Fish Immunoglobulins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
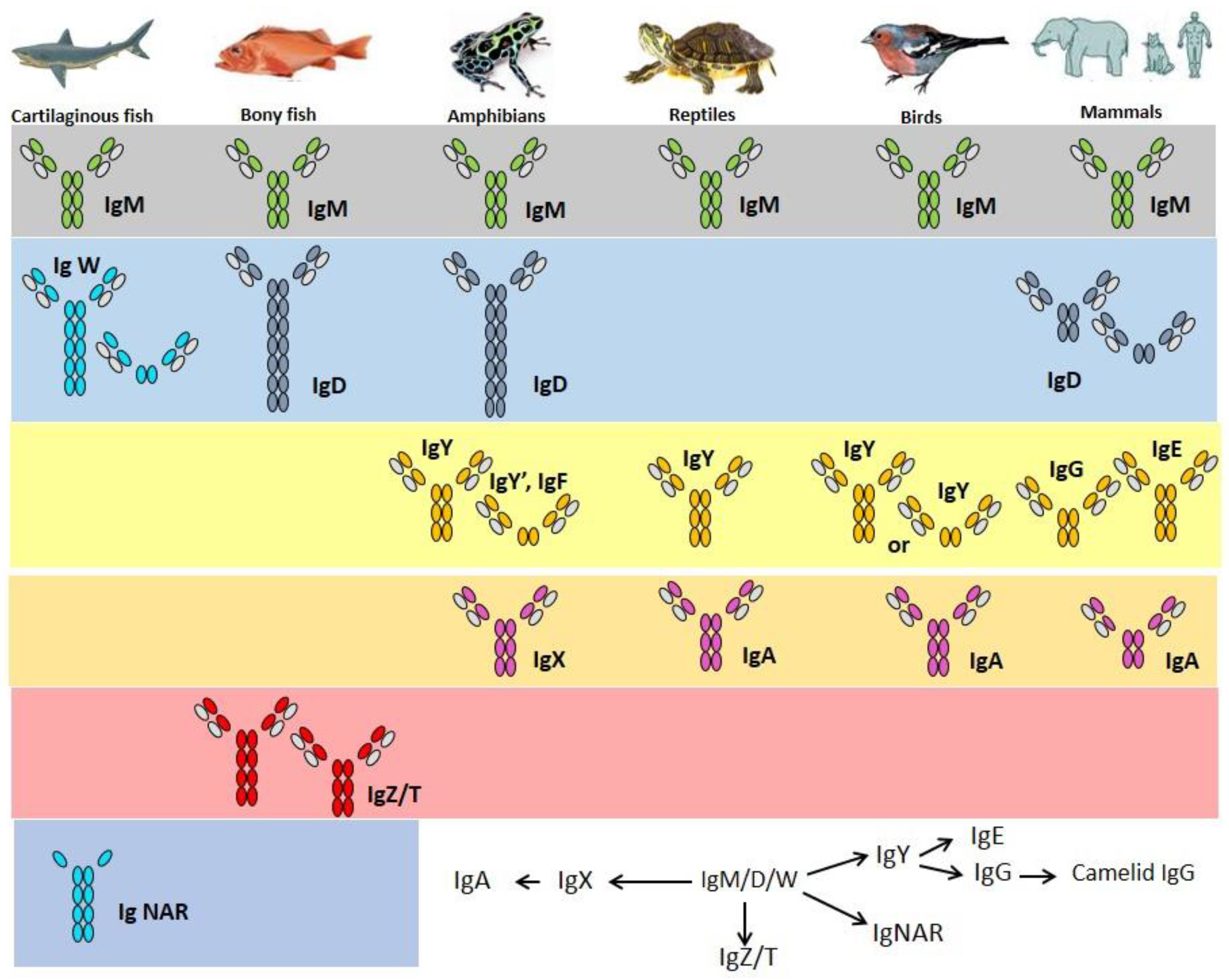
2. Immunoglobulins
3. Cartilaginous Fish IgH
3.1. IgM
3.2. IgW
3.3. IgNAR
4. Bony Fish IgH
4.1. IgM
4.2. IgD
4.3. IgT/Z
5. Fish IgL
5.1. Cartilaginous Fish IgL
5.2. Teleost Fish IgL
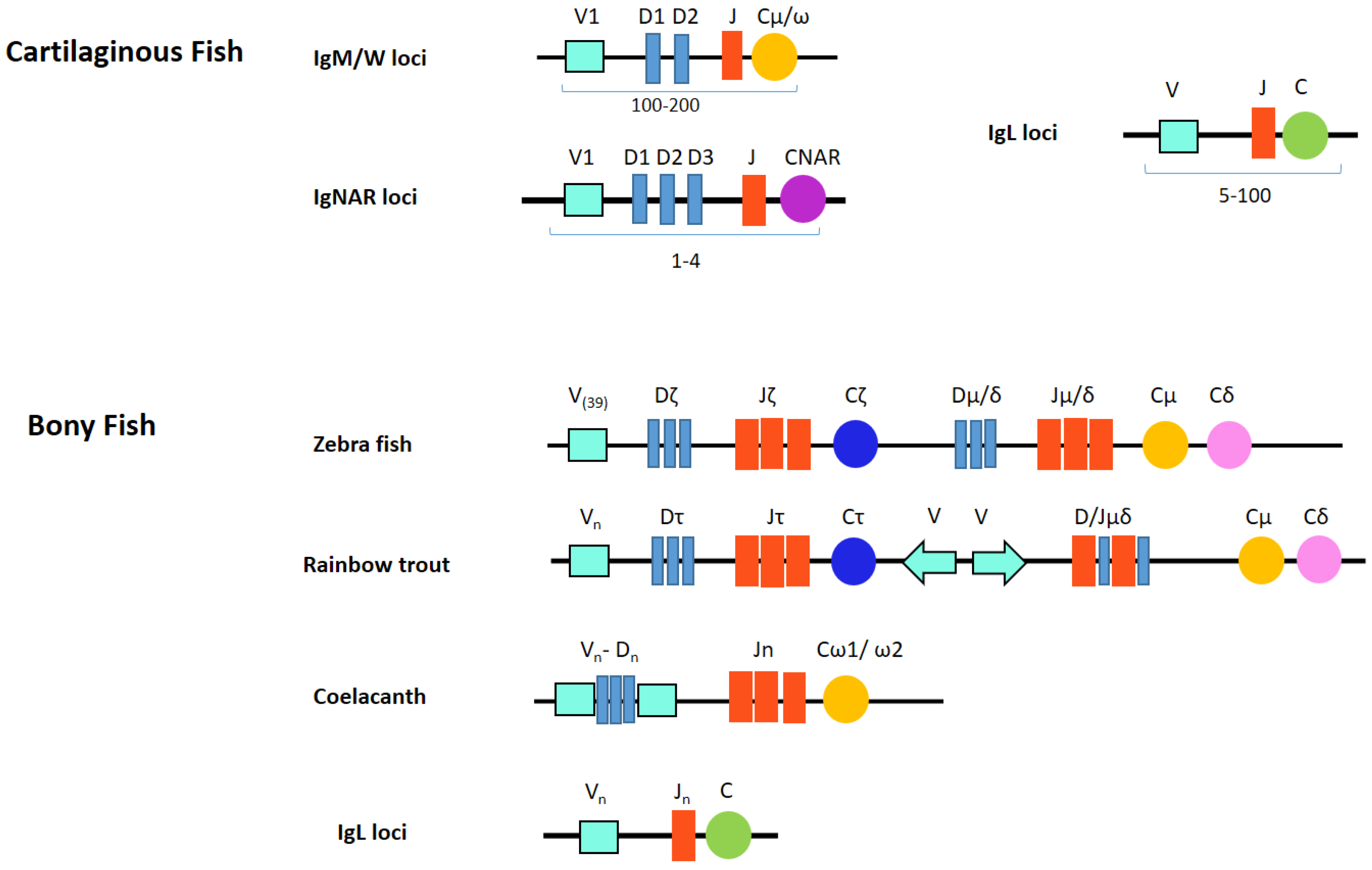
6. Fish Ig Locus Organization
6.1. Cartilaginous Fish Ig Locus Organization
6.2. Bony Fish Ig Locus Organization
7. Fish Ig Repertoire Analysis
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCR | B cell receptor |
| CDR | complementarity determining region |
| CH | constant heavy |
| CL | constant light |
| D | diversity |
| Fab | fragment antigen-binding |
| Fc | fragment crystallizable |
| GALT | gut associated lymphoid tissue |
| Ig | immunoglobulin |
| IgH | immunoglobulin heavy chain |
| IgL | immunoglobulin light chain |
| IgSF | immunoglobulin superfamily |
| J | joining |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| MYA | million years ago |
| N | non-template |
| P | palindromic |
| RAG | recombination activating gene |
| SALT | skin associated lymphoid tissue |
| Sec | secreted |
| SHM | somatic hypermutation |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| TdT | terminal nucleotidyl transferase |
| Tm | transmembrane |
| V | variable |
| VH | variable heavy |
| VL | variable light |
| VLR | variable lymphocyte receptor |
References
- Rauta, P.R.; Nayak, B.N.; Das, S. Immune system and immune responses in fish and their role in comparativeimmunity study: A model for higher organisms. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 148, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa, S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 1983, 302, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litman, G.W.; Rast, J.P.; Fugmann, S.D. The origins of vertebrate adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warr, G.W. The adaptive immune system of fish. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1997, 90, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sunyer, J.O. Fishing for mammalian paradigms in the teleost immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, A.; Amemiya, C.T. Phylogeny of lower vertebrates and their immunological structures. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 248, 67–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.F.; Barclay, A.N. The immunoglobulin superfamily—Domains for cell surface recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1988, 6, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, C.; Folch, H.; Enriquez, R.; Moran, G. Innate and adaptive immunity in teleost fish: A review. Vet. Med. 2011, 56, 486–503. [Google Scholar]
- Behring, E.; Kitasato, S. Uber das zustandekommen der diphtherie- immunitat und der Tetanus-immunitat bei thieren. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr 1890, 49, 1113–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Janeway, C.A.; Travers, P., Jr.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. Immunobiology; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.K.; Lichtman, A.H.; Pillai, S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 6th ed.; Saunders/Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; p. 566. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, H.W., Jr.; Cavacini, L. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125 (Suppl. S2), S41–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.P.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Janeway, C. Janeway’s Immunobiology, 7th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 887. [Google Scholar]
- Janeway, C. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease, 6th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 823. [Google Scholar]
- Solem, S.T.; Stenvik, J. Antibody repertoire development in teleosts—A review with emphasis on salmonids and Gadus morhua L. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombout, J.H.; Yang, G.; Kiron, V. Adaptive immune responses at mucosal surfaces of teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancer, Z.; Amemiya, C.T.; Ehrhardt, G.R.; Ceitlin, J.; Gartland, G.L.; Cooper, M.D. Somatic diversification of variable lymphocyte receptors in the agnathan sea lamprey. Nature 2004, 430, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Hirano, M.; Herrin, B.R.; Li, J.; Yu, C.; Sadlonova, A.; Cooper, M.D. Dual nature of the adaptive immune system in lampreys. Nature 2009, 459, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogozin, I.B.; Iyer, L.M.; Liang, L.; Glazko, G.V.; Liston, V.G.; Pavlov, Y.I.; Aravind, L.; Pancer, Z. Evolution and diversification of lamprey antigen receptors: Evidence for involvement of an AID-APOBEC family cytosine deaminase. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrin, B.R.; Cooper, M.D. Alternative adaptive immunity in jawless vertebrates. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, H.; Herrin, B.R.; Alder, M.N.; Catera, R.; Yan, X.J.; Chiorazzi, N.; Cooper, M.D. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia monitoring with a lamprey idiotope-specific antibody. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, J.G.; Miya, M.; Lam, K.; Tay, B.H.; Danks, J.A.; Bell, J.; Walker, T.I.; Venkatesh, B. Evolutionary origin and phylogeny of the modern holocephalans (Chondrichthyes: Chimaeriformes): A mitogenomic perspective. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clem, L.W.; Small, P.A., Jr. Phylogeny of immunoglobulin structure and function. I. Immunoglobulins of the lemon shark. J. Exp. Med. 1967, 125, 893–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, H.; Flajnik, M.F. Antibody repertoire development in cartilaginous fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettinello, R.; Dooley, H. The immunoglobulins of cold-blooded vertebrates. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 1045–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miracle, A.L.; Anderson, M.K.; Litman, R.T.; Walsh, C.J.; Luer, C.A.; Rothenberg, E.V.; Litman, G.W. Complex expression patterns of lymphocyte-specific genes during the development of cartilaginous fish implicate unique lymphoid tissues in generating an immune repertoire. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumfelt, L.L.; Lohr, R.L.; Dooley, H.; Flajnik, M.F. Diversity and repertoire of IgW and IgM VH families in the newborn nurse shark. BMC Immunol. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, Y.; Flajnik, M. IgD, like IgM, is a primordial immunoglobulin class perpetuated in most jawed vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10723–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchalonis, J.; Edelman, G.M. Polypeptide Chaini of Immunoglobulins from the Smooth Dogfish (Mustelus canis). Science 1966, 154, 1567–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flajnik, M.F. Comparative analyses of immunoglobulin genes: Surprises and portents. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonocore, F.; Gerdol, M. Alternative adaptive immunity strategies: Coelacanth, cod and shark immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 69, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumfelt, L.L.; Avila, D.; Diaz, M.; Bartl, S.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. A shark antibody heavy chain encoded by a nonsomatically rearranged VDJ is preferentially expressed in early development and is convergent with mammalian IgG. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.; Huang, J.L.; Lui, M.F.; Malecek, K.; Ohta, Y.; Mooers, A.; Hsu, E. The evolution of multiple isotypic IgM heavy chain genes in the shark. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7461–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumfelt, L.L.; McKinney, E.C.; Taylor, E.; Flajnik, M.F. The development of primary and secondary lymphoid tissues in the nurse shark Ginglymostoma cirratum: B-cell zones precede dendritic cell immigration and T-cell zone formation during ontogeny of the spleen. Scand. J. Immunol. 2002, 56, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, E.W., Jr.; Sigel, M.M. Distribution of 19S and 7S IgM antibodies during the immune response in the nurse shark. J. Immunol. 1971, 106, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leslie, G.A.; Clem, L.W. Reactivity of normal shark immunoglobulins with nitrophenyl ligands. J. Immunol. 1970, 105, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dooley, H.; Flajnik, M.F. Shark immunity bites back: Affinity maturation and memory response in the nurse shark, Ginglymostoma cirratum. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Bromage, E.S.; Kaattari, S.L. The strength of B cell interaction with antigen determines the degree of IgM polymerization. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohman, V.S.; Stewart, S.E.; Rumfelt, L.L.; Greenberg, A.S.; Avila, D.W.; Flajnik, M.F.; Steiner, L.A. J chain in the nurse shark: Implications for function in a lower vertebrate. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 6016–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, Y.; Kondo, H.; Caipang, C.M.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T. cDNA cloning of the immunoglobulin heavy chain genes in banded houndshark Triakis scyllium. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellows, F.C.I.; Hird, F.J.R. Fatty acid binding proteins in the serum of various animals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1981, 68, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. IgM-mediated opsonization and cytotoxicity in the shark. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1997, 61, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.L.; Sim, R.B.; Flajnik, M.F. Immunobiology of the Shark; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 307. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, K.; Tomonaga, S.; Kajii, T. A second class of immunoglobulin other than IgM present in the serum of a cartilaginous fish, the skate, Raja kenojei: Isolation and characterization. Mol. Immunol. 1984, 21, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harding, F.A.; Amemiya, C.T.; Litman, R.T.; Cohen, N.; Litman, G.W. Two distinct immunoglobulin heavy chain isotypes in a primitive, cartilaginous fish, Raja erinacea. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6369–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.K.; Strong, S.J.; Litman, R.T.; Luer, C.A.; Amemiya, C.T.; Rast, J.P.; Litman, G.W. A long form of the skate IgX gene exhibits a striking resemblance to the new shark IgW and IgNARC genes. Immunogenetics 1999, 49, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berstein, R.M.; Schluter, S.F.; Shen, S.; Marchalonis, J.J. A new high molecular weight immunoglobulin class from the carcharhine shark: Implications for the properties of the primordial immunoglobulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3289–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Hughes, A.L.; Guo, J.; Avila, D.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. A novel “chimeric” antibody class in cartilaginous fish: IgM may not be the primordial immunoglobulin. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemiya, C.T.; Alfoldi, J.; Lee, A.P.; Fan, S.; Philippe, H.; Maccallum, I.; Braasch, I.; Manousaki, T.; Schneider, I.; Rohner, N.; et al. The African coelacanth genome provides insights into tetrapod evolution. Nature 2013, 496, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, N.R.; Ota, T.; Litman, G.W.; Hansen, J.; Parra, Z.; Hsu, E.; Buonocore, F.; Canapa, A.; Cheng, J.F.; Amemiya, C.T. Genome complexity in the coelacanth is reflected in its adaptive immune system. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2014, 322, 438–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.E.; Crouch, K.; Cao, W.; Muller, M.R.; Wu, L.; Steven, J.; Lee, M.; Liang, M.; Flajnik, M.F.; Shih, H.H.; et al. Characterization of the immunoglobulin repertoire of the spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Tacchi, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Salinas, I. Intraclass diversification of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes in the African lungfish. Immunogenetics 2014, 66, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumfelt, L.L.; Diaz, M.; Lohr, R.L.; Mochon, E.; Flajnik, M.F. Unprecedented multiplicity of Ig transmembrane and secretory mRNA forms in the cartilaginous fish. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, T.; Rast, J.P.; Litman, G.W.; Amemiya, C.T. Lineage-restricted retention of a primitive immunoglobulin heavy chain isotype within the Dipnoi reveals an evolutionary paradox. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2501–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengten, E.; Wilson, M. Antibody repertoires in fish. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2015, 57, 193–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Ohta, Y.; Saltis, M.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. Evolutionarily conserved TCR binding sites, identification of T cells in primary lymphoid tissues, and surprising trans-rearrangements in nurse shark. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 6950–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Avila, D.; Hughes, M.; Hughes, A.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. A new antigen receptor gene family that undergoes rearrangement and extensive somatic diversification in sharks. Nature 1995, 374, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielonka, S.; Empting, M.; Grzeschik, J.; Konning, D.; Barelle, C.J.; Kolmar, H. Structural insights and biomedical potential of IgNAR scaffolds from sharks. mAbs 2015, 7, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, K.H.; Greenberg, A.S.; Greene, L.; Strelets, L.; Avila, D.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. Structural analysis of the nurse shark (new) antigen receptor (NAR): Molecular convergence of NAR and unusual mammalian immunoglobulins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11804–11809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, M.; Stanfield, R.L.; Greenberg, A.S.; Flajnik, M.F. Structural analysis, selection, and ontogeny of the shark new antigen receptor (IgNAR): Identification of a new locus preferentially expressed in early development. Immunogenetics 2002, 54, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Flajnik, M.F. Somatic hypermutation of the new antigen receptor gene (NAR) in the nurse shark does not generate the repertoire: Possible role in antigen-driven reactions in the absence of germinal centers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14343–14348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, S.D. Overview and discovery of IgNARs and generation of VNARs. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 911, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, O.V.; Olland, A.; Piche-Nicholas, N.; Godbole, A.; King, D.; Svenson, K.; Calabro, V.; Muller, M.R.; Barelle, C.J.; Somers, W.; et al. Atypical antigen recognition mode of a shark immunoglobulin new antigen receptor (IgNAR) variable domain characterized by humanization and structural analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17408–17419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krah, S.; Schroter, C.; Zielonka, S.; Empting, M.; Valldorf, B.; Kolmar, H. Single-domain antibodies for biomedical applications. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 38, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Los Rios, M.; Criscitiello, M.F.; Smider, V.V. Structural and genetic diversity in antibody repertoires from diverse species. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 33, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ekiert, D.C.; Ahmad, I.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bazirgan, O.; Torkamani, A.; Raudsepp, T.; Mwangi, W.; Criscitiello, M.F.; et al. Reshaping antibody diversity. Cell 2013, 153, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streltsov, V.A.; Varghese, J.N.; Carmichael, J.A.; Irving, R.A.; Hudson, P.J.; Nuttall, S.D. Structural evidence for evolution of shark Ig new antigen receptor variable domain antibodies from a cell-surface receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12444–12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feige, M.J.; Grawert, M.A.; Marcinowski, M.; Hennig, J.; Behnke, J.; Auslander, D.; Herold, E.M.; Peschek, J.; Castro, C.D.; Flajnik, M.; et al. The structural analysis of shark IgNAR antibodies reveals evolutionary principles of immunoglobulins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8155–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.P.; Abregu, F.A.; Krishnan, U.V.; Proll, D.F.; Streltsov, V.A.; Doughty, L.; Hattarki, M.K.; Nuttall, S.D. Dimerisation strategies for shark IgNAR single domain antibody fragments. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 315, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, E. Assembly and expression of shark Ig genes. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3517–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, C.D.; Ohta, Y.; Dooley, H.; Flajnik, M.F. Noncoordinate expression of J-chain and Blimp-1 define nurse shark plasma cell populations during ontogeny. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 3061–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.R.; Saunders, K.; Grace, C.; Jin, M.; Piche-Nicholas, N.; Steven, J.; O'Dwyer, R.; Wu, L.; Khetemenee, L.; Vugmeyster, Y.; et al. Improving the pharmacokinetic properties of biologics by fusion to an anti-HSA shark VNAR domain. mAbs 2012, 4, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovaleva, M.; Ferguson, L.; Steven, J.; Porter, A.; Barelle, C. Shark variable new antigen receptor biologics—A novel technology platform for therapeutic drug development. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2014, 14, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho-Villegas, T.; Mata-Gonzalez, T.; Paniagua-Solis, J.; Sanchez, E.; Licea, A. Human TNF cytokine neutralization with a vNAR from Heterodontus francisci shark: A potential therapeutic use. mAbs 2013, 5, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaink, H.P.; Jansen, H.J.; Dirks, R.P. Advances in genomics of bony fish. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2014, 13, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillatreau, S.; Six, A.; Magadan, S.; Castro, R.; Sunyer, J.O.; Boudinot, P. The astonishing diversity of Ig classes and B cell repertoires in teleost fish. Front. Immunol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flajnik, M.F.; Kasahara, M. Origin and evolution of the adaptive immune system: Genetic events and selective pressures. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombout, J.W.; Blok, L.J.; Lamers, C.H.; Egberts, E. Immunization of carp (Cyprinus carpio) with a Vibrio anguillarum bacterin: Indications for a common mucosal immune system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1986, 10, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, C.J.; Clem, L.W. The metabolic relationships of the immunoglobulins in fish serum, cutaneous mucus, and bile. J. Immunol. 1981, 127, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morrison, R.N.; Nowak, B.F. The antibody response of teleost fish. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet Med. 2002, 11, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Bengten, E.; Miller, N.W.; Clem, L.W.; Du Pasquier, L.; Warr, G.W. A novel chimeric Ig heavy chain from a teleost fish shares similarities to IgD. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4593–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, M.; Edholm, E.S.; Stafford, J.L.; Bengten, E.; Miller, N.W.; Wilson, M. B cell receptor accessory molecules in the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clem, L.W. Phylogeny of immunoglobulin structure and function. IV. Immunoglobulins of the giant grouper, Epinephelus itaira. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lobb, C.J.; Clem, L.W. Phylogeny of immunoglobulin in structure and function-X. Humoral immunoglobulins of the sheepshead, Archosargus probatocephalus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1981, 5, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, C.J.; Clem, L.W. Phylogeny of immunoglobulin structure and function. XI. Secretory immunoglobulins in the cutaneous mucus of the sheepshead, Archosargus probatocephalus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1981, 5, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcombe, B.M.; Chang, R.J.; Taves, C.J.; Winkelhake, J.L. Evolution of antibody structure and effector functions: Comparative hemolytic activities of monomeric and tetrameric IgM from rainbow trout, Salmo gairdnerii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1985, 80, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, M. Role of natural and immune IgM antibodies in immune responses. Mol. Immunol. 2000, 37, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Kaattari, I.M.; Ma, C.; Kaattari, S. The teleost humoral immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaattari, S.; Evans, D.; Klemer, J. Varied redox forms of teleost IgM: An alternative to isotypic diversity? Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleteiro, M.C.; Richards, R.H. Identification of lymphocytes in the epidermis of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. Fish Dis. 1985, 8, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshra, H.; Gelman, A.E.; Sunyer, J.O. Structural and functional characterization of complement C4 and C1s-like molecules in teleost fish: Insights into the evolution of classical and alternative pathways. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, N.R. The classical complement pathway: Activation and regulation of the first complement component. Adv. Immunol. 1985, 37, 151–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pohlenz, C.; Buentello, A.; Criscitiello, M.F.; Mwangi, W.; Smith, R.; Gatlin, D.M., 3rd. Synergies between vaccination and dietary arginine and glutamine supplementation improve the immune response of channel catfish against Edwardsiella ictaluri. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Bromage, E.; Kaattari, I.; Kaattari, S. Transduction of binding affinity by B lymphocytes: A new dimension in immunological regulation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, K.D.; Jones, D.R.; Raison, R.L. Antibody-antigen kinetics following immunization of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) with a T-cell dependent antigen. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2002, 26, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaattari, S.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Khor, I.W.; Kaattari, I.M.; Shapiro, D.A. Affinity maturation in trout: Clonal dominance of high affinity antibodies late in the immune response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2002, 26, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, H.; Chen, L.; Deiss, T.C.; Jacobs, N.; Nabity, M.B.; Young, M.H.; Criscitiello, M.F. DNP-KLH yields changes in Leukocyte populations and immunoglobulin isotype use with different immunization routes in Zebrafish. Front. Immunol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hordvik, I.; Voie, A.M.; Glette, J.; Male, R.; Endresen, C. Cloning and sequence analysis of two isotypic IgM heavy chain genes from Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 2957–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, D.S.; Fahey, J.L. A new class of human immunoglobulins. I. A unique myeloma protein. J. Exp. Med. 1965, 121, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, D.S.; Fahey, J.L. A new class of human immunoglobulins. II. Normal serum Igd. J. Exp. Med. 1965, 121, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Xu, W.; Wilson, M.; He, B.; Miller, N.W.; Bengten, E.; Edholm, E.S.; Santini, P.A.; Rath, P.; Chiu, A.; et al. Immunoglobulin D enhances immune surveillance by activating antimicrobial, proinflammatory and B cell-stimulating programs in basophils. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Rabbani, H.; Shimizu, A.; Hammarstrom, L. Mapping of the chicken immunoglobulin heavy-chain constant region gene locus reveals an inverted alpha gene upstream of a condensed upsilon gene. Immunology 2000, 101, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, M.L.; Middleton, D.L.; Hazard, S.; Warr, G.W. The immunoglobulin heavy chain locus of the duck. Genomic organization and expression of D, J, and C region genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 46729–46736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, M.; Wei, Z.