Eco-Friendly Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis Method Using Medicinal Plant Fungal Endophytes—Biological Activities and Molecular Docking Analyses
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Endophytic Fungal Isolation from Bergenia Ciliate Leaves
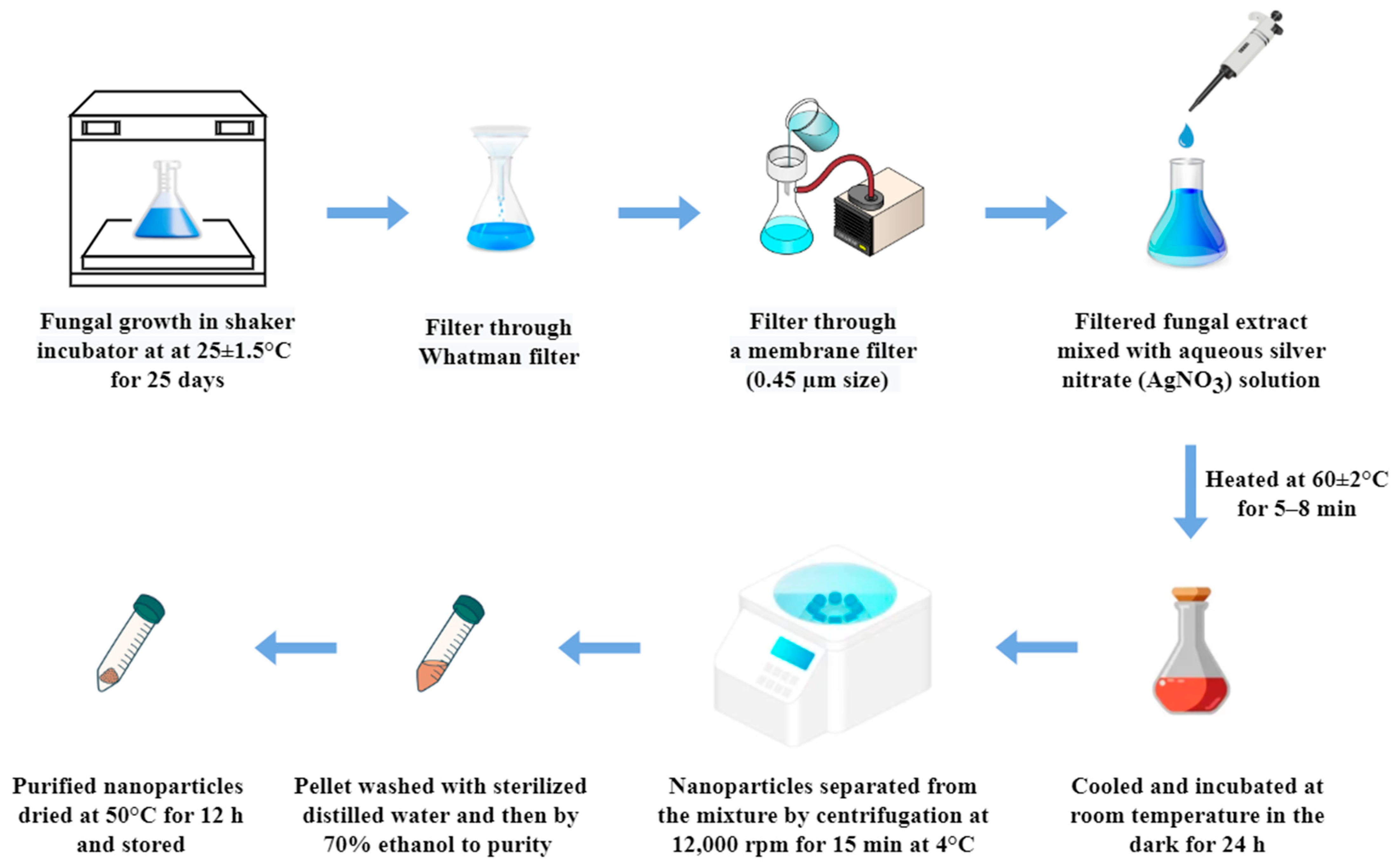
2.2. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis Using Fungal Broth
2.3. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticle
2.3.1. UV Spectroscopy
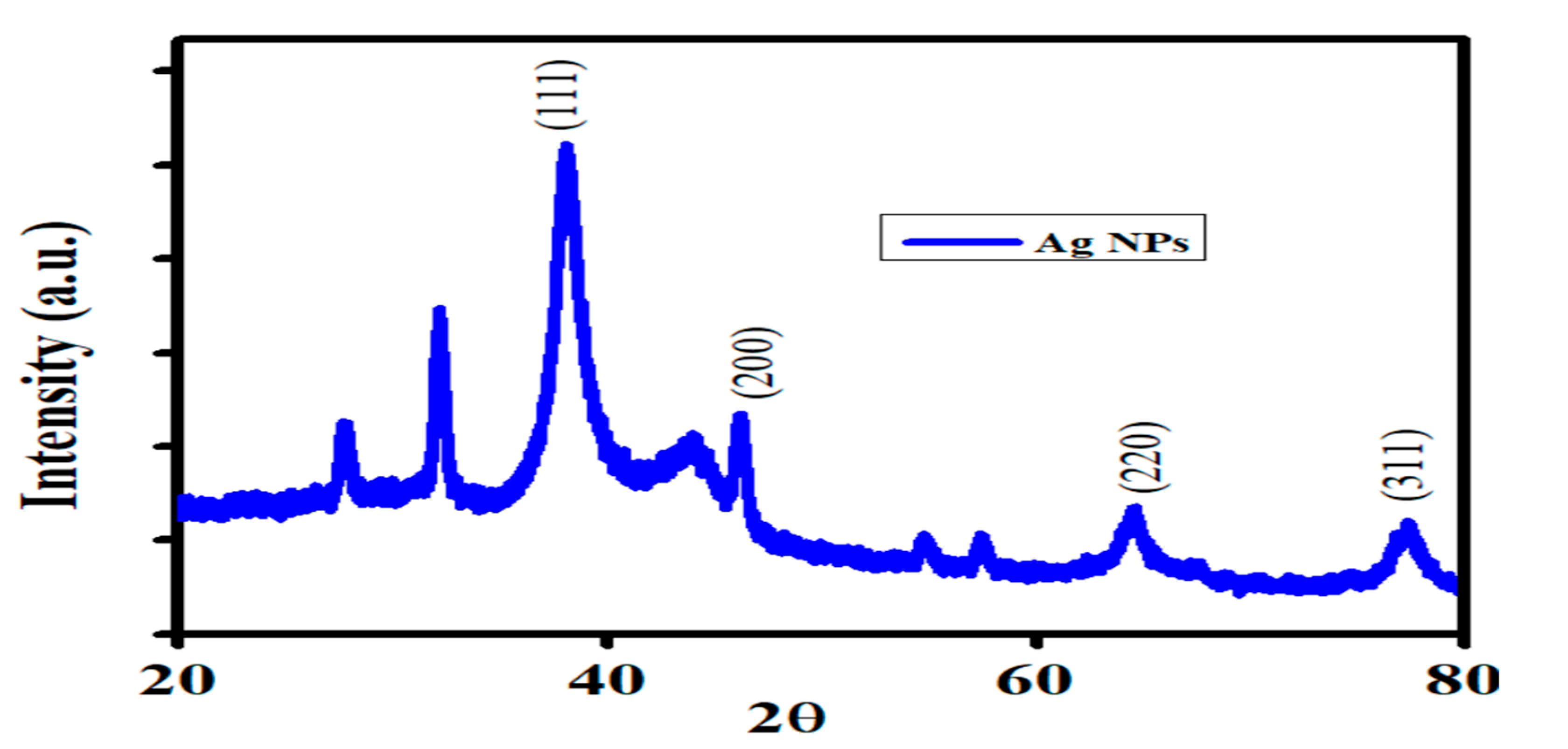
2.3.2. XRD (X-Ray Diffraction) Analysis
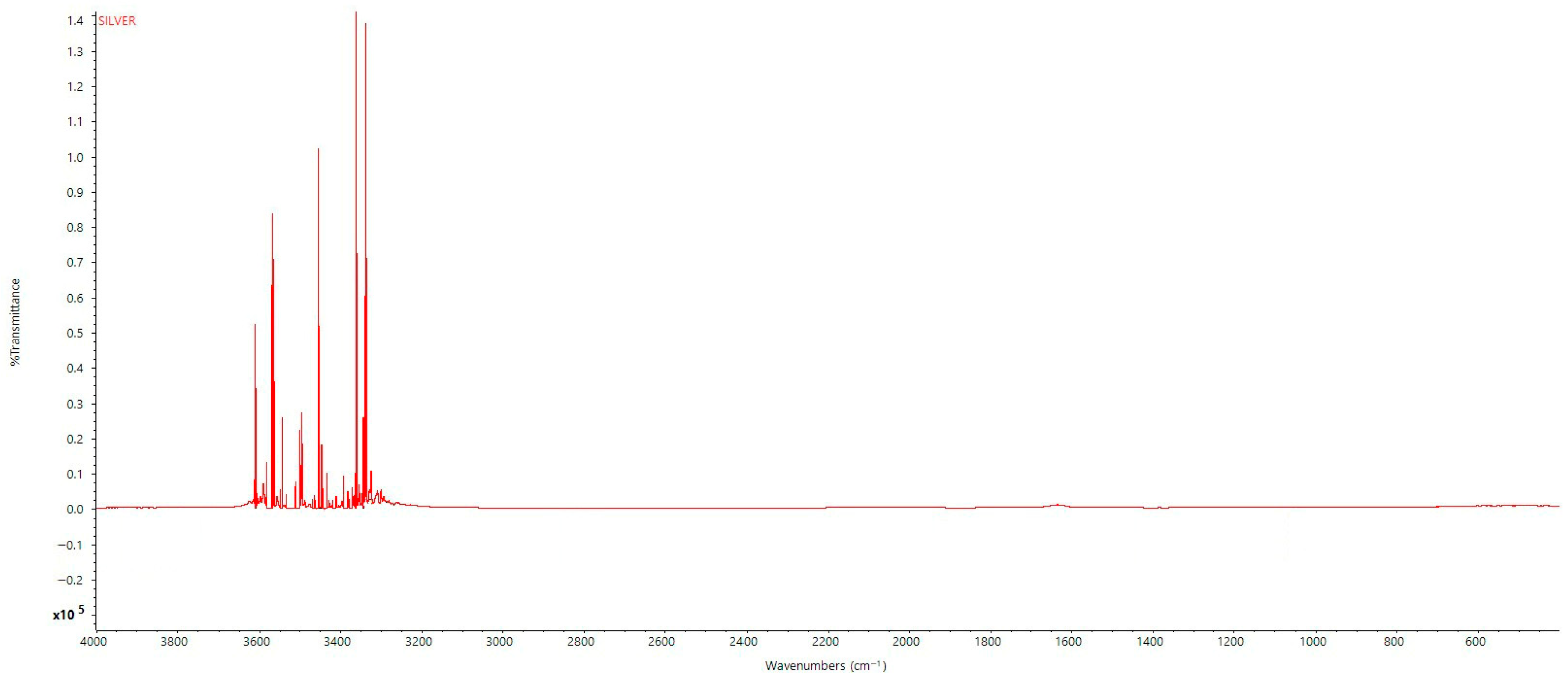
2.3.3. FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) Analysis
2.3.4. SEM with EDX Analysis
2.3.5. TEM-Analysis
2.3.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.3.7. GC–MS (Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry) Analysis of Synthesized AgNPs
2.4. Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized AgNPs
2.5. Molecular Docking of the Major Component of the FANPs Against Pathogenic Bacteria
2.6. ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion) Properties and Drug-Likeness Prediction of DMSF
2.7. Antioxidant Activity of Synthesized FANPs
2.8. Antiproliferative Analysis of Synthesized FANPs
2.8.1. Culturing of Cancer Cell Line
2.8.2. MTT Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. UV Spectrophotometer Analysis
3.2. XRD (X-Ray Diffraction) Analysis
3.3. FTIR Analysis of Synthesized Nanoparticle, Silver Nitrate, and Washed Silver Nanoparticle
3.4. SEM with EDX
3.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis of FANPs
3.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3.7. GC-MS Analysis of FANPs
3.8. Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized Silver NPs
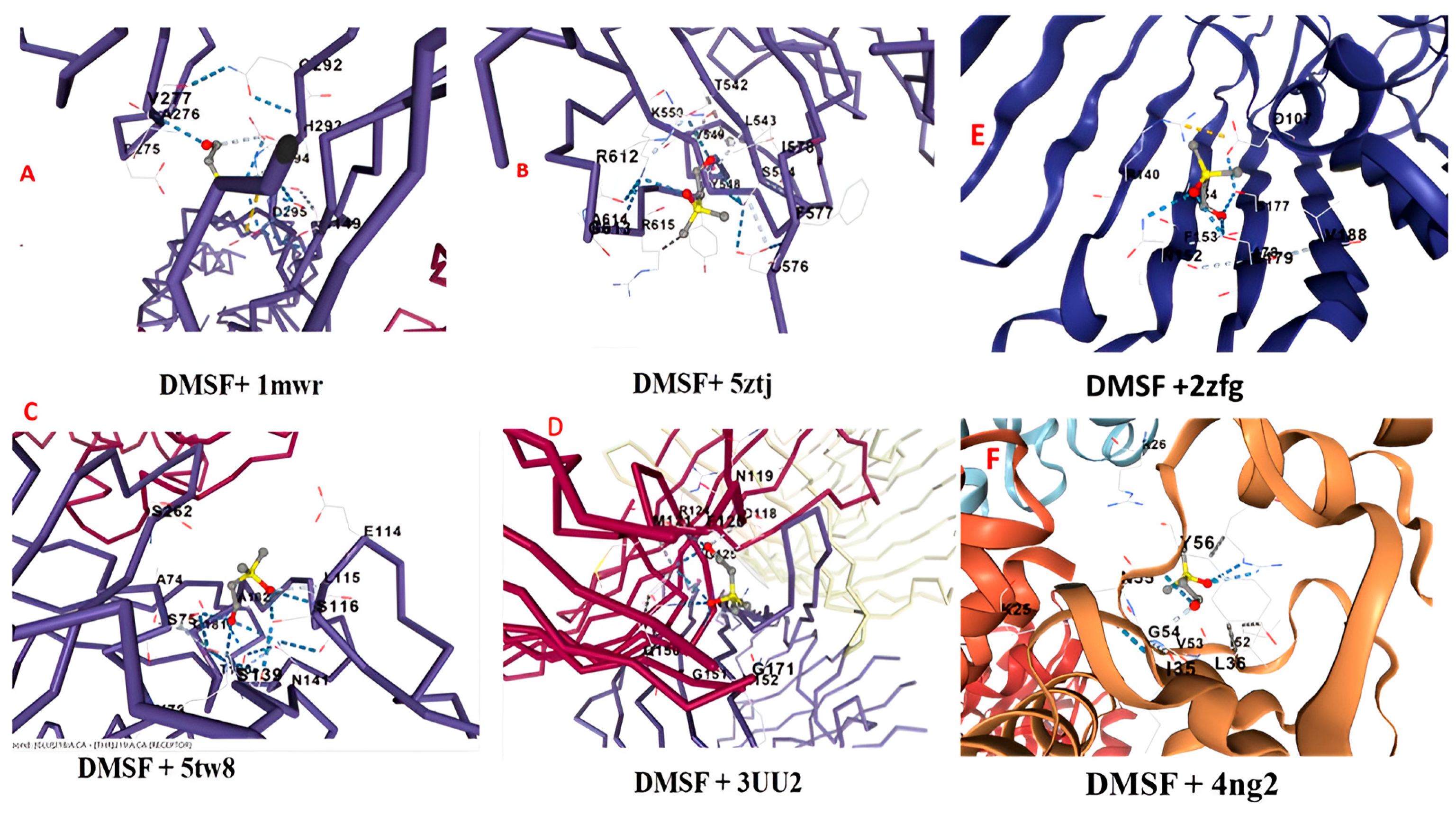
3.9. Molecular Docking of DMSF with Proteins of Pathogenic Bacteria
3.10. ADME and Drug-likeness Prediction of Active Molecule i.e., Dimethylsulfoxonium Formylmethylide
3.11. Antioxidant Activity of Synthesized Fungal Assisted Nanoparticle
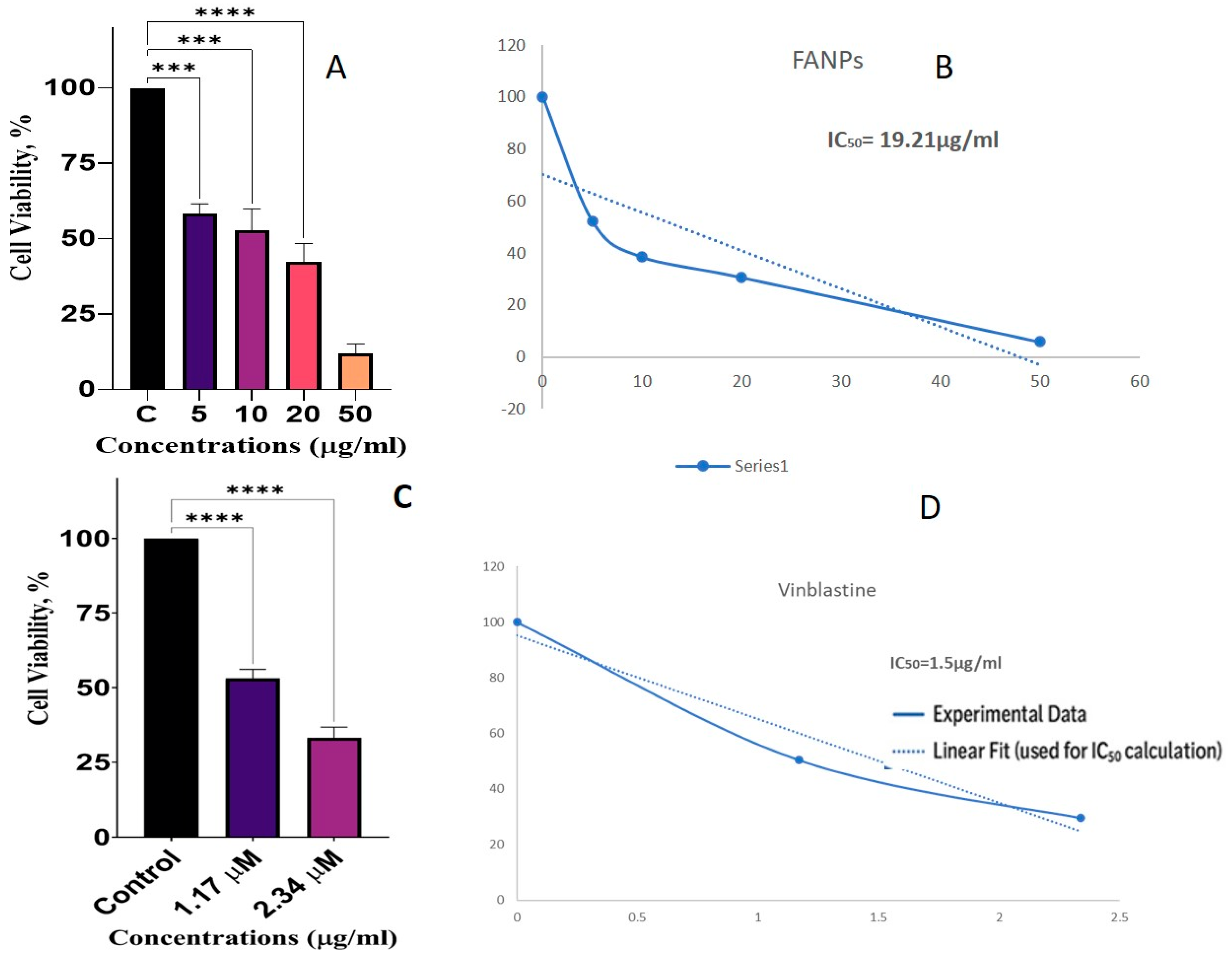
3.12. Anticancer Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohseniazar, M.; Barin, M.; Zarredar, H.; Alizadeh, S.; Shanehbandi, D. Potential of microalgae and lactobacilli in biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles. Bioimpacts 2011, 1, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, G.; Hansen, M.S.J. Block, Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW): Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-49-638149-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, W.R.; Pillsbury, D.M. Argyria. The Pharmacology of Silver. Arch. Derm. Syphilol. 1940, 41, 995–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, H.H.; Garza-Treviño, E.N.