Abstract
This paper presents a general method, called “self-parameterization”, for designing one-dimensional (1-D) chaotic maps that provide wider chaotic regions compared to existing 1-D maps. A wide chaotic region is a desirable property, as it helps to provide robust performance by enlarging the design space in many hardware-security applications, including reconfigurable logic and encryption. The proposed self-parameterization scheme uses only one existing chaotic map, referred to as the seed map, and a simple transformation block. The effective control parameter of the seed map is treated as an intermediate variable derived from the input and control parameter of the self-parameterized map, under some constraints, to achieve the desired functionality. The widening of the chaotic region after adding self-parameterization is first demonstrated on three ideal map functions: Logistic; Tent; and Sine. A digitized version of the scheme was developed and realized in a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) implementation. An analog version of the proposed scheme was developed with very low transistor-count analog topologies for hardware-constrained integrated circuit (IC) implementation. The chaotic performance of both digital and analog implementations was evaluated with bifurcation plots and four established chaotic entropy metrics: the Lyapunov Exponent; the Correlation Coefficient; the Correlation Dimension; and Approximate Entropy. An application of the proposed scheme was demonstrated in a random number generator design, and the statistical randomness of the generated sequence was verified with the NIST test.
1. Introduction
Chaotic behavior is observed in non-linear deterministic dynamic systems [1]. For a specific parameter range, the system generates an aperiodic sequence, where the time trajectory of the sequence shows high sensitivity to the initial value. In chaotic conditions, even if the system starts from two very close initial states, the output sequence becomes drastically different [2,3]. The inception of chaos theory was marked by Henri Poincaré’s observation of non-periodic orbits, in his study on the three-body problem in the 1880s (translated in [4]); however, to see further development in chaos theory, the world had to wait for the invention of digital computers. When repeated iterative computation became easier by virtue of digital computers, Edward Lorenz made an accidental discovery during his work on weather prediction [5]. Lorenz’s work was reported in a 1963 publication ([6]), which is regarded as a seminal work of chaos theory in the modern scientific community.
There is a wide range of variety in chaotic systems. Chaotic systems can be one-dimensional (1-D), where only one function describes the evolution of a single state variable. On the other hand, there are multi-dimensional (multi-D) chaotic systems, where the time evolution of more than one state variable is described with the same number of functions. Based on the nature of time steps in evolution, chaotic systems can be continuous-time, where the time steps of the trajectory are continuous. Continuous-time systems require at least three state variables, where the governing functions contain the time-derivative terms. Another variant is a discrete-time chaotic system, where the trajectory evolves in discrete time steps, and the next state of the system is a function of the previous state. Discrete-time systems can have one or more state variables. Well-known examples of 1-D discrete-time maps are the Sine map [7], the Tent map [8], and the Logistic map [8], while the Hénon map [9] (discrete time) and the Lorenz system [10] (continuous time) are examples of multi-D maps. Each variant has its own advantages and shortcomings: for example, multi-dimensional chaotic systems are used for generating higher-entropy chaos, in preference to 1-D systems, but with the compromise of the additional hardware cost [11]. Generally, the hardware implementation of discrete-time systems is simpler than continuous-time systems, where 1-D discrete-time systems provide the most straightforward designs. Although 1-D discrete-time chaotic systems are claimed to be vulnerable to signal prediction by many present-day modeling techniques [12], 1-D discrete-time chaotic systems have proved to be very efficient choices as the building blocks for complex and highly secure chaotic systems [11,13]: this is why we find the exploration of a hardware-efficient technique to improve 1-D chaotic systems to be a potential research direction; hence, we will limit our discussion to 1-D discrete-time chaotic systems.
The aperiodicity of a chaotic system is different from randomness, as the evolution of the trajectory through time is deterministic, so that we can always reproduce the identical chaotic sequence, given the knowledge of all the system parameters and the initial state. The initial state sensitivity is popularly known as the `butterfly effect’: this term was coined by Lorenz in a lecture [14] illustrating that if a butterfly flaps its wings in Brazil, then, as a consequence, that minor perturbation could, several weeks later, have changed sunny weather in Texas into a tornado. This deterministic aperiodicity, and the sensitive dependence on the initial state, have nominated chaotic systems for a number of hardware security explorations, including encryption [15,16,17,18,19,20,21], random number generation [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30], reconfigurable logic [31,32], Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) [33,34,35], side-channel attack mitigation [36,37,38], secure communication [39,40,41,42], and logic obfuscation [37,43].
Securing resource-constrained devices, such as IoT (internet of things), has become a serious concern in this era of connected devices [44]. Generally, vendors prioritize price and speed over security, for small-sized and battery-powered devices [45]: because of constrained chip area and power, sophisticated encryption protocols, such as Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), are not an option for these devices. This creates a serious security threat, as not only do such devices collect and record sensitive human data, but also, in most cases, they communicate with a centralized server: as a result, they are at risk of being physically tampered with, and becoming the target of information theft or being used as an entry point to the centralized server [45,46]. In this scenario, software-based security solutions are not suitable, as these hardware-constrained devices lack the required computing and memory support [45]. Moreover, as software-generated keys are stored in the file systems, they become vulnerable to different attacks [47]. To address these issues, hardware-based security systems are being extensively explored for resource-constrained devices [48]. Familiar examples of hardware-based security protocols include Physically Unclonable Function (PUF)-based authentication [49], and the use of Hardware Security Modules (HSM) to add a hardware-based security layer to the system architecture [50].
The building block of most hardware-based security systems is one or more circuit blocks that generate unpredictable outputs: this unpredictability is generated by different techniques, including the mismatch between the phase jitter of a pair of ring oscillators [33], and fluctuation in quantum phenomena [51]. Along with those techniques, chaotic systems are also being extensively explored as potential candidates for hardware-based security applications [52]. The aperiodic response, and the extreme initial state-sensitivity of chaotic circuits, from comparatively simple and hardware-efficient designs, have created the broad prospect of using chaos-generating circuits as the building blocks of the entropy source in hardware-based security protocols for resource-constrained devices [33].
Most security applications based on chaotic systems are limited to either software-based encryption algorithms [39,53] or hardware implementations, either in a purely digital Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) domain [7] or analog circuits using off-the-shelf components, such as operational amplifiers or multipliers [54]. Digital or discrete-component-based analog designs are not suitable for hardware-constrained integrated circuit (IC) implementations, because of their large area and high power demand. The analog Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)-based designs of classical chaotic maps, including the Logistic map [55], the Sine map [56], and the Tent map [57], have been reported; however, in the analog CMOS designs as well, the circuits turned out to be complex and hardware-hungry. On the other hand, some reported chaotic maps leveraged the built-in non-linearity in MOS transistors, and proposed simpler 1-D chaotic maps, with characteristic curves similar to classical mathematical functions, which are capable of generating discrete-time chaotic sequences [58,59,60].
1-D chaotic maps are useful, as they offer simplicity of implementation. A downside of 1-D maps is that chaos occurs for a limited parameter range. Furthermore, a good chaotic property (with high chaotic entropy) is not persistent over the whole parameter range of that limited chaotic window: as a result, any inevitable variations in the operating condition or parameter value degrade the chaotic properties, and may even push the system out of the desired chaotic region to an undesired periodic (non-chaotic) region [7]. Moreover, a wide chaotic range increases the security performance of the applications, like reconfigurable logic, by increasing the total functionality space [61]. Multiple schemes have been reported to widen the chaotic range. Dynamic parameter control is one of those techniques whereby the output of one map is linearly transformed to the chaotic parameter range of a second map, and the second map is controlled using the transformed values. The dynamic parameter control scheme has been explored both on mathematical maps [7] and on CMOS-based chaotic systems [22]. There is a report in which the output of multiple 1-D chaotic maps are averaged [62] to get a final map that offers a wider chaotic region than the constituent maps. These reported schemes offer a wide chaotic range, with promising chaotic properties, but with additional hardware costs, by involving more than one chaotic map. To present a hardware-efficient scheme, we introduced, in a conference publication [63], the idea of self-parameterization, where only one chaotic map was used to implement a self-parameterized chaotic map (SPM) that provided a wide chaotic range. This paper is an elaborate extension of [63]. The additional contributions of this paper, compared to the conference publication, are as follows:
- We present the idea of self-parameterization in more detail.
- At first, similar to the conference paper, the scheme is demonstrated in the case of three ideal mathematical maps: Logistic, Sine, and Tent maps.
- A general design methodology, in the light of stability analysis, was added to this paper.
- Similar to the conference paper, we present a design for a digitized SPM that can be implemented in FPGA.
- Then, we show the hardware-efficient CMOS-based designs for the analog implementation of SPM. In this paper, we present three different topologies of maps, and introduce the corresponding low transistor-count transformation circuits.
- The chaotic performance of the proposed designs was analyzed with different entropy metrics, along with one additional entropy metric, in this paper.
- We added an application of the proposed scheme in this paper. The application was demonstrated in a random number generator design. The cryptographic applicability of the random number generator was verified with an established statistical tool.
The remaining portion of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the SPM scheme; Section 3 discusses SPM implementation with ideal mathematical chaotic maps; Section 4 presents the digitization and FPGA implementation details of SPMs on mathematical maps; the CMOS implementation of SPMs is discussed in Section 5; the hardware efficiency of the proposed design is elaborated in Section 6; an application of the proposed scheme is presented in Section 7; finally, Section 8 gives the concluding remarks.
2. Proposed Scheme
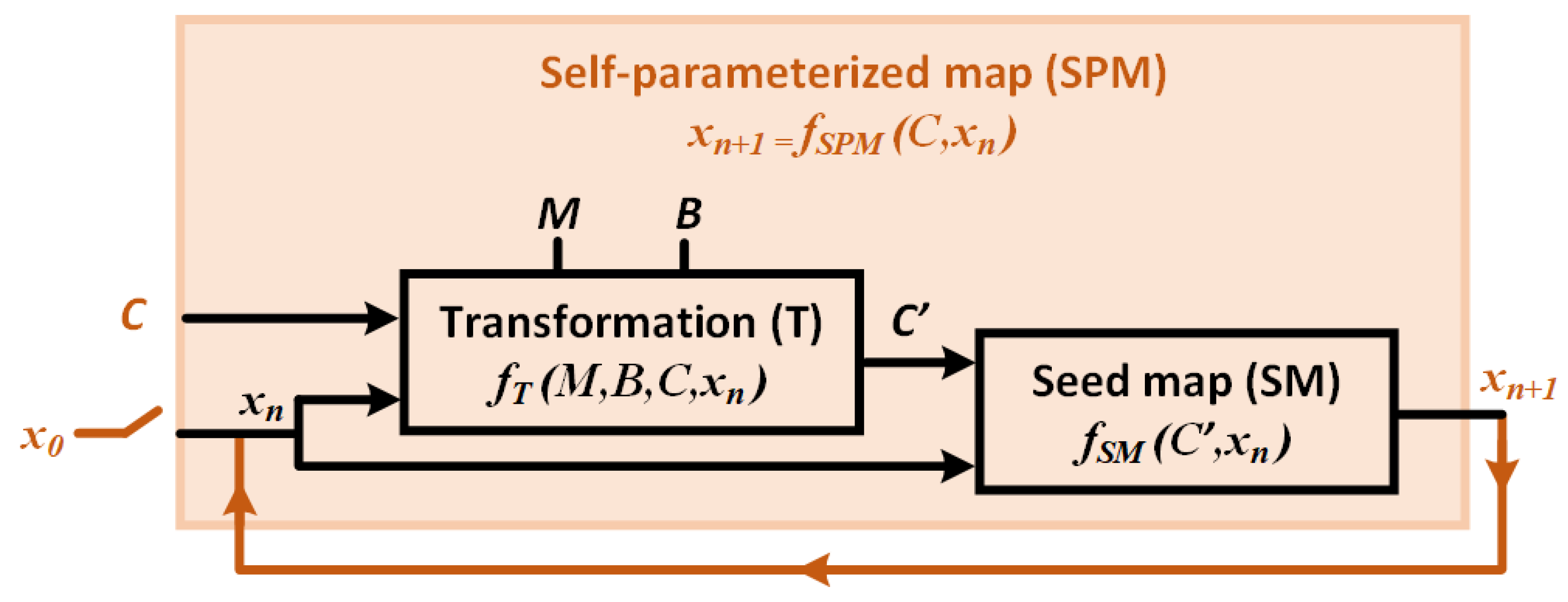
The schematic of the proposed self-parameterized map (SPM) is presented in Figure 1: it is a non-linear function () that maps a present-state value () to the following state (); the control parameter, C, modulates the characteristic of the non-linear mapping. The overall schematic represents an iterative system where, after starting from an initial state, , at each iteration, the SPM output () is fed back as the input () for the following state: in this way, a sequence of discrete-time values is generated. Depending on the value of C, the sequence will have a finite period or it will be chaotic (infinite period).
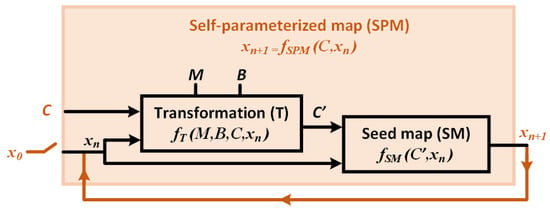
Figure 1.
Schematic of self-parameterization.
Inside the SPM structure, the transformation block (T) represents a linear transformation function (). The T-block transforms and the control parameter, C, with the help of a multiplier variable, M, and a biasing constant, B, to generate an intermediate variable, , which acts as the effective control parameter of the seed map (SM) that modulates the non-linear mapping of the seed map inside the SPM block. The transformation is designed in such a way that always keeps the seed map in its chaotic region of operation: in this way, at each iteration, the SPM transforms its input () and control parameter (C) to parameterize its own non-linear function (), so as to ensure a nearly “robust” chaotic operation. A chaotic system is considered robust if there exists no periodic region in the whole region of operation [64]. If the whole region of operation is divided into multiple narrow chaotic regions and periodic regions, this is sometimes referred to as “frail chaos” [39]. Widening the chaotic region is important, because a narrow chaotic region—or, in other words, the existence of periodic regions—can be detrimental to many chaos-based applications, because then any run-time perturbation may shift the system out of that narrow chaotic window [62].
3. Analytical Function-Based Maps
3.1. Design Methodology
We will first explore the SPM technique, using three ideal non-linear map functions: the Logistic map, the Sine map, and the Tent map. Table 1 shows the mathematical expressions (2nd column), the ranges of the output (3rd column), the control parameter range (4th column), and the range of the control parameter values that result in chaotic operations (5th column).

Table 1.
Analytical expression for the three 1-D maps.
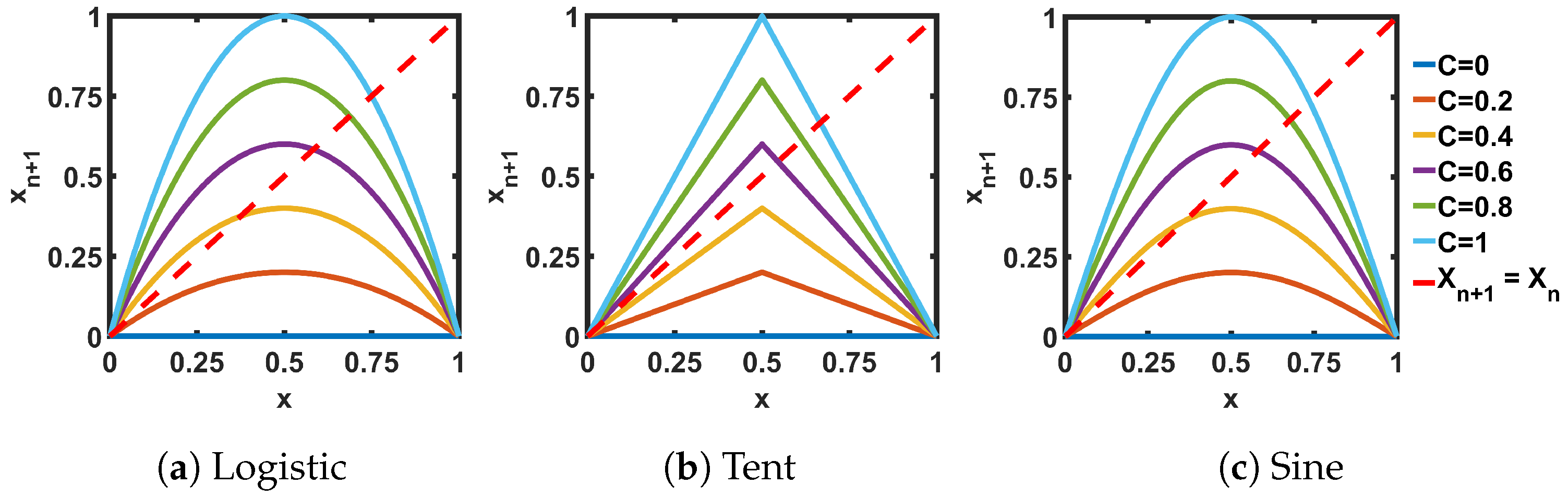
Figure 2 shows the transfer characteristics of three ideal seed maps of interest, while Figure 3 presents the transfer characteristics when two seed maps are connected in series (). In both the single (Figure 2) and the cascaded (Figure 3) cases, the intersection points of the red dashed lines with the transfer curves represent the fixed points. Fixed points are those points where the next state () of the non-linear map circuit is equal to the present state (). If a fixed point is stable, then when an iterative sequence reaches that value it will be stuck to that fixed point for consecutive iterations. On the other hand, an unstable fixed point repels the trajectory, and as a result, the sequence never reaches that point. The stability of a fixed point depends on the slope of the transfer curve at the intersection points with the = -line. If the slope is less than 1, then the fixed point is stable, otherwise it is unstable [2].
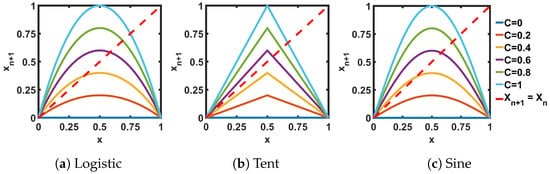
Figure 2.
Transfer curves for ideal seed maps.
