Abstract
Developing urban and peri-urban ecosystem services with nature-based solutions (NBS) and participatory approaches can help achieve more resilient and sustainable environments for cities and urban areas in the face of climate change. The co-creation process is increasingly recognised as the way forward to deal with environmental issues in cities, allowing the development of associated methods and tools that have been described and published for specific stages. It is argued that the co-creation process comprises various interlinked stages, corresponding stakeholders, and subsequent methods and tools that need to be mapped and integrated across all stages. In this study, a Life Cycle Co-Creation Process (LCCCP) for NBS is developed, building on continuous improvement cycles and Design Thinking methodologies, and for which the stages and substages, involved stakeholders and engagement methods and tools are mapped and defined. For stakeholders, the actors of an Urban Living Lab (ULL) are adapted to the LCCCP; for the engagement methods and tools, the goals of stakeholder engagement are used as a guide to select examples of co-creation methods and tools. The developed LCCCP comprises five stages, i.e., CoExplore, CoDesign, CoExperiment, CoImplement and CoManagement, creating a unique path that can be followed by practitioners for NBS co-creation.
1. Introduction
Climate change has increased the need for urban areas to adapt to hazards threatening the liveability of cities, as well as the urban social and economic systems [1]. Threats related to changing climatic conditions, such as flooding, drought, heat stress and urban heat island effects, are exacerbated due to the increasing proportion of the population now living in cities [2]. More than half of the world’s population lives in urban centres, and it is expected that, by 2030, more than 60% of the world population will live in urban areas. Hence, one in every three persons is likely to experience the direct impacts of climate change in cities [3]. Being centres of development and one of the main emission sources of greenhouse gases, the future of global sustainability will be determined by how well cities implement mitigation and adaptation measures to deal with those threats [4].
Besides impacting urban areas and human populations, the impacts of climate change have direct and indirect consequences for urban ecosystems, biodiversity and the environmental services they provide to the population [5]. Considering that urban ecosystems and biodiversity represent an important role in climate change adaptation and mitigation, cities must develop a long-term systems-based approach that considers the impacts on urban areas and the human population. Urban areas evolve and are being reshaped constantly as urbanisation advances and more inhabitants are migrating towards metropolitan areas [6]. Hence, “urban planning is a continuous process of foreseeing, anticipating, and preparing for the future” while seeking a balance between interests from different stakeholders and sectors [7] (p. 76). Considering that climate change is constantly generating new challenges for cities, the concept of continuous improvement and innovative measures (combining or integrating urban planning and climate change) need to be taken into consideration.
Developing urban and peri-urban ecosystem services with a nature-based and participatory approach can help achieve more resilient and sustainable environments for cities and urban areas [5]. In fact, the claim for new participatory approaches to deal with complex environmental challenges is related to failures in top-down decision- and policy-making processes to deal with those challenges [8,9,10]. These processes were traditionally positioned in the domain of trained experts, lacking detailed local knowledge and support from communities [11]. Moreover, urban biodiversity and ecosystems need to be safeguarded and enhanced for them to deliver critical, nature-based co-benefits that promote the well-being of its inhabitants.
Nature-based solutions (NBS) are solutions that can help support climate change mitigation and adaptation in urban settings [5]. Namely, NBS are cost-effective solutions to societal challenges that are inspired and supported by nature, and that help building resilience by providing benefits across the three pillars of sustainability: economic, environmental, and social [12]. The NBS concept builds on the related ecosystem approach, which advocates an integrated management of the different ecosystem services and the living resources in a sustainable way [13]. Hence, NBS are designed to bring natural processes to urban settings, support economic growth and enhance overall well-being.
The Sustainable Development Goal 11 (SDG 11), promoted by the United Nations, aims to “Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable” [14], supporting the idea that cities are key actors in climate change actions for sustainable futures. Considering that 75% of the European population lives in urban areas, SDG 11 is of great importance for the European Union’s Research and Innovation NBS Agenda. Furthermore, there are a series of benefits associated with NBS that align directly with several SDG 11 targets, such as temperature reduction, carbon sequestration, pollutant fixation and urban food production [15].
Environmental issues related to urban areas have been subject of public debate, in which it is particularly important to integrate knowledge from multiple actors to ensure effective interventions [16]. Being considered cost-effective solutions for climate change adaptation, NBS aim to reconnect people with nature, raise awareness of social benefits and create demand for natural environments [12]. Today, urban settings are seen by different stakeholders as a natural space to develop ideas in a Living Lab (LL) setting [17]. The LL concept is based on the idea that innovation processes, underpinned by a co-creation approach, effectively contribute to the creation of innovations that have added-value to end-users [18].
As described by the European Network of Living Labs (ENoLL) [19], LLs are defined as “user-centred, open innovation ecosystems based on systematic user co-creation approach, integrating research and innovation processes in real life communities and settings”, thereby noting that LLs often have a strong focus on social value creation and civic engagement, more so than in commercial activities [20]. The Urban Living Lab (ULL) concept is used when talking about LLs with a focus on more urban innovation and, thus, not only on facilitating the interaction between stakeholders. In ULLs, the main focus shifts from being user-centred to being citizen-centred [19]. Given that the ULL concept is based on the idea that innovation processes should be performed in a co-creative way as in as to provide benefits for their users, the ULL concept can be applied to the generation of NBS.
The term co-creation was initially used by Prahalad and Ramaswamy [21] and is considered an evolution of the cooperative design used by trade unions in Scandinavia between the 1960 and 1970s. Given that cooperative design referred to a co-creation process, the goal has always been to describe a process in which stakeholders are engaged to be part of a problem-solving process in which they all take part as co-designers. Even though co-creation as a concept appeared in 2000 and was used mostly to engage end-users in the design of a product or service, it was fully adopted around 2010 when it was expanded to include all stakeholders [22].
The importance of co-creation in urban development resides in the fact that it takes place between “economic and social actors within networks interacting and exchanging across and through networks” [23] (p. 5). This means that co-creation is more than a direct developer/customer relationship as it considers stakeholders as part of an ecosystem and, as such, understands the complex nature of relationships and the systemic interactions that take place among stakeholders [24]. Framing the development in the sense of a business ecosystem, each stakeholder is responsible for the achievement of a solution and, as such, should be part of the entire decision-making process, including the development, co-creation and design of the process [25].
Considering that all the stakeholders involved in the development of solutions are affected and affect decisions both directly and indirectly, the co-creation approach is increasingly mentioned as the way forward with environment-related issues [14] (pp. 20–23). Thus, various co-creation methods and tools have been developed and applied over the decades to this end. These methods and tools are, however, developed, described and published for specific stages of the co-creation process, and not for the entire process. We argue, however, that the co-creation process comprises various interlinked stages, corresponding stakeholders and subsequent methods and tools, which need to be mapped and integrated across all stages of the co-creation process. In fact, Bradwell and Marr [26] state that it is an absolute necessity for a successful co-creation process to have a methodology that supports its properties as to ensure that the aim of the process is met.
Hence, the objective of this study is to identify and describe the stages, stakeholders, and methods and tools of the Life Cycle Co-Creation Process (LCCCP) for nature-based urban climate change adaptation. To this end, a documental analysis and literature review is performed to obtain an enhanced understanding of the concepts of co-creation, nature-based solutions, life cycle approach, continuous improvement methodologies, Design Thinking and stakeholder engagement methods and tools. From the information compiled, the proposal for the LCCCP is designed, including corresponding stages and substages. In turn, stakeholders involved in each stage are defined using the ULL actors. Finally, a series of methods and tools to promote stakeholder engagement are identified and mapped across the LCCCP stages.
This study is expected to go beyond previous studies by providing a new approach to the co-creation process, instead of focusing on a particular stage and, at the same time, identifying the stakeholders, and methods and tools for each of the stages and substages of the LCCCP. By combining methodologies from the field of co-creation, Business Process Management (BPM) and process improvement, the LCCCP brings together the stages of these different methods in a new approach that covers the innovation lifecycle from the very initial phases of exploration and engagement (e.g., Design Thinking [27]) to the later stages of implementation and maintenance (e.g., PDCA and DMAIC cycles [28,29]). By identifying and defining the different stages of the LCCCP for NBS, this study provides a comprehensive framework to develop NBS in cities using a co-creative approach. The stages presented here intend to cover the complete LCCCP and are designed based on systemic and life cycle thinking approaches, in which the interactions of the co-creation process are taken into account.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. The next section describes the methodology used to design the LCCCP. Section 3 presents concepts of systemic thinking, life cycle approach and continuous improvement, which were necessary to understand how the PDCA Cycle (Plan, Do, Check, Act) [28], DMAIC Cycle (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve and Control) [29] and Design Thinking [27] approach could be used to define the stages of the LCCCP. This section also presents aspects of stakeholder management and participation, the Quadruple Helix Model (QHM) approach and roles within a ULL and, finally, the main goals and examples of toolkits that could be used to facilitate stakeholder engagement. Section 4 describes the LCCCP for nature-based urban climate change adaptation, including the various stages, the stakeholders involved in each stage, and some examples of methods and tools that could promote stakeholder engagement during the co-creation process. Finally, Section 5 comprises the discussion of the LCCCP design and presents recommendations for future studies.
2. Materials and Methods
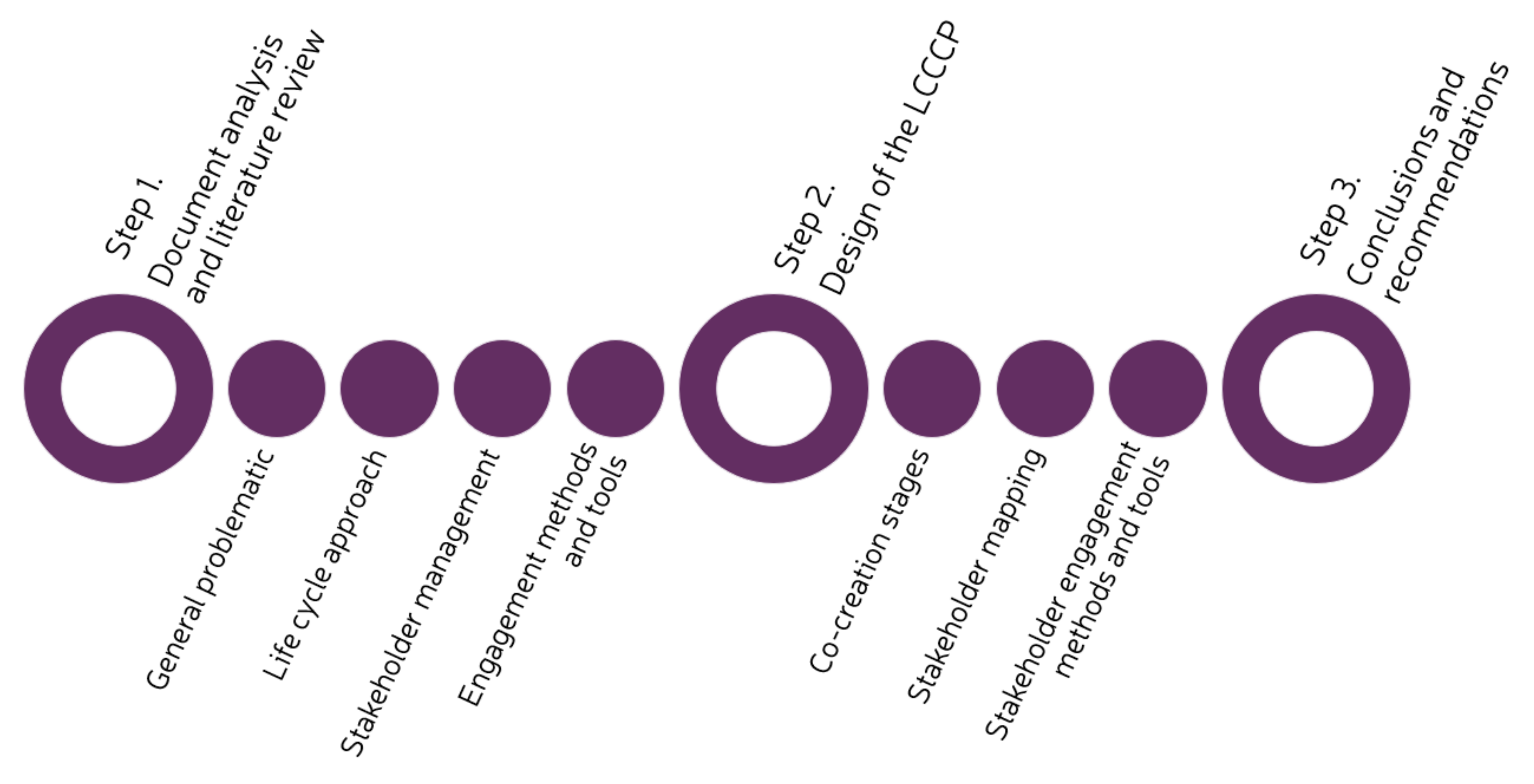
The methodology followed in this study comprises three steps, which include a document analysis and literature review, the design of the LCCCP and the formulation of conclusions and recommendations (see Figure 1).
