Hepatic Macrophages in Chronic Hepatitis B: Balancing Immunity and Pathology
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
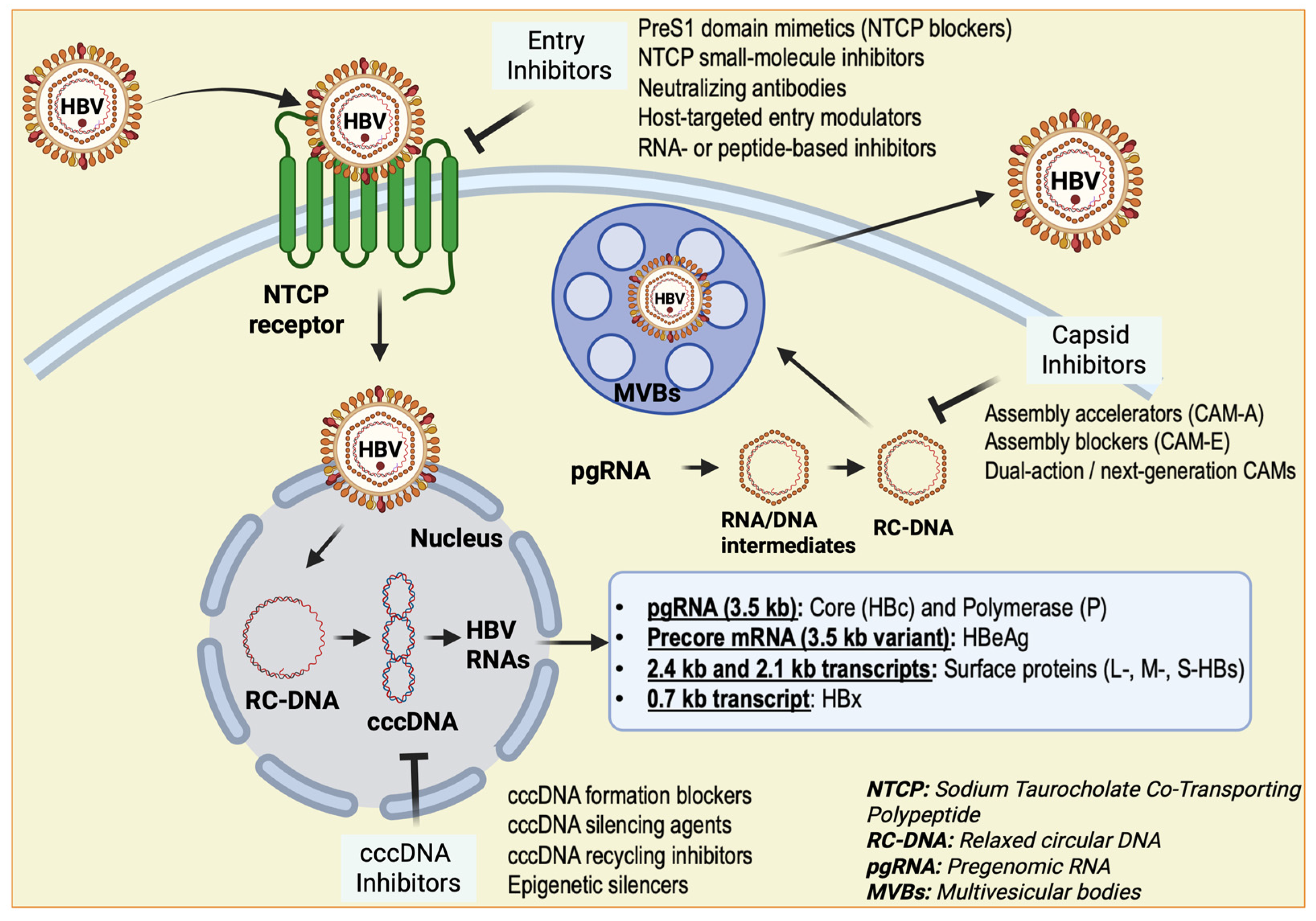
2. Macrophages: Origin, Subtypes, and Functions
2.1. Monocyte-Derived vs. Tissue-Resident
2.2. Functional Polarization of Macrophages: M1 vs. M2 Phenotypes
2.3. Role of Macrophages in HBV Immunity and Tissue Homeostasis
3. Immune Evasion Mechanisms Used by HBV to Subvert Macrophage Functions
4. Macrophages and HBV-Induced Liver Damage
4.1. Role of Macrophage-Derived Cytokines in Liver Damage
4.2. Cytokine Balance: A Determinant of Disease Outcome
4.3. Role of Macrophages in Liver Repair
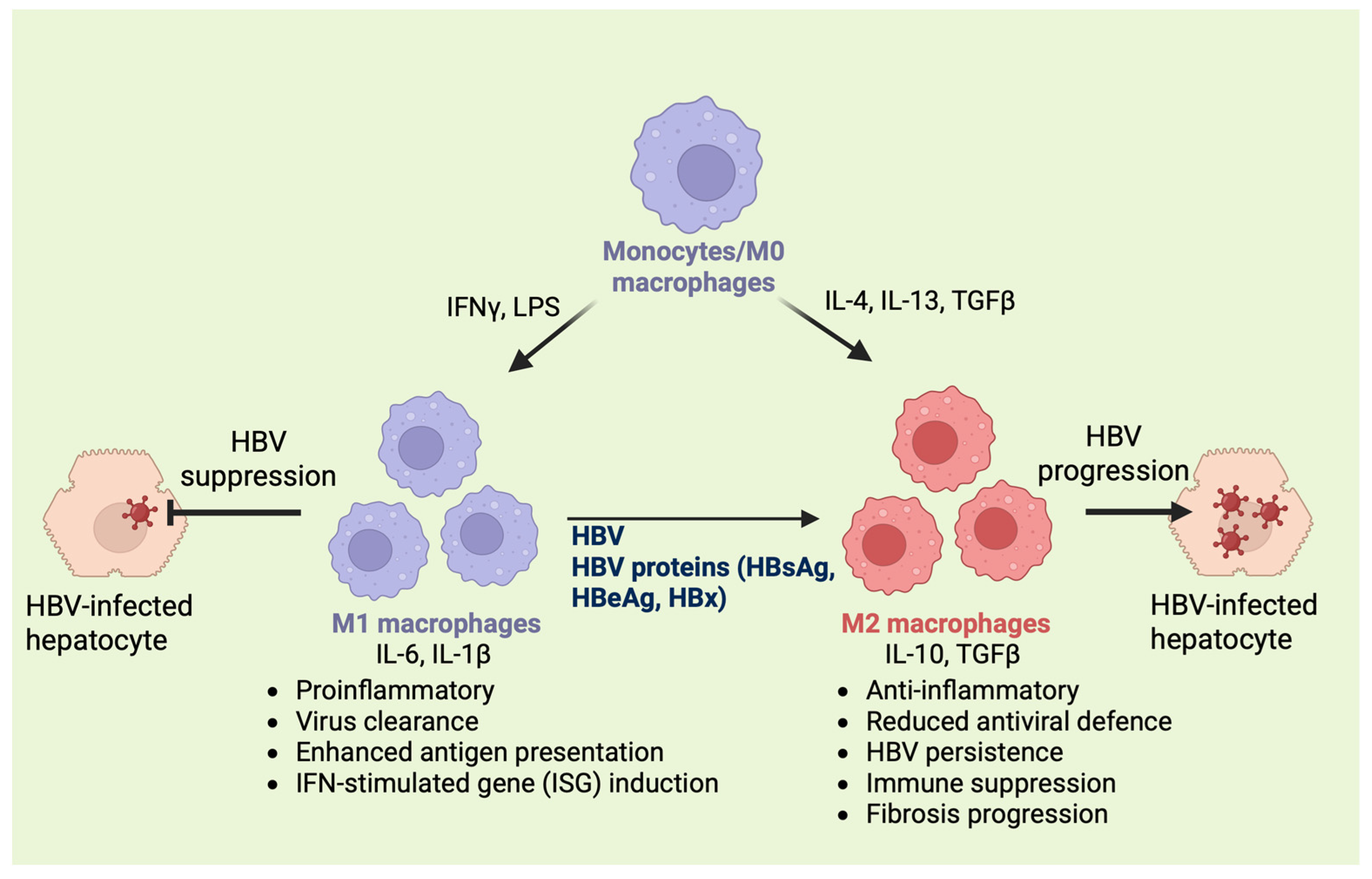
5. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Studies Identifying Distinct Macrophage Subsets in HBV or HBV-Related HCC
6. Therapeutic Implications
6.1. TLR Agonists
6.2. CCR2/CCL2 Inhibitors
6.3. Immune Modulators Targeting Macrophage Function
6.4. Nanoparticle-Based Strategies for Targeting Macrophages
| Therapeutic Strategy | Example Agents | Mechanism of Action | Therapeutic Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agents currently in clinical use (Approved/Standard of Care): | |||
| Nucleos(t)ide Analogues | Tenofovir, Entecavir | Inhibit HBV polymerase and reduce viral replication | Decrease viral load, prevent progression of liver disease [127,128] |
| Interferon-Alpha (IFN-α) | Pegylated IFN-α | Stimulate macrophages, NK cells, and dendritic cells to produce antiviral cytokines. | Induce viral suppression and immune restoration [129] |
| Agents in clinical development: | |||
| TLR Agonists | GS-9620 (TLR7), Selgantolimod (TLR8) | Activate macrophages and innate immunity through type I interferon and pro-inflammatory cytokines. | Suppress HBV replication, enhance antiviral immune response [130,131] |
| CCR2/CCL2 Inhibitors | Cenicriviroc | Inhibit monocyte recruitment to the liver, reducing infiltration of pro-fibrotic macrophages. | Limit inflammation and liver fibrosis [132] |
| CSF-1/CSF-1R Inhibitors | Pexidartinib | Modulate or deplete macrophage subsets via CSF-1R inhibition | Suppress immunosuppressive macrophages and support immune activation [133] |
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors | Anti-PD-1, Anti-PD-L1 | Restore exhausted T cells and downregulate PD-L1 expression on macrophages. | Enhance T cell activity, reduce immune suppression [134]. |
| Therapeutic Vaccines | GS-4774, NASVAC | Stimulate virus-specific T cell responses and macrophage activation | Boost adaptive immunity and reduce HBV persistence [135] |
| Preclinical/early translational approaches: | |||
| Liposome-Encapsulated Agents | Mannose-functionalized liposomes | Target mannose receptors on macrophages for selective uptake | Deliver siRNAs or immune modulators to hepatic macrophages [136] |
| Ligand-Conjugated Nanoparticles | CD163- or scavenger receptor-targeted systems | Enhance macrophage-specific delivery and reduce systemic toxicity in cancer models. Although CD163-targeted nanoparticles have not yet been tested in HBV, the upregulation of CD163 in hepatic macrophages during chronic HBV makes it a promising target for selective macrophage-specific delivery. | Improve therapeutic specificity and effectiveness [137]. |
| RNA-Based Therapeutics | siRNA/mRNA nanoparticles | Silence fibrotic or immunosuppressive genes in macrophages | Reprogram macrophages and aid viral clearance [138] |
| Hybrid/Stimuli-Responsive Systems | Enzyme/pH-sensitive nanocarriers | Controlled release triggered by the inflammatory liver environment | Precision delivery to modulate macrophage activity in HBV livers [139] |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cccDNA | Covalently closed circular DNA |
| HSC | Hepatic stellate cell |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HbcAg | Hepatitis B core antigen |
| HbsAg | Hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HSPG | Heparan sulfate proteoglycans |
| HBeAg | Hepatitis B e antigen |
| IRF3 | Interferon regulatory factor 3 |
| ISG | Interferon-stimulated genes |
| IL-18 | Interleukin-18 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| MDMs | Monocyte-derived macrophages |
| NTCP | Sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| rcDNA | Relaxed circular DNA |
| CX3CL1 | C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1 |
| CX3CR1 | C-X3-C motif chemokine receptor 1 |
| CCL2 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| PRRs | Pattern recognition receptors |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand 1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| STING | Stimulator of interferon genes |
| RIG-I | Retinoic acid-inducible gene I |
| CSF-1 | Colony-stimulating factor 1 |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
