Predicting Protein–Protein Interactions Based on Ensemble Learning-Based Model from Protein Sequence
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Position Specific Scoring Matrix
2.3. Locality Preserving Projections
2.4. Rotation Forest
- (1)
- Set X is randomly divided into K disjoint subsets; each subset contains the number of features is .
- (2)
- Form a new matrix by choosing the corresponding column of the feature in the subset from the training dataset S. And applying a bootstrap sampling technique from seventy-five percent of the original training dataset S to generate a new matrix .
- (3)
- Employ C feature by adopting the PCA method in matrix . The principal component coefficients are stored in , which can be represented as .
- (4)
- Construct a sparse rotation matrix , in which matrix contain coefficients. The matrix can be defined as:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation Criteria
3.2. Prediction Ability Assess
3.3. Performance Comparison of RF with Other Models
3.4. Performance on Independent Dataset
3.5. Comparison with Other Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; You, Z.H.; Chen, X.; Li, J.Q.; Yan, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.A. An ensemble approach for large-scale identification of protein-protein interactions using the alignments of multiple sequences. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5149–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, P.; Gingras, A.C. History of protein-protein interactions: From egg-white to complex networks. Proteomics 2012, 12, 1478–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashi, I.; Tomoko, C.; Ritsuko, O.; Mikio, Y.; Masahira, H.; Yoshiyuki, S. A comprehensive two-hybrid analysis to explore the yeast protein interactome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4569–4574. [Google Scholar]
- Tarassov, K.; Messier, V.; Landry, C.R.; Radinovic, S.; Molina, M.M.S.; Shames, I.; Malitskaya, Y.; Vogel, J.; Bussey, H.; Michnick, S.W. An in Vivo Map of the Yeast Protein Interactome. Science 2008, 320, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Snyder, M. Protein chip technology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, A.C.; Bosche, M.; Krause, R.; Grandi, P.; Marzioch, M.; Bauer, A.; Schultz, J.; Rick, J.M.; Michon, A.M.; Cruciat, C.M.; et al. Functional organization of the yeast proteome