Life Is Simple—Biologic Complexity Is an Epiphenomenon
Abstract
:1. Evolution from Unicellular to Multicellular
2. The First Principles of Life
3. The Fractal Nature of Life
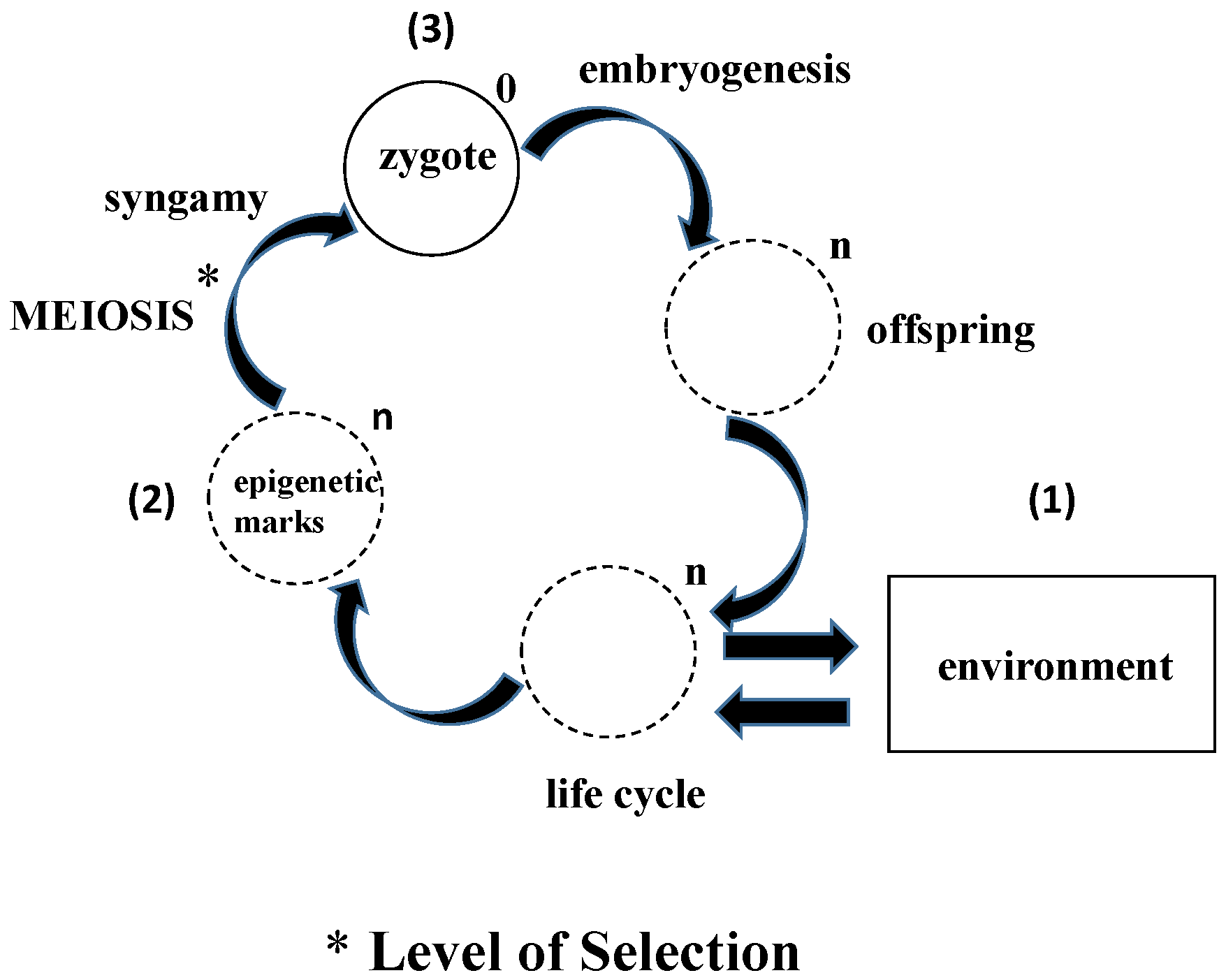
4. What Does Epigenetic Inheritance Tell Us about the Life Cycle
5. We Are All Spandrels
6. What the Unicellular Level of Selection Offers that Is Unavailable to the Top-down Approach
6.1. Re-Calibration of Biology and Its Terminology
6.2. Deep Understanding of Physiology
6.3. A Brief “History” of Lung Surfactant
6.4. Interrelationships between Human Physiology and that of Other Organisms
6.5. Predictive Value of the Comparative Cellular–Molecular Approach
7. Why Did Receptor Genes in Particular Duplicate
8. The Exception that Proves the Rule
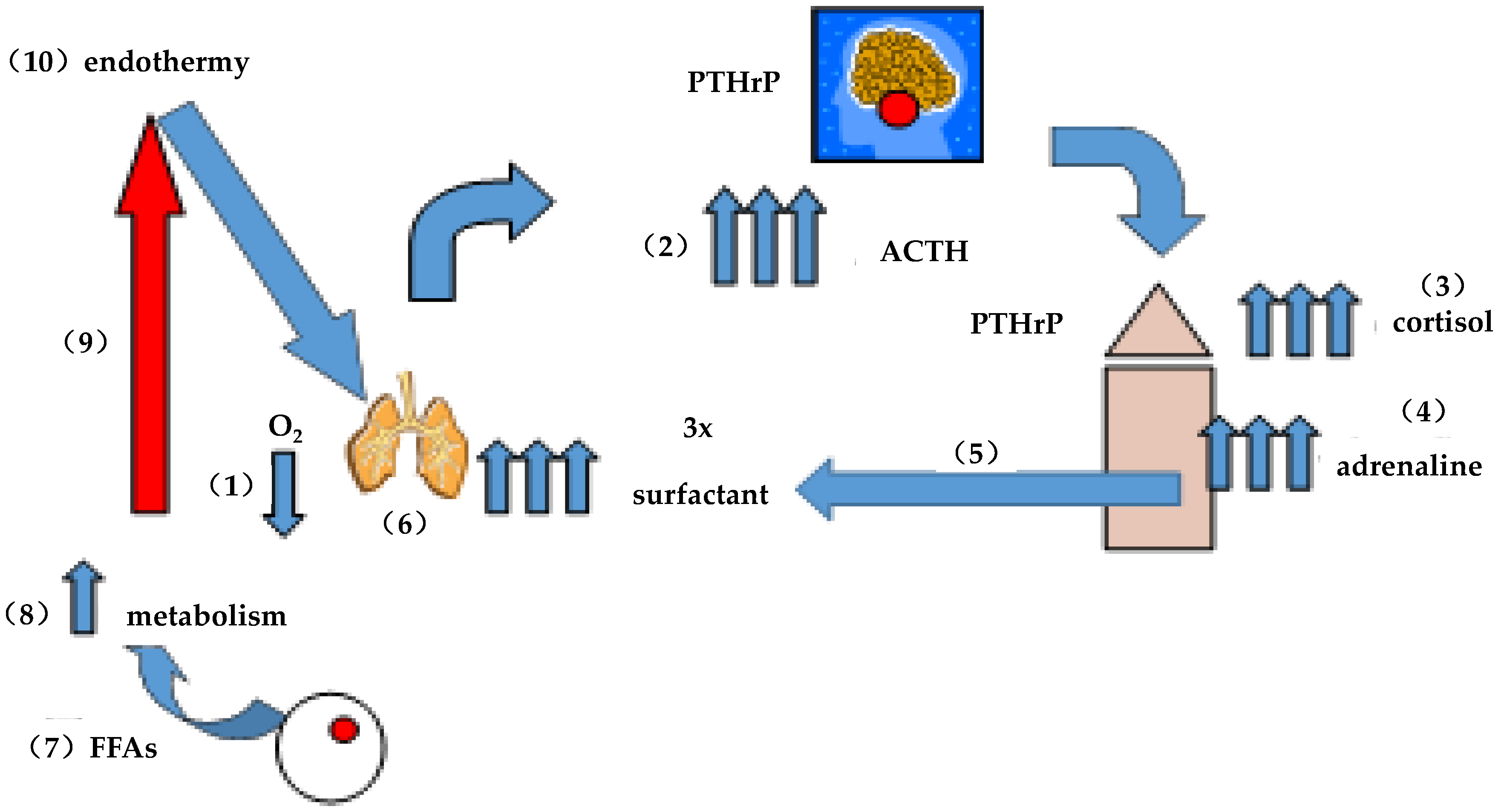
9. Hibernation as Reverse Evolution of Endothermy/Homeothermy
10. Predictive Power of the Cellular–Molecular Approach to Evolution
11. Fractal Basis for Complex Physiology Reveals Its Unicellular Essence
12. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deamer, D.W. Role of amphiphilic compounds in the evolution of membrane structure on the early earth. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 1986, 17, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, N.; Allen, J.F.; Martin, W. How did LUCA make a living? Chemiosmosis in the origin of life. Bioessays 2010, 32, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baverstock, K.; Rönkkö, M. The evolutionary origin of form and function. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 2261–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, N.; Hittinger, C.T.; Carroll, S.B. Evolution of key cell signaling and adhesion protein families predates animal origins. Science 2003, 301, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raven, J.A.; Giordano, M.; Beardall, J.; Maberly, S.C. Algal evolution in relation to atmospheric CO2: Carboxylases, carbon-concentrating mechanisms and carbon oxidation cycles. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, K. Summing up. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, S.F.; Carrier, D.R. The coupled evolution of breathing and locomotion as a game of leapfrog. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2006, 79, 997–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korade, Z.; Kenworthy, A.K. Lipid rafts, cholesterol, and the brain. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, D.O.; Carr, J.A. Vertebrate Endocrinology; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sokol, S.Y. Spatial and temporal aspects of Wnt signaling and planar cell polarity during vertebrate embryonic development. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2015, 42, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnard, P.A.; Deamer, D.W. Membrane self-assembly processes: Steps toward the first cellular life. Anat. Rec. 2002, 268, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S. The cell as the mechanistic basis for evolution. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2015, 7, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, R.M.; Eisner, D.; Gurney, A.; Jones, O.; Muallem, S.; Verkhratsky, A. Evolution of calcium homeostasis: From birth of the first cell to an omnipresent signaling system. Cell Calcium 2007, 42, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempe, S.; Kazmierczak, J. Biogenesis and early life on Earth and Europa: Favored by an alkaline ocean? Astrobiology 2002, 2, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berner, R.A.; Vandenbrooks, J.M.; Ward, P.D. Oxygen and evolution. Science 2007, 316, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Duve, C. Peroxisomes and related particles in historical perspective. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1982, 386, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margulis, L.; Bermudes, D. Symbiosis as a mechanism of evolution: Status of cell symbiosis theory. Symbiosis 1985, 1, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Cell evolution and Earth history: Stasis and revolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 969–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Chen, X. Epigenetic regulation of germ cells-remember or forget? Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2015, 31, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, G.; Shapiro, H. Further studies on the parthenogenetic activation of rabbit eggs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1940, 26, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmut, I.; Schnieke, A.E.; McWhir, J.; Kind, A.J.; Campbell, K.H. Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature 1997, 385, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, S.J.; Lewontin, R.C. The spandrels of San Marco and the Panglossian paradigm: A critique of the adaptationist programme. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1979, 205, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, E. The concept of function in modern physiology. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 2245–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Reik, W. Epigenetic reprogramming in plant and animal development. Science 2010, 330, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, H.D.; Santos, F.; Green, K.; Dean, W.; Reik, W. Epigenetic reprogramming in mammals. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ho, S.M. Epigenetics meets endocrinology. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 46, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Gayle, D.; Babu, J.; Ross, M.G. Programmed obesity in intrauterine growth-restricted newborns: Modulation by newborn nutrition. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutilainen, R.; Jääskeläinen, J. Premature adrenarche: Etiology, clinical findings, and consequences. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 145, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A.T.; Firtel, R.A. Regulation of chemotaxis by the orchestrated activation of Ras, PI3K, and TOR. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 85, 873–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebert, S.P.; Dellschaft, N.S.; Chan, L.L.; Street, H.; Henry, M.; Francois, C.; Sharma, V.; Fainberg, H.P.; Patel, N.; Roda, J.; et al. Maternal nutrient restriction during late gestation and early postnatal growth in sheep differentially reset the control of energy metabolism in the gastric mucosa. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, G.J. Emile Zuckerkandl, Linus Pauling, and the molecular evolutionary clock, 1959–1965. J. Hist. Biol. 1998, 31, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnaeus, C. Systema Naturae, Sive Regna Tria Naturae Systematice Proposita Per Classes, Ordines, Genera, & Species; Haak: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1735. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, C.B.; Orgeig, S.; Sullivan, L.C.; Ling, N.; Bennett, M.B.; Schürch, S.; Val, A.L.; Brauner, C.J. The origin and evolution of the surfactant system in fish: Insights into the evolution of lungs and swim bladders. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2004, 77, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, C.B.; Orgeig, S. Pulmonary surfactant: The key to the evolution of air breathing. News Physiol. Sci. 2003, 18, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S.; Rehan, V.K. Evolutionary Biology, Cell-Cell Communication and Complex Disease; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Torday, J.S.; Rehan, V.K. Lung evolution as a cipher for physiology. Physiol. Genom. 2009, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S.; Rehan, V.K. On the evolution of the pulmonary alveolar lipofibroblast. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 340, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S.; Rehan, V.K. Evolution, the Logic of Biology; Wiley-Blackwell: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, S.F.; Sander, M. Reconstructing the evolution of the respiratory apparatus in tetrapods. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2004, 144, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncker, H.R. Vertebrate lungs: Structure, topography and mechanics. A comparative perspective of the progressive integration of respiratory system, locomotor apparatus and ontogenetic development. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2004, 144, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Collins, J.E.; Andrews, R.M.; Stemple, D.; Gong, Z. Comparative transcriptome analyses indicate molecular homology of zebrafish swimbladder and mammalian lung. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, F. Evolution and tinkering. Science 1977, 196, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, L.P.; Kovacs, C.S.; De Paepe, M.E.; Tsai, S.W.; Torday, J.S.; Kronenberg, H.M. Arrested pulmonary alveolar cytodifferentiation and defective surfactant synthesis in mice missing the gene for parathyroid hormone-related protein. Dev. Dyn. 2004, 230, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliarulo, C.; Salvatore, P.; Napoli, C. Targeting vascular niche by parathyroid hormone. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, J.S.; Chow, B.K.; Lee, L.T. Evolution of parathyroid hormone receptor family and their ligands in vertebrate. Front. Endocrinol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.L.; Cardoso, J.C.; Power, D.M.; Canário, A.V. Functional characterization and evolution of PTH/PTHrP receptors: Insights from the chicken. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galhardo, R.S.; Hastings, P.J.; Rosenberg, S.M. Mutation as a stress response and repair: Power and promise of molecular definition. Kidney Int. 2007, 53, 826–835. [Google Scholar]
- Aris-Brosou, S.; Chen, X.; Perry, S.F.; Moon, T.W. Timing of the functional diversification of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in fish and other vertebrates. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1163, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.B.; Mathieu-Costello, O. Structure, strength, failure, and remodeling of the pulmonary blood-gas barrier. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999, 61, 543–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaber, M.; Koch, W.J.; Rockman, H.; Smith, B.; Bond, R.A.; Sulik, K.K.; Ross, J., Jr.