References
- Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B: The virus and disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonderup, M.W.; Spearman, C.W. Global Disparities in Hepatitis B Elimination-A Focus on Africa. Viruses 2022, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report 2024: Action for Access in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672 (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Schweitzer, A.; Horn, J.; Mikolajczyk, R.T.; Krause, G.; Ott, J.J. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimakawa, Y.; Lemoine, M.; Njai, H.F.; Bottomley, C.; Ndow, G.; Goldin, R.D.; Jatta, A.; Jeng-Barry, A.; Wegmuller, R.; Moore, S.E.; et al. Natural history of chronic HBV infection in West Africa: A longitudinal population-based study from The Gambia. Gut 2016, 65, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.I.; Rajbhandari, R.; Kew, M.C.; Vento, S.; Preiser, W.; Hoepelman, A.I.; Theron, G.; Cotton, M.; Cohn, J.; Glebe, D.; et al. Mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus in sub-Saharan Africa: Time to act. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e358–e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitford, K.; Liu, B.; Micallef, J.; Yin, J.K.; Macartney, K.; Van Damme, P.; Kaldor, J.M. Long-term impact of infant immunization on hepatitis B prevalence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, Y. Progress on global hepatitis elimination targets. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 8199–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgi, C.; D’Souza, S.; Osiowy, C.; Coffin, C.S.; Cooper, C.L. Chronic hepatitis B virus persistence: Mechanisms, consequences and implications for achieving cure. Ann. Hepatol. 2025, 30, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revill, P.A.; Locarnini, S.A. New perspectives on the hepatitis B virus life cycle in the human liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddleston, A.L.W.F.; Mondelli, M. Immunopathological mechanisms of liver cell injury in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 1986, 3, S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C. HBV and the immune response. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Kuo, C.F.; Akbari, O.; Ou, J.H. Maternal-Derived Hepatitis B Virus e Antigen Alters Macrophage Function in Offspring to Drive Viral Persistence after Vertical Transmission. Immunity 2016, 44, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Duan, X.; Yang, C.; Xu, M.; Chen, L. Macrophage Phenotypes and Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure-Dupuy, S.; Durantel, D.; Lucifora, J. Liver macrophages: Friend or foe during hepatitis B infection? Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Yang, D.; Lu, M. Toll-like receptor-mediated innate immunity orchestrates adaptive immune responses in HBV infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 965018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Cao, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, E.; Lu, M. Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus and Toll-Like Receptors: Current Status and Potential Therapeutic Use for Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yi, Z.; Ma, C.; Sun, B.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, X.; Hui, L.; Xia, Y. Innate immune recognition in hepatitis B virus infection. Virulence 2025, 16, 2492371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S. Innate immune evasion by hepatitis B virus-mediated downregulation of TRIF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Gao, H.; Guo, S.; Kang, X.; Yuan, J.; Lv, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yi, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Mechanisms underlying the compromised clinical efficacy of interferon in clearing HBV. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Kouadir, M.; Song, H.; Shi, F. Recent advances in the mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Hao, R.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Tien, P.; Guo, D. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 3368–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Duan, Z.; Duan, W.; Ruan, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Activation of the cGAS-STING pathway by viral dsDNA leading to M1 polarization of macrophages mediates antiviral activity against hepatitis B virus. Immunobiology 2024, 229, 152810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yum, S.; Li, M.