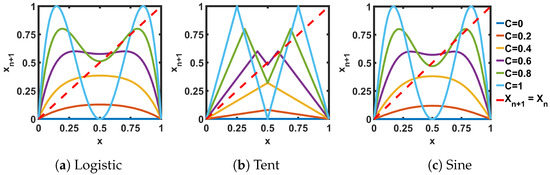
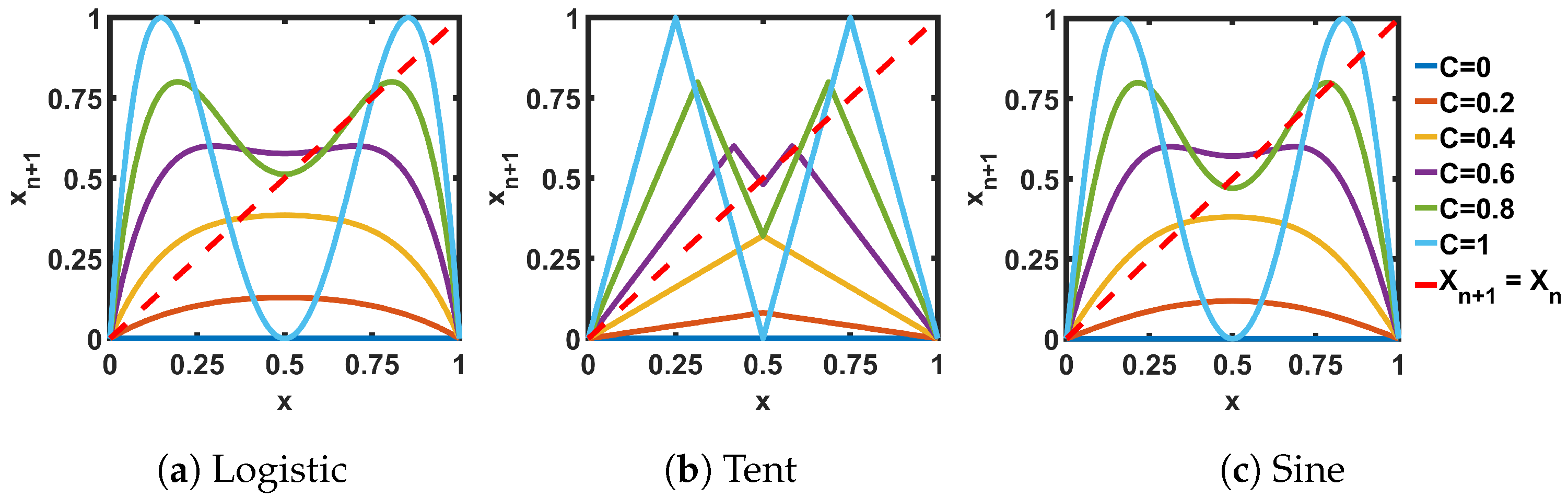
Figure 3.
Transfer curves for the cascaded pairs (two maps connected in series) ideal seed maps.
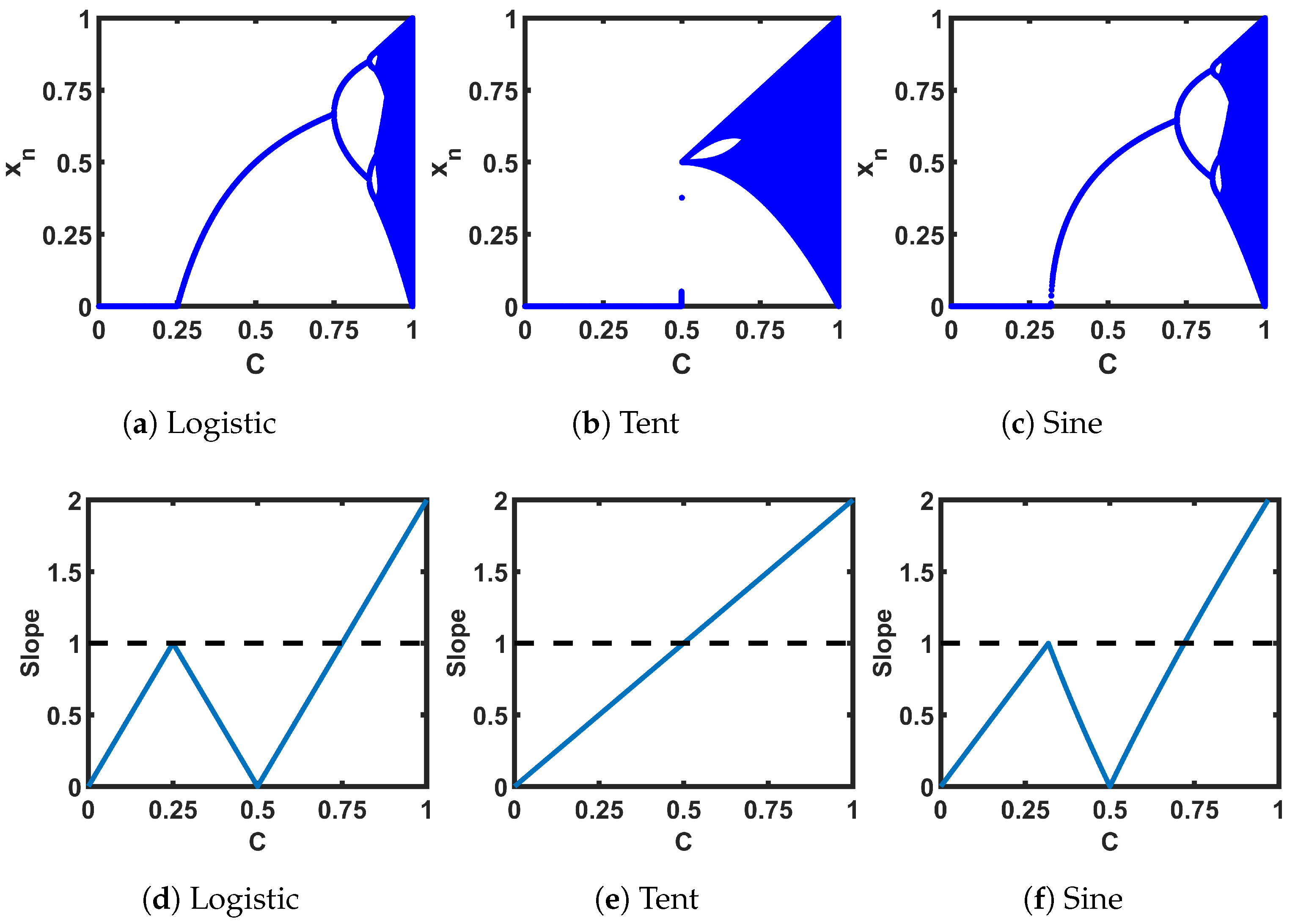
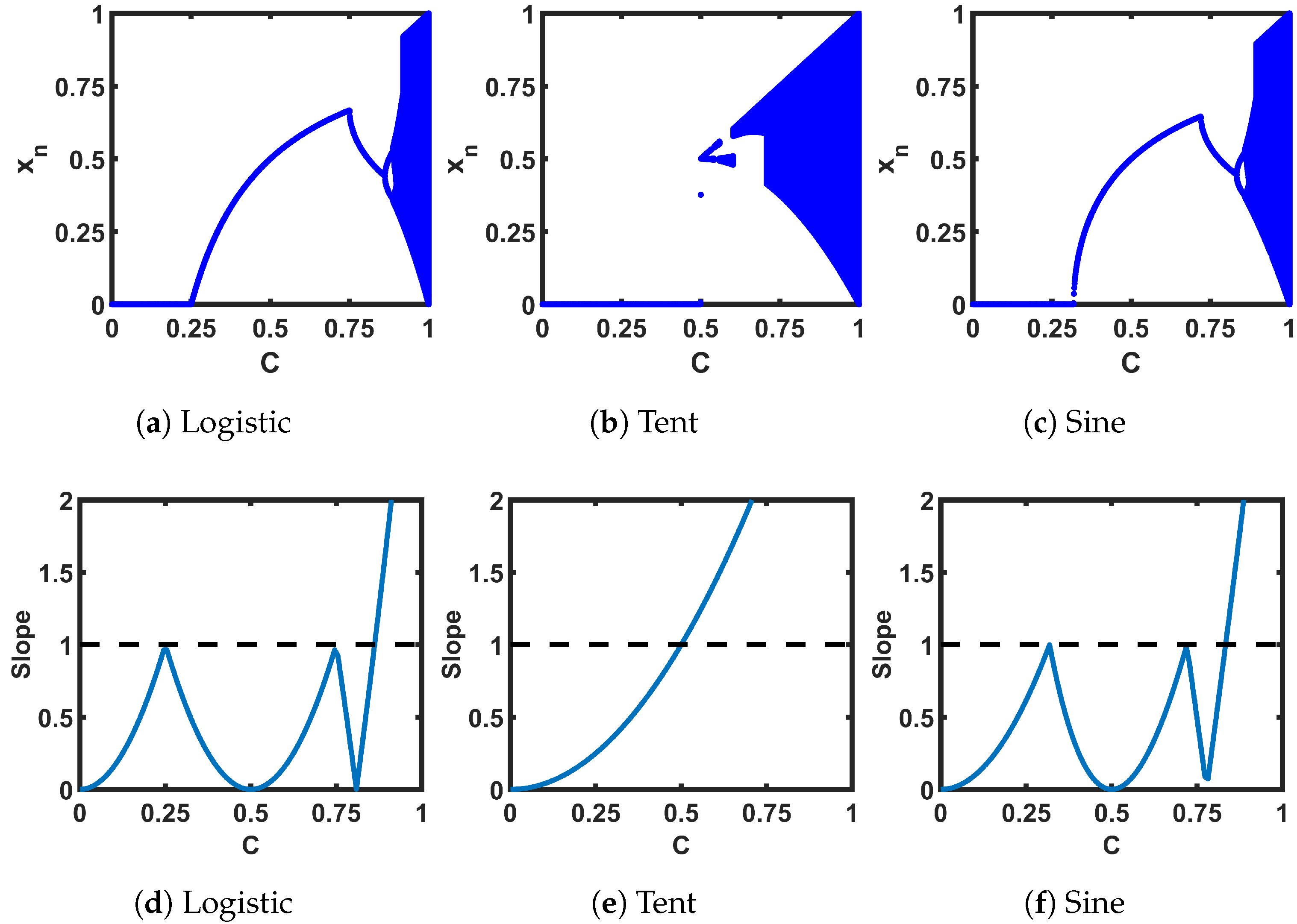
Figure 4a–c show the plots of steady-state sequence values (truncating the first 1000 from 15,000 iterations) for each seed map at different control parameter values (C). Figure 4d–f show the plots of the slopes of the transfer curves at the fixed points. Figure 4a–c are called bifurcation plots: as we can see, for example, in Figure 4a, the steady-state sequence bifurcates to a period of 2 at C = 0.75, where the C ≤ 0.75 region corresponds to stable fixed points. With the change of C, consecutive bifurcations happen until it hits the chaotic regions (dark blue regions in the plots). We can see that the slope of Figure 4d–f that corresponds to the fixed regions is less than 1.
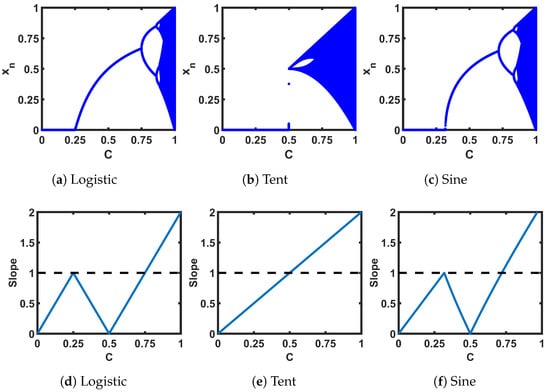
Figure 4.
(a–c) Bifurcation plots of the seed maps; (d–f) slope of the transfer curve at the intersection between the transfer curves and -line.
Figure 5a–c show the bifurcation plots of the cascaded pairs of the ideal seed maps. The regions with an even-numbered period in Figure 4a–c are reduced by half in Figure 5a–c: that means, what is a period of two in the single case, is now a fixed point in the cascaded case. In the slope plots of Figure 5d–f, also, we can identify the fixed point regions where the slope (for the cases of multiple intersections, the intersection with the minimum slope is taken) is less than 1. Hence, to ensure robust chaotic performance, we need to modulate the transfer characteristics in such a way that we can avoid the fixed points and the periodic regions:
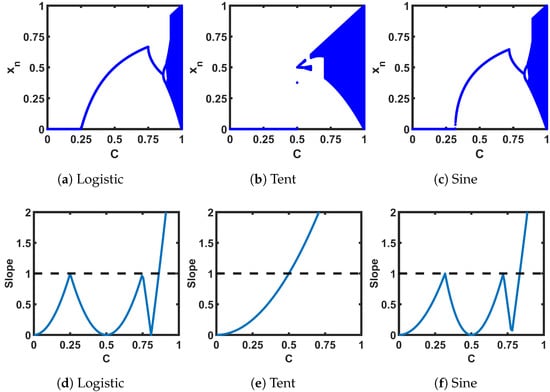
Figure 5.
(a–c) Bifurcation plots of the cascaded pairs of the seed maps; (d–f) slope of the cascaded transfer curve at the intersection between the transfer curves and -line.
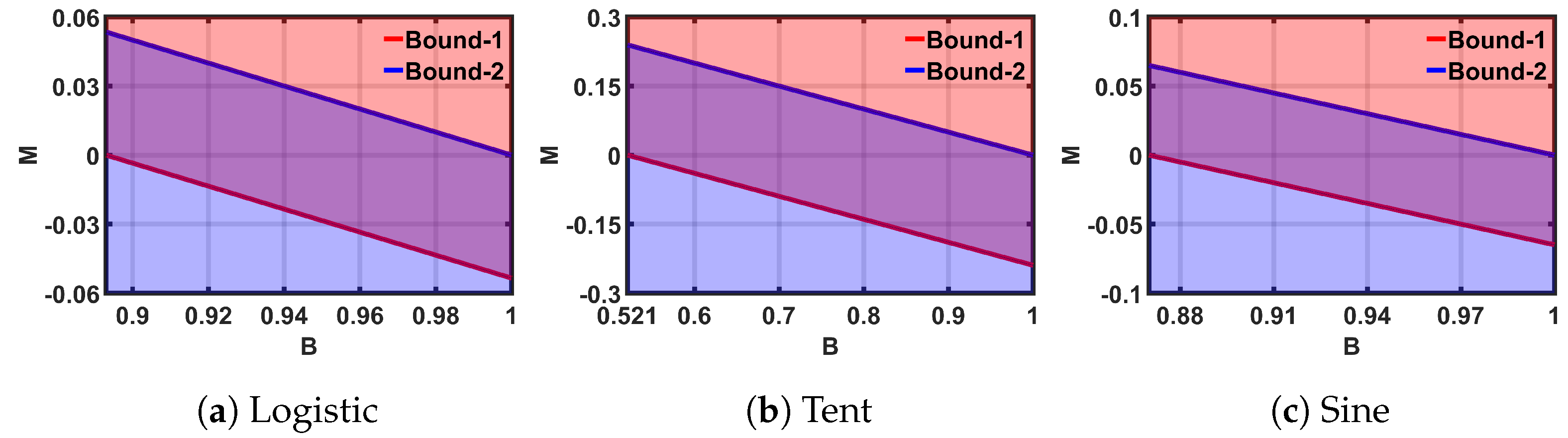
We propose the linear transformation expressed in (1), to perform the transformation of the T-block in the SPM schematic (Figure 1). The range of the sequence, [,], the range of the control parameter, [,], and the chaotic range of the corresponding seed map, [,], are used to form the inequalities shown in (2), (3), and (4). The inequalities are used to solve for two design parameters, M, and B. The solution ensures that the T-block maps any combination of and C into , such that .
Figure 6 plots the boundary condition shown in (2), (3), and (4): for example, in the case of the Tent map, the region above the ’Bound-1’ line in Figure 6b satisfies (3), and the region below the ’Bound-2’ line satisfies (4); the horizontal-axis limit for Figure 6 satisfies (2). Hence, the purple region of the plot gives the solution space for M and B. We can pick any convenient (B,M) point from the solution space to implement the SPM.
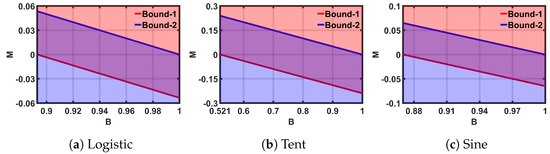
Figure 6.
Solution-spaces for ideal maps.
