Temporal Variation and Assembly Process of Fish Communities in a Typical Canalized River After the 10-Year Fishing Ban
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Phylogeny Construction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
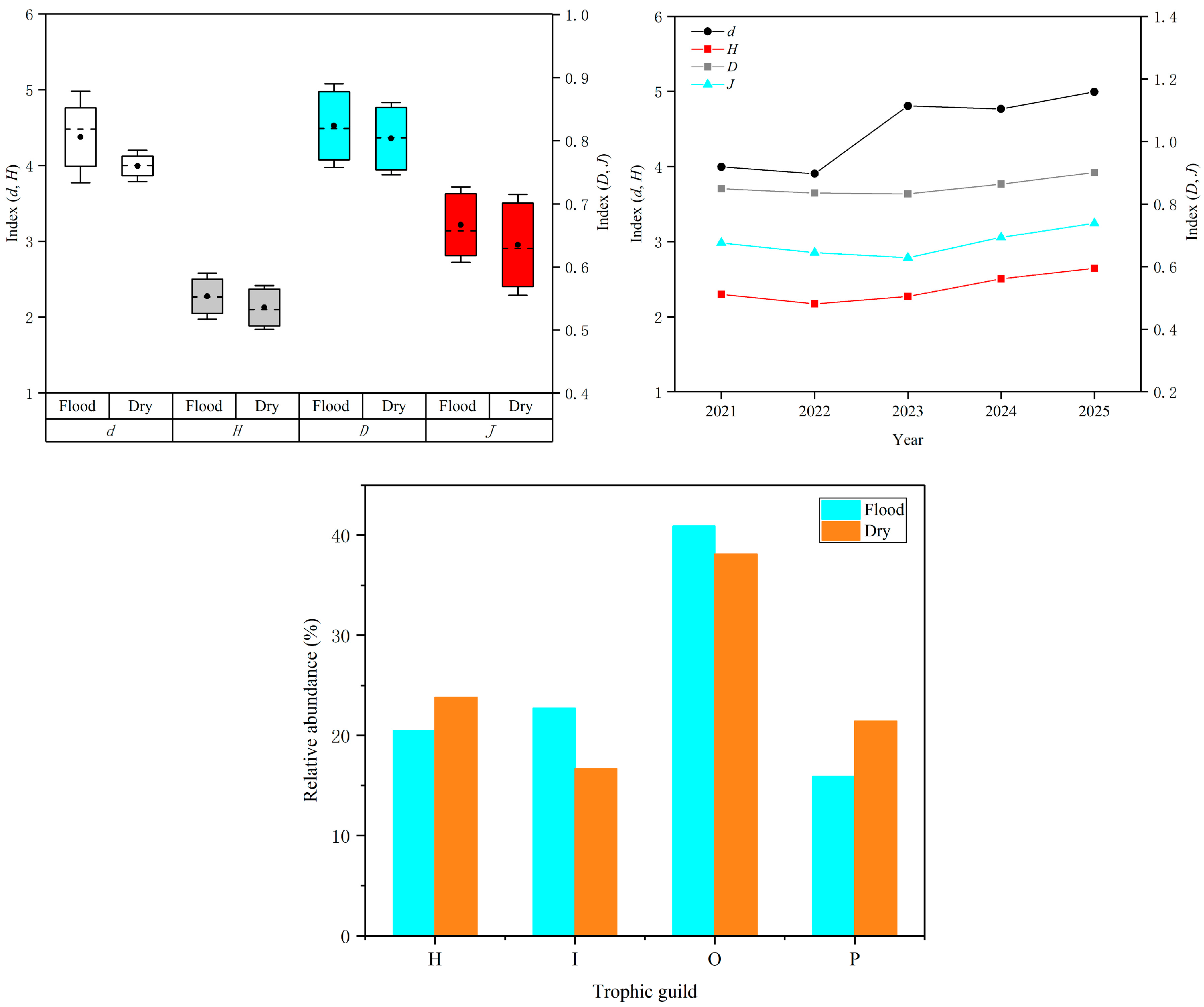
3.1. Fish Species Composition
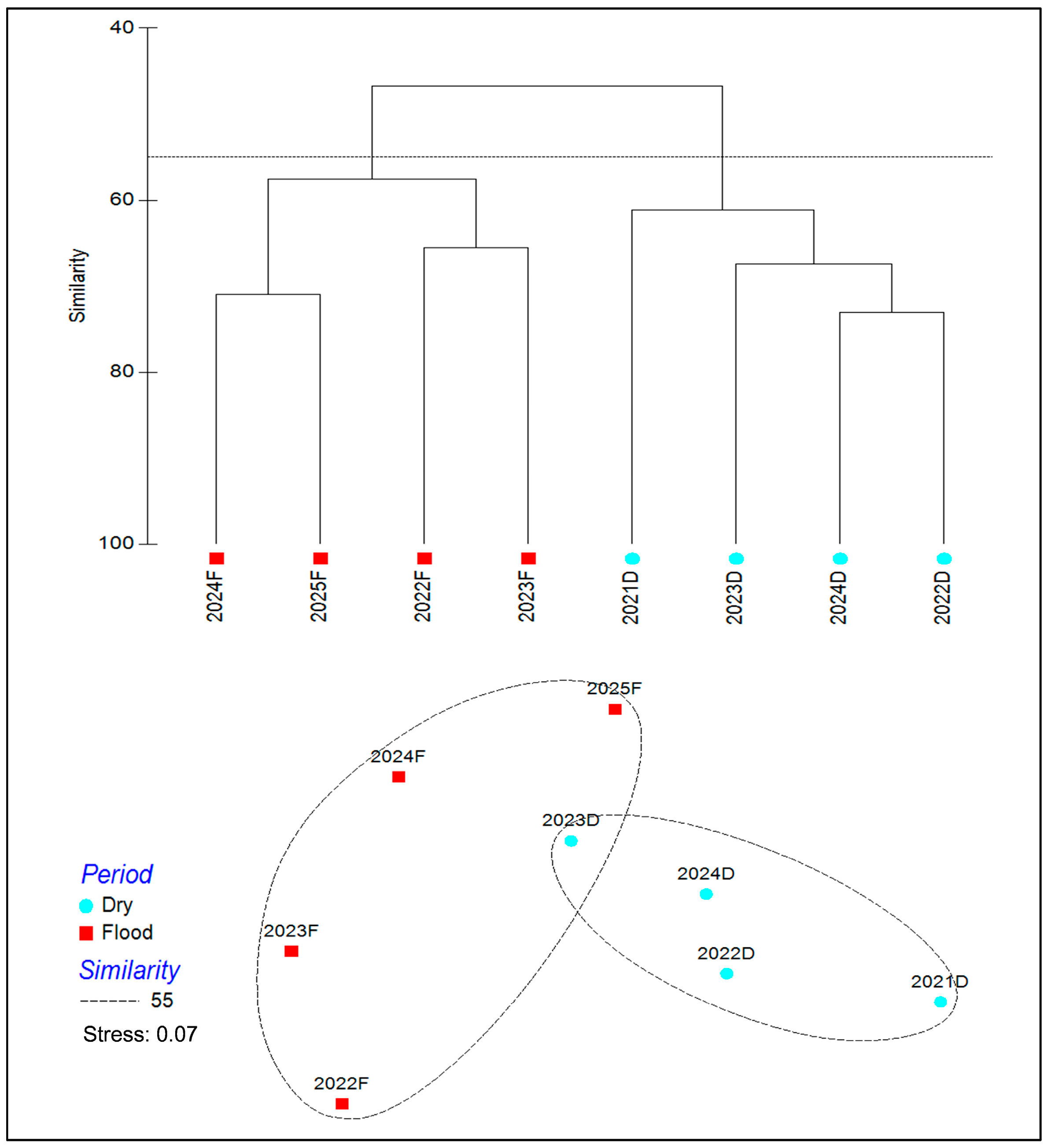
3.2. Temporal Variation in Fish Communities
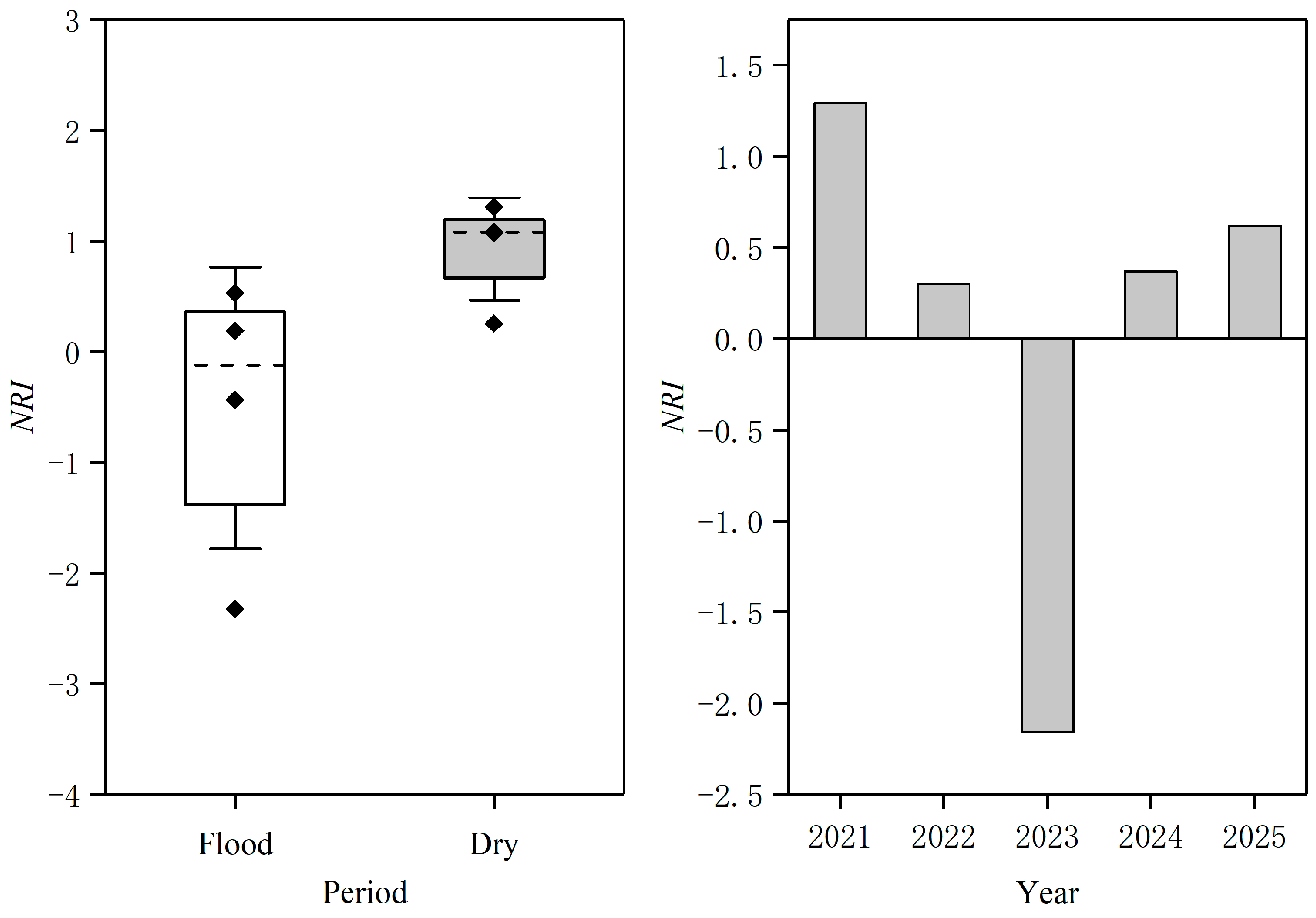
3.3. Assembly Process of Fish Communities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, R.J.; Driscoll, C.T.; Likens, G.E. Importance of hydrogen ions and aluminium in regulating the structure and function of stream ecosystems: An experimental test. Freshw. Biol. 1987, 18, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.; Chu, E. Sustaining living rivers. Hydrobiologia 2004, 423, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Tang, T.; Deng, H. Discussion on freshwater ecosystem service and its evaluation index system. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 14, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zarfl, C.; Tockner, K.; Olden, J.D.; Campos, Z.; Muniz, F.; Svenning, J.-C.; Jähnig, S.C. Hydropower impacts on riverine biodiversity. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.E. Impounded Rivers: Perspectives for Ecological Management; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, D.L.; Meeuwig, J.J.; Vincent, A.C.J. Freshwater protected areas: Strategies forconservation. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, F.; Xia, Z.; Qin, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Changes in fish assemblages following the implementation of a complete fishing closure in the Chishui River. Fish. Res. 2021, 243, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shen, L.; He, Y.; Tian, H.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.; Mei, Z.; Wei, N.; Wang, L.; Zhu, T.; et al. Status of aquatic organisms resources and their environments in Yangtze River system (2017–2021). Aquac. Fish. 2024, 9, 833–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Xie, S. Distribution, endemism and conservation status of fishes in the Yangtze River basin, China. In Ecosystems Biodiversity; Grillo, O., Venora, G., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qu, X.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hughes, R.M. Challenges to saving China’s freshwater biodiversity: Fishery exploitation and landscape pressures. Ambio 2020, 49, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jarić, I.; Roberts, D.L.; He, Y.; Du, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Wei, Q. Extinction of one of the world’s largest freshwater fishes: Lessons for conserving the endangered Yangtze fauna. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Infante, D.M.; Olden, J.D.; Gao, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y. River–lake connectivity, wetland, and human stress factors shape fish diversity (alpha and beta) patterns in the middle and lower Yangtze River, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 3809–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Fan, J.; Guo, F.; Carpenter-Bundhoo, L.; Huang, G.; Shi, Y.; Ao, Y.; Wang, J. Assessing the impact of river connectivity on fish biodiversity in the Yangtze River basin using a multi-index evaluation framework. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Zhao, N.; Sun, H.; Ye, L.; Zhai, J. Changes and relationships of climatic and hydrological droughts in the Jialing River basin, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. The Fish Resources and Angling Fishery Status in the Middle Reaches of JIALING RIVER. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; He, X. Status of fish resources in the lower reaches of the Jialing River. Freshw. Fish. 2008, 38, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhou, X. An analysis of ichthyologic fauna of Jialing River. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2012, 5, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, H. Patterns of Fishes Diversity in Jialing River and Resources Vicissitude in the Middle and Lower Basin. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Du, P.; Yang, K. The calculation and proposals of the hydraulic structure’s influence on the fish resource in the Jialing River. J. Sichuan Teach Coll. 1989, 10, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. The Study on Community Structure and Population Biology Research of the Main Economic Fish for the Middle Reaches of Jialing River Pengan. Master’s Thesis, China West Normal University, Nanchong, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Xiong, X.; Wu, N.; Zeng, Y.; Fohrer, N. Length-weight relationships of two fish species from the Jialing River, the largest tributary of the upper Yangtze River, China. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2018, 34, 1373–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, S.; Buhan, E.; Winemiller, K.O.; Yilmaz, H. Fish assemblage structure of Koycegiz Lagoon–Estuary, Turkey: Spatial and temporal distribution patterns in relation to environmental variation. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Logez, M.; Xu, J.; Tao, S.; Villéger, S.; Brosse, S. Human impacts on global freshwater fish biodiversity. Science 2021, 371, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Lasso, C.A.; Rosales, J. Stability and spatio-temporal structure in fish assemblages of two floodplain lagoons of the lower Orinoco River. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2009, 7, 719–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X. Conservation Biology of Rare and Endemic Fishes of the Yangtze River. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Changes in fish resources 5 years after implementation of the 10-year fishing ban in the Chishui River, the first river with a complete fishing ban in the Yangtze River Basin. Ecol. Process. 