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Z.J. TBK1 recruitment to STING activates both IRF3 and NF-κB that mediate immune defense against tumors and viral infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100225118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, H. Novel insights into the role of cGAS-STING signaling in HBV infection. Virology 2025, 611, 110639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Lee, J.; Ning, Q.; Lim, J.; Eoh, H.; Wang, S.; Hurrell, B.P.; Akbari, O.; Ou, J.J. Hepatitis B virus e antigen induces atypical metabolism and differentially regulates programmed cell deaths of macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Lv, H.; Liu, C.; Su, X.; Yu, Z.; Song, S.; Bian, H.; Tian, M.; Qin, C.; Qi, J.; et al. HBeAg mediates inflammatory functions of macrophages by TLR2 contributing to hepatic fibrosis. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Du, X.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase Disrupts K63-Linked Ubiquitination of STING To Block Innate Cytosolic DNA-Sensing Pathways. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2287–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Z. HBV-Induced Immune Imbalance in the Development of HCC. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure-Dupuy, S.; Delphin, M.; Aillot, L.; Dimier, L.; Lebossé, F.; Fresquet, J.; Parent, R.; Matter, M.S.; Rivoire, M.; Bendriss-Vermare, N.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-induced modulation of liver macrophage function promotes hepatocyte infection. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1086–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, A.J.; Protzer, U. Targeting Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to Cure Chronic HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Laar, L.; Saelens, W.; De Prijck, S.; Martens, L.; Scott, C.L.; Van Isterdael, G.; Hoffmann, E.; Beyaert, R.; Saeys, Y.; Lambrecht, B.N.; et al. Yolk Sac Macrophages, Fetal Liver, and Adult Monocytes Can Colonize an Empty Niche and Develop into Functional Tissue-Resident Macrophages. Immunity 2016, 44, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honold, L.; Nahrendorf, M. Resident and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez Vasquez, J.D.; Nkongolo, S.; Traum, D.; Sotov, V.; Kim, S.C.; Mahamed, D.; Mehrotra, A.; Patel, A.; Chen, D.Y.; Fung, S.; et al. Virus-associated inflammation imprints an inflammatory profile on monocyte-derived macrophages in the human liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e175241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, M.C. Macrophage polarization: Reaching across the aisle? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1348–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango Duque, G.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bility, M.T.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Luan, Y.; Li, F.; Chi, L.; Zhang, L.; Tu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and immunopathogenesis in a humanized mouse model: Induction of human-specific liver fibrosis and M2-like macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Hu, H.; Xiong, J.; Wang, N.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; et al. Hepatitis B Core Antigen Impairs the Polarization While Promoting the Production of Inflammatory Cytokines of M2 Macrophages via the TLR2 Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöcker, U.; Schultz, U.; Schaller, H.; Protzer, U. Endotoxin stimulates liver macrophages to release mediators that inhibit an early step in hepadnavirus replication. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5525–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hösel, M.; Quasdorff, M.; Wiegmann, K.; Webb, D.; Zedler, U.; Broxtermann, M.; Tedjokusumo, R.; Esser, K.; Arzberger, S.; Kirschning, C.J.; et al. Not interferon, but interleukin-6 controls early gene expression in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, H.W.; Chen, H.; Xing, Z.Z.; You, H.; Cong, M.; Jia, J.D. Hepatitis B virus particles preferably induce Kupffer cells to produce TGF-β1 over pro-inflammatory cytokines. Dig. Liver Dis. 2012, 44, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.H.; Chou, Y.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Tsai, K.N.; Hu, C.P.; Jeng, K.S.; Chen, M.L.; Chang, C. Transforming growth factor-β1 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication by the reduction of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α expression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yin, W.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Kupffer cell-derived IL-10 plays a key role in maintaining humoral immune tolerance in hepatitis B virus-persistent mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Yang, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Facilitates Hepatitis B Virus Replication through Binding with Type I Interferon (IFN) Receptor 1 To Repress IFN/JAK/STAT Signaling. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01824-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Lefebvre, A.T.; Horuzsko, A. Kupffer Cell Metabolism and Function. J. Enzymol. Metab. 2015, 1, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto, N.; Kanai, T. Role of toll-like receptors in immune activation and tolerance in the liver. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Tacke, F. Hepatic macrophages in homeostasis and liver diseases: From pathogenesis to novel therapeutic strategies. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispe, I.N. Liver antigen-presenting cells. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venzin, V.; Beccaria, C.G.; Perucchini, C.; Delfino, P.; Bono, E.B.; Giustini, L.; Moalli, F.; Grillo, M.; Fumagalli, V.; Laura, C.; et al. CD4+ T cells license Kupffer cells to reverse CD8+ T cell dysfunction induced by hepatocellular priming. Nat. Immunol. 2025, 26, 1352–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tao, Q.; Sun, M.; Wu, J.Z.; Yang, W.; Jian, P.; Peng, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, P. Kupffer cells are associated with apoptosis, inflammation and fibrotic effects in hepatic fibrosis in rats. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Gong, J.; Chen, Y. Role of Kupffer cells in tolerance induction after liver transplantation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1179077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, R.; Xu, L.; Yin, W.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lian, Z.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Kupffer Cells Support Hepatitis B Virus-Mediated CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion via Hepatitis B Core Antigen-TLR2 Interactions in Mice. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Salcedo, R.; Mivechi, N.F.; Trinchieri, G.; Horuzsko, A. The proinflammatory myeloid cell receptor TREM-1 controls Kupffer cell activation and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3977–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; Qu, M.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Huang, M.; Pan, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the heterogeneity of liver-resident immune cells in human. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacParland, S.A.; Liu, J.C.; Ma, X.Z.; Innes, B.T.; Bartczak, A.M.; Gage, B.K.; Manuel, J.; Khuu, N.; Echeverri, J.; Linares, I.; et al. Single cell RNA sequencing of human liver reveals distinct intrahepatic macrophage populations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, L.G.; Wei, Z.; Schulte, A.; Cline, H.M.; Bernard, M.P.; Buchweitz, J.P.; McGill, M.R.; Luyendyk, J.P. Kupffer cell expression of macrophage receptor with collagenous structure modulates macrophage gene induction and limits acute liver injury. Toxicol. Sci. 2025, 205, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, P.; Mao, T.; Tian, Z.; Li, X. The role and therapeutic targeting of the CCL2/CCR2 signaling axis in inflammatory and fibrotic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1497026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Yin, S.; Issa, R.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Li, J. Key role of macrophages in the progression of hepatic fibrosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, K.; Jin, N.; Tang, B.; Zhang, W. Macrophage in liver Fibrosis: Identities and mechanisms. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, S.; Ishida, Y.; Chiu, T.-P.; Saito, T.; Wang, S.; Ann, D.K.; Ou, J.-h.J. Macrophages activated by hepatitis B virus have distinct metabolic profiles and suppress the virus via IL-1β to downregulate PPARα and FOXO3. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Li, Q. Hepatic macrophage niche: A bridge between HBV-mediated metabolic changes with intrahepatic inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1414594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Li, H.; Liu, K.; Zhang, P.; Zhuang, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Cheng, K.; Ming, Y. Intrahepatic macrophage reprogramming associated with lipid metabolism in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Jiang, J.; Yang, L.; Xin, J.; Shi, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, K.; Hassan, H.M.; et al. PBMC transcriptomics identifies immune-metabolism disorder during the development of HBV-ACLF. Gut 2022, 71, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adugna, A.; Azanaw Amare, G.; Jemal, M. Current Advancements in Serum Protein Biomarkers for Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocyte Remodeling and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2025, 13, e70171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Qin, S.; Zhang, F.; Hu, W.