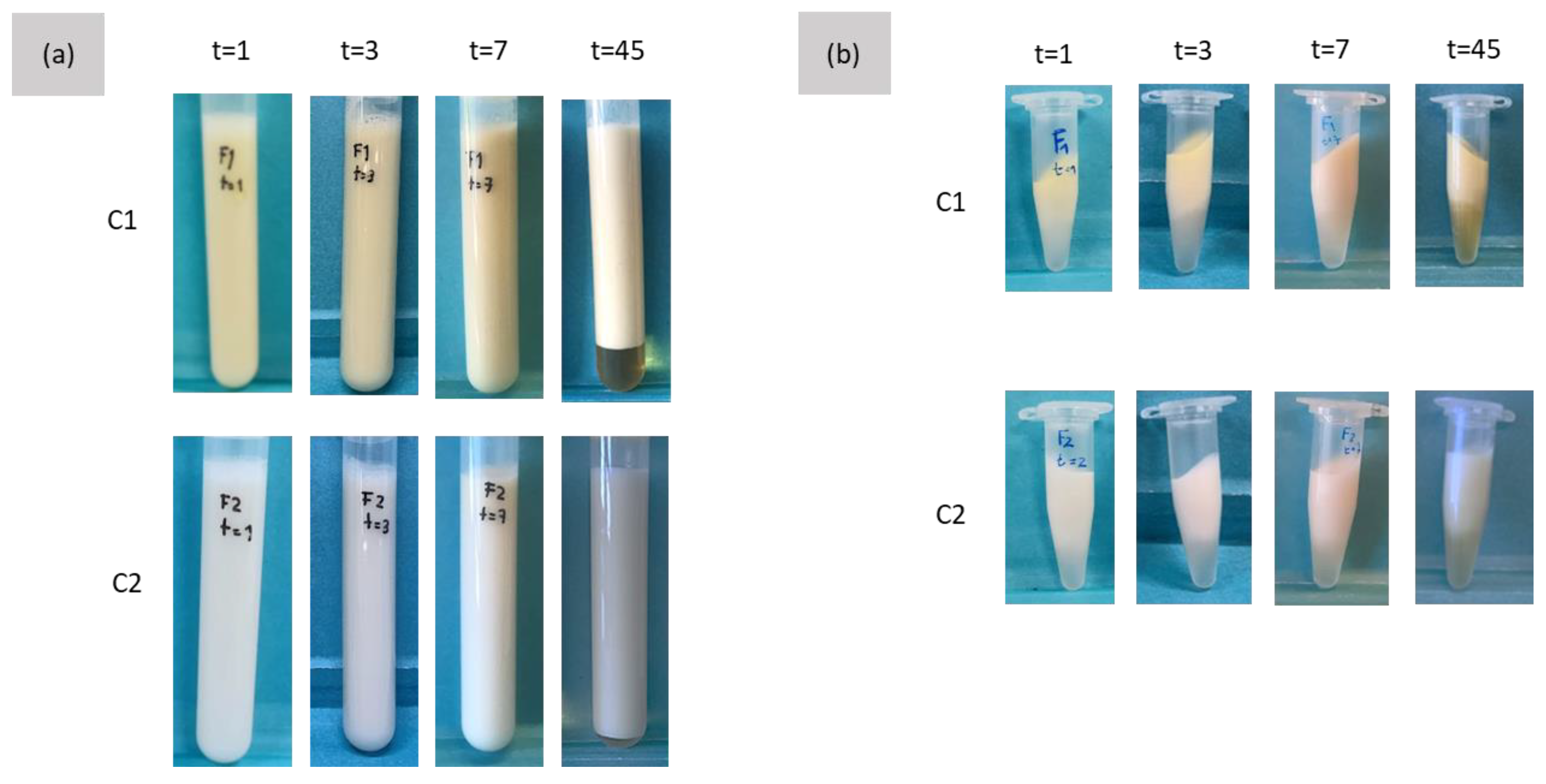
3.3.7. Accelerated Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enescu, C.D.; Bedford, L.M.; Potts, G.; Fahs, F. A Review of Topical Vitamin C Derivatives and Their Efficacy. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosenca, M.; Obreza, A.; Pečar, S.; Gašperlin, M. A New Approach for Increasing Ascorbyl Palmitate Stability by Addition of Non-irritant Co-antioxidant. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia Campos, P.M.B.G.; Gianeti, M.D.; Camargo, F.B.; Gaspar, L.R. Application of Tetra-Isopalmitoyl Ascorbic Acid in Cosmetic Formulations: Stability Studies and in vivo efficacy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravetti, S.; Clemente, C.; Brignone, S.; Hergert, L.; Allemandi, D.; Palma, S. Ascorbic Acid in Skin Health. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, S.; Tajerzadeh, H.; Farboud, E. Formulation and Evaluation of a Vitamin C Multiple Emulsion. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2006, 11, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telang, P.S. Vitamin C in Dermatology. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2013, 4, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheraz, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, I.; Shaikh, R.H.; Vaid, F.H.M.; Iqbal, K. Formulation and Stability of Ascorbic Acid in Topical Preparations. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2011, 2, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, N.; Chiang, Z. Topical Vitamin C and the Skin. JCAD J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2017, 14, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Sheraz, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Shaikh, R.H.; Vaid, F.H.M.; Ur Rehman Khattak, S.; Ansari, S.A. Photostability and Interaction of Ascorbic Acid in Cream Formulations. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Kobayashi, I.; Neves, M.A.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M. Preparation and characterization of water-in-oil emulsions loaded with high concentration of L-Ascorbic acid. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macan, A.M.; Kraljević, T.G.; Raić-Malić, S. Therapeutic Perspective of Vitamin C and Its Derivatives. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.Y.; Selim, M.A.; Shea, C.R.; Grichnik, J.M.; Omar, M.M.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Pinnell, S.R. UV Photoprotection by Combination Topical Antioxidants Vitamin C and Vitamin E. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheraz, M.; Khan, M.; Ahmed, S.; Kazi, S.; Ahmad, I. Stability and Stabilization of Ascorbic Acid. Househ. Pers. Care Today 2015, 10, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gallarate, M.; Carlotti, M.; Trotta, M.; Bovo, S. On the Stability of Ascorbic Acid in Emulsified Systems for Topical and Cosmetic Use. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 188, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caritá, A.C.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Shultz, J.D.; Michniak-Kohn, B.; Chorilli, M.; Leonardi, G.R. Vitamin C: One Compound, Several Uses. Advances for Delivery, Efficiency and Stability. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 24, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschke, T.; Koop, U.; Düsing, H.-J.; Filbry, A.; Sauermann, K.; Jaspers, S.; Wenck, H.; Wittern, K.-P. Topical Activity of Ascorbic Acid: From in vitro Optimization to in vivo Efficacy. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 17, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, C.; Genies, C.; Bacqueville, D.; Tourette, A.; Borotra, N.; Chaves, F.; Sanches, F.; Gaudry, A.L.; Bessou-Touya, S.; Duplan, H. Ascorbic Acid 2-Glucoside: An Ascorbic Acid Pro-Drug with Longer-Term Antioxidant Efficacy in Skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, B.M.; Silva, J.C.; Lima, J.C.; Reis, M.A.M.; Freitas, F. Antioxidant Potential of the Bio-Based Fucose-Rich Polysaccharide FucoPol Supports Its Use in Oxidative Stress-Inducing Systems. Polymers 2021, 13, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, B.M.; Freitas, F.; Lima, J.C.; Silva, J.C.; Reis, M.A.M. Photoprotective Effect of the Fucose-Containing Polysaccharide FucoPol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concórdio-Reis, P.; Pereira, C.V.; Batista, M.P.; Sevrin, C.; Grandfils, C.; Marques, A.C.; Fortunato, E.; Gaspar, F.B.; Matias, A.A.; Freitas, F.; et al. Silver Nanocomposites Based on the Bacterial Fucose-Rich Polysaccharide Secreted by Enterobacter A47 for Wound Dressing Applications: Synthesis, Characterization and in vitro Bioactivity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, B.M.; Lima, J.C.; Dionísio, M.; Silva, J.C.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.A.M. Demonstration of the Cryoprotective Properties of the Fucose-Containing Polysaccharide FucoPol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, S.; Pereira, J.R.; Gil, C.V.; Torres, C.A.V.; Reis, M.A.M.; Freitas, F. Development of Olive Oil and α-Tocopherol Containing Emulsions Stabilized by FucoPol: Rheological and Textural Analyses. Polymers 2022, 14, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, S.; Torres, C.A.V.; Sevrin, C.; Grandfils, C.; Reis, M.A.M.; Freitas, F. Extraction of the Bacterial Extracellular Polysaccharide FucoPol by Membrane-Based Methods: Efficiency and Impact on Biopolymer Properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, S.; Freitas, F. Formulation of the Polysaccharide FucoPol into Novel Emulsified Creams with Improved Physicochemical Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, S.; Pereira, J.R.; Guerreiro, B.M.; Baptista, F.; Silva, J.C.; Freitas, F. Cosmetic Emulsion Based on the Fucose-Rich Polysaccharide FucoPol: Bioactive Properties and Sensorial Evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 225, 113252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.A.V.; Marques, R.; Ferreira, A.R.V.; Antunes, S.; Grandfils, C.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.A.M. Impact of Glycerol and Nitrogen Concentration on Enterobacter A47 Growth and Exopolysaccharide Production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-K.; Zhong, L.; Santiago, J.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Barrier Repair Effects of Topical Application of Some Plant Oils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, Z. The Uses and Properties of Almond Oil. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2010, 16, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavica, Č.; Zec, G.; Nati, M.; Fotiri, M. Almond (Prunus dulcis) Oil. In Fruit Oils: Chemistry and Functionality; Ramadan, M.F., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Chapter 6; pp. 149–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, S.; Fitas, M.; Martins, A.M.; Pinto, P.