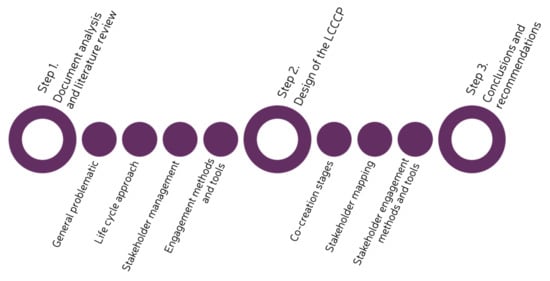
Figure 1.
Methodology.
The first step of the methodology entailed a document analysis and literature review. A systematic approach was used, in which the keywords that were used during the review were identified according to the research question and objectives. Given that co-creation is central to this study, understanding the evolution and meaning of the term was important to define the different stages of the review. In turn, new topics to be researched were identified, such as continuous process improvement, stakeholder roles within a ULL, and general objectives of methods and tools for stakeholder engagement. The review was divided into the following four topics:
- General problematic—keywords: climate change, urban areas, climate extremes, co-creation, ULL and NBS;
- Life cycle approach—keywords: systemic thinking, continuous improvement, Kaizen™, Six Sigma, Design Thinking, co-creation framework and co-creation stages;
- Stakeholder management—keywords: stakeholder identification, ULL and QHM; and
- Engagement methods and tools—keywords: stakeholder engagement methods, tools and techniques;
and corresponding keywords were identified by the authors based on their experience in this area of research and further refined based on the results obtained using the keyword search.
During the review, different combinations of the keywords listed above were used to identify papers related to co-creation in urban settings. The main databases used were Science Direct, Scopus and ProQuest, considering the period between 2010 and 2018 (given the co-creation methodology involving all stakeholders has been evolving since 2010 [22]). The reference management software Mendeley was used to compile the documents and papers used in the literature review.
To identify the relevant papers out of the papers retrieved using the keyword search (based on title, abstract and keywords), two rounds of review were performed. In the first round, 172 papers were short-listed based on titles and abstracts. In the second round, short-listed papers were read, and 29 were selected to be included in this study. In both rounds of review, papers that did not fit the study or did not result to be relevant were excluded. During this review, 23 additional papers were identified (based on references) and considered for inclusion following this same methodology. Hence, a total of 195 papers were retrieved in the process, out of which 107 papers were studied in detail during the reviewing process, and 38 papers were finally selected for inclusion in this study. This approach was used to obtain a rapid overview of relevant and recent papers in the areas of interest. While a keyword search does face various issues, such as a large amount of results, many irrelevant results and keywords considered out-of-context [30], some of these issues were overcome by applying the two rounds of review (efficiently excluding irrelevant results; identifying keywords in context) and selecting additional relevant papers from the references mentioned in the short-listed papers.
For the framing of the general problematic, the book “Climate Change and Cities: Second Assessment Report of the Urban Climate Change Research Network” by Rosenzweig et al., 2018 was used [31]. As for ULL related concepts, official documents from ENoLL [19] were used, as well as papers produced by ULL researchers and practitioners. Given that Kaizen™ [32] and Six Sigma [28] are methodologies that are internationally certified by official agencies, information from these agencies was also used.
The second step entailed the design of the LCCCP, thereby building on the information compiled in the document analysis and literature review. The proposal for the design of the LCCCP co-creation stages was based on different continuous improvement [28,32,33] and Design Thinking [34] methods. During the process of identifying these co-creation stages and given that the LCCCP was designed with the objective to promote stakeholder engagement during all these stages, the mapping of stakeholders to be involved across each of these stages was based on the ULL concept and QHM approach [35]. Lastly, methods and tools to facilitate stakeholder engagement were identified and given as examples of methods and tools that can be used in each of these stages, mostly based on the U4IoT project [36], the MindTools webpage [37], the Service Design Tools webpage [38] and the UNaLab co-creation Toolkit [39].
Finally, after identifying and defining the three dimensions of the LCCCP (stages, stakeholders, and methods and tools), general conclusions and recommendations were derived. These were based on the document analysis and literature review, as well as the authors’ experience in the field.
3. Co-Creation Concepts
For the three dimensions of the LCCCP to be defined, background information on a series of topics was required. Understanding the concepts of systemic thinking and life cycle approach was necessary, to understand how the PDCA Cycle [28], DMAIC Cycle [29] and Design Thinking [27] could be used to define the stages of the LCCCP (Section 3.1). After understanding these concepts and how they can be applied to NBS, aspects of stakeholder management and participation, as well as the QHM and roles within a ULL were reviewed (Section 3.2). Finally, the main goals and examples of toolkits that could be used to facilitate stakeholder engagement are presented (Section 3.3).
3.1. Systemic Thinking and Life Cycle Approaches
Environmental problems are complex and dynamic, as they are part of a broader system and are interlinked with different processes [40]. Hence, solving environmental problems requires flexible and transparent decision-making processes that are able to embrace the diversity of knowledge and the understanding of the problem, values and needs [9].
A systemic thinking approach facilitates the understanding of complex systems or challenges and their interrelations, while allowing a global view, avoiding simplifications and developing simple interventions for transforming them [40,41]. This approach provides a framework in which patterns can be identified, allowing for the replication of processes in different scenarios in which the same patterns are identified [41]. The life cycle approach follows the systemic thinking approach as it considers, not only, everything and everyone involved in the product or service life cycle, but also, all relevant impacts on the economy, environment and society [42].
Processes are in continuous evolution and, as such, their analysis cannot be done with a static approach. The life cycle approach is considered to be the foundation of any consideration of improvement in a process and, hence, a framework with such characteristics is considered important. There are several methodologies and methods that focus on improving processes, including:
- The PDCA cycle [28] used in the Kaizen™ method [32] that forms the basis of the cycle of continuous improvement;
- The DMAIC cycle [29], as an evolution of the PDCA cycle [28], developed as the basis of the Six Sigma methodology [28]; and
- The Design Thinking approach for co-creation [27] that can be compared to the methodologies and methods described above.
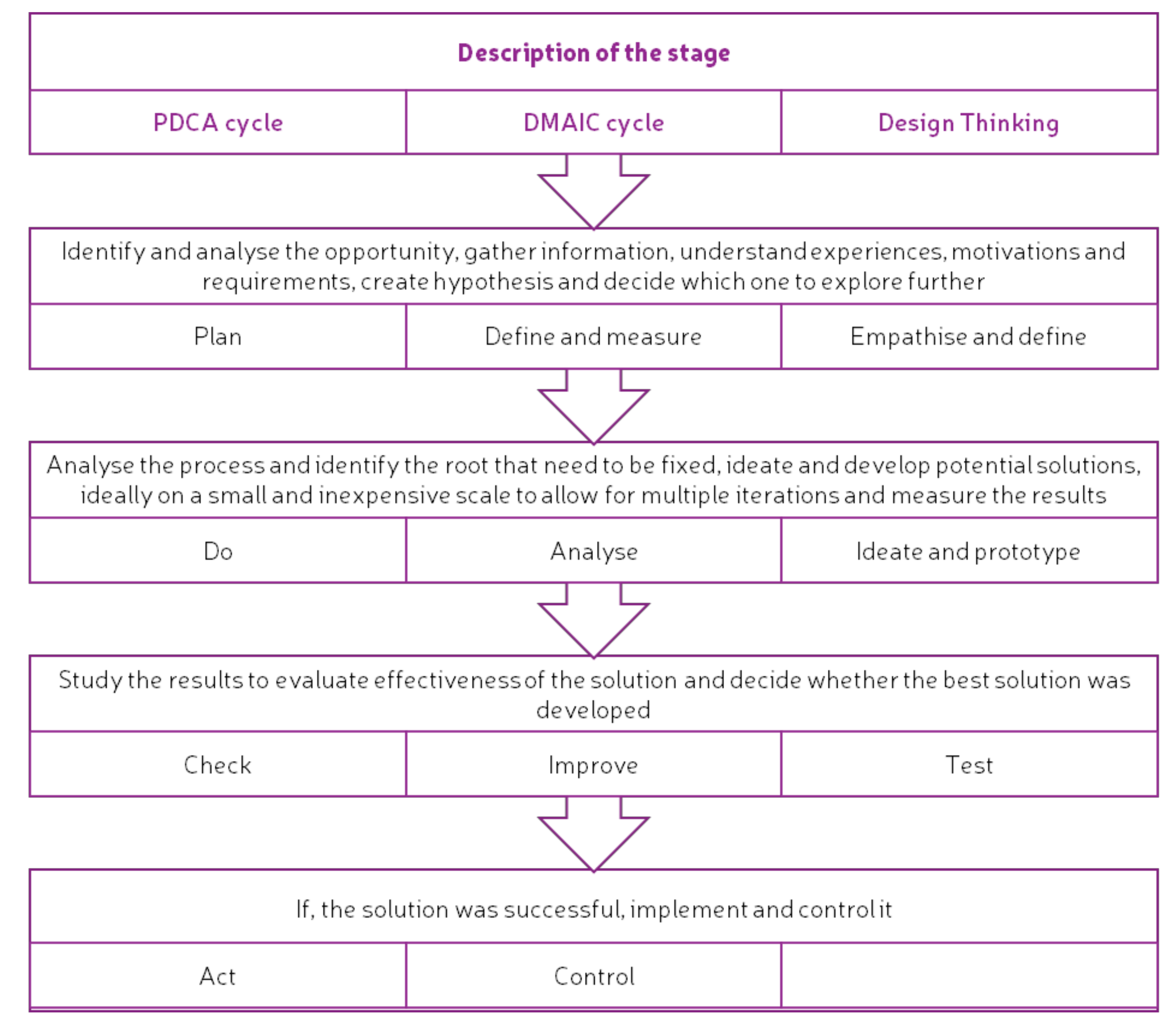
Even though methodologies and methods, such as Kaizen™’s continuous improvement (PDCA cycle [28,32]) and Six Sigma (DMAIC cycle [29]), are very structured and rely on data to perform measurements and improvements, a parallel between them and the stages of Design Thinking [27] can be made (see Figure 2).
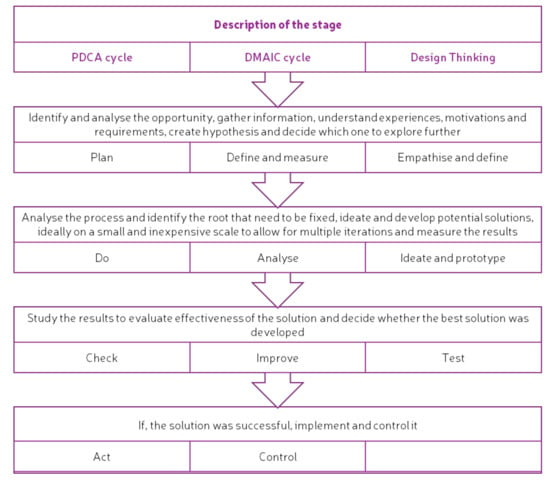
Figure 2.
Comparison between PDCA, DMAIC and Design Thinking stages. Adapted from [32,38,41].
Although all of the approaches, methodologies and methods mentioned above consider continuous improvement in a different way, they all start when the opportunity for improvement has been identified and finish when the solution is designed (as in the case of Design Thinking [27]) or implemented (as in the PDCA and DMAIC cycles [28,29]). Regardless of their constraints, when considering the co-creation process as more than just coming up with a solution to a problem, and bearing in mind that the cycles mentioned above (PDCA and DMAIC cycles [28,29]) are the basis of most continuous improvement processes, there are some frameworks in literature defining steps for co-creation that mostly use a Design Thinking approach [1,27,43,44,45]. These three approaches provide a solid basis for the design of the LCCCP for NBS.
3.2. Stakeholders in Participatory Processes
Climate change presents complex and dynamic challenges for cities. To overcome such challenges, engagement of relevant stakeholders is important because a reduction in conflict, building of trust and facilitation of learning among stakeholders can happen when a participatory approach to environmental issues is implemented [10]. The involvement of different stakeholders is essential when adaptation measures are developed in existing urban areas. These stakeholders have different levels of knowledge, interests, roles and agendas in the process [46]. A participatory approach allows stakeholders to meet each other, share their knowledge, understand the problem and identify the most desirable adaptation measures [1].
ULLs follow the QHM approach [35] to define its main actors, as it clusters the protagonists of innovation-generating processes into four comprehensive categories [35,47]:
- Academia and research centres. Historically this sector has always been fundamental in knowledge production and has only recently become a contributor to innovation thanks to the crucial role that knowledge has gained in development processes. This sector has become a key actor of economic and cultural growth.
- Industry and business. Also known as the commercial market or the economic category. Frequently a strong actor that leads technological and organisational innovation and usually has the role of generating, producing and distributing products and services. Produces innovations alone or associated with other stakeholders.
- Government and public sector. The innovation within this sector is framed within new ideas that create value for society, and thus, this innovation usually comes through policies, strategies and initiatives. The role of these institutions is to support both industry and academia for the application of information to development.
- Civil society. Represents citizens or users who provide knowledge about their needs, experiences and expectations. As they are directly affected by any changes made in an urban context, they can provide first-hand information regarding the challenge at hand and, thus, become innovation users. By including civil society to the Triple Helix Model (THM), thus creating the QHM, the innovation shifts from technical to social.
