Irisin Attenuates Muscle Impairment during Bed Rest through Muscle-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Biologic Samples and Measurements
2.3. Anthropometric Characteristics and Body Composition
2.4. Muscle Characteristic
2.5. Muscle Fiber Analysis
2.6. Adipose Tissue Gene Expression
2.7. Muscle Tissue Gene Expression
2.8. Statistics
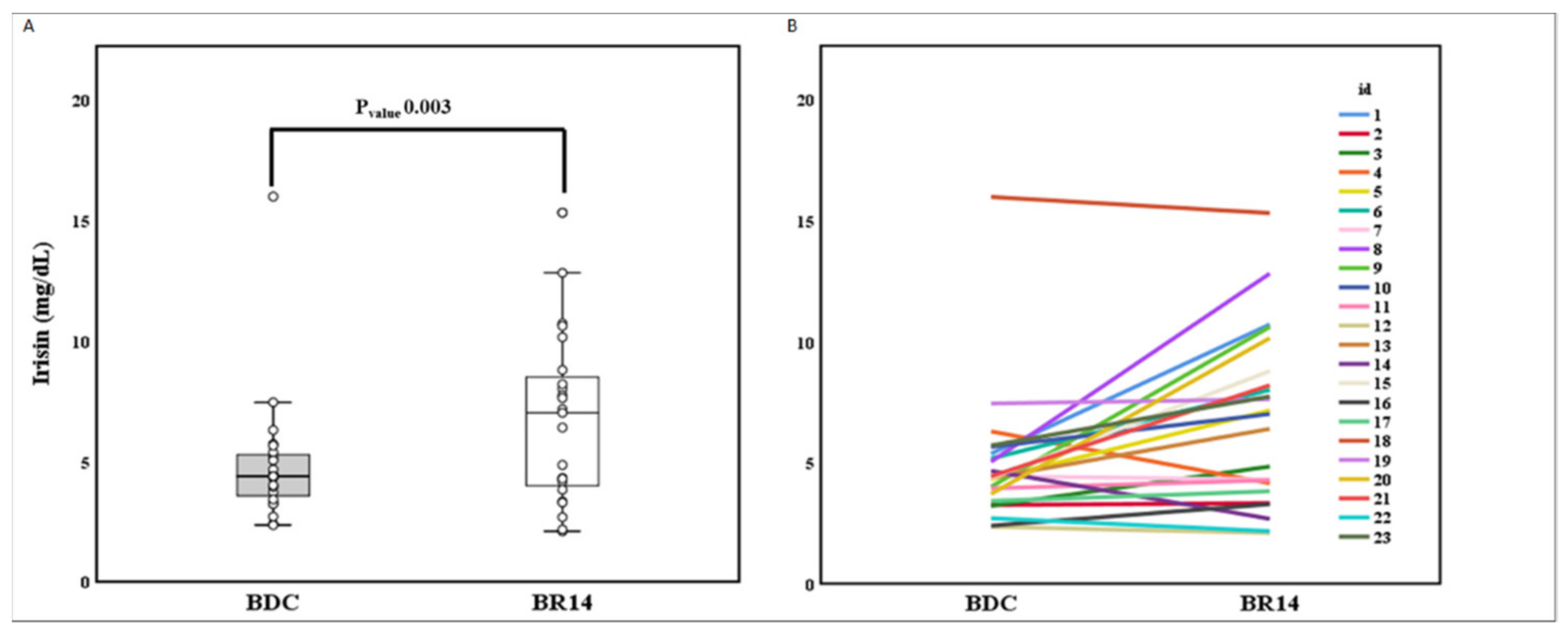
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Correlations between Irisin and Body Composition, Muscle Performance, and Fiber Type Properties
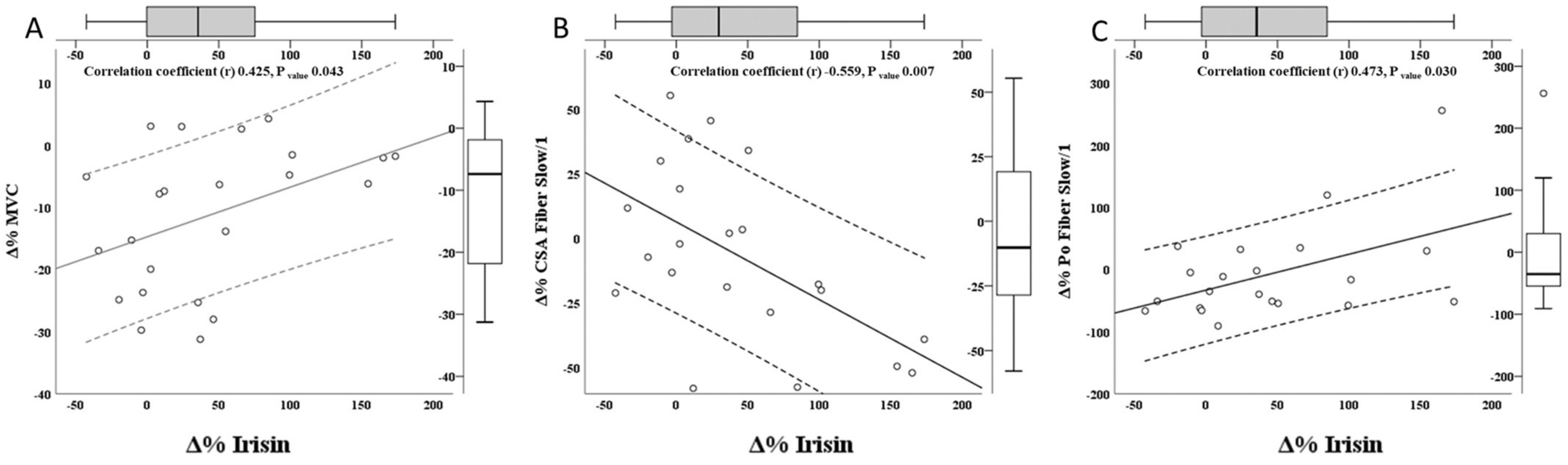
3.2. Correlation between Irisin Variation and Variation of Body Composition, Muscle Performance, and Fiber Type Properties
3.3. Effect of 14-Day BR and Tertiles BDC Irisin on Body Composition, Muscle Parameters, and Fiber Type Properties
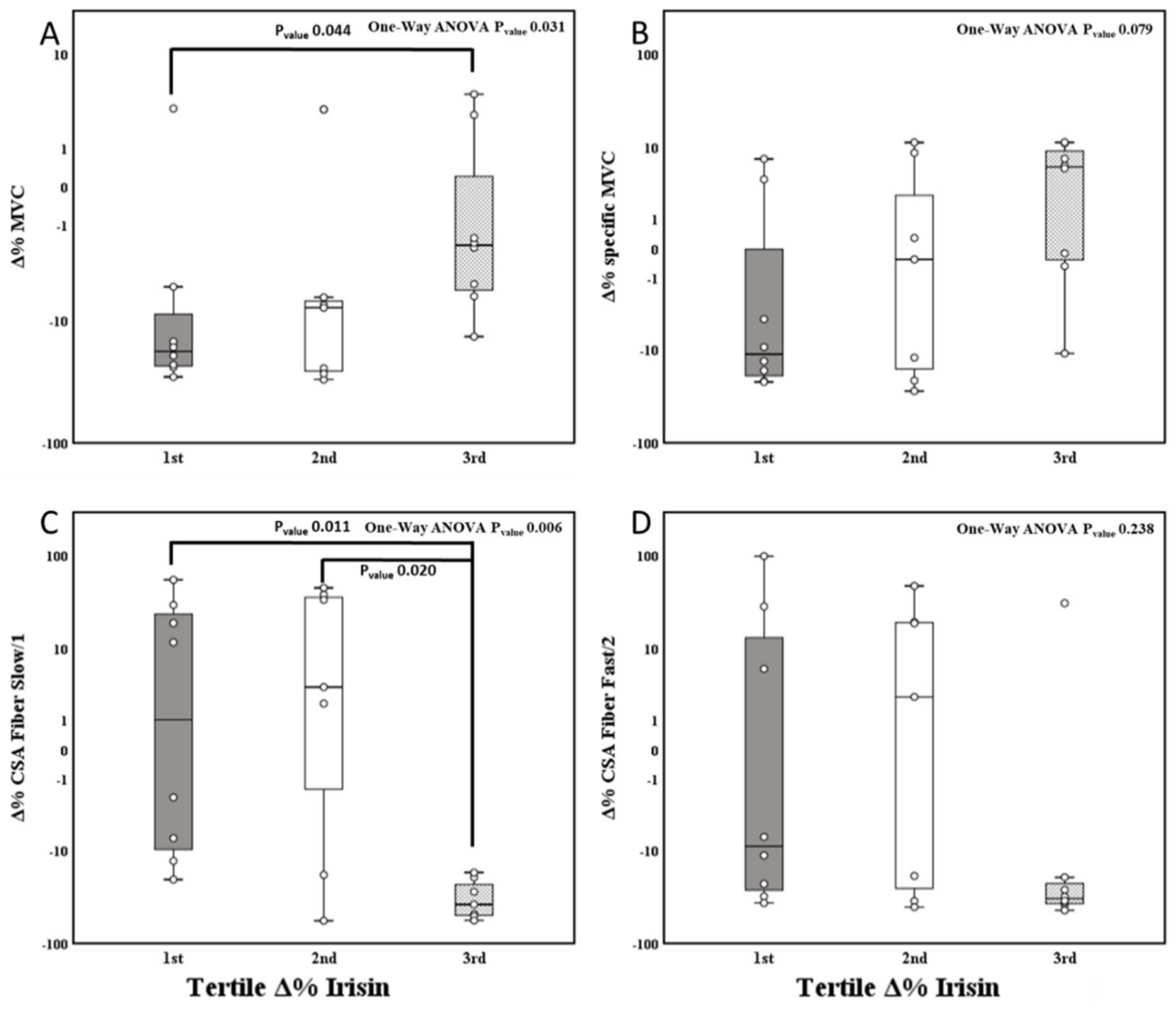
3.4. Effect of 14-Day BR and Tertile Irisin Variation on the Body Composition, Muscle Parameters, and Fiber Type Properties
3.5. Bivariate and Multivariate Linear Regression Analyses
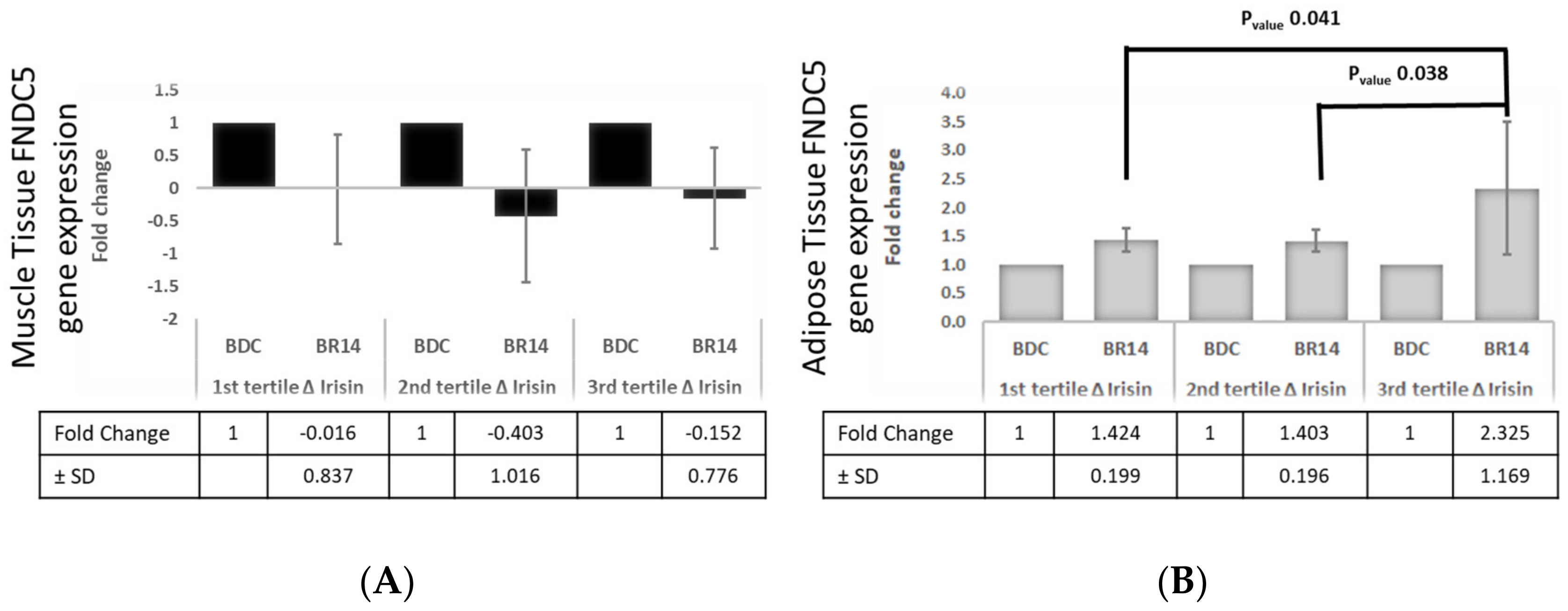
3.6. Tertiles of Δ%Irisin, Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue and Muscle FNDC5 Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Δ%CSA | percentage change of CSA between BDC and BR14 |
| Δ%Irisin | percentage change of irisin between BDC and BR14 |
| Δ%MVC | percentage change of MVC between BDC and BR14 |
| Δ%P0 | percentage change of P0 between BDC and BR14 |
| ΔCSA | absolute change of CSA between BDC and BR14 |
| ΔIrisin | absolute change of irisin between BDC and BR14 |
| ΔMVC | absolute change of MVC between BDC and BR14 |
| BCM | body cellular mass |
| BDC | baseline data collection |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BR | bed rest |
| BR14 | 14th day of bed rest |
| CCT | computerized cognitive training |
| CSA | cross-sectional area of fiber |
| F0 | isometric force of fiber |
| FFM | fat free mass |
| FM | fat mass |
| FNDC5 | membrane protein fibronectin type III domain-containing protein-5 |
| FNDC5ge | FNDC5 gene expression |
| MEP | maximal explosive power of lower limb |
| MM | muscle mass |
| MVC | maximal voluntary contraction of knee extensors |
| P0 | specific force of fiber |
