Soil Microbial Community Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Alpine Marsh Wetlands with Different Degradation Levels in Qilian Mountain National Park, Qinghai, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Plot Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Soil Microbial DNA Extraction and Gene Analysis
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
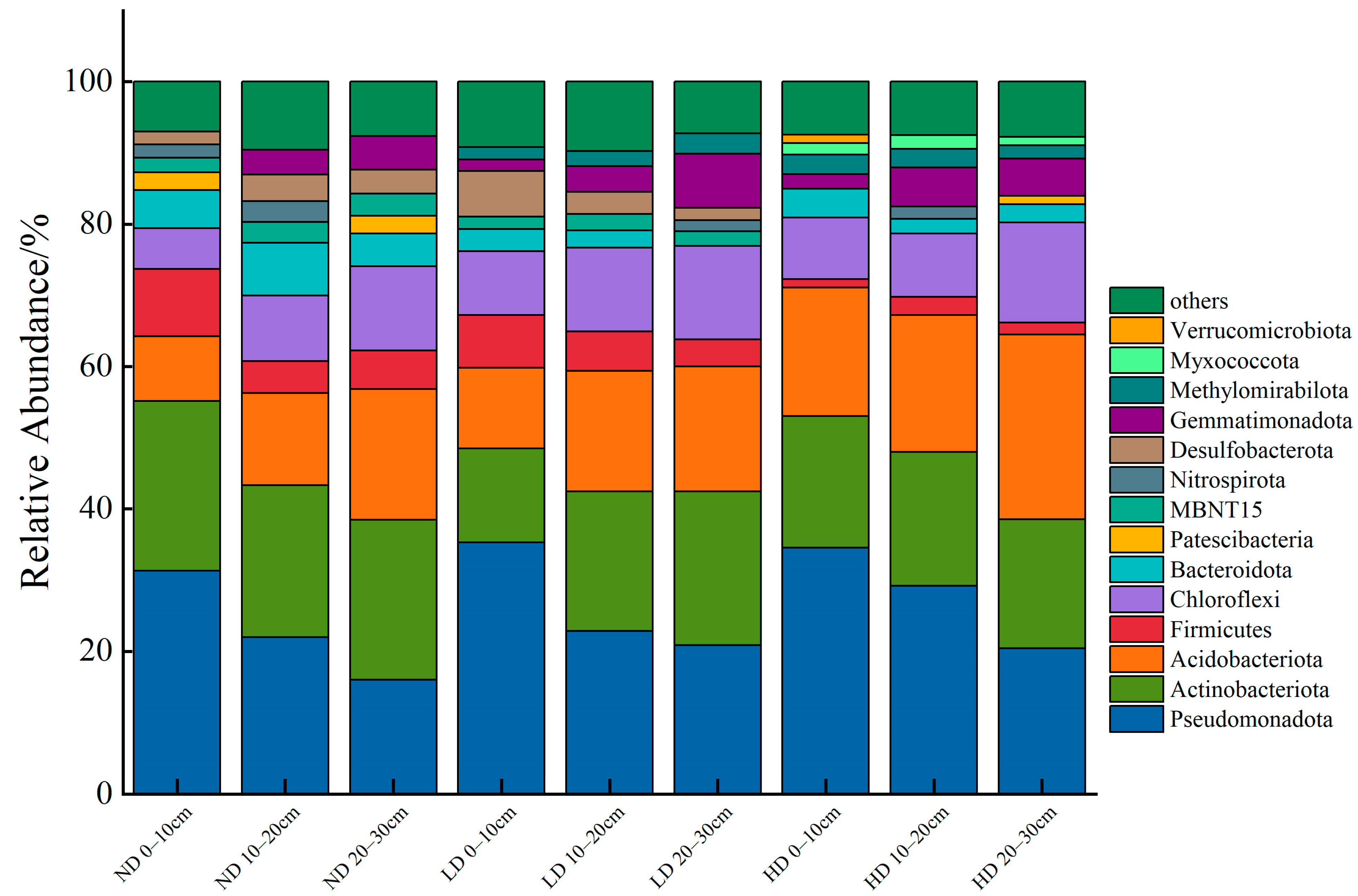
3.1. Microbial Community Composition and α-Diversity Characteristics in the 0–30 cm Soil Layer of Marsh Wetlands
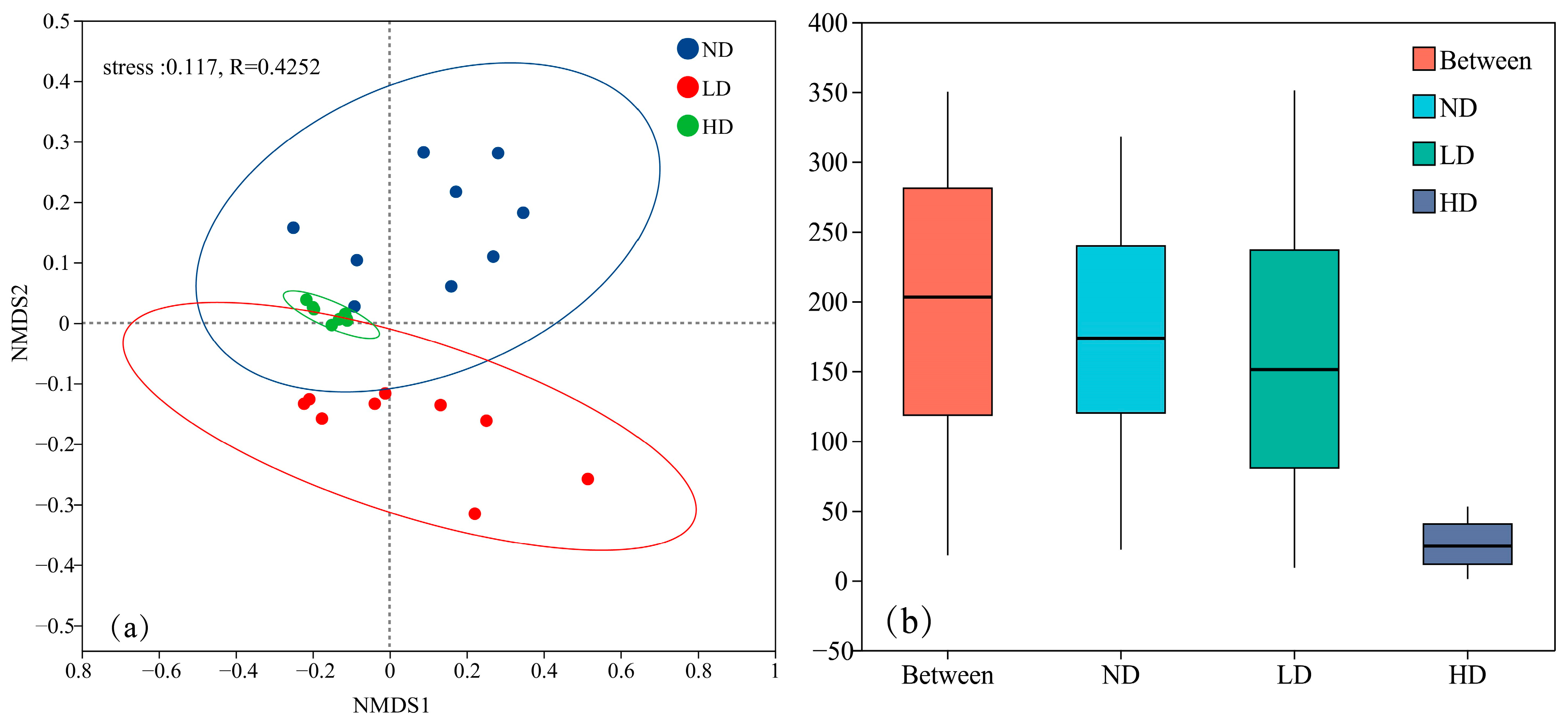
3.2. Analysis of Microbial Community Beta Diversity in Marsh Wetlands
3.3. Functional Profiling of Soil Microbial Communities in Marsh Wetlands Across Degradation Gradients
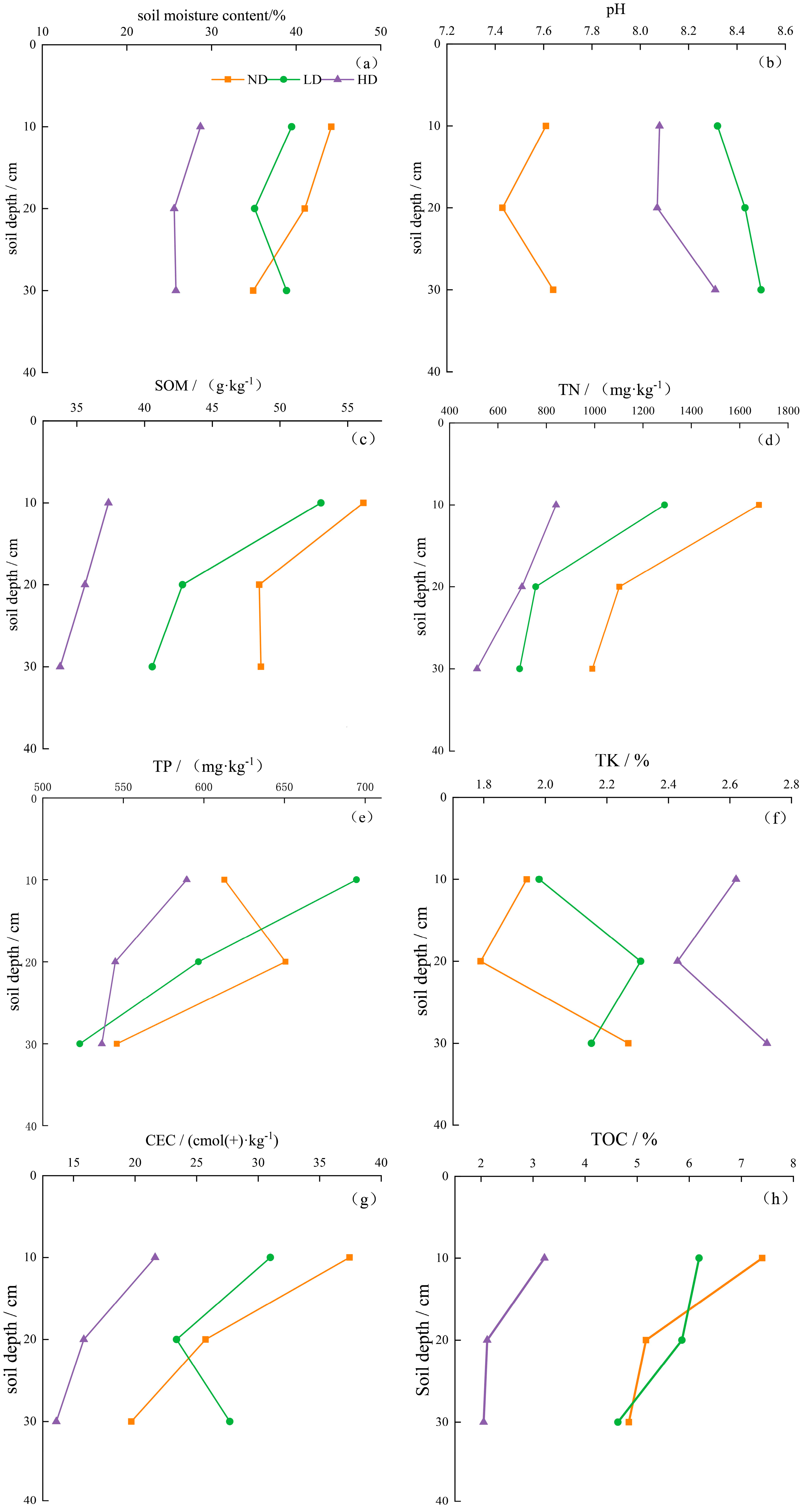
3.4. Impact Characteristics of Degraded Alpine Marsh Wetlands on Soil Physicochemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation in Soil Physicochemical Properties Across Degradation Levels and Soil Depths in Alpine Marsh Wetlands
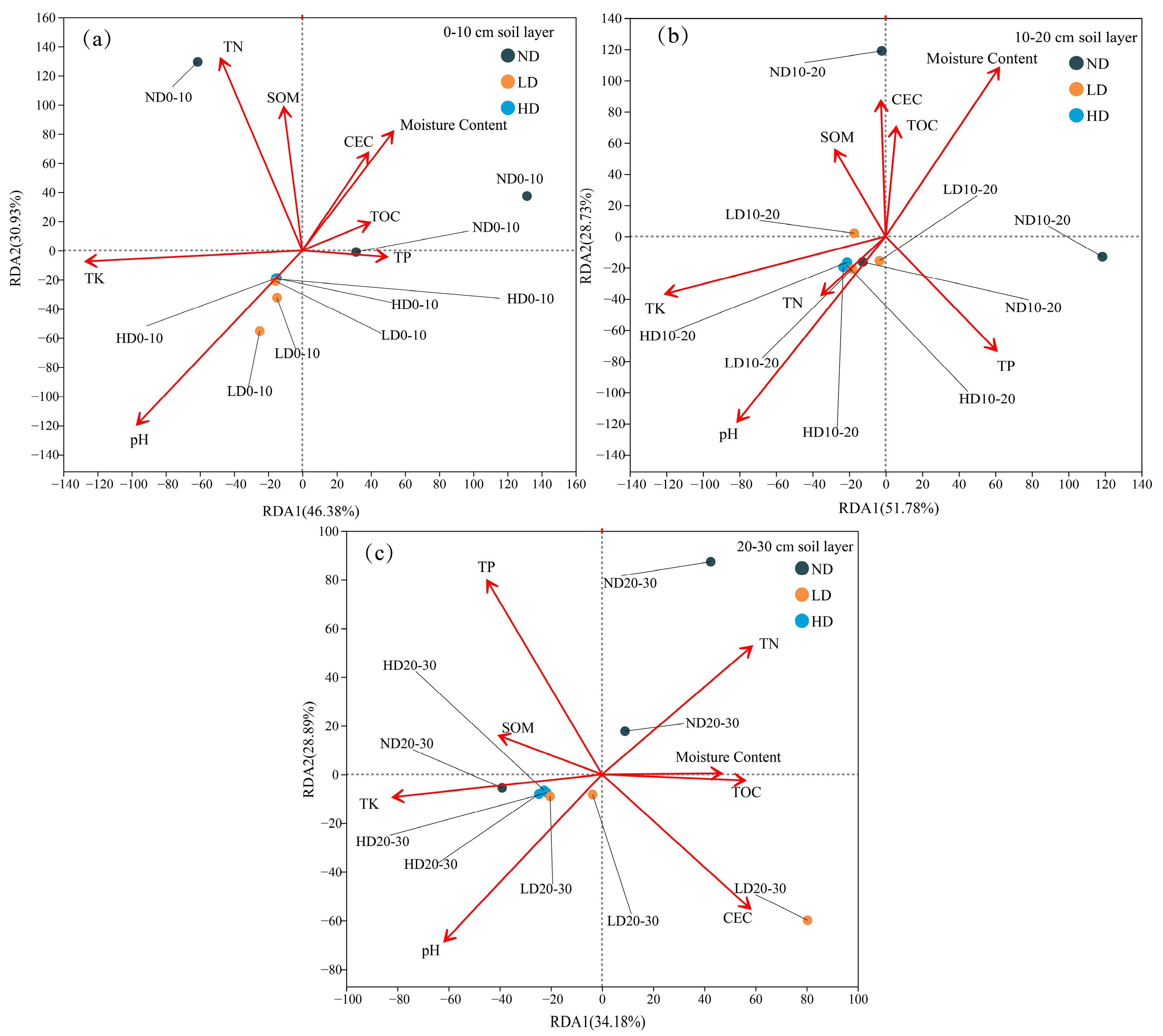
4.2. Microbial Community Structure in Relation to Soil Factors and Their Interactive Dynamics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, H. Analysis of the causes of wetland degradation in China. Rural. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yi, Y.; Song, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Lu, Q. Hydrological response of alpine wetlands to climate warming in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Fu, S.; Cui, Y.; Fulati, G.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J. Dynamic Monitoring and Restorability Evaluation of Alpine Wetland in the Eastern Edge of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 51, e02948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulaizi, M.; Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Jia, H. Response of soil bacterial community to alpine wetland degradation in arid Central Asia. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 990597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F. Alpine wetland degradation affects carbon cycle function genes but does not reduce soil microbial diversity. Catena 2025, 249, 108637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, P.L.I.G.M.; Chalmers, G.; Chittleborough, D. A review of properties of organic matter fractions in soils of mangrove wetlands: Implications for carbon storage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 201, 109660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, Z. How to measure wetland destruction and risk: Wetland damage index. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Yu, Z.; Yang, G.; Wan, R. Role of flooding patterns in the biomass production of vegetation in a typical herbaceous wetland, Poyang Lake Wetland, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 521358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmuller, H.E.; Chambers, L.G. Characterization of coastal wetland soil organic matter: Implications for wetland submergence. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Qi, D.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, C.; Liu, X. Dynamic response of the cbbL carbon sequestration microbial community to wetland type in Qinghai Lake. Biology 2023, 12, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Cui, L.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, D. Bacterial community structure and functional characteristics of soil in carex tussock marsh wetland with different degradation levels. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, M.; Jin, J.; Fu, M. Effects of different nitrogen applications and straw return depth on straw microbial and carbon and nitrogen cycles in paddy fields in the cool zone. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Nie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J. Responses of soil inhabiting nitrogen-cycling microbial communities to wetland degradation on the Zoige Plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 2192–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, K.; Yan, Z.; Liu, L.; Kang, E.; Kang, X. Soil water content shapes microbial community along gradients of wetland degradation on the Tibetan Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 824267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Nie, S.; Liang, J.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Hua, S.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Deng, L.; et al. Effects of heavy metals and soil physicochemical properties on wetland soil microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, E.; Li, H.; Du, Q. Three-dimensional dynamic characteristics of vegetation and its response to climatic factors in the Qilian Mountains. Catena 2022, 208, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Xu, G.; He, X.; Luo, D. Influences of seasonal soil moisture and temperature on vegetation phenology in the Qilian Mountains. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mao, X.; Wei, X.; Yu, H.; Tang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gou, L. Exploring the driving forces of potential marsh wetlands formation and distribution in the Qilian Mountains of Qinghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, H.; He, H.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Interannual characteristics and driving mechanism of CO2 fluxes during the growing season in an alpine wetland ecosystem at the southern foot of the Qilian Mountains. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1013812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q. Assessment of ecotourism environmental carrying capacity in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangen, B.A.; Bansal, S.; Jones, S.; Dixon, C.S.; Nahlik, A.M.; DeKeyser, E.S.; Hargiss, C.L.M.; Mushet, D.M. Using a vegetation index to assess wetland condition in the Prairie Pothole Region of North America. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 889170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, G.; Zhang, T.; Fang, K.; Tuo, M.; Wan, S.; Wang, B. Effects of grazing intensity on soil microbial community characteristics in desert steppe. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, S. Effects of reduced simulated rainfall on soil nutrients and microbial community in Robinia pseudoacacia plantations. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 5916–5925. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Mao, X.; Song, X.; Yu, H.; Yao, N.; Li, M.; Xiao, F.; Xie, S. Effects of biochar and water-retention agents on water-holding characteristics of urban green space soil in alpine areas: A case study of Xining City. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, T.; Mlahlwa, A.V.; Abd Elbasit, M.A.M.; Newete, S.W. The impact of Tamarix invasion on the soil physicochemical properties. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Gong, L.; Ma, X.; Zhu, H.; Ding, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, H. The oasisization process promotes the transformation of soil organic carbon into soil inorganic carbon. Land 2024, 13, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, X.; Yu, H.; Guo, S.; Shangguan, Y.; Chen, Q.; Fan, H.; et al. Changes in soil physicochemical properties and bacterial communities at different soil depths after long-term straw mulching under a no-till system. Soil 2021, 7, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. Impact of ecological restoration on the physicochemical properties and bacterial communities in alpine mining area soils. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, M.; Reading, L.; Dawes, L.; Miska, M.; Egodawatta, P. Potential of soil minerals to sequester soil organic carbon. Geoderma 2023, 436, 116549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Xu, G.; Yan, R.; Huang, Y.; Feng, L.; Yi, J.; Xue, X.; Liu, H. Effects of alpine grassland degradation on soil microbial communities in Qilian Mountains of China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 23, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, B.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. The influence mechanism of soil pore structure on spatial variability of soil water and nutrients in the mining-induced subsidence area of China northwest. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Yan, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Kang, X. Soil pH and nutrients shape the vertical distribution of microbial communities in an alpine wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.C.; Pan, J.P.; An, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.P. Effects of alpine meadow degradation on the soil physical and chemical properties in Maqu, China. Res. Cold Arid. Reg. 2024, 16, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. Research on Advanced Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal in Constructed Wetlands with Composite Fillers Based on Waterworks Sludge. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N. Study on the Characteristics of Soil Iron Oxides and Organic Carbon in Caohai Wetland. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, G.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y. Responses of soil fungal community composition and function to wetland degradation in the Songnen Plain, northeastern China. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1441613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fu, W.; Chu, X. Effects of continuous nitrogen fertilizer application on the diversity and composition of rhizosphere soil bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Liu, F. Soil pH and organic carbon properties drive soil bacterial communities in surface and deep layers along an elevational gradient. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 646124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y. Analysis on Responses of Plant, Soil and Microorganism to Exogenous Nutrient Addition in Degraded Alpine Meadows. Master’s Thesis, Qinghai University, Xining, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Qian, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Sui, X.; Zhang, X. Diversity and composition of soil Acidobacterial communities in different temperate forest types of Northeast China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhang, N.; Han, H.; Ren, H.; Hou, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Effect of carbon source on microbial diversity in bulking sludge. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2021, 47, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.M.; Liu, J.X.; Hu, Y.Q.; He, L.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zheng, Q.R.; Chai, B.F. Taxonomic and Functional Diversity of Soil Microbial Communities in Subalpine Meadow with Different Degradation Degrees in Mount Wutai. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 2918–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Anslan, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Harend, H.; et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Jiao, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Qiao, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Y. Response dynamics and sustainability of the microbial community structure in biocrusts to moderate disturbance: Results of long-term effects. Geoderma 2022, 405, 115460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.M.; Zhang, J.; Xue, K.; Wu, L.; Deng, Y.; Deng, J.; Hale, L.; Zhou, X.; He, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Microbial functional diversity covaries with permafrost thaw-induced environmental heterogeneity in tundra soil. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Liu, M.; Meng, Z.; Wu, C.; Bao, C.; Xu, B.; Wang, G.