How Reclamation Policy Shapes China’s Coastal Wetland Ecosystem Services
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
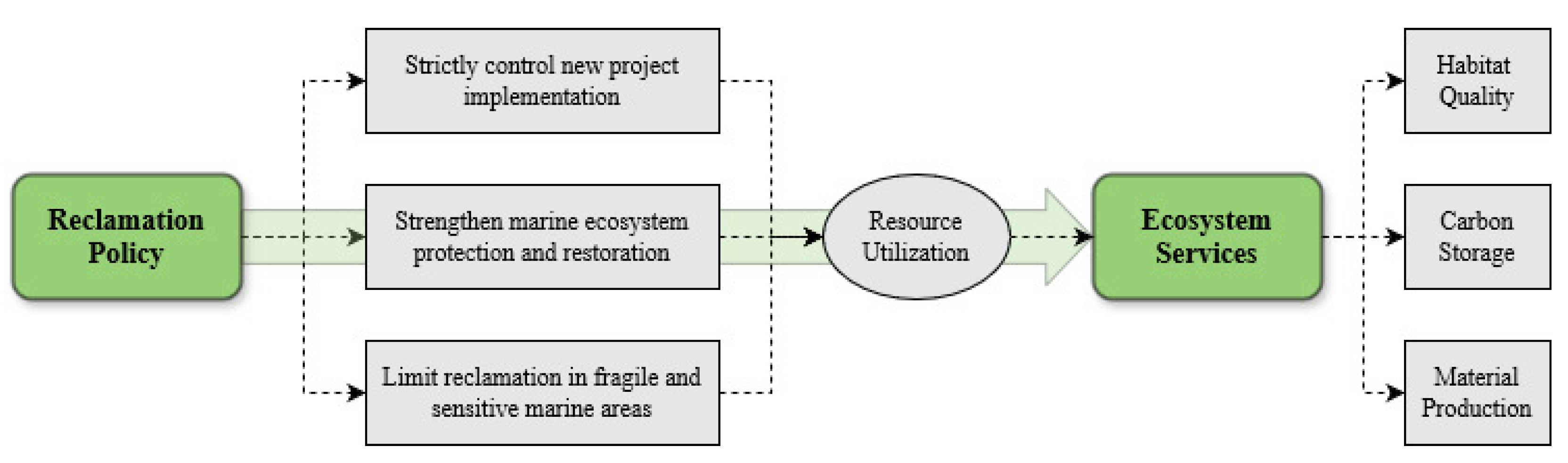
2.1. Theoretical Framework
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Data Source
2.4. Ecosystem Services Assessment
2.4.1. Habitat Quality
2.4.2. Carbon Storage
2.4.3. Material Production
2.4.4. Limitations of the InVEST Model
2.5. Method of Policy Impacts Evaluation
- Cut-off point 1 (): it corresponds to the implementation of stricter annual reclamation quota management, marking a significant initial tightening of supervision [9]. Operationally, we set the cut-off for the transition.
2.6. Variable Selection
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Ecosystem Services
3.2. Impacts of Reclamation Policies on the Ecosystem Services
3.3. Robustness Tests for Regression Discontinuity
4. Discussion
4.1. Policy Impacts on Ecosystem Services in Coastal Wetlands
4.2. Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chuai, X.W.; Huang, X.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Li, J.B.; Lu, Q.L.; Qi, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Zuo, T.H.; Lu, J.Y. Land use and ecosystems services value changes and ecological land management in coastal Jiangsu, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 57, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.-j.; Yue, Q. China’s coastal wetlands: Ecological challenges, restoration, and management suggestions. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 37, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. Chapter 27—The Value of Coastal Wetland Ecosystem Services. In Coastal Wetlands, 2nd ed.; Perillo, G.M.E., Wolanski, E., Cahoon, D.R., Hopkinson, C.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 947–964. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; Groot, R.d.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellemann, C.; Corcoran, E.; Duarte, C.; Valdes, L.; Young, C.; Fonseca, L.; Grimsditch, G. Blue Carbon—The Role of Healthy Oceans in Binding Carbon; UN Environment, GRID-Arendal: Arendal, Norway, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gedan, K.; Kirwan, M.; Wolanski, E.; Barbier, E.; Silliman, B. The Present and Future Role of Coastal Wetland Vegetation in Protecting Shorelines: Answering Recent Challenges to the Paradigm. Clim. Change 2010, 106, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.; Cristina, S.; Perillo, G.; Turner, R.; Ahsan, D.; Cragg, S.; Luo, Y.; Tu, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Anthropogenic, Direct Pressures on Coastal Wetlands. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ding, D.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Shen, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, C. Change of sea reclamation and the sea-use management policy system in China. Mar. Policy 2020, 115, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.J.; Phinn, S.R.; DeWitt, M.; Ferrari, R.; Johnston, R.; Lyons, M.B.; Clinton, N.; Thau, D.; Fuller, R.A. The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats. Nature 2019, 565, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Lin, C.; Jin, D.; Rao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y. Modeling the total allowable area for coastal reclamation: A case study of Xiamen, China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2013, 76, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennish, M. Environmental threats and environmental future of estuaries. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wu, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Drivers, trends, and potential impacts of long-term coastal reclamation in China from 1985 to 2010. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 170, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, B.; Cui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, T.; Wu, S. Economic and ecological trade-offs of coastal reclamation in the Hangzhou Bay, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Gu, D.; Zheng, W. Landscape pattern change and its cumulative environmental effects of coastal wetlands in southern Laizhou Bay. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 2437–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Melville, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Piersma, T.; Li, B. Rethinking China’s new great wall. Science 2014, 346, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Xu, X.; Zou, Z.; Chen, B.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, J.; Liu, D.; Pan, L.; et al. Rebound in China’s coastal wetlands following conservation and restoration. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H. Hydrodynamic changes due to coastal reclamation activities in Daya Bay. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2019, 22, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Pu, R.; Sun, C.; Cao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, P.; Wang, L.; Gong, H. Ecosystem service valuation of bays in East China Sea and its response to sea reclamation activities. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1095–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Xie, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Yan, J.; Yu, S.; Liu, K.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Z. Impact of Large-scale Reclamation on Coastal Wetlands and Implications for Ecological Restoration, Compensation, and Sustainable Exploitation Framework. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Hou, W.; Song, Y. Development Trend, Environmental and Ecological Impacts, and Policy Recommendations for Bohai Sea Reclamation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 3311–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Ecological problems and countermeasures caused by land reclamation. Ocean. Dev. Manag. 2013, 30, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, X. Comparative Studies: Coastal Reclamation Management between China and Abroad. J. Ocean. Univ. China (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 5, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Cheng, J.; Yi, W.; Liu, S.; Xie, Z. Transitions and suggestions for China’s coastal port reclamation policies. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2023, 236, 106532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Shi, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Z. Changes of ecosystem service value under the rapid urbanization in the coastal zone of Zhejiang Province. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2017, 36, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cao, K.; Feng, L. Integrative assessment and management implications on ecosystem services loss of coastal wetlands due to reclamation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S101–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Xue, X.; Shi, L.; Gao, L. Urban spatial expansion and its impacts on island ecosystem services and landscape pattern: A case study of the island city of Xiamen, Southeast China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2013, 81, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, P.J.; Pattanayak, S.K. Money for Nothing? A Call for Empirical Evaluation of Biodiversity Conservation Investments. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, S. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.; Bagstad, K.J.; Voigt, B.; Johnson, G.W.; Portela, R.; Honzák, M.; Batker, D. A Methodology for Adaptable and Robust Ecosystem Services Assessment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrouse, B.C.; Clement, J.M.; Semmens, D.J. A GIS application for assessing, mapping, and quantifying the social values of ecosystem services. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Douglass, J.; Wolny, S.; Arkema, K.; Bernhardt, J.; Bierbower, W.; Chaumont, N.; Denu, D.; Fisher, D.; Glowinski, K.; et al. InVEST 3.9.0 User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project; Stanford University; University of Minnesota; The Nature Conservancy; World Wildlife Fund: Standford, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Harms, M.; Balvanera, P. Methods for mapping ecosystem service supply: A review. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. 2012, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquete, C.; Piroddi, C.; Drakou, E.G.; Gurney, L.; Katsanevakis, S.; Charef, A.; Egoh, B. Current Status and Future Prospects for the Assessment of Marine and Coastal Ecosystem Services: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasky, S.; Nelson, E.; Pennington, D.; Johnson, K.A. The Impact of Land-Use Change on Ecosystem Services, Biodiversity and Returns to Landowners: A Case Study in the State of Minnesota. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2011, 48, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhead, J.W.; Stratford, C.; Sharps, K.; Jones, L.; Ziv, G.; Clarke, D.; Oliver, T.H.; Bullock, J.M. Empirical validation of the InVEST water yield ecosystem service model at a national scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerry, A.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Arkema, K.; Bernhardt, J.; Guannel, G.; Kim, C.