Peptidylarginine Deiminase (PAD) and Post-Translational Protein Deimination—Novel Insights into Alveolata Metabolism, Epigenetic Regulation and Host–Pathogen Interactions
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alveolata Collection
2.2. Histology
2.3. Protein Extraction
2.4. Isolation of Deiminated Proteins—F95 Enrichment
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis
2.6. Silver Staining
2.7. LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry) Analysis of F95 Enriched Proteins
2.8. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
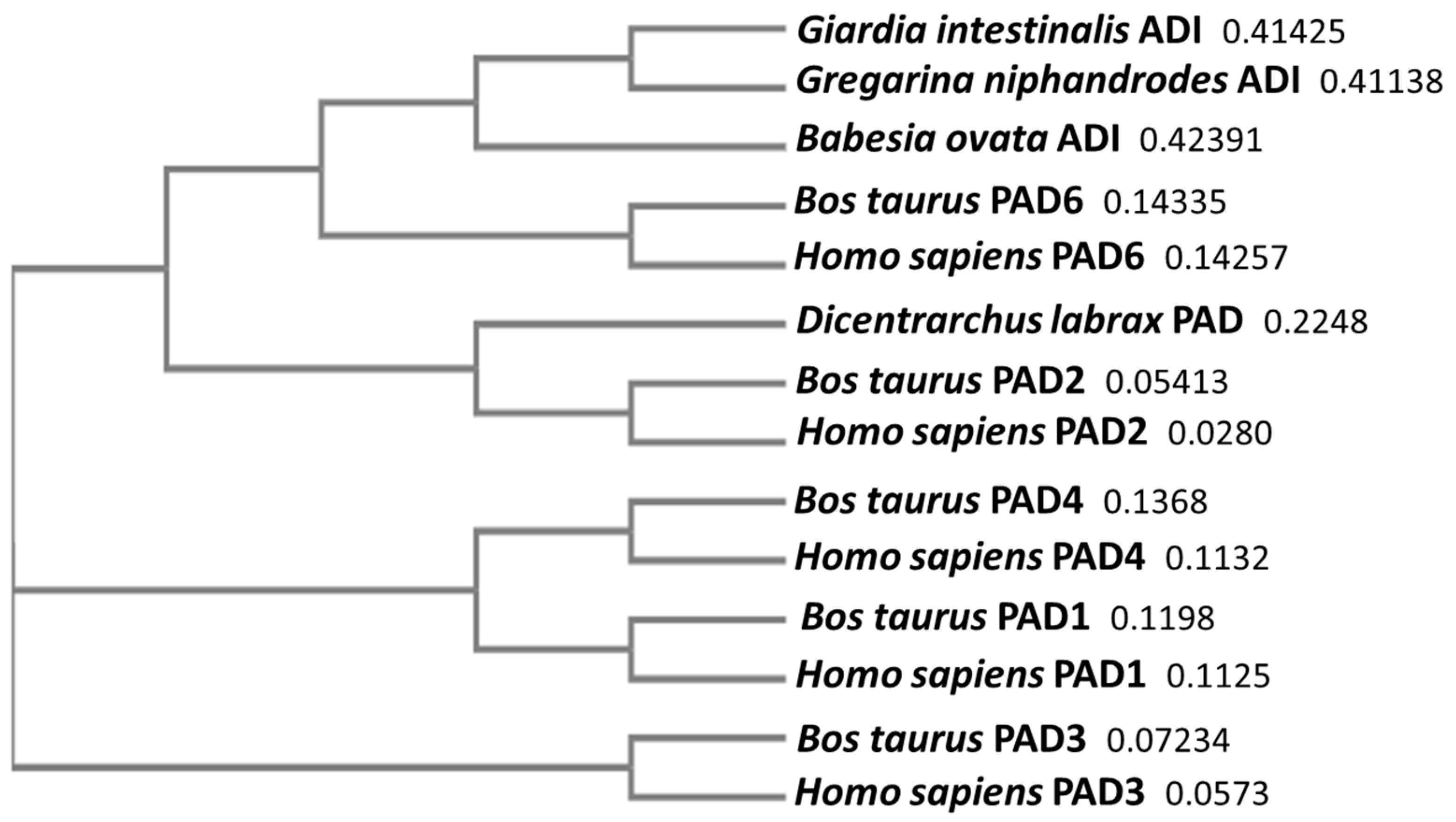
2.9. Phylogenetic Comparison of Alveolata PAD Homologues
3. Results
3.1. PAD Protein Homologue and Deiminated Protein Detection in Alveolates
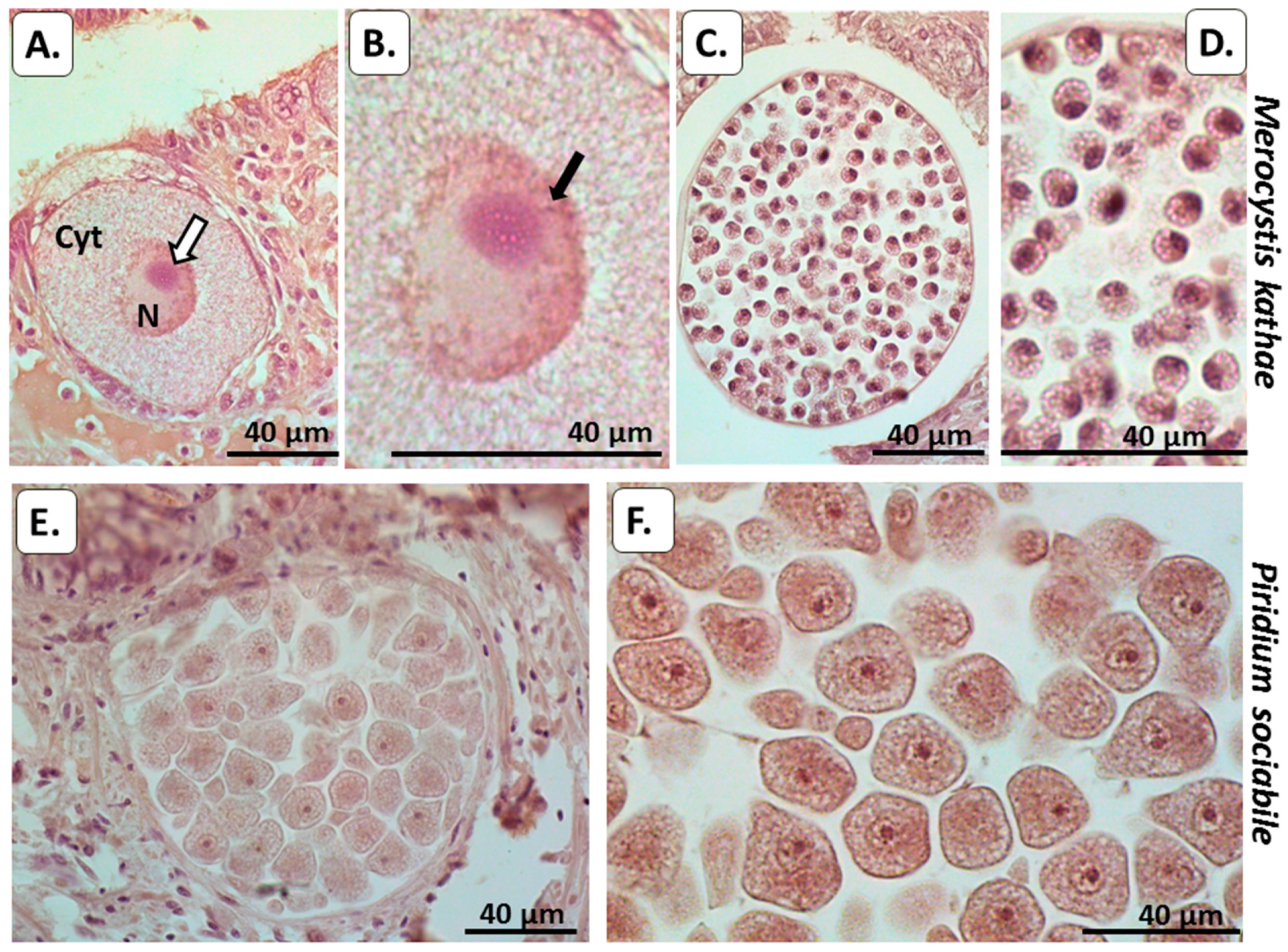
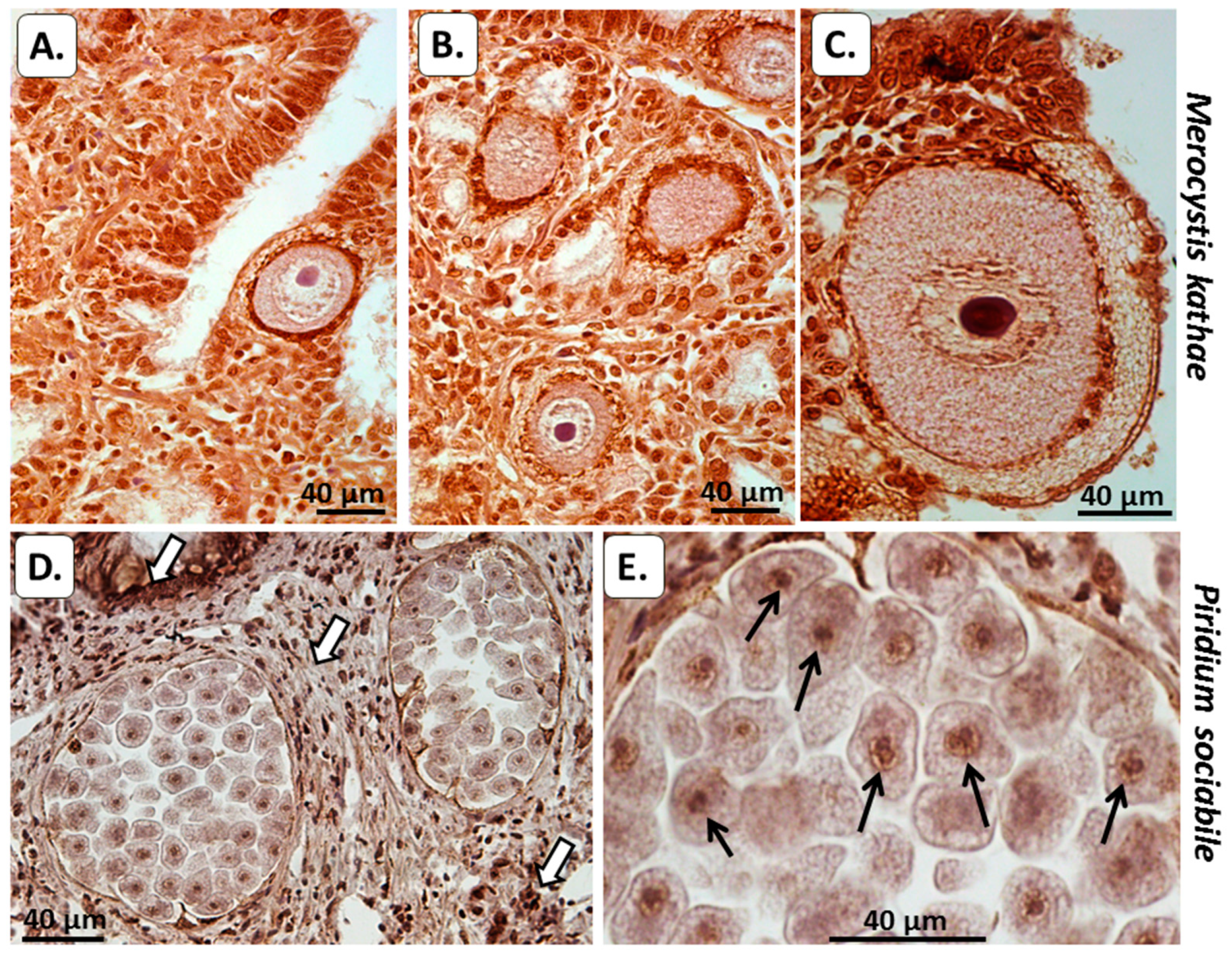
3.2. Histological Analysis of PAD and Protein Deimination in Alveolata
3.2.1. Peptidylarginine Deiminase (PAD)
3.2.2. Total Deiminated Protein Detection Using Pan-Citrulline Antibody F95
3.2.3. Deiminated/Citrullinated Histone H3
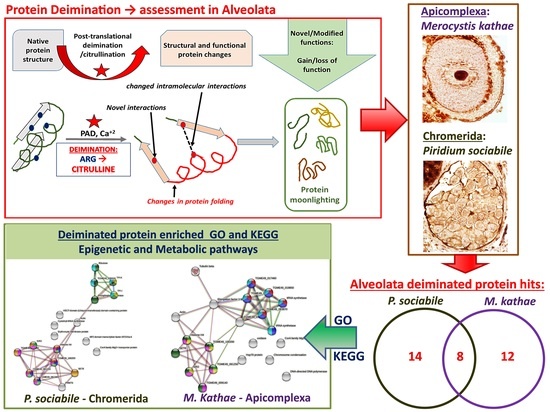
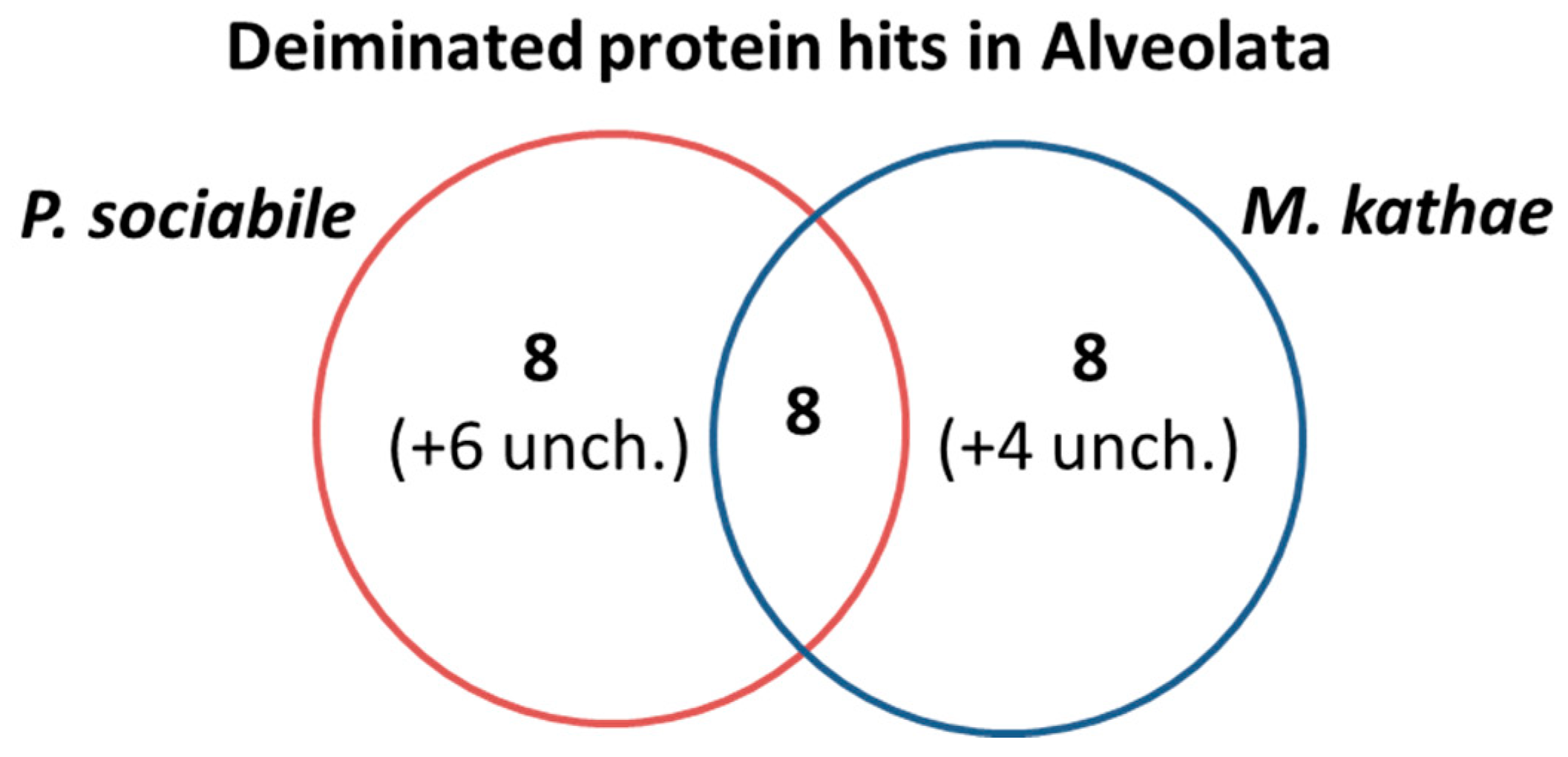
3.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Deiminated Protein Targets in Alveolata
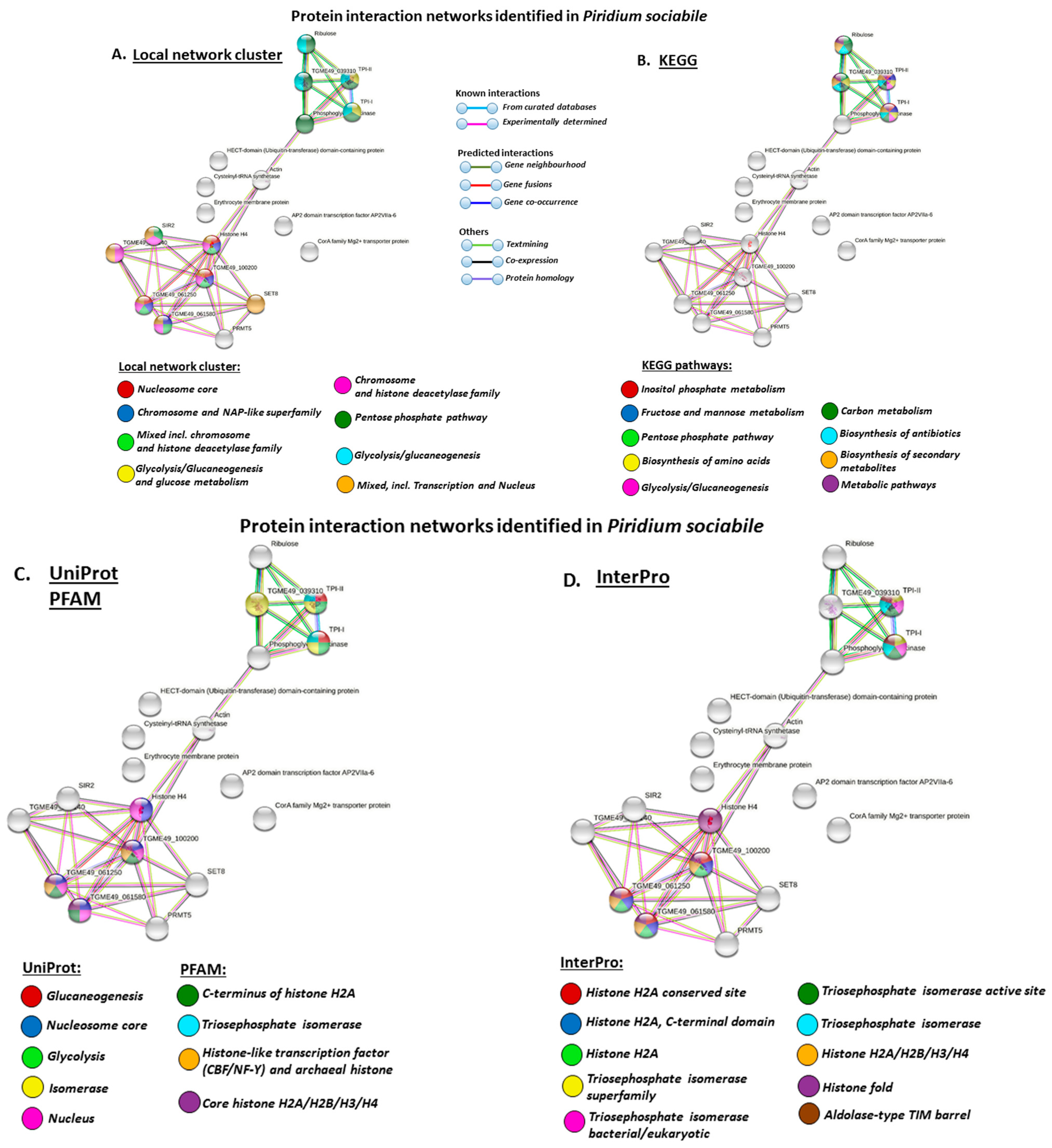
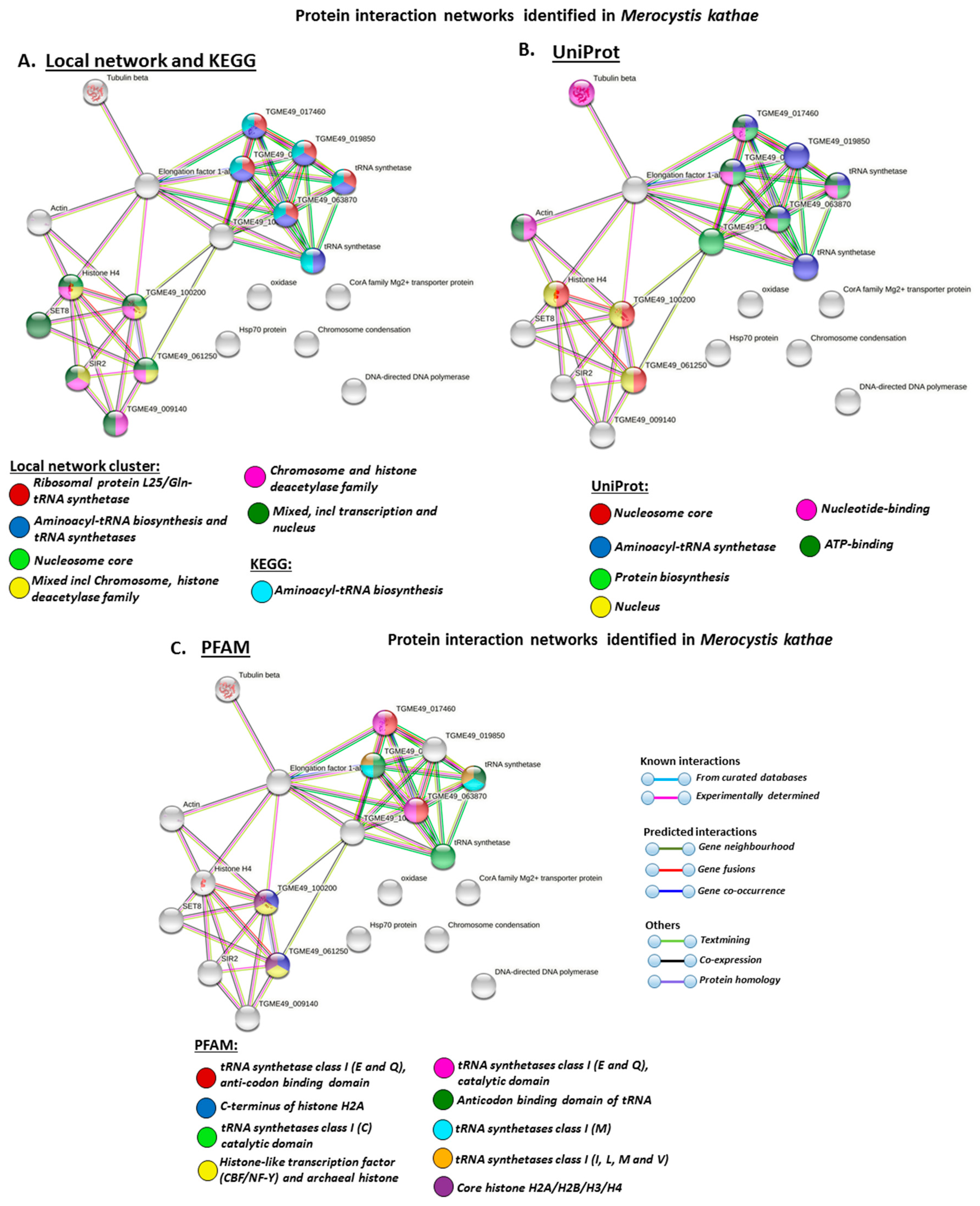
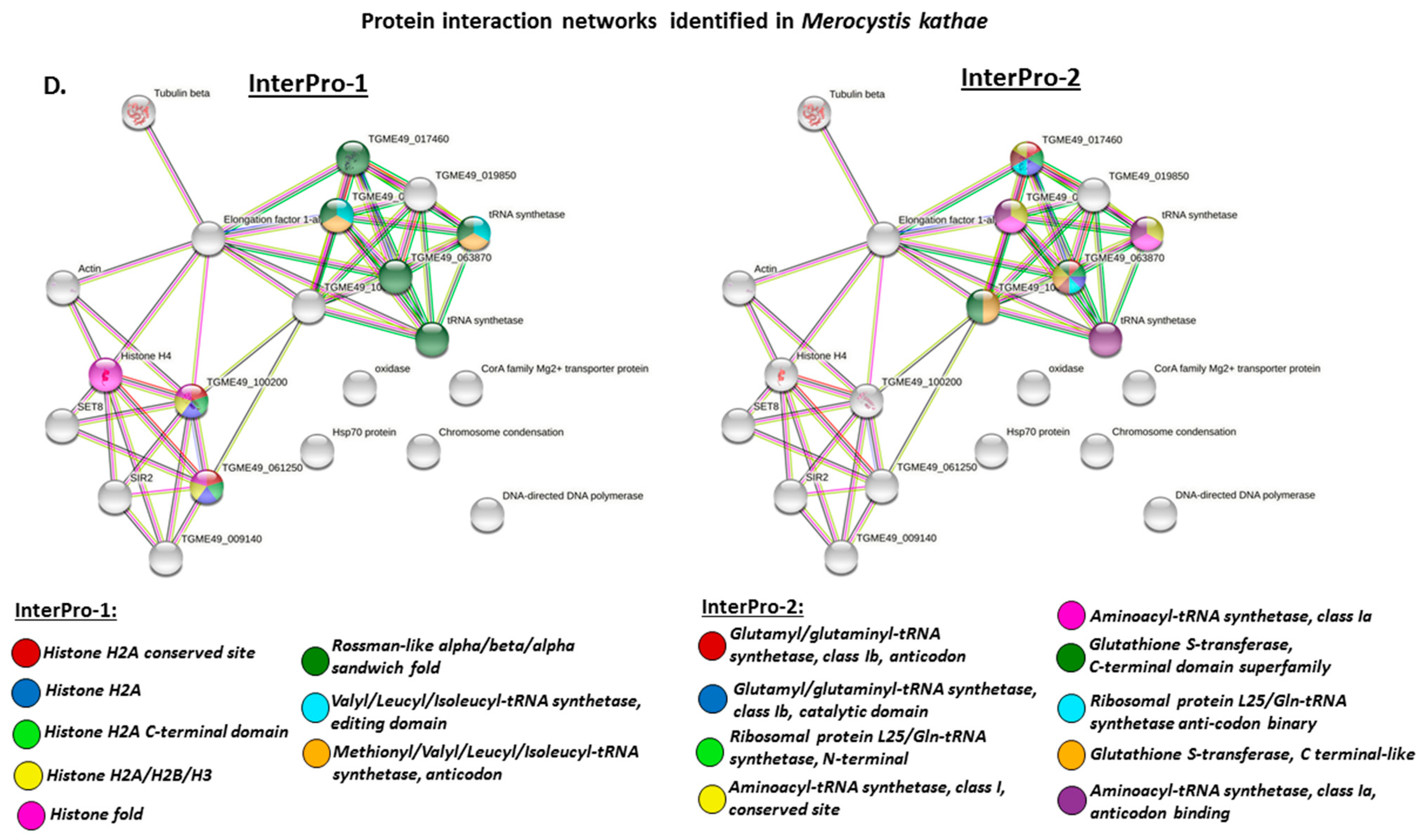
3.4. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Identification of Deiminated Proteins in Alveolata
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Cell diversification in heterotrophic flagellates. In The Biology of Free-Living Heterotrophic Flagellates; Patterson, D.J., Larsen, J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1991; pp. 113–131. ISBN 978-0-19-857747-8. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, R.B.; Oborník, M.; Janouskovec, J.; Chrudimský, T.; Vancová, M.; Green, D.H.; Wright, S.W.; Davies, N.W.; Bolch, C.J.; Heimann, K.; et al. A photosynthetic alveolate closely related to apicomplexan parasites. Nature 2008, 451, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adl, S.M.; Simpson, A.G.; Lane, C.E.; Lukeš, J.; Bass, D.; Bowser, S.S.; Brown, M.W.; Burki, F.; Dunthorn, M.; Hampl, V.; et al. The revised classification of eukaryotes [published correction appears in J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2013 May-Jun;60:321. Shadwick, Lora [corrected to Shadwick, Laura]. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2012, 59, 429–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portman, N.; Slapeta, J. The flagellar contribution to the apical complex: A new tool for the eukaryotic Swiss Army knife? Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.; Fuss, J.; Kristmundsson, A.; Bignell, J.; Marit, F.; Bjorbækmo, M.; Mangot, J.-F.; Keeling, P.; del Campo, J.; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K.; et al. X-cells are globally distributed, genetically divergent fish parasites related to perkinsids and dinoflagellates. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.S. Genetics. Themes and variations in apicomplexan parasite biology. Science 2005, 309, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartošová-Sojková, P.; Oppenheim, R.D.; Soldati-Favre, D.; Lukeš, J. Epicellular Apicomplexans: Parasites “On the Way In”. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005080. [Google Scholar]
- Seed, J.R. Protozoa: Pathogeneses and defenses. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kristmundsson, Á.; Freeman, M.A. Harmless sea snail parasite causes mass mortalities in numerous commercial scallop populations in the northern hemisphere. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oborník, M.; Modrý, D.; Lukeš, M.; Cernotíková-Stříbrná, E.; Cihlář, J.; Tesařová, M.; Kotabová, E.; Vancová, M.; Prášil, O.; Lukeš, J. Morphology, ultrastructure and life cycle of Vitrella brassicaformis n. sp., n. gen., a novel chromerid from the Great Barrier Reef. Protist 2012, 163, 306–323. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, N.; MacFadden, G.I. The mother of all parasites. Future Microbiol. 2008, 3, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, V.; Kolísko, M.; Hehenberger, E.; Irwin, N.A.T.; Leander, B.S.; Kristmundsson, Á.; Freeman, M.A.; Keeling, P.J. Multiple Independent Origins of Apicomplexan-Like Parasites. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 2936–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, R. The Life History of Merocystis kathae in the Whelk, Buccinum undatum. Parasitology 1935, 27, 399–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisue, N.; Hasimoto, T. Phylogeny and evolution of apicoplasts and apicomplexan parasites. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, Y.H.; Ansari, H.; Otto, T.D.; Klinger, C.M.; Kolisko, M.; Michálek, J.; Saxena, A.; Shanmugam, D.; Tayyrov, A.; Veluchamy, A.; et al. Chromerid genomes reveal the evolutionary path from photosynthetic algae to obligate intracellular parasites. Elife 2015, 4, e06974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakin, W.J. Notes on a new coccidian Merocystis kathae (n. gen. et sp.,) occurring in the renal organ of the whelk. Arch. Protist. 1911, XXIII, 1115. [Google Scholar]
