Inkjet Printed Fully-Passive Body-Worn Wireless Sensors for Smart and Connected Community (SCC)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
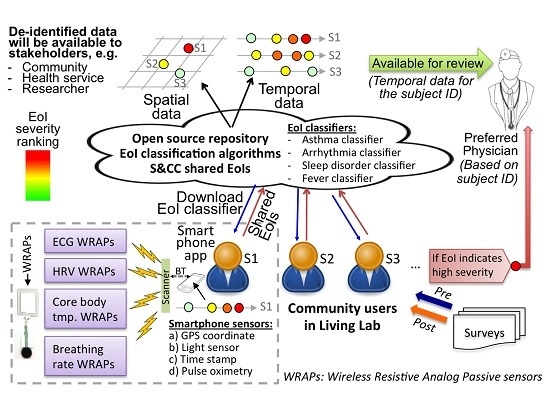
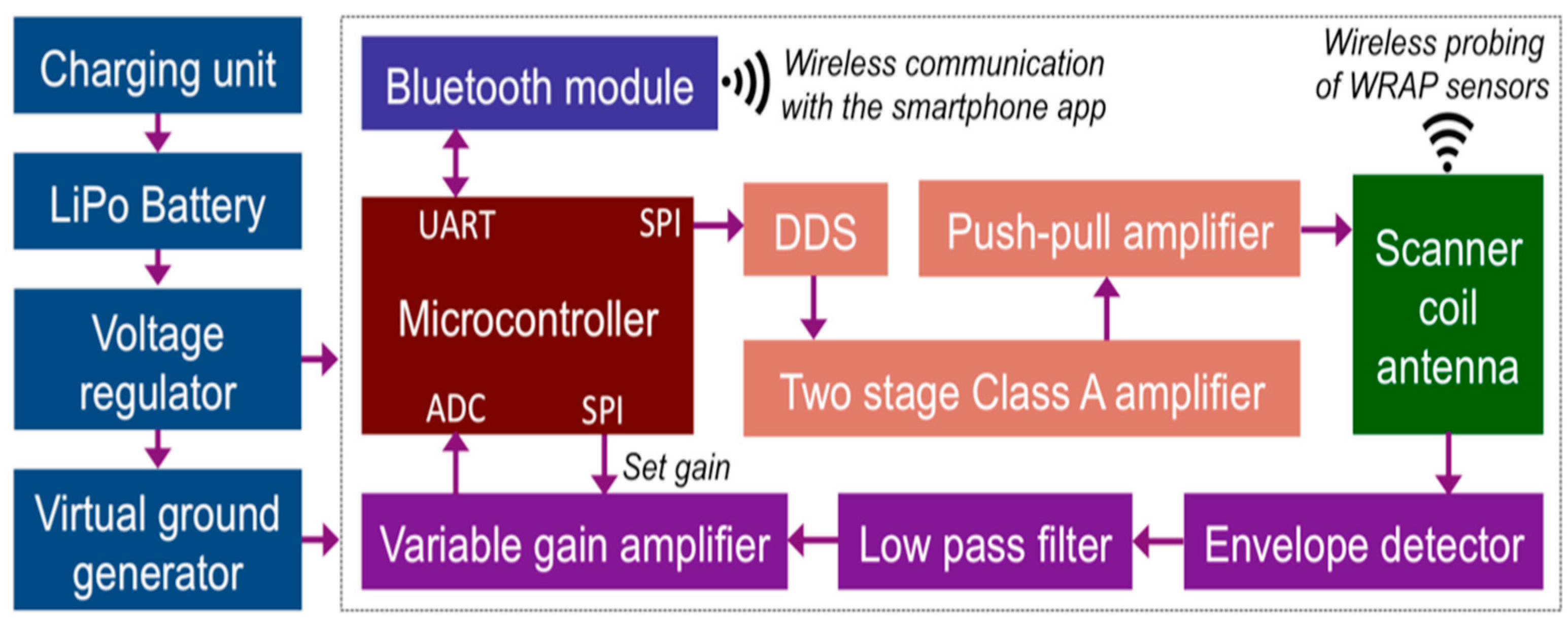
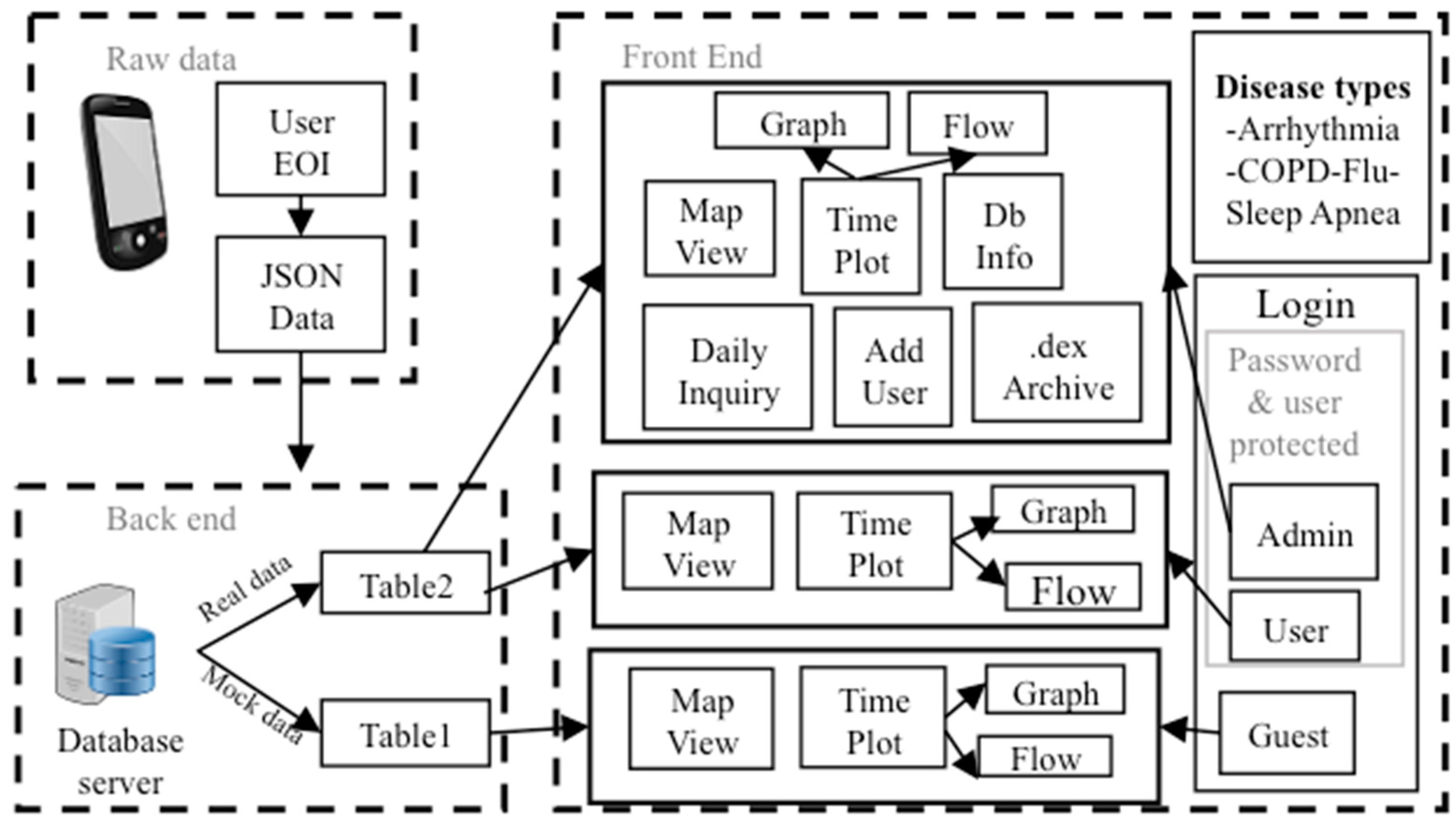
2.1. A. Overall System Description
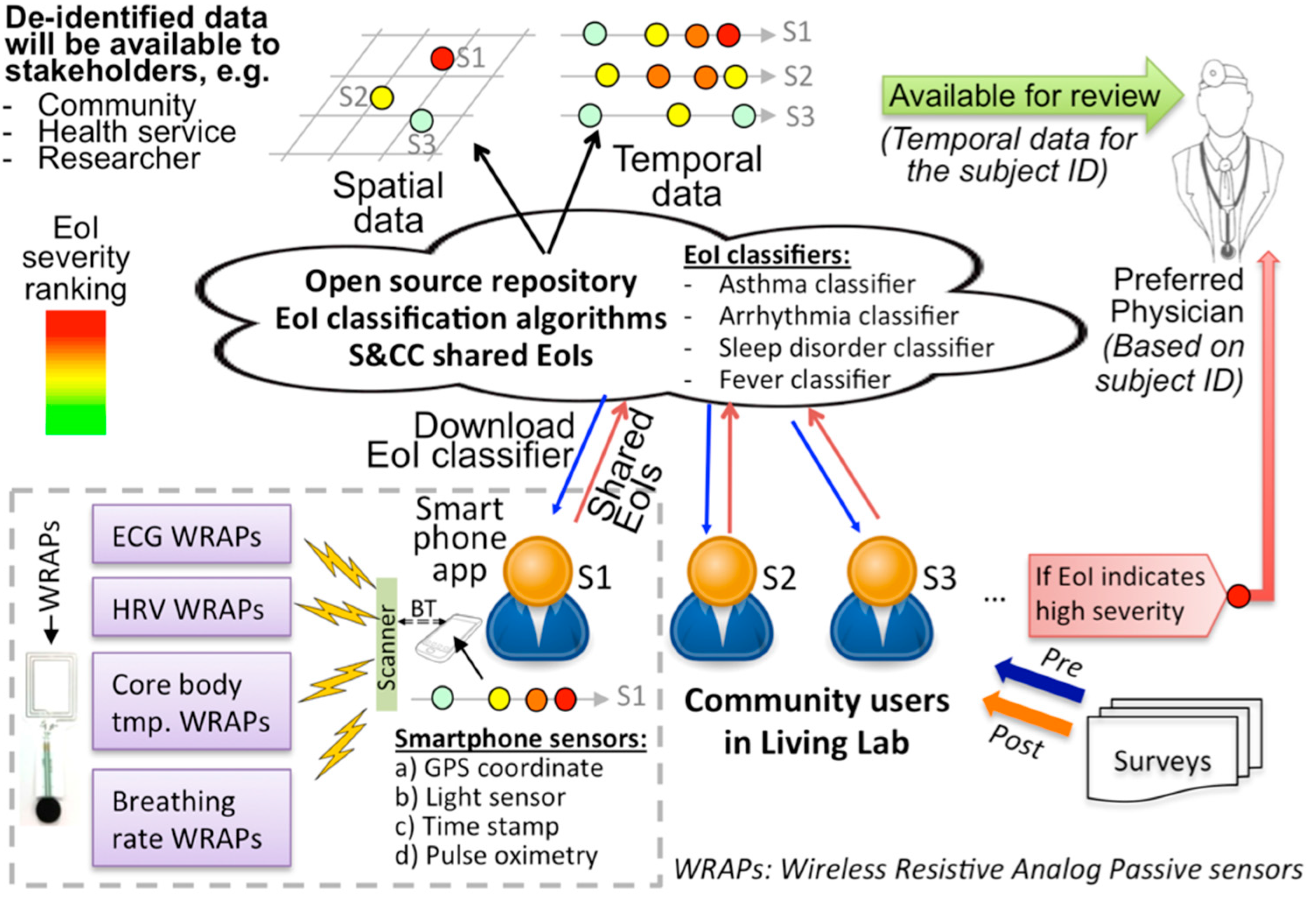
2.2. B. WRAP Sensor Operation Theory
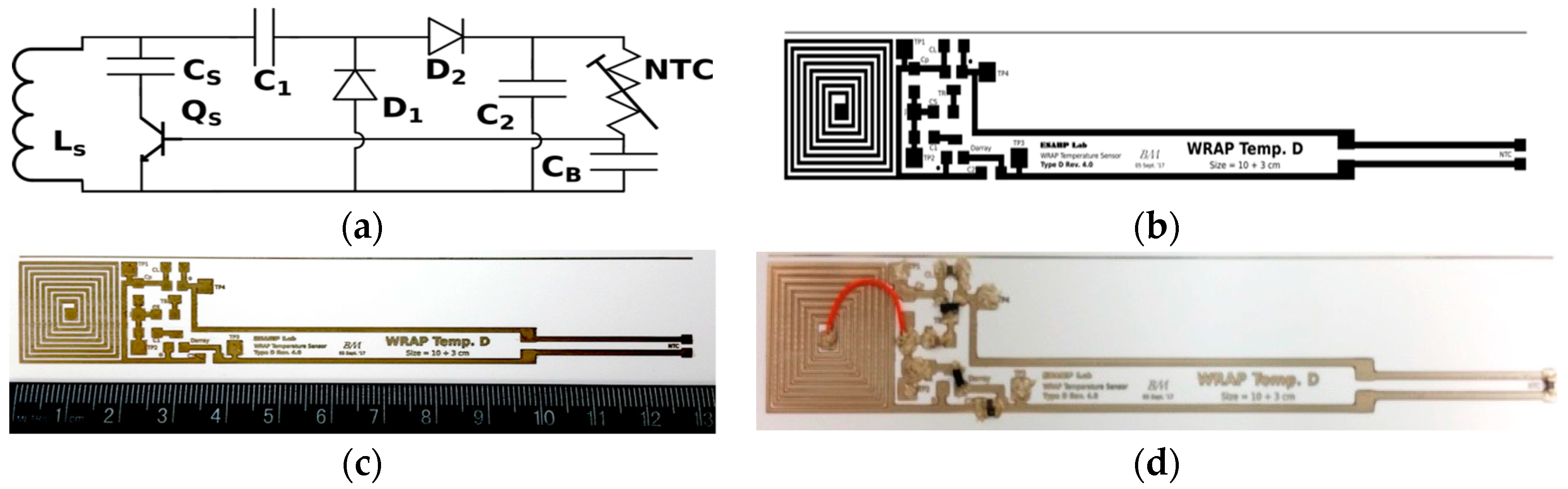
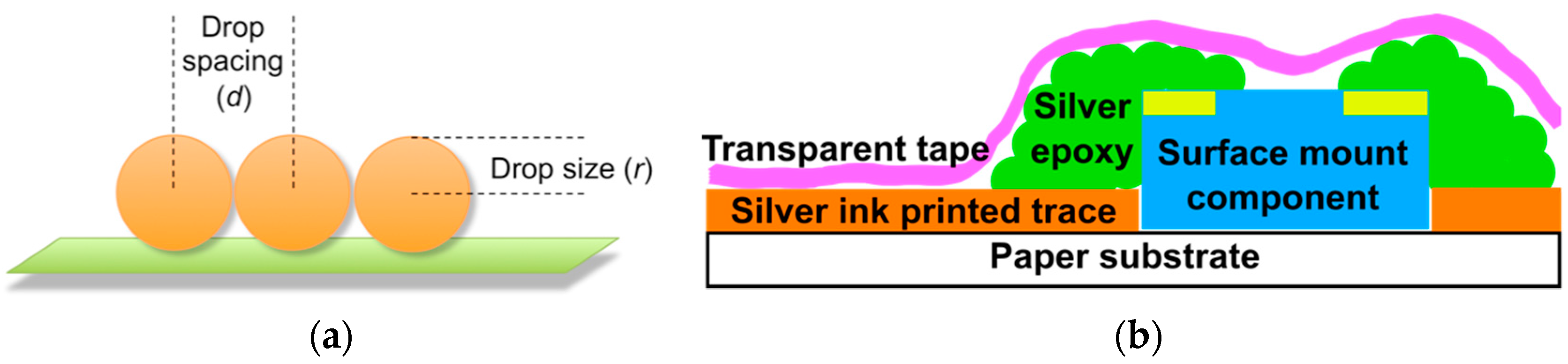
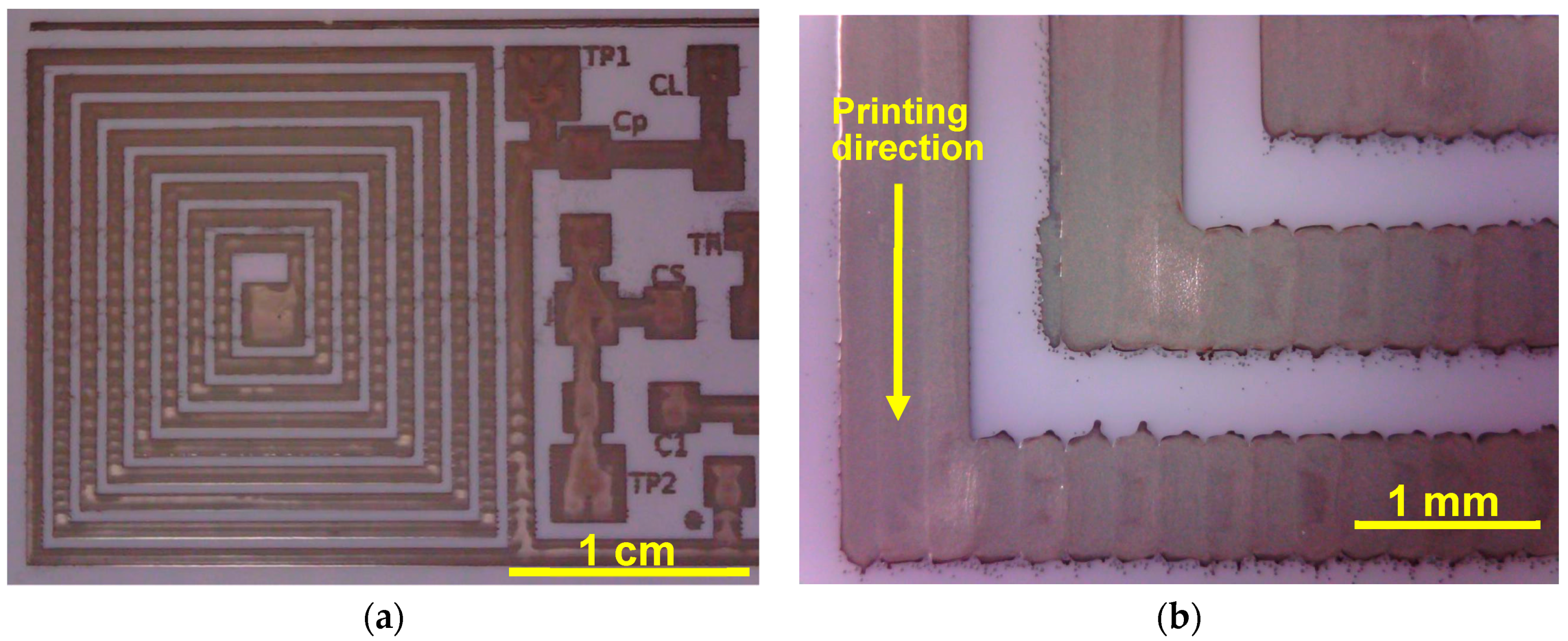
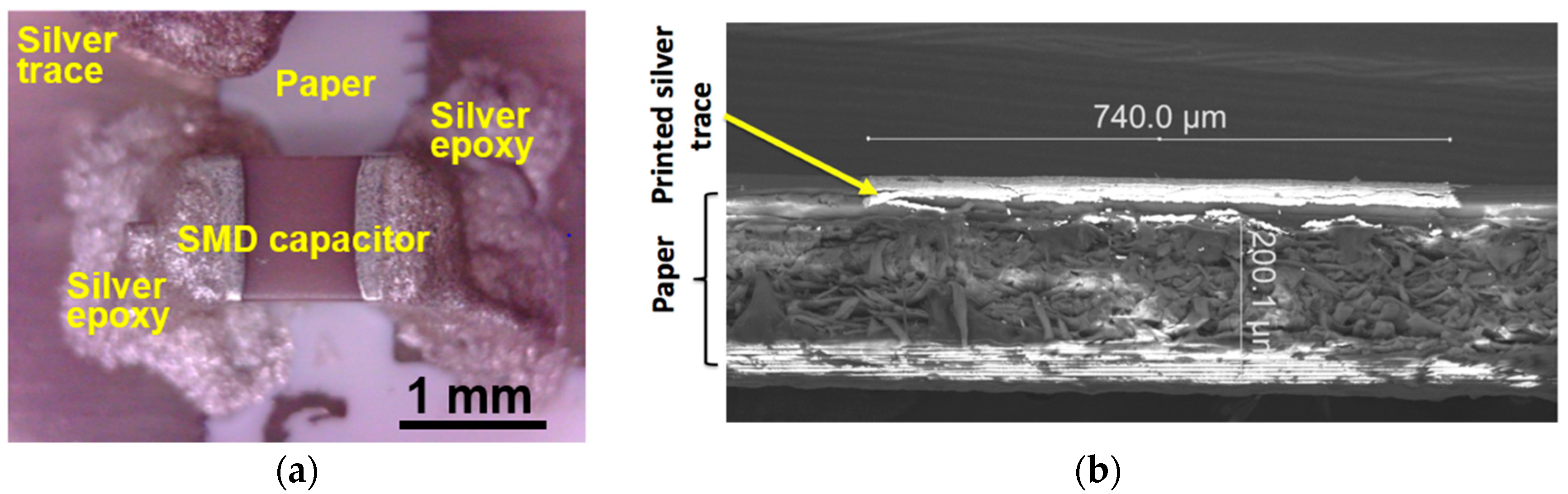
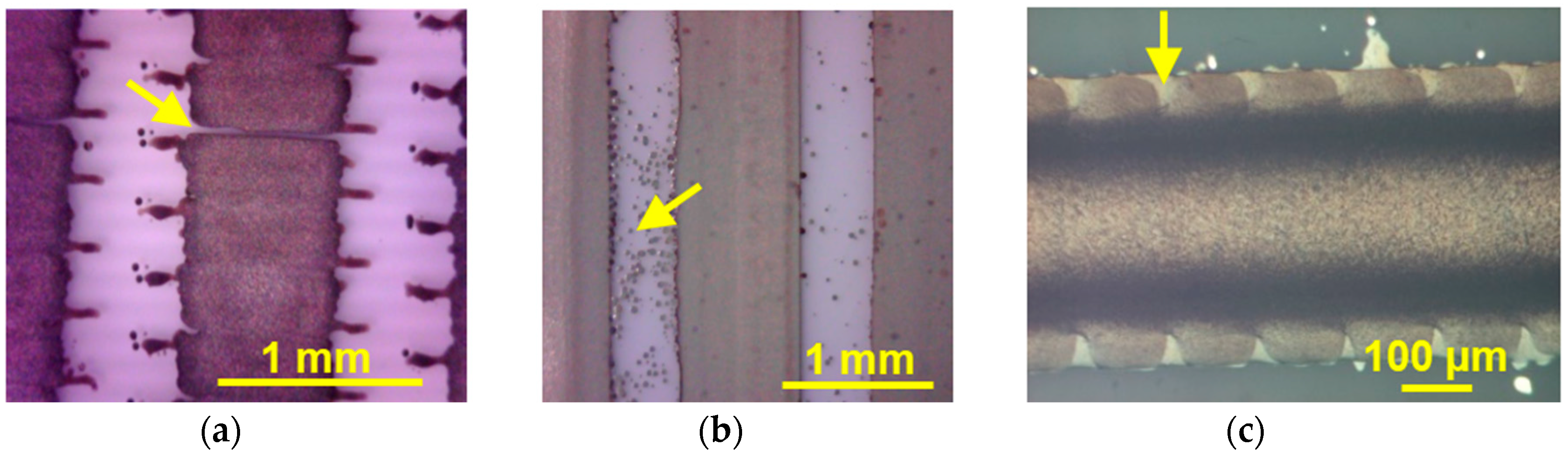
2.3. C. Inkjet Printed WRAP Sensors
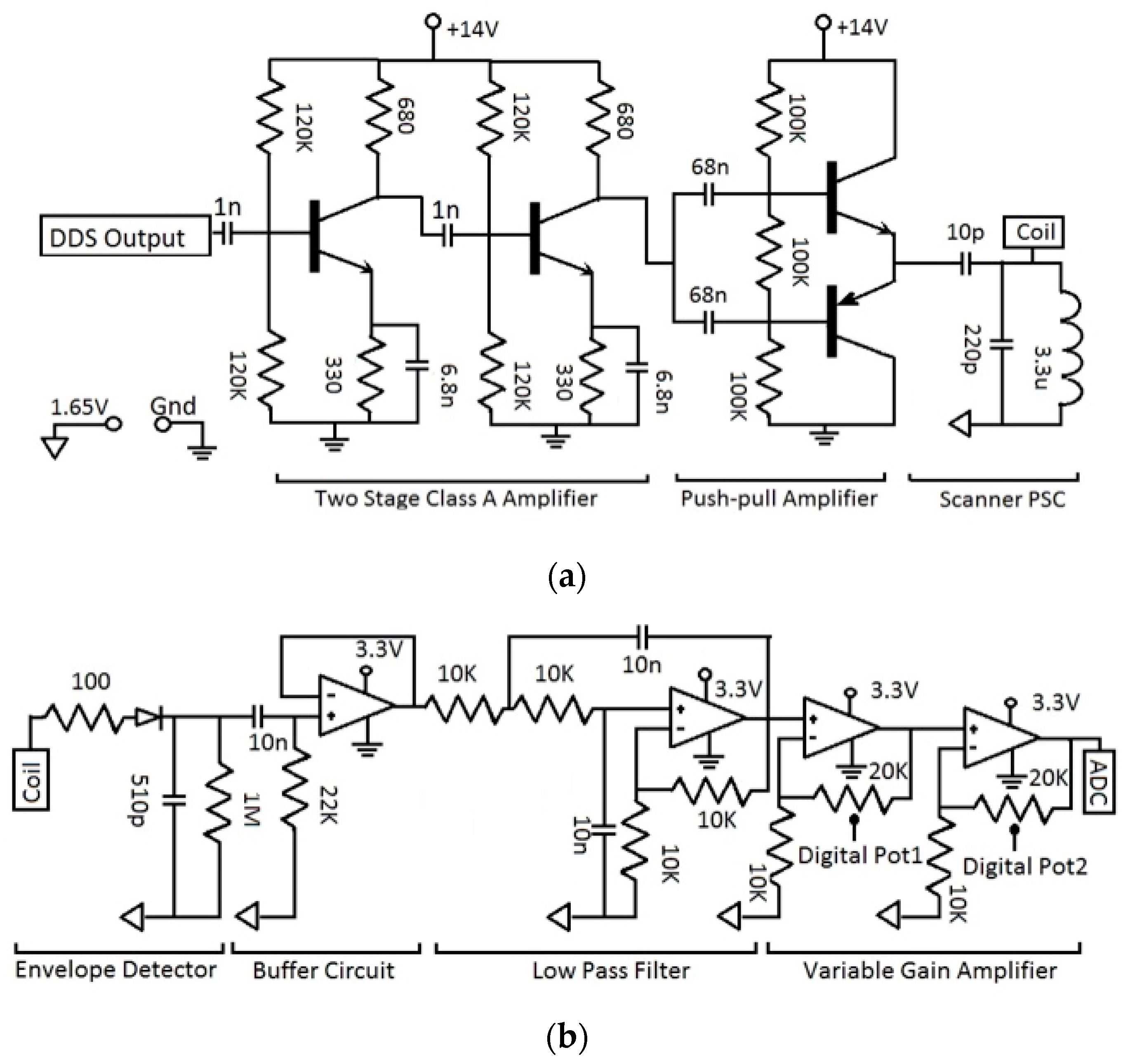
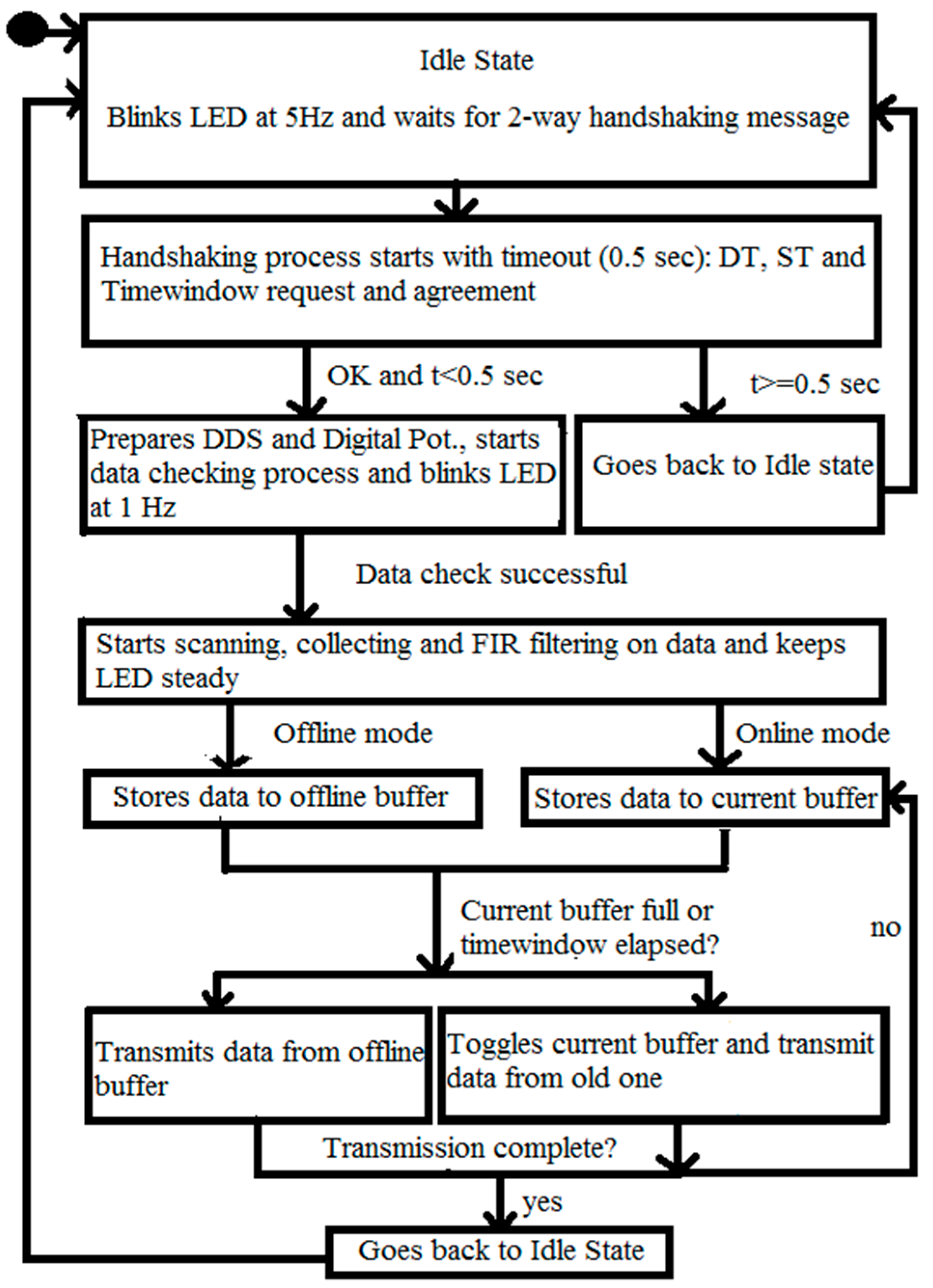
2.4. C. Wearable Scanner
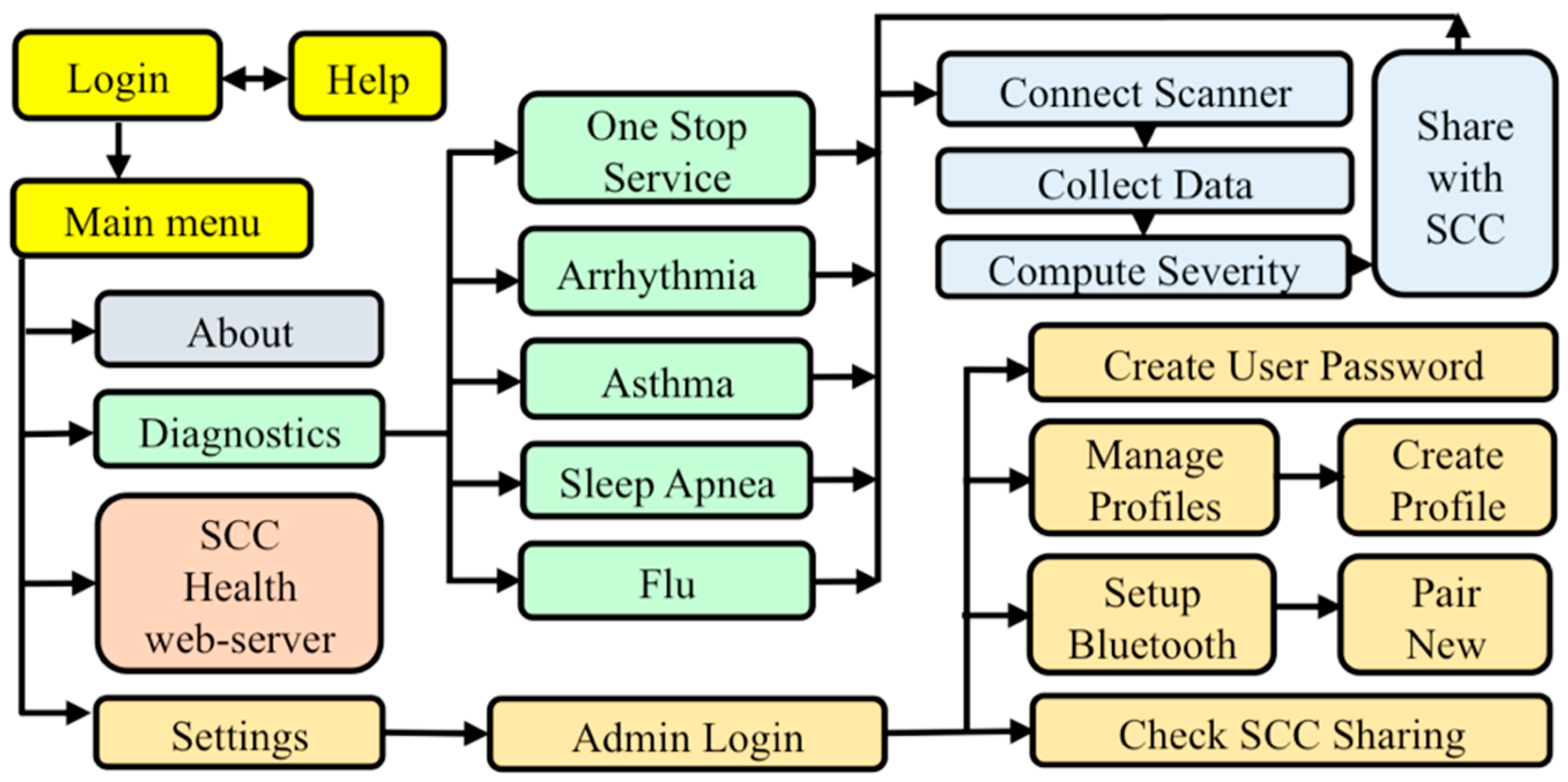
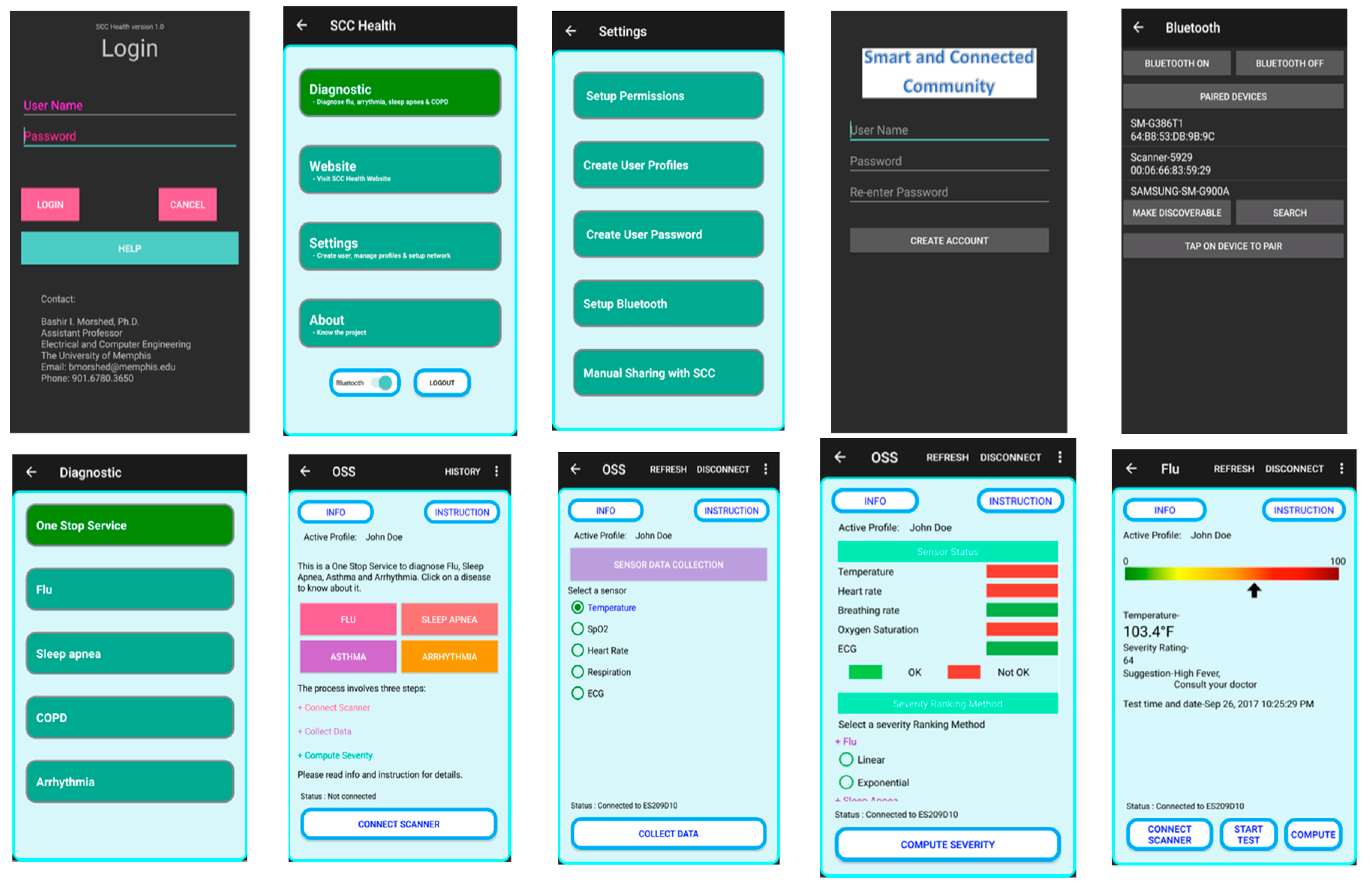
2.5. D. SCC Health Smartphone App
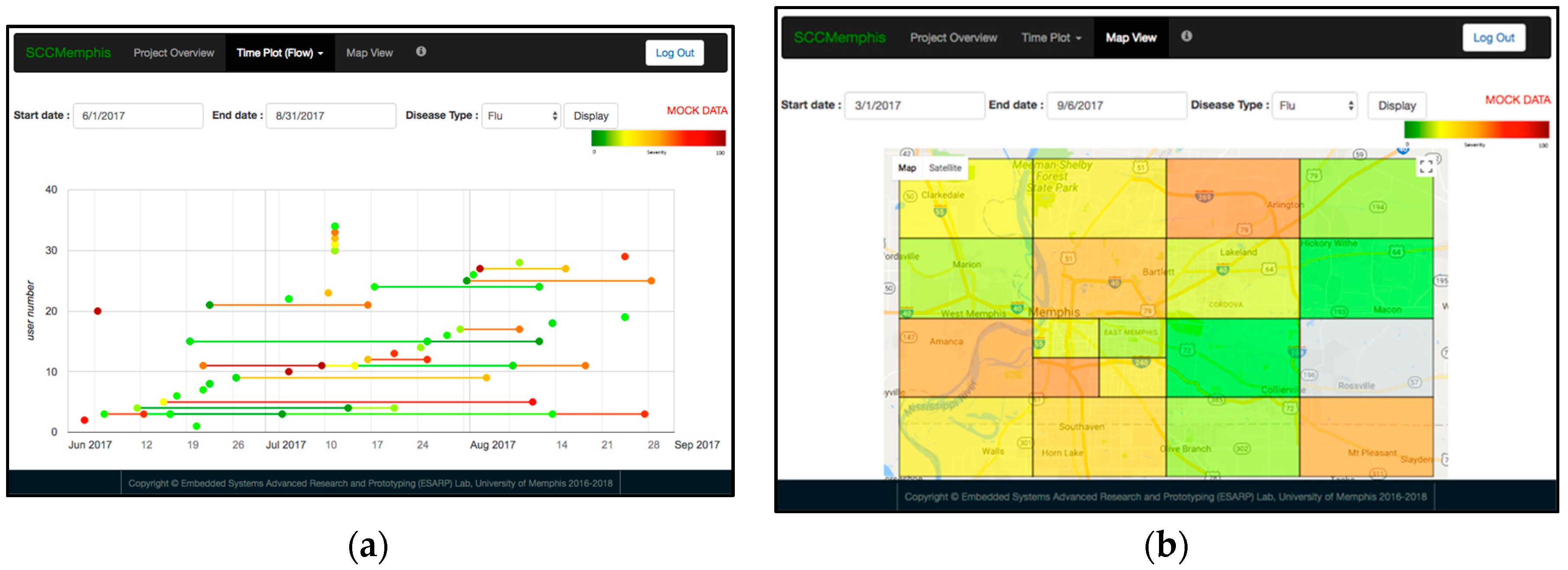
2.6. E. SCC Health Web-Server
3. Results
3.1. Printing Related Results
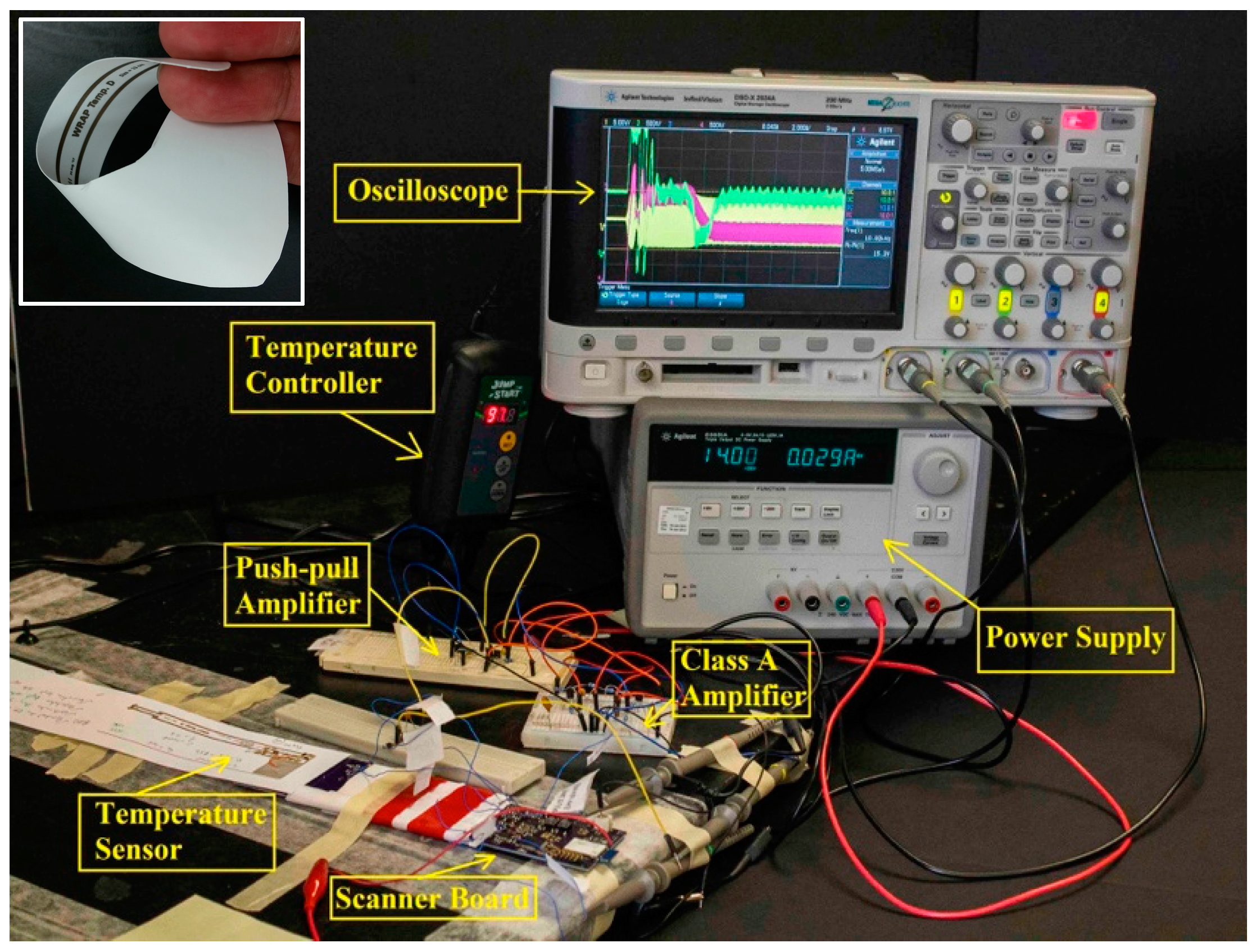
3.2. Wearable Scanner Device
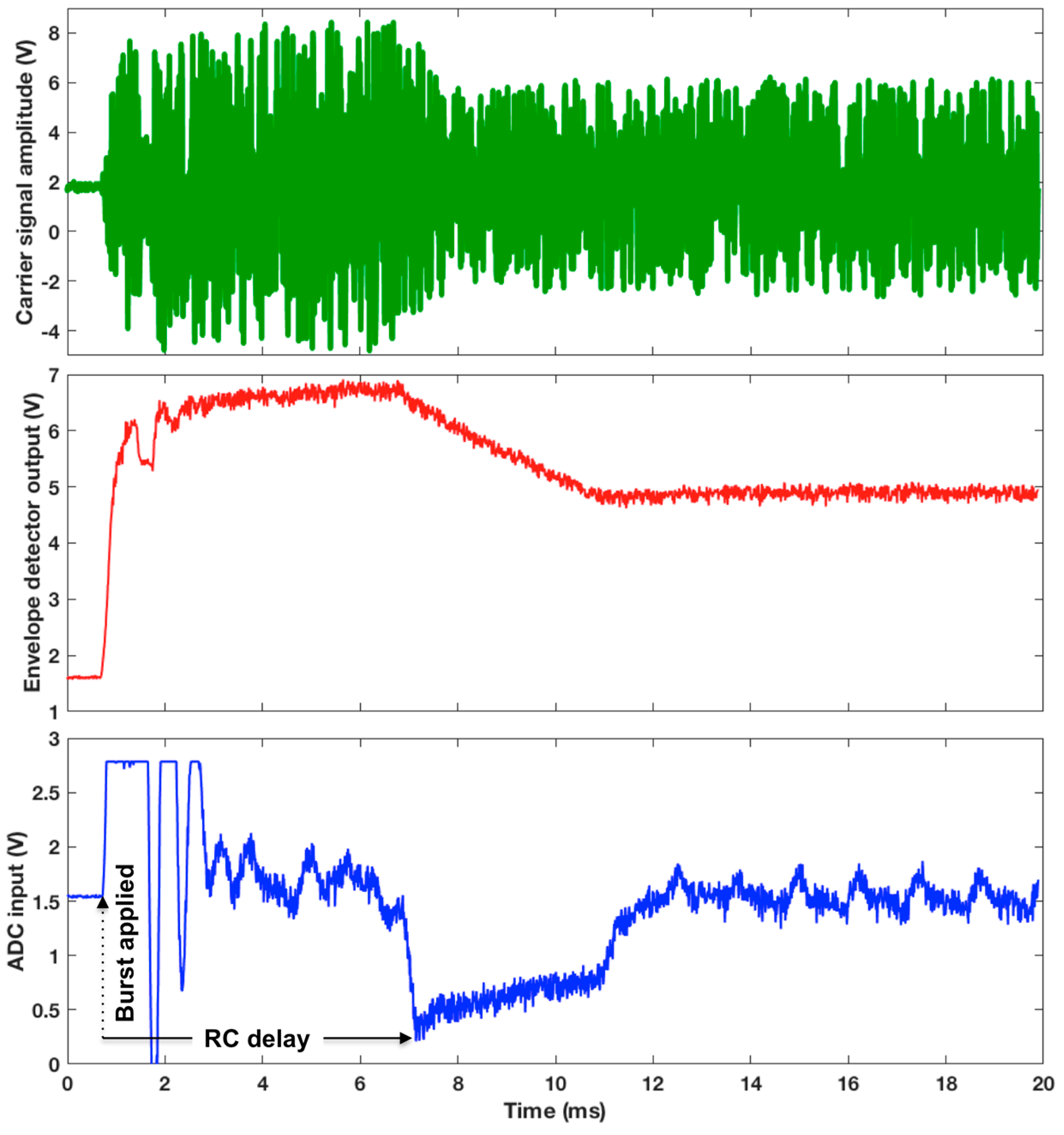
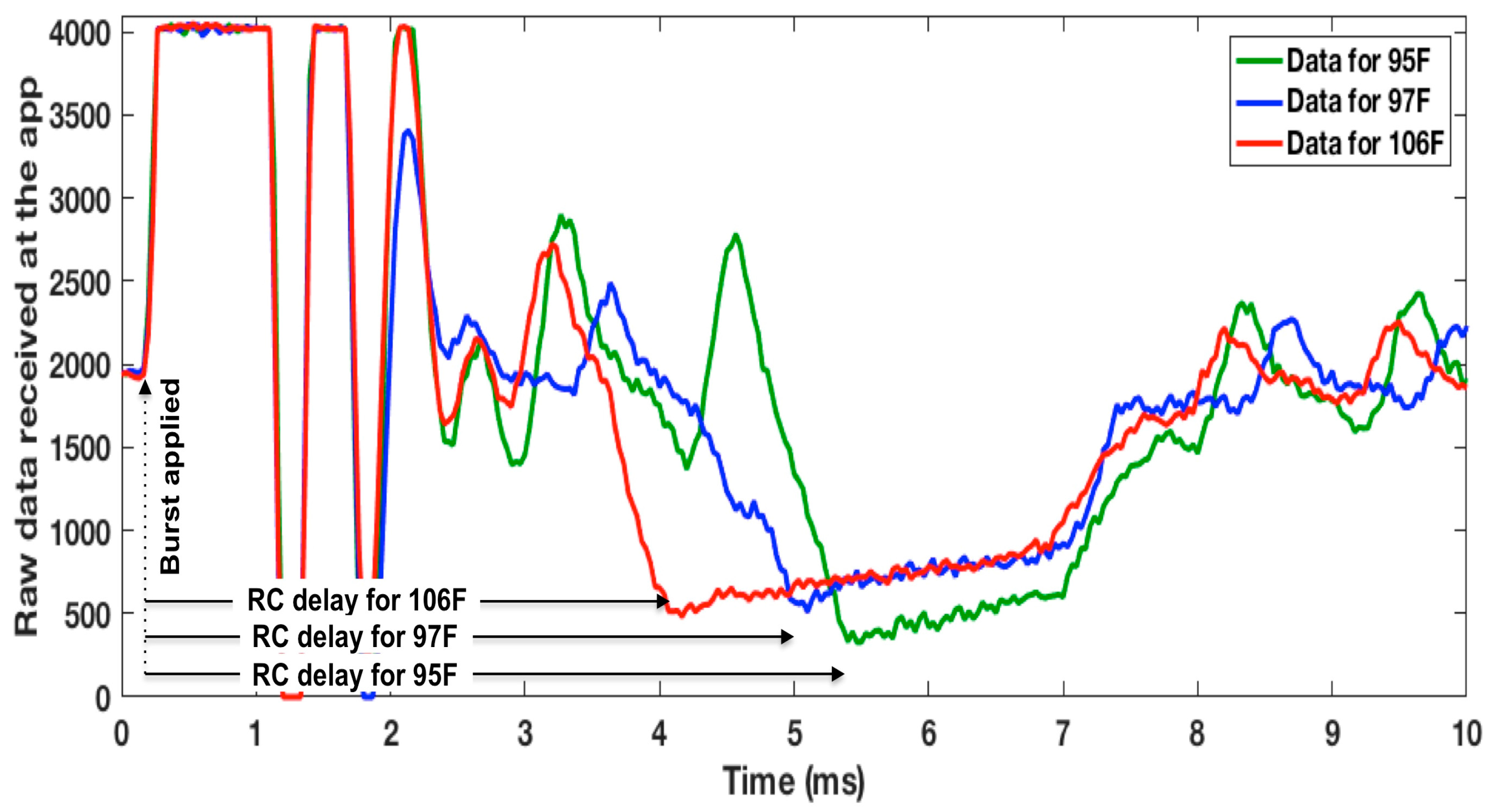
3.3. WRAP Sensor Test Results
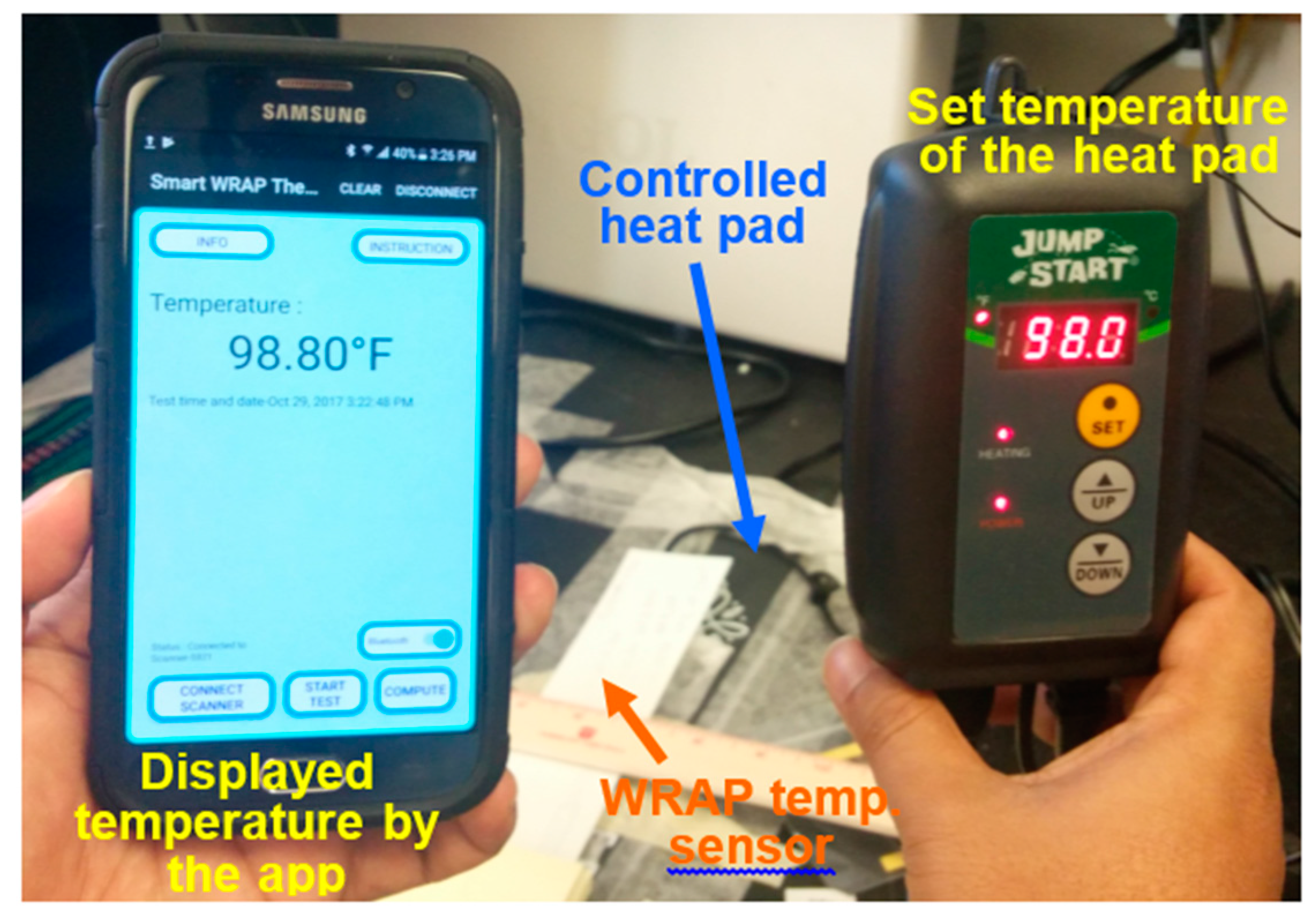
3.4. Functional SCC Health App
3.5. SCC Health Web-Server Test with Mock Data
4. Discussions and Future Plan
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riley, W.T.; Rivera, D.E.; Atienza, A.A.; Nilsen, W.; Allison, S.M.; Mermelstein, R. Health behavior models in the age of mobile interventions: Are our theories up to the task? Transl. Behav. Med. 2011, 1, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, A.; Koehler, C.; Tanenbaum, J.; Nguyen, D.H. Why We Use and Abandon Smart Devices. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Osaka, Japan, 7–11 September 2015; pp. 635–646. [Google Scholar]