2023, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. Niche tradeoffs, neutrality, and community structure: A stochastic theory of resource competition, invasion, and community assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10854–10861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibold, M.A.; McPeek, M.A. Coexistence of the niche and neutral perspectives in community ecology. Ecology 2006, 87, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, D.; Canham, C.D.; Beaudet, M.; Messier, C. Reconciling niche and neutrality: The continuum hypothesis. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 9, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; He, F.; Fang, J. Community assembly: The relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory. Biodivers. Sci. 2009, 17, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, J.M. Assembly of Species Communities; Belknap Press of Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 342–444. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell, S.P. Neutral theory and the evolution of ecological equivalence. Ecology 2006, 87, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G. The distribution of abundance in neutral communities. Am. Nat. 2000, 155, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, N.; Paradis, E.; Bruggemann, H.; Planes, S. Community assembly and diversification in Indo-Pacific coral reef fishes. Ecol. Evol. 2011, 1, 229–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santorelli, S., Jr.; Magnusson, W.; Ferreira, E.; Caramaschi, E.; Zuanon, J.; Amadio, S. Phylogenetic community structure: Temporal variation in fish assemblage. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2146–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, W.; Shen, Y. Environmental DNA Insights into the Spatial Status of Fish Diversity in the Mainstem of the Jialing River. Animals 2025, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, F.; He, S.; Zhou, T.; Li, S.; Zeng, Y. Length–weight relationships and diversity status of fishes in the midstream of the Jialing River, a tributary of the upper Yangtze River, China. Diversity 2023, 15, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.H. The Fishes of SICHUAN, China; Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology: Chengdu, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y. Fauna Sinica, Osteichthyes, Cypriniformes II.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Cao, W.X. Red List of Biodiversity: Vertebrates, Volume V, Freshwater Fishes; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, F.; Qin, Q.; Liu, H.; Cao, W.; Gao, X. Diet composition and trophic guild structure of fish assemblage in headwaters of the Chishui River, a tributary of the upper Yangtze River, China. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2018, 101, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, H. Food Web Structure and Trophic Interactions Revealed by Stable Isotope Analysis in the Midstream of the Chishui River, a Tributary of the Yangtze River, China. Water 2021, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Information theory in ecology. Soc. Gen. Syst. Res. 1957, 31, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 10, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Chapman, M.G. On resemblance measures for ecological studies, including taxonomic dissimilarities and a zero-adjusted Bray–Curtis coefficient for denuded assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; Primer-E. Ltd.: Auckland, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, C.O.; Ackerly, D.D.; McPeek, M.A.; Donoghue, M.J. Phylogenies and community ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 475–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.O. Exploring the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities: An example for rain forest trees. Am. Nat. 2000, 156, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotelli, N.J. Null model analysis of species co-occurrence patterns. Ecology 2000, 81, 2606–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPSS. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0; SPSS Inc. Ltd.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, E. OriginPro 9.1: Scientific data analysis and graphing software-software review. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.D.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Castello, L.; Murphy, B.R.; Xie, S. Potential effects of dam cascade on fish: Lessons from the Yangtze River. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.L.; McMahon, T.E.; Thurow, R.F. Decline of the migratory form in Bull Charr, Salvelinus Confluentus, and implications for conservation. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2002, 64, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Tang, C.; Xie, W.; Yan, J.; Li, R.; Ye, Z.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Duan, X.; Wei, Q. Analysis of fish resources status and diversity in the middle reaches of Tuojiang River. J. Fish. China 2023, 47, 029308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y. eDNA reveals spatial homogenization of fish diversity in a mountain river affected by a reservoir cascade. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 361, 121248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. Utilization and protection status of fish resources in Jialing River. Tianjin Agric. Sci. 2014, 20, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajado, R.A.; Oliveira, L.S.d.; Corrêa, J.M.S.; Silva-Cajado, F.K.S.d.; Zacardi, D.M. Seasonal hydrology shapes the taxonomic and functional diversity of fish associated with aquatic macrophytes in a neotropical floodplain lake. Aquat. Sci. 2025, 87, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.B.; Arantes, C.C.; Freitas, C.E.C.; Petrere, M., Jr.; Ribeiro, F.R.V. Seasonal hydrology and fish assemblage structure in the floodplain of the lower Amazon River. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2021, 30, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Huang, J.; Huang, L.; Wu, Z.; Deng, M.; Xu, L.; Gao, M. Species composition and temporal-spatial variation of the fish community in Guijiang River. J. Hydroecology 2019, 40, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lou, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Seasonal variations of fish assemblage in Chishui Reach of the Chishui River. Freshw. Fish. 2015, 45, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, F.; Yang, H.; Zeng, P.; Ma, X. Investigating the impact of the construction of the Duliu River dam in China on the spatiotemporal changes of fish communities. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, M.; Mu, S.; Kang, X.; Chen, Y. Fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Juma River in Haihe River basin. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2023, 47, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, R.; Wang, W.; Duan, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y. Diversity and spatiotemporal dynamics of fish communities in the Chongqing section of the upper Yangtze River based on eDNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Tian, H.; Xiang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Yu, L.; Duan, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; Liu, M. Impact of the fishing ban on fish diversity and population structure in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 12, 1530716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, D.; Wang, Y.; Ge, H.; Zhang, C.; Liang, L.; Zhong, X. Recovery of Coilia nasus resources after implementation of the 10-year fishing ban in the Yangtze River: Implied from the Yangtze River Estuary and its adjacent sea areas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1474996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft Nathan, J.B.; Cornwell, W.K.; Webb, C.O.; Ackerly, D.D. Trait evolution, community assembly, and the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities. Am. Nat. 2007, 170, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yu, D.; Gao, X.; Liu, H. Mechanism of fish community assembly in middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2020, 44, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q. Spatial Pattern, Assembly Rules and Temporal Dynamics of Fish Communities in the Chishui River. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ingram, T.; Shurin, J.B. Trait-based assembly and phylogenetic structure in northeast Pacific rockfish assemblages. Ecology 2009, 90, 2444–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, G.; Gislason, H.; Graham, K.; Hill, L.; Jin, X.; Koranteng, K.; Manickchand-Heileman, S.; Payá, I.; Sainsbury, K.; Sanchez, F.; et al. Impact of fishing on size composition and diversity of demersal fish communities. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, E.; Zang, C.; Cao, W. Evaluating the status of China’s continental fish and analyzing their causes of endangerment through the red list assessment. Biodivers. Sci. 2016, 24, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Lei, G. Freshwater fish biodiversity in the Yangtze River basin of China: Patterns, threats and conservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 1649–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P. Biodiversity crisis in the Yangtze River:The culprit was dams, followed by overfishing. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 1279–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lin, P.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, H. Situations and conservation strategies of fish resources in the Yangtze river basin. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2019, 43, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | n | TL Range (cm) | BW Range (g) | IRI | ICUN | Trophic Guild |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cypriniformes | ||||||
| Catostomidae | ||||||
| Myxocyprinus asiaticus | 2 | 25.8–33.9 | 204.5–553.7 | 0.1 | CR | I |
| Cyprinidae | ||||||
| Ctenopharyngodon idella | 80 | 27.6–77.7 | 295.0–5450.0 | 124.8 | LC | H |
| Squaliobarbus curriculus | 2 | 49.5–53.0 | 1194.7–1280.3 | 0.2 | LC | O |
| Pseudolaubuca sinensis | 6 | 19.5–25.5 | 43.5–137.8 | 0.5 | LC | O |
| Pseudolaubuca engraulis | 12 | 15.7–25.2 | 24.0–96.1 | 0.9 | LC | O |
| Hemiculter leucisculus | 49 | 14.0–26.0 | 31.9–157.3 | 15.0 | LC | O |
| Hemiculter tchangi | 20 | 21.0–27.5 | 62.2–173.2 | 3.9 | LC | O |
| Chanodichthys oxycephaloides | 1841 | 19.9–53.0 | 24.9–1291.8 | 4044.0 | LC | I |
| Chanodichthys mongolicus | 42 | 25.0–57.0 | 106.6–1475.2 | 32.2 | LC | P |
| Culter alburnus | 2 | 25.8–36.0 | 131.9–347.5 | 0.1 | LC | P |
| Chanodichthys erythropterus | 83 | 21.6–77.0 | 97.5–3720.0 | 128.5 | LC | P |
| Xenocypris argentea | 3 | 19.2–22.5 | 79.1–95.0 | 0.1 | LC | H |
| Xenocypris davidi | 571 | 25.8–58.5 | 100.0–2360.0 | 1827.2 | LC | H |
| Xenocypris fangi | 234 | 27.3–62.4 | 186.9–2575.0 | 350.6 | VU | H |
| Plagiognathops microlepis | 240 | 20.2–66.7 | 71.7–3145.0 | 719.2 | LC | H |
| Distoechodon tumirostris | 1 | 65.9–65.9 | 2615.2–2615.2 | 0.1 | LC | H |
| Megalobrama amblycephala | 1 | 51.7–51.7 | 1625.0–1625.0 | 0.1 | LC | H |
| Pseudobrama simoni | 382 | 15.5–37.6 | 35.2–1499.7 | 230.2 | LC | H |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 15 | 27.0–57.0 | 192.7–3500.0 | 8.4 | LC | H |
| Hypophthalmichthys nobilis | 48 | 30.4–110.0 | 205.6–12015.0 | 102.5 | LC | I |
| Hemibarbus labeo | 1245 | 14.4–38.7 | 27.7–1442.3 | 2076.0 | LC | O |
| Hemibarbus maculatus | 75 | 16.0–43.2 | 42.5–845.3 | 59.5 | LC | I |
| Sarcocheilichthys sinensis | 4 | 16.2–18.2 | 45.4–89.2 | 0.2 | LC | O |
| Squalidus argentatus | 8 | 12.0–16.7 | 18.3–50.7 | 0.7 | LC | O |
| Rhinogobio typus | 86 | 19.7–37.9 | 45.6–377.8 | 37.6 | LC | I |
| Rhinogobio cylindricus | 3 | 20.5–24.8 | 60.6–97.0 | 0.1 | LC | I |