| QMV | quadriceps femoris muscle volume |
| V0 | unloaded shortening velocity of fiber |
References
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-α-Dependent Myokine That Drives Brown-Fat-like Development of White Fat and Thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.Y.; Panagiotou, G.; Mougios, V.; Brinkoetter, M.; Vamvini, M.T.; Schneider, B.E.; Mantzoros, C.S. FNDC5 and Irisin in Humans: I. Predictors of Circulating Concentrations in Serum and Plasma and II. MRNA Expression and Circulating Concentrations in Response to Weight Loss and Exercise. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Wrann, C.D.; Jedrychowski, M.; Vidoni, S.; Kitase, Y.; Nagano, K.; Zhou, C.; Chou, J.; Parkman, V.-J.A.; Novick, S.J.; et al. Irisin Mediates Effects on Bone and Fat via AV Integrin Receptors. Cell 2018, 175, 1756–1768.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Anastasilakis, A.D.; Efstathiadou, Z.A.; Makras, P.; Perakakis, N.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Irisin in Metabolic Diseases. Endocrine 2018, 59, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Ezquerro, S.; Méndez-Giménez, L.; Frühbeck, G. Crosstalk between Adipokines and Myokines in Fat Browning. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroya, F. Irisin, Turning Up the Heat. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaianni, G.; Cuscito, C.; Mongelli, T.; Pignataro, P.; Buccoliero, C.; Liu, P.; Lu, P.; Sartini, L.; Di Comite, M.; Mori, G.; et al. The Myokine Irisin Increases Cortical Bone Mass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12157–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaianni, G.; Mongelli, T.; Cuscito, C.; Pignataro, P.; Lippo, L.; Spiro, G.; Notarnicola, A.; Severi, I.; Passeri, G.; Mori, G.; et al. Irisin Prevents and Restores Bone Loss and Muscle Atrophy in Hind-Limb Suspended Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.Y.; Mougios, V.; Kabasakalis, A.; Fatouros, I.; Siopi, A.; Douroudos, I.I.; Filippaios, A.; Panagiotou, G.; Park, K.H.; Mantzoros, C.S. Exercise-Induced Irisin Secretion Is Independent of Age or Fitness Level and Increased Irisin May Directly Modulate Muscle Metabolism through AMPK