Fish Peroxiredoxins and Their Role in Immunity
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Peroxiredoxins in Mammals
2.1. General Description
2.2. Roles in Immunity
3. Peroxiredoxins in Fish
3.1. Description and Presence of Fish Prxs
3.2. Prx1 (NKEF-A) in Fish Immunity
| Fish Species | Stimulant | Effect | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) | Mitogens | ConA, PHA | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | [47] |
| PAMPs | LPS | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | ||
| CpG ODNs | ↑ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | |||
| Poly I:C | ↑ prx2 in HKLs | |||
| Bacteria | V. anguillarum | ↑ prx1 in HKLs | ||
| P. damselae | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | |||
| Virus | NNV | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | ||
| ↑ prx1, prx2 in vivo | ||||
| Parasite | E. leei | ↑ prx1, prx2, prx3, prx5 in exposed fish and parasite-free | [46] | |
| ↓ prx1, prx2, prx3, prx, prx6 in parasitized fish | ||||
| ≈ prx4 | ||||
| European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) | Mitogens | ConA, PHA | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | [47] |
| PAMPs | LPS | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | ||
| CpG ODNs | ↑ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | |||
| Poly I:C | ↑ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | |||
| Bacteria | V. anguillarum | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | ||
| P. damselae | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | |||
| Virus | NNV | ≈ prx1, prx2 in HKLs | ||
| ↑ prx2 in vivo | ||||
| Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) | Bacteria | A. hydrophyla | ↑ prx1 in spleen | [62] |
| E. tarda | ↑ prx1 and Prx1 in spleen | [63] | ||
| Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) | PAMPs | LPS | ↑ prx1 in spleen | [45] |
| Spotted green pufferfish (Tetraodon nigroviridis) | PAMPs | LPS | ↑ prx1, prx2 in spleen | [40] |
| Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) | Virus | SVCV | ↑ prx1 and prx2 in PBLs | [44] |
| ↓ prx1 in gills | ||||
| ↓ prx2 in HK | ||||
| ↑ Prx2 | ||||
| Lamprey (Lampetra japonica) | PAMPs | LPS | ↑ prx2 in spleen | [38] |
| Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | PAMPs | LPS | ≈ Prx1 in MØ | [56] |
| ↑ Prx1 in RTS11 | ||||
| Zymosan | ≈ Prx1 in MØ | |||
| Bacteria | V. ordalii | ↑ Prx1 in MØ | ||
| Virus | VHSV | ↑ prx1 in B, HK | [58] | |
| ↑ prx1 in RTS11 | [57] | |||
| ↑ prx1 in PBLs | [59] | |||
| ISAV | ≈ Prx1 in RTS11 | [56] | ||
| Parasite | C. rogercresseyi | ↑ Prx1 in spleen, HK | ||
| Vaccine | VHSV DNA vaccine + infection | ↑ prx1 | [58] | |
| Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) | Virus | IHNV | ↓ Prx2 | [52] |
| Parasite | N. perurans | ↓ prx1 in gill | [48] | |
| Large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) | Vaccine | V. alginolyticus, V. parahemolyticus, and A. hydrophila | ↑ Prx1, Prx2,Prx4 in spleen | [37] |
| Rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus) | PAMPs | Poly I:C | ↑ prx6 in liver | [49] |
| Virus | Iridovirus | ↑ prx6 in liver | ||
| Miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) | Bacteria | V. anguillarum | ↑ prx2, prx3, prx4, prx5 in kidney, spleen | [35,36] |
| Ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis) | Bacteria | V. alginolytics | ↑ prx2 in gut | [33] |
| A. hydrophila | ↑ prx2 in all tissues | |||
| ↑ Prx2 in liver | ||||
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Bacteria | A. hydrophila | ↑ prx3 and prx5 in gill | [55] |
| ↑ Prx3 and Prx5 in gill | ||||
| Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) | PAMPs | Poly I:C | ↑ prx6 in liver, spleen | [34] |
| Bacteria | V. anguillarum | ↑ prx6 in liver, spleen | ||
| ↑ prx2 | [39] | |||
| S. iniae | ↑ prx6 in liver, spleen | [34] | ||
| Fish Species | Prx | Approximation | Effects Observed | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) | Prx1 | Expression plasmids | ↓ NNV expression in brain | This study |
| Prx2 | ||||
| Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) | Prx1 | Recombinant | Antioxidant defence | [48] |
| Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) | Prx1 | Expression plasmids | ↓ bacterial infection | [63] |
| knockdown | ↓ bacterial resistance | |||
