Doxorubicin Dose-Dependent Impact on Physiological Balance—A Holistic Approach in a Rat Model
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model Development
2.2. Physiological and Autonomic Evaluation
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Baro- and Chemoreceptor Reflex Evaluation
2.4.2. Analysis of BP and HR Variability
2.5. Catecholamines ELISA
2.6. Heart Histology
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Dose-Dependent Effects of DOX in Physiological and Autonomic Parameters
3.1.1. DOX Treatment Leads to a Decrease in Blood Pressure and Heart Rate without Changes in Respiratory Frequency
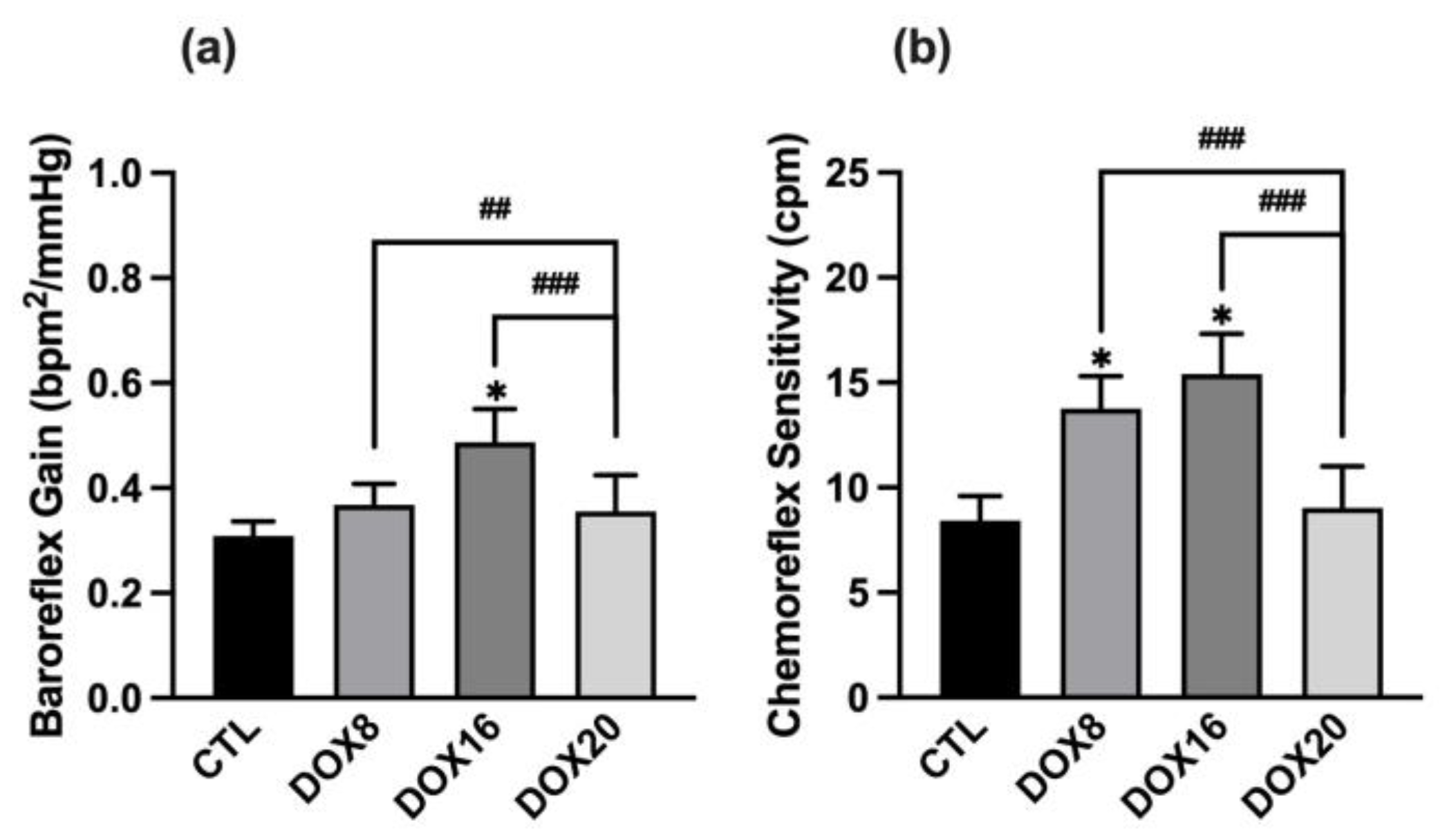
3.1.2. DOX16 Caused Baroreflex and Chemoreceptor Reflexes Impairments
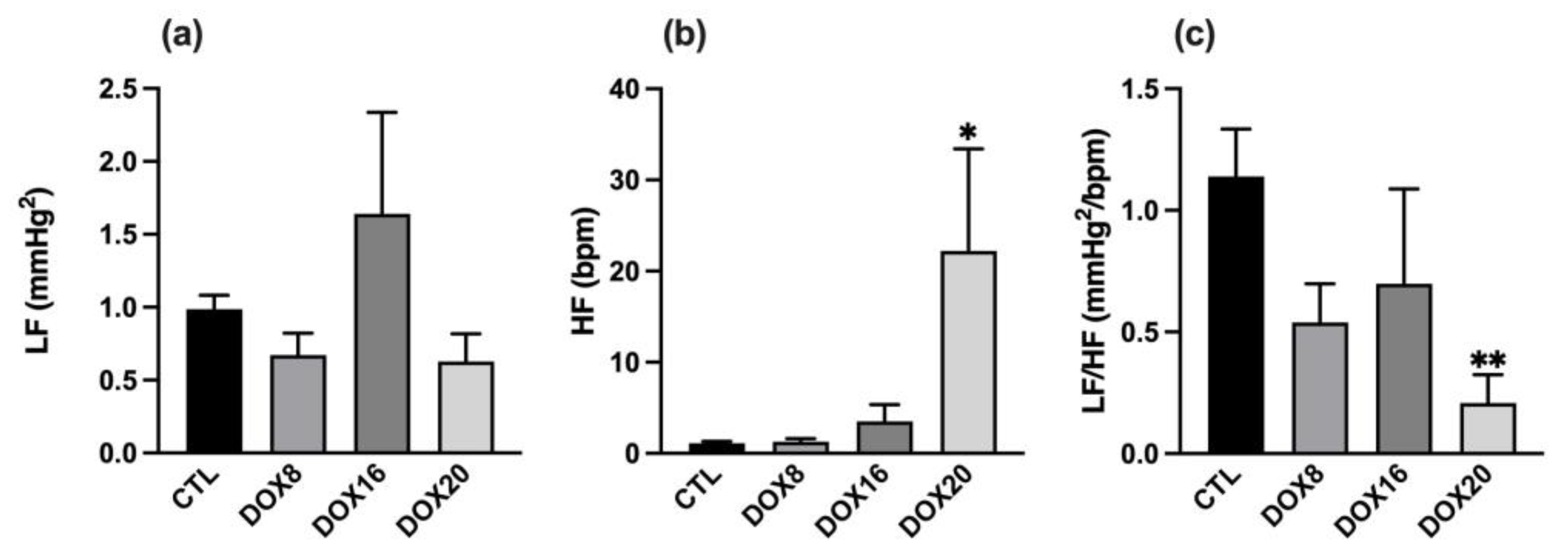
3.1.3. Positive Correlation between DOX Dosage and Autonomic Nervous System Output
3.2. Changes in Urinary Catecholamines
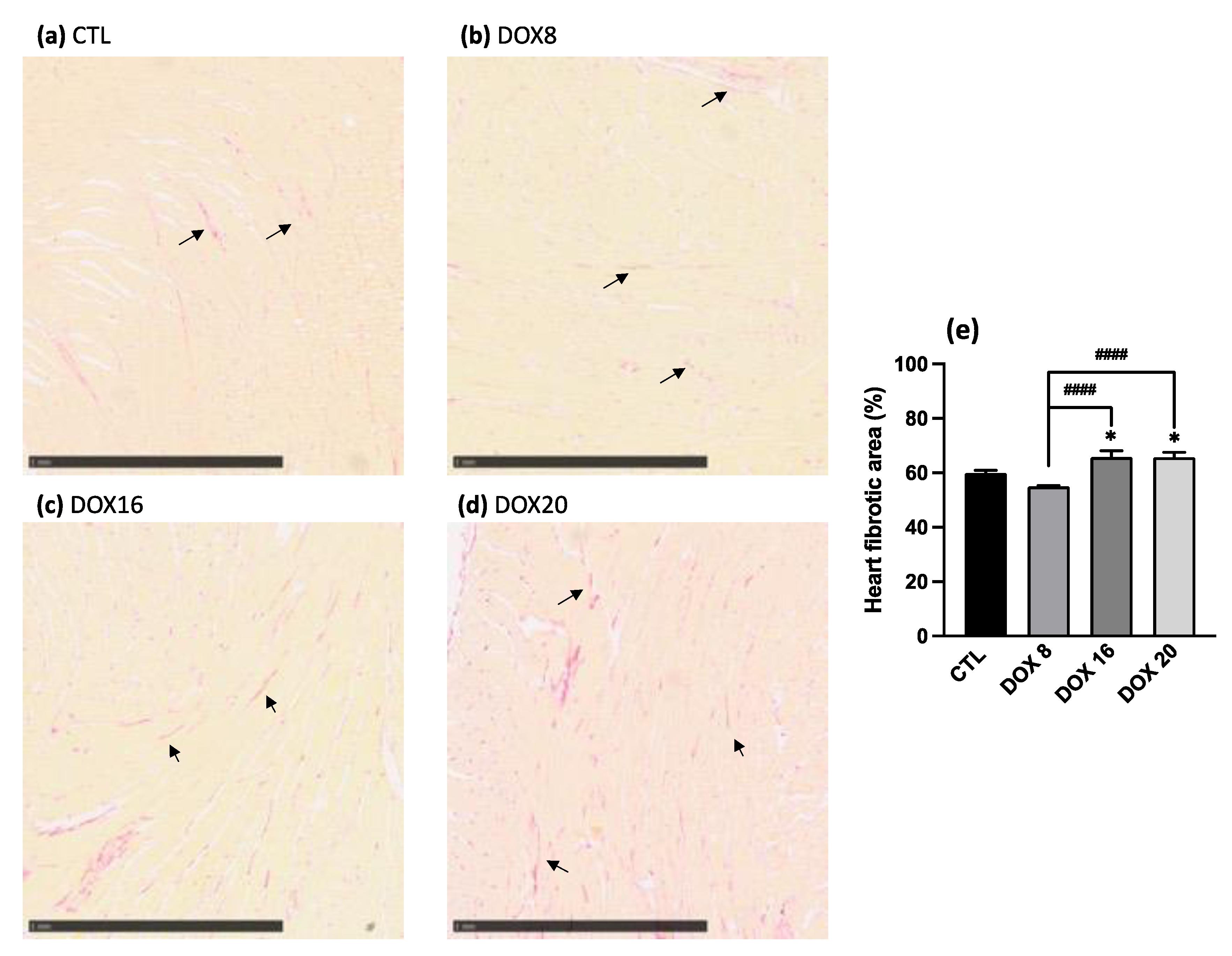
3.3. Increased Heart Fibrotic Area through Collagen Quantification with Higher DOX Dosages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Awan, P.; Ingal, K.S.; Atasha, N.; Liskovic, I.; Boniface, S. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.C.; Ozolls, R.F.; Myers, C.E. The Antracycline Antineoplastic Drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 305, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamorano, J.L.; Lancellotti, P.; Rodriguez Muñoz, D.; Aboyans, V.; Asteggiano, R.; Galderisi, M.; Habib, G.; Lenihan, D.J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Lyon, A.R.; et al. 2016 ESC Position Paper on Cancer Treatments and Cardiovascular Toxicity Developed under the Auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2768–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, V.; Caldeira, E.; Afonso, A.; Machado, F.; Amaro-Leal, Â.; Laranjo, S.; Rocha, I. Cardiovascular Dysautonomia in Patients with Breast Cancer. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2022, 16, e187419242206271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, N.; Weil, R.M.; Advani, P.P. Inter-individual Variation and Cardioprotection in Anthracycline-induced Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Layard, M.W.; Basa, P.; Hugh, B.S.; Davis, L.; Von Hoff, A.L.; Rozencweig, M.; Muggia, F.M. Risk Factors for Doxorubicin-Lnduced Congestive Heart Failure. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 91, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztajzel, J. Heart Rate Variability: A Noninvasive Electrocardiographic Method to Measure the Autonomic Nervous System. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2004, 134, 514–522. [Google Scholar]