by systematic analysis of protein complexes. Nature 2002, 415, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, G.D.; Doron, B.; Hogue, C.W. BIND: The biomolecular interaction network database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenarios, I.; Salwinski, L.; Duan, X.J.; Higney, P.; Kim, S.M.; Eisenberg, D. DIP, the Database of Interacting Proteins: A research tool for studying cellular networks of protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Licata, L.; Briganti, L.; Peluso, D.; Perfetto, L.; Iannuccelli, M.; Galeota, E.; Sacco, F.; Palma, A.; Nardozza, A.P.; Santonico, E.; et al. MINT, the molecular interaction database: 2012 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D857–D861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; You, Z.H.; Huang, D.S.; Wang, B. T-LSE: A Novel Robust Geometric Approach for Modeling Protein-Protein Interaction Networks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, D.S.; Han, K. An algorithm for finding functional modules and protein complexes in protein-protein interaction networks. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2008, 2008, 860270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.F.; Zhao, X.M.; Huang, D.S. Predicting protein-protein interactions from protein sequences using meta predictor. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Huang, D.S.; Wang, B.; Chen, P. Identifying Protein-Protein Interfacial Residues in Heterocomplexes Using Residue Conservation Scores. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 38, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.G.; Xia, J.F.; Li, X.L.; Huang, D.S. Predicting protein-protein interactions from sequence using correlation coefficient and high-quality interaction dataset. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, B.; Wong, H.S.; Huang, D.S. Prediction of protein B-factors using multi-class bounded SVM. Protein Pept. Lett. 2007, 14, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.M.; Cheung, Y.M.; Huang, D.S. A novel approach to extracting features from motif content and protein composition for protein sequence classification. Neural Netw. 2005, 18, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Deng, S.P.; You, Z.H.; Huang, D.S. Identifying spurious interactions in the protein-protein interaction networks using local similarity preserving embedding. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2017, 14, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.Z.; Yuan, C.A.; Zhang, Y.H.; Han, K.; Nandi, A.K.; Honig, B.; Huang, D.S. Mutli-features prediction of protein translational modification sites. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2018, 15, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.F.; Zhao, X.M.; Song, J.N.; Huang, D.S. APIS: Accurate prediction of hot spots in protein interfaces by combining protrusion index with solvent accessibility. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.B.; You, Z.H.; Li, L.P.; Huang, D.S.; Zhou, F.F.; Yang, S. Improving prediction of self-interacting proteins using stacked sparse auto-encoder with PSSM profiles. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.P.; Huang, D.S. SFAPS: An R package for structure/function analysis of protein sequences based on informational spectrum method. Methods 2014, 69, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.S.; Zhang, L.; Han, K.; Deng, S.P.; Yang, K.; Zhang, H.B. Prediction of protein-protein interactions based on protein-protein correlation using least squares regression. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Huang, D.S.; Jiang, C.J. A new strategy for protein interface identification using manifold learning method. IEEE Trans. Nano-Biosci. 2014, 13, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.K.; You, Z.H.; Ji, Z.; Zhu, L.; Huang, D.S. Assessing and predicting protein interactions by combining manifold embedding with multiple information integration. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- You, Z.H.; Lei, Y.K.; Huang, D.S.; Zhou, X.B. Using manifold embedding for assessing and predicting protein interactions from high-throughput experimental data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2744–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alguwaizani, S.; Park, B.; Zhou, X.; Huang, D.S.; Han, K. Predicting interactions between virus and host proteins using repeat patterns and composition of amino acids. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1391265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, H.C.; You, Z.H.; Huang, D.S.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.H.; Li, L.P. A deep learning framework for robust and accurate prediction of ncRNA-protein interactions using evolutionary information. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.S.; Zhao, X.M.; Huang, G.B.; Cheung, Y.M. Classifying protein sequences using hydropathy blocks. Pattern Recognit. 2006, 39, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, P.; Huang, D.S.; Li, J.J.; Lok, T.M.; Lyu, M.R. Predicting protein interaction sites from residue spatial sequence profile and evolution rate. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.M.; Huang, D.S.; Cheung, Y.M. A novel hybrid GA/RBFNN technique for protein classification. Protein Pept. Lett. 2005, 12, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wong, H.S.; Huang, D.S. Inferring protein-protein interacting sites using residue conservation and evolutionary information. Protein Pept. Lett. 2006, 13, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.F.; Han, K.; Huang, D.S. Sequence-based prediction of protein-protein interactions by means of rotation forest and autocorrelation descriptor. Protein Pept. Lett. 2010, 17, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhu, W.; Yu, K.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H. Predicting protein–protein interactions based only on sequences information. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4337–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, Z.H.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, C.H.; Yu, H.J.; Deng, S.P.; Ji, Z. Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences using a novel multi-scale continuous and discontinuous feature set. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, B.; Yu, Z.; Lawrence, P.J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y. Improving protein-protein interactions prediction accuracy using XGBoost feature selection and stacked ensemble classifier. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 123, 103899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.J.; Yuan, D.C.; Chai, T.Y.; Tang, J. KPCA and ELM ensemble modeling of wastewater effluent quality indices. Procedia Eng. 2011, 15, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousef, A.; Charkari, N.M. A novel method based on new adaptive LVQ neural network for predicting protein–protein interactions from protein sequences. J. Theor. Biol. 2013, 336, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.A.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, X. Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences based on continuous and discrete wavelet transform features. Molecules 2018, 23, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahiri, J.; Yaghoubi, O.; Mohammad-Noori, M.; Ebrahimpour, R.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. PPIevo: Protein–protein interaction prediction from PSSM based evolutionary information. Genomics 2013, 102, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Roe, D.; Faulon, J.L. Predicting protein–protein interactions using signature products. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribskov, M.; McLachlan, A.D.; Eisenberg, D. Profile analysis: Detection of distantly related proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 4355–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Yuan, J. Using radial basis function on the general form of Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition and PSSM to predict subcellular locations of proteins with both single and multiple sites. Biosystems 2013, 113, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Varshney, G.C.; Raghava, G.P.S. Prediction of mitochondrial proteins of malaria parasite using split amino acid composition and PSSM profile. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 338–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Niyogi, P. Locality preserving projections. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2004, 16, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.J.; Kuncheva, L.I.; Alonso, C.J. Rotation forest: A new classifier ensemble method. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, L.; Lumini, A. An ensemble of K-local hyperplanes for predicting protein–protein interactions. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, L. Hyperplanes for predicting protein–protein interactions. Neurocomputing 2005, 69, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.H.; Lei, Y.K.; Zhu, L.; Xia, B.; Wang, B. Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences with ensemble extreme learning machines and principal component analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bock, J.R.; Gough, D.A. Whole-proteome interaction mining. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Yi, J.; Aishwarya, S.V.; Lan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, T.H.; Leone, G.; Jin, V.X. QChIPat: A quantitative method to identify distinct binding patterns for two biological ChIP-seq samples in different experimental conditions. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.Z.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y.Y. Prediction of protein-protein interactions using local description of amino acid sequence. Adv. Comput. Sci. Educ. Appl. 2011, 202, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xia, J.F.; Gui, J. Prediction of protein-protein interactions from protein sequence using local descriptors. Protein Pept. Lett. 2010, 17, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Yu, L.Z.; Wen, Z.N.; Li, M.L. Using support vector machine combined with auto covariance to predict protein-protein interactions from protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3025–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
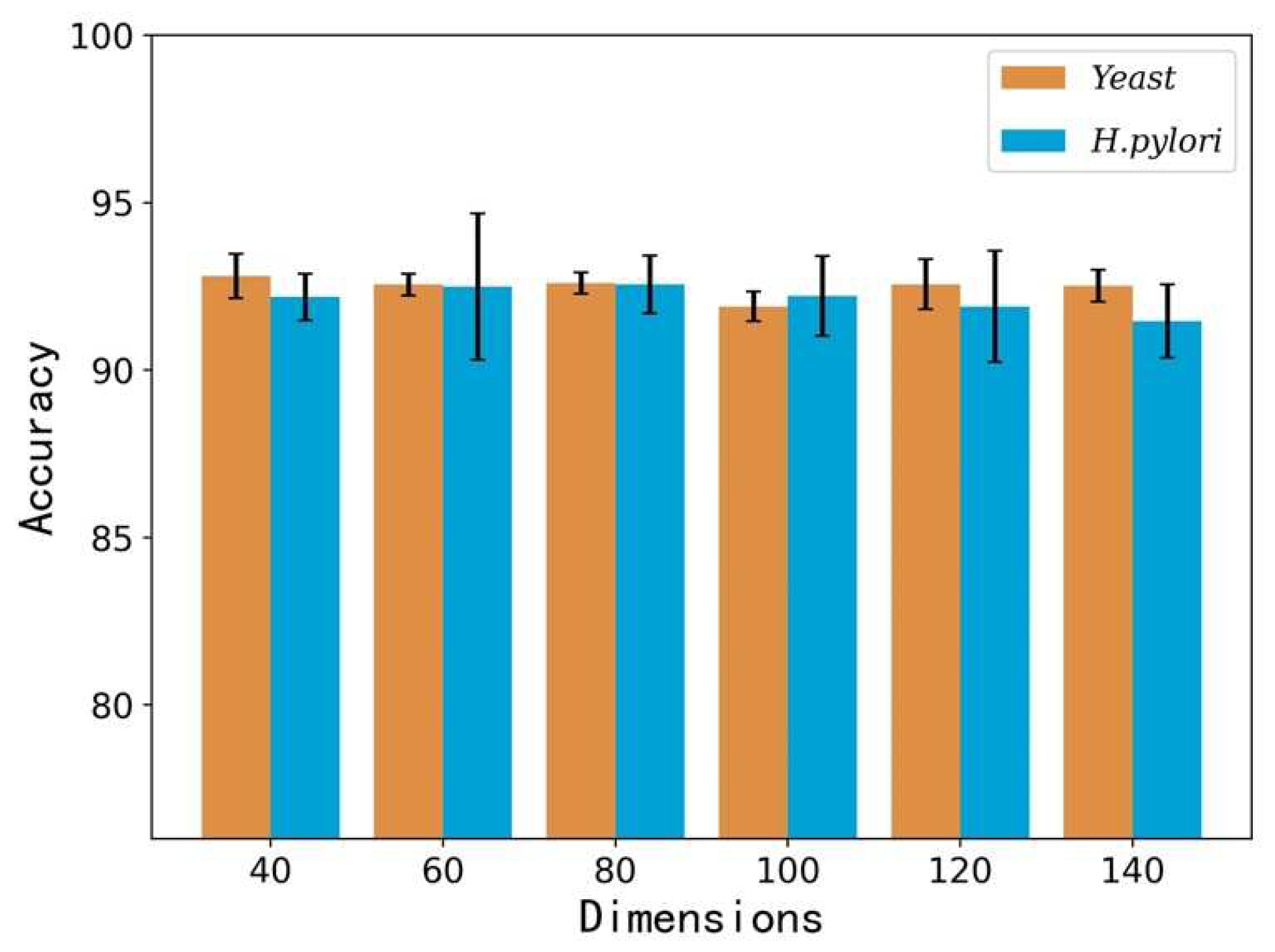
| Feature Vectors | Dataset | Acc. (%) | Prec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | Yeast | 92.81 ± 0.66 | 96.80 ± 0.68 | 88.55 ± 0.95 | 86.61 ± 1.15 |
| H. pylori | 92.18 ± 0.70 | 93.66 ± 2.21 | 90.56 ± 1.52 | 85.54 ± 1.15 | |
| 60 | Yeast | 92.55 ± 0.32 | 96.56 ± 0.53 | 88.25 ± 0.81 | 86.16 ± 0.31 |
| H. pylori | 92.49 ± 2.18 | 94.59 ± 2.13 | 90.12 ± 2.59 | 86.16 ± 3.67 | |
| 80 | Yeast | 92.60 ± 0.32 | 96.37 ± 0.55 | 88.51 ± 0.54 | 86.23 ± 0.57 |
| H. pylori | 92.56 ± 0.86 | 94.11 ± 0.99 | 90.82 ± 0.93 | 86.22 ± 1.47 | |
| 100 | Yeast | 91.90 ± 0.44 | 94.94 ± 0.90 | 88.52 ± 0.46 | 85.08 ± 0.73 |
| H. pylori | 92.21 ± 1.19 | 94.10 ± 1.74 | 90.12 ± 2.31 | 85.63 ± 2.03 | |
| 120 | Yeast | 92.56 ± 0.75 | 96.44 ± 0.79 | 88.40 ± 0.93 | 86.19 ± 1.27 |
| H. pylori | 91.90 ± 1.66 | 93.94 ± 1.14 | 89.56 ± 2.56 | 85.14 ± 2.81 | |
| 140 | Yeast | 92.52 ± 0.48 | 95.96 ± 0.32 | 88.77 ± 0.79 | 86.12 ± 0.81 |
| H. pylori | 91.46 ± 1.09 | 92.74 ± 2.54 | 89.89 ± 1.84 | 84.34 ± 1.84 |
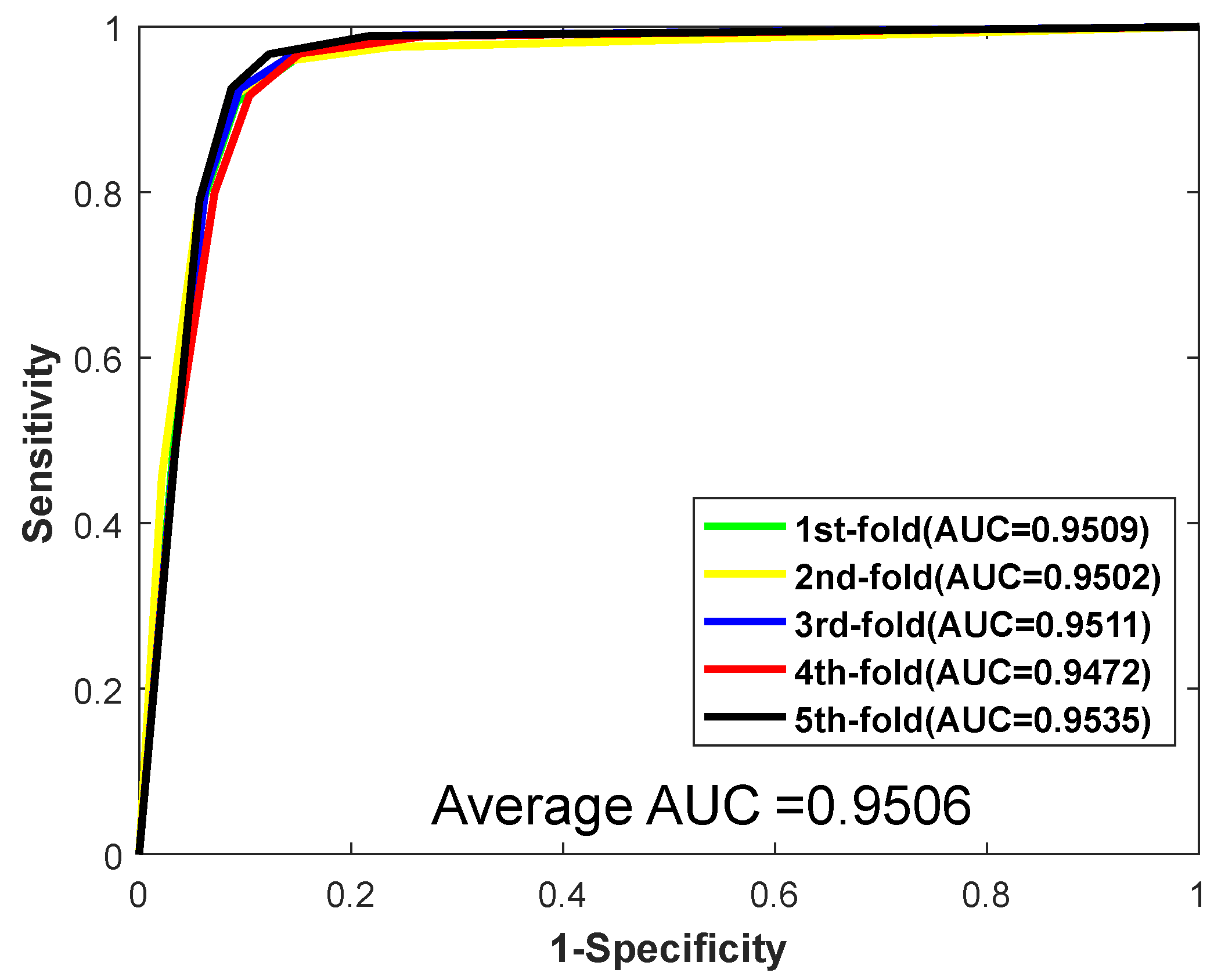
| Testing Set | Acc. (%) | Prec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC. (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 92.58 | 97.34 | 88.14 | 86.23 | 0.9509 |
| 2 | 92.80 | 96.24 | 88.78 | 86.58 | 0.9502 |
| 3 | 92.85 | 97.39 | 88.35 | 86.68 | 0.9511 |
| 4 | 92.00 | 95.91 | 87.44 | 85.20 | 0.9472 |
| 5 | 93.83 | 97.13 | 90.02 | 88.37 | 0.9535 |
| Average | 92.81 ± 0.66 | 96.80 ± 0.68 | 88.55 ± 0.95 | 86.61 ± 1.15 | 0.9506 ± 0.0023 |