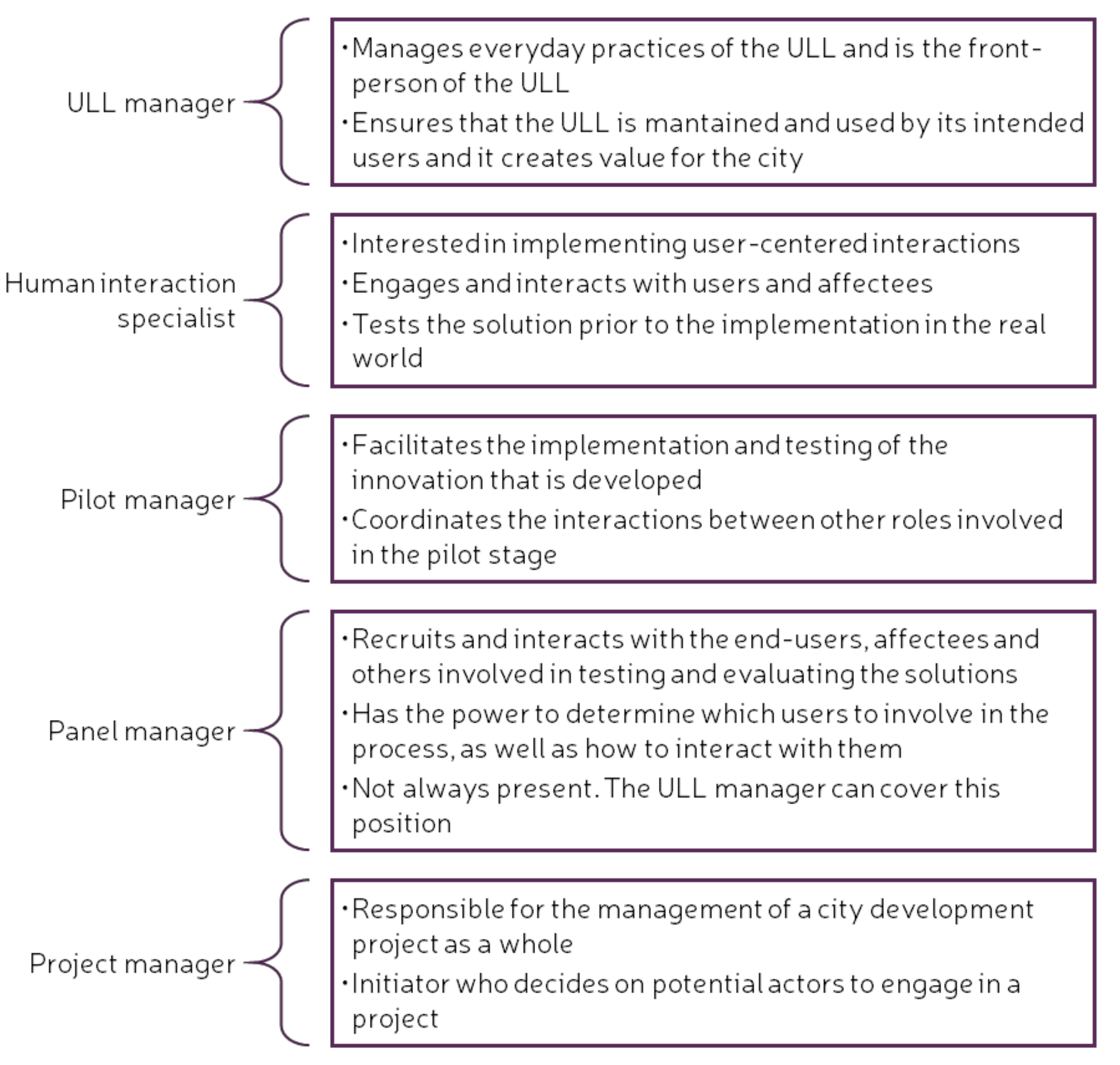
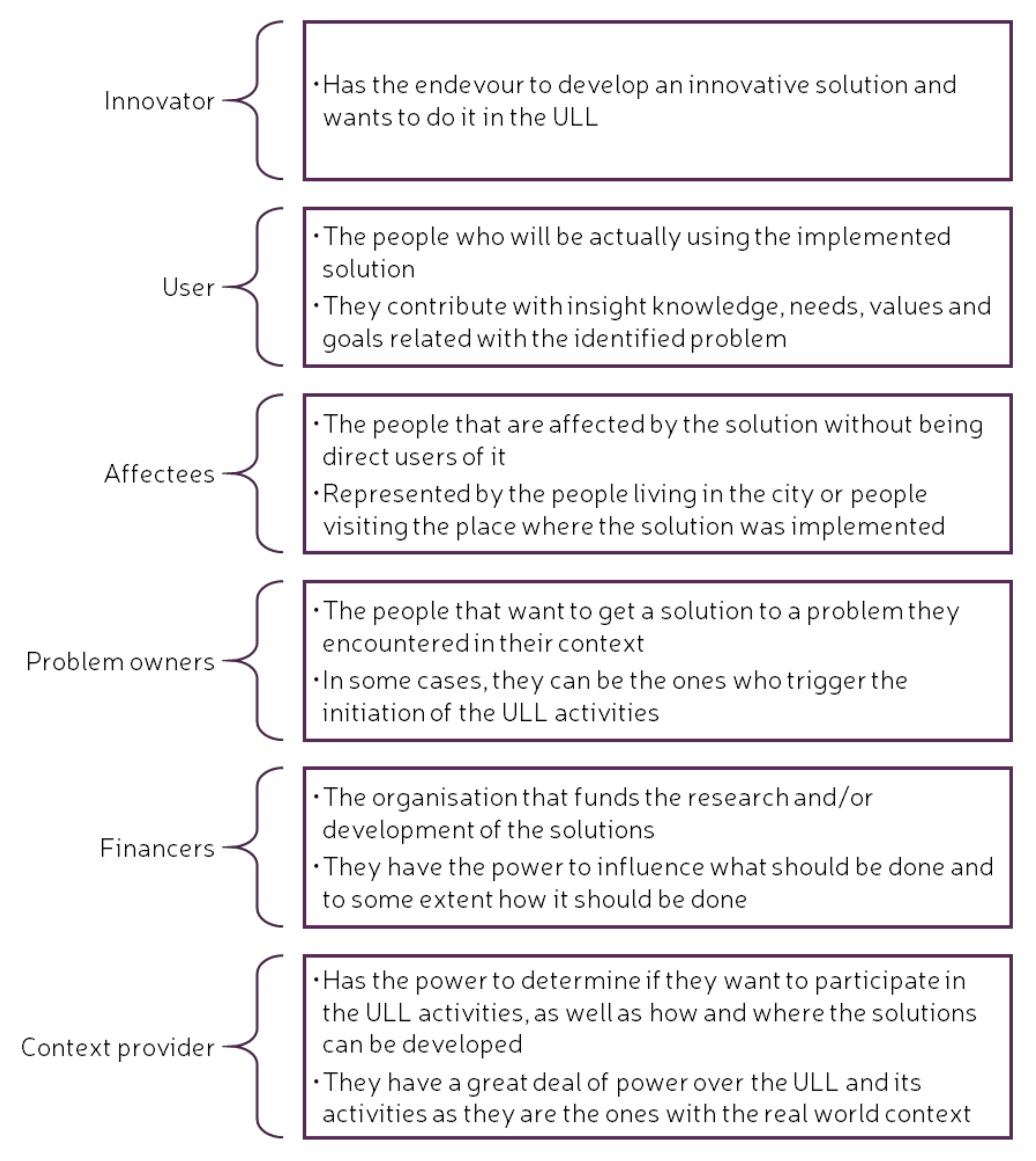
Besides the categories used for the QHM, a series of specific roles within a ULL are identified. These can be either internal, for setting up and managing a ULL, or external, for managing ULL activities [48]. These roles describe the responsibilities of the stakeholders when working on a project that will be implemented in a ULL setting. It is important to note that several roles can be performed by the same person. Figure 3 and Figure 4 list the internal and external roles of the key stakeholders in a ULL, as well as describe briefly the main responsibilities of each role [48].
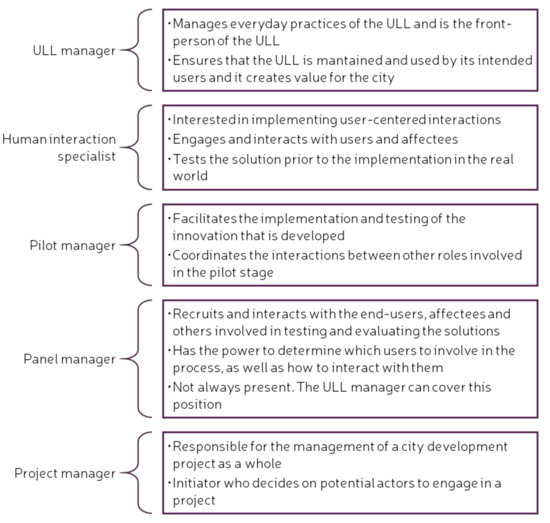
Figure 3.
Internal roles of key stakeholders in an Urban Living Lab (ULL). Adapted from [48].
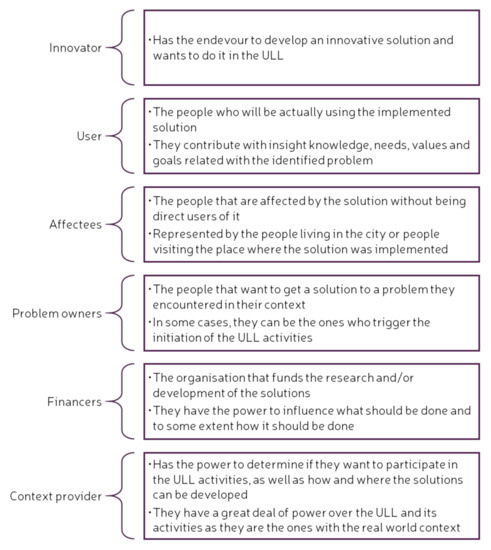
Figure 4.
External roles of key stakeholders in a ULL. Adapted from [48].
The specific internal and external roles of some stakeholders in a ULL were taken into account when identifying which stakeholders should participate in each stage of the LCCCP.
3.3. Methods and Tools for Stakeholder Engagement
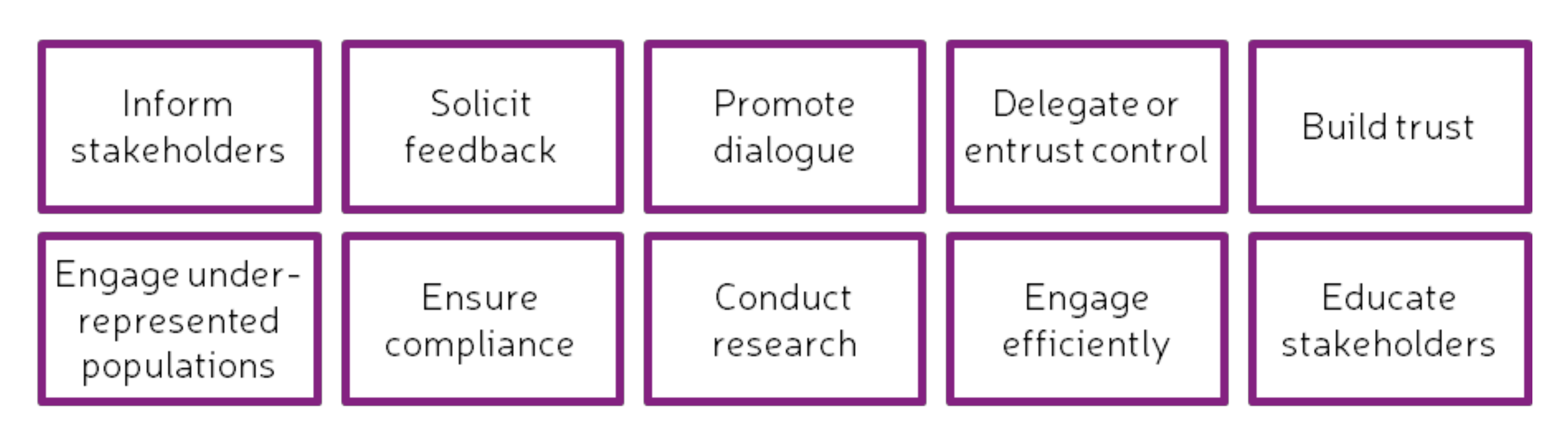
Involving key stakeholders during the early stages of a participatory process has proven to be of great importance for obtaining a positive outcome [49,50]. Thus, engagement must capture relevant knowledge throughout the duration of the project and amongst stakeholders, reflecting the needs of the communities and understanding that they can vary over time [9]. Considering that stakeholder engagement is usually a complicated and messy process, tainted with conflict, disagreement and diverging points of view [50], the goals of the engagement process should be clear from the beginning. The most common goals are shown in Figure 5.
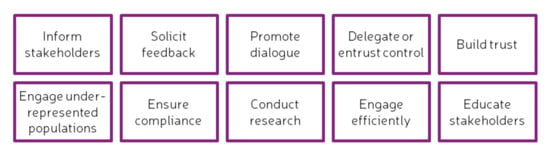
Figure 5.
Management goals for stakeholder engagement. Adapted from [50].