Activation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2154–E2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G. Energy Sensing by the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and Its Effects on Muscle Metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2011, 70, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Ando, D.; Goto, K.; Kiuchi, M.; Yamakita, M.; Koyama, K. High-Intensity Exercise Causes Greater Irisin Response Compared with Low-Intensity Exercise under Similar Energy Consumption. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2014, 233, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecksteden, A.; Wegmann, M.; Steffen, A.; Kraushaar, J.; Morsch, A.; Ruppenthal, S.; Kaestner, L.; Meyer, T. Irisin and Exercise Training in Humans—Results from a Randomized Controlled Training Trial. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, C.; Leal, V.O.; Marinho, S.M.; Barroso, S.G.; Rocha, G.S.; Boaventura, G.T.; Mafra, D. Resistance Exercise Training Does Not Affect Plasma Irisin Levels of Hemodialysis Patients. Horm. Metab. Res. 2013, 45, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norheim, F.; Langleite, T.M.; Hjorth, M.; Holen, T.; Kielland, A.; Stadheim, H.K.; Gulseth, H.L.; Birkeland, K.I.; Jensen, J.; Drevon, C.A. The Effects of Acute and Chronic Exercise on PGC-1α, Irisin and Browning of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Humans. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekkala, S.; Wiklund, P.K.; Hulmi, J.J.; Ahtiainen, J.P.; Horttanainen, M.; Pöllänen, E.; Mäkelä, K.A.; Kainulainen, H.; Häkkinen, K.; Nyman, K.; et al. Are Skeletal Muscle FNDC5 Gene Expression and Irisin Release Regulated by Exercise and Related to Health? J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 5393–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, E.; Norheim, F.; Thiede, B.; Holen, T.; Ohashi, T.; Schering, L.; Lee, S.; Brenmoehl, J.; Thomas, S.; Drevon, C.A.; et al. Irisin—A Myth Rather than an Exercise-Inducible Myokine. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedrychowski, M.P.; Wrann, C.D.; Paulo, J.A.; Gerber, K.K.; Szpyt, J.; Robinson, M.M.; Nair, K.S.; Gygi, S.P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Detection and Quantitation of Circulating Human Irisin by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, R.R.; Shockett, P.; Webb, N.D.; Shah, U.; Castracane, V.D. A Transient Elevated Irisin Blood Concentration in Response to Prolonged, Moderate Aerobic Exercise in Young Men and Women. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amuri, A.; Raparelli, V.; Sanz, J.M.; Capatti, E.; Di Vece, F.; Vaccari, F.; Lazzer, S.; Zuliani, G.; Dalla Nora, E.; Neri, L.M.; et al. Biological Response of Irisin Induced by Different Types of Exercise in Obese Subjects: A Non-Inferiority Controlled Randomized Study. Biology 2022, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdiova, T.; Balaz, M.; Vician, M.; Maderova, D.; Vlcek, M.; Valkovic, L.; Srbecky, M.; Imrich, R.; Kyselovicova, O.; Belan, V.; et al. Effects of Obesity, Diabetes and Exercise on Fndc5 Gene Expression and Irisin Release in Human Skeletal Muscle and Adipose Tissue: In Vivo and in Vitro Studies. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmons, J.A.; Baar, K.; Davidsen, P.K.; Atherton, P.J. Is Irisin a Human Exercise Gene? Nature 2012, 488, E9–E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.Y.; Mougios, V.; Skraparlis, A.; Kabasakalis, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Irisin in Response to Acute and Chronic Whole-Body Vibration Exercise in Humans. Metabolism 2014, 63, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yang, L.; Ruan, J.; Gu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Z. The Effects of Both Age and Sex on Irisin Levels in Paired Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid in Healthy Humans. Peptides 2019, 113, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, H.; Nakajima, T.; Haruyama, A.; Shibasaki, I.; Hasegawa, T.; Sawaguchi, T.; Kuwata, T.; Obi, S.; Arikawa, T.; Sakuma, M.; et al. Association of Serum Concentrations of Irisin and the Adipokines Adiponectin and Leptin with Epicardial Fat in Cardiovascular Surgery Patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreani, M.; Rejc, E.; Taboga, P.; Ganzini, A.; Pišot, R.; Šimunič, B.; Biolo, G.; Reggiani, C.; Passaro, A.; Narici, M.; et al. Effects of 14 Days of Bed Rest and Following Physical Training on Metabolic Cost, Mechanical Work, and Efficiency during Walking in Older and Young Healthy Males. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pišot, R.; Marusic, U.; Biolo, G.; Mazzucco, S.; Lazzer, S.; Grassi, B.; Reggiani, C.; Toniolo, L.; di Prampero, P.E.; Passaro, A.; et al. Greater Loss in Muscle Mass and Function but Smaller Metabolic Alterations in Older Compared with Younger Men Following 2 Wk of Bed Rest and Recovery. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 120, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejc, E.; Floreani, M.; Taboga, P.; Botter, A.; Toniolo, L.; Cancellara, L.; Narici, M.; Šimunič, B.; Pišot, R.; Biolo, G.; et al. Loss of Maximal Explosive Power of Lower Limbs after 2 Weeks of Disuse and Incomplete Recovery after Retraining in Older Adults. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzer, S.; Pozzo, R.; Rejc, E.; Antonutto, G.; Francescato, M.P. Maximal Explosive Muscle Power in Obese and Non-Obese Prepubertal Children. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2009, 29, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria, C.; Toniolo, L.; Verratti, V.; Cancellara, P.; Pietrangelo, T.; Marconi, V.; Paoli, A.; Pogliaghi, S.; Fanò, G.; Reggiani, C.; et al. Improved VO2 Uptake Kinetics and Shift in Muscle Fiber Type in High-Altitude Trekkers. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Dalla Nora, E.; Morieri, M.L.; Soavi, C.; Sanz, J.M.; Zurlo, A.; Fellin, R.; Zuliani, G. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Plasma Levels: Relationship with Dementia and Diabetes in the Elderly Population. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Murawska-Cialowicz, E.; Wojna, J.; Zuwala-Jagiello, J. Crossfit Training Changes Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Irisin Levels at Rest, after Wingate and Progressive Tests, and Improves Aerobic Capacity and Body Composition of Young Physically Active Men and Women. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roca-Rivada, A.; Castelao, C.; Senin, L.L.; Landrove, M.O.; Baltar, J.; Belén Crujeiras, A.; Seoane, L.M.; Casanueva, F.F.; Pardo, M. FNDC5/Irisin Is Not Only a Myokine but Also an Adipokine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamparo, P.; Minetti, A.E.; di Prampero, P.E. Interplay among the Changes of Muscle Strength, Cross-Sectional Area and Maximal Explosive Power: Theory and Facts. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 88, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karastergiou, K.; Fried, S.K.; Xie, H.; Lee, M.-J.; Divoux, A.; Rosencrantz, M.A.; Chang, R.J.; Smith, S.R. Distinct Developmental Signatures of Human Abdominal and Gluteal Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Depots. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Miselli, M.A.; Sanz, J.M.; Dalla Nora, E.; Morieri, M.L.; Colonna, R.; Pišot, R.; Zuliani, G. Gene Expression Regional Differences in Human Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Amuri, A.; Sanz, J.M.; Lazzer, S.; Pišot, R.; Šimunič, B.; Biolo, G.; Zuliani, G.; Gasparini, M.; Narici, M.; Grassi, B.; et al. Irisin Attenuates Muscle Impairment during Bed Rest through Muscle-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk. Biology 2022, 11, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070999
D’Amuri A, Sanz JM, Lazzer S, Pišot R, Šimunič B, Biolo G, Zuliani G, Gasparini M, Narici M, Grassi B, et al. Irisin Attenuates Muscle Impairment during Bed Rest through Muscle-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk. Biology. 2022; 11(7):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070999
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Amuri, Andrea, Juana Maria Sanz, Stefano Lazzer, Rado Pišot, Bostjan Šimunič, Gianni Biolo, Giovanni Zuliani, Mladen Gasparini, Marco Narici, Bruno Grassi, and et al. 2022. "Irisin Attenuates Muscle Impairment during Bed Rest through Muscle-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk" Biology 11, no. 7: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070999
APA StyleD’Amuri, A., Sanz, J. M., Lazzer, S., Pišot, R., Šimunič, B., Biolo, G., Zuliani, G., Gasparini, M., Narici, M., Grassi, B., Reggiani, C., Dalla Nora, E., & Passaro, A. (2022). Irisin Attenuates Muscle Impairment during Bed Rest through Muscle-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk. Biology, 11(7), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070999