-K.; Marsik, M.; Papenfus, M.; Toft, J.; Verutes, G.; et al. Modeling benefits from nature: Using ecosystem services to inform coastal and marine spatial planning. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2012, 8, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tussadiah, A.; Sujiwo, A.S.; Andesta, I.; Daeli, W. Assessment of coastal ecosystem services and its condition for policy management plan in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuepper, D.; Finger, R. Regression discontinuity designs in agricultural and environmental economics. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2023, 50, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbens, G.; Lemieux, T. Regression Discontinuity Design: A Guide to Practice. J. Econom. 2008, 142, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H. Regression Discontinuity Design: Theoretical Developments and Extended Applications. China J. Econ. 2022, 9, 325–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. Governing the Commons: The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, R.; He, Q.; Black, A.; Ghobadian, A.; Gallear, D. Environmental regulations, innovation and firm performance: A revisit of the Porter hypothesis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 155, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xiaohui, Z.; Luyao, M.; Zeng, X. How does environmental regulation promote firm performance? Evidence from Chinese environmentally friendly firms. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2025, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Zhuo, Y.; Wang, X. Evaluating the Performance of Ecological Conservation Red Line Based on Counterfactual Framework: A Case of Ningbo City. China Land Sci. 2023, 37, 128–140. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, W.; Xia, H.; Wu, T.; Xiong, J.; Zhong, P.; Chen, Y. Spatio-temporal evolution of habitat quality and ecological red line assessment in Zhejiang Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 6406–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Y. Study on the Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Habitat Quality and Its Terrain Gradient Effects of the Middle of the Yangtze River Economic Belt Based on InVEST Model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, K.; Sun, S.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J. Research on the Spatiotemporal Variation of Carbon Storage in the Coastal Zone of Liaoning Province Based on InVEST Model. Geoscience 2022, 36, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhong, C.; Wang, F.; Cheng, C.; Lv, X.; Chen, X. Spatial-temporal Evolution and Prediction of Ecosystem Carbon Stocks on Hainan Island by Coupling the InVEST and FLUS Models. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jin, Y.W.; Sun, T.; Yang, Z.F.; Cai, Y.P.; Yi, Y.J. Trade-offs among ecosystem services in coastal wetlands under the effects of reclamation activities. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S. Randomized experiments from non-random selection in US House elections. J. Econom. 2008, 142, 675–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yin, X.; Shao, M. Natural and anthropogenic factors on China’s ecosystem services: Comparison and spillover effect perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Liang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ni, X.; Luan, Q. Net Effect and Mechanism Analysis of Hainan International Tourism Island Construction on Urban Construction Land Expansion. China Land Sci. 2022, 36, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Q.; Song, Y. Does China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt policy impact on local ecosystem services? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Güneralp, B.; Kreuter, U.P.; Güneralp, İ.; Filippi, A.M. Spatial and temporal changes in biodiversity and ecosystem services in the San Antonio River Basin, Texas, from 1984 to 2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Lin, N.; Cao, B.; Ye, X.; Pang, B.; Du, W.; Dou, H.; Zou, C.; Xu, C.; Xu, D.; et al. Assessing the effectiveness of Ecological Conservation Red Line for mitigating anthropogenic habitat degradation in river corridors. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L. The evolution of habitat quality and its response to land use change in the coastal China, 1985–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedler, J.; Kercher, S. Wetland Resources: Status, Trends, Ecosystem Services, and Restorability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 15, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, C. Freshwater input structures soil properties, vertical accretion, and nutrient accumulation of Georgia and U.S tidal marshes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.; Buckley, B. “A Strikingly Rich Zone”: Nutrient Enrichment and Secondary Production in Coastal Marine Ecosystems. Estuaries 2002, 25, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooij, B.v. The People’s Regulation: Citizens and Implementation of Law in China. Columbia J. Asian Law 2012, 25, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Threat | Max_dist (km) | Weight | Decay | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | 0.5 | 0.2 | Linear | Based on [47,48,49]. |
| Construction Land | 0.2 | 0.5 | Exponential |
| LULC | Habitat | Threats | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | Construction Land | |||
| Farmland | 7.74 | 57.83 | 1.32 | Based on [47,48,49]. |
| Forest | 28.38 | 95.35 | 2.15 | |
| Grassland | 14.29 | 75.7 | 8.46 | |
| Wetland | 20.75 | 160.42 | 2.65 | |
| Construction Land | 0.00 | 20.78 | 0.00 | |
| Unused Land | 1.82 | 15.88 | 0.00 | |
| Sea | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| LULC | C_Above | C_Below | C_Soil | C_Dead | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | 7.74 | 5.26 | 57.83 | 1.32 | Based on [50,51]. |
| Forest | 28.38 | 10.82 | 95.35 | 2.15 | |
| Grassland | 14.29 | 15.19 | 75.7 | 8.46 | |
| Wetland | 20.75 | 13.6 | 160.42 | 2.65 | |
| Construction Land | 0.00 | 0.00 | 20.78 | 0.00 | |
| Unused Land | 1.82 | 0.00 | 15.88 | 0.00 | |
| Sea | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| HQ | CS | MP | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2017 | 2011 | 2017 | 2011 | 2017 | ||||||
| Yi,t | ΔYi,t | Yi,t | ΔYi,t | Yi,t | ΔYi,t | Yi,t | ΔYi,t | Yi,t | ΔYi,t | Yi,t | ΔYi,t |
| 0.001 (0.44) | 0.375 *** (3.19) | −0.001 (−0.41) | −0.172 *** (−3.57) | 0.002 (0.42) | 9.111 *** (3.23) | 0.003 (0.82) | 1.798 ** (2.42) | 0.003 (0.65) | 1.166 ** (2.12) | 0.002 (0.27) | 0.872 *** (3.76) |
| Item | Outcome Variable | Break Point | Methods | Coef. of Di,t | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ | ΔYi,t | 2011 | Replacement bandwidth | 0.75 | 0.122 * (1.86) |
| 1.25 | 0.375 *** (3.20) | ||||
| Replacement kernel function | Rectangle | 0.271 *** (3.37) | |||
| Replacement breakpoint | 2010 | −0.173 ** (−2.48) | |||
| 2012 | −0.046 (−0.50) | ||||
| 2017 | Replacement bandwidth | 0.75 | −0.033 (−1.01) | ||
| 1.25 | −0.163 *** (−3.37) | ||||
| Replacement kernel function | Rectangle | −0.187*** (−3.84) | |||
| Replacement breakpoint | 2016 | 0.074 * (1.94) | |||
| 2018 | −0.207 *** (−3.06) | ||||
| CS | 2011 | Replacement bandwidth | 0.75 | 3.437 ** (2.23) | |
| 1.25 | 9.086*** (3.24) | ||||
| Replacement kernel function | Rectangle | 6.834 *** (3.57) | |||
| Replacement breakpoint | 2010 | −4.116 *** (−2.94) | |||
| 2012 | −1.845 (−0.88) | ||||
| 2017 | Replacement bandwidth | 0.75 | 1.798 ** (2.42) | ||
| 1.25 | 0.000 (.) | ||||
| Replacement kernel function | Rectangle | −1.005 (−1.14) | |||
| Replacement breakpoint | 2016 | 1.942 *** (5.27) | |||
| 2018 | −5.717 *** (−6.11) | ||||
| MP | 2011 | Replacement bandwidth | 0.75 | 0.891 (1.29) | |
| 1.25 | 1.327 *** (2.82) | ||||
| Replacement kernel function | Rectangle | 1.191 *** (3.22) | |||
| Replacement breakpoint | 2010 | 0.880 * (1.90) | |||
| 2012 | −1.995 ** (−2.57) | ||||
| 2017 | Replacement bandwidth | 0.75 | 0.518 *** (2.81) | ||
| 1.25 | 0.670 ** (2.36) | ||||
| Replacement kernel function | Rectangle | 0.640 ** (2.25) | |||
| Replacement breakpoint | 2016 | 0.564 * (1.66) | |||
| 2018 | −0.730 * (−1.94) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuo, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.; Li, G. How Reclamation Policy Shapes China’s Coastal Wetland Ecosystem Services. Systems 2025, 13, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13060431
Zhuo Y, Li T, Xu Z, Li G. How Reclamation Policy Shapes China’s Coastal Wetland Ecosystem Services. Systems. 2025; 13(6):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13060431
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuo, Yuefei, Tiantian Li, Zhongguo Xu, and Guan Li. 2025. "How Reclamation Policy Shapes China’s Coastal Wetland Ecosystem Services" Systems 13, no. 6: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13060431
APA StyleZhuo, Y., Li, T., Xu, Z., & Li, G. (2025). How Reclamation Policy Shapes China’s Coastal Wetland Ecosystem Services. Systems, 13(6), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13060431