- Huikuri, H.V.; Stein, P.K. Heart Rate Variability in Risk Stratification of Cardiac Patients. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 56, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camm, A.J.; Malik, M.; Bigger, T.; Breithardt, G.; Cerutti, S.; Cohen, R.J.; Coumel, P.; Fallen, E.L.; Kennedy, H.L.; Kleiger, R.E.; et al. Heart Rate Variability Standards of Measurement, Physiological Interpretation, and Clinical Use. Eur. Heart J. 1996, 17, 354–381. [Google Scholar]
- Potočnik, N.; Perše, M.; Cerar, A.; Injac, R.; Finderle, Ž. Cardiac Autonomic Modulation Induced by Doxorubicin in a Rodent Model of Colorectal Cancer and the Influence of Fullerenol Pretreatment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.E.; El-Gowilly, S.M.; Sharabi, F.M. Possible Ameliorative Effect of Ivabradine on the Autonomic and Left Ventricular Dysfunction Induced by Doxorubicin in Male Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 72, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousiainen, T.; Vanninen, E.; Jantunen, E.; Remes, J.; Ritanen, E.; Vuolteenaho, O.; Hartikainen, J. Neuroendocrine Changes during the Evolution of Doxorubicin-Induced Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Adult Lymphoma Patients. Clin. Sci. 2001, 101, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjeerdsma, G.; Meinardi, M.T.; Van Der Graaf, W.T.A.; Van Den Berg, M.P.; Mulder, N.H.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Vries, E.G.E.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J. Early Detection of Anthracycline Induced Cardiotoxicity in Asymptomatic Patients with Normal Left Ventricular Systolic Function: Autonomic versus Echocardiographic Variables. Heart 1999, 81, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, N.; Dokshokova, L.; Perumal Vanaja, I.; Prando, V.; Cnudde, S.J.A.; Di Bona, A.; Bariani, R.; Schirone, L.; Bauce, B.; Angelini, A.; et al. Neurotoxic Effect of Doxorubicin Treatment on Cardiac Sympathetic Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.; Nelson, K.A. Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction in Advanced Cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2002, 10, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, S.L.P.d.M.M.; Brandão, S.C.S.; Andrade, L.R.; Maia, R.J.C.; Markman Filho, B. Cardiac Sympathetic Hyperactivity after Chemotherapy: Early Sign of Cardiotoxicity? Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2015, 105, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Koshy, S.; Hui, D.; Palmer, J.L.; Shin, K.; Bozkurt, M.; Wamique Yusuf, S. Prognostic Value of Heart Rate Variability in Patients with Cancer. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 32, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syukri, A.; Hatta, M.; Amir, M.; Rohman, M.S.; Mappangara, I.; Kaelan, C.; Wahyuni, S.; Bukhari, A.; Junita, A.R.; Primaguna, M.R.; et al. Doxorubicin Induced Immune Abnormalities and Inflammatory Responses via HMGB1, HIF1-α, and VEGF Pathway in Progressive of Cardiovascular Damage. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 76, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Bawa-Khalfe, T.; Lu, L.S.; Lyu, Y.L.; Liu, L.F.; Yeh, E.T.H. Identification of the Molecular Basis of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokoohinia, Y.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Moieni-Arya, M.; Mostafaie, A.; Mohammadi-Motlagh, H.R. Osthole Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Apoptosis in PC12 Cells through Inhibition of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and ROS Production. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 156848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaigne, D.; Hurt, C.; Neviere, R. Mitochondria Death/Survival Signaling Pathways in Cardiotoxicity Induced by Anthracyclines and Anticancer-Targeted Therapies. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 951539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osataphan, N.; Phrommintikul, A.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Effects of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity on Cardiac Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitochondrial Function: Insights for Future Interventions. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6534–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhang, A.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Jia, H. Doxorubicin-Induced Cognitive Impairment: The Mechanistic Insights. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 673340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosman, M.; Krüger, D.N.; Favere, K.; Wesley, C.D.; Neutel, C.H.G.; Van Asbroeck, B.; Diebels, O.R.; Faes, B.; Schenk, T.J.; Martinet, W.; et al. Doxorubicin Impairs Smooth Muscle Cell Contraction: Novel Insights in Vascular Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robison, T.W.; Ciri, S.N.; Schiedt, M.; Parker, H.R.; Ishizaki, G.; Curry, D.L. Effects of Intravenous Infusion of Doxorubicin on Blood Chemistry, Blood Pressure and Heart Rate in Rabbits? J. Appl. Toxicol. 1985, 5, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinucci, K.; Grant, M.K.O.; Melaku, W.; Nair, C.; Zordoky, B.N. Exposure to Doxorubicin Modulates the Cardiac Response to Isoproterenol in Male and Female Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podyacheva, E.Y.; Kushnareva, E.A.; Karpov, A.A.; Toropova, Y.G. Analysis of Models of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy in Rats and Mice. A Modern View from the Perspective of the Pathophysiologist and the Clinician. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 670479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festing, M.F.W.; Altman, D.G. Guidelines for the Design and Statistical Analysis of Experiments Using Laboratory Animals. ILAR J. 2002, 43, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvachiy, L.; Geraldes, V.; Amaro-Leal, Â.; Rocha, I. Persistent Effects on Cardiorespiratory and Nervous Systems Induced by Long-Term Lead Exposure: Results from a Longitudinal Study. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, V.; Carvalho, M.; Goncalves-Rosa, N.; Tavares, C.; Laranjo, S.; Rocha, I. Lead Toxicity Promotes Autonomic Dysfunction with Increased Chemoreceptor Sensitivity. Neurotoxicology 2016, 54, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvachiy, L.; Amaro-Leal, Â.; Outeiro, T.F.; Rocha, I.; Geraldes, V. Intermittent Lead Exposure Induces Behavioral and Cardiovascular Alterations Associated with Neuroinflammation. Cells 2023, 12, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, H.; Nishida, Y. The Very Low-Frequency Band of Heart Rate Variability Represents the Slow Recovery Component after a Mental Stress Task. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, A.; Roulaud, M.; Antoine-Jonville, S.; De Bisschop, C.; Denjean, A. Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability: Interchangeability between Autoregressive Analysis and Fast Fourier Transform. J. Electrocardiol. 2006, 39, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, C.; Martins, C.; Superior, I.; Lisboa, T.; Laranjo, P.; Rocha, S. Computational Tools for Assessing Cardiovascular Variability. In Proceedings of the 1st Portuguese Biomedical Engineering Meeting, Lisbon, Portugal, 1–4 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Junqueira, L.C.U.; Bignolas, G.; Brentani, R.R. Picrosirius Staining plus Polarization Microscopy, a Specific Method for Collagen Detection in Tissue Sections. Histochem. J. 1979, 11, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchtler, H.; Waldrop, F.S.; Valentine, L.S. Polarization Microscopic Studies of Connective Tissue Stained with Picro Sirius Red F3BA. Beiträge Pathol. 1973, 150, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, A.M.; Mouchaers, K.T.B.; Schalij, I.; Grunberg, K.; Meijer, G.A.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Van Der Laarse, W.J.; Beliën, J.A.M. Rapid Quantification of Myocardial Fibrosis: A New Macro-Based Automated Analysis. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2010, 33, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwill, J.R.; Morgan, B.J.; Charkoudian, N. Peripheral Chemoreflex and Baroreflex Interactions in Cardiovascular Regulation in Humans. J. Physiol. 