| Lamprey (Lampetra japonica) | Prx2 | Recombinant | Antioxidant defence | [38] |
| Protected DNA from in vitro oxidation | ||||
| Large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) | Prx4 | Recombinant | Antioxidant defence | [37] |
| Prx4 injection | ↓ NF-κB activity | |||
| ↓ tnfa, chemokines | ||||
| ↑ il10 | ||||
| ↑ bacterial resistance | ||||
| Knockdown by siRNA | ↑ NF-κB activity | |||
| ↑ tnfa, chemokines | ||||
| ↓ il10 | ||||
| ↓ bacterial resistance | ||||
| Prx4 without the N-terminal motif | ↓ NF-κB activity | [64] | ||
| ↓ bacterial resistance | ||||
| No antioxidant function | ||||
| Rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus) | Prx6 | Recombinant | Protected DNA from in vitro oxidation | [49] |
| Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) | Prx6 | Recombinant | Protected hepatocytes from peroxide treatment | [34] |
3.3. Prx2 (NKEF-B) in Fish Immunity
3.4. Functions of Prx3
3.5. Functions of Prx4
3.6. Functions of Prx5
3.7. Functions of Prx6
4. Preliminary Functional Data in European Sea Bass
4.1. Methodology
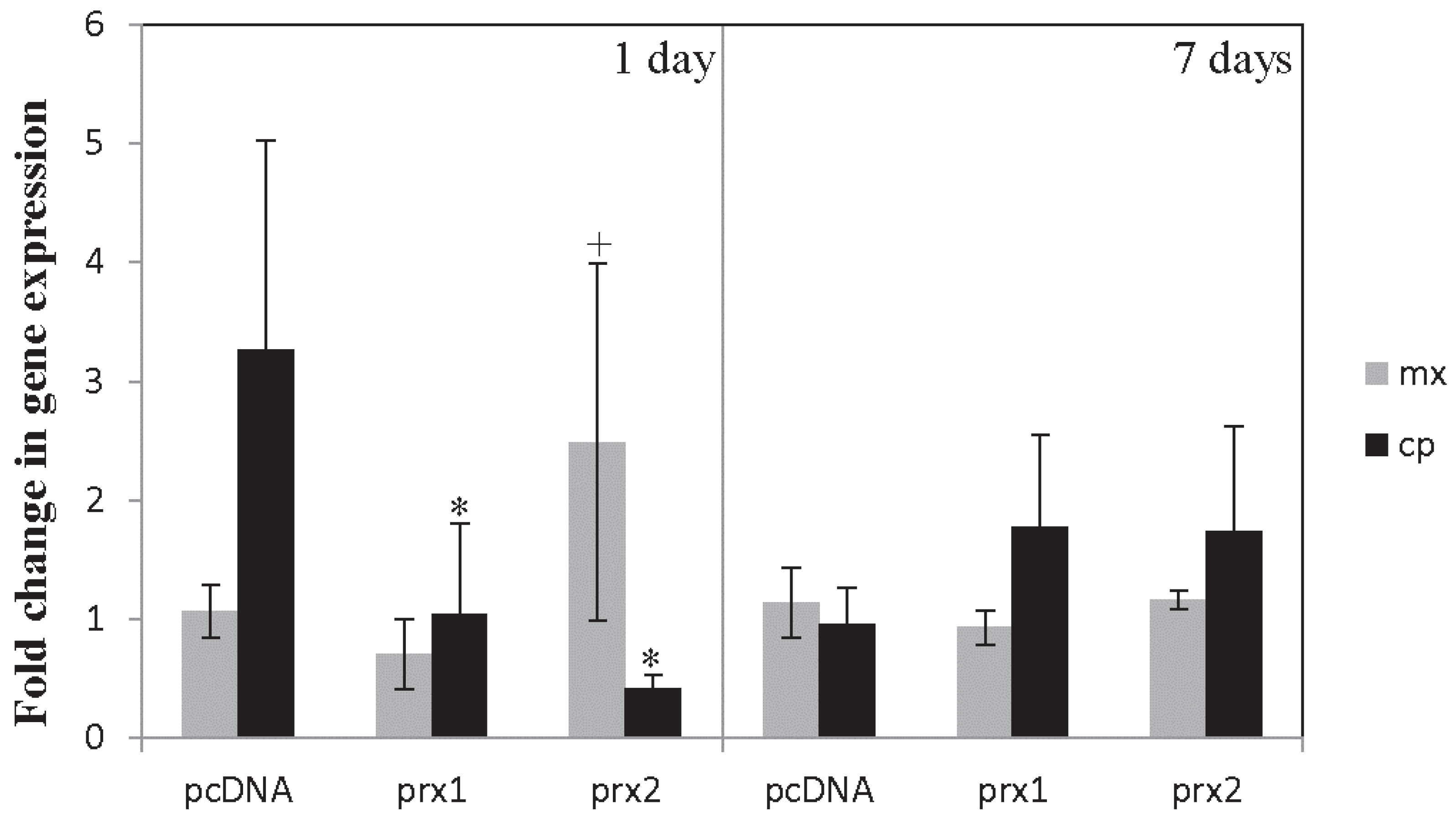
4.2. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreyev, A.Y.; Kushnareva, Y.E.; Starkov, A.A. Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry 2005, 70, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanschmann, E.M.; Godoy, J.R.; Berndt, C.; Hudemann, C.; Lillig, C.H. Thioredoxins, glutaredoxins, and peroxiredoxins—Molecular mechanisms and health significance: From cofactors to antioxidants to redox signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1539–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlenius, T.C.; Tonissen, K.F. Thioredoxin and cancer: A role for thioredoxin in all states of tumour oxygenation. Cancers 2010, 2, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novo, E.; Parola, M. Redox mechanisms in hepatic chronic wound healing and fibrogenesis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourquet, S.; Huang, M.E.; D’Autreaux, B.; Toledano, M.B. The dual functions of thiol-based peroxidases in H2O2 scavenging and signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.; Karplus, P.A.; Poole, L.B. Typical 2-Cys peroxiredoxins—Structures, mechanisms and functions. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.G.; Chae, H.Z.; Kim, K. Peroxiredoxins: A historical overview and speculative preview of novel mechanisms and emerging concepts in cell signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, Z.A.; Schroder, E.; Robin Harris, J.; Poole, L.B. Structure, mechanism and regulation of peroxiredoxins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T. Close teamwork between Nrf2 and peroxiredoxins 1 and 6 for the regulation of prostaglandin D and E production in macrophages in acute inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Warabi, E.; Yanagawa, T. Novel roles of peroxiredoxins in inflammation, cancer and innate immunity. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2012, 50, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Rhee, S.G.; Stadtman, E.R. The isolation and purification of a specific “protector” protein which inhibits enzyme inactivation by a thiol/Fe(III)/O2 mixed-function oxidation system. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 4704–4711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, B.; Hecht, H.J.; Flohe, L. Peroxiredoxins. Biol. Chem. 2002, 383, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shau, H.; Roth, M.D.; Golub, S.H. Regulation of natural killer function by nonlymphoid cells. Nat. Immun. 1993, 12, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sauri, H.; Ashjian, P.H.; Kim, A.T.; Shau, H. Recombinant natural killer enhancing factor augments natural killer cytotoxicity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 59, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geiben-Lynn, R.; Kursar, M.; Brown, N.V.; Addo, M.M.; Shau, H.; Lieberman, J.; Luster, A.D.; Walker, B.D. HIV-1 antiviral activity of recombinant natural killer cell enhancing factors, NKEF-A and NKEF-B, members of the peroxiredoxin family. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnula, V.L.; Lehtonen, S.; Sormunen, R.; Kaarteenaho-Wiik, R.; Kang, S.W.; Rhee, S.G.; Soini, Y. Overexpression of peroxiredoxins I, II, III, V, and VI in malignant mesothelioma. J. Pathol. 