- Article
Assessment of Potential Heat Resources in Stratified Lakes in Poland in the Era of the Search for Clean Energy Sources
- Mariusz Ptak,
- Teerachai Amnuaylojaroen and
- Mariusz Sojka
- + 2 authors
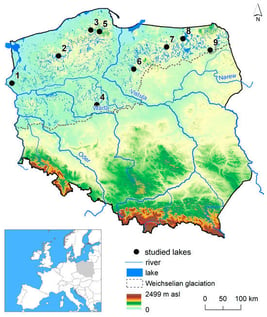
The emission of greenhouse gases associated with the combustion of hydrocarbons is a key factor in climate change, and in this context, increasing emphasis is being placed on the development of clean energy sources. The novel contribution of the article lies in identifying the energy potential of surface waters within energy systems transitioning away from fossil fuels. In the case of Poland, whose energy system has been based on coal for many decades, there are still many opportunities to expand energy production from renewable sources. One such source is the heat contained in surface waters. The research presented in this article focuses on the thermal structure of nine stratified lakes in Poland, examining changes over time and across different spatial profiles. Considering all temperature profiles, values ranged from 8.3 °C in May to 10.1 °C in September. In general, water warming occurs from May to the July–August transition, reaching a maximum of over 6 °C, while cooling takes place in the later phase of the analyzed season at a lower level, not exceeding 6 °C. It was found that the most thermally stable part of the water body was the layer between 15 m in depth and the bottom of the lakes, for which the heat resources were calculated. Using the basic physical properties of water, the amount of heat for this layer was determined. Assuming that technological processes do not reduce the water temperature below 4 °C (maximum water density), the hypothetical amount of available energy ranges from 630 to 101,000 MWh. The results indicate the high energy potential of lakes, which could be utilized in the future, provided further legal and economic analyses are conducted for specific cases. The study highlights the need to expand the long-term thermal monitoring of lakes, covering their entire vertical structure. Priority for such measurements should be given to lakes located near human settlements, as these have the highest potential for practical use.
5 February 2026



![(A)—Primary energy pathways in the two scenarios [10]. (B)—Change in CO2 emissions from fuel combustion and avoided emissions from deployment of selected clean technologies [11].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/resources/resources-15-00025/article_deploy/html/images/resources-15-00025-g001-550.jpg)