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Kong, F.; Pan, X.; Zheng, K.; Tang, R. Regulation of Pattern-Recognition Receptor Signaling by HBX During Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 829923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Qian, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, M.; Shi, B.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen selectively inhibits TLR2 ligand-induced IL-12 production in monocytes/macrophages by interfering with JNK activation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5142–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhao, K.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J. Hepatitis B surface antigen impairs TLR4 signaling by upregulating A20 expression in monocytes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0090924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosaka, T.; Ohtani, M.; Yamashita, J.; Murata, Y.; Akazawa, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, K.; Naito, T.; Imamura, Y.; Koneri, K.; et al. PD-L1(+) tumor-associated macrophages induce CD8(+) T Cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasia 2025, 69, 101234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.P.; de Carvalho, A.; Paiva, A.; Borges, O. Insights into Immune Exhaustion in Chronic Hepatitis B: A Review of Checkpoint Receptor Expression. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Lin, L.; Huang, J.; Huang, W.; Cai, M.; Cai, W.; Guo, Y.; et al. HBV suppresses macrophage immune responses by impairing the TCA cycle through the induction of CS/PDHC hyperacetylation. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Zeng, R.; Pan, W. The hijacking of HBV by small extracellular vesicles inhibits M1 macrophages to facilitate immune evasion. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Niu, J.; Shi, Y. Exosomes target HBV-host interactions to remodel the hepatic immune microenvironment. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouwaki, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Daito, T.; Sanada, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Mifsud, E.J.; Leong, C.R.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Kohara, M.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Including Exosomes Regulate Innate Immune Responses to Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeno, S.; Kodama, T.; Murai, K.; Motooka, D.; Fukushima, A.; Nishio, A.; Hikita, H.; Tatsumi, T.; Okamoto, T.; Kanto, T.; et al. Intrahepatic Exhausted Antiviral Immunity in an Immunocompetent Mouse Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Zong, Q.; Duan, Z.; Liu, F.; Duan, W.; Ruan, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Interferon-induced polarization of M1 macrophages mediates antiviral activity against the hepatitis B virus via the hepcidin-ferroportin axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 134, 112219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Lin, S.S.; Ho, Y.C.; Chen, F.L.; Yang, C.C. The immune response induced by hepatitis B virus principal antigens. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 3, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Tiegs, G.; Horst, A.K. TNF in the liver: Targeting a central player in inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Tovar, E.; Muriel, P. Molecular Mechanisms That Link Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in the Liver. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhang, T.; Tang, L.; Li, Y. Cytokines and Chemokines in HBV Infection. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 805625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M. Involvement of Interleukin 6 in Hepatitis B Viral Infection. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, M.; Zohora, F.T.; Anka, A.U.; Ali, K.; Maleknia, S.; Saffarioun, M.; Azizi, G. Interleukin-6 cytokine: An overview of the immune regulation, immune dysregulation, and therapeutic approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lin, H.; Wu, G.; Zhu, M.; Li, M. IL-6/STAT3 Is a Promising Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 760971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oft, M. Immune regulation and cytotoxic T cell activation of IL-10 agonists—Preclinical and clinical experience. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 44, 101325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Ellis, G.; Pallant, C.; Lopes, A.R.; Khanna, P.; Peppa, D.; Chen, A.; Blair, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Gill, U.; et al. IL-10-producing regulatory B cells in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, P.; Barili, V.; Rossi, M.; Montali, I.; Vecchi, A.; Acerbi, G.; Laccabue, D.; Zecca, A.; Penna, A.; Missale, G.; et al. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of T Cell Dysfunction in Chronic HBV Infection and Related Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gingold, J.A.; Su, X. Immunomodulatory TGF-β Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.S.; Wu, S.D.; Wang, S.Q.; Li, L.; She, W.M.; Li, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Jiang, W. IL-10-producing regulatory B-cells suppressed effector T-cells but enhanced regulatory T-cells in chronic HBV infection. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppa, D.; Micco, L.; Javaid, A.; Kennedy, P.T.; Schurich, A.; Dunn, C.; Pallant, C.; Ellis, G.; Khanna, P.; Dusheiko, G.; et al. Blockade of immunosuppressive cytokines restores NK cell antiviral function in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Zhai, N.C.; Song, H.X.; Yang, Y.; Cui, A.; Li, T.Y.; Tu, Z.K. The Role of Immune Cells in Chronic HBV Infection. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2015, 3, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, I.S.; Park, S.H. Immune-mediated Liver Injury in Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Immune Netw. 2015, 15, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Abdel-Hafiz, H.; Ali, A.; Fatima, K.; Damanhouri, G.A.; Azhar, E.; Chaudhary, A.G.; Qadri, I. Potential mechanisms of hepatitis B virus induced liver injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12462–12472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilperoort, M.; Ngai, D.; Sukka, S.R.; Avrampou, K.; Shi, H.; Tabas, I. The role of efferocytosis-fueled macrophage metabolism in the resolution of inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 319, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taru, V.; Szabo, G.; Mehal, W.; Reiberger, T. Inflammasomes in chronic liver disease: Hepatic injury, fibrosis progression and systemic inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinhaes, C.L.; Cruz, L.A.B.; Menezes, R.C.; Carmo, T.A.; Arriaga, M.B.; Queiroz, A.T.L.; Barral-Netto, M.; Andrade, B.B. Chronic Hepatitis B Infection Is Associated with Increased Molecular Degree of Inflammatory Perturbation in Peripheral Blood. Viruses 2020, 12, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhao, W.; Yin, S.; Lei, F.; Pang, X.; Sun, W.; Feng, L.; Jia, S.; Li, W.; et al. Single-cell profiling reveals monocyte heterogeneity and association with liver fibrosis in patients with chronic HBV. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9, e0672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, C.; Yong, X.; Zhou, W.; Xie, Y.; Shu, J. Integrative Single-Cell and Bulk Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies Macrophage-Related Gene Signatures Predictive of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhosis. Genes 2025, 16, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.W.-H.; Tsui, Y.-M.; Chan, L.-K.; Sze, K.M.-F.; Zhang, X.; Cheu, J.W.-S.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Lee, J.M.-F.; Chan, A.C.-Y.; Cheung, E.T.-Y.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing shows the immunosuppressive landscape and tumor heterogeneity of HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Naz, W.; Yousaf, T.; Sun, J.; Wu, Q.; Guo, M.; Tian, G.; Sun, G. Viral-Track integrated single-cell RNA-sequencing reveals HBV lymphotropism and immunosuppressive microenvironment in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmares, M.; Delphin, M.; Chardès, B.; Pons, C.; Riedinger, J.; Michelet, M.; Rivoire, M.; Verrier, B.; Salvetti, A.; Lucifora, J.; et al. Insights on the antiviral mechanisms of action of the TLR1/2 agonist Pam3CSK4 in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected hepatocytes. Antivir. Res. 2022, 206, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Suarez, A.A.; Plissonnier, M.L.; Grand, X.; Michelet, M.; Giraud, G.; Saez-Palma, M.; Dubois, A.; Heintz, S.; Diederichs, A.; Van Renne, N.; et al. TLR8 agonist selgantolimod regulates Kupffer cell differentiation status and impairs HBV entry into hepatocytes via an IL-6-dependent mechanism. Gut 2024, 73, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; Brunetto, M.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Ferrari, C.; Massetto, B.; Nguyen, A.-H.; Joshi, A.; Woo, J.; Lau, A.H.; Gaggar, A.; et al. Safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamics of vesatolimod (GS-9620) in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, T.H.; Al-Yami, A.; Mtiraoui, N.; Gharbi, J.; Ben M’hadheb, M. Downregulation of Toll-Like Receptor Gene Expression Among Hepatitis B Virus-Positive Human Patients. Cureus 2025, 17, e90391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, S.; Ren, L.; Chen, P.; Wang, M.