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y.; Hu, X.; Ren, L.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, R.; Guo, Y.; et al. Analysis of immunoglobulin transcripts in the ostrich Struthio camelus, a primitive avian species. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Olp, J.J.; Miller, R.D. On the genomics of immunoglobulins in the gray, short-tailed opossum Monodelphis domestica. Immunogenetics 2009, 61, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Bao, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y. A preliminary analysis of the immunoglobulin genes in the African elephant (Loxodonta africana). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edholm, E.S.; Bengten, E.; Wilson, M. Insights into the function of IgD. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Gomez, F.; Greene, W.; Rego, K.; Hansen, J.D.; Costa, G.; Kataria, P.; Bromage, E.S. Discovery and characterization of secretory IgD in rainbow trout: Secretory IgD is produced through a novel splicing mechanism. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashoof, S.; Goodroe, A.; Du, C.C.; Eubanks, J.O.; Jacobs, N.; Steiner, J.M.; Tizard, I.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Criscitiello, M.F. Ancient T-independence of mucosal IgX/A: Gut microbiota unaffected by larval thymectomy in Xenopus laevis. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengten, E.; Quiniou, S.M.; Stuge, T.B.; Katagiri, T.; Miller, N.W.; Clem, L.W.; Warr, G.W.; Wilson, M. The IgH locus of the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, contains multiple constant region gene sequences: Different genes encode heavy chains of membrane and secreted IgD. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 2488–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hordvik, I.; Thevarajan, J.; Samdal, I.; Bastani, N.; Krossoy, B. Molecular cloning and phylogenetic analysis of the Atlantic salmon immunoglobulin D gene. Scand. J. Immunol. 1999, 50, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvik, J.; Jorgensen, T.O. Immunoglobulin D (IgD) of Atlantic cod has a unique structure. Immunogenetics 2000, 51, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, S.; Chapman, J.; Stupka, E.; Putnam, N.; Chia, J.M.; Dehal, P.; Christoffels, A.; Rash, S.; Hoon, S.; Smit, A.; et al. Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 2002, 297, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisapoome, P.; Ohira, T.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T. Genes of the constant regions of functional immunoglobulin heavy chain of Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Immunogenetics 2004, 56, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.S.; Wang, Y.P.; Yan, W.; Chang, M.X.; Yao, W.J.; Xu, Q.Q.; Wang, X.X.; Gao, Q.; Nie, P. Ig heavy chain genes and their locus in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambon-Deza, F.; Sanchez-Espinel, C.; Magadan-Mompo, S. Presence of an unique IgT on the IGH locus in three-spined stickleback fish (Gasterosteus aculeatus) and the very recent generation of a repertoire of VH genes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.D.; Landis, E.D.; Phillips, R.B. Discovery of a unique Ig heavy-chain isotype (IgT) in rainbow trout: Implications for a distinctive B cell developmental pathway in teleost fish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6919–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilova, N.; Bussmann, J.; Jekosch, K.; Steiner, L.A. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus in zebrafish: Identification and expression of a previously unknown isotype, immunoglobulin Z. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savan, R.; Aman, A.; Sato, K.; Yamaguchi, R.; Sakai, M. Discovery of a new class of immunoglobulin heavy chain from fugu. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 3320–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savan, R.; Aman, A.; Nakao, M.; Watanuki, H.; Sakai, M. Discovery of a novel immunoglobulin heavy chain gene chimera from common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Immunogenetics 2005, 57, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryo, S.; Wijdeven, R.H.; Tyagi, A.; Hermsen, T.; Kono, T.; Karunasagar, I.; Rombout, J.H.; Sakai, M.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M.; Savan, R. Common carp have two subclasses of bonyfish specific antibody IgZ showing differential expression in response to infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.A.