2003, 552, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E. The Arterial Baroreflex Functional Organization and Involvement in Neurologic Disease. Neurology 2008, 71, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, H.D.; Li, Y.L.; Ding, Y. Arterial Chemoreceptors and Sympathetic Nerve Activity: Implications for Hypertension and Heart Failure. Hypertension 2007, 50, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lončar-Turukalo, T.; Vasić, M.; Tasić, T.; Mijatović, G.; Glumac, S.; Bajić, D.; Japunžić-Žigon, N. Heart Rate Dynamics in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranakarl, C.; Kijtawornrat, A.; Chansaisakorn, W.; Trisiriroj, M.; Ngamdamrongkiat, C.; Taecholarn, T.; Sonpee, J.; Chanwathik, W. Changes in Electrophysiology, Heart Rate Variability and Proteinuria in Clinical Dogs Treated with Doxorubicin Chemotherapy. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2014, 44, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, M.; Lončar-Turukalo, T.; Tasić, T.; Matić, M.; Glumac, S.; Bajić, D.; Popović, B.; Japundžić-Žigon, N. Cardiovascular Variability and β-ARs Gene Expression at Two Stages of Doxorubicin–Induced Cardiomyopathy. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 362, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjo, S.; Geraldes, V.; Oliveira, M.; Rocha, I. Insights into the Background of Autonomic Medicine. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2017, 36, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, H.D.; Sun, S.-Y. Chemoreflex Function in Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2000, 5, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturriaga, R.; Alcayaga, J.; Chapleau, M.W.; Somers, V.K. Carotid Body Chemoreceptors: Physiology, Pathology, and Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1177–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Nie, G.; Dai, Y. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation-Related Signaling Pathways in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Octavia, Y.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Gabrielson, K.L.; Janssens, S.; Crijns, H.J.; Moens, A.L. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 52, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, P.; Salvatorelli, E.; Minotti, G. Cardiotoxicity of Antitumor Drugs. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenneman, C.G.; Sawyer, D.B. Cardio-Oncology: An Update on Cardiotoxicity of Cancer-Related Treatment. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros-Lima, D.J.M.; Carvalho, J.J.; Tibirica, E.; Borges, J.P.; Matsuura, C. Time Course of Cardiomyopathy Induced by Doxorubicin in Rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Yang, J.J.; Shi, K.H.; Li, J. Wnt Signaling Pathway in Cardiac Fibrosis: New Insights and Directions. Metabolism 2016, 65, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, R.R.S. Cardiac Fibrosis in Oncologic Therapies. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2022, 29, 100575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappetta, D.; Rossi, F.; Piegari, E.; Quaini, F.; Berrino, L.; Urbanek, K.; De Angelis, A. Doxorubicin Targets Multiple Players: A New View of an Old Problem. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 127, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rababa’h, A.M.; Guillory, A.N.; Mustafa, R.; Hijjawi, T. Oxidative Stress and Cardiac Remodeling: An Updated Edge. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2018, 14, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prud’homme, G.J. Pathobiology of Transforming Growth Factor β in Cancer, Fibrosis and Immunologic Disease, and Therapeutic Considerations. Lab. Investig. 2007, 87, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanaraman, B.; Joseph, J.; Kalivendi, S.; Wang, S.; Konorev, E.; Kotamraju, S. Doxorubicin-Induced Apoptosis: Implications in Cardiotoxicity. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 234, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Cai, L.; Kang, Y.J. Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy A Brief Review. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2001, 1, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldin, O.P.; Mattison, D.R. Sex Differences in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 48, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Martin, J.; Orme, L.; Seddon, B.; Desai, J.; Nicholls, W.; Thomson, D.; Porter, D.; McCowage, G.; Underhill, C.; et al. Gender Differences in Doxorubicin Pharmacology for Subjects with Chemosensitive Cancers of Young Adulthood. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afonso, A.I.; Amaro-Leal, Â.; Machado, F.; Rocha, I.; Geraldes, V. Doxorubicin Dose-Dependent Impact on Physiological Balance—A Holistic Approach in a Rat Model. Biology 2023, 12, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12071031
Afonso AI, Amaro-Leal Â, Machado F, Rocha I, Geraldes V. Doxorubicin Dose-Dependent Impact on Physiological Balance—A Holistic Approach in a Rat Model. Biology. 2023; 12(7):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12071031
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfonso, Ana I., Ângela Amaro-Leal, Filipa Machado, Isabel Rocha, and Vera Geraldes. 2023. "Doxorubicin Dose-Dependent Impact on Physiological Balance—A Holistic Approach in a Rat Model" Biology 12, no. 7: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12071031
APA StyleAfonso, A. I., Amaro-Leal, Â., Machado, F., Rocha, I., & Geraldes, V. (2023). Doxorubicin Dose-Dependent Impact on Physiological Balance—A Holistic Approach in a Rat Model. Biology, 12(7), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12071031