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Caron, M.G.; Giros, B. Essential role of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 in cardiac development and function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12974–12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matkovich, S.J.; Diwan, A.; Klanke, J.L.; Hammer, D.J.; Marreez, Y.; Odley, A.M.; Brunskill, E.W.; Koch, W.J.; Schwartz, R.J.; Dorn, G.W., II. Cardiac-specific ablation of G-protein receptor kinase 2 redefines its roles in heart development and beta-adrenergic signaling. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S. Homeostasis as the mechanism of evolution. Biology 2015, 4, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, A.F.; Ruben, J.A. Endothermy and activity in vertebrates. Science 1979, 206, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtman, R.J. Stress and the adrenocortical control of epinephrine synthesis. Metabolism 2002, 51, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, E.E.; Brown, E.R.; Torday, J.S.; Madansky, D.L.; Taeusch, H.W., Jr. The effect of epinephrine on tracheal fluid flow and surfactant efflux in fetal sheep. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1978, 118, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khoo, J.C.; Aquino, A.A.; Steinberg, D. The mechanism of activation of hormone-sensitive lipase in human adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 53, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Soni, K.G.; Semache, M.; Casavant, S.; Fortier, M.; Pan, L.; Mitchell, G.A. Lipolysis and the integrated physiology of lipid energy metabolism. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 95, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbé, S.M.; Caron, A.; Bakan, I.; Laplante, M.; Carpentier, A.C.; Lecomte, R.; Richard, D. In vivo measurement of energy substrate contribution to cold-induced brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2046–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S. A central theory of biology. Med. Hypotheses 2015, 85, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochachka, P.W.; Somero, G.N. The adaptation of enzymes to temperature. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1968, 27, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, K.; Perez-Gil, J.; Ruano, M.L.; Worthman, L.A.; Stewart, J.; Casals, C.; Keough, K.M. Phase transitions in films of lung surfactant at the air-water interface. Biophys. J. 1998, 74, 2983–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawaliby, R.; Trubbia, C.; Delporte, C.; Noyon, C.; Ruysschaert, J.M.; Van Antwerpen, P.; Govaerts, C. Phosphatidylethanolamine is a key regulator of membrane fluidity in eukaryotic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3658–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, P.; Labandeira, C.; Laurin, M.; Berner, R.A. Confirmation of Romer’s Gap as a low oxygen interval constraining the timing of initial arthropod and vertebrate terrestrialization. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16818–16822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, B.A.; Sund, M.; Grant, M.A.; Pfaff, K.L.; Holthaus, K.; Zon, L.I.; Kalluri, R. Zebrafish to humans: Evolution of the alpha3-chain of type IV collagen and emergence of the autoimmune epitopes associated with Goodpasture syndrome. Blood 2006, 107, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, A.D.; Levy, J.B.; Lightstone, L.; Pusey, C.D. Goodpasture’s disease. Lancet 2001, 358, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.J.; Keough, K.M. Lipid composition of lung and lung lavage fluid from map turtles (Malaclemys geographica) maintained at different environmental temperatures. Can. J. Biochem. 