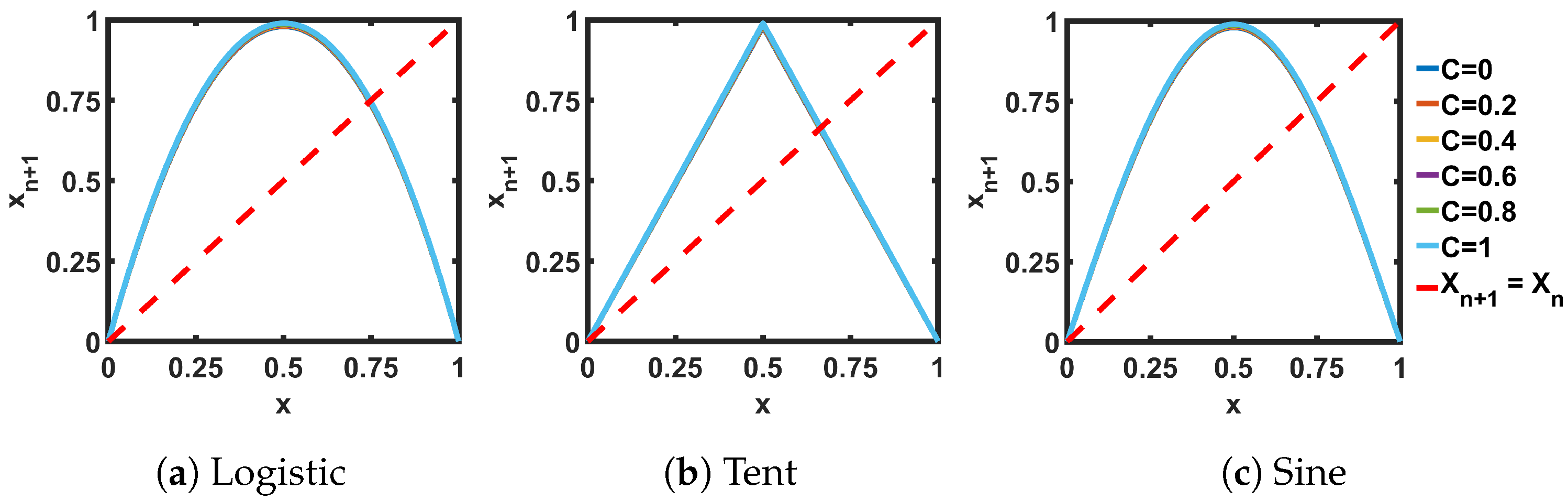
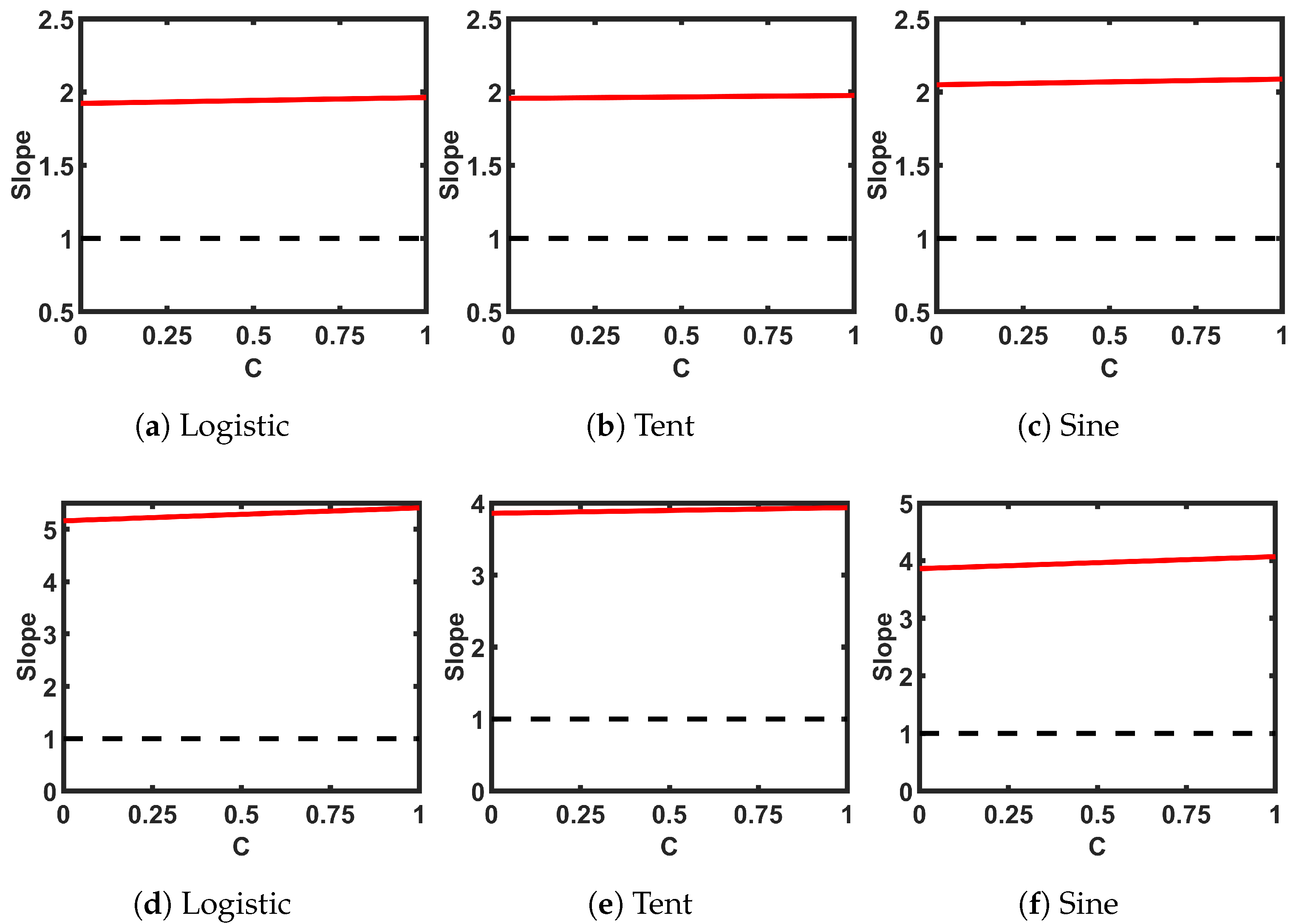
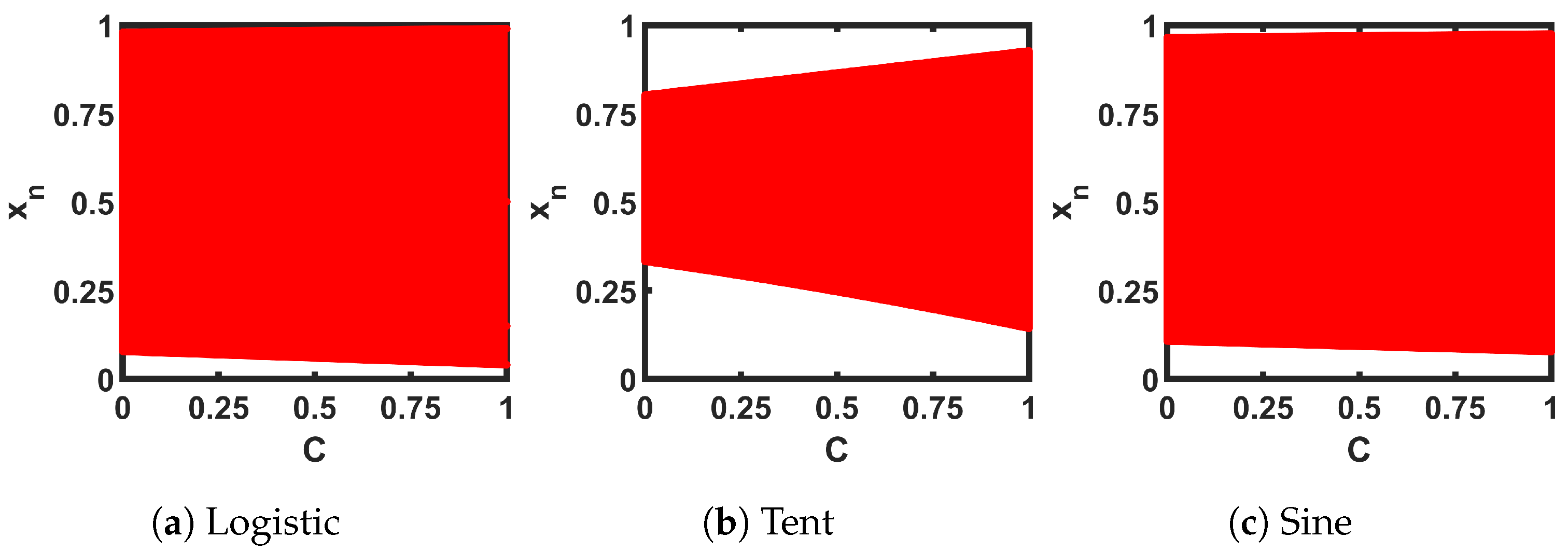
Table 2 presents the analytical expressions for the three SPMs with ideal seed maps. The table shows selected values for two design parameters, M and B. Figure 7 shows the transfer curves of the three SPMs. The slopes of the single and cascaded pairs in Figure 8 show that the slope is greater than 1 for any value of C, indicating that the SPMs do not have fixed points or a period of 2 anywhere in the whole design space. For cascaded maps, there are multiple intersecting points and the shown slope is the minimum intersection slope. The bifurcation plots in Figure 9 show wider chaotic regions compared to the corresponding seed maps.

Table 2.
Analytical expression for the three SPMs.
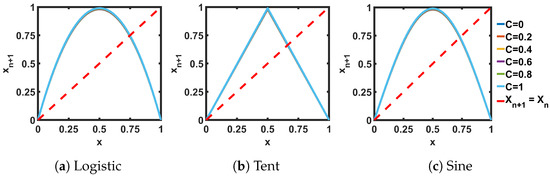
Figure 7.
Transfer curves for self-parameterized maps (SPMs). The transformation parameters for the SPMs are: Logistic: ; Tent: ; Sine: .
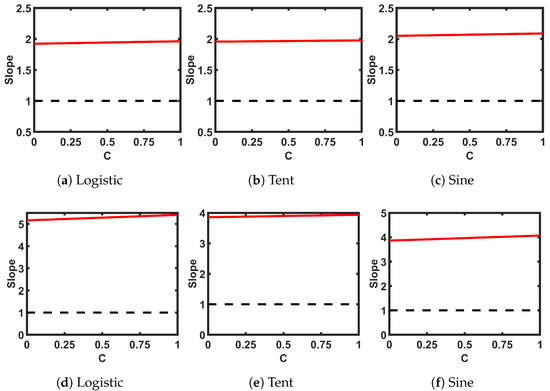
Figure 8.
Slopes of the (self-parameterized map) SPMs’ transfer curves at the intersections between the transfer curves and -line: (a–c) single map; (d–f) cascaded pairs.
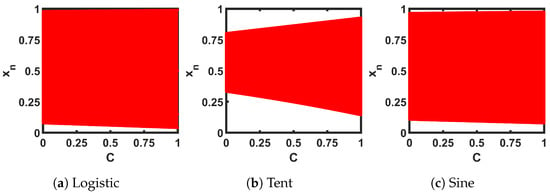
Figure 9.
Bifurcation plots of the self-parameterized maps, generated from ideal seed maps—Logistic, Tent, and Sine.
3.2. Chaotic Performance Evaluation
The chaotic performance was analyzed with four established entropy matrices: the Lyapunov Exponent (LE); the Correlation Coefficient (CC); the Correlation Dimension (); and Approximate Entropy ().
3.2.1. The Lyapunov Exponent
The Lyapunov Exponent (LE) is one of the most widely used chaotic entropy metrics to quantify sensitive dependence on the initial state. The defines the average separation rate of two trajectories starting from two very close initial states. A positive value indicates chaotic behavior, while a 0 or negative indicates a finite period [65]. The analytical expression for the of a 1-D system is shown in (5) [2]:
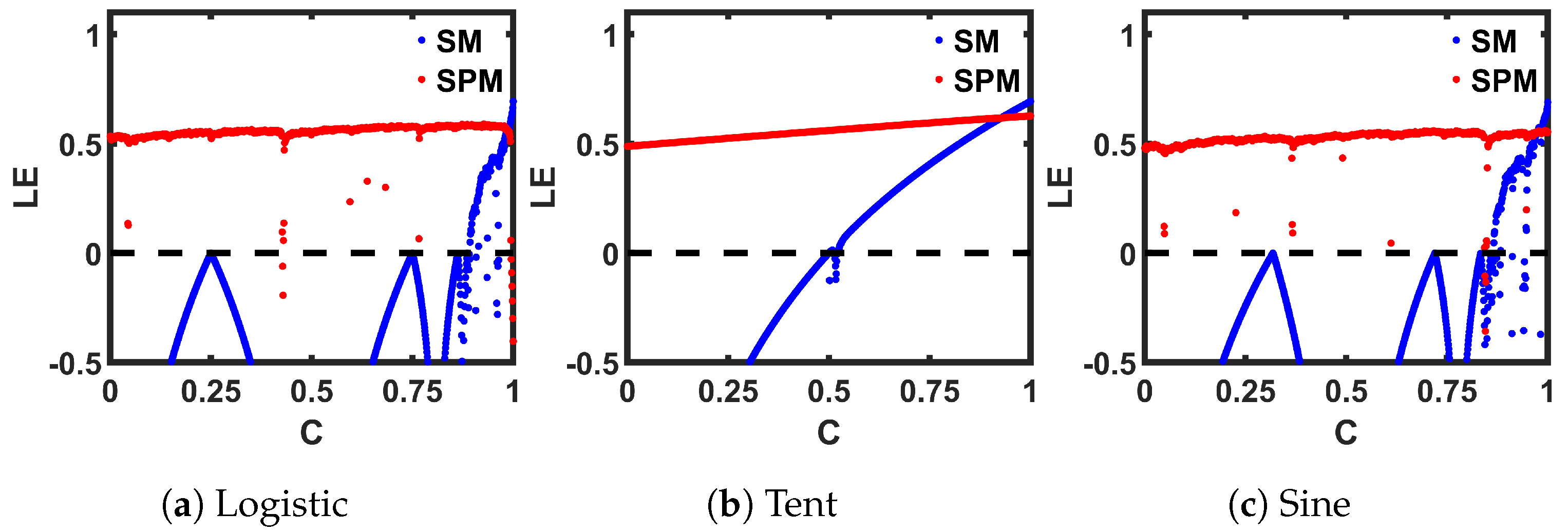
Here, denotes the transfer function of a 1-D map, and N is the total iteration count. The of the seed chaotic map and the SPM are calculated with 14,000 steady-state discrete-time values for each C, and then plotted, as shown in Figure 10. Compared to the seed maps (SM), the corresponding SPMs provide a positive across a wider range of C.
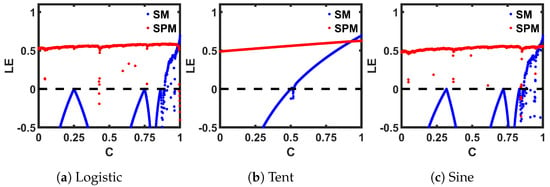
Figure 10.
Lyapunov Exponent (LE) comparison of seed maps (SM) to corresponding self-parameterized maps (SPM).
3.2.2. Correlation Coefficient
We used the Correlation Coefficient () measurement as our second entropy metric, to verify the sensitive dependence on the initial state and the control parameter. We performed two sets of measurements: one for the initial state dependence (), and the other one for the control parameter dependence (). To measure the sensitivity of the system output on the initial state (), we generated two sets of discrete-time sequences, one with and another with , where denoted a small variation. We chose = in this case. Then, we measured the correlation between those two sequences, using (6).
Here, the operator calculates the expectation, denotes the mean, and is the standard deviation. Similarly, we used (7) to calculate the correlation coefficient between two sequences—one generated with the control parameter, C, and another with .
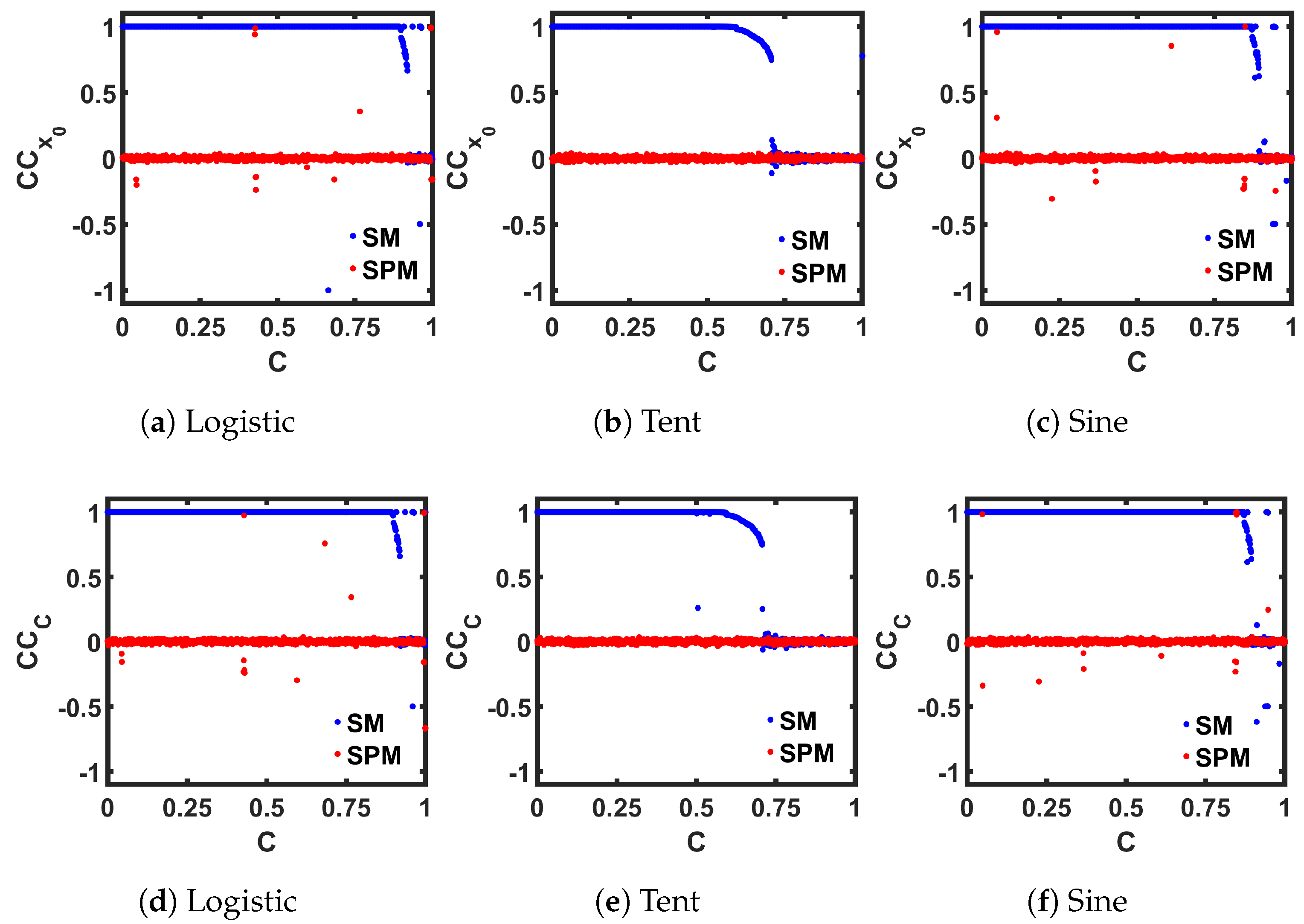
We performed the measurements for a range of C values, and compared the results between the seed maps and the corresponding SPMs in Figure 11. As we can see, in the case of the seed maps, the periodic regions of each map show a perfect correlation of 1, while in the chaotic regions, even that small variation resulted in two very different chaotic sequences, and we obtained values close to 0, indicating almost no correlation. In both measurements, for all three maps, the SPM versions offer a almost throughout the whole C range, indicating a wider chaotic region compared to the corresponding seed maps.
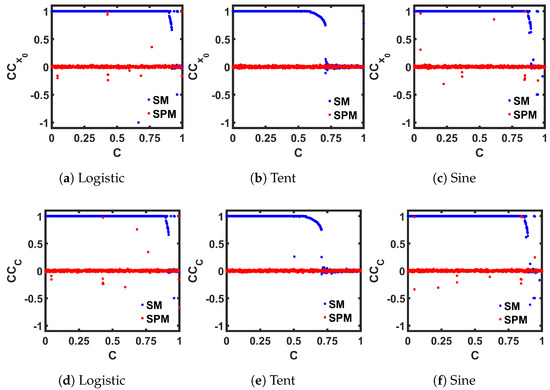
Figure 11.
Comparison of seed maps (SM) to corresponding self-parameterized maps (SPM), in terms of the Correlation Coefficient measurement, by varying the initial state (), and by varying the control parameter ().