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Marto, J. Replacing Synthetic Ingredients by Sustainable Natural Alternatives: A Case Study Using Topical O/W Emulsions. Molecules 2020, 25, 4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, J.S.; Santos, V.; Weiss-Angeli, V.; Gomes, L.B.; Veras, D.G.; Dani, N.; Mexias, A.S.; Bergmann, C.P. Evaluation and Characterization of Melo Bentonite Clay for Cosmetic Applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 175, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifah, S.N.; Azhar, S.; Ashari, S.E.; Salim, N. Development of a Kojic Monooleate-Enriched Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion as a Potential Carrier for Hyperpigmentation Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6465–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Akhtar, N.; Menaa, A.; Menaa, F. A Novel Cassia fistula (L.)-Based Emulsion Elicits Skin Anti-Aging Benefits in Humans. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenzato, A.; Costantini, A.; Meloni, M.; Maramaldi, G.; Meneghin, M.; Baratto, G. Formulating O/W Emulsions with Plant-Based Actives: A Stability Challenge for an Effective Product. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.A.V.; Ferreira, A.R.V.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.A.M.; Coelhoso, I.; Sousa, I.; Alves, V.D. Rheological Studies of the Fucose-rich Exopolysaccharide FucoPol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Domínguez, M.L.; Raigón, M.D.; Prohens, J. Diversity for Olive Oil Composition in a Collection Of Varieties from the Region of Valencia (Spain). Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Tortosa, M.C.; Granados, S.; Quiles, J.L. Chemical Composition, Types and Characteristics of Olive Oil. In Olive Oil and Health; Quiles, J.L., Carmen, R.-T.M., Parven, Y., Eds.; CAB International: London, UK, 2006; Volume 10, p. 2002. ISBN 9781845930684.36. [Google Scholar]
- Blekas, G.; Tsimidou, M.; Boskou, D. Olive Oil Composition. In Olive Oil: Chemistry and Technology, 2nd ed.; Boskou, D., Ed.; AOCS Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 41–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, C.A.; Nypelö, T.E.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose Nanofibrils for One-Step Stabilization of Multiple Emulsions (W/O/W) Based on Soybean Oil. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnell, S.R.; Yang, H.; Omar, M.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.; DeBuys, H.V.; Walker, L.C.; Wang, Y.; Levine, M. Topical L-Ascorbic Acid: Percutaneous Absorption Studies. Dermatol. Surg. 2001, 27, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-P.; Chen, F. Degradation of Ascorbic Acid in Aqueous Solution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 5078–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochhead, R.Y. The Role of Polymers in Cosmetics: Recent Trends. ACS Symp. Ser. 2007, 961, 3–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.F. Emulsion Formation, Stability, and Rheology. In Emulsion Formation, Stability, and Rheology; Tadros, T.F., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, F.; Zendehboudi, S. A Comprehensive Review on Emulsions and Emulsion Stability in Chemical and Energy Industries. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 97, 281–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitake, D.; Balyan, S.; Devi, P.B.; Shetty, P.H. Interface between Food Grade Flavour and Water Soluble Galactan Biopolymer to form a Stable Water-In-Oil-In-Water Emulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitake, D.; Balyan, S.; Devi, P.B.; Shetty, P.H. Evaluation of Oil-In-Water (O/W) Emulsifying Properties of Galactan Exopolysaccharide from Weissella confusa KR780676. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J. Critical Review of Techniques and Methodologies for Characterization of Emulsion Stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Nour, A.H. Emulsion Types, Stability Mechanisms and Rheology: A Review. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Stud. 2018, 1, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pla, J.J.; Martín-Biosca, Y.; Sagrado, S.; Villanueva-Camañas, R.M.; Medina-Hernández, M.J. Evaluation of the pH Effect of Formulations on the Skin Permeability of Drugs by Biopartitioning Micellar Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1047, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaslina, N.F.; Faujan, N.H.; Mohamad, R.; Ashari, S.E. Effectct of Addition of PVA/PG to Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion Kojic Monooleate Formulation on Droplet Size: Three-Factors Response Surface. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, H.; Braga, V.D.A. Development, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Polysorbate Based O/W Emulsion Containing Polyphenols Derived from Hippophae rhamnoides and Cassia fistula. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Kaur, M.; Mahajan, M.; Jain, S.K. Development, Characterization and Evaluation of Nanocarrier Based Formulations of Antipsoriatic Drug “Acitretin” for Skin Targeting. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, T.G. Stabilization of L-Ascorbic Acid in Cosmetic Emulsions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 57, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.; Ceglie, A.; Ambrosone, L. Biocompatible Water-in-Oil Emulsion as a Model to Study Ascorbic Acid Effect on Lipid Oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 4635–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, H.; Le Dréau, Y.; Piccerelle, P.; Kister, J. The evaluation of Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Emulsions Aging Process Using Classical Techniques and a New Method: FTIR. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 289, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.; Han, B.; Fan, J.; Kou, M.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Z.-J.; Pan, W.; Zhou, W. Characterization of Structure and Stability of Emulsions Stabilized with Cellulose Macro/Nano particles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estanqueiro, M.; Conceição, J.; Amaral, M.H.; Lobo, J.M.S. Characterization, Sensorial Evaluation and Moisturizing Efficacy of Nanolipidgel Formulations. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 36, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbstein, H.; Schubert, H. Developments in the Continuous mechanical Production of Oil-in-Water Macro-Emulsions. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 1995, 34, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenso, A.; Simões, S.; Marto, J.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Almeida, A.J. Colloidal Disperse Systems: Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions. In Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery; Eloy, J.O., Abriata, J.P., Marchetti, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 9783030633882.58. [Google Scholar]
- Dapčević Hadnadev, T.; Dokić, P.; Krstonošić, V.; Hadnadev, M. Influence of Oil Phase Concentration on Droplet Size Distribution and Stability of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2012, 115, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-H.; Lu, W.-C. Effects of Storage Conditions on the Physical Stability of D-Limonene Nanoemulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal-Figiel, B. The Formation of Stable W/O, O/W, W/O/W Cosmetic Emulsions in an Ultrasonic Field. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2007, 85, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eh Suk, V.R.; Khalid, K.; Misran, M. Preparation and Characterization of Ylang-Ylang (Cananga odorata) Essential Oil and Ascorbic Acid Loaded Olive Oil-in-Water Emulsion. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2019, 46, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, P.; Kumar, V.; Mishra, I.M. Study the Electro-Viscous Effect on Stability and Rheological Behavior of Surfactant-stabilized Emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveyard, R.; Clint, J.H.; Nees, D.; Paunov, V.N. Compression and Structure of Monolayers of Charged Latex Particles at Air/Water and Octane/Water Interfaces. Langmuir 1999, 16, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- César, F.C.S.; Maia Campos, P.M.B.G. Influence of Vegetable Oils in the Rheology, Texture Profile and Sensory Properties of Cosmetic Formulations Based on Organogel. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 42, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazal, W.; Musa, K.B.; Mohsan, N.; Khakemin, K. Comparison of Some Physico-Chemical Properties of Different Oils Available in the Local Market in Pakistan. Int. J. Recent Res. Asp. 2015, 2, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tafuro, G.; Costantini, A.; Baratto, G.; Francescato, S.; Busata, L.; Semenzato, A. Characterization of Polysaccharidic Associations for Cosmetic Use: Rheology and Texture Analysis. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.; Gonçalves, L.; Marto, J.; Martins, A.M.; Silva, A.N.; Pinto, P.; Martins, M.; Fraga, C.; Ribeiro, H.M. Investigations of Olive Oil Industry By-Products Extracts with Potential Skin Benefits in Topical Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paximada, P.; Tsouko, E.; Kopsahelis, N.; Koutinas, A.A.; Mandala, I. Bacterial Cellulose as Stabilizer of o/w Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito, A.C.F.; Sierakowski, M.R.; Reicher, F.; Feitosa, J.P.; de Paula, R.C.M. Dynamic Rheological Study of Sterculia Striata and Karaya Polysaccharides in Aqueous Solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmaleki, K.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Mohammadi, R.; Fadavi, G.; Meybodi, N.M. The Effect of pH and Salt on the Stability and Physicochemical Properties of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Prepared with Gum Tragacanth. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, N.; Muñoz, J.; Cox, P.W.; Heuer, A.; Guerrero, A. Influence of Chitosan Concentration on the Stability, Microstructure And Rheological Properties of O/W Emulsions Formulated with High-Oleic Sunflower Oil and Potato Protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiki, Y.; Horn, R.G.; Prestidge, C.A. Droplet Structure Instability in Concentrated Emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 320, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, G.; Grisel, M.; Picard, C. Impact of Emollients on the Spreading Properties of Cosmetic Products: A Combined Sensory and Instrumental Characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochhead, R.Y. The Use of Polymers in Cosmetic Products. In Cosmetic Science and Technology: Theoretical Principles and Applications; Sakamoto, K., Lochhead, R., Maibach, H., Yamashita, Y., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 171–221. ISBN 9780128020548. [Google Scholar]
- Thanasukarn, P.; Pongsawatmanit, R.; McClements, D.J. Influence of Emulsifier Type on Freeze-Thaw Stability of Hydrogenated Palm Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| INCI Name | Function | Concentration (wt.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous phase | C1 | C2 | |
| Water | Solvent | q.s. 100 | q.s. 100 |
| FucoPol | Emulsifier agent | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| L-ascorbic acid | Antioxidant | 8.0 | 15 |