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; et al. Effects of different restoration stages on soil microbial community composition and diversity in Naolihe Wetland, China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1403849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Degradation | Dominant Vegetation | Plot Overview |
|---|---|---|
| Non-degraded (ND) | Kobresia schoenoides, Blysmus sinocompressus | The area has abundant surface water, almost no dry patches, and a rich diversity of plant species |
| Low-level degraded (LD) | The abundance of wetland plants such as Kobresia schoenoides has decreased, while species like Kobresia humilis and Kobresia capillifolia have become more prevalent | Surface water is limited, with a few dry patches present, and the plant species are relatively diverse |
| Heavily degraded (HD) | Toxic species, including Polygonum viviparum and Stellera chamaejasme L., have become the dominant components of the plant community | The area lacks surface water, supports low plant diversity, exhibits a high density of rodent burrows, and shows evident signs of desertification |
| Sample | Ace | Chao | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ND0–10 cm | 3449.04 ± 121.81 bc | 3318.57 ± 64.75 bc | 5.31 ± 0.17 d | 0.0515 ± 0.0192 a |
| ND10–20 cm | 3255.61 ± 277.06 c | 3167.34 ± 272.91 bc | 5.78 ± 0.29 c | 0.0204 ± 0.0154 b |
| ND20–30 cm | 2723.88 ± 94.68 d | 2691.66 ± 77.7 d | 5.90 ± 0.12 bc | 0.0108 ± 0.0022 b |
| LD0–10 cm | 3237.74 ± 353.28 c | 3098.48 ± 296.6 cd | 5.90 ± 0.36 bc | 0.0209 ± 0.0247 b |
| LD10–20 cm | 3212.51 ± 396.25 c | 3112.44 ± 408.04 cd | 6.00 ± 0.13 bc | 0.0093 ± 0.0004 b |
| LD20–30 cm | 2736.43 ± 359.29 d | 2690.46 ± 338.46 d | 5.79 ± 0.14 c | 0.0146 ± 0.0107 b |
| HD 0–10 cm | 4092.91 ± 120.22 a | 3925.01 ± 73.91 a | 6.52 ± 0.01 a | 0.0044 ± 0.0002 b |
| HD10–20 cm | 3629.70 ± 91.48 bc | 3555.86 ± 57.30 ab | 6.23 ± 0.07 ab | 0.0059 ± 0.0007 b |
| HD20–30 cm | 3833.48 ± 182.35 ab | 3746.66 ± 132.50 a | 6.36 ± 0.07 a | 0.0053 ± 0.0005 b |
| ND | 3142.84 ± 375.50 a | 3059.19 ± 327.15 a | 5.66 ± 0.31 a | 0.0276 ± 0.0213 a |
| LD | 3062.23 ± 282.43 a | 2967.13 ± 239.70 a | 5.90 ± 0.11 a | 0.0149 ± 0.0058 a |
| HD | 3852.03 ± 232.16 b | 3742.51 ± 184.61 b | 6.37 ± 0.15 b | 0.0052 ± 0.0008 a |