- Patten, R. Notes on a new protozoon, Piridium sociabile n. gen. n. sp. from the foot of Buccinum undatum. Parasitology 1936, 28, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, V.; Kwong, W.K.; Husnik, F.; Irwin, N.A.T.; Kristmundsson, Á.; Gestal, C.; Freeman, M.; Keeling, P.J. Phylogenomics identifies a new major subgroup of apicomplexans, Marosporida class. nov., with extreme apicoplast genome reduction. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 13, evaa244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristmundsson, Á.; Erlingsdóttir, Á.; Freeman, M.A. Is an apicomplexan parasite is responsible for the collapse of the Iceland scallop (Chlamys islandica) stock? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, S.; Kristmundsson, Á.; Freeman, M.A.; Levenque, M.; Stokesbury, K. The condition of gray meat in the Atlantic sea scallop, Placopecten magellanicus, and the identification of a known pathogenic scallop apicomplexan. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 141, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Zendman, A.J.; van Venrooij, W.J.; Pruijn, G.J. PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: Genes, features and involvement in disease. Bioessays 2003, 25, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebl, A.; Köllner, B.; Anders, E.; Wimmers, K.; Goldammer, T. Peptidylarginine deiminase gene is differentially expressed in freshwater and brackish water rainbow trout. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Hayes, P.; Hristova, M.; Bragason, B.Þ.; Nicholas, A.P.; Dodds, A.W.; Gudmundsdottir, S.; Lange, S. Post-translational Protein Deimination in Cod (Gadus morhua L.) Ontogeny—Novel Roles in Tissue Remodelling and Mucosal Immune Defences? Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 87, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Bragason, B.T.; Bricknell, I.R.; Bowden, T.; Nicholas, A.P.; Hristova, M.; Guðmundsdóttir, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Lange, S. Peptidylarginine deiminase and deiminated proteins are detected throughout early halibut ontogeny—Complement components C3 and C4 are post-translationally deiminated in halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 92, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins in extracellular vesicles and plasma of nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum)—Novel insights into shark immunity. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Petersen, L.H.; Lange, S. Deimination Protein Profiles in Alligator mississippiensis Reveal Plasma and Extracellular Vesicle-Specific Signatures Relating to Immunity, Metabolic Function, and Gene Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, T.J.