| Glycerine | Emollient/humectant | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Methyl paraben | Preservative | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| TEA | pH regulator | q.s. | q.s. |
| Oil phase | |||
| Cetyl alcohol | Co-emulsifier agent | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Olea europaea (Olive) fruit oil | Oil, dispersed phase | 30 | - |
| Prunus amygdalus dulcis (almond) oil | Oil, dispersed phase | - | 30 |
| α-tocopherol | Antioxidant | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Natural Oil | L-Ascorbic Acid (wt.%) | E24 (%) | ƞ (Pa.s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olea europaea | 5 | 89 ± 0.0 | 3.33 | |
| 8 | 96 ± 0.0 | 2.71 | ||
| 10 | 96 ± 0.0 | 2.52 | This study | |
| 15 | 96 ± 0.0 | 1.92 | ||
| Prunus amygdalus dulcis | 5 | 98 ± 0.0 | 3.23 | |
| 8 | 98 ± 0.0 | 3.82 | This study | |
| 10 | 98 ± 0.0 | 4.59 | ||
| 15 | 99 ± 0.0 | 5.15 | ||
| Olea europaea (Formulation C) | - | 98 ± 0.0 | 28.1 | [24] |
| Formulation | Time (Days) | Textural Parameters | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firmness (N) | Consistency (mJ) | Cohesiveness (N) | Adhesiveness (mJ) | |||
| C1 | 1 | 0.039 | 0.065 | 1.027 | 0.077 | This study |
| 3 | 0.071 | 0.078 | 0.759 | 0.063 | ||
| 7 | 0.064 | 0.177 | 0.817 | 0.075 | ||
| 45 | 0.086 | 0.186 | 0.949 | 0.038 | ||
| C2 | 1 | 0.039 | 0.053 | 1.069 | 0.073 | This study |
| 3 | 0.064 | 0.099 | 0.950 | 0.078 | ||
| 7 | 0.064 | 0.129 | 1.377 | 0.079 | ||
| 45 | 0.077 | 0.153 | 0.924 | 0.057 | ||
| C | 1 60 | 0.194 0.047 | 0.385 0.160 | 1.035 1.004 | 0.387 0.129 | [24] |
| Temperature (°C) | Formulation | pH | Conductivity (µs/cm) | Droplet Size (µm) | EI (%) | ƞ (Pa.s) | Firmness (N) | Consistency (mJ) | Cohesiveness (N) | Adhesiveness (mJ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | C1 | 6.6 | 1593 ± 12 | 150 ± 7.7 | 95 | 1.7 | 0.100 | 0.198 | 0.784 | 0.062 |
| C2 | 6.1 | 2561 ± 45 | 11.8 ± 0.5 | 100 | 2.8 | 0.065 | 0.205 | 0.914 | 0.083 | |
| 30 | C1 | 6.6 | 1596 ± 7.1 | 90.5 ± 3.2 | 81 | 2.2 | 0.099 | 0.200 | 0.979 | 0.043 |
| C2 | 6.4 | 2563 ± 29 | 8.97 ± 0.4 | 94 | 1.9 | 0.080 | 0.021 | 0.833 | 0.054 | |
| 20 | C1 | 6.8 | 2728 ± 12 | 17.0 ± 3.3 | 90 | 3.2 | 0.086 | 0.186 | 0.949 | 0.038 |
| C2 | 6.0 | 3893 ± 51 | 36.8 ± 2.4 | 93 | 2.4 | 0.077 | 0.153 | 0.924 | 0.057 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baptista, S.; Baptista, F.; Freitas, F. Development of Emulsions Containing L-Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol Based on the Polysaccharide FucoPol: Stability Evaluation and Rheological and Texture Assessment. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10020056
Baptista S, Baptista F, Freitas F. Development of Emulsions Containing L-Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol Based on the Polysaccharide FucoPol: Stability Evaluation and Rheological and Texture Assessment. Cosmetics. 2023; 10(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaptista, Sílvia, Filipa Baptista, and Filomena Freitas. 2023. "Development of Emulsions Containing L-Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol Based on the Polysaccharide FucoPol: Stability Evaluation and Rheological and Texture Assessment" Cosmetics 10, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10020056
APA StyleBaptista, S., Baptista, F., & Freitas, F. (2023). Development of Emulsions Containing L-Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol Based on the Polysaccharide FucoPol: Stability Evaluation and Rheological and Texture Assessment. Cosmetics, 10(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10020056







