NRAS Mutations May Be Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Rosai Dorfman Disease: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Enrollment
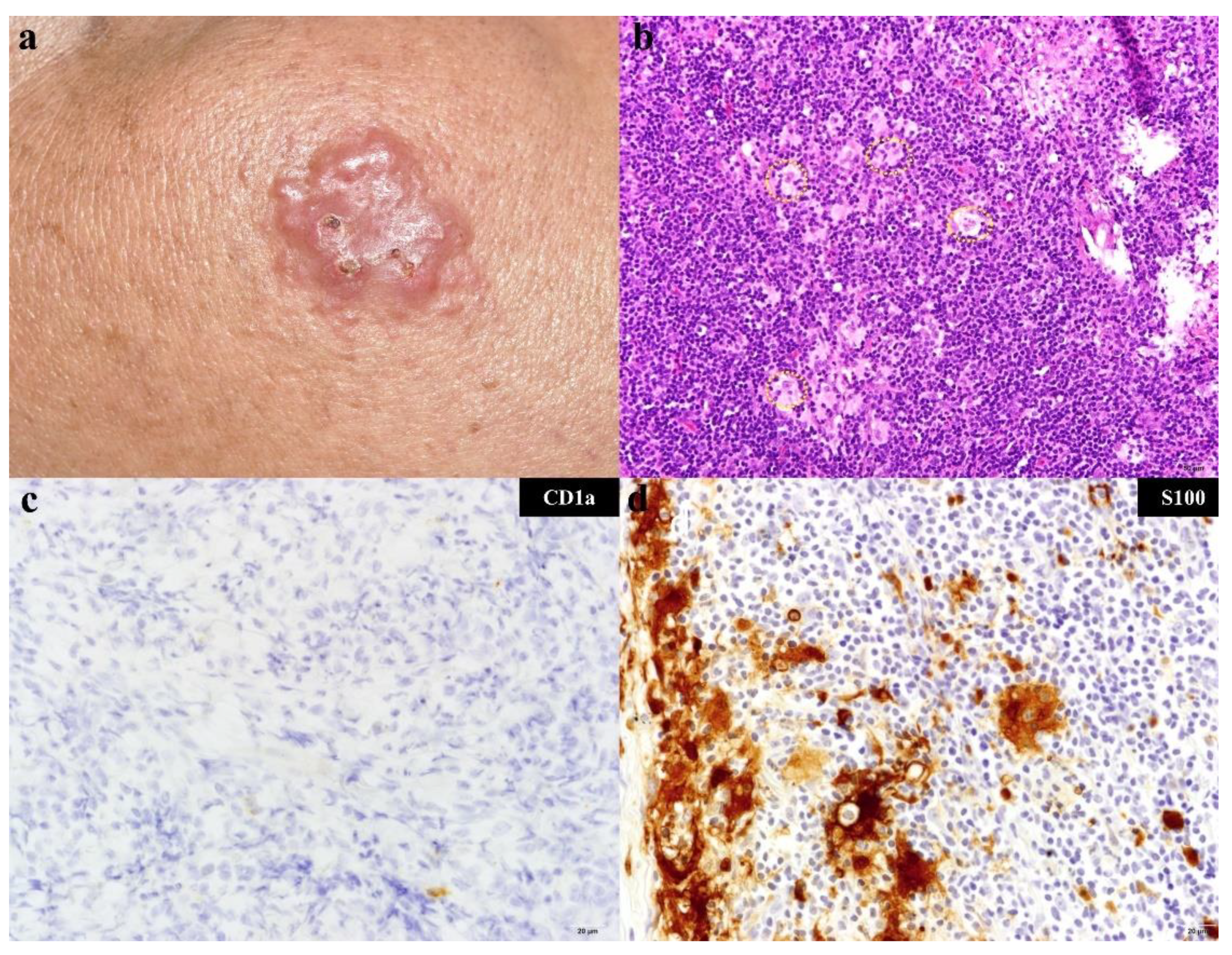
2.2. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Mutation Analysis for KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| BRAF | v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 |
| MAP2K1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 |
| NRAS | neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma 2 viral oncogene homolog |
| ARAF | serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf |
| RDD | Rosai–Dorfman disease |
| LCH | Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
| ECD | Erdheim–Chester disease |
| ESR | erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| RD | Rosai–Dorfman |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| RTK | receptor tyrosine kinases |
| GRB2 | growth factor receptor binding protein 2 |
| GEFs | guanine nucleotide exchange factors |
| SOS | Son of Sevenless protein |
| MAPKKK | mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase |
| MAPKK | mitogen activated protein kinase kinase |
References
- Destombes, P. Adenitis with lipid excess, in children or young adults, seen in the Antilles and in Mali (4 cases). Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1965, 58, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Rosai, J.; Dorfman, R.F. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. A newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch. Pathol. 1969, 87, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Writing Group of the Histiocyte Society. Histiocytosis syndromes in children. Lancet 1987, 1, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emile, J.F.; Abla, O.; Fraitag, S.; Horne, A.; Haroche, J.; Donadieu, J.; Requena-Caballero, L.; Jordan, M.B.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Allen, C.E.; et al. Revised classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages. Blood 2016, 127, 2672–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosai, J.; Dorfman, R.F. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: A pseudolymphomatous benign disorder. Analysis of 34 cases. Cancer 1972, 30, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, F.; Lennert, K. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: Fifteen new cases. Cancer 1976, 37, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlister, W.H.; Herman, T.; Dehner, L.P. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease). Pediatr. Radiol. 1990, 20, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucar, E.; Rosai, J.; Dorfman, R.F. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. Current status and future directions. Arch. Dermatol. 1988, 124, 1211–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Liu, H.N.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, W.R.; Hu, C.H. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: clinicopathological profiles, spectrum and evolution of 21 lesions in six patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 154, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawerani, H.; Sanchez, R.L.; Rosai, J.; Dorfman, R.F. The cutaneous manifestations of sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. Arch. Dermatol. 1978, 114, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; LeBoit, P.E. Histologic features of cutaneous sinus histiocytosis (Rosai-Dorfman disease): study of cases both with and without systemic involvement. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1992, 19, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Febrer, I.; Aliaga, A. Sinus histiocytosis confined to the skin. Case report and review of the literature. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1995, 17, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenn, T.; Calonje, E.; Granter, S.R.; Leonard, N.; Grayson, W.; Fletcher, C.D.; McKee, P.H. Cutaneous rosai-dorfman disease is a distinct clinical entity. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2002, 24, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley, E.H. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease) in a patient with elevated Epstein-Barr virus titers. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 1991, 83, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levine, P.H.; Jahan, N.; Murari, P.; Manak, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Detection of human herpesvirus 6 in tissues involved by sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease). J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 166, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, M.; Barozzi, P.; Garber, R.; Maiorana, A.; Bonacorsi, G.; Artusi, T.; Trovato, R.; Marasca, R.; Torelli, G. Expression of human herpesvirus-6 antigens in benign and malignant lymphoproliferative diseases. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, W.Y.; Yip, T.T.; Chan, J.K. The Rosai-Dorfman disease histiocytes are not infected by Epstein-Barr virus. Histopathology 1994, 25, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortonne, N.; Fillet, A.M.; Kosuge, H.; Bagot, M.; Frances, C.; Wechsler, J. Cutaneous Destombes-Rosai-Dorfman disease: Absence of detection of HHV-6 and HHV-8 in skin. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2002, 29, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kismet, E.; Köseoglu, V.; Atay, A.A.; Deveci, S.; Demirkaya, E.; Tuncer, K. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy in three brothers. Pediatr. Int. 2005, 47, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalian-Very, G.; Vergilio, J.A.; Degar, B.A.; MacConaill, L.E.; Brandner, B.; Calicchio, M.L.; Kuo, F.C.; Ligon, A.H.; Stevenson, K.E.; Kehoe, S.M.; et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood 2010, 116, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroche, J.; Charlotte, F.; Arnaud, L.; von Deimling, A.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Hervier, B.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Launay, D.; Lesot, A.; Mokhtari, K.; et al. High prevalence of BRAF V600E mutations in Erdheim-Chester disease but not in other non-Langerhans cell histiocytoses. Blood 2012, 120, 2700–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahm, F.; Capper, D.; Preusser, M.; Meyer, J.; Stenzinger, A.; Lasitschka, F.; Berghoff, A.S.; Habel, A.; Schneider, M.; Kulozik, A.; et al. BRAFV600E mutant protein is expressed in cells of variable maturation in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood 2012, 120, e28–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, A.C.; Hu, X.; Kip, S.; Castellar, E.R.P.; Rumilla, K.M.; Vrana, J.A.; Vassallo, R.; Ryu, J.H.; Yi, E.S. BRAF V600E expression in Langerhans cell histiocytosis: clinical and immunohistochemical study on 25 pulmonary and 54 extrapulmonary cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Hampton, O.A.; Shen, X.; Simko, S.J.; Shih, A.; Abhyankar, H.; Lim, K.P.; Covington, K.R.; Trevino, L.; Dewal, N.; et al. Mutually exclusive recurrent somatic mutations in MAP2K1 and BRAF support a central role for ERK activation in LCH pathogenesis. Blood 2014, 124, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emile, J.F.; Diamond, E.L.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Charlotte, F.; Hyman, D.M.; Kim, E.; Rampal, R.; Patel, M.; Ganzel, C.; et al. Recurrent RAS and PIK3CA mutations in Erdheim-Chester disease. Blood 2014, 124, 3016–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, H.; Jeon, Y.K.; Huh, J.; Choi, S.J.; Choi, Y.D.; Cha, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, G.; Min, S.; Kim, J.E. Frequent detection of BRAF(V600E) mutations in histiocytic and dendritic cell neoplasms. Histopathology 2014, 65, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.S.; van Halteren, A.; Quispel, W.T.; van den Bos, C.; Bovée, J.V.; Patel, B.; Badalian-Very, G.; van Hummelen, P.; Ducar, M.; Lin, L.; et al. MAP2K1 and MAP3K1 mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2015, 54, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, E.L.; Durham, B.H.; Haroche, J.; Yao, Z.; Ma, J.; Parikh, S.A.; Wang, Z.; Choi, J.; Kim, E.