- High Confidence Software and Systems Coordinating Group. Networking and Information Technology Research and Development Program. High-Confidence Medical Devices: Cyber-Physical Systems for 21st Century Health Care. Available online: http://www.nitrd.gov/About/MedDevice-FINAL1-web.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Hu, L.; Wu, H.; Mantia, F.L.; Yang, Y.; Cui, Y. Thin, flexible secondary Li-Ion paper batteries. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5843–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeby, S.; White, N. Energy Harvesting for Autonomous Systems; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shakhsheer, Y.; Silver, J.D.; Klinefelter, A.; Nagaraju, M.; Boley, J.; Pandey, J.; Shrivastava, A.; Carlson, E.J.; et al. A batteryless 19 μW MICS/ISM-band energy harvesting body sensor node SoC for ExG applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.K.; Fathy, A.; Wang, Y.; Kuhn, M.; Mahfouz, M. Hastle-free vitals. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2014, 15, S25–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhiuzzi, C.; Caizzone, S.; Marrocco, G. Wireless sensing of things by passive RFID technology. IEEE Trans. Antenna Propag. 2012. Available online: https://iris.unipa.it/retrieve/handle/10447/100765/135912/10-Review.pdf (access on 5 November 2017).
- Yeager, D.J.; Powledge, P.S.; Prasad, R.; Wetherall, D.; Smith, J.R. Wirelessly-charged UHF tags for sensor data collection. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on RFID, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 16–17 April 2008; pp. 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Want, R. An Introduction to RFID Technology. IEEE Pervas. Comput. 2006, 5, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Song, K.; Lee, H.; Cho, H.; Yoo, H. A low-energy crystal-less double-FSK sensor node transceiver for wireless body-area network. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 2678–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkenzeller, K. The RFID Handbook: Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards and Identification; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sawan, M.; Hu, Y.; Coulombe, J. Wireless smart implants dedicated to multichannel monitoring and microstimulation. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2005, 5, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashirullah, R. Wireless implants. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2010, 11, S14–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.J.; Besnoff, J.S.; Reynolds, M.S. Modulated backscatter for ultra-low power uplinks from wearable and implantable devices. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Workshop on Medical Communication Systems, New York, NY, USA, 13 August 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitin, P.V.; Rao, K.V.S. Theory and measurement of backscattering from RFID tags. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2006, 48, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamalis, B.; Gavalas, D.; Konstantopoulos, C.; Pantziou, G. Clustering in wireless sensor networks. In RFID and Sensor Networks: Architectures, Protocols, Security, and Integrations, 1st ed.; Zhang, Y., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Chapter 12; pp. 323–353. [Google Scholar]
- Dementyev, A.; Smith, J.R. A wearable UHF RFID-based EEG system. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on RFID, Penang, Malaysia, 30 April–2 May 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, K.D.; Anderson, D.J.; Hetke, J.F.; Kipke, D.R.; Najafi, K. Wireless implantable microsystems: High-density electronic interfaces to the nervous system. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 76–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickamasinghe, A.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Sample, A.P. Windware: Supporting ubiquitous computing with passive sensor enabled RFID. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on RFID, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–10 April 2014; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, E.J.H.; Smith, F.D.; Sullivan, K.M.E.; Franks, N.R. Do ants make direct comparisons? Proc. R. Soc. B 2009, 276, 2635–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, M.; Swenson, N.C.; Picard, R.W. A wearable sensor for unobtrusive, long-term assessment of electrodermal activity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Popovic, Z.; Falkenstein, E.A.; Costinett, D.; Zane, R. Low-power far-field wireless powering for wireless sensors. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenstein, E.; Costinett, D.; Zane, R.; Popovic, Z. Far-field RF-powered variable duty cycle wireless sensor platform. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2011, 58, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollazedeh, M.; Murrari, K.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Thakor, N.V. Wireless micropower instrumentation for multimodal acquisition of electrical and chemical neural activity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2009, 3, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Yan, L.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, H. A 5.2 mW self-configured wearable body sensor network controller and a 12 μW wirelessly powered sensor for a continuous health monitoring system. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towe, B.C. Passive Backscatter Biotelemetry for Neural Interfacing. In Proceedings of the 3rd International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, Kohala Coast, HI, USA, 2–5 May 2007; pp. 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Towe, B.C. Systems and Methods for Wireless Transmission of Biopotentials. U.S. Patent 2010/0198039 A1, 5 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, H.A.; Depp, S.W.; Koelle, A.R.; Freyman, R.W. Interrogation, and Detection System. U.S. Patent 4075632, 21 February 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Schwerdt, H.N.; Xu, W.; Shekhar, S.; Abbaspour-Tamijani, A.; Towe, B.C.; Miranda, F.A.; Chae, J. A fully-pasive wireless microsystem for recording of neuropotentials using RF backscattering methods. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2011, 20, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwerdt, H.N.; Miranda, F.A.; Chae, J. Analysis of electromagnetic fields induced in operation of a wireless fully passive backscattering neurorecording microsystems in emulated human head tissue. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdt, H.N.; Chae, J.; Miranda, F.A. Wireless performance of a fully passive neurorecording microsystem embedded in dispersive human head phantom. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, Chicago, IL, USA, 9 July 2012; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Riistama, J.; Aittokallio, E.; Verho, J.; Lekkala, J. Totally passive wireless biopotential measurement sensor by utilizing inductively coupled resonance circuits. Sens. Actuators A 2010, 157, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Fu, Q.; Deng, J.; Yan, G.; Zhou, D.; Gong, S.; Hu, Y. An integrated passive impedance loaded SAW sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karilainen, A.; Finnberg, T.; Uelzen, T.; Dembowski, K.; Månuller, J. Mobile Patient Monitoring Based on Impedance-Loaded SAW-Sensors. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2004, 51, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, J.E.; Redish, A.D. Wireless communication with implanted medical devices using the conductive properties of the body. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2011, 8, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consul-Pacareu, S.; Arellano, D.; Morshed, B.I. Body-worn Fully-Passive Wireless Analog Sensors for Physiological Signal Capture through Load Modulation using Resistive Transducers. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Healthcare Innovation and Point-of-Care Technologies Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 8–10 October 2014; pp. 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Consul-Pacareu, S.; Arellano, D.; Morshed, B.I. Body-worn Fully-Passive Wireless Analog Sensors for Biopotential Measurement through Load Modulation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Topical Conference on Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems (BioWireleSS), San Diego, CA, USA, 25–28 January 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Morshed, B.I. Impedance Phlebography Based Pulse Sensing Using Inductively-Coupled Inkjet-Printed WRAP Sensor. In Proceedings of the Invited Paper, Commission B (Special Session: Wearable Antennas and Electronics), National Radio Science Meeting, Boulder, CO, USA, 4–6 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Park, H.; Bonato, P.; Chan, L.; Rodgers, M. A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.L.; Ding, X.R.; Poon, C.C.Y.; Lo, B.P.