| Saurogobio dabryi | 21 | 12.4–24.5 | 12.0–91.3 | 4.7 | LC | O |
| Saurogobio punctatus | 24 | 15.6–22.5 | 21.6–108.3 | 5.0 | --- | O |
| Spinibarbus sinensis | 27 | 22.2–60.4 | 146.3–3040.0 | 32.1 | LC | O |
| Onychostoma simum | 32 | 19.2–57.6 | 122.7–2320.0 | 18.6 | NT | H |
| Onychostoma macrolepis | 1 | 24.5–24.5 | 140.2–140.2 | 0.0 | VU | H |
| Bangana rendahli | 5 | 37.6–40.0 | 612.6–796.6 | 0.2 | DD | H |
| Procypris rabaudi | 104 | 12.6–41.2 | 24.2–942.7 | 78.9 | VU | O |
| Cyprinus carpio | 137 | 18.5–88.3 | 92.4–9000.0 | 656.5 | LC | O |
| Cyprinus carpio Songpu | 8 | 20.9–40.2 | 184.2–950.5 | 1.7 | --- | O |
| Carassius auratus | 475 | 15.2–34.6 | 66.8–705.3 | 718.8 | LC | O |
| Siluriformes | ||||||
| Bagridae | ||||||
| Tachysurus fulvidraco | 24 | 14.3–32.1 | 34.6–205.4 | 3.5 | LC | O |
| Tachysurus vachellii | 66 | 14.9–38.0 | 20.9–318.6 | 40.7 | LC | O |
| Tachysurus nitidus | 9 | 14.5–24.6 | 17.4–153.0 | 0.7 | LC | O |
| Tachysurus dumerili | 1 | 25.2–25.2 | 104.7–104.7 | 0.0 | NT | P |
| Tachysurus crassilabris | 209 | 12.6–33.5 | 17.4–338.1 | 146.7 | LC | O |
| Tachysurus emarginatus | 89 | 13.5–28.2 | 23.7–193.0 | 19.9 | DD | I |
| Tachysurus pratti | 3 | 21.1–23.0 | 76.4–89.1 | 0.1 | VU | I |
| Hemibagrus macropterus | 17 | 17.5–42.3 | 43.2–414.5 | 5.2 | LC | I |
| Siluridae | ||||||
| Silurus asotus | 21 | 13.3–66.0 | 15.6–414.5 | 11.6 | LC | P |
| Silurus meridionalis | 6 | 38.6–54.5 | 357.5–991.6 | 1.4 | LC | P |
| Perciformes | ||||||
| Sinipercidae | ||||||
| Siniperca chuatsi | 1078 | 13.1–31.2 | 26.0–505.1 | 1203.3 | LC | P |
| Siniperca kneri | 47 | 16.7–28.8 | 76.2–391.9 | 10.2 | LC | P |
| Siniperca scherzeri | 45 | 15.7–30.9 | 55.8–390.0 | 19.2 | LC | P |
| Gobiidae | ||||||
| Rhinogobius giurinus | 8 | 0.9–5.4 | 2.1–6.2 | 0.2 | LC | I |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Wei, T.; Xu, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, T. Temporal Variation and Assembly Process of Fish Communities in a Typical Canalized River After the 10-Year Fishing Ban. Biology 2025, 14, 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091208
Qin Q, Li Y, Chen P, Wei T, Xu J, Zhang F, Zhou T. Temporal Variation and Assembly Process of Fish Communities in a Typical Canalized River After the 10-Year Fishing Ban. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091208
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Qiang, Yuanfeng Li, Peng Chen, Ting Wei, Jianghaoyue Xu, Fubin Zhang, and Tong Zhou. 2025. "Temporal Variation and Assembly Process of Fish Communities in a Typical Canalized River After the 10-Year Fishing Ban" Biology 14, no. 9: 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091208
APA StyleQin, Q., Li, Y., Chen, P., Wei, T., Xu, J., Zhang, F., & Zhou, T. (2025). Temporal Variation and Assembly Process of Fish Communities in a Typical Canalized River After the 10-Year Fishing Ban. Biology, 14(9), 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091208