| Degradation Level | Primary Metabolic Functions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolism | Genetic Information Processing | Environmental Information Processing | Cellular Processes | Human Diseases | Organismal Systems | |
| ND0–10 cm | 77.87% | 6.74% | 5.49% | 4.58% | 3.55% | 1.77% |
| ND10–20 cm | 78.26% | 7.08% | 5.12% | 4.38% | 3.38% | 1.77% |
| ND20–30 cm | 78.63% | 7.34% | 4.87% | 4.28% | 3.14% | 1.74% |
| LD0–10 cm | 77.10% | 6.91% | 5.65% | 4.93% | 3.57% | 1.84% |
| LD10–20 cm | 78.26% | 7.21% | 5.11% | 4.45% | 3.21% | 1.76% |
| LD20–30 cm | 78.30% | 7.39% | 4.96% | 4.45% | 3.16% | 1.74% |
| HD0–10 cm | 77.85% | 6.90% | 5.14% | 4.51% | 3.77% | 1.84% |
| HD10–20 cm | 78.03% | 7.23% | 4.98% | 4.46% | 3.51% | 1.80% |
| HD20–30 cm | 78.73% | 7.34% | 4.69% | 4.20% | 3.29% | 1.75% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Mao, X.; Yu, H.; Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, K.; Jin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Soil Microbial Community Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Alpine Marsh Wetlands with Different Degradation Levels in Qilian Mountain National Park, Qinghai, China. Biology 2025, 14, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060598
Zhang J, Mao X, Yu H, Jin X, Zhang L, Du K, Jin Y, Yang Y, Wang X. Soil Microbial Community Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Alpine Marsh Wetlands with Different Degradation Levels in Qilian Mountain National Park, Qinghai, China. Biology. 2025; 14(6):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060598
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jintao, Xufeng Mao, Hongyan Yu, Xin Jin, Lele Zhang, Kai Du, Yanxiang Jin, Yongxiao Yang, and Xianying Wang. 2025. "Soil Microbial Community Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Alpine Marsh Wetlands with Different Degradation Levels in Qilian Mountain National Park, Qinghai, China" Biology 14, no. 6: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060598
APA StyleZhang, J., Mao, X., Yu, H., Jin, X., Zhang, L., Du, K., Jin, Y., Yang, Y., & Wang, X. (2025). Soil Microbial Community Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Alpine Marsh Wetlands with Different Degradation Levels in Qilian Mountain National Park, Qinghai, China. Biology, 14(6), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060598