3.2.3. Correlation Dimension
The Correlation Dimension () was our third metric, which was used to measure the space dimensionality occupied by a time series. We followed the algorithm proposed in [66], to calculate the of a time series (discrete-time sequence in our case). For a generated discrete-time sequence {}, with an embedding dimension of e, the could be calculated using (8):
Here, is the correlation integral, which is defined as shown (9):
In (9), () denotes the unit step function; () = 1 if ≥ 0 and () = 0 if < 0: here, l is the time delay unit, and its value is equal to 1 for the discrete-time system. The time-series is defined by:
If exists, then the can be calculated from the slope of the log−log plot of versus , as defined by (11):
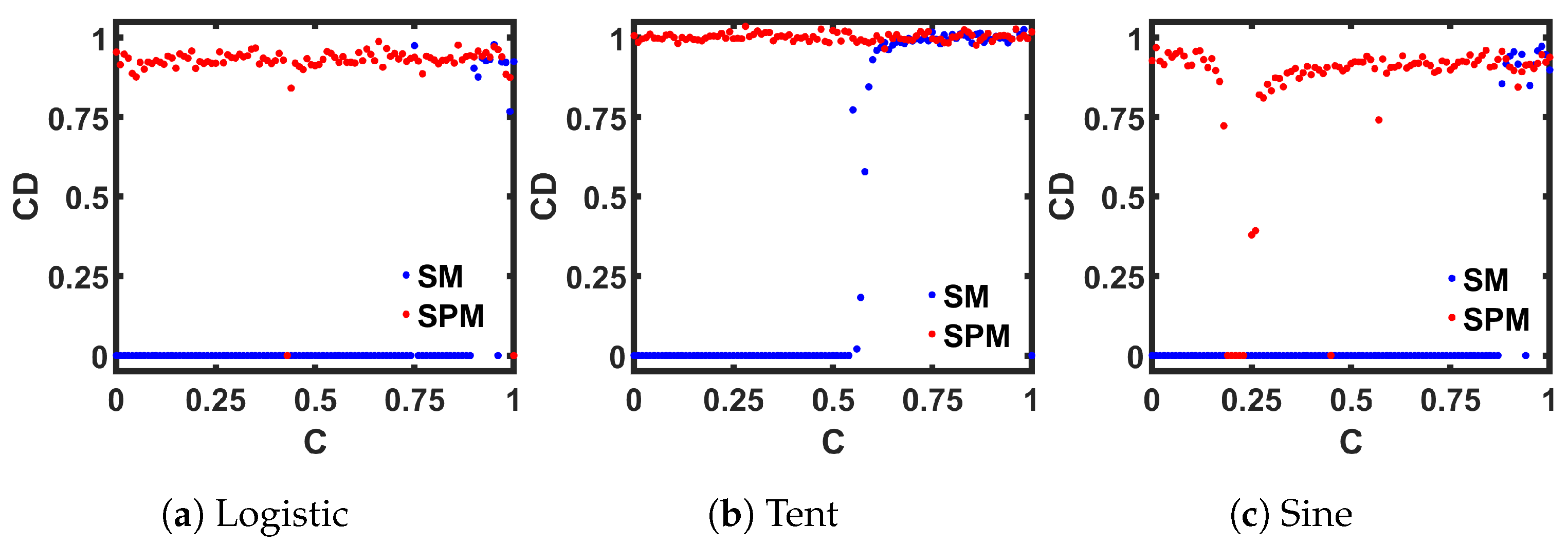
The value of the is large for a dynamic system that can generate outputs with a large number of dimensionality and irregular attractors. The is close to zero when the attractors have a low degree of freedom. Figure 12 shows the calculated results where we used e = 2 on steady-state discrete-time values. The periodic regions show , and the chaotic areas show . The wider chaotic window from the SPM can also be identified from this measurement.
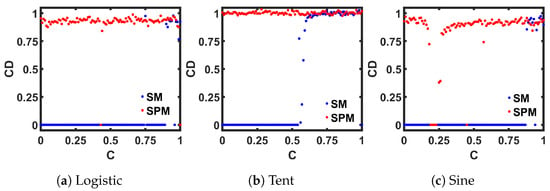
Figure 12.
Comparison of seed maps (SM) to corresponding self-parameterized maps (SPM), in terms of the Correlation Dimension (CD) measurement.
3.3. Approximate Entropy
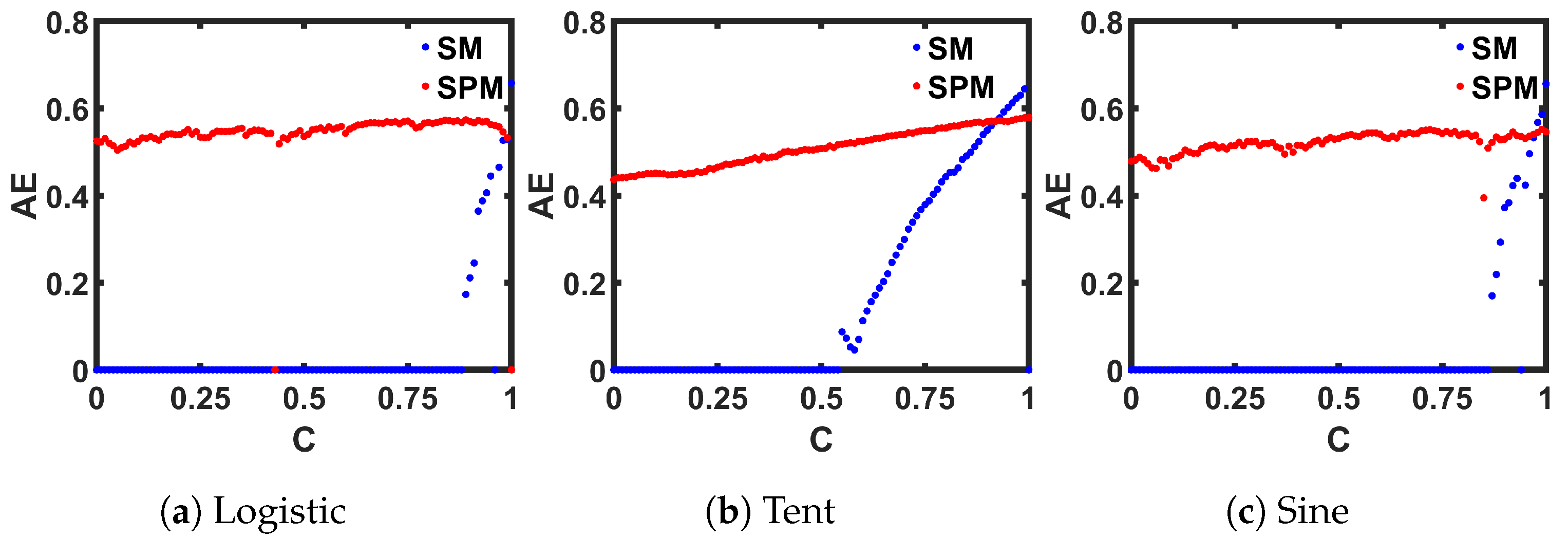
The last entropy metric that we want to employ for examining chaotic complexity is called Approximate Entropy (). was developed to quantify the regularity in time-series data [67]. The unpredictability of fluctuation in a time series is returned as a scalar value in measurements. A higher value indicates a better (than previous observations) unpredictability of the next point in a time series. A MATLAB-provided built-in function ([68]) is used to calculate the for three ideal maps, and are plotted in Figure 13. Similar to the previous measurements, 14,000 steady-state discrete-time values are used to compute at each control parameter, C. The chaotic regions of the plots correspond to higher values than the periodic regions, and the SPM traces show consistently high values over a wide range.
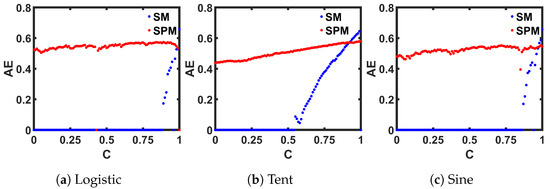
Figure 13.
Comparison of seed maps (SM) to corresponding self-parameterized maps (SPMs), in terms of the Approximate Entropy (AE) measurement.
4. Design for FPGA Implementation
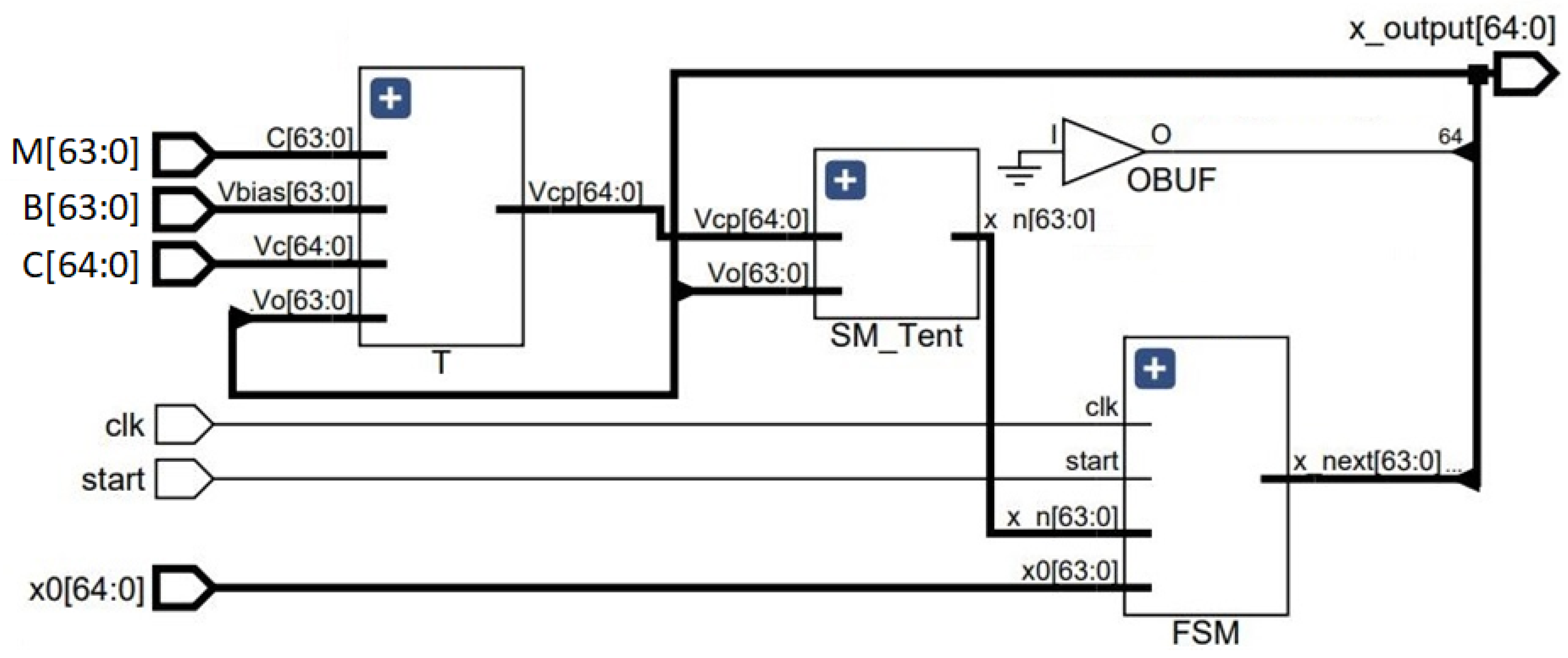
In this section, we present a general framework of the digital design for implementing the SPMs in an FPGA. We picked SPM-Tent for the demonstration. Figure 14 shows the schematic of the digital implementation of SPM-Tent. Sequence values in the range [0, 1] are represented with 65-bit binary numbers. Inputs to the digital circuit of Figure 14 are represented with different bit sizes, as required. The ’SM_Tent’ block in Figure 14 performed the Tent mapping with the combinational logic operation. ’T’ denotes another combinational block that transformed the output from every iteration, and fed to the ’SM_Tent’ block as the control parameter. The sequential operation of the circuit was handled by the ’FSM’ block that passed the output of the present state to be used as the next state input. The signal timed the circuit, and the input continued the iteration loop when it was . The circuit was written in Verilog, and was simulated in Xilinx/Vivado.
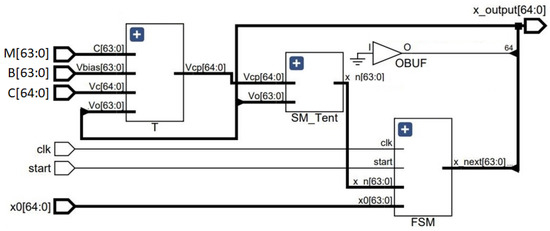
Figure 14.
Schematic for the digital implementation of self-parameterized Tent map.
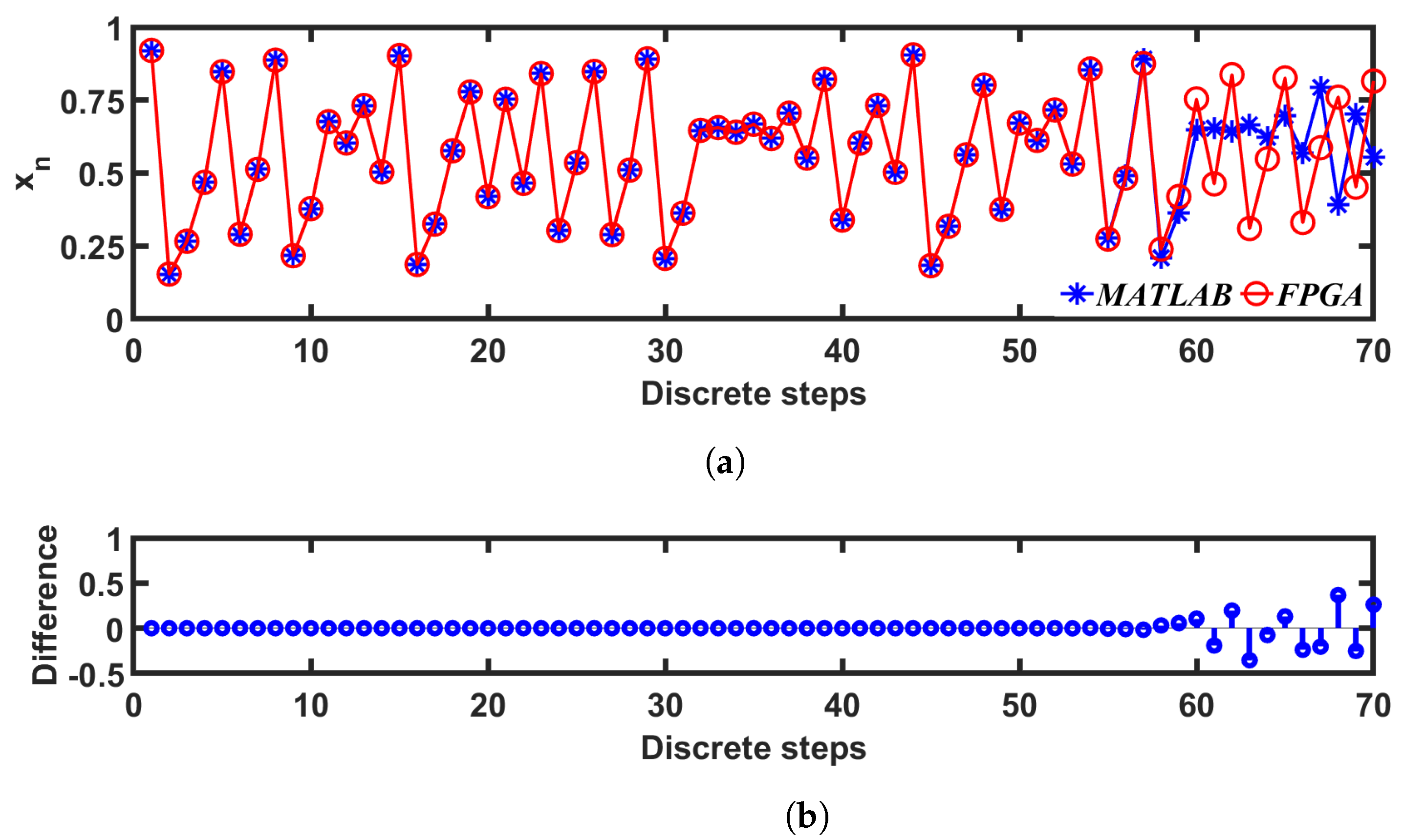
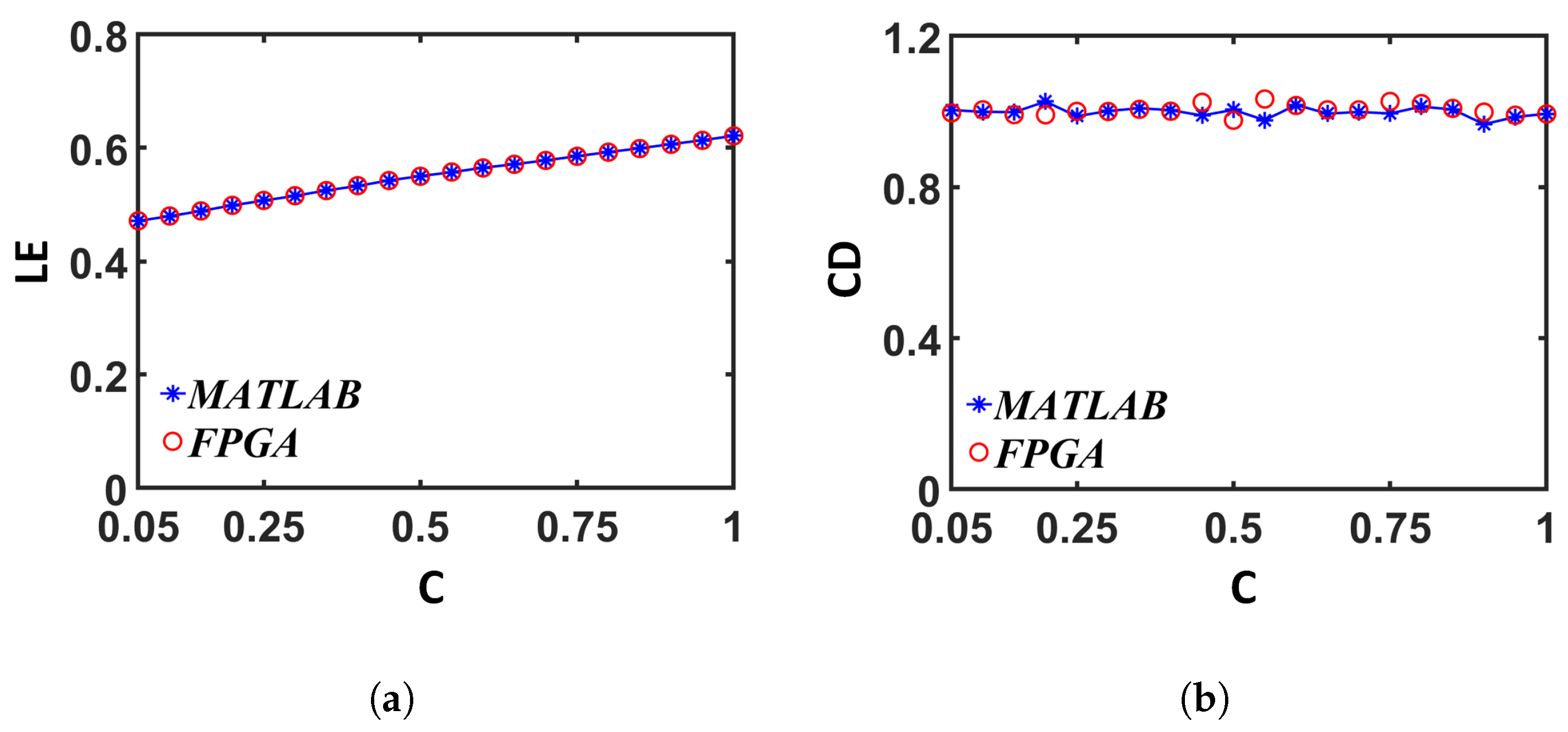
We verified the output from the digital implementation with an analytical model done in MATLAB: for this verification, two sets of discrete-time sequences were generated—one with MATLAB (as mentioned in Section 3), and the other one from Vivado, with = , C = , B = , and M = . The values of the first 70 iterations from the MATLAB and FPGA (Vivado simulation result) implementations are compared in Figure 15. The difference between the number representation and the finite precision numbers resulted in a divergence after approximately 60 iterations: this divergence was not a deviance from accuracy because, in terms of application, neither one of the implementations was more accurate than the other. What is more significant is whether the chaotic entropy values were similar in both implementations. We calculated the values from the generated sequences according to [69] and plotted in Figure 16a. The values were calculated for both sequences, as described in Section 3.2.3, and compared in Figure 16b. We can see a good match from the plots in both cases.