To promote the engagement of stakeholders and to achieve the management goals mentioned above, different strategies, methods and tools have been designed and implemented specifically for participatory processes. A method describes a process used to effectively complete a task, while a tool generates an output from information that is introduced in it [51]. A robust toolbox of stakeholder strategies can help managers to design effective participatory approaches. These methods and tools should be defined and structured in a way that allows managers to plan, implement, reflect and evaluate the decisions made by the stakeholders [50]. Participatory and user-centred methodologies, such as Design Thinking and co-creation, provide a framework for methods and tools to be designed and focused on stakeholder engagement [1].
There are many co-creation stakeholder engagement methods and tools. These are, for example, compiled in the toolkit developed for the U4IoT project [36], the MindTools webpage [37], the Service Design Tools webpage [38] and the UNaLab co-creation Toolkit [39]. The aim of the latter is to support the development of ULL for co-creation and experimentation of NBS as well as to collect methods, tools and techniques for stakeholder engagement. Some of the methods and tools found in the toolkits mentioned above, as well as the main goals for stakeholder engagement (see Figure 5), were used to identify the methods and tools that can be used in each of the stages and substages of the LCCCP.
4. Life Cycle Co-Creation Process (LCCCP)
This section describes the Life Cycle Co-Creation Process (LCCCP) for nature-based urban climate change adaptation, including the various stages, the stakeholders involved in these stages, and some examples of methods and tools that could promote stakeholder engagement during the co-creation process. The co-creation path was conceptualised using the stages, stakeholders, and methods and tools as components.
Business Process Management (BPM) is a framework that provides the guidelines for organisations to optimise their performance. Thus, BPM is a systematic approach to process improvement [33]. Even though this paper does not focus on process improvement, some of the concepts of BPM can be used to frame the co-creation life cycle in a more comprehensive way. BPM relies on the identification of processes with their different components, spanning from a broad view of the organisation and relying on a systemic thinking approach, to the definition of the tasks of each process [33].
First, by using BPM as an inspiration, and considering co-creation as a macro process, stages and substages in co-creation are identified. The stages are designed to give a general guide for the co-creation process while the substages provide more detail into each of the stages. The developed co-creation path was inspired by the PDCA and DMAIC cycles [28,29], and the Design Thinking methodology [27], with the main stages and substages presented and described in Section 4.1.
Second, the stakeholders to be engaged in each stage were identified after reviewing the QHM approach [35] and the actors of ULL with a citizen-centred approach, considering both the internal and external actors. The ULL actors were used to identify the stakeholders that should participate in specific stages [48]. Considering the specific roles identified for ULL, Section 4.2 identifies the stakeholders that should participate in the stages and substages presented in the co-creation path.
Finally, using the most common goals of stakeholder engagement mentioned above, examples of methods and tools to promote engagement were identified, taking into consideration that a robust toolbox of stakeholder strategies can help managers to design effective participatory approaches. Section 4.3 describes the general objective that methods and tools for stakeholder engagement should have for each of the main stages, and presents a series of examples taken from projects and partners experience (e.g., U4IoT [36] and UNaLab [52]).
The three components mentioned above form the skeleton of the co-creation path. The stages represent the road for co-creation, while the specific stakeholders and methods and tools support the objectives of each of these stages. Figure 6 shows a conceptual integration of the three designed components. The proposed conceptual integration of LCCCP stages follows the principle of continuous improvement of the PDCA and DMAIC cycles [28,29], and thus, it is not a proposal for a linear process but, instead, a continuous and iterative process that feeds itself constantly.
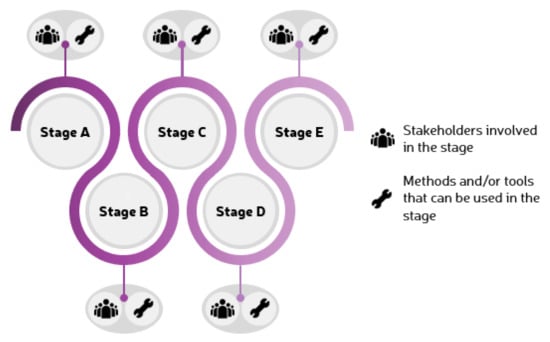
Figure 6.
Conceptual integration of the Life Cycle Co-Creation Process (LCCCP) stages, stakeholders, and methods and tools.
4.1. Co-Creation Life Cycle
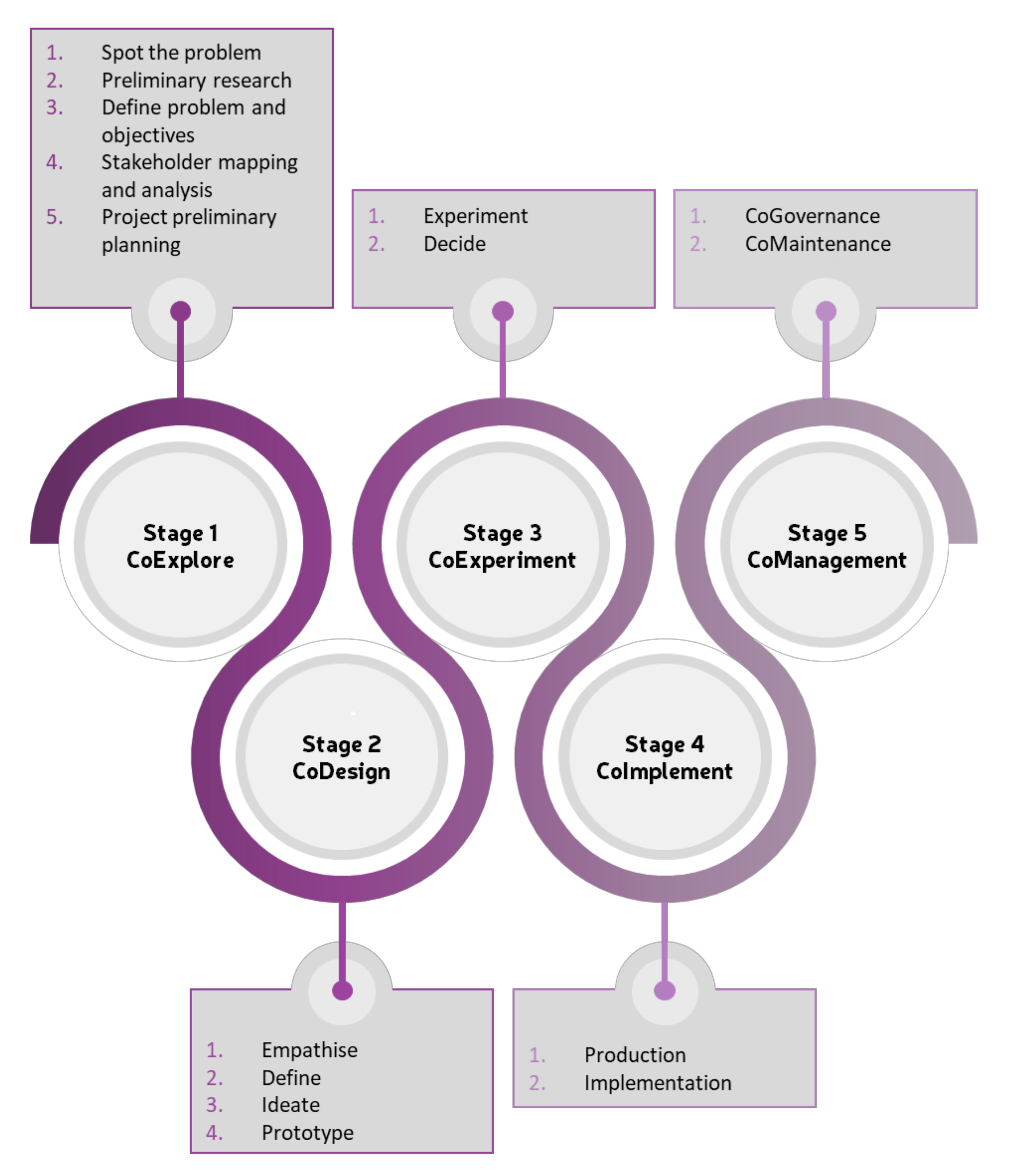
The LCCCP consists of five stages and a series of specific substages. The first stage, CoExplore, represents the initial step taken prior to ideating a solution with the stakeholders. The second stage, CoDesign, covers the complete process of the potential solution(s) ideation process until the prototypes design. The CoDesign stage is complemented by the third stage, CoExperiment, in which the prototypes are tested (and feedback information is sent to the CoDesign stage) until the most desirable solution is identified. The fourth stage, CoImplement, describes the process of implementation of the solutions. Finally, the fifth stage, CoGovernance, represents what happens after the solution is implemented and covers the maintenance and governance of the solutions. It is important to notice that the process is highly iterative and, as such, users can go back to previous stages as many times as needed. The power of the iterative loop is that the potentials of all stages, roles involved, efforts required, results, etc., can be considered and tested in the prototyping substage. Figure 7 shows the LCCCP with the stages and substages.
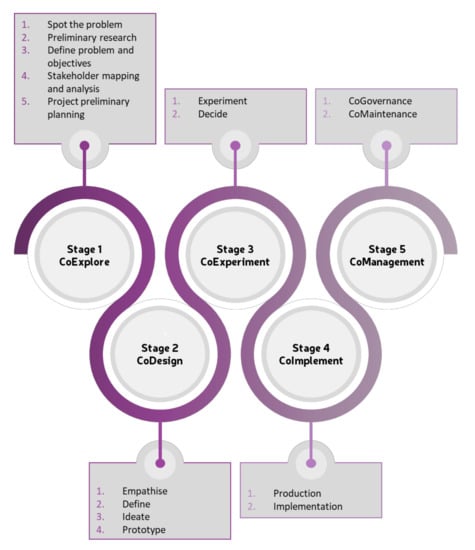
Figure 7.
LCCCP with stages and substages.
4.1.1. Stage 1: Initiative—CoExplore
This stage represents the beginning of the LCCCP and, as such, it covers all the preparatory steps needed to create and implement solutions. It is mostly inspired by the Plan step of the PDCA Cycle and the Define step of the DMAIC Cycle. This stage begins when one of the stakeholders of the project spots a problem, and it ends when the mapping and analysis of the stakeholders that will take part in the process is completed and the preliminary planning of the project is done. The CoExplore stage will provide all the information needed to create a solid foundation for the process, including information related specifically to the problem and information on the stakeholders. The main purpose of this stage is to identify and analyse the problem, gather initial data and create hypotheses. It also covers the identification and selection of stakeholders and, thus, it will also allow for information, such as experiences, motivations and requirements, to be gathered. The substages that are part of the CoExplore stage are the following:
- (1).
- Spot the problem. This substage represents the beginning of the process and, as such, it is considered the trigger for the co-creation process. In this stage, the current or emerging problem(s) are identified by the stakeholders—be it through structured research or identified by chance. An example of a problem identified by chance is when a citizen feels that the temperature in the city centre is higher than in the rest of the city (heat island effect). In this stage, a general approach is developed, while the consequences or causes are not analysed. It is important to reach a consensus across the stakeholders considering what the main problem(s) that need to be solved are. In this stage, any information available is used to understand the context of the problem(s). The main questions that need to be answered in this substage are [53]:
- What is the current problem?
- What is the scope of the current problem?
- How is the project framed, and what are the internal and external relations?
- What is the future problem?
- (2).
- Preliminary research. After mapping the problem(s) and agreeing on which are the main one(s), a preliminary research needs to be performed. Data-rich evidence on the problem(s) is collected, including characteristics, scale and extent, cause and effect and all associated costs (economic, social and environmental). The objective of this substage is to demonstrate that the problem(s) creates constraints for achieving stated goals and objectives at the local, regional or global level. In this substage, additional problems might be identified. The following questions can provide guidance in this stage [53]:
- How is the problem preventing the achievement of the objectives?
- What does the problem mean (feel, think, say, do) from the different viewpoints of all stakeholders involved?
- Can the effects of the problem be measured?
- What are the drivers that influence the problem?
- How will the drivers of the problem change over time?
- Will the problem increase gradually, or will there be a stepwise increase?
- What are the symptoms of the problem?
- What are the causes of the problem?
- Are there dependencies between this problem and others?
- Are there other initiatives under development that influence the problem?
- (3).
- Define the problem and objectives. After establishing a comprehensive understanding of the problem(s), which will enable effective action, the problem(s) need to be prioritised and correctly defined. The following questions can be used for prioritising [53]:
- Which problem presents the greatest obstacle to achieving the goals and objectives?
- Which problem prevents the most important objective from being achieved?
After identifying the problem(s) that will be tackled with a participatory planning approach, the problem(s) needs to be described in a comprehensive way. For this, a design brief can be used, in which a general and simple description of the problem(s) should be stated. This brief will work as an initial roadmap and means of communication between the stakeholders, and it should not be seen as a static document as it can be modified during the project. For this brief, questions such as the following could be used [54]:- What is the purpose?
- Why are we doing this now?
- Are we going down the right path?
- Who are we serving?
- What are our initial success metrics?
- (4).
- Stakeholder mapping and analysis. In this substage, the main objective is to identify the stakeholders of the project. This substage will allow to understand stakeholders, their background, thoughts, beliefs, expectations and relations, with the aim to facilitate and enhance the co-creation process. For this stage, the QHM, and the internal and external roles of a ULL must be taken into consideration.