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Singh, D.K. Silver nanoparticles are broad-spectrum bactericidal and virucidal compounds. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as antibacterial agent: Ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasen, H.J. A historical review of the use of silver in the treatment of burns. II. Renewed interest for silver. Burns 2000, 26, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Phadtare, S.; Sastry, M. Interfacing biology with nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2005, 5, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhan, G.; Zheng, B.; Sun, D.; Lu, F.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Q. Biogenic silver nanoparticles by Cacumen platycladi extract: Synthesis, formation mechanism, and antibacterial activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 9095–9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, W. Biomimetic synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their aggregates using a polypeptide sequence. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 21, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polavarapu, L.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Growth and galvanic replacement of silver nanocubes in organic media. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4355–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, M.N.; Natalio, F.; Cambaz, M.A.; Panthöfer, M.; Branscheid, R.; Kolb, U.; Tremel, W. Controlled synthesis of linear and branched Au@ZnO hybrid nanocrystals and their photocatalytic properties. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9944–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Oleylamine in nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.G.; Ballester, A. Mechanism and applications of metal nanoparticles prepared by bio-mediated process. Rev. Adv. Sci. Eng. 2014, 3, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Fundamentals of green chemistry: Efficiency in reaction design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Green chemistry for nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5778–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.; Eghbali, N. Green chemistry: Principles and practice. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbalalu, D.; Lalley, J.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Varma, R.S. Greener techniques for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts, enzymes, bacteria, biodegradable polymers, and microwaves. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, M.T.; Hentschel, M.K.; Heinrichs, C.; Roitsch, S.; Prechtl, M.H.G. Fast track to nanomaterials: Microwave-assisted synthesis in ionic liquid media. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 14149–14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otari, S.V.; Patil, R.M.; Waghmare, S.R.; Ghosh, S.J.; Pawar, S.H. A novel microbial synthesis of catalytically active Ag–alginate biohydrogel and its antimicrobial activity. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 9966–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alani, F.; Moo-Young, M.; Anderson, W. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by a new strain of Streptomyces sp. compared with Aspergillus fumigatus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, G.; Purushothaman, B.; Rangasamy, S.; Song, J.M. Investigating the versatility of multifunctional silver nanoparticles: Preparation and inspection of their potential as wound treatment agents. Int. Nano Lett. 2016, 6, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plant extracts-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Rai, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Controlling the optical properties of lemongrass extract synthesized gold nanotriangles and potential application in infrared-absorbing optical coatings. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, F.; Janen, A.; Kukhtareva, T.; Edwards, V.; Curley, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization, application, and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 5221–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadlou, M.; Maghsoudi, H.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. A review on green silver nanoparticles based on plants: Synthesis, potential applications, and eco-friendly approach. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 446–463. [Google Scholar]
- Vishwakarma, S.; Chaudhry, V.; Chand, S.; Sagar, K.; Gupta, K.K.; Bhardwaj, N.; Prasad, R.; Kumar, P.; Chandra, H. The Potential of Fungal Endophytes in Plants: Sources of Bioactive Compounds. Indian J. Microbial. 2024, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, H.; Kumari, P.; Prasad, R.; Gupta, S.C.; Yadav, S. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity displayed by a fungal endophyte Alternaria alternata isolated from Picrorhiza kurroa from Garhwal Himalayas, India. Bioact. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 33, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.S.; Cheng, M.J.; Der Wu, M.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Chai, C.Y.; Kwan, A.L. New Metabolite from the Endophytic Fungus Corynespora smithii. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leman-Loubière, C.; Le Goff, G.; Retailleau, P.; Debitus, C.; Ouazzani, J. Sporothriolide-Related Compounds from the Fungus Hypoxylon monticulosum CLL-205 Isolated from a Sphaerocladina Sponge from the Tahiti Coast. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2850–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, D.; Jin, J.O. Bergenia Genus: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Molecules 2020, 25, 5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriarni, D.; Kasiamdari, R.S. Isolation and identification of endophytic fungi from leaves and stem of Calopogonium mucunoides. J. Trop. Biodivers. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.K.; Chhajlani, M.; Shrivastava, B.D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their characterization by XRD. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 836, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondwal, M.; Pant, G.J.N. Biological evaluation and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Calotropis procera. Int. J. Pharm. Bio. Sci. 2013, 4, 635–643. [Google Scholar]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Aloe vera leaf extract-mediated green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their In Vitro antimicrobial activity against spoilage fungi and pathogenic bacteria strains. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, H.; Srivastava, J.; Agarwal, R.K. Fundamental Techniques in Microbiology; John Publisher Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2016; ISBN 978-81-928544-1-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, H.; Patel, D.; Kumari, P.; Jangwan, J.S.; Yadav, S. Phyto-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles of Berberis aristata: Characterization, antioxidant activity, and antibacterial activity with special reference to urinary tract pathogens. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, H.; Chaudhry, V.; Sagar, K.; Pradhan, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Thakur, G.S.; Dubey, R.C. Effect of Hawan samagri used for the agnihotra against human pathogenic bacteria responsible for foodborne and airborne infections. Vegetos 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead- and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihantini, A.I.; Tachibana, S. Antioxidant compounds produced by Pseudocercospora sp. ESL 02, an endophytic fungus isolated from Elaeocarpus sylvestris. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.R.; Stringer, S.J.; Agarwal, G.; Jones, S.E.; Stone, M.O. Biomimetic synthesis and patterning of silver nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2002, 1, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.; Ahmad, A.; Mandal, D.; Senapati, S.; Sainkar, S.R.; Khan, M.I.; Parishcha, R.; Ajaykumar, P.V.; Alam, M.; Kumar, R.; et al. Fungus-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their immobilization in the mycelial matrix: A novel biological approach to nanoparticle synthesis. Nano Lett. 2001, 1, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Senapati, S.; Mandal, D.