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.L.; Yang, G.Z.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, Y.T. Unobtrusive Sensing and Wearable Devices for Health Informatics. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1538–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, H.; Khan, H.R. Handbook of Thin Film Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Osch, T.H.J.; Percelaer, J.; de Laat, A.W.M.; Schubert, U.S. Inkjet printing of narrow conductive tracks on untreated polymeric substrates. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niittynen, J.; Sowade, E.; Kang, H.; Baumann, R.R.; Mäntysalo, M. Comparison of laser and intense pulse light sintering (IPL) for inkjet-printed copper nanoparticle layers. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, G.; Safavi-Naeini, S.; Sangary, N.; Tentzeris, M.M. Inkjet printing of ultrawideband (UWB) antennas on paper-based substrates. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.S.; Cooper, J.R.; Tentzeris, M.M. Multi-layer RF Capacitors on Flexible Substrates Utilizing Inkjet Printed Dielectric Polymers. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2013, 23, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, B.J.; Lee, C.K.; Oh, J.H. All-inkjet-printed electrical components and circuit fabrication on a plastic substrate. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 97, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKerrcher, G.; Perez, J.G.; Shamim, A. Fully Inkjet Printed RF Inductors and Capacitors Using Polymer Dielectric and Silver Conductive Ink with through Vias. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2015, 62, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Lu, N.; Ma, R.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, R.H.