- (5).
- Project preliminary planning. The last part of the CoExplore stage is the preliminary project planning. This substage sets the context for all subsequent steps of the LCCCP. In this substage, the targets and performance indicators are identified, as well as the main milestones to be achieved during the project. The main output of this substage is the roadmap to follow during the project, with the main stakeholders of each milestone and task identified. The preliminary planning should be available for all stakeholders and should clearly state the objectives and expected results. The following questions can help create the preliminary planning [55]:
- What is the real problem we are trying to solve?
- What are our objectives, and how will solving this problem help achieve those objectives?
- What is our current target audience and what is the ideal audience? Are there multiple audience segments?
- Who are our stakeholders and how do we expect them to participate in the project?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of our current system?
- What are our other constraints, such as timeline and budget?
- How will success be measured?
4.1.2. Stage 2: Create—CoDesign
This stage is mostly based on the Design Thinking methodology [27]. It allows stakeholders to identify solutions and new opportunities together and, in the end, create prototypes of the solutions to be tested later in the process. It starts with empathising with involved stakeholders to understand their actual needs and wishes. After identifying what the stakeholders consider as possible solutions, a deeper analysis of the information needs to be performed as to understand the primary problem(s) or pain points the stakeholders have. The pains and gains identification will allow for a better solution design, which is done in the ideation substage. To finalise this stage, prototypes of the solutions are built. This substage receives constant feedback from the CoExperiment stage until the most desirable solution(s) are identified and accepted by the stakeholders. The substages that are part of the CoDesign stage are the following:
- (1).
- Empathise. This substage allows the stakeholders to see the problem(s) and potential solution(s) from different perspectives and, as such, it allows for a deeper understanding of the underlying motivations of the stakeholders. It is important to not only understand the physical needs of the stakeholders but also their psychological needs. This substage will allow the designers, developers and/or planners to set-aside their own assumptions and needs in order to gain insight into the users and their needs [34].
- (2).
- Define. In this substage, all the insights gained during the empathising process are put together and analysed. The main objective of this stage is to synthesise the information gathered and define the core problems that have been identified. Understanding how the stakeholders feel about the current solution(s) and why they think they need new and/or improved solution(s), can help set the framework for the following steps [56]. Questions such as the following can help in defining the core problems [55]:
- What is the problem or pain point the user is experiencing?
- What products and/or solutions do they currently use to solve that problem or pain point?
- What are the shortcomings of their current solution?
- How could the new/improved solution(s) be better?
- What feature should be prioritised in the new/improved solution(s), and which might be added later?
- (3).
- Ideate. The core task to be performed in this substage is idea generation. For this substage to be a success, the information gathered in the previous steps is essential as it provides the input to generate potentially successful solutions. This substage intends to go beyond the obvious solutions and increase the innovative potential of the solution(s) while bringing together perspectives and strengths of different stakeholders. In this substage, a divergent approach to ideation is used, in which as many ideas as possible are considered [57].
- (4).
- Prototype. The objective of this substage is to converge the ideas and solutions obtained in the Ideate substage. A conscious evaluation of the ideas is performed in order to identify which solution(s) best align with the objectives. When the most desirable ideas are identified, inexpensive prototypes are created for further testing. Prototyping allows to test hypothesis and potential solutions within a shorter timeframe, and with fewer resources [58]. This substage helps to find answers to vital questions, such as the following [55]:
- Are we sure we are solving the right problem?
- How will our idea meet our users’ needs and relieve their pains?
- Is our solution technically feasible?
4.1.3. Stage 3: Evaluate—CoExperiment
The CoExperiment stage allows to study the results, evaluate the effectiveness and decide whether the most desirable solution was developed. This stage gives continuous feedback to the CoDesign stage in order to fine-tune the solutions and identify the most desirable solution(s). It consists of two substages, the first one covering the experimentation in which the prototypes created in the last substage of the CoDesign stage are tested; the second one covers the decision of whether the solution tested is the best one or whether it needs to be discarded or improved. The number of iterations between CoDesign and CoExperiment can be as many as needed, in order to identify the most desirable solution(s) for the identified problem. The substages that are part of the CoExperiment stage are the following:
- (1).
- Experiment. This substage focusses on usability testing, as to share the prototype with real users and to receive their feedback. Besides receiving feedback, this substage also provides a deeper understanding of the users, as they could potentially express desires or preoccupation that differ from the already identified ones. It allows empathising even more with the users. The results of this stage might lead to new information that changes the way the problem was defined in the Define substage. It may also generate new solution(s) in the Ideate substage and lead to a new iteration of the Prototype substage [59].
- (2).
- Decide. This substage complements the Experiment substage, as it occurs when a decision regarding the prototype is made. For this stage, the information about the objectives, constraints, needs and wishes would need to be clear for the design team, as to make the decision about which of the tested prototypes represents the most desirable solution. In the case that the most desirable solution is not yet identified, feedback is sent to the CoDesign stage in order to begin a new iteration. The following questions will provide the necessary information to make a decision regarding the tested prototype:
- Does the solution work as intended?
- Does it solve our users’ primary problem(s) and pain points?
- How could it be improved?
4.1.4. Stage 4: Implement—CoImplement
After identifying the most desirable solution(s), this stage covers the implementation. The production and implementation of solutions vary depending on the solution itself and, as such, only a general description of the substages is given. This stage covers the management of the planned solution and its overall budget. Major activities involved in this stage are the detailed planning and design of the solutions, commissioning, risk management and the final delivery of the solution [55]. The substages that are part of the CoImplement stage are the following:
- (1).
- Production. This substage covers the production of the solution(s) and overall control of the budget. The major activities that comprise this stage are the following [60]:
- Detailed planning and design of initiatives;
- Construction (for infrastructure initiatives) and commissioning;
- Risk management relevant to these activities; and
- Delivery on time, within budget and to agreed quality specifications.
- (2).
- Implementation. After the solution(s) is delivered, its implementation needs to take place. This means gathering the stakeholders in order to hand-in the solution(s), justify and explain it, and share information about how it can be maintained. This stage is crucial as it will set the ground for future implementations and enhance trust building.
4.1.5. Stage 5: Control—CoManagement
After the solution(s) are implemented, the control stage starts in which a defined governance structure must be determined and put in place. The maintenance of the solution(s) must also be considered, as it might rely too much on a few stakeholders and, as such, end-up being forgotten. The substages that are part of the CoManagement stage are the following:
- (1).
- CoGovernance. For this substage, a clear governance structure must be defined and shared with all stakeholders. Considering the process followed in a participatory approach, it is important to understand that the governance, or co-governance, of the solutions must continue along the same line. Co-governance implies that the decisions are made at the lowest levels possible, recognising that the decision power of each stakeholder is equitable: “rather than viewing [collaborative and co-governance arrangements] as ‘solutions to problems’ we must view these arrangements as a starting point for [new or restored] relationships, which will continue to evolve as time passes” [61]. The following should be taken into account when setting-up co-governance arrangements [60]:
- New requirements for local government(s) to regularly review arrangements for delivering services;
- Public expectations of increased participation and access to decision makers; and
- The increase in and complexity of “wicked problems” requiring innovative solutions.
- (2).
- CoMaintenance. In relation to the concept of co-ownership, it needs to be defined who will be the owner(s) of the implemented solution(s). Some of the responsibility must rest with the end-users as they should be co-owners of the solution(s) given that they are the ones directly affected by it. The challenge of this substage is to convince stakeholders that they take part in the ownership of the solution(s) and, as such, should also take part in the maintenance of it [62].
Good and open communication during the entire project is crucial in order to maintain and support the motivation of stakeholders. All stakeholders should be given the opportunity to provide input on a formal as well as an informal basis during the entire process. Given that there are many communication tools that vary in reach and complexity (e.g., teleconference, email, file sharing, website, newsletter, social media, phone calls, events and mobile apps), the communication channels should be adjusted according to the relevance, closeness and technological capacity of the stakeholders [63].
Engaging stakeholders, including the community, during co-creation processes can lead to a more comprehensive process. It could provide insight into problems that were not identified previously or shed a new light on known problems. A planning or development process that does not engage with stakeholders could risk identifying and tackling only the best known or most acute problems without a broader strategic context [9,49,53,63].
4.2. Stakeholders Per Stage and Substage
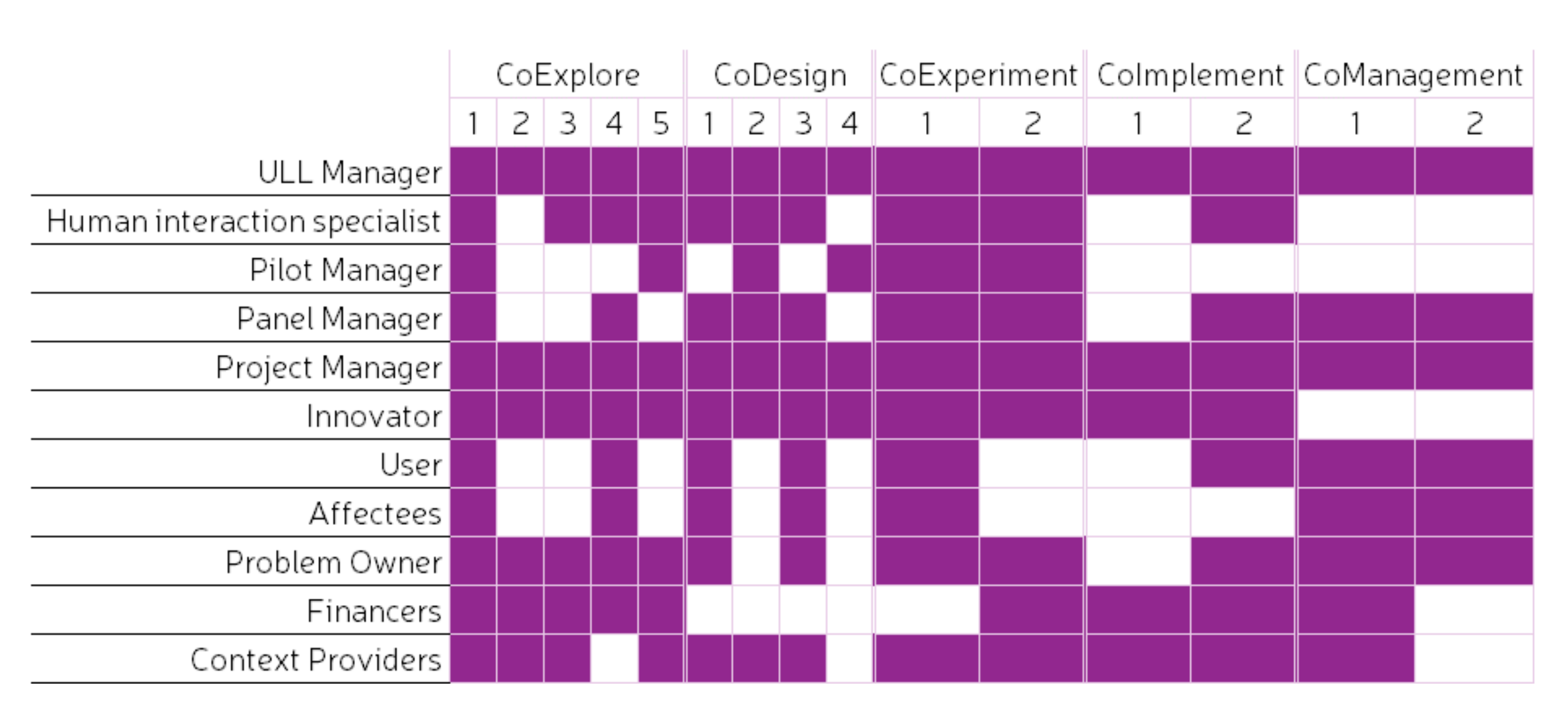
This section presents the most crucial stakeholders or actors that should be included in each of the abovementioned stages and substages. This should not be taken as a definitive list of stakeholders but, instead, as guidance. Stakeholders vary considerably depending on the project and whether the project involves public or private institutions or, alternatively, whether the project is developed in public–private partnerships. The summary of findings regarding internal and external actors of ULL [48] is used as a basis for the definition of the actors. The stakeholders proposed to be included at each stage and substage are shown in Figure 8.
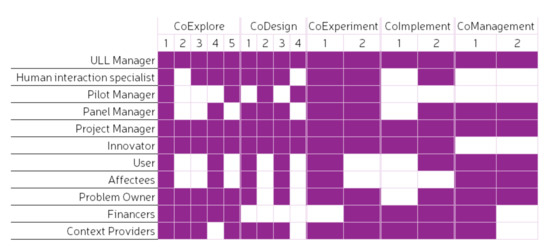
Figure 8.
Stakeholders across the stages and substages of the LCCCP. Adapted from [48].