1981, 59, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibel, E.R.; Taylor, C.R.; Hoppeler, H. Variations in function and design: Testing symmorphosis in the respiratory system. Respir. Physiol. 1992, 87, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, V.; Wert, S.E.; Stahlman, M.T.; Postle, A.D.; Xu, Y.; Ikegami, M.; Whitsett, J.A. Deletion of Scap in alveolar type II cells influences lung lipid homeostasis and identifies a compensatory role for pulmonary lipofibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4018–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamillapalli, R.; Wysolmerski, J. The calcium-sensing receptor couples to Galpha(s) and regulates PTHrP and ACTH secretion in pituitary cells. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 204, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocchi, G.; Aragona, F.; Malendowicz, L.K.; Nussdorfer, G.G. PTH and PTH-related peptide enhance steroid secretion from human adrenocortical cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Nic a’ Bháird, N.; Goldberg, R.; Tipton, K.F. Catechol-O-methyltransferase and its role in catecholamine metabolism. Adv. Neurol. 1990, 53, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Isowa, S.; Shimo, T.; Ibaragi, S.; Kurio, N.; Okui, T.; Matsubara, K.; Hassan, N.M.; Kishimoto, K.; Sasaki, A. PTHrP regulates angiogenesis and bone resorption via VEGF expression. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2755–2767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butler, D.G. Structure and function of the adrenal gland of fishes. Am. Zool. 1973, 13, 839–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.W. From Fish to Philospopher; Little Brown & Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Latta, H. An approach to the structure and function of the glomerular mesangium. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1992, 2, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, R.J.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D.; Bover, J.; Rodríguez-Puyol, M. Parathyroid hormone-related protein: Roles in the glomerulus. Exp. Nephrol. 1999, 7, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, R.; Wan, L.; May, C. Vasoactive drugs and acute kidney injury. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, N.C.; Becker, S.A.; Jamshidi, N.; Thiele, I.; Mo, M.L.; Vo, T.D.; Srivas, R.; Palsson, B.Ø. Global reconstruction of the human metabolic network based on genomic and bibliomic data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S. Pleiotropy as the mechanism for evolving novelty: Same signal, different result. Biology 2015, 4, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambertz, M.; Grommes, K.; Kohlsdorf, T.; Perry, S.F. Lungs of the first amniotes: why simple if they can be complex? Biol. Lett. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, J.N. Development, structure, and function of a novel respiratory organ, the lung-air sac system of birds: To go where no other vertebrate has gone. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2006, 81, 545–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S.; Department of Pediatrics, Harbor-UCLA, Torrance, CA, USA. Personal observation, 2005.