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins and B cells of teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1346–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashoof, S.; Pohlenz, C.; Chen, P.L.; Deiss, T.C.; Gatlin, D., 3rd; Buentello, A.; Criscitiello, M.F. Expressed IgH mu and tau transcripts share diversity segment in ranched Thunnus orientalis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 43, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.A.; Salinas, I.; Li, J.; Parra, D.; Bjork, S.; Xu, Z.; LaPatra, S.E.; Bartholomew, J.; Sunyer, J.O. IgT, a primitive immunoglobulin class specialized in mucosal immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Parra, D.; Gomez, D.; Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.A.; von Gersdorff Jorgensen, L.; Heinecke, R.D.; Buchmann, K.; LaPatra, S.; Sunyer, J.O. Teleost skin, an ancient mucosal surface that elicits gut-like immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13097–13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamblott, M.J.; Litman, G.W. Genomic organization and sequences of immunoglobulin light chain genes in a primitive vertebrate suggest coevolution of immunoglobulin gene organization. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3733–3739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Flajnik, M.F. Four primordial immunoglobulin light chain isotypes, including lambda and kappa, identified in the most primitive living jawed vertebrates. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 2683–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rast, J.P.; Anderson, M.K.; Ota, T.; Litman, R.T.; Margittai, M.; Shamblott, M.J.; Litman, G.W. Immunoglobulin light chain class multiplicity and alternative organizational forms in early vertebrate phylogeny. Immunogenetics 1994, 40, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Steiner, L.; Kasahara, M.; Flajnik, M.F. Isolation of a shark immunoglobulin light chain cDNA clone encoding a protein resembling mammalian kappa light chains: Implications for the evolution of light chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10603–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleurant, M.; Changchien, L.; Chen, C.T.; Flajnik, M.F.; Hsu, E. Shark Ig light chain junctions are as diverse as in heavy chains. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5574–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohman, V.S.; Schuchman, D.B.; Schluter, S.F.; Marchalonis, J.J. Genomic clone for sandbar shark lambda light chain: Generation of diversity in the absence of gene rearrangement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 9882–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscitiello, M.F. What the shark immune system can and cannot provide for the expanding design landscape of immunotherapy. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.K.; Sun, X.; Miracle, A.L.; Litman, G.W.; Rothenberg, E.V. Evolution of hematopoiesis: Three members of the PU.1 transcription factor family in a cartilaginous fish, Raja eglanteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.-J.; Song, Y.-L.; Lu, X.-B.; Chen, D.-D.; Xia, X.-Q.; Sunyer, J.O.; Zhang, Y.-A. Preferential combination between the light and heavy chain isotypes of fish immunoglobulins. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, A.M.; Yeo, G.; Howe, K.; Maddox, B.J.; Steiner, L.A. Immunoglobulin light chain (IgL) genes in zebrafish: Genomic configurations and inversional rearrangements between (V(L)–J(L)–C(L)) gene clusters. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, E.; Criscitiello, M.F. Diverse immunoglobulin light chain organizations in fish retain potential to revise B cell receptor specificities. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, R.M.; Schluter, S.F.; Bernstein, H.; Marchalonis, J.J. Primordial emergence of the recombination activating gene 1 (RAG1): Sequence of the complete shark gene indicates homology to microbial integrases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9454–9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluter, S.F.; Bernstein, R.M.; Bernstein, H.; Marchalonis, J.J. ‘Big Bang’ emergence of the combinatorial immune system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rast, J.P.; Smith, L.C.; Loza-Coll, M.; Hibino, T.; Litman, G.W. Genomic insights into the immune system of the sea urchin. Science 2006, 314, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugmann, S.D.; Messier, C.; Novack, L.A.; Cameron, R.A.; Rast, J.P. An ancient evolutionary origin of the Rag1/2 gene locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3728–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinds, K.R.; Litman, G.W. Major reorganization of immunoglobulin VH segmental elements during vertebrate evolution. Nature 1986, 320, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Tranchina, D.; Ohta, Y.; Flajnik, M.F.; Hsu, E. Hypermutation in shark immunoglobulin light chain genes results in contiguous substitutions. Immunity 2002, 16, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Lee, V.; Finn, A.; Senger, K.; Zarrin, A.A.; Du Pasquier, L.; Hsu, E. Origin of Immunoglobulin Isotype Switching. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Fitch, D.; Flajnik, M.F.; Hsu, E. Rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes in shark germ cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Feng, W.; Weedon, J.; Hua, P.; Stefanov, D.; Ohta, Y.; Flajnik, M.F.; Hsu, E. The multiple shark Ig H chain genes rearrange and hypermutate autonomously. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.; Amemiya, C.; Luer, C.; Litman, R.; Rast, J.; Niimura, Y.; Litman, G. Complete genomic sequence and patterns of transcription of a member of an unusual family of closely related, chromosomally dispersed Ig gene clusters in Raja. Int. Immunol. 1994, 6, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malecek, K.; Lee, V.; Feng, W.; Huang, J.L.; Flajnik, M.F.; Ohta, Y.; Hsu, E. Immunoglobulin heavy chain exclusion in the shark. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edholm, E.S.; Wilson, M.; Sahoo, M.; Miller, N.W.; Pilstrom, L.; Wermenstam, N.E.; Bengten, E. Identification of Igsigma and Iglambda in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, and Iglambda in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua. Immunogenetics 2009, 61, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, A.M.; Romanowski, K.E.; Maddox, B.J. Targeted annotation of immunoglobulin light chain (IgL) genes in zebrafish from BAC clones reveals kappa-like recombining/deleting elements within IgL constant regions. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuike, M.; de Boer, J.; von Schalburg, K.R.; Cooper, G.A.; McKinnel, L.; Messmer, A.; So, S.; Davidson, W.S.; Koop, B.F. Evolution of duplicated IgH loci in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. BMC Genom. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, H.; Tan, E.; Watabe, S.; Asakawa, S. Characterization of the torafugu (Takifugu rubripes) immunoglobulin heavy chain gene locus. Immunogenetics 2015, 67, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y. The immunoglobulin gene loci in the teleost Gasterosteus aculeatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magadan-Mompo, S.; Sanchez-Espinel, C.; Gambon-Deza, F. Immunoglobulin heavy chains in medaka (Oryzias latipes). BMC Evol. Biol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengten, E.; Quiniou, S.; Hikima, J.; Waldbieser, G.; Warr, G.W.; Miller, N.W.; Wilson, M. Structure of the catfish IGH locus: Analysis of the region including the single functional IGHM gene. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, A.M.; Moustafa, F.M.; Romanowski, K.E.; Steiner, L.A. Zebrafish immunoglobulin IgD: Unusual exon usage and quantitative expression profiles with IgM and IgZ/T heavy chain isotypes. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 2220–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Yan, Z.; Feng, M.; Peng, D.; Guo, Y.; Hu, X.; Ren, L.; Sun, Y. Identification of sturgeon IgD bridges the evolutionary gap between elasmobranchs and teleosts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daggfeldt, A.; Bengten, E.; Pilstrom, L. A cluster type organization of the loci of the immunoglobulin light chain in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) indicated by nucleotide sequences of cDNAs and hybridization analysis. Immunogenetics 1993, 38, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.D.; Waldbieser, G.C.; Lobb, C.J. Patterns of receptor revision in the immunoglobulin heavy chains of a teleost fish. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5605–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.; Danz, H.; Kataria, P.; Bromage, E. A holistic view of the dynamisms of teleost IgM: A case study of Streptococcus iniae vaccinated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Kaattari, I.M.; Kaattari, S.L. The differential dynamics of antibody subpopulation expression during affinity maturation in a teleost. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.; Jouneau, L.; Pham, H.P.; Bouchez, O.; Giudicelli, V.; Lefranc, M.P.; Quillet, E.; Benmansour, A.; Cazals, F.; Six, A.; et al. Teleost fish mount complex clonal IgM and IgT responses in spleen upon systemic viral infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.; Hedeholm, R.B.; Heinemeier, J.; Bushnell, P.G.; Christiansen, J.S.; Olsen, J.; Ramsey, C.B.; Brill, R.W.; Simon, M.; Steffensen, K.F.; et al. Eye lens radiocarbon reveals centuries of longevity in the Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus). Science 2016, 353, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mashoof, S.; Criscitiello, M.F. Fish Immunoglobulins. Biology 2016, 5, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040045
Mashoof S, Criscitiello MF. Fish Immunoglobulins. Biology. 2016; 5(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleMashoof, Sara, and Michael F. Criscitiello. 2016. "Fish Immunoglobulins" Biology 5, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040045
APA StyleMashoof, S., & Criscitiello, M. F. (2016). Fish Immunoglobulins. Biology, 5(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040045