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; et al. Diverse and targetable kinase alterations drive histiocytic neoplasms. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, V.; Margolskee, E.; Kluk, M.; Giorgadze, T.; Orazi, A. Rosai–Dorfman disease harboring an activating KRAS K117N missense mutation. Head Neck Pathol. 2016, 10, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, S.; Medeiros, L.J.; Patel, K.P.; Li, S.; Pina-Oviedo, S.; Li, J.; Garces, J.C.; Khoury, J.D.; Yin, C.C. Mutually exclusive recurrent KRAS and MAP2K1 mutations in Rosai-Dorfman disease. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matter, M.S.; Bihl, M.; Juskevicius, D.; Tzankov, A. Is Rosai-Dorfman disease a reactve process? Detection of a MAP2K1 L115V mutation in a case of Rosai-Dorfman disease. Virchows Arch. 2017, 471, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.H.; Gasilina, A.; Roychoudhury, J.; Clark, J.; McCormack, F.X.; Pressey, J.; Grimley, M.S.; Lorsbach, R.; Ali, S.; Bailey, M.; et al. Real-time genomic profiling of histiocytoses identifies early-kinase domain BRAF alterations while improving treatment outcomes. JCI. Insight 2017, 2, e89473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.; Shanmugam, V.; Jagannathan, J. Rosai-Dorfman Disease with Activating KRAS Mutation—Response to Cobimetinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2398–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatobene, G.; Haroche, J.; Hélias-Rodzwicz, Z.; Charlotte, F.; Taly, V.; Ferreira, A.M.; Abdo, A.N.R.; Rocha, V.; Emile, J.F. BRAF V600E mutation detected in a case of Rosai-Dorfman disease. Haematologica 2018, 103, e377–e379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, T.E.; Wachsmann, M.; Oliver, D.; Abedin, Z.; Ye, D.; Burns, D.K.; Raisanen, J.M.; Greenberg, B.M.; Hatanpaa, K.J. BRAF mutation leading to central nervous system rosai-dorfman disease. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiljo, M.; García-Lora, E.; Tercedor, J.; Massare, E.; Esquivias, J.; García-Mellado, V. Purely cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Dermatology 1995, 191, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abla, O.; Jacobsen, E.; Picarsic, J.; Krenova, Z.; Jaffe, R.; Emile, J.F.; Durham, B.H.; Braier, J.; Charlotte, F.; Donadieu, J.; et al. Consensus recommendations for the diagnosis and clinical management of Rosai-Dorfman-Destombes disease. Blood 2018, 131, 2877–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juskevicius, R.; Finley, J.L. Rosai-Dorfman disease of the parotid gland: cytologic and histopathologic findings with immunohistochemical correlation. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2001, 125, 1348–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce-Brand, C.; Schneider, J.W.; Schubert, P. Rosai-Dorfman disease: an overview. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Griffin, A.C.; Zhang, P.J.; Palmer, J.N.; Gupta, P. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman Disease): A case report and review of 49 cases with fine needle aspiration cytology. Cytojournal 2011, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroumpouzos, G.; Demierre, M.F. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: histopathological presentation as inflammatory pseudotumor. A literature review. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2002, 82, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebazaa, A.; Trabelsi, S.; Denguezli, M.; Sriha, B.; Belajouza, C.; Nouira, R. Extensive purely cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease responsive to acitretin. Int. J. Dermatol. 2007, 46, 1208–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.Y.; Kong, J.C.; Shi, D.R.; Lu, H.F.; Zhu, X.Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.W. Cutaneous rosai-dorfman disease: a clinical and histopathologic study of 25 cases in China. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fening, K.; Bechtel, M.; Peters, S.; Zirwas, M.; Darabi, K. Cutaneous rosai-dorfman disease persisting after surgical excision: report of a case treated with acitretin. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2010, 3, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Fumerton, R.; Ball, N.; Zhou, Y. Refractory cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease responsive to cryotherapy. Cutis 2011, 87, 296–299. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.S.; Son, S.J.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, J.H. Therapeutic challenge of dapsone in the treatment of purely cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 36, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutlubay, Z.; Bairamov, O.; Sevim, A.; Demirkesen, C.; Mat, M.C. Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report with nodal and cutaneous involvement and review of the literature. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2014, 36, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.X.; Jin, X.H.; Mou, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, K.; Zhu, W.J.; Li, F.Q. Combined treatment for cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: a report of 2 cases. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 6, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Subash, J.J.; Kesty, C.; Kesty, K.R.; Asgari, M.; Jorizzo, J. Low-dose weekly methotrexate used to treat cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 43, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.H.; Ba, W.; Li, C.X. Cutaneous Rosai–Dorfman disease presenting with multiple nodules on the thighs and buttocks. Int. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 2, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, G.; McClain, K.L.; Pittaluga, S.; Rao, V.K.; Jaffe, E.S. Development of disseminated histiocytic sarcoma in a patient with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome and associated Rosai-Dorfman disease. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolch, W. Coordinating ERK/MAPK signalling through scaffolds and inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCain, J. The MAPK (ERK) pathway: investigational combinations for the treatment of BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.B.; Salomão, D.R.; Smith, W.M.; Pulido, J.S.; Garrity, J.A. Ophthalmic findings of Rosai-Dorfman disease. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 188, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Mukai, S.; Kamoto, T.; Kataoka, H. Extranodal Rosai-Dorfman disease of the kidney: a case report. Hum. Pathol. Case Rep. 2019, 17, 200306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janku, F.; Diamond, E.L.; Goodman, A.M.; Raghavan, V.K.; Barnes, T.G.; Kato, S.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Durham, B.H.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Kurzrock, R. Molecular profiling of tumor tissue and plasma cell-free DNA from patients with non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Mol. Cancer. Ther. 2019, 18, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Laird, J.H.; Chau, K.W.; Chelius, M.R.; Lok, B.H.; Yahalom, J. Langerhans cell histiocytosis in adults is associated with a high prevalence of hematologic and solid malignancies. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papo, M.; Diamond, E.L.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Emile, J.F.; Roos-Weil, D.; Gupta, N.; Durham, B.H.; Ozkaya, N.; Dogan, A.; Ulaner, G.A.; et al. High prevalence of myeloid neoplasms in adults with non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood 2017, 130, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Pathak, S.; Gujral, S. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy—A review of seven cases. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2006, 49, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edelman, A.; Patterson, B.; Donovan, K.; Malone, J.; Callen, J. Rosai-Dorfman disease with a concurrent mantle cell lymphoma. JAAD Case Rep. 2018, 5, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, P.; Rao, S. Rosai-Dorfman disease and Hodgkin lymphoma synchronously involving the same lymph node: A rare case report with review of literature. Curr. Med. Res. Pract. 2019, 9, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, S.; Yin, C.C.; Patel, K.P.; Khoury, J.D.; Manning, J.T., Jr.