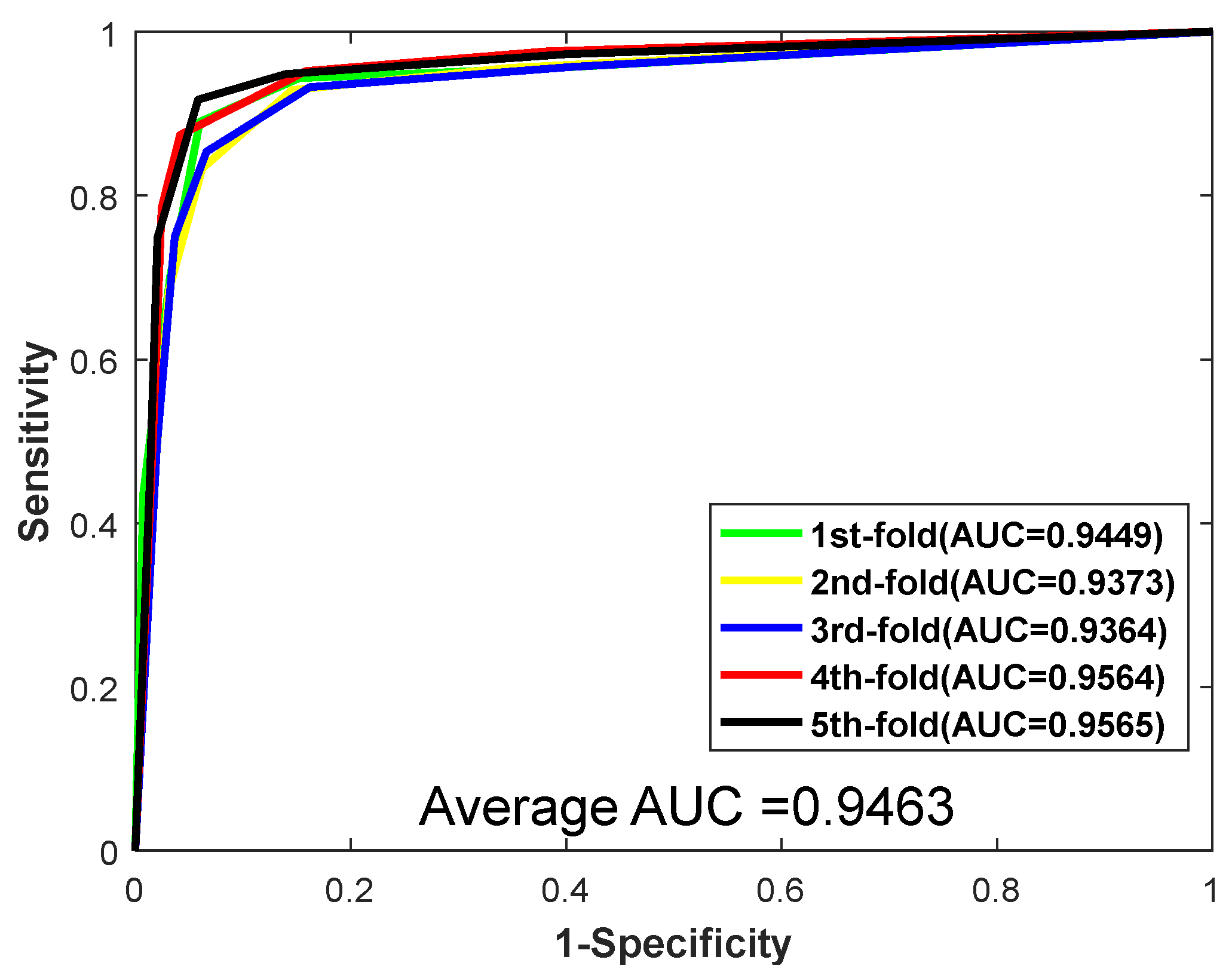
| Testing Set | Acc. (%) | Prec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC. (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 92.80 | 93.50 | 91.52 | 86.61 | 0.9449 |
| 2 | 91.77 | 93.19 | 89.97 | 84.87 | 0.9373 |
| 3 | 91.60 | 93.49 | 90.10 | 84.59 | 0.9364 |
| 4 | 93.65 | 95.02 | 92.07 | 88.10 | 0.9564 |
| 5 | 92.97 | 95.32 | 90.44 | 86.91 | 0.9565 |
| Average | 92.56 ± 0.86 | 94.11 ± 0.99 | 90.82 ± 0.93 | 86.22 ± 1.47 | 0.9463 ± 0.0098 |
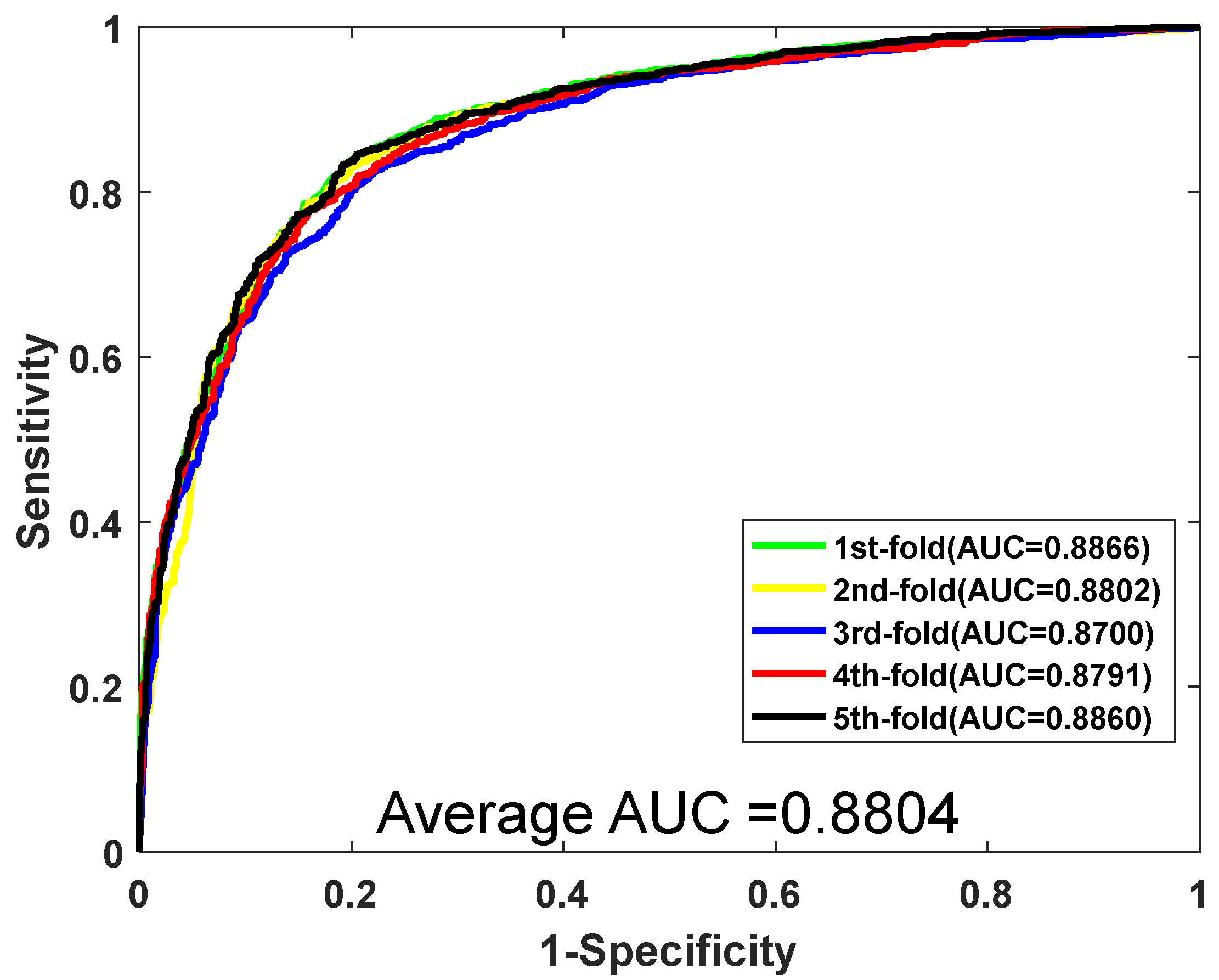
| Testing Set | Acc. (%) | Prec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC. (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 81.27 | 83.41 | 79.90 | 69.53 | 0.8866 |
| 2 | 81.18 | 81.28 | 80.02 | 69.42 | 0.8802 |
| 3 | 79.48 | 80.85 | 78.37 | 67.37 | 0.8700 |
| 4 | 80.33 | 80.54 | 79.07 | 68.37 | 0.8791 |
| 5 | 81.36 | 80.88 | 80.95 | 69.65 | 0.8860 |
| Average | 80.72 ± 0.81 | 81.39 ± 1.16 | 79.66 ± 0.98 | 68.87 ± 0.98 | 0.8804 ± 0.0067 |
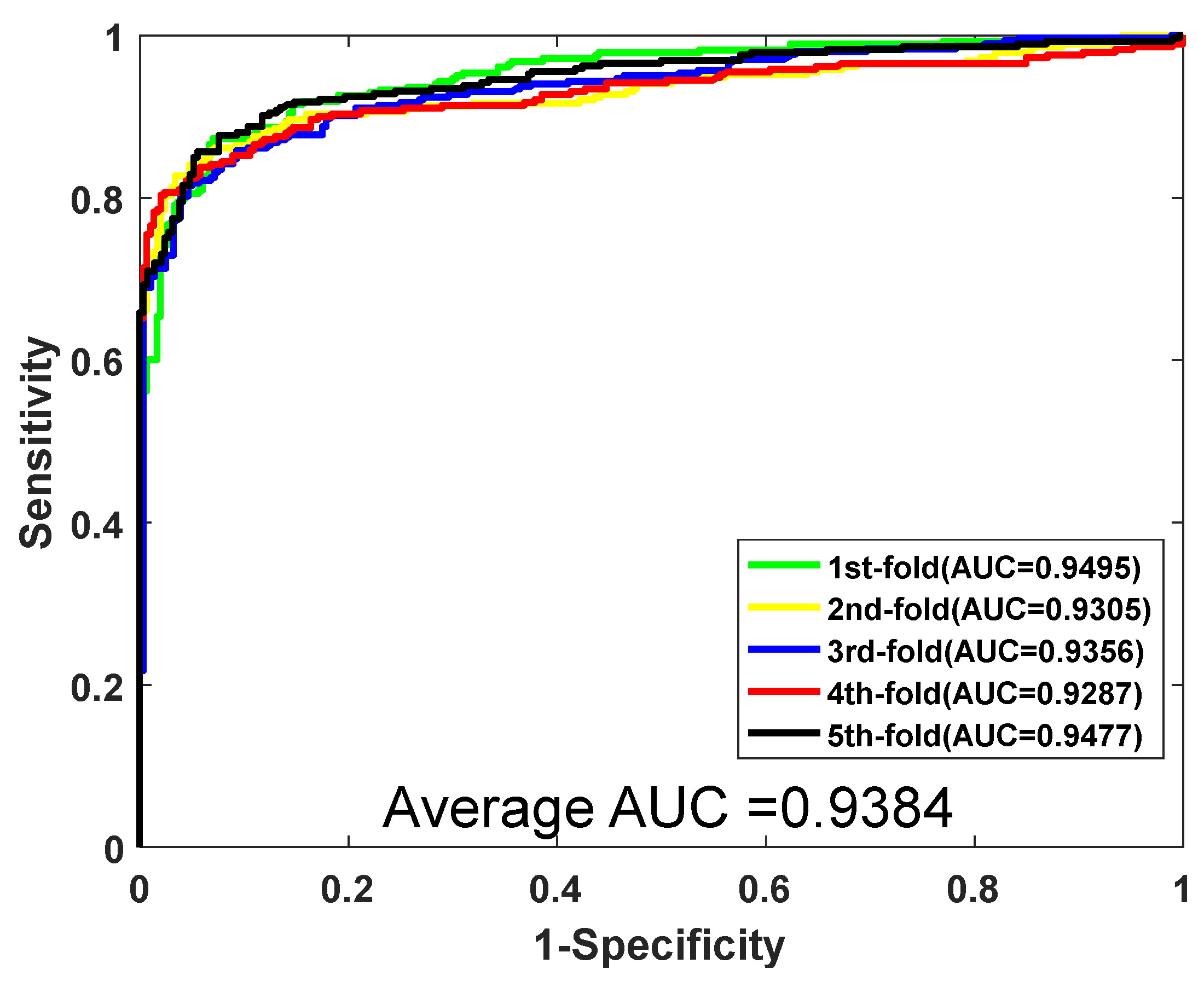
| Testing Set | Acc. (%) | Prec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC. (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 88.16 | 88.21 | 87.28 | 79.11 | 0.9495 |
| 2 | 89.37 | 92.83 | 85.12 | 80.91 | 0.9305 |
| 3 | 87.65 | 90.81 | 84.82 | 78.32 | 0.9356 |
| 4 | 88.85 | 94.47 | 82.41 | 80.02 | 0.9287 |
| 5 | 89.54 | 92.96 | 85.67 | 81.21 | 0.9477 |
| Average | 88.71 ± 0.80 | 91.86 ± 2.42 | 85.06 ± 1.76 | 79.91 ± 1.21 | 0.9384 ± 0.0097 |
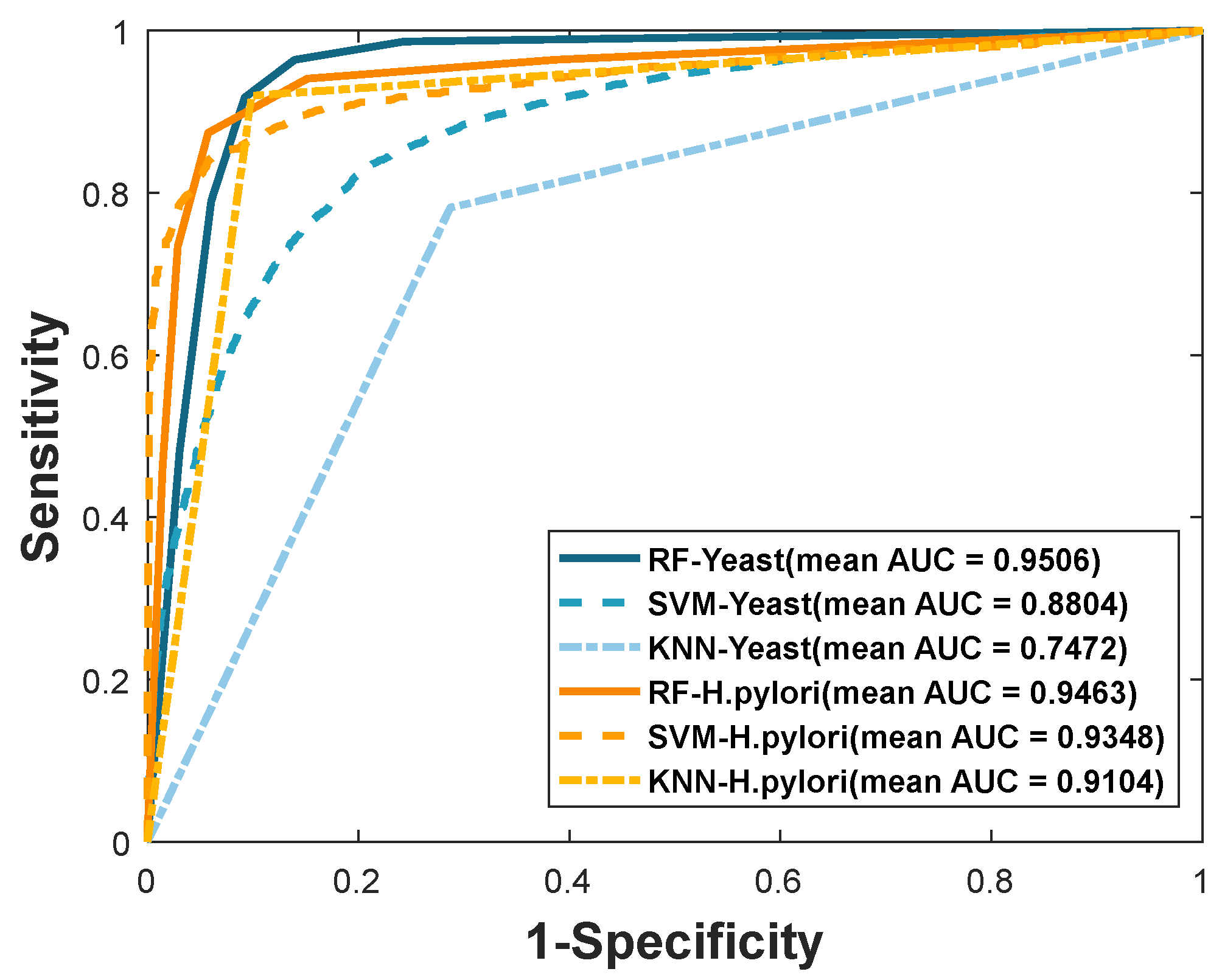
| Dataset | Model | Accu. (%) | Prec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC. (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yeast | RF | 92.81 ± 0.66 | 96.80 ± 0.68 | 88.55 ± 0.95 | 86.61 ± 1.15 | 0.9506 ± 0.0023 |
| SVM | 80.72 ± 0.81 | 81.39 ± 1.16 | 79.66 ± 0.98 | 68.87 ± 0.98 | 0.8804 ± 0.0067 | |
| KNN | 74.73 ± 1.38 | 76.57 ± 2.18 | 71.28 ± 1.18 | 62.15 ± 1.31 | 0.7472 ± 0.0139 | |
| H. pylori | RF | 92.56 ± 0.86 | 94.11 ± 0.99 | 90.82 ± 0.93 | 86.22 ± 1.47 | 0.9463 ± 0.0098 |
| SVM | 88.71 ± 0.80 | 91.86 ± 2.42 | 85.06 ± 1.76 | 79.91 ± 1.21 | 0.9384 ± 0.0097 | |
| KNN | 91.05 ± 1.01 | 91.85 ± 1.72 | 90.12 ± 0.94 | 83.70 ± 1.64 | 0.9104 ± 0.0101 |
| Species | Test Pairs | Accu. (%) |
|---|---|---|
| H. sapiens | 1412 | 88.60 |
| M. musculus | 313 | 97.44 |
| H. pylori | 1420 | 94.44 |
| C. elegans | 4013 | 93.60 |