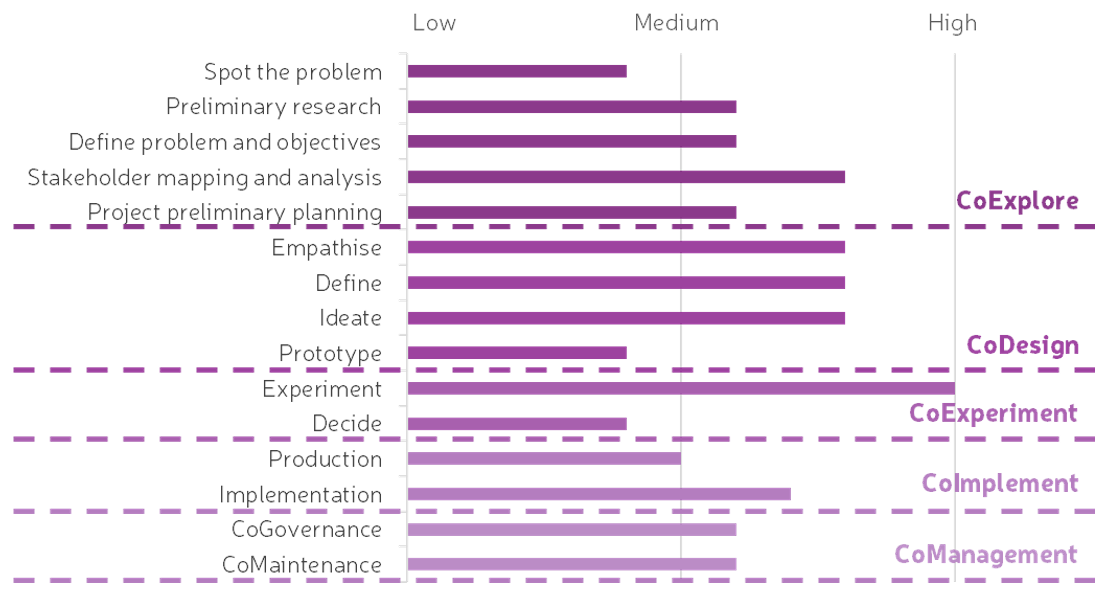
The engagement of the stakeholders can vary across the different stages and substages of the project, which allows for different methods and tools to be used during the different stages and substages of the process. The stages in which stakeholder engagement is more prominent are the CoDesign and CoExperiment stages, while less stakeholder engagement is needed in the CoExplore and CoImplement stages [1]. Even though an important level of engagement from stakeholders is expected in these latter stages (mostly the planners or developers of the project), these require mostly good and open communication channels with the rest of the stakeholders. The CoManagement stage needs to promote further engagement of the stakeholders as it happens towards the end of the project. As previously indicated, good communication and engaging activities are crucial to provide the necessary methods and tools for stakeholders to remain engaged with the solution even after the project is finished. Figure 9 shows the level of engagement that is expected by the stakeholders across each of the stages and substages.
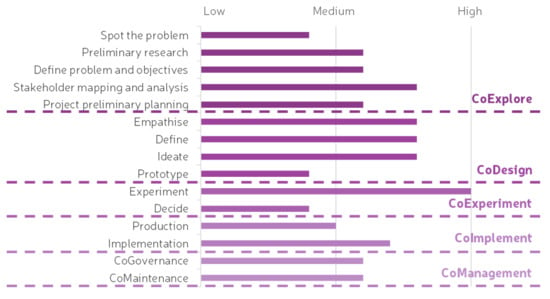
Figure 9.
Level of engagement expected from stakeholders across the different stages and substages of the LCCCP. Adapted from [1,48].
4.3. Methods and Tools for Stakeholder Engagement
Considering that stakeholder engagement has been identified as an important factor for the benefit identification of a project, methods and tools to promote stakeholder engagement are of high importance during the co-creation process. Benefits of co-creation are improved when multiple points-of-view are integrated, as the identified solutions are more likely to reflect the needs of diverse stakeholders and, accordingly, facilitate stakeholder buy-in to the project [44].
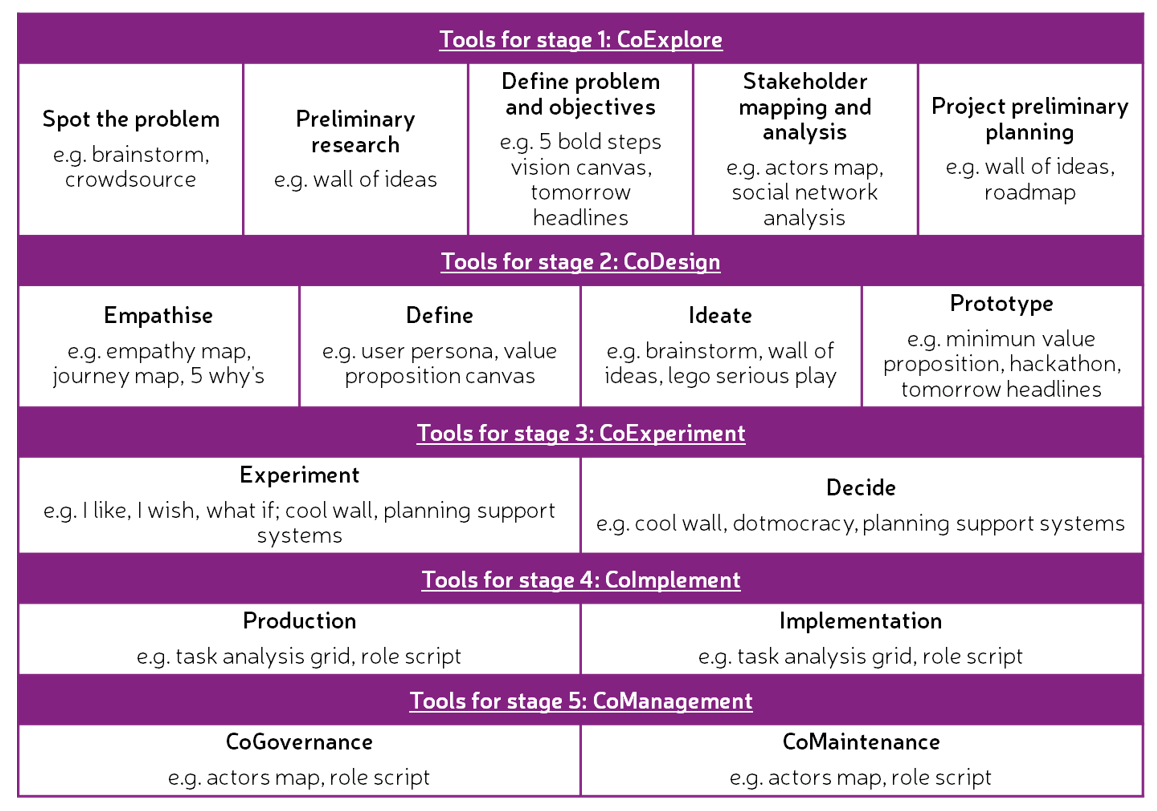
In this study, the main goals of the engagement process [50] were matched with the five (5) stages of the LCCCP in order to provide a comprehensive framework for selecting stakeholder engagement methods and tools. Some examples of stakeholder engagement methods and tools that can be used in the substages were selected. Toolkits for co-creation and user-centred design, such as the one developed for the U4IoT project [64], MindTools [37], Service Design Tools [38] and UNaLab project [39], were used as the main source of information. The selected methods and tools corresponding to each of the stages and substages are shown in Figure 10 and described in Section 4.3.1 to Section 4.3.4.
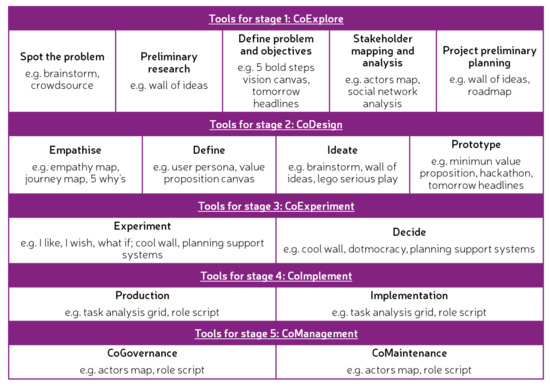
Figure 10.
Methods and tools (in grey) for stakeholder engagement across the stages and substages of the LCCCP. Adapted from [50].
4.3.1. Methods and Tools for Stage 1: CoExplore
The substages that are part of the CoExplore stage are ‘Spot the problem’, ‘Preliminary research’, ‘Define the problem and objectives’, ‘Stakeholder mapping and analysis’ and ‘Project preliminary planning’. In the ‘Spot the problem’ substage, the following methods are suggested:
- Brainstorm. This is an effective method to generate ideas on a specific issue due to the combination of a relaxed, informal approach to problem-solving with lateral thinking. This method encourages people to come up with thoughts and ideas that can be seen as crazy or non-plausible at first. When the participants feel free to relax and joke around during the activity, more creative ideas will be produced [65]. This method could be complemented with the Creative Matrix, which allows expanding the boundaries of the brainstorming process [66].
- Crowdsource. This method is used to engage stakeholders with a common goal. It is commonly powered by technologies, social media and web 2.0. It relies on the ever-growing connectivity and targets large groups of stakeholders [67]. This is an evolution of participatory methods, such as workshops, focus groups or world cafés, in which groups of stakeholders are brought together to discuss different questions led by a moderator.
In the ‘Preliminary research’ substage, the following tool is suggested:
- Wall of ideas. Also known as research wall, design wall, research board, ideation wall, inspiration board, mood board or pinboard. The main idea of this tool is to have a large vertical surface to display data and ideas. This tool allows a better exploration and visualisation process while gathering input from the stakeholders [68].
In the ‘Define problem and objectives’ substage, the following method and tool are suggested:
- Five bold steps vision canvas. This tool allows for the vision of the project to be viewed from a critical and realistic perspective. Vision themes need to be identified, and concrete examples in which those themes are shown need to be described. After obtaining the information related to the vision, five bold steps are defined that will help achieve the vision—hence outlining the path towards a concrete strategy [69].
- Tomorrow headlines. This method creates fictional articles published in magazines or journals, in which the developers and planners project themselves in the future and try to understand what kind of impact the solution may have. This method allows understanding how the solution will be presented to the users and what reaction(s) it may generate [70].
In the ‘Stakeholder mapping and analysis’ substage, the following methods are suggested:
- Actors map. This method supports the visualisation of communities, helping the actors to understand and discuss their relative position and relations within a system. The map reveals which actors are involved in a network, how they are linked, how much influence they have and what their goals are [71].
- Social network analysis. This method is used to investigate and visualise social structures using networks. It is mostly used to investigate the relations amongst stakeholders but could also provide support when categorising them [49].
Finally, in the ‘Project preliminary planning’ substage, the following method and tool are suggested:
- Wall of ideas. See Section 4.3.1. (Methods and Tools for Stage 1: CoExplore).
- Roadmap. This is a flexible method that is used for strategic and long-term planning. The end result of the tool is a structured means to explore and communicate the different components of a project, such as objectives, existing and future technologies, measures, stakeholders and challenges [72,73].
4.3.2. Methods and Tools for Stage 2: CoDesign
The substages that are part of the CoDesign stage are ‘Empathise’, ‘Define’, ‘Ideate’ and ‘Prototype’. In the ‘Empathise’ substage, the following methods and tools are suggested:
- Empathy map. This is a collaborative tool, developed by the consulting group in communications and businesses XPLANE, which provides insight to potential problems that can arise in different stages of the co-creation process. The ultimate goal of the empathy map is for a stakeholder to empathise with another stakeholder in order to gain insight to the different aspects of their sensory experience [74].
- Journey map. This is a tool used to create a narrative that follows users’ interactions with the proposed solution(s). This map can help empathise with the users and better understand their needs and feelings and provides a visual representation of the elements that affect the user’s experience [75].
- Five Whys. This is an easy and effective method that allows the identification of the root cause of a problem. It can be used for troubleshooting, quality improvement and problem-solving, being more efficient when used to resolve simple or moderately difficult problems. The method follows an interview technique that allows the researcher and participants to gain a deeper understanding of the root cause during the interviews [76].
In the ‘Define’ substage, the following method and tool are suggested:
- User persona. This is a method that allows creating a fictional representation of the ideal user of a product and/or service. The user persona needs to incorporate needs, goals and observed behaviour patterns of the target audience. One persona should be created for each identified user group [77].
- Value proposition canvas. This tool allows the team to think differently about the users and what can be offered to them, allowing the users to also think differently about the product/service provider as their needs and/or wishes are addressed directly [78]. The canvas comprises two different sections: the customer segment and the value proposition. It is important to start with the customer and, in turn, define the jobs-to-be-done, pains and gains.
In the ‘Ideate’ substage, the following methods and tool are suggested:
- Brainstorm. See Section 4.3.1. (Methods and Tools for Stage 1: CoExplore).
- Wall of ideas. See Section 4.3.1. (Methods and Tools for Stage 1: CoExplore).
- Lego serious play. This method is used for many purposes and facilitates the exchange of thoughts and ideas between participants from different disciplines. Lego Serious Play can be used at any stage of development but tends to be most suitable at an early stage of the process (to create ideas) or at pivotal points in the project (to discuss experiences) [79]. Participants are faced with a question and asked to answer the question by building a Lego model as a metaphorical representation of their answer and/or idea.
In the ‘Prototype’ substage, the following methods are suggested:
- Minimum value proposition (MVP). This is a prototyping method in which a solution is developed with enough features to satisfy early users. The complete set of characteristics of the solutions are only designed and developed after receiving enough feedback from the users. It is the first prototype that is made [80].