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Functional Roles of Chemokine Receptor CCR2 and Its Ligands in Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzo, M.; Ferro, A.; Navarro-Tableros, V.M.; Gaido, A.; Fornengo, P.; Altruda, F.; Romagnoli, R.; Moestrup, S.K.; Calvo, P.L.; Fagoonee, S. Current Treatment Regimens and Promising Molecular Therapies for Chronic Hepatobiliary Diseases. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Lucas, K.J.; Francque, S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Ratziu, V.; Gadano, A.C.; Rinella, M.; Charlton, M.; Loomba, R.; et al. Tropifexor plus cenicriviroc combination versus monotherapy in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Results from the phase 2b TANDEM study. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1223–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Qin, A.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chen, P.J. Novel Pegylated Interferon for the Treatment of Chronic Viral Hepatitis. Viruses 2022, 14, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Z.; Fang, L.; Liu, J. Recent advances in understanding T cell activation and exhaustion during HBV infection. Virol. Sin. 2023, 38, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yan, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Z.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, P.; et al. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Immunotherapy Employed in Treating Hepatitis B Virus Infection-Related Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Literature Review. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, H.T.; Tsai, H.F.; Liao, H.J.; Lin, Y.J.; Chen, L.; Chen, P.J.; Hsu, P.N. PD-1 blockage reverses immune dysfunction and hepatitis B viral persistence in a mouse animal model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, M.K.; Pallett, L.J. Defective T-cell immunity in hepatitis B virus infection: Why therapeutic vaccination needs a helping hand. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colino, C.I.; Lanao, J.M.; Gutierrez-Millan, C. Targeting of Hepatic Macrophages by Therapeutic Nanoparticles. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Zhou, F.; Ge, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Mannosylated liposomes for targeted gene delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Gao, P.; Li, Q.; He, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, L. Advances in Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems for Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Therapy: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, M.; Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Elmowafy, E.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; Awad, G.A.S. An integrated vitamin E-coated polymer hybrid nanoplatform: A lucrative option for an enhanced in vitro macrophage retention for an anti-hepatitis B therapeutic prospect. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, S.; Schulze, A.; Dandri, M.; Petersen, J. The replication cycle of hepatitis B virus. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.N.; Kuo, C.F.; Ou, J.J. Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus Persistence. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverniti, V.; Ligat, G.; Debing, Y.; Kum, D.B.; Baumert, T.F.; Verrier, E.R. Capsid Assembly Modulators as Antiviral Agents against HBV: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, S.; Zhao, S.; Xu, X.; Poongavanam, V.; Menéndez-Arias, L.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X. Targeting hepatitis B virus cccDNA levels: Recent progress in seeking small molecule drug candidates. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Cheng, S.; Ren, F.; Gu, H.; Wu, D.; Yao, X.; Tan, M.; Huang, A.; Chen, J. Epigenetic regulation and its therapeutic potential in hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA. Genes Dis. 2025, 12, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrier, E.R.; Colpitts, C.C.; Sureau, C.; Baumert, T.F. Hepatitis B virus receptors and molecular drug targets. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Yuan, W.; Yu, D.; Zhang, K.; Shi, B.; Chen, X.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptors of HBV envelope proteins inhibit hepatitis B surface antigen secretion. Gut 2024, 73, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.F.U.H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B Reactivation Associated With Immune Suppressive and Biological Modifier Therapies: Current Concepts, Management Strategies, and Future Directions. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipery, A.; Gehring, A.J.; Isogawa, M. Mechanisms of HBV immune evasion. Antivir. Res. 2020, 179, 104816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantly, A.; Yeakle, K.; Bouchard, M.J.; Gaskill, P.J.; Nonnemacher, M.R. The role of liver macrophages in viral liver pathogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2025, 117, qiaf088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Ye, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y. Comparison of efficacy and safety of tenofovir and entecavir in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzil, M.; Chaudhary, A.J.; Kashif, T.; Qureshi, A.A.; Muhammad, A.; Khan, F.; Faisal, M.S.; Khaqan, M.A.; Ali, H.; Dababneh, Y.; et al. Switching to Tenofovir Therapy Versus Continuation of Entecavir for Patients With Hepatitis B Virus Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JGH Open 2024, 8, e70055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzella, G.; Saracco, G.; Festi, D.; Rosina, F.; Marchetto, S.; Jaboli, F.; Sostegni, R.; Pezzoli, A.; Azzaroli, F.; Cancellieri, C.; et al. Long-term results with interferon therapy in chronic type B hepatitis: A prospective randomized trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2246–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.J.; Dunbar, P.R.; Brooks, A.E.; Zhang, F.; Chen, D.; Wallin, J.J.; van Buuren, N.; Arora, P.; Fletcher, S.P.; Tan, S.K.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the oral TLR8 agonist selgantolimod in individuals with chronic hepatitis B under viral suppression. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.J.; Lim, Y.S.; Gordon, S.C.; Visvanathan, K.; Sicard, E.; Fedorak, R.N.; Roberts, S.; Massetto, B.; Ye, Z.; Pflanz, S.; et al. The oral toll-like receptor-7 agonist GS-9620 in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Ratziu, V.; Harrison, S.A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Aithal, G.P.; Caballeria, J.; Francque, S.; Farrell, G.; Kowdley, K.V.; Craxi, A.; et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of cenicriviroc for treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with fibrosis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1754–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T.; Yakoub, M.A.; Chandler, A.; Christ, A.B.; Yang, G.; Ouerfelli, O.; Rajasekhar, V.K.; Yoshida, A.; Kondo, H.; Hata, T.; et al. CSF1/CSF1R Signaling Inhibitor Pexidartinib (PLX3397) Reprograms Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Stimulates T-cell Infiltration in the Sarcoma Microenvironment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Massari, M.; Loggi, E.; Biasini, E.; Sacchelli, L.; Cavallo, M.C.; Silini, E.M.; Andreone, P.; Missale, G.; et al. Antiviral intrahepatic T-cell responses can be restored by blocking programmed death-1 pathway in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, A.S.; Pan, C.Q.; Han, S.H.; Trinh, H.N.; Fessel, W.J.; Rodell, T.; Massetto, B.; Lin, L.; Gaggar, A.; Subramanian, G.M.; et al. Randomized phase II study of GS-4774 as a therapeutic vaccine in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.E.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Jia, Y.; Han, Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Yan, Z. Hepatic macrophage targeted siRNA lipid nanoparticles treat non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Control. Release 2022, 343, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skytthe, M.K.; Graversen, J.H.; Moestrup, S.K. Targeting of CD163(+) Macrophages in Inflammatory and Malignant Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunse, T.; Kosinska, A.D.; Michler, T.; Protzer, U. PD-L1 Silencing in Liver Using siRNAs Enhances Efficacy of Therapeutic Vaccination for Chronic Hepatitis B. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Sato, Y.; Munakata, T.; Kakuni, M.; Tateno, C.; Sanada, T.; Hirata, Y.; Murakami, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Chayama, K.; et al. Novel pH-sensitive multifunctional envelope-type nanodevice for siRNA-based treatments for chronic HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Pathania, A.S.; Bhat, S.A.; Adepoju, L.A.; Kharbanda, K.K.; Osna, N.A. Hepatic Macrophages in Chronic Hepatitis B: Balancing Immunity and Pathology. Biology 2026, 15, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology15010076
Pathania AS, Bhat SA, Adepoju LA, Kharbanda KK, Osna NA. Hepatic Macrophages in Chronic Hepatitis B: Balancing Immunity and Pathology. Biology. 2026; 15(1):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology15010076
Chicago/Turabian StylePathania, Anup S., Sajad A. Bhat, Lukman A. Adepoju, Kusum K. Kharbanda, and Natalia A. Osna. 2026. "Hepatic Macrophages in Chronic Hepatitis B: Balancing Immunity and Pathology" Biology 15, no. 1: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology15010076
APA StylePathania, A. S., Bhat, S. A., Adepoju, L. A., Kharbanda, K. K., & Osna, N. A. (2026). Hepatic Macrophages in Chronic Hepatitis B: Balancing Immunity and Pathology. Biology, 15(1), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology15010076