- Owerkowicz, T.; Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, University of California, Irvine, CA, USA. Personal observation, 2005.
- Braun, E.J.; Sweazea, K.L. Glucose regulation in birds. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodman, P.S.; McHenry, H.M. Bioenergetics and the origin of hominid bipedalism. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1980, 52, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanville, E.J.; Seebacher, F. Compensation for environmental change by complementary shifts of thermal sensitivity and thermoregulatory behaviour in an ectotherm. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 4869–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, G.D. An Introduction to Hinduism; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chaya, M.S.; Kurpad, A.V.; Nagendra, H.R.; Nagarathna, R. The effect of long term combined yoga practice on the basal metabolic rate of healthy adults. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaya, M.S.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Shastry, S.; Kishore, R.P.; Nagendra, H.; Nagarathna, R.; Raj, T.; Thomas, T.; Vaz, M.; Kurpad, A.V. Insulin sensitivity and cardiac autonomic function in young male practitioners of yoga. Natl. Med. J. India 2008, 21, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Denninger, P.; Bleckmann, A.; Lausser, A.; Vogler, F.; Ott, T.; Ehrhardt, D.W.; Frommer, W.B.; Sprunck, S.; Dresselhaus, T.; Grossmann, G. Male-female communication triggers calcium signatures during fertilization in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramoino, P.; Dini, F.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A.; Guella, G.; Usai, C. Biophysical effects of the natural product euplotin C on the Paramecium membrane. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural. Behav. Physiol. 2009, 195, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadag, A.; Sakurai, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, P.; Desai, M.; Ross, M.G.; Torday, J.S.; Rehan, V.K. Effect of maternal food restriction on fetal rat lung lipid differentiation program. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vryonidou, A.; Paschou, S.A.; Muscogiuri, G.; Orio, F.; Goulis, D. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Metabolic syndrome through the female life cycle. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.H.; Buggey, J.; Lee, Y.K.; Kimmel, A.R. Chemoattractant stimulation of TORC2 is regulated by receptor/G protein-targeted inhibitory mechanisms that function upstream and independently of an essential GEF/Ras activation pathway in Dictyostelium. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cota, D.; Proulx, K.; Smith, K.A.; Kozma, S.C.; Thomas, G.; Woods, S.C.; Seeley, R.J. Hypothalamic mTOR signaling regulates food intake. Science 2006, 312, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priogene, I. Order out of Chaos; Bantam: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Polanyi, M. Life’s irreducible structure: Live mechanisms and information in DNA are boundary conditions with a sequence of boundaries above them. Science 1968, 160, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torday, J.S. Life Is Simple—Biologic Complexity Is an Epiphenomenon. Biology 2016, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5020017
Torday JS. Life Is Simple—Biologic Complexity Is an Epiphenomenon. Biology. 2016; 5(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorday, John S. 2016. "Life Is Simple—Biologic Complexity Is an Epiphenomenon" Biology 5, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5020017
APA StyleTorday, J. S. (2016). Life Is Simple—Biologic Complexity Is an Epiphenomenon. Biology, 5(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5020017