- Hackathon. An event of any duration in which people get together to solve problems. Using a competition scenario, participants are faced with a question or objective and asked to answer it by coming up with a solution to it. The concept is similar to Lego Serious Play, but the Hackathon is done at a larger scale as the participants are asked to come up with a prototype of the solution they are proposing [76].
- Tomorrow headlines. See Section 4.3.1. (Methods and Tools for Stage 1: CoExplore).
4.3.3. Methods and Tools for Stage 3: CoExperiment
The substages that are part of the CoExperiment stage are ‘Experiment’ and ‘Decide’. In the ‘Experiment’ substage, the following method and tool are suggested:
- I Like, I Wish, What if. This is a facilitated team feedback method in which feedback is collected in a constructive and positive environment. It was initially designed to suit interdisciplinary teams by creating an easy-to-use format in which everyone feels comfortable. Because of the positive connotation of the statements “I like, I wish, What if”, the participants that are usually uncomfortable with sharing direct criticism feel comfortable with this format [81].
- Cool wall. This tool consists of a large poster on which participants can stick cards. The cards contain images of the neighbourhood (e.g., day and night situations) and potential solutions for inspiration. Also, empty cards are provided for people to add their own ideas. The wall has four categories: seriously uncool (not nice at all), uncool (not so nice), cool (nice) and sub-zero (really nice). Participants choose cards they find interesting and write what they do in that area, and why they like it or do not like it there [82].
In the ‘Decide’ substage, the following method and tool are suggested:
- Cool wall. See Section 4.3.3. (Methods and Tools for Stage 3: CoExperiment).
- Dotmocracy. This is an established facilitation method used to vote with dot stickers or with a marker. It allows all participants to vote for one or more ideas that they like, being a quick and simple method to prioritise a long list of options. The tool helps to create a sense of engagement among the participants as they feel directly responsible for the decision and allows them to take part in the decision process [83].
Across the ‘Experiment’ as well as the ‘Decide’ substages, the following tool is suggested:
- Planning support systems (PSS). PSS are developed as computer-based geo-information instruments that assist planners in the process of making decisions, helping them to explore and manage their activities [84]. As described by Russo et al. (2018, p. 10), PSS are “a decision support tool to assist data-driven land use planning”. The Landscapes Toolkit [85] and the Systemic Decision Support Tool (SDST) [86] are examples of scenario simulation tools that allow to assess the impacts, benefits and co-benefits of stakeholder-defined solutions.
4.3.4. Methods and Tools for Stage 4: CoImplement
The substages that are part of the CoImplement stage are ‘Production’ and ‘Implementation’. Across these substages, the following tools are suggested:
- Task analysis grid. The aim of this tool is to show, in a schematic way, the scope of and information associated with the project, as well as the stakeholders that participate in it. Each column represents a scenario, describes the task and is followed by all the sub-tasks needed to complete the task. They can be colour-coded and prioritised and, as such, they allow stakeholders to better understand where they are involved and what they need to do [87].
- Role script. This tool provides the stakeholders with a series of scripts, one for each situation that they could face. It represents a scenic representation of the situation and instructs the stakeholder on what to do with notes, comments and advices [88].
4.3.5. Methods and Tools for Stage 5: CoManagement
The substages that are part of the CoManagement stage are ‘CoGovernance’ and ‘CoMaintenance’. Across these substages, the following method and tool are suggested:
- Actors map. See Section 4.3.1. (Methods and Tools for Stage 1: CoExplore).
- Role script. See Section 4.3.4. (Methods and Tools for Stage 4: CoImplement).
As noted in the methods and tools mentioned above, most of them (e.g., brainstorm and wall of ideas) can be used in more than one substage due to their versatility. It is important to note that the methods and tools identified in this section do not cover the complete universe of methods and tools available but, instead, intend to show a small sample of the ones available.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
The objective of this study was to identify and characterise the stages across the life cycle co-creation process (LCCCP) for nature-based urban climate change adaptation, including the stakeholders to be engaged, as well as the methods and tools that can be used to promote stakeholder engagement in each stage. Stages and substages of the LCCCP were identified and defined, building on continuous improvement approaches, such as the PDCA cycle (Kaizen™ [28,32]), the DMAIC cycle [29] and the Design Thinking methodology [27]. In each of these stages and substages, the stakeholders involved were mapped based on the internal and external actors of the Urban Living Lab (ULL) approach. Examples of stakeholder engagement methods and tools were proposed for each of these stages and substages, with the goal of obtaining a higher level of engagement from the various stakeholders. [50].
Given the identified need for a methodology that supports co-creation in order to ensure its success [26] and given that co-creation is considered the way forward in environment related issues [18,43,63,89,90], the LCCCP developed in this paper provides a comprehensive and well-defined co-creation process that can be used to develop NBS for urban climate change adaptation. As such, it can contribute to more sustainable and resilient cities in the face of global change.
This study goes beyond previous studies in various ways. First, a unique co-creation path, named the LCCCP, was created using continuous improvement approaches and the Design Thinking methodology. The LCCCP starts with the identification of the problem(s) that need to be addressed using a co-creation process and finishes when the solution(s) has been implemented and is being managed by stakeholders. In contrast, the continuous improvement approaches and Design Thinking methodology developed in most previous studies only cover some of the stages [1,27,63]. Second, the main stakeholders that should participate in stage and substage were identified using the ULL internal and external actors [48]. The level of engagement expected from the stakeholders was also identified (adapted from [1,48]). Third, the main goals for stakeholder engagement [50] were adapted for each of the LCCCP stages, and examples of methods and tools that could help achieve those goals were provided. Finally, this study is the first of its kind that attempts to provide a complete overview of the co-creation process, thereby identifying the stakeholders that should participate, as well as providing examples of methods and tools to promote their engagement in each stage of the LCCCP.
The creation of the LCCCP proved that a parallel between the PDCA cycle [28], DMAIC cycle [29] and Design Thinking methodology [27] can be made. The LCCCP that was developed integrates most of the stages described in the PDCA and DMAIC cycles [28,29] and Design Thinking methodology [27] and created a unique path that can be followed by co-creation practitioners. The developed LCCCP comprises five stages (CoExplore, CoDesign, CoExperiment, CoImplement and CoManagement) and identifies the stakeholders, as well as the engagement methods and tools for co-creation in one study and, as such, provides a comprehensive and easy to follow guide for co-creation practitioners. Practitioners will benefit as they can follow the co-creation process step-by-step, while reducing the risk of missing important stages, incorrectly involving and/or excluding relevant stakeholders and inappropriately using stakeholder engagement methods and tools.
It is of high importance to have a deep understanding of the different roles that stakeholders can adopt during the co-creation process in a ULL. How the selection of stakeholders can be made has not been considered in detail in this article but should be taken into careful consideration during the process. The actors may vary depending on the ULL, the stakeholders that take part in the process and the project that will be developed.
Many different methods and tools for stakeholder engagement can be found in literature, and despite the extensive amount of information and step-by-step guides available, identifying the most appropriate method and tool requires experience and practice. The real experience of adopting co-creation and applying the methods and tools in real-life settings is a significant part of the knowledge needed to identify the best methods and tools. Further research is needed to create a specific framework for stakeholder engagement tools in which the main objective of the methods and tools, as well as their selection criteria, can be described. The methods and tools presented in this article are to be considered a small sample and not an exhaustive list. Literature provides several different examples of methods and tools, often collated in toolkits, that can be used for stakeholder engagement. It is important to understand that all methods and tools can be tailored to specified goals and stakeholder perspectives and, as such, they should be considered to be in continuous development and evolution.
Similarly, the importance of real-life experience is necessary in adopting and adapting the LCCCP in a context as multifaceted as climate change adaptation. The process addresses wicked problems with the purpose of involving the multiple stakeholders throughout all stages and is, therefore, so complex that empirical studies are needed to further test and evaluate the process. The nature of the LCCCP, consisting of stages from existing processes (e.g., Design Thinking) where empirical studies and practice-based evidence are already present, contributes to the validity of the individual stages. Yet empirical studies on the implementation of the LCCCP process as a holistic approach should be conducted by cities implementing NBS.
Some caveats remain. First, as the LCCCP has not been applied and, thus, feedback from practitioners needs to be obtained. Further development of the stages and substages identified for the LCCCP needs to be done in order to gain a better understanding of the outputs and deliverables expected from each of them. This will allow practitioners to acquire a reference framework that will help them to apply co-creation in the exploration, design, experimentation, implementation and management of nature-based and other solutions. For this, direct feedback from co-creation practitioners needs to be obtained in order to fine-tune the developed LCCCP. Second, it is important to develop a monitoring structure in which the LCCCP can be consistently analysed to determine how successful the process is. In the case that a stage or substage has not achieved its goals, the monitoring structure should provide the necessary information to identify shortcomings and how to solve them. Finally, a literature review of co-creation related studies needs to be performed to compare them with the LCCCP. A mapping of the studies along the LCCCP to indicate which stage(s) are considered, which stakeholders are involved and which methods and tools are used, can provide additional input to further develop the co-creation path.
Author Contributions
M.I.D.-W. conducted the conceptualization, investigation, methodology and the original draft preparation, P.R. and. S.V. conducted the overall supervision of the investigation and P.R., S.V. and I.V. conducted the review and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper has been developed in the context of the UNaLab Project (https://www.unalab.eu/), which has received funding from the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 730052, Topic: SCC-2-2016-2017: Smart Cities and Communities Nature Based Solutions. Thanks are also due for the financial support to FCT/MCTES (UIDP/50017/2020+UIDB/50017/2020) through national funds, and the co-funding by European funds when applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the entire team at ENoLL for openly sharing documentation and knowledge that were of high relevance to this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Van De Ven, F.; Snep, R.; Koole, S.; Brolsma, R.; Van Der Brugge, R.; Spijker, J.; Vergroesen, T. Adaptation Planning Support Toolbox: Measurable performance information based tools for co-creation of resilient, ecosystem-based urban plans with urban designers, decision-makers and stakeholders. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 66, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN DESA. World Population Prospects. The 2017 Revision. Key Findings and Advance Tables. World Population Prospects. 2017. Available online: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/Publications/Files/WPP2017_KeyFindings.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2018).
- UN DESA. The World’s Cities in 2016: Data Booklet. Available online: http://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/urbanization/the_worlds_cities_in_2016_data_booklet.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2018).
- Seto, K.C.; Reenberg, A.; Boone, C.G.; Fragkias, M.; Haase, D.; Langanke, T.; Marcotullio, P.; Munroe, D.K.; Olah, B.; Simon, D. Urban land teleconnections and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7687–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhearson, T.; Karki, M.; Herzog, C.; Fink, H.S.; Abbadie, L.; Kremer, P.; Clark, C.M.; Palmer, M.I.; Perini, K.; Dubbeling, M.; et al. Urban Ecosystems and Biodiversity. In Climate Change and Cities; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 257–318. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, D.A.; Blake, R.; Grimm, A.; Hamdi, R.; Kim, Y.; Horton, R.; Rosenzweig, C.; Alverson, K.; Gaffin, S.; Crane, S. Urban Climate Science. In Climate Change and Cities; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 27–60. [Google Scholar]
- Gencer, E.; Folorunsho, R.; Linkin, M. Disasters and Risk in Cities. In Climate Change and Cities: Second Assessment Report of the Urban Climate Change Research Network; Rosenzweig, C., Solecki, W., Romero-Lankao, P., Mehrotra, S., Dhakal, S., Ali Ibrahim, S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 61–98. [Google Scholar]
- Beierle, T.C.; Konisky, D. Values, conflict, and trust in participatory environmental planning. J. Policy Anal. Manag. 2000, 19, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.S. Stakeholder participation for environmental management: A literature review. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 2417–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.; Vella, S.; Challies, E.; De Vente, J.; Frewer, L.; Hohenwallner-Ries, D.; Huber, T.; Neumann, R.K.; Oughton, E.A.; Del Ceno, J.S.; et al. A theory of participation: What makes stakeholder and public engagement in environmental management work? Restor. Ecol. 2017, 26, S7–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, E.D.G.; Dougill, A.J.; Mabee, W.E.; Reed, M.; McAlpine, P. Bottom up and top down: Analysis of participatory processes for sustainability indicator identification as a pathway to community empowerment and sustainable environmental management. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 78, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission EU. Nature-Based Solutions|Environment—Research and Innovation. 2017. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/research/environment/index.cfm?pg=nbs (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Faivre, N.; Fritz, M.; Freitas, T.; De Boissezon, B.; Vandewoestijne, S. Nature-Based Solutions in the EU: Innovating with Nature to Address Social, Economic and Environmental Challenges. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. Sustainable Development Goals: Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform. 2017. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/?menu=1300 (accessed on 3 January 2018).
- Raymond, C.M.; Berry, P.; Breil, M.; Nita, M.R.; Kabisch, N.; De Bel, M.; Enzi, V.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Geneletti, D.; Cardinaletti, M.; et al. An Impact Evaluation Framework to Support Planning and Evaluation of Nature-Based Solutions Projects. Report Prepared by the EKLIPSE Expert Working Group on Nature-Based Solutions to Promote Climate Resilience in Urban Areas. 2017. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/research/environment/pdf/renaturing/eklipse_report1_nbs-02022017.pdf#view=fit&pagemode=none (accessed on 9 April 2018).