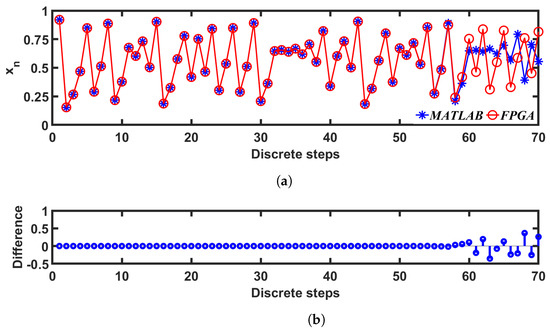
Figure 15.
Comparison between the simulated trajectory from the digital implementation (FPGA) and the analytical model (MATLAB).
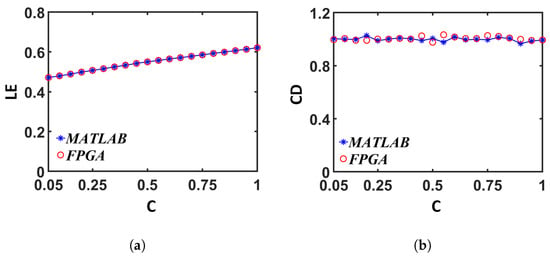
Figure 16.
Comparison between the results from the digital implementation (FPGA) and the analytical model (MATLAB): (a) Lyapunov Exponent (LE) (b); Correlation Dimension (CD).
5. CMOS Implementation
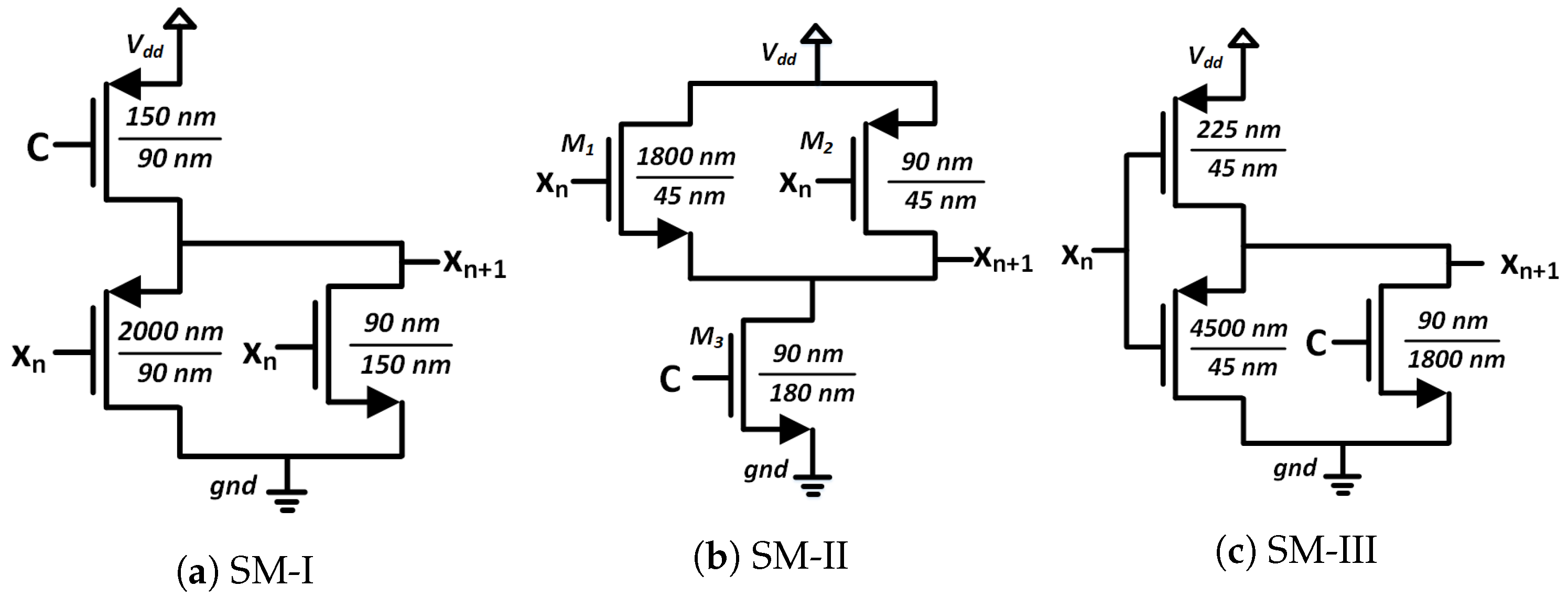
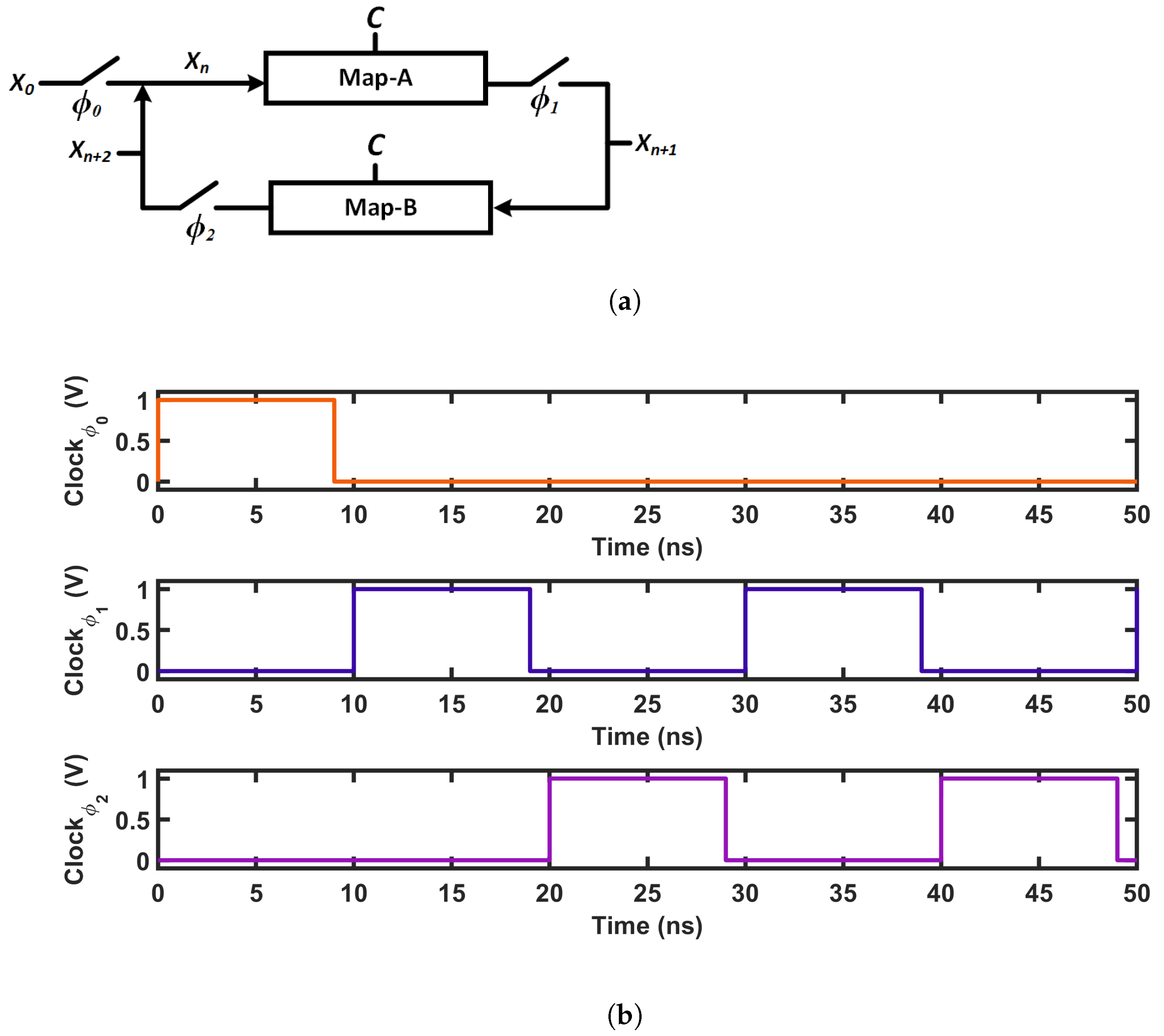
To demonstrate the self-parameterization scheme in CMOS, we picked three CMOS-based seed maps from the topologies presented in [60]. Figure 17 presents the schematics of the CMOS seed maps, and Figure 18 shows the corresponding transfer curves. In the CMOS case, the iterative operation was performed with the chaotic oscillator shown in Figure 19a. In the schematic, ’Map-A’ and ’Map-B’ represent two identical nonlinear map circuits. A switch, , was used to feed the initial state, , to the system. At each iteration, an analog voltage, , passed through the forward path containing ’Map-A’, and we obtained the next state output, . In the feedback path of a general discrete-time oscillator, the voltage is sampled with switches, and the hold operation is performed with capacitors. The sampling is done with two switches, and . Here, the switches, , and were run by non-overlapping clock pulses, as shown in Figure 19. To reduce the hardware cost from a large holding capacitor, the hold operation of our design was performed with the capacitance arising from the CMOS gates of the second map, ’Map-B’. An iteration loop completed when the output of the feedback path, , was fed back to the forward path, as the input for the next iteration. At each iteration, we sampled two analog voltages, , and . The discrete-time analog voltages were recorded for 15,000 iteration loops. Then, we obtained the steady-state output, by discarding the first 1000 iterations. The steady-state discrete-time values were used for analyzing the chaotic performance. Steady-state output voltage sequences were generated for a range of control voltage (C) values, and were plotted with respect to C, to generate the bifurcation plots in Figure 20, where the dark-blue regions in the bifurcation plots indicate chaotic operation.
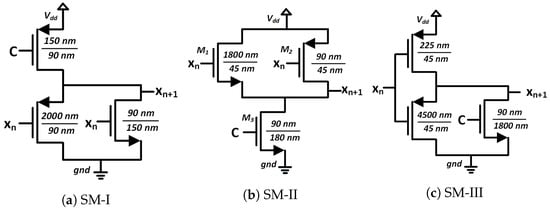
Figure 17.
Schematics of the CMOS seed maps (SM).
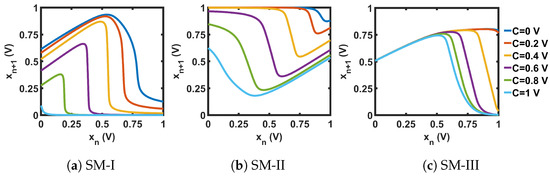
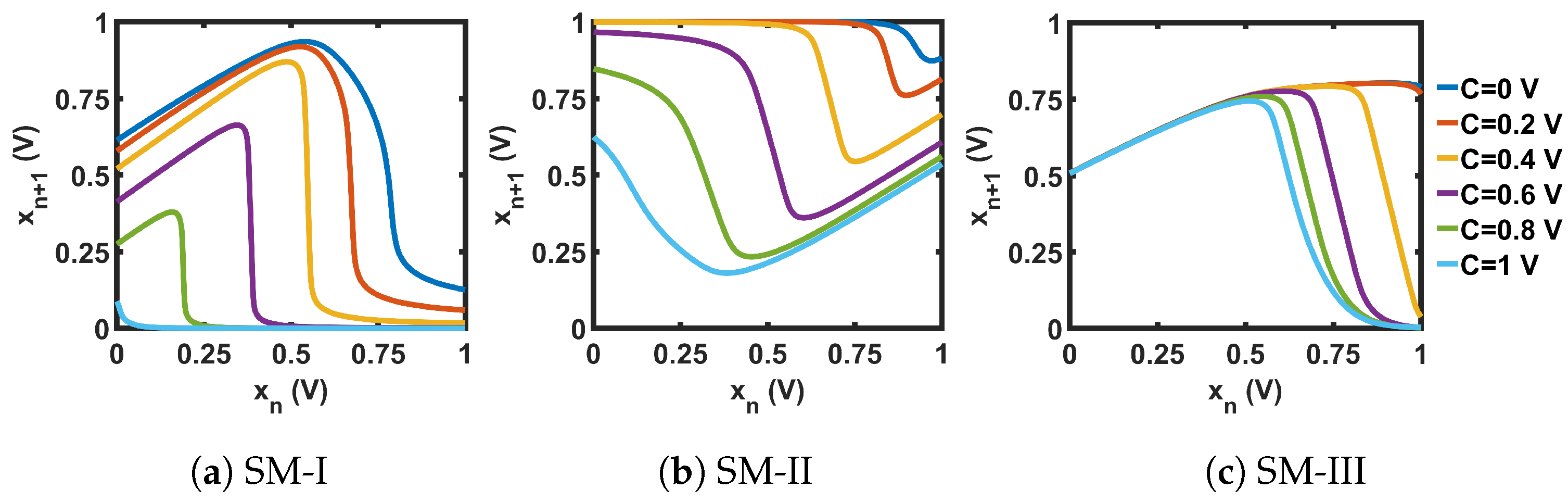
Figure 18.
Transfer curves for the CMOS seed maps (SM).
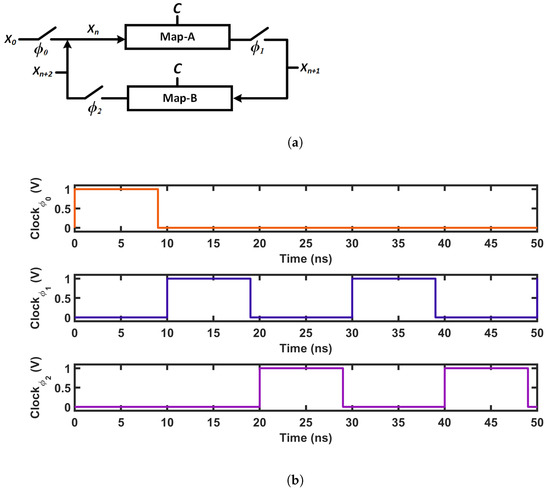
Figure 19.
(a) Chaotic oscillator (b) Clocking scheme.
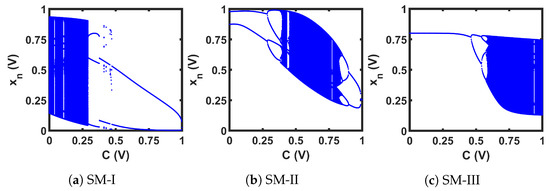
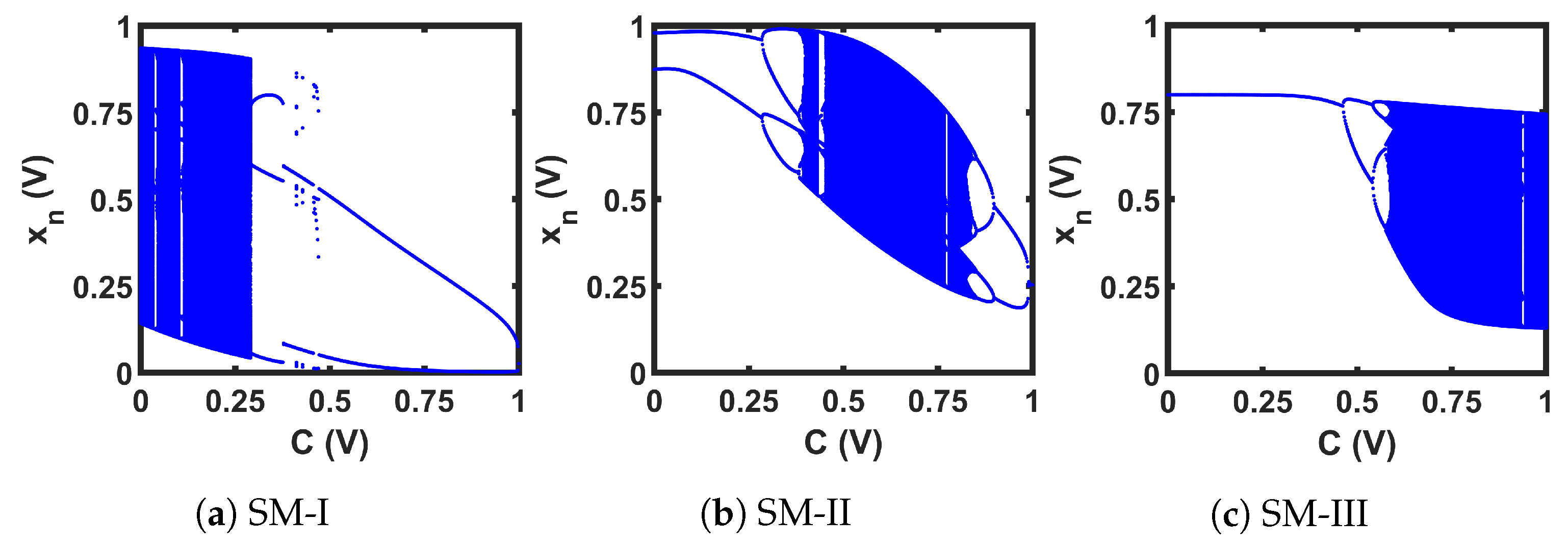
Figure 20.
Bifurcation of the CMOS seed maps (SM).
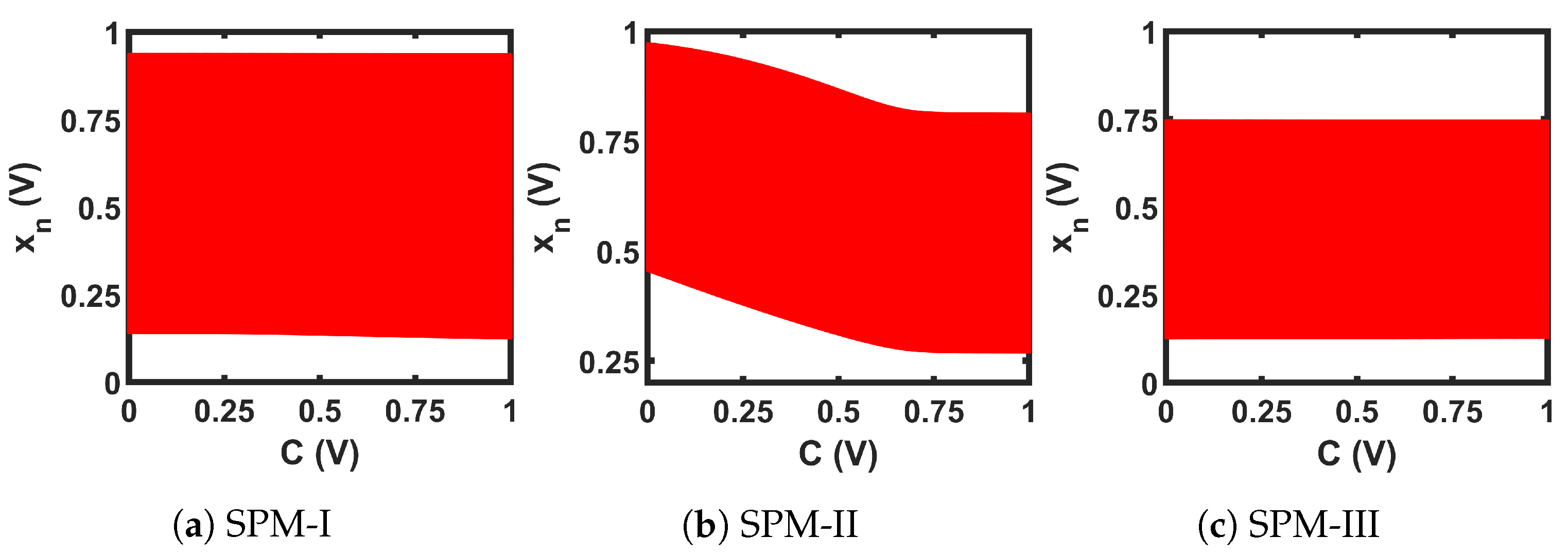
As we can see from the bifurcation plots of Figure 20, the chaotic regions did not cover the whole design space, 0 V ≤ C ≤ 1 V. We used these three chaotic maps as the seed map (SM) for demonstrating three CMOS-based SPM implementations. As the chaotic regions of SM-I, SM-II, and SM-III were situated at three different regions of the design space (left for SM-I, at the middle portion for SM-II, and right-aligned for SM-III), we selected these three as representative examples, to show that SPM can be constructed with any chaotic map having a chaotic range anywhere in the design space.