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2003, 4, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; Durán, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Mechanistic aspects in the biogenic synthesis of extracellular metal nanoparticles by peptides, bacteria, fungi, and plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballotin, D.; Fulaz, S.; Souza, M.L.; Corio, P.; Rodrigues, A.G.; Souza, A.O.; Gaspari, P.M.; Gomes, A.F.; Gozzo, F.; Tasic, L. Elucidating protein involvement in the stabilization of the biogenic silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami-Shabani, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Norouzian, D.; Amini, A.; Gholami-Shabani, Z.; Imani, A. Antimicrobial activity and physical characterization of silver nanoparticles green synthesized using nitrate reductase from Fusarium oxysporum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 4084–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gour, A.; Jain, N.K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqtedar, M.; Aslam, M.; Akhyar, M.; Shehzaad, A.; Abdullah, R.; Kaleem, A. Extracellular biosynthesis, characterization, and optimization of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Bacillus mojavensis BTCB15 and its antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y. Fungus-mediated green synthesis of nano-silver using Aspergillus sydowii and its antifungal/antiproliferative activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, V.; Govindarajan, K. Silver nanoparticles and their in vitro cytotoxic behavior—A fungi-aided synthesis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2023, 20, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forough, M.; Farhadi, K. Biological and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2010, 34, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logeswari, P.; Silambarasan, S.; Abraham, J. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts and analysis of their antimicrobial properties. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2015, 19, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkammash, N.M. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Artemisia sieberi and Calotropis procera medical plant extracts and their characterization using SEM analysis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2017, 14, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhainsa, K.C.; D’Souza, S.F. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 47, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, Z.; Maliszewska, I.H.; Grochowalska, B.; Polowczyk, I.; Kozlecki, T. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using microorganisms. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2008, 26, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Nawale, L.U.; Arkile, M.; Shedbalkar, U.U.; Kulkarni, M.; Koli, P.B. Chemical and biological nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, A.; Zafar, S.; Zahid, K.; Shah, M.S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Al-Misned, F.; Mahboob, S. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Coriandrum sativum L. J. Infect. Pub. Health 2019, 12, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Sakthivel, N. Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles by microbes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 156, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomorodian, K.; Pourshahid, S.; Sadatsharifi, A.; Mehryar, P.; Pakshir, K.; Mohammad, J.R.; Monfared, A.A. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles by Aspergillus species. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5435397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danagoudar, A.; Pratap, G.K.; Shantaram, M.; Ghosh, K.; Kanade, S.R.; Sannegowda, L.K.; Joshi, C.G. Antioxidant, cytotoxic and anti-cholinesterase activity of green silver nanoparticles synthesized using Aspergillus austroafricanus CGJ-B3 (endophytic fungus). Anal. Chem. Lett. 2021, 11, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumberland, S.A.; Lead, J.R. Particle size distributions of silver nanoparticles at environmentally relevant conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 9099–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.T.; Brown, M.; Williams, F. Dimethylsulfoxonium Formylmethylide: A review of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer properties. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 2490–2502. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.K.; Patel, R.; Wang, X. Antioxidant and lipid-modulating effects of 9-Octadecenoic acid. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 154, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Laaeiby, A. A promising natural anticancer compound derived from Gymnoascus dankaliensis. Arch. Razi Inst. 2023, 78, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, M.R.; Chand, M.B.; Pant, B. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Dendrobium moniliforme extracts and the detection of related compounds by GC-MS. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2018, 18, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.T.; Ghaly, M.F.; Fahmi, S.M. Antibacterial activities of hexadecanoic acid methyl ester and green-synthesized silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyugi, D.A.; Ayorinde, F.O.; Gugssa, A.; Allen, A.; Izevbigie, E.B.; Eribo, B.; Anderson, W.A. Biological activity and mass spectrometric analysis of Vernonia amygdalina fractions. J. Biosci. Tech. 2011, 2, 287–304. [Google Scholar]