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Pina-Oviedo, S.; Johnson, M.R.; González, S.; et al. Focal Rosai-Dorfman disease coexisting with lymphoma in the same anatomic site: a localized histiocytic proliferation associated with MAPK/ERK pathway activation. Mod Pathol. 2019, 32, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, S.; Stutte, H.J.; Frizzera, G. Hodgkin’s disease and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy-like changes. Histopathology 1991, 19, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.A.; Furtado, L.V.; Betz, B.L.; Kiel, M.J.; Weigelin, H.C.; Lim, M.S.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S. High prevalence of somatic MAP2K1 mutations in BRAF V600E-negative Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood 2014, 124, 1655–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Maldonado, C.; Zimmer, Y.; Medová, M. A Comparative Analysis of Individual RAS Mutations in Cancer Biology. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.; Curtin, J.A.; Pinkel, D.; Bastian, B.C. Congenital melanocytic nevi frequently harbor NRAS mutations but no BRAF mutations. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, J.A.; Bassett, R.L., Jr.; Ng, C.S.; Curry, J.L.; Joseph, R.W.; Alvarado, G.C.; Rohlfs, M.L.; Richard, J.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Kim, K.B.; et al. NRAS mutation status is an independent prognostic factor in metastatic melanoma. Cancer 2012, 118, 4014–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerami, P.; Paller, A.S. Making a mountain out of a molehill: NRAS, mosaicism, and large congenital nevi. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2127–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modest, D.P.; Ricard, I.; Heinemann, V.; Hegewisch-Becker, S.; Schmiegel, W.; Porschen, R.; Stintzing, S.; Graeven, U.; Arnold, D.; von Weikersthal, L.F.; et al. Outcome according to KRAS-, NRAS- and BRAF-mutation as well as KRAS mutation variants: pooled analysis of five randomized trials in metastatic colorectal cancer by the AIO colorectal cancer study group. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, I.A.; Lewis, P.D.; Mattos, C. A comprehensive survey of Ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, B.H.; Diamond, E.L.; Abdel-Wahab, O. Histiocytic neoplasms in the era of personalized genomic medicine. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhara, H.; Ashida, A.; Koga, H.; Ogawa, E.; Uchiyama, A.; Uchiyama, R.; Hayashi, K.; Kiniwa, Y.; Okuyama, R. NRAS mutations in primary and metastatic melanomas of Japanese patients. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 19, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheen, Y.S.; Liao, Y.H.; Liau, J.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Jee, S.H.; Chu, C.Y. Prevalence of BRAF and NRAS mutations in cutaneous melanoma patients in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2016, 115, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.L.; Qiu, M.Z.; Tang, T.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.X.; Lei, M.J.; Guan, W.L.; He, C.Y. Gene mutation profiling in Chinese colorectal cancer patients and its association with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, I.; Tanda, E.T.; Dalmasso, B.; Pastorino, L.; Andreotti, V.; Bruno, W.; Boutros, A.; Spagnolo, F.; Ghiorzo, P. Non-BRAF Mutant Melanoma: Molecular Features and Therapeutical Implications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient No | Age/Gender | Site | Presentation | Associated Finding | Treatment | Gene Mutation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 47/Female | Right Leg | One Painful Flesh-Colored Nodule | Anemia (Hb: 8.6, Mcv: 64.8), History of Thalassemia | Excision | No Mutation was Detected |
| 2 | 48/Male | Left Back and Left Neck | One 12 × 5 cm Erythematous Plaque on Left Neck and one 6 × 3 cm Erythematous Plaque on Left Back for one More Year | No Systemic Symptom | Excision | No Mutation was Detected |
| 3 | 62/Male | Left Back | One Soft and Tender Subcutaneous Nodule for 2 Years | No Systemic Symptom | Excision | No Mutation was Detected |