- Frantzeskaki, N.; Kabisch, N. Designing a knowledge co-production operating space for urban environmental governance—Lessons from Rotterdam, The Netherlands and Berlin, Germany. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 62, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juujärvi, S.; Pesso, K. Actor Roles in an Urban Living Lab: What Can We Learn from Suurpelto, Finland? Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2013, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogstie, J.; Ståhlbröst, A.; Holst, M.; Jelle, T.; Kulseng, L.; Gudmundsdottir, A. Using a Living Lab Methodology for Developing Energy Savings Solutions. In Proceedings of the 19th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 15–17 August 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- ENoLL. About Us|European Network of Living Labs. 2018. Available online: http://enoll.org/about-us/ (accessed on 2 April 2018).
- Baccarne, B.; Schuurman, D.; Mechant, P.; De Marez, L. The Role of Urban Living Labs in a Smart City. In Proceedings of the XXV ISPIM Conference Innovation for Sustainable Economy &Society, Dublin, Ireland, 8–11 June 2014; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Prahalad, C.K.; Ramaswamy, V. Co-Opting Costumer Competence. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2000, 78, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gioia, S. A Brief History of Co-Creation—The XPLANE Collection—Medium. 2015. Available online: https://medium.com/the-xplane-collection/a-brief-history-of-co-creation-2e4d615189e8 (accessed on 18 February 2018).
- Vargo, S.L.; Lusch, R.F. Service-dominant logic: Continuing the evolution. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2008, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, R.; Occhiocupo, N.; Clarke, J. Motives and resources for value co-creation in a multi-stakeholder ecosystem: A managerial perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 4033–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkova, A.; Gustafsson, M. Business models for industrial ecosystems: A modular approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 29–30, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradwell, P.; Marr, S. Making the most of collaboration an international survey of public service co-design. Demos 2008, 23, 2–53. [Google Scholar]
- Dam, R.; Siang, T. 5 Stages in the Design Thinking Process|Interaction Design Foundation. 2018. Available online: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/5-stages-in-the-design-thinking-process (accessed on 6 May 2018).
- Graves, A. PDCA—Six Sigma Terminology. 2013. Available online: http://www.sixsigmadaily.com/pdca-plan-do-check-act/ (accessed on 6 May 2018).
- Formation, X.L. DMAIC. 2018. Available online: https://www.xl-formation.com/dmaic (accessed on 7 May 2018).
- Efron, S.E.; Ravid, R. Writing the Literature Review: A Practical Guide; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; p. 298. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Solecki, W.; Romero-Lankao, P.; Mehrotra, S.; Dhakal, S.; Ali Ibrahim, S. Climate Change and Cities Second Assessment Report of the Urban Climate Change Research Network; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kaizen Institute. Kaizen Institute Consulting Group|About Us. 2018. Available online: https://www.kaizen.com/about-us.html (accessed on 6 May 2018).
- Van Der Aalst, W.M.P.; La Rosa, M.; Santoro, F.M. Business process management: Don’t forget to improve the process! Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2016, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, R.; Siagn, T. Design Thinking: Getting Started with Empathy|Interaction Design Foundation. 2018. Available online: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/design-thinking-getting-started-with-empathy (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Cavallini, S.; Soldi, R.; Friedl, J.; Volpe, M. Using the Quadruple Helix Approach to Accelerate the Transfer of Research and Innovation Results to Regional Growth—European Union Committee of the Regions. 2016. Available online: http://www.europa.eu (accessed on 17 May 2018).
- U4IoT. User Engagement for Large Scale Pilots in the Internet of Things. 2018. Available online: https://u4iot.eu/ (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- MindTools. Management Training and Leadership Training—Online. 2018. Available online: https://www.mindtools.com/ (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- Tassi, R. Service Design Tools|Communication Methods Supporting Design Processes. 2009. Available online: http://www.servicedesigntools.org/ (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- UNaLab. UNaLab Co-Creation Toolkit. 2020. Available online: https://unalab.enoll.org/ (accessed on 8 March 2020).
- Seiffert, M.E.B.; Loch, C. Systemic thinking in environmental management: Support for sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 13, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, G.; Bartlett, L. Systemic Thinking—Prodsol International Ltd. 2017. Available online: http://systemicthinking.com/ (accessed on 18 April 2018).
- UNEP UNEP. Why Take A Life Cycle Approach? 2004. Available online: https://www.lifecycleinitiative.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/2004-WhytakeLCA-EN.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Voorberg, W.H.; Bekkers, V.J.J.M.; Tummers, L.G. A Systematic Review of Co-Creation and Co-Production: Embarking on the social innovation journey. Public Manag. Rev. 2015, 17, 1333–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeys, L.A.; Huemann, M. Project benefits co-creation: Shaping sustainable development benefit. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1196–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izvercianu, M.; Şeran, S.A.; Branea, A.-M. Prosumer-oriented Value Co-creation Strategies for Tomorrow’s Urban Management. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 124, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stigt, R.; Driessen, P.P.J.; Spit, T.J.M. A user perspective on the gap between science and decision-making. Local administrators’ views on expert knowledge in urban planning. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 47, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finquelievich, S. Knowledge Societies Policy Handbook; IFAP/UNESCO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ståhlbröst, A.; Bergvall-Kareborn, B.; Eriksson, C.I. Stakeholders in Smart City Living Lab Processes. In Proceedings of the 21st Americas Conference on Information Systems, Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 13–15 August 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, M.S.; Graves, A.; Dandy, N.; Posthumus, H.; Hubacek, K.; Morris, J.; Stringer, L.C. Who’s in and why? A typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1933–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mease, L.A.; Erickson, A.; Hicks, C. Engagement takes a (fishing) village to manage a resource: Principles and practice of effective stakeholder engagement. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 212, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.; Pandey, M.M. Research Methodology: Tools and Techniques. Bridge Center. Available online: http://www.euacademic.org/BookUpload/9.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- UNaLab. 2018. Available online: https://unalab.eu/home (accessed on 30 March 2018).
- ATAP. Australian Transport Assessment and Planning Guidelines—F2 Problem identification & Assessment—Australian Transport and Infrastructure Council. 2016. Available online: https://atap.gov.au/framework/delivery/files/f6_delivery.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Tran, J. The Design Brief: A North Star for Any Project—Peer Insight|Innovation Consulting [Internet]. 2015. Available online: http://www.peerinsight.com/musings/2015/2/11/design-brief-the-north-star-for-any-project (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Andrews, W. The Drawbackwards Design Thinking Process—Design. 2017. Available online: https://design.org/blog/drawbackwards-design-thinking-process/ (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Dam, R.; Siang, T. Stage 2 in the Design Thinking Process: Define the Problem and Interpret the Results|Interaction Design Foundation. 2017. Available online: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/stage-2-in-the-design-thinking-process-define-the-problem-and-interpret-the-results (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Dam, R.; Siang, T. Stage 3 in the Design Thinking Process: Ideate|Interaction Design Foundation. 2017. Available online: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/stage-3-in-the-design-thinking-process-ideate (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Dam, R.; Siang, T. Stage 4 in the Design Thinking Process: Prototype|Interaction Design Foundation. 2017. Available online: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/stage-4-in-the-design-thinking-process-prototype (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Dam, R.; Siang, T. Stage 5 in the Design Thinking Process: Test|Interaction Design Foundation. 2017. Available online: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/stage-5-in-the-design-thinking-process-test (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- ATAP. Australian Transport Assessment and Planning Guidelines—F6 Delivery—Australian Transport and Infrastructure Council. 2016. Available online: https://atap.gov.au/framework/delivery/files/f6_delivery.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Dodson, G. Moving Forward, Keeping the Past in Front of Us. Treaty Settlements, Conservation, Co-Governance and Communication. In Communication Issues in Aotearoa New Zealand: A Collection of Research Essays; Dodson, G., Papoutsaki, E., Eds.; Epress Unitec: Auckland, New Zealand, 2014; pp. 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Prizeman, O. Maintenance of shared spaces: Courtyards of Tbilisi. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 6, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Amenta, L.; Attademo, A.; Cerreta, M.; Formato, E.; Remøy, H.; Arciniegas, G. REPAiR—REsource Management in Peri-urban Areas: Going Beyond Urban Metabolism. In D5.1: PULLs Handbook; DiARC: Napoli, Italy, 2017; Available online: http://h2020repair.eu/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Deliverable_5.1_PULLs_Handbook.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2018).
- U4IoT. End-User Engagement Toolkit. 2018. Available online: https://u4iot.eu/end-user-engagement-toolkit (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- MindTools. Brainstorming Generating Many Radical, Creative Ideas. 2016. Available online: https://www.mindtools.com/brainstm.html (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Naude, D. Design Thinking Tools—The Creative Matrix—Dawid’s Blog. 2017. Available online: https://dawidnaude.com/design-thinking-tools-the-creative-matrix-dfe0d15427d (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Crowdsourcing Week. What is Crowdsourcing?|Crowdsourcing Week. 2018. Available online: https://crowdsourcingweek.com/what-is-crowdsourcing/ (accessed on 7 June 2018).
- Van der Pijl, P. How to Create a Thousand Ideas in No Time. 2017. Available online: http://designabetterbusiness.com/2017/11/09/get-thousand-ideas-no-time/ (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Van der Pijl, P. 5 Steps to Design a Vision Beyond a Vision Statement—Design a Better Business. 2016. Available online: http://designabetterbusiness.com/2016/10/03/5-steps-design-vision-beyond-vision-statement/ (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Tassi, R. Tomorrow Headlines|Service Design Tools. 2009. Available online: http://www.servicedesigntools.org/tools/14 (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Manichinelly, M. Net-Map Toolbox, a Social Network Analisys Tool for Community/Locality Systems Projects: Openp2pdesign.org. 2009. Available online: http://www.openp2pdesign.org/2009/complexity/net-map-toolbox-a-social-network-analisys-tool-for-community-locality-systems-projects/?lp_lang_pref=it%22%5Ct%22_blank (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Phaal, R.; Farrukh, C.J.P.; Probert, D.R. Technology roadmapping—A planning framework for evolution and revolution. Technol. Forecast Soc. Chang. 2004, 71, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Ouden, E.; Valkenburg, R.; Postmes, L. R4E—Roadmaps for Energy Final City Report. Smart Urban Spaces Eindhoven. 2018. Available online: http://roadmapsforenergy.eu/wp-content/uploads/2017/final_city_reports/20170818_D6.4_Final_City_Report_Smart_Urban_Spaces_Eindhoven.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- XPLANE. Empathy Map. 2018. Available online: http://x.xplane.com/empathymap (accessed on 24 January 2018).
- Frick, T. What Is a Customer Journey Map? Mightybytes. 2017. Available online: https://www.mightybytes.com/blog/customer-journey-map-template-download/ (accessed on 7 June 2018).
- MindTools. 5 Whys—Problem-Solving Skills From MindTools. 2015. Available online: https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_5W.htm (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Veal, R. How to Define A User Persona. 2016. Available online: https://careerfoundry.com/en/blog/ux-design/how-to-define-a-user-persona/ (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Voorhorst, F. Expressive Product Design|The Value Proposition CanvasThe Value Proposition Canvas—Expressive Product Design. 2016. Available online: https://www.expressiveproductdesign.com/value-proposition-canvas/ (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Lego. LEGO.com Serious Play The Method. 2018. Available online: https://www.lego.com/en-us/seriousplay/the-method (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Forbes. What Is A Minimum Viable Product, And Why Do Companies Need Them? 2018. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/quora/2018/02/27/what-is-a-minimum-viable-product-and-why-do-companies-need-them/#db1b9bb382ca (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Dam, R.; Siang, T. Test Your Prototypes: How to Gather Feedback and Maximise Learning|Interaction Design Foundation. 2018. Available online: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/test-your-prototypes-how-to-gather-feedback-and-maximise-learning (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- TU/e LightHouse Smart Light Eindhoven. 2017. Available online: http://www.tue-lighthouse.nl/SmartlightEHV.html (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- What Is Dotmocracy?—Dotmocracy. 2017. Available online: https://dotmocracy.org/what_is/ (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Geertman, S.; Stillwell, J. Planning support systems: An inventory of current practice. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2004, 28, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnet, I.C.; Roebeling, P.C.; Williams, K.J.; Holzworth, D. Landscapes Toolkit: An integrated modelling framework to assist stakeholders in exploring options for sustainable landscape development. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban Nature Labs (UNaLab). Project Proposal Submitted to H2020-SCC-2016-2017 (Smart and Sustainable Cities) on 06-09-2016 and Funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme Under Grant Agreement No. 730052 Topic: SCC-2-2016. 2016. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/730052 (accessed on 20 December 2017).
- Tassi, R. Task Analysis Grid|Service Design Tools. 2009. Available online: http://www.servicedesigntools.org/tools/137 (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Tassi, R. Role Script|Service Design Tools. 2009. Available online: http://www.servicedesigntools.org/tools/44 (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Sanders, E.B.-N.; Stappers, P.J. Co-creation and the new landscapes of design. CoDesign 2008, 4, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Feuvre, M.; Medway, D.; Warnaby, G.; Ward, K.; Goatman, A. Understanding stakeholder interactions in urban partnerships. Cities 2016, 52, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).