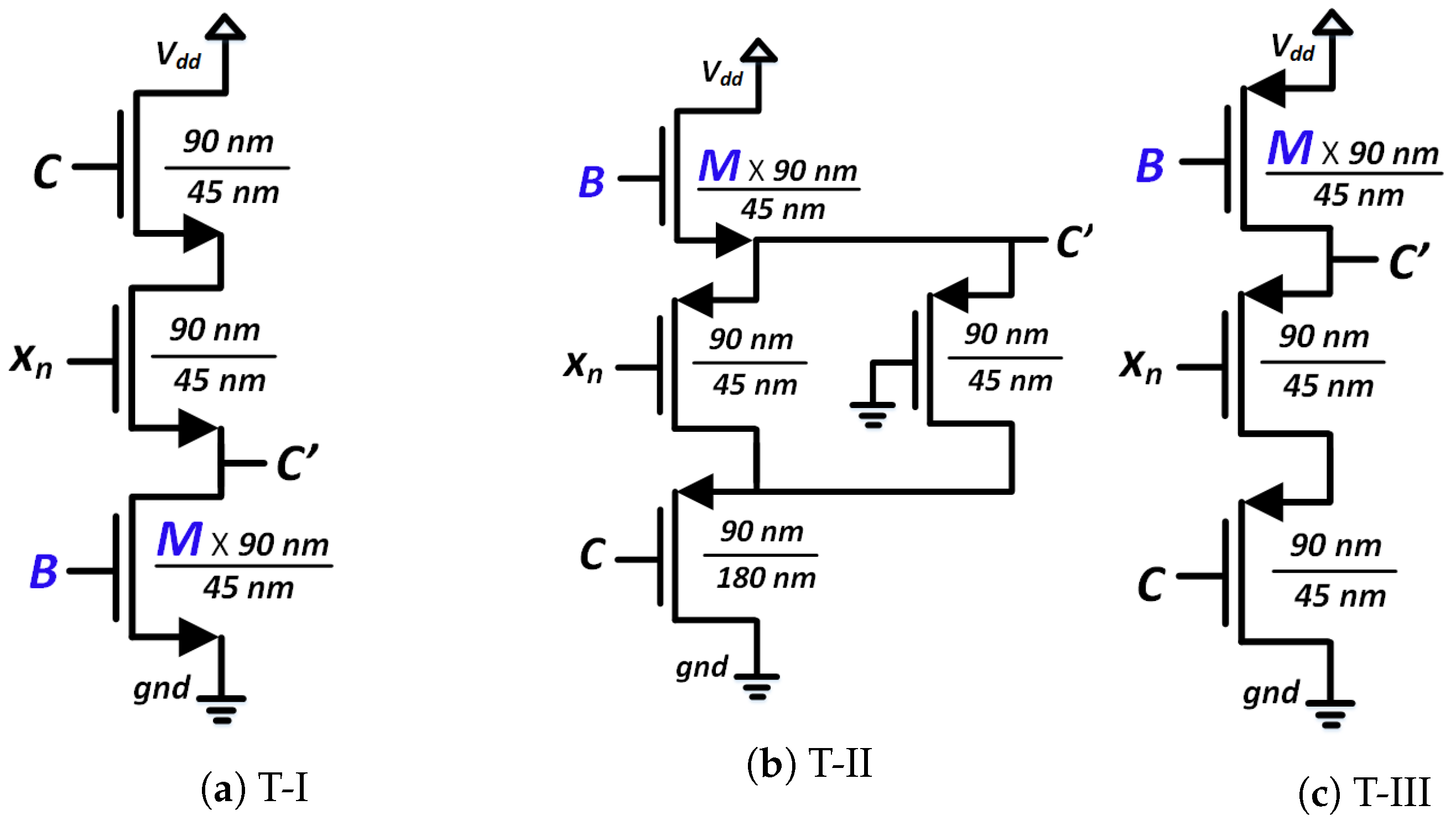
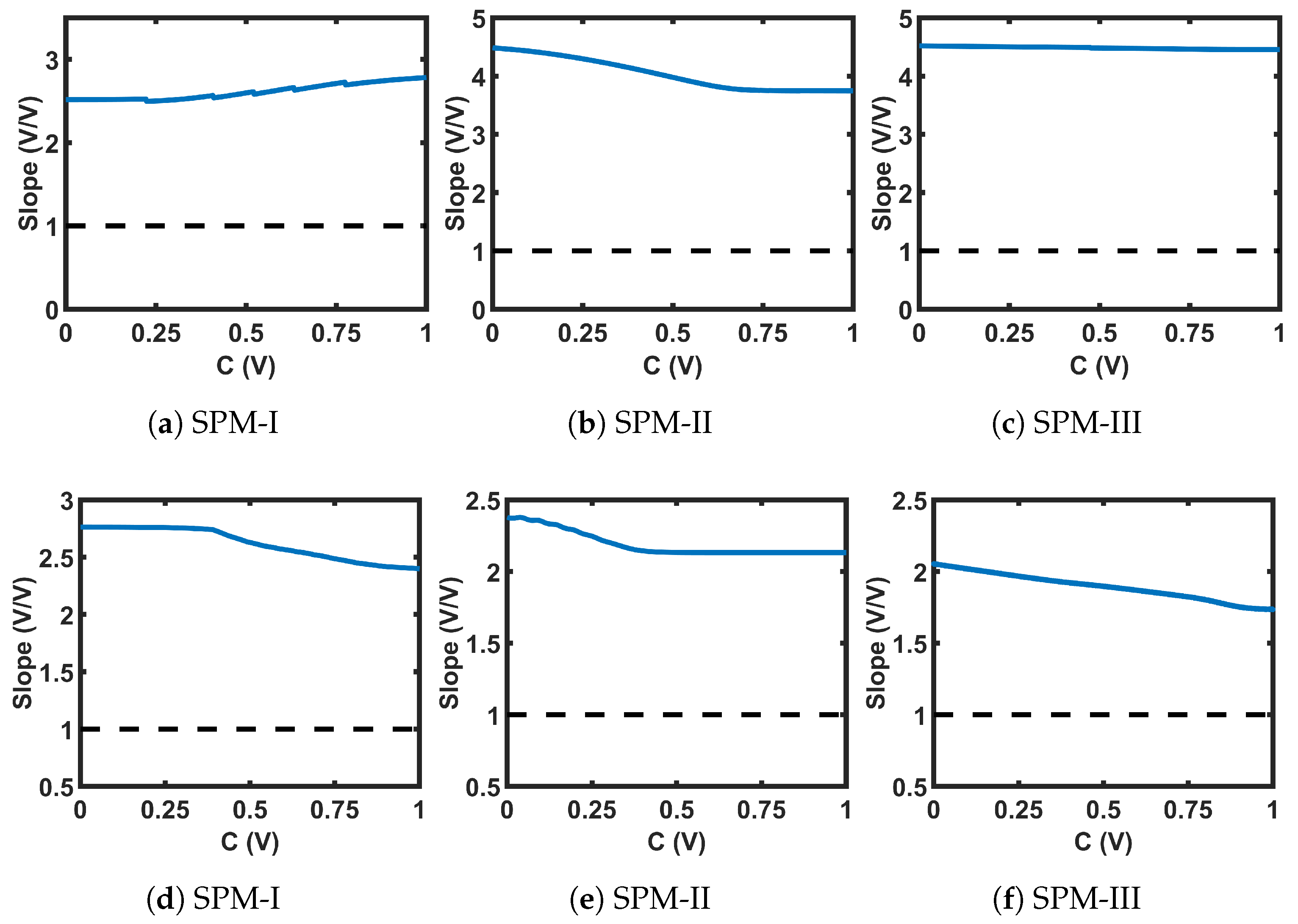
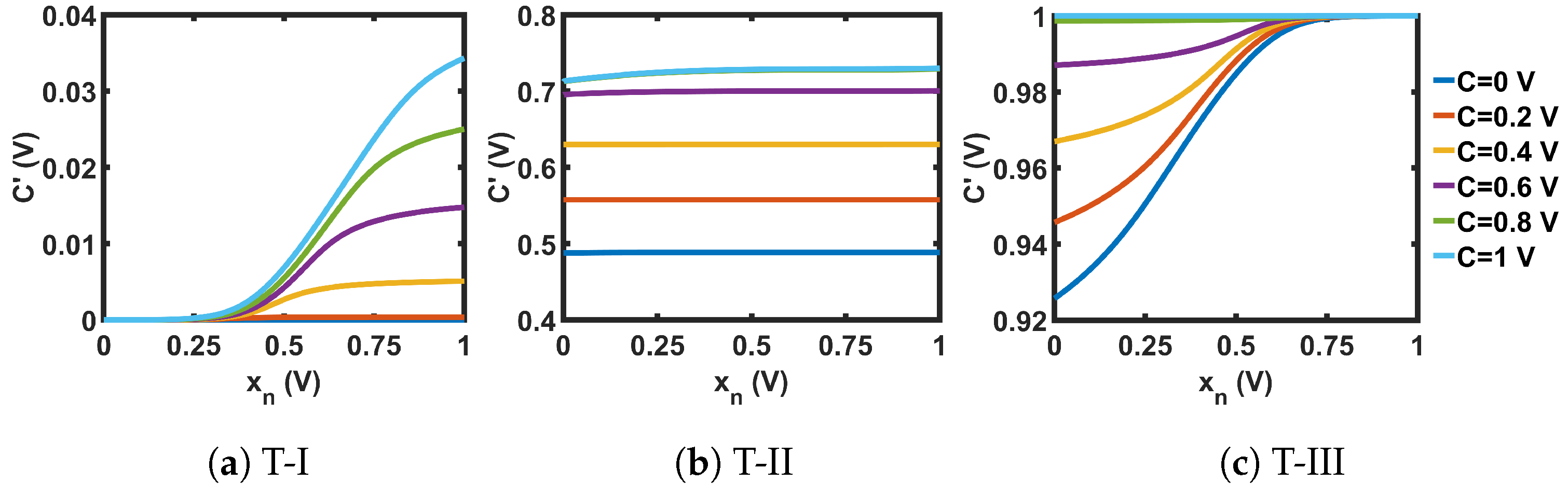
The circuits shown in Figure 21 were used for the transformation blocks of the CMOS seed maps. The topology used for each T-block depended on the position of the chaotic region in the design space. Each T-block topology had two design parameters, B and M. Here, B was used as the gate voltage of one transistor, and M as the multiplication factor with the width of that MOS. We used the stability analysis of fixed points to design for B and M. We extensively explored a pool of reasonable design choices for B and M, until we obtained a slope for single and cascaded SPM greater than 1 (the condition for avoiding fixed points) across the whole design space. Figure 22 shows the plots of the slopes for the three SPMs under consideration. The chosen transformation parameters were: SPM-I: B = 1 V, M = 4; SPM-II: B = 0.73 V, M = 1; and SPM-III: B = 0 V, M = 2. The transfer characteristics of the T-block with the chosen design parameter values are shown in Figure 23. T-blocks transform any combination of the global control parameter, C, and the input, , to generate a transformed control parameter, , that ensures chaotic operation for a particular seed map. Figure 24 shows the transfer characteristics of the three SPMs.
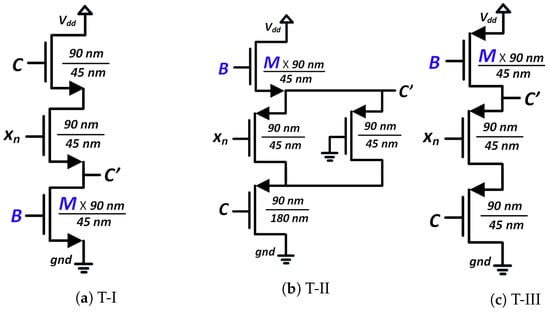
Figure 21.
Schematics of the MOS-based non-linear transformation (T)-blocks.
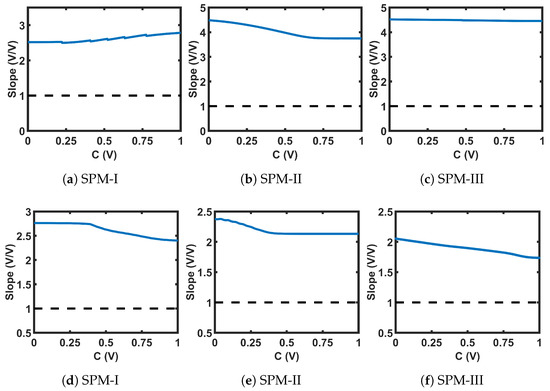
Figure 22.
Slopes of the self-parameterized map (SPM) transfer curves at the intersections between the transfer curves and -line: (a–c) single SPM; (d–f) cascade of two SPMs.
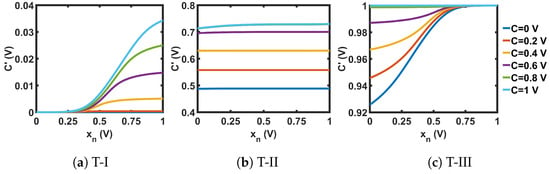
Figure 23.
Transfer curves of the non-linear transformation (T)-blocks.
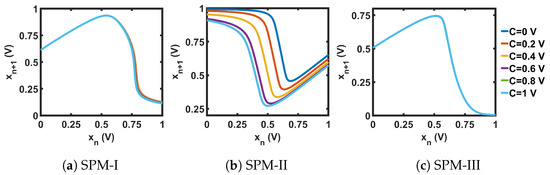
Figure 24.
Transfer curves for the non-linear transformation (T)-blocks.
To generate the sequence from the SPMs, we used the same chaotic oscillator setup as presented in Figure 19. In this case, ’Map-A’ and ’Map-B’ consisted of two identical SPMs: for example, the oscillator for SPM-I consisted of two SPM-I maps, where each SPM-I contained an SM-I and a T-I, as shown in the schematic of the SPM scheme in Figure 1.