2002, 196, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, J.Y.; Chae, H.Z.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, Z.Y.; Yoo, Y.J. Peroxiredoxin-I is an autoimmunogenic tumour antigen in non-small cell lung cancer. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 2873–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell, J.R.; Wang, X.Y.; Minderman, H.; Gollnick, S.O. Peroxiredoxin 1 stimulates secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by binding to TLR4. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shichita, T.; Hasegawa, E.; Kimura, A.; Morita, R.; Sakaguchi, R.; Takada, I.; Sekiya, T.; Ooboshi, H.; Kitazono, T.; Yanagawa, T.; et al. Peroxiredoxin family proteins are key initiators of post-ischemic inflammation in the brain. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäschke, A.; Mi, H.; Tropschug, M. Human T cell cyclophilin18 binds to thiol-specific antioxidant protein Aop1 and stimulates its activity. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 277, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.P.; Hwang, Y.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, K.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.; Chae, H.Z. Cyclophilin A binds to peroxiredoxins and activates its peroxidase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29826–29832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Kim, T.; Chae, H.Z.; Kim, K.T.; Ha, H. Regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and thiol-specific antioxidant protein PAG by direct interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15504–15510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambruso, D.R.; Ellison, M.A.; Thurman, G.W.; Leto, T.L. Peroxiredoxin 6 translocates to the plasma membrane during neutrophil activation and is required for optimal NADPH oxidase activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbecki, J.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Gutowska, I.; Chlubek, D. The effect of reactive oxygen species on the synthesis of prostanoids from arachidonic acid. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 64, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.; Moreno, J.J. Role of Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 on arachidonic acid release induced by reactive oxygen species. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 392, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.M.; Moriarty-Craige, S.; Jones, D.P. Nuclear and cytoplasmic peroxiredoxin-1 differentially regulate NF-κB activities. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egler, R.A.; Fernandes, E.; Rothermund, K.; Sereika, S.; de Souza-Pinto, N.; Jaruga, P.; Dizdaroglu, M.; Prochownik, E.V. Regulation of reactive oxygen species, DNA damage, and C-Myc function by peroxiredoxin 1. Oncogene 2005, 24, 8038–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Yu, X.; Ip, C.; Mohler, J.L.; Bogner, P.N.; Park, Y.M. Peroxiredoxin 1 interacts with androgen receptor and enhances its transactivation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9294–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, K.Y. A novel function of peroxiredoxin 1 (Prx-1) in apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-mediated signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertz, M.; Fischer, F.; Leipelt, M.; Wolters, D.; Steegborn, C. Identification of Peroxiredoxin 1 as a novel interaction partner for the lifespan regulator protein p66Shc. Aging 2009, 1, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, W.S.; Ip, C.; Chae, H.Z.; Park, E.M.; Park, Y.M. Prx1 suppresses radiation-induced c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase signaling in lung cancer cells through interaction with the glutathione S-transferase Pi/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase complex. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7136–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourich, D.V.; Hansen, J.; Leong, J. Natural killer cell enhancement factor-like gene in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Immunogenetics 1995, 42, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.Q.; Niu, H.; Shi, Y.H.; Li, M.Y. Increased liver protein and mRNA expression of natural killer cell-enhancing factor B (NKEF-B) in ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis) after Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.J.; Hu, Y.H.; Zhang, M.; Sun, L. Analysis of the expression and antioxidative property of a peroxiredoxin 6 from Scophthalmus maximus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, T. Gene structure, immune response and evolution: Comparative analysis of three 2-Cys peroxiredoxin members of miiuy croaker, Miichthys miiuy. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Xu, T.; Wang, R.; Sun, Y. Miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) Peroxiredoxin2: Molecular characterization, genomic structure and immune response against bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Mu, Y.; Ao, J.; Chen, X. Peroxiredoxin IV regulates pro-inflammatory responses in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) and protects against bacterial challenge. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Q. Molecular cloning, expression and antioxidant activity of a peroxiredoxin 2 homologue from Lampetra japonica. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, U.X.; Fan, T.; Meng, L.; Ren, G.C.; Chen, S.L. Molecular identification and expression analysis of the natural killer cell enhancing factor (NKEF) gene from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.R.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J.Z. Cloning and characterisation of two natural killer enhancing factor genes (NKEF-A and NKEF-B) in pufferfish, Tetraodon nigroviridis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Chen, S.L.; Ji, X.S. Cloning and expression analysis of natural leveller enhancing factor from Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). High Technol. Lett. 2005, 15, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, D.L.; Loo, G.H.; Menz, R.I.; Schuller, K.A. Cloning and functional characterization of a typical 2-Cys peroxiredoxin from southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2010, 156, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, G.H.; Schuller, K.A. Cloning and functional characterization of a peroxiredoxin 4 from yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 156, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Gao, L.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Hu, W.; Guo, Q.L. Structure, organization and expression of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) NKEF-B gene. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.W.; Waldbieser, G.C. Genomic organisation and expression of the natural killer cell enhancing factor (NKEF) gene in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Bermejo-Nogales, A.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Kaushik, S.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of six peroxiredoxin paralogous genes in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata): Insights from fish exposed to dietary, pathogen and confinement stressors. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, M.A.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Arizcun, M.; Meseguer, J.; Cuesta, A. Regulation of natural killer enhancing factor (NKEF) genes in teleost fish, gilthead seabream and European sea bass. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 55, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, G.H.; Sutton, D.L.; Schuller, K.A. Cloning and functional characterisation of a peroxiredoxin 1 (NKEF A) cDNA from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and its expression in fish infected with Neoparamoeba perurans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Zoysa, M.; Ryu, J.H.; Chung, H.C.; Kim, C.H.; Nikapitiya, C.; Oh, C.; Kim, H.; Saranya Revathy, K.; Whang, I.; Lee, J. Molecular characterization, immune responses and DNA protection activity of rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus), peroxiredoxin 6 (Prx6). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Wang, R.; Gao, Y.; Xu, T. Genomic organization, single nucleotide polymorphism and functional characterization of natural killer enhancing factor (NKEF-A) in Miichthys miiuy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Evenhuis, J.P.; Thorgaard, G.H.; Ristow, S.S. Cloning, characterization and genomic structure of the natural killer cell enhancement factor (NKEF)-like gene from homozygous clones of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booy, A.T.; Haddow, J.D.; Ohlund, L.B.; Hardie, D.B.; Olafson, R.W. Application of isotope coded affinity tag (ICAT) analysis for the identification of differentially expressed proteins following infection of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) with infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) or Renibacterium salmoninarum (BKD). J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jurado, J.; Fuentes-Almagro, C.A.; Guardiola, F.A.; Cuesta, A.; Esteban, M.A.; Prieto-Álamo, M.J. Proteomic profile of the skin mucus of farmed gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). J. Proteom. 2015, 120, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, S.; Silva, T.; Cordeiro, O.; Rodrigues, P.; Guy, D.R.; Bron, J.E.; Taggart, J.B.; Bell, J.G.; Tocher, D.R. Effects of genotype and dietary fish oil replacement with vegetable oil on the intestinal transcriptome and proteome of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). BMC Genom. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, A.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, A.; Tian, J.; Ming, Q.; Feng, Z. iTRAQ analysis of gill proteins from the zebrafish (Danio rerio) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethke, J.; Rojas, V.; Berendsen, J.; Cardenas, C.; Guzman, F.; Gallardo, J.A.; Mercado, L. Development of a new antibody for detecting natural killer enhancing factor (NKEF)-like protein in infected salmonids. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordás, M.C.; Cuesta, A.; Mercado, L.; Bols, N.C.; Tafalla, C. Viral hemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV) up-regulates the cytotoxic activity and the perforin/granzyme pathway in the rainbow trout RTS11 cell line. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, A.; Tafalla, C. Transcription of immune genes upon challenge with viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) in DNA vaccinated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Vaccine 2009, 27, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utke, K.; Bergmann, S.; Lorenzen, N.; Köllner, B.; Ototake, M.; Fischer, U. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, infected with viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, A.; Esteban, M.A.; Meseguer, J. The expression profile of TLR9 mRNA and CpG ODNs immunostimulatory actions in the teleost gilthead seabream points to a major role of lymphocytes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2091–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, A.; Salinas, I.; Esteban, M.A.; Meseguer, J. Unmethylated CpG motifs mimicking bacterial DNA triggers the local and systemic innate immune parameters and expression of immune-relevant genes in gilthead seabream. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.S.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Sun, L. Identification and analysis of the immune effects of CpG motifs that protect Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Sun, L. Edwardsiella tarda-regulated proteins in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus): Identification and evaluation of antibacterial potentials. J. Proteom. 2015, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Lian, F.M.; Teng, Y.B.; Ao, J.; Jiang, Y.L.; He, Y.X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, C.Z.; Chen, X. The N-terminal beta-sheet of peroxiredoxin 4 in the large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea is involved in its biological functions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, M.J. Immune defence systems. In Biology of Farmed Fish; Black, K.D., Pickering, A.D., Eds.; Sheffield Academic Press: Sheffield, UK, 1998; pp. 180–221. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, C.A.; Krause, D.S.; Carman, C.V.; Das, S.; Dubey, D.P.; Abraham, J.L.; Bronson, R.T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Orkin, S.H.; van Etten, R.A. Essential role for the peroxiredoxin Prdx1 in erythrocyte antioxidant defence and tumour suppression. Nature 2003, 424, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiumi, H.; Tsujita, T.; Shida, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Ikeo, K.; Seya, T. Prediction of the prototype of the human Toll-like receptor gene family from the pufferfish, Fugu rubripes, genome. Immunogenetics 2003, 54, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sepulcre, M.P.; Alcaraz-Perez, F.; Lopez-Munoz, A.; Roca, F.J.; Meseguer, J.; Cayuela, M.L.; Mulero, V. Evolution of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) recognition and signaling: Fish TLR4 does not recognize LPS and negatively regulates NF-κB activation. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuil, G.; BonamiI, J.R.; Pepin, J.F.; Pichot, Y. Viral infection (picorna-like virus) associated with mass mortalities in hatchery-reared sea-bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae and juveniles. Aquaculture 1991, 97, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castric, J.; Thiéry, R.; Jeffroy, J.; de Kinkelin, P.; Raymond, J.C. Sea bream Sparus aurata, an asymptomatic contagious fish host for nodavirus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2001, 47, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Guardiola, F.A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A.; Cuesta, A. Nodavirus infection induces a great innate cell-mediated cytotoxic activity in resistant, gilthead seabream, and susceptible, European sea bass, teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, T.; Imajo-Ohmi, S.; Fukuda, H.; Kano, S.; Miyake, K.; Watanabe, N. Mast cell-mediated immune responses through IgE antibody and Toll-like receptor 4 by malarial peroxiredoxin. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, G.E.; Taylor, T.E.; Molyneux, M.E.; Wirima, J.J.; Vassalli, P.; Hommel, M.; Lambert, P.H. Tumour necrosis factor and disease severity in children with falciparum malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.Y.; Chae, H.Z.; Rhee, S.G.; Jeang, K.T. Regulatory role for a novel human thioredoxin peroxidase in NF-κB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30952–30961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haridas, V.; Ni, J.; Meager, A.; Su, J.; Yu, G.L.; Zhai, Y.; Kyaw, H.; Akama, K.T.; Hu, J.; van Eldik, L.J.; Aggarwal, B.B. TRANK, a novel cytokine that activates NF-κB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fisher, A.B. Peroxiredoxin 6: A bifunctional enzyme with glutathione peroxidase and phospholipase A2 activities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, Y.; Morcillo, P.; Meseguer, J.; Buonocore, F.; Esteban, M.A.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A. Characterization of the interferon pathway in the teleost fish gonad against the vertically transmitted viral nervous necrosis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2176–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, J.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A.; Tafalla, C. Immune effects observed after the injection of plasmids coding for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) CK5B, CK6 and CK7A chemokines demonstrate their immunomodulatory capacity and reveal CK6 as a major interferon inducer. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Sun, B.; Robertsen, B. Adjuvant activity of fish type I interferon shown in a virus DNA vaccination model. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valero, Y.; Martínez-Morcillo, F.J.; Esteban, M.Á.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A. Fish Peroxiredoxins and Their Role in Immunity. Biology 2015, 4, 860-880. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040860
Valero Y, Martínez-Morcillo FJ, Esteban MÁ, Chaves-Pozo E, Cuesta A. Fish Peroxiredoxins and Their Role in Immunity. Biology. 2015; 4(4):860-880. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040860
Chicago/Turabian StyleValero, Yulema, Francisco J. Martínez-Morcillo, M. Ángeles Esteban, Elena Chaves-Pozo, and Alberto Cuesta. 2015. "Fish Peroxiredoxins and Their Role in Immunity" Biology 4, no. 4: 860-880. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040860
APA StyleValero, Y., Martínez-Morcillo, F. J., Esteban, M. Á., Chaves-Pozo, E., & Cuesta, A. (2015). Fish Peroxiredoxins and Their Role in Immunity. Biology, 4(4), 860-880. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040860