| Model | Acc. (%) | Prec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ensemble of HKNN [47] | 86.60 | 85.00 | 86.70 | N/A |
| HKNN [48] | 84.00 | 84.00 | 86.00 | N/A |
| Ensemble ELM [49] | 87.50 | 88.95 | 86.15 | 78.13 |
| Signature products [40] | 83.40 | 85.70 | 79.90 | N/A |
| Phylogenetic bootstrap [50] | 75.80 | 80.20 | 69.80 | N/A |
| Boosting [51] | 79.52 | 81.69 | 80.37 | 70.64 |
| Proposed method | 92.56 | 94.11 | 90.82 | 86.22 |
| Method | Model | Acc. (%) | Prec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| You’s work [49] | PCA-EELM | 87.00 ± 0.29 | 87.59 ± 0.32 | 86.15 ± 0.43 | 77.36 ± 0.44 |
| Zhou’s work [52] | SVM+LD | 88.56 ± 0.33 | 89.50 ± 0.60 | 87.37 ± 0.22 | 77.15 ± 0.68 |
| Yang’s work [53] | Cod1 | 75.08 ± 1.13 | 74.75 ± 1.23 | 75.81 ± 1.20 | N/A |
| Cod2 | 80.04 ± 1.06 | 95.44 ± 0.30 | 96.25 ± 1.26 | N/A | |
| Cod3 | 80.41 ± 0.47 | 65.50 ± 1.44 | 97.90 ± 1.06 | N/A | |
| Cod4 | 86.15 ± 1.17 | 90.24 ± 1.34 | 81.03 ± 1.74 | N/A | |
| Guo’s work [54] | ACC | 89.33 ± 2.67 | 88.87 ± 6.16 | 89.93 ± 3.68 | N/A |
| AC | 87.36 ± 1.38 | 87.82 ± 4.33 | 87.30 ± 4.68 | N/A | |
| Proposed method | RF | 92.81 ± 0.66 | 96.80 ± 0.68 | 88.55 ± 0.95 | 86.61 ± 1.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, X.; Xiao, M.; You, Z.; Yan, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Shang, B. Predicting Protein–Protein Interactions Based on Ensemble Learning-Based Model from Protein Sequence. Biology 2022, 11, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070995
Zhan X, Xiao M, You Z, Yan C, Guo J, Wang L, Sun Y, Shang B. Predicting Protein–Protein Interactions Based on Ensemble Learning-Based Model from Protein Sequence. Biology. 2022; 11(7):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070995
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Xinke, Mang Xiao, Zhuhong You, Chenggang Yan, Jianxin Guo, Liping Wang, Yaoqi Sun, and Bingwan Shang. 2022. "Predicting Protein–Protein Interactions Based on Ensemble Learning-Based Model from Protein Sequence" Biology 11, no. 7: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070995
APA StyleZhan, X., Xiao, M., You, Z., Yan, C., Guo, J., Wang, L., Sun, Y., & Shang, B. (2022). Predicting Protein–Protein Interactions Based on Ensemble Learning-Based Model from Protein Sequence. Biology, 11(7), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070995