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Won, S.M.; Tao, H.; Islam, A.; et al. Epidermal electronics. Science 2011, 333, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Mathewson, K.E.; Jang, K.I.; Kim, J.; Fu, H.; Huang, X.; Chava, P.; Wang, R.; et al. Soft microfluidic assemblies of sensors, circuits, and radios for the skin. Science 2014, 344, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Ghaffari, R.; Lu, N.; Rogers, J.A. Flexible and stretchable electronics for biointegrated devices. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noroozi, B.; Morshed, B.I. PSC Optimization of 13.56-MHz Resistive Wireless Analog Passive Sensors. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 3548–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, B.I. Dual Coil for Remote Probing of Signals using Resistive Wireless Analog Passive Sensors (rWAPS). In Proceedings of the Invited Paper, Commission B, National Radio Science Meeting, Boulder, CO, USA, 6–9 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Noroozi, B.; Morshed, B.I. Formal Method for PSC Design Optimization of 13.56 MHz Resistive Wireless Analog Passive Sensors (rWAPS). Presented at the IEEE Radio and Wireless Week Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 24–27 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
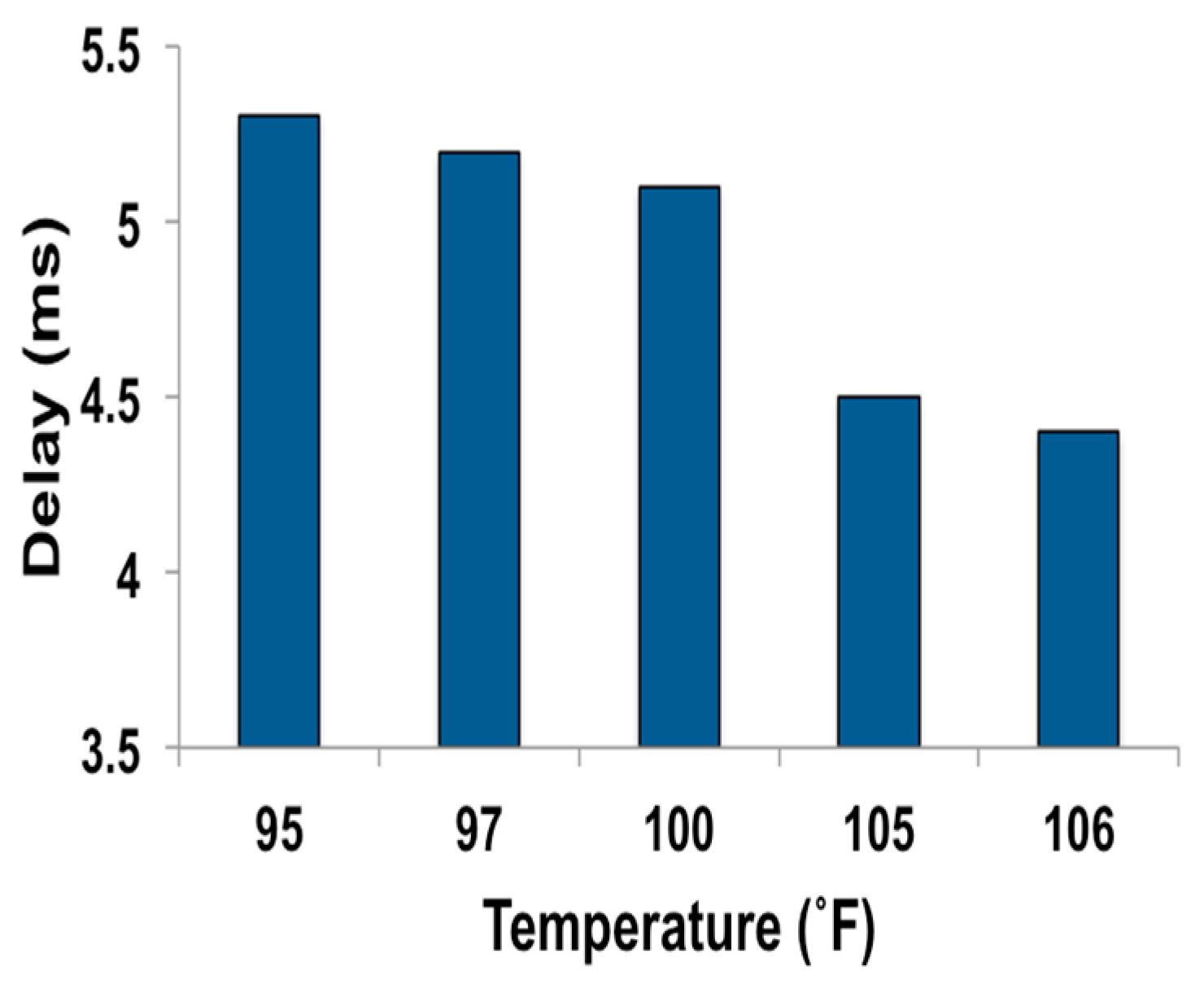
| Temp. (°F) | Severity | Suggestive Prompt | EoI Rating | Color Code for EoI Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 97 | Normal | Normal | 0 | Dark green |
| 98 | Normal | Normal | 0.1 | Green |
| 99 | Normal | Normal | 0.2 | Light green |
| 100 | Low grade fever | Low fever, Consider consulting your doctor | 0.3 | Green-yellow |
| 101 | Low grade fever | Low fever, Consider consulting your doctor | 0.4 | Yellow |
| 102 | Intermediate fever | Medium fever, consult your doctor | 0.5 | Yellow-orange |
| 103 | High grade fever | High fever, consult your doctor | 0.6 | Orange |
| 104 | High grade fever | High fever, consult your doctor | 0.7 | Orange-red |
| 105 | Extreme fever | Very high fever, consult your doctor immediately | 0.8 | Red |