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Extracellular vesicles and post-translational protein deimination signatures in haemolymph of the American lobster (Homarus americanus). Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, T.J.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Post-translational protein deimination signatures and extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the Atlantic horseshoe crab (Limulus polyphemus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 110, 103714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, T.J.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Extracellular Vesicles and Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Mollusca—The Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis), Soft Shell Clam (Mya arenaria), Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) and Atlantic Jacknife Clam (Ensis leei). Biology 2020, 9, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novák, L.; Zubáčová, Z.; Karnkowska, A.; Kolisko, M.; Hroudová, M.; Stairs, C.W.; Simpson, A.G.; Keeling, P.J.; Roger, A.J.; Čepička, I.; et al. Arginine deiminase pathway enzymes: Evolutionary history in metamonads and other eukaryotes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Gavinho, B.; Sabatke, B.; Feijoli, V.; Rossi, I.V.; da Silva, J.M.; Evans-Osses, I.; Palmisano, G.; Lange, S.; Ramirez, M.I. Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibition abolishes the production of large extracellular vesicles from Giardia intestinalis, affecting host-pathogen interactions by hindering adhesion to host cells. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, E.; Scavenius, C.; Kantyka, T.; Jusko, M.; Mizgalska, D.; Szmigielski, B.; Potempa, B.; Enghild, J.J.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Blom, A.M.; et al. Peptidyl arginine deiminase from Porphyromonas gingivalis abolishes anaphylatoxin C5a activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32481–32487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Matewele, P.; Mastroianni, G.; Kraev, I.; Brotherton, D.; Awamaria, B.; Nicholas, A.P.; Lange, S.; Inal, J.M. Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibitors reduce bacterial membrane vesicle release and sensitize bacteria to antibiotic treatment. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Shindia, A.A.; AbouZaid, A.A.; Yassin, A.M.; Ali, G.S.; Sitohy, M.Z. Biochemical characterization of pepti-dylarginine deiminase-like orthologs from thermotolerant Emericella dentata and Aspergillus nidulans. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2019, 124, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- György, B.; Toth, E.; Tarcsa, E.; Falus, A.; Buzas, E.I. Citrullination: A posttranslational modification in health and disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1662–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Serum and Serum-Extracellular Vesicles of Bos taurus Reveal Immune, Anti-Pathogenic, Anti-Viral, Metabolic and Cancer-Related Pathways for Deimination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, M.; Alasmari, D.; Assiri, A.; Mattar, E.; Aljaddawi, A.A.; Alattas, S.G.; Redwan, E.M. An Overview of the Intrinsic Role of Citrullination in Autoimmune Disorders. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7592851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicker, K.L.; Thompson, P.R. The protein arginine deiminases: Structure, function, inhibition, and disease. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Peptidylarginine deiminases in citrullination, gene regulation, health and pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witalison, E.E.; Thompson, P.R.; Hofseth, L.J. Protein Arginine Deiminases and Associated Citrullination: Physiological Functions and Diseases Associated with Dysregulation. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Gallagher, M.; Kholia, S.; Kosgodage, U.S.; Hristova, M.; Hardy, J.; Inal, J.M. Peptidylarginine Deiminases–Roles in Cancer and Neurodegeneration and Possible Avenues for Therapeutic Intervention via Modulation of Exosome and Microvesicle (EMV) Release? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Thompson, P.R. Protein Arginine Deiminases (PADs): Biochemistry and Chemical Biology of Protein Citrullination. Acc. Chem Res. 2019, 52, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palić, D.; Ostojić, J.; Andreasen, C.B.; Roth, J.A. Fish cast NETs: Neutrophil extracellular traps are released from fish neutrophils. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; Nascimento, M.T.; Froment, G.S.; Soares, R.P.; Morgado, F.N.; Conceição-Silva, F.; Saraiva, E.M. Leishmania amazonensis promastigotes induce and are killed by neutrophil extracellular traps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6748–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, M.; Lindberg, M.R.; Kennett, M.J.; Xiong, N.; Wang, Y. PAD4 is essential for antibacterial innate immunity mediated by neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortjens, B.; de Boer, O.J.; de Jong, R.; Antonis, A.F.; Piñeros, Y.S.S.; Lutter, R.; van Woensel, J.B.; Bem, R.A. Neutrophil extracellular traps cause airway obstruction during respiratory syncytial virus disease. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villagra-Blanco, R.; Silva, L.M.R.; Conejeros, I.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Pinniped- and Cetacean-Derived ETosis Contributes to Combating Emerging Apicomplexan Parasites (Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum) Circulating in Marine Environments. Biology 2019, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobernack, T.; du Teil Espina, M.; Mulder, L.M.; Palma Medina, L.M.; Piebenga, D.R.; Gabarrini, G.; Zhao, X.; Janssen, K.; Hulzebos, J.; Brouwer, E.; et al. A Secreted Bacterial Peptidylarginine Deiminase Can Neutralize Human Innate Immune Defenses. mBio 2018, 9, e01704–e01718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Nishitsuji, H.; Kurihara, K.; Hayashi, T.; Masuda, T.; Kannagi, M. Suppression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by arginine deiminase of Mycoplasma arginini. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, C.J. Protein moonlighting: What is it, and why is it important? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Svansson, V.; Hayes, P.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins and extracellular vesicles—Novel serum biomarkers in whales and orca. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 34, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Svansson, V.; Skírnisson, K.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins and extracellular vesicles as novel biomarkers in pinnipeds: Grey seal (Halichoerus gryptus) and harbour seal (Phoca vitulina). Biochimie 2020, 171–172, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.A.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Protein deimination and extracellular vesicle profiles in Antarctic seabirds. Biology 2020, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamenter, M.E.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Huynh, K.W.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Post-translational deimination of immunological and metabolic protein markers in plasma and extracellular vesicles of naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.; Kraev, I.; Magnadóttir, B.; Dodds, A.W. Complement component C4-like protein in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.)—Detection in ontogeny and identification of post-translational deimination in serum and extracellular vesicles. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 101, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Kraev, I.; Guđmundsdóttir, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Lange, S. Extracellular vesicles from cod (Gadus morhua L.) mucus contain innate immune factors and deiminated protein cargo. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 99, 103397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Dodds, A.W.; Gudmundsdottir, S.; Lange, S. Extracellular vesicles, deiminated protein cargo and microRNAs are novel serum biomarkers for environmental rearing temperature in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraro, S.P.; De Souza, G.F.; Gallo, S.W.; Da Silva, B.K.; De Oliveira, S.D.; Vinolo, M.A.R.; Saraiva, E.M.; Porto, B.N. Respiratory Syncytial Virus induces the classical ROS-dependent NETosis through PAD-4 and necroptosis pathways activation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, V.; Sousa, F.H.; Shakamuri, P.; Svoboda, P.; Buch, C.; D’Acremont, M.; Christophorou, M.A.; Pohl, J.; Stevens, C.; Barlow, P.G. Citrullination Alters the Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Activities of the Human Cathelicidin LL-37 During Rhinovirus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, A.P.; Whitaker, J.N. Preparation of a monoclonal antibody to citrullinated epitopes: Its characterization and some applications to immunohistochemistry in human brain. Glia 2002, 37, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Gögel, S.; Leung, K.Y.; Vernay, B.; Nicholas, A.P.; Causey, C.P.; Thompson, P.R.; Greene, N.D.; Ferretti, P. Protein deiminases: New players in the developmentally regulated loss of neural regenerative ability. Dev. Biol. 2011, 355, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.; Rocha-Ferreira, E.; Thei, L.; Mawjee, P.; Bennett, K.; Thompson, P.R.; Subramanian, V.; Nicholas, A.P.; Peebles, D.; Hristova, M.; et al. Peptidylarginine deiminases: Novel drug targets for prevention of neuronal damage following hypoxic ischemic insult (HI) in neonates. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielman, A.; Wilson, M.L.; Levine, J.F.; Piesman, J. Ecology of Ixodes Dammini-Borne Human Babesiosis and Lyme Disease. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1985, 30, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despommier, D.D.; Gwadz, R.W.; Hotez, P.J. Parasitic Diseases, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; Paris, France; Tokyo, Japan; Hong Kong; Barcelona, Spain; Budapest, Hungary, 1995; pp. 224–226. ISBN 978-0-387-94223-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ristic, M.; Ambroise-Thomas, P.; Kreier, J.P. Malaria and Babesiosis: Research Findings and Control Measures. In New Perspectives in Clinical Microbiology; Nijhoff, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 100–170. ISBN 978-0-89838-675-2. [Google Scholar]