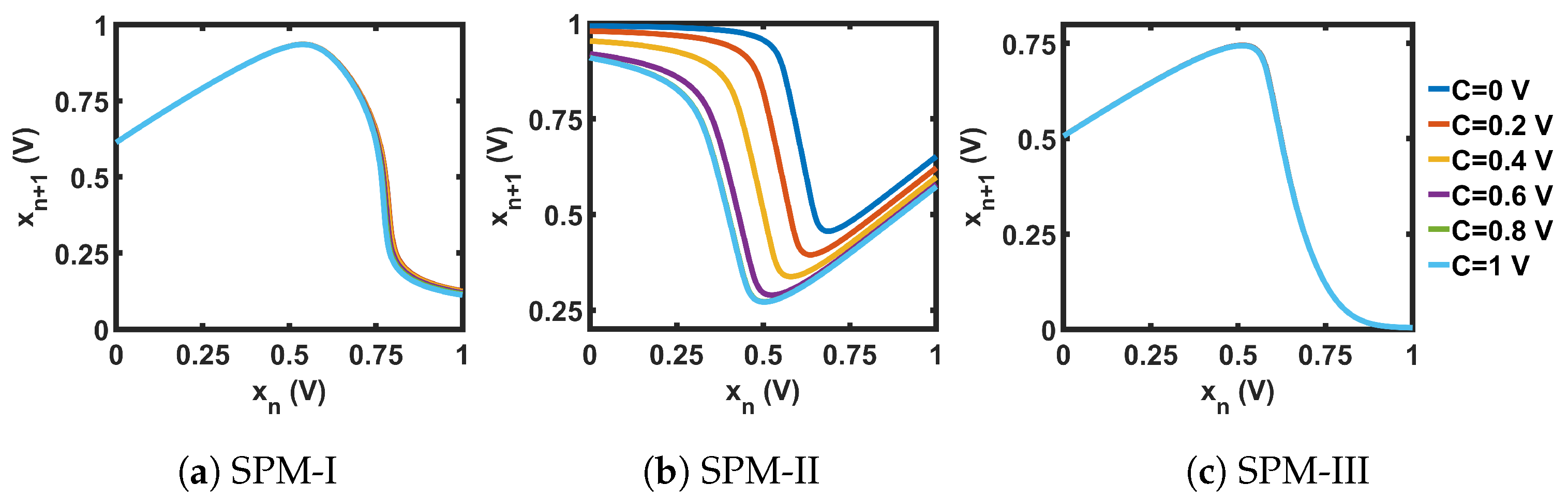
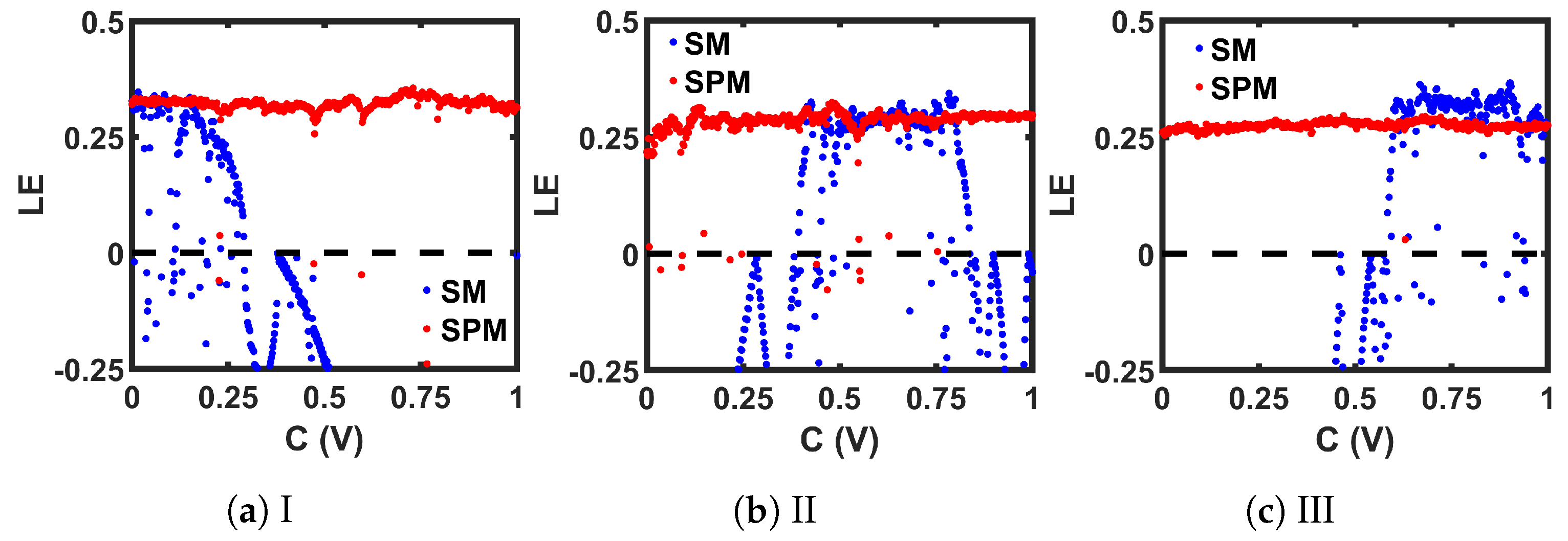
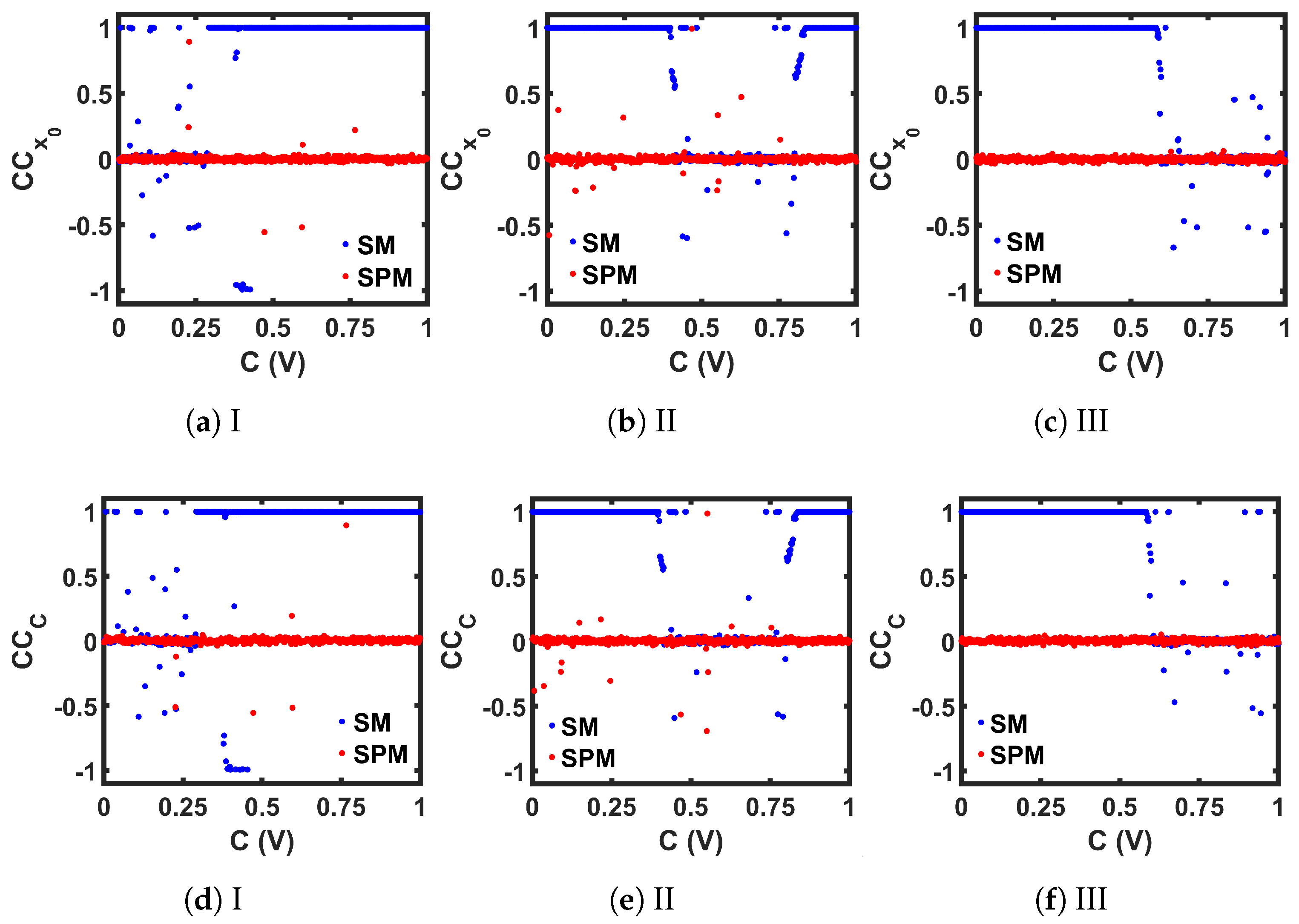
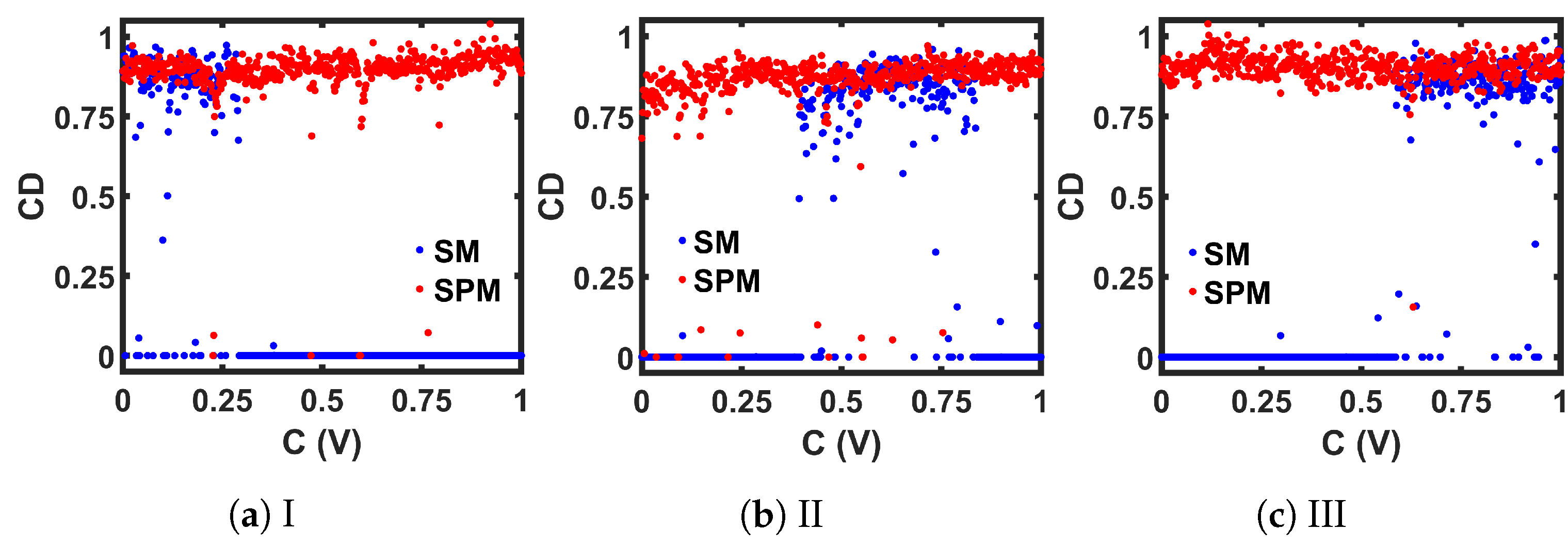
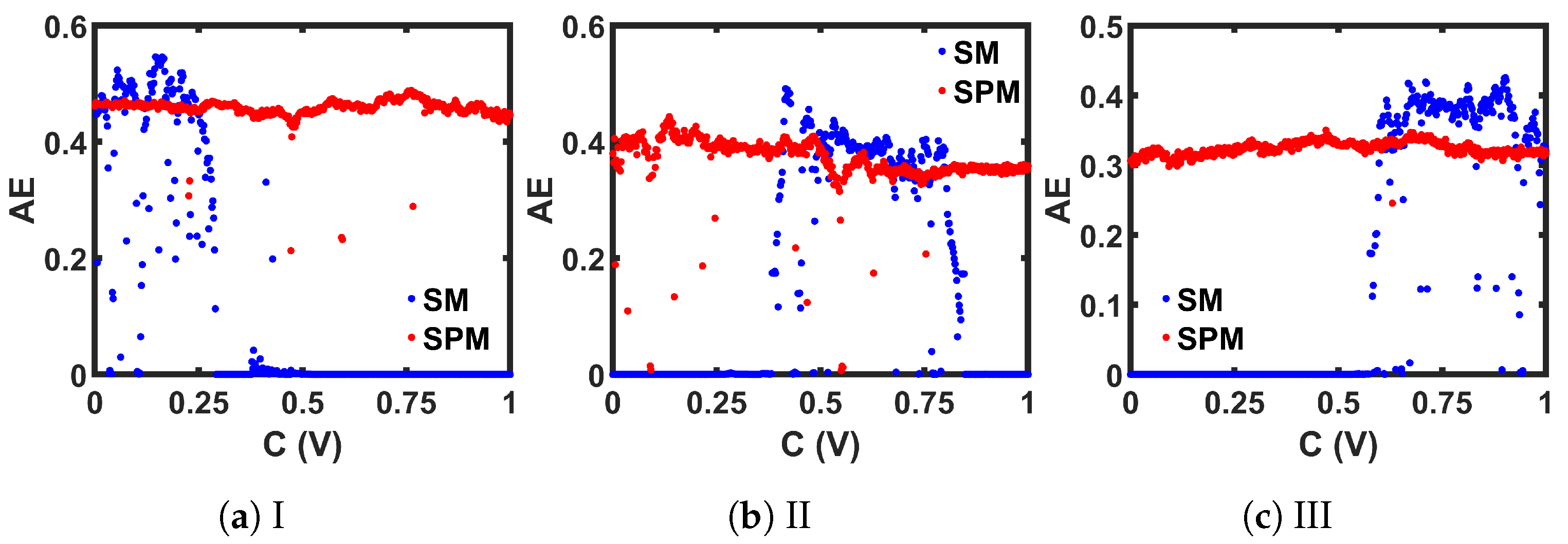
The chaotic oscillator was simulated to generate 15,000 sequence values for a range of C values. The last 14,000 steady-state values were used for chaotic performance analysis. Figure 25 shows the bifurcation plots for the three SPMs, where we can see that the chaotic region covered the whole design space. Figure 26, Figure 27, Figure 28 and Figure 29 present the comparison of , , , and , respectively, between each seed map and the corresponding SPM. Each chaotic entropy measurement verified the widening of the chaotic range in the SPM.
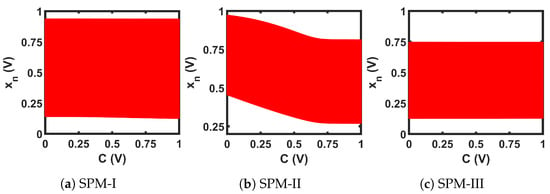
Figure 25.
Bifurcation plots of the CMOS-based self-parameterized maps (SPMs).
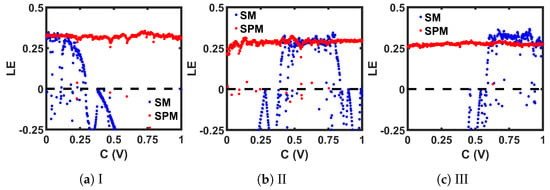
Figure 26.
Lyapunov Exponent (LE) comparison between CMOS-based implementations of seed maps (SMs) and corresponding self-parameterized maps (SPMs).
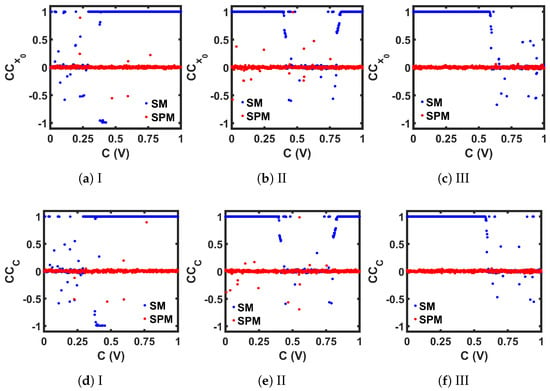
Figure 27.
Comparison between the CMOS-based seed maps (SM) and the corresponding self-parameterized maps (SPM), in terms of the correlation coefficient measurement by varying the initial state () and by varying the control parameter ().
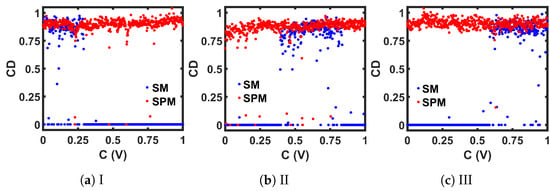
Figure 28.
Comparison between the CMOS-based implementations of seed maps (SM) and the corresponding self-parameterized maps (SPM), in terms of the correlation dimension (CD) measurement.
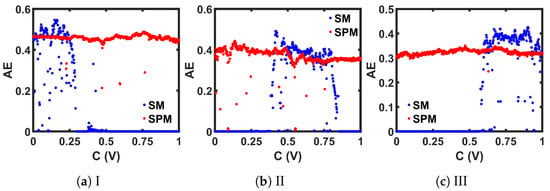
Figure 29.
Comparison between the CMOS-based implementations of seed maps (SM) and the corresponding self-parameterized maps (SPM), in terms of the approximate entropy (AE) measurement.
6. Hardware Efficiency
The proposed self-parameterization scheme is hardware-efficient in two aspects. Firstly, to provide a wider chaotic range, it employs only one non-linear map. This hardware advantage can be leveraged for both digital and analog implementations. All the digital implementations proposed in [7,39], and [70] used more than one non-linear mapping to get a wide chaotic region. Moreover, most proposed techniques use complex transformations, such as exponential, and sine mapping, to modulate the control parameter. Unlike those techniques, the proposed digitized SPM method uses a simple linear transformation to modulate the control parameter: this is the second aspect of the hardware efficiency of our proposed design, and is more pronounced in the analog implementation. An analog method of chaotic range widening was proposed in [22]. A linear transformation was proposed, to modulate the output of one map before using it as the control parameter for a second map. A linear transformation can involve costly hardware setup, as it requires some arithmetic operation with operational amplifiers: hence, in the proposed SPM technique for IC implementation, we have simplified the transformation operation to a simple nonlinear transformation, comprising only three to four small MOSFETs (Figure 21). This non-linear transformation is also more cost-effective, compared to the transmission gate-based transformations proposed in the preceding conference paper ([63]). In this way, the proposed design gives us a significant hardware benefit compared to the previously proposed works.
7. Application
We have seen that the proposed SPM scheme provides a wide chaotic window, while employing low transistor-count mapping and transformation circuits: as a result, this chaotic system can be useful in a number of hardware-based security protocols in the IC domain, including chaos-based logic generators for side-channel attack mitigation, physically unclonable systems, and chaotic random number generation. This paper demonstrates the application of our proposed self-parameterization method in a random number generator (RNG) circuit.
7.1. Design of RNG
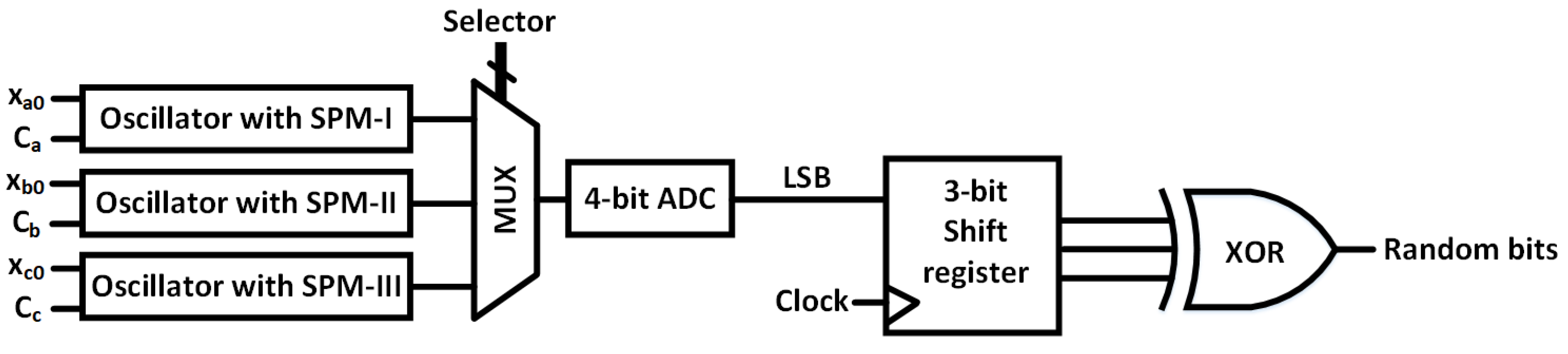
Figure 30 shows the schematic of the RNG. The basic architecture of this RNG was presented in [22]. A multiplexer (MUX) selects sequentially among three chaotic oscillators that are constructed with three CMOS-based SPM topologies, as discussed in Section 5. The analog voltages from the chaotic oscillators are converted to binary with a 4-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC), and the least significant bit (LSB) is stored in a 3-bit shift register. The XOR of those 3 bits generates 1 random bit. Three phase-shifted clocks with a 33.33% duty cycle run three oscillators, in such a way that we obtain one XOR output at every clock cycle. To generate a random data set for statistical analysis, we used 100 unique sets of three initial states. We used each set to provide three initial states for three oscillators, and generated 1 million binary bits. Three control voltages were used for the three oscillators, and were kept fixed across the 100 runs. In this way, a data set of 100 million binary bits was generated and used for the following statistical test.
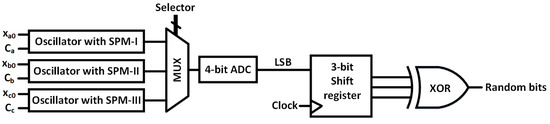
Figure 30.
Schematic of the proposed random number generator.