| 106 | Extreme fever | Very high fever, consult your doctor immediately | 0.9 | Dark red |
| 107 | Medical emergency | Extremely high fever, consult your doctor immediately | 1.0 | Dark red-Maroon |
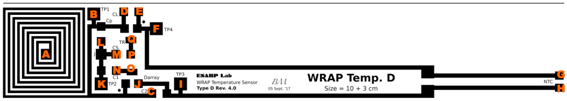
| Pads | R (Ω) | Pads | R (Ω) | Pads | R (Ω) | Pads | R (Ω) | Pads | R (Ω) | Pads | R (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-B | 13.3 | A-D | 13.4 | E-F | 0.1 | H-I | 2.3 | K-L | 0.2 | N-O | 0.1 |
| A-C | 13.2 | B-D | 0.3 | E-G | 2.6 | H-J | 2.6 | K-M | 0.3 | P-Q | 0.1 |
| B-C | 0.9 | C-D | 1.0 | F-G | 2.6 | I-J | 0.4 | L-M | 0.1 |
| Scanner Device | Power Consumption |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller board with DDS on | 94.5 mW |
| Microcontroller board with DDS off | 72.9 mW |
| Analog amplifier | 406 mW |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morshed, B.I.; Harmon, B.; Zaman, M.S.; Rahman, M.J.; Afroz, S.; Rahman, M. Inkjet Printed Fully-Passive Body-Worn Wireless Sensors for Smart and Connected Community (SCC). J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2017, 7, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea7040026
Morshed BI, Harmon B, Zaman MS, Rahman MJ, Afroz S, Rahman M. Inkjet Printed Fully-Passive Body-Worn Wireless Sensors for Smart and Connected Community (SCC). Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2017; 7(4):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea7040026
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorshed, Bashir I., Brook Harmon, Md Sabbir Zaman, Md Juber Rahman, Sharmin Afroz, and Mamunur Rahman. 2017. "Inkjet Printed Fully-Passive Body-Worn Wireless Sensors for Smart and Connected Community (SCC)" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 7, no. 4: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea7040026
APA StyleMorshed, B. I., Harmon, B., Zaman, M. S., Rahman, M. J., Afroz, S., & Rahman, M. (2017). Inkjet Printed Fully-Passive Body-Worn Wireless Sensors for Smart and Connected Community (SCC). Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 7(4), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea7040026