- Salih, L.; Eid, F.; Elhaw, M.; Hamed, A. Profiling of volatile constituents and biological activity studies of Ruprechita polystachya Griseb cultivated in Egypt. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 4719–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindappa, M.; Farheen, H.; Chandrappa, C.P.; Rai, R.V.; Raghavendra, V.B. Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using extract of endophytic fungi, Penicillium species of Glycosmis mauritiana, and its antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 035014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netala, V.R.; Bethu, M.S.; Pushpalatha, B.; Baki, V.B.; Aishwarya, S.; Rao, J.V.; Tartte, V. Biogenesis of silver nanoparticles using endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis microspora and evaluation of their antioxidant and anticancer activities. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5683–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, D.; Qian, Y.; Guan, B.; Gao, S.; Cui, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Wang, L. Fungus-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Aspergillus terreus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sagar, A.; Rana, J.; Rani, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity using fungus Talaromyces purpureogenus isolated from Taxus baccata Linn. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2022, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xing, Y.; Li, C.D.; Xu, Q.; Shen, L.; Chandrakaushik, A.; Wein, D.Q. An integrated approach: Pan-cancer analysis and structure-based virtual screening of GPR15. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizot, F.; Lang, R. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 89, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


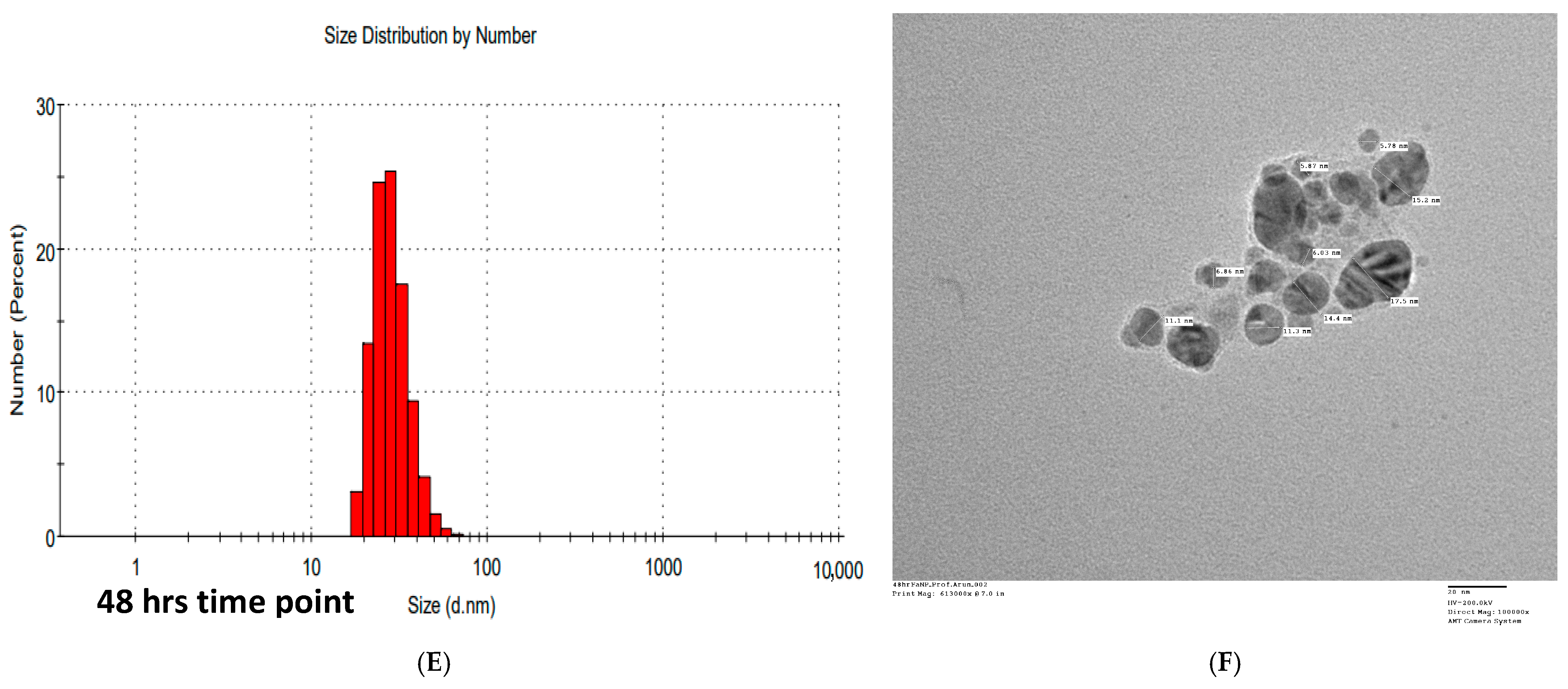
| S. No | Characterization Technique | Average Particle Size | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | XRD (Scherrer equation) | 18.6 nm | Crystallite size only; based on (111) diffraction peak |
| 2 | TEM | 11.0–20.4 nm | Physical core size; direct visualization of shape and distribution |
| 3 | DLS | ~100 nm | Hydrodynamic diameter; includes capping agents and surrounding media |
| Peak | Name | Area% | R.Time | Base m/z | Biological Activity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dimethylsulfoxonium formylmethylide | 98.88 | 3.566 | 63.15 | Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer | [65,66] |
| 2 | Hexadecanoic acid | 0.61 | 18.141 | 74.05 | Antimicrobial, anti-proliferative effects | [67,68] |
| 3 | 9-Octadecenoic acid | 0.51 | 19.812 | 55.10 | Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer | [69] |
| S.No. | Name of Microorganism | Gram Reaction | Zone of Inhibition in mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO | Gentamicin | Chloramphenicol | AgNPs | |||