7.2. NIST
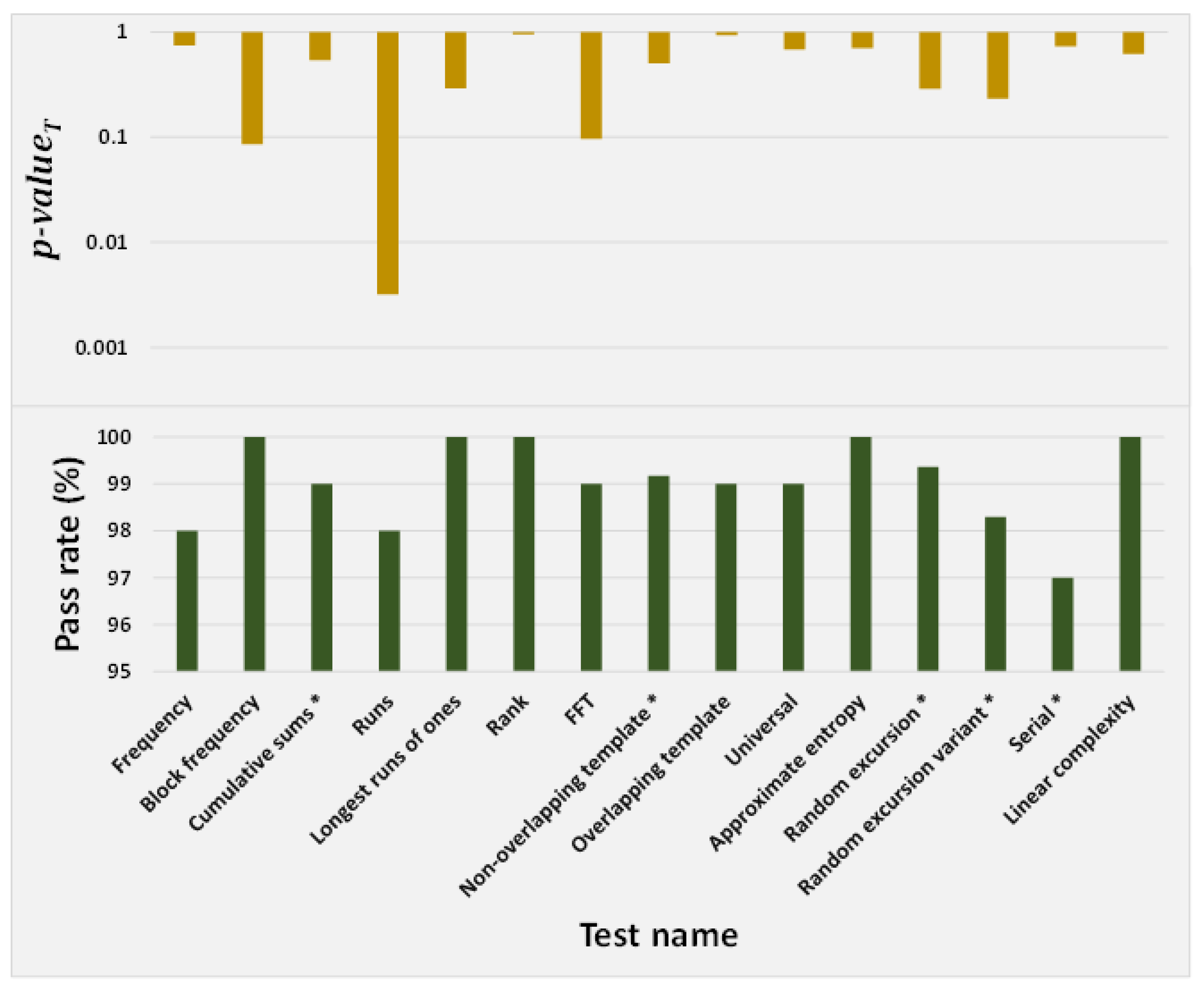
The NIST SP 800-22 Test Suite from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) offers 15 statistical sub-tests to measure the randomness in a sequence [71]. The test is performed with a bit-stream length of 1 million, and a significance level of 0.01. A sequence with 100 bit-streams (each bit-stream consists of 1 million binary bits) will pass a particular test if at least 96 out of the 100 bit-streams generate p-values greater than 0.01. The test suite allocates each one of the 100 generated p-values in 10 sub-intervals from 0 to 1, and evaluates the uniformity in the distribution with a -test. The sequence under test is considered uniform if the p-value generated from the -test (refers to p−) is greater than or equal to 0.0001. The NIST results are presented in Figure 31. The results show that the generated sequence passed both the pass rate threshold of 96% and the p− threshold of 0.0001 for all the 15 sub-tests.
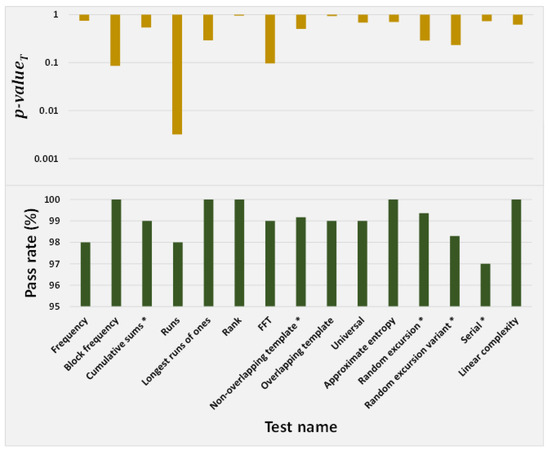
Figure 31.
Results of the NIST test. Averages of multiple tests were used for the cases of ’*’-marked test names.
7.3. Hardware Considerations
The most hardware-demanding part of this RNG design is the ADC [22]. The ADC overhead increases exponentially with the number of bits. The ADC bit length required for an RNG to pass the NIST test is directly related to the chaotic complexity of the map used. The stronger the chaotic property of the maps, the lower will be the ADC bit length that is required to ensure the adequate randomness of the RNG output to pass the NIST test. The design proposed in [22] required at least an 8-bit ADC to pass the NIST test. The proposed RNG design of this paper employed a 4-bit ADC, and still passed the NIST test. This improvement in the design indicates the promising chaotic properties of the proposed SPM topologies.
The simulation for the CMOS-based implementation was done in the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis)-class circuit simulator of Cadence, which is called Spectre, and a 45 nm CMOS process was used. There was no stochastic component added to the simulations: as a result, the simulation results were purely deterministic, which means that, given the same set of system parameters (C, , and so on), a chaotic oscillator will generate an identical chaotic sequence every time we run the simulation. Hence, the simulated number sequence from the proposed RNG is not truly random, because the simulation result is reproducible. This aperiodic but reproducible number sequence is called a pseudo-random sequence, and the circuit is called a pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) [52]. Our proposed RNG circuit is a PRNG in the simulation; however, in a physical chip, there will inevitably be cycle-to-cycle perturbations, such as the noise-driven drift of node voltages, power supply noise, temperature variation over the course of operation, and so on. These variations, even if they are small in amplitude, will eventually be amplified by the chaotic nature of the circuit, and the circuit response will not be deterministic anymore, making it close to a true random number generator (TRNG) in practice [60,72]. Apart from cycle-to-cycle run-time variation, the physical chip will be subjected to another type of variation, which is process variation. Due to process variations, the response from two different chips, even with the exact same design, will be different. The advantage of process variation is that we will get physically unclonable random number generators, and the effect of the variation will be amplified by the chaotic nature of the circuits [73]. On the other hand, the challenging part is to ensure that the circuit still remains in the chaotic region, as the location of the chaotic region in the bifurcation plot may shift from the simulation results, due to the process-driven variations [74,75].
8. Conclusions
In this work, we have presented a hardware-efficient scheme for developing robust chaotic systems. Unlike traditional schemes requiring more than one chaotic map, the proposed self-parameterization scheme provides a wide chaotic range, by using only one chaotic map. The general design methodology was presented, and is applicable to any 1-D chaotic map. The theoretical aspect of the reasoning behind how self-parameterization is widening the chaotic range was demonstrated in detail, with the help of a stability analysis. The self-parameterization idea was first realized in the case of three ideal mathematical chaotic systems. The digitization of the scheme was presented, to show its applicability to FPGA-based implementations. The proposed scheme was then implemented with full-custom CMOS circuits. It was demonstrated that self-parameterization can be realized in analog CMOS by using hardware-efficient topologies with minimal transistor count. The chaotic performance of the proposed scheme was analyzed with established chaotic entropy measures, to justify the performance improvement. An application of the proposed scheme was demonstrated in a random number generator, and the statistical randomness of the generated sequence was verified with the NIST test. Depending on the design requirement, both analog and digital designs are suitable for implementing entropy-generating blocks for hardware-security applications in hardware-constrained implementations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: P.S.P., A.D. and M.S.H.; investigation: M.S.; resources: M.R.H.; writing—original draft: P.S.P.; supervision: M.S.H. All the authors took part in reviewing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Partial support for this research was provided by the Woodrow W. Everett, Jr. SCEEE Development Fund, in cooperation with the Southeastern Association of Electrical Engineering Department Heads.
Data Availability Statement
Detailed design methodology and used design parameters are presented in the article. No additional data sharing is applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hirsch, M.W.; Smale, S.; Devaney, R.L. Differential Equations, Dynamical Systems, and an Introduction to Chaos; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Strogatz, S.H. Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: With Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Csernák, G.; Stépán, G. Digital control as source of chaotic behavior. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2010, 20, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poincaré, H. The Three-Body Problem and the Equations of Dynamics: Poincaré’s Foundational Work on Dynamical Systems Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 443. [Google Scholar]
- Muthuswamy, B.; Banerjee, S. A Route to Chaos Using FPGAs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, Y. Dynamic parameter-control chaotic system. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2015, 46, 3330–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hua, Z.; Pun, C.M.; Chen, C.P. Cascade chaotic system with applications. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 45, 2001–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shameri, W.F.H. Dynamical properties of the Hénon mapping. Int. J. Math. Anal. 2012, 6, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales, O.A.; Han, G.; De Gyvez, J.P.; Sánchez-Sinencio, E. Lorenz-based chaotic cryptosystem: A monolithic implementation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Fundam. Theory Appl. 2000, 47, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.S.; Hardy, P.; Sadia, M.; Hasan, M.S. A 2D Chaotic Oscillator for Analog IC. IEEE Open J. Circuits Syst. 2022, 3, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Pun, C.M.; Chen, C.P. 2D Sine Logistic modulation map for image encryption. Inf. Sci. 2015, 297, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y. 2D logistic-modulated-sine-coupling-logistic chaotic map for image encryption. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 14081–14098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, J. Chaos: Making a New Science; Penguin: Westminster, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Bao, L.; Chen, C.P. A new 1D chaotic system for image encryption. Signal Process. 2014, 97, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mowafy, M.; Gharghory, S.; Abo-Elsoud, M.; Obayya, M.; Allah, M.F. Chaos Based Encryption Technique for Compressed H264/AVC Videos. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 124002–124016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Fu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, L.; Tie, M.; Sham, C.W. Protection of image ROI using chaos-based encryption and DCNN-based object detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 5743–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrich, J. Image encryption based on chaotic maps. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. Computational Cybernetics and Simulation, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 October 1997; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 2, pp. 1105–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.I. A new chaotic key-based design for image encryption and decryption. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Geneva, Switzerland, 28–31 May 2000; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 4, pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhy, M.I.; Shehata, A.E. Chaotic algorithms for data encryption. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7–11 May 2001; Proceedings (Cat. No. 01CH37221). IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 997–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Jakimoski, G.; Kocarev, L. Analysis of some recently proposed chaos-based encryption algorithms. Phys. Lett. 2001, 291, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.S.; Sadia, M.; Hasan, M.S. Design of a Dynamic Parameter-Controlled Chaotic-PRNG in a 65 nm CMOS process. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 14th Dallas Circuits and Systems Conference (DCAS), Dallas, TX, USA, 15–16 November 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, R.; Bu, L.; Del Rosario, E.; Kinsy, M.A. Towards Programmable All-Digital True Random Number Generator. In Proceedings of the 2020 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, Virtual Event, 7–9 September 2020; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Patidar, V.; Sud, K.K.; Pareek, N.K. A pseudo random bit generator based on chaotic logistic map and its statistical testing. Informatica 2009, 33, 441–452. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, M.; Rhouma, R.; Belghith, S. A very efficient pseudo-random number generator based on chaotic maps and s-box tables. Int. Comput. Electr. Autom. Control Inf. Eng. 2015, 9, 481–485. [Google Scholar]
- Tutueva, A.V.; Butusov, D.N.; Pesterev, D.O.; Belkin, D.A.; Ryzhov, N.G. Novel normalization technique for chaotic Pseudo-random number generators based on semi-implicit ODE solvers. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference Quality Management, Transport and Information Security, Information Technologies (IT&QM&IS), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 24–30 September 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Nardo, L.G.; Nepomuceno, E.G.; Arias-Garcia, J.; Butusov, D.N. Image encryption using finite-precision error. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 123, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, H. Pseudo-random number generator based on logistic chaotic system. Entropy 2019, 21, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Bosque, M.; Pérez-Resa, A.; Sánchez-Azqueta, C.; Celma, S. A new randomness-enhancement method for chaos-based cryptosystem. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th Latin American Symposium on Circuits & Systems (LASCAS), Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 25–28 February 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Min, L.; Hu, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Study on pseudorandomness of some pseudorandom number generators with application. In Proceedings of the 2013 Ninth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Emeishan, China, 14–15 December 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Kia, B.; Jahed-Motiagh, M.R. A novel dynamically reconfigurable logic block based on chaos. Ifac Proc. Vol. 2006, 39, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshaghaghi, H.R.; Kia, B.; Ditto, W.; Jahed-Motlagh, M.R. Reconfigurable logic blocks based on a chaotic Chua circuit. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 41, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołofit, K.; Wieczorek, P.Z. Chaos-Based Physical Unclonable Functions. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Huang, C.; Cheng, H. Design, Implementation and Analysis of PUF Structure Based on Chaos. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering (CISCE), Vitural, 14–16 May 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Kalanadhabhatta, S.; Kumar, D.; Anumandla, K.K.; Reddy, S.A.; Acharyya, A. PUF-based secure chaotic random number generator design methodology. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (Vlsi) Syst. 2020, 28, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illuri, B.; Jose, D. Design and implementation of hybrid integration of cognitive learning and chaotic countermeasures for side channel attacks. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 5427–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohl, J.; Yan, L.K.; Rose, G.S. A two-dimensional chaotic logic gate for improved computer security. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 58th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2–5 August 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Popp, T.; Mangard, S.; Oswald, E. Power analysis attacks and countermeasures. IEEE Des. Test Comput. 2007, 24, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, Y. Exponential chaotic model for generating robust chaos. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 3713–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, E.; Grebogi, C.; Yorke, J.A. Controlling chaotic dynamical systems. In Chaos: Soviet-American Perspective on Nonlinear Science; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 1990; pp. 153–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zaher, A.A.; Abu-Rezq, A. On the design of chaos-based secure communication systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2011, 16, 3721–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kuang, J.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Lu, H.; Hu, G. Chaos-based secure communications in a large community. Phys. Rev. 2002, 66, 065202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, G.S. A chaos-based arithmetic logic unit and implications for obfuscation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Tampa, FL, USA, 9–11 July 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, S.; Mohd, B.J.; Hayajneh, T. Hardware security in IoT devices with emphasis on hardware Trojans. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2019, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Njilla, L. Hardware assisted chaos based iot authentication. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Banff, AL, Canada, 9–11May 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, B.; Raouf, S.M.; Abdelkader, S.; Camel, T.; Said, S.; Lei, H. An Efficient and Reliable Chaos-Based IoT Security Core for UDP/IP Wireless Communication. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 49625–49656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadeh, Y.E.H.; Hogrefe, D. A survey on secret key generation mechanisms on the physical layer in wireless networks. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2015, 8, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornaros, G. Hardware-assisted Machine Learning in Resource-constrained IoT Environments for Security: Review and Future Prospective. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 58603–58622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Gu, C.; Chang, C.H. PUF-based mutual authentication and key exchange protocol for peer-to-peer IoT applications. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Gutiérrez, A.J.; Castillo, E.; Escobar-Molero, A.; Alvarez-Bermejo, J.A.; Morales, D.P.; Parrilla, L. Integration of Hardware Security Modules and Permissioned Blockchain in Industrial IoT Networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 114331–114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phalak, K.; Ash-Saki, A.; Alam, M.; Topaloglu, R.O.; Ghosh, S. Quantum puf for security and trust in quantum computing. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2021, 11, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, L.; Tang, Q.; Cai, S.; Song, Y.; Xu, Q. A survey on true random number generators based on chaos. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2019, 2019, 2545123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Paul, P.S.; Dhungel, A.; Sadia, M.; Hossain, M.R. Design, Analysis, and Application of Flipped Product Chaotic System. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 125181–125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Ramírez, R.D.; Arellano-Delgado, A.; Murillo-Escobar, M.A.; Cruz-Hernández, C. A New 4D Hyperchaotic System and Its Analog and Digital Implementation. Electronics 2021, 10, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Hernandez, J.; Diaz-Mendez, A.; Vazquez-Medina, R.; Alejos-Palomares, R. Analog current-mode implementation of a logistic-map based chaos generator. In Proceedings of the 2009 52nd IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Cancun, Mexico, 2–5 August 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 812–814. [Google Scholar]
- Farfan-Pelaez, A.; Del-Moral-Hernández, E.; Navarro, J.; Van Noije, W. A CMOS Implementation of the Sine-circle Map. In Proceedings of the 48th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 7–10 August 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 1502–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Callegari, S.; Setti, G.; Langlois, P.J. A CMOS tailed tent map for the generation of uniformly distributed chaotic sequences. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Hong Kong, China, 9–12 1997; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 2, pp. 781–784. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, P.; Juncu, V. Compact discrete-time chaos generator circuit. Electron. Lett. 2003, 39, 1431–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, P.; Juncu, V. An area and power efficient discrete-time chaos generator circuit. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2005 European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design, Cork, UK, 29 August–1 September 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 2–87. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, P.S.; Sadia, M.; Hossain, M.R.; Muldrey, B.; Hasan, M.S. Cascading CMOS-Based Chaotic Maps for Improved Performance and Its Application in Efficient RNG Design. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 33758–33770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadia, M.; Paul, P.S.; Hossain, M.R.; Muldrey, B.; Hasan, M.S. Robust Chaos with Novel 4-Transistor Maps. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Paul, P.S.; Sadia, M.; Hossain, M.R. Integrated Circuit Design of an Improved Discrete Chaotic Map by Averaging Multiple Seed Maps. In Proceedings of the SoutheastCon 2021, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–13 March 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, P.S.; Dhungel, A.; Sadia, M.; Hossain, M.R.; Muldrey, B.; Hasan, M.S. Self-Parameterized Chaotic Map: A Hardware-efficient Scheme Providing Wide Chaotic Range. In Proceedings of the 2021 28th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems (ICECS), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 28 November–1 December 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zeraoulia, E. Robust Chaos and Its Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2012; Volume 79. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. Nonlinear Phenom. 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P.; Procaccia, I. Characterization of strange attractors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MathWorks. Approximate Entropy. 2022. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/predmaint/ref/approximateentropy.html (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- MathWorks. Characterize the Rate of Separation of Infinitesimally Close Trajectories. 2021. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/predmaint/ref/lyapunovexponent.html (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y. Sine chaotification model for enhancing chaos and its hardware implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Technical Report; Booz-allen and Hamilton inc Mclean va: McLean, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cicek, I.; Pusane, A.E.; Dundar, G. A novel design method for discrete time chaos based true random number generators. Integration 2014, 47, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanta, A.S.; Majumder, M.B.; Hasan, M.S.; Rose, G.S. Physically unclonable and reconfigurable computing system (purcs) for hardware security applications. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2020, 40, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncu, V.; Rafiei-Naeini, M.; Dudek, P. Integrated circuit implementation of a compact discrete-time chaos generator. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2006, 46, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, B.; Mobley, K.; Ditto, W.L. An integrated circuit design for a dynamics-based reconfigurable logic block. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 2017, 64, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).