| 4 | 46/Male | Right Cheek | One Mildly Itchy Erythematous Nodular Plaque for 5 Months | No Systemic Symptom | Biopsy and Intralesional Corticosteroid Injection | Nras G13s, Nras A59v, Nras A146t |
| 5 | 32/Female | Right Zygomatic Area | One 0.6 cm Subcutaneous Nodule | Steatocystoma Multiplex Polychondritis | Excision | Nras G13s, Nras A146t |
| 6 | 17/Female | Left Thigh | One 8 × 8 cm Tender Hard Brownish Plaque with Some Whitish Component for 3 Years | Small but Palpable Reactive Lymphadenopathy on Bilateral Inguinal Areas and Then Remission | Oral and Topical Corticosteroids | Specimen A: Nras G12d; Specimen B: Nras G12n, Nras A146t |
| 7 | 38/Male | Left Thigh | One 7 × 7 cm Flesh-Colored Asymptomatic Indurated Subcutaneous Mass for 1.5 Months | Anemia (Hb: 12.8, Mcv: 87.1) | Oral Corticosteroids | Nras A146t |
| Major Characteristics |
|
|
|
|
|
| Minor Characteristics |
|
|
|
| Reference | Case Number of RDD | Primary Site of RDD | Result of Gene Mutation | Ref No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venkataraman et al., 2010 | 1 | Axillary Lymph Node 1 | Germline Missense Mutation in Exon 9 of the TNFRSF6 Gene. | [51] |
| Haroche et al., 2012 | 23 | Not Available. | BRAF: 0% | [21] |
| Diamond et al., 2016 | 8 | Lymph Node: 4 cases; Pituitary Stalk: 1 case; Cheek: 1 case; Meninges: 1 case; Axillary soft tissue: 1 case. | KRAS: 2 cases (25%); NRAS: 1 case (12.5%); ARAF: 1 case (12.5%); Wild Type: 4 cases (50%). | [28] |
| Shanmugam et al., 2016 | 1 | Submandibular Salivary Gland | KRAS K117N | [29] |
| Garces et al., 2017 | 21 | Lymph Node: 8 cases; Soft Tissue: 7 cases; Breast: 3 cases; Bone: 3 cases; Nasopharynx: 1 case. | Genetic Mutation was Detected in 7 cases (33%) 2, including KRAS (n = 4) and MAP2K1 (n = 3). No mutation was Identified in ARAF, BRAF, PIK3CA, or any Other Genes Assessed. | [30] |
| Matter et al., 2017 | 1 | Buttock Subcutaneous Tumor with Multiple Hypermetabolic Lesions of the Bones and Bone Destruction. | MAP2K1 L115V Mutation | [31] |
| Lee et al., 2017 | 11 | Not available. | Mutation was Detected in 5 cases: 1) case 1: KRAS K117N; 2) case 2: CBL C384Y, GNAQ Q209H, KRAS K117N, KRAS A146V; 3) case 3: KRAS K117N; 4) case 4: KDM5A amplification; 5) case 5: FBXW7 E113D. No Mutation was Detected in Other 6 cases. | [32] |
| Jacobsen et al., 2017 | 1 | Perirenal Soft Tissue Mass | KRAS codon 12 (p.G12R) | [33] |
| Fatobene et al., 2018 | 1 | Cervical Lymph Node | BRAF V600E Mutation | [34] |
| Choi et al., 2018 | 6 | All Are Not Purely Cutaneous RDD | BRAF: 0% | [54] |
| Richardson et al., 2018 | 1 | Central Nervous System | Deletion in the β3-αC Loop of the Kinase Domain in exon 12 of BRAF | [35] |
| Tanaka et al., 2019 | 1 | Kidney | K- and N-RAS: 0% | [55] |
| Janku et al., 2019 | 3 | Not mention | One RDD Patient Harbored a CAPZA2-BRAF Fusion and a RAF1 Amplification; the Other 2 RDD patients had a GNAS R201C and APC E1157fs Mutation, respectively. | [56] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.-J.; Li, S.-H.; Liao, J.-B.; Chiou, C.-C.; Wu, C.-S.; Chen, C.-C. NRAS Mutations May Be Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Rosai Dorfman Disease: A Pilot Study. Biology 2021, 10, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050396
Wu K-J, Li S-H, Liao J-B, Chiou C-C, Wu C-S, Chen C-C. NRAS Mutations May Be Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Rosai Dorfman Disease: A Pilot Study. Biology. 2021; 10(5):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050396
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kuan-Jou, Shu-Hao Li, Jia-Bin Liao, Chien-Chun Chiou, Chieh-Shan Wu, and Chien-Chin Chen. 2021. "NRAS Mutations May Be Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Rosai Dorfman Disease: A Pilot Study" Biology 10, no. 5: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050396
APA StyleWu, K.-J., Li, S.-H., Liao, J.-B., Chiou, C.-C., Wu, C.-S., & Chen, C.-C. (2021). NRAS Mutations May Be Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Rosai Dorfman Disease: A Pilot Study. Biology, 10(5), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050396