| 1 | Escherichia coli | GNB | NA | 10.9 | 23.5 | 15.7 ± 0.07 |
| 2 | Salmonella typhi | GNB | NA | 21.2 | 23.0 | 18.1 ± 0.07 |
| 3 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | GNB | NA | 20.4 | 29.3 | 15.5 ± 0.28 |
| 4 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | GNB | NA | 11.3 | 28.4 | 16.2 ± 0.14 |
| 5 | Bacillus cereus | GPB | NA | 19.8 | 26.6 | 15.0 ± 0.14 |
| 6 | Staphylococcus aureus | GPB | NA | 27.3 | 26.1 | 20.8 ± 1.20 |
| 7 | Bacillus subtilis | GPB | NA | 27.2 | 36.6 | 18.9 ± 0.35 |
| 8 | Streptococcus pneumoniae | GPB | NA | 23.2 | 24.3 | 17.6 ± 0.28 |
| Ligand + Protein | Cur Pocket Id | Vina Score (Binding Affinity) | Cavity Score | Centre (x, y, z) | Docking Size (x, y, z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSF + 5tw8 | C1 | −4.0 | 1541 | 33, −60, 5 | 22, 16, 33 |
| DMSF + 1mwr | C1 | −3.8 | 16,608 | 20, 34, 37 | 35, 34, 28 |
| DMSF + 3uu2 | C1 | −3.9 | 987 | −34. −35, 11 | 16,16,16 |
| DMSF + 5ztj | C2 | −3.5 | 123 | 23, 35, 35 | 16, 16, 16 |
| DMSF + 2zfg | C3 | −3.8 | 699 | −12, 41, 4 | 16, 16, 16 |
| DMSF + 4ng2 | C3 | −3.8 | 2457 | 5, 50, 8 | 24, 28, 35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandra, H.; Vishwakarma, S.; Makwana, N.; Kharat, A.S.; Chaudhry, V.; Chand, S.; Prasad, R.; Prakash, S.; Katara, A.; Yadav, A.; et al. Eco-Friendly Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis Method Using Medicinal Plant Fungal Endophytes—Biological Activities and Molecular Docking Analyses. Biology 2025, 14, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080950
Chandra H, Vishwakarma S, Makwana N, Kharat AS, Chaudhry V, Chand S, Prasad R, Prakash S, Katara A, Yadav A, et al. Eco-Friendly Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis Method Using Medicinal Plant Fungal Endophytes—Biological Activities and Molecular Docking Analyses. Biology. 2025; 14(8):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080950
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandra, Harish, Sagar Vishwakarma, Nilesh Makwana, Arun S. Kharat, Vijeta Chaudhry, Sumit Chand, Rajendra Prasad, Soban Prakash, Annapurna Katara, Archana Yadav, and et al. 2025. "Eco-Friendly Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis Method Using Medicinal Plant Fungal Endophytes—Biological Activities and Molecular Docking Analyses" Biology 14, no. 8: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080950
APA StyleChandra, H., Vishwakarma, S., Makwana, N., Kharat, A. S., Chaudhry, V., Chand, S., Prasad, R., Prakash, S., Katara, A., Yadav, A., Nigam, M., & Mishra, A. P. (2025). Eco-Friendly Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis Method Using Medicinal Plant Fungal Endophytes—Biological Activities and Molecular Docking Analyses. Biology, 14(8), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080950