- Toso, M.A.; Omoto, C.K. Gregarina niphandrodes may lack both a plastid genome and organelle. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2007, 54, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, T.; Muth, A.; Thompson, P.R.; Coonrod, S.A.; Zhang, X. Peptidylarginine deiminase 1-catalyzed histone citrullination is essential for early embryo development. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisingh, M.T.; Skillman, K.M. Epigenetic Variation and Regulation in Malaria Parasites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Yin, S.; Hu, Y.; Sun, M.; Wei, J.; Huang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Dai, X.; Chen, H.; Mu, J.; et al. Epigenetic editing by CRISPR/dCas9 in Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffers, V.; Tampaki, Z.; Kim, K.; Sullivan, W.J., Jr. A latent ability to persist: Differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2355–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabeena, C.A.; Rajavelu, A. Epigenetic Players of Chromatin Structure Regulation in Plasmodium falciparum. Chembiochem 2019, 20, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanagas, L.; Contreras, S.M.; Angel, S.O. Apicomplexa and Histone Variants: What’s New? In Chromatin and Epigenetics; Logie, C., Knoch, T.A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-78984-493-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, W.J., Jr. Histone H3 and H3.3 variants in the protozoan pathogens Plasmodium falciparum and Toxoplasma gondii. DNA Seq. 2003, 14, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougdour, A.; Maubon, D.; Baldacci, P.; Ortet, P.; Bastien, O.; Bouillon, A.; Barale, J.C.; Pelloux, H.; Ménard, R.; Hakimi, M.A. Drug inhibition of HDAC3 and epigenetic control of differentiation in Apicomplexa parasites. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, E.S.; Paight, C.; Lane, C.E. Metabolic Contributions of an Alphaproteobacterial Endosymbiont in the Apicomplexan Cardiosporidium cionae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, P.W.; Bolling, L.C.; Calvert, M.E.; Sarmento, O.F.; Berkeley, E.V.; Shea, M.C.; Hao, Z.; Jayes, F.C.; Bush, L.A.; Shetty, J.; et al. ePAD, an oocyte and early embryo-abundant peptidylarginine deiminase-like protein that localizes to egg cytoplasmic sheets. Dev. Biol. 2003, 256, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurttas, P.; Vitale, A.M.; Fitzhenry, R.J.; Cohen-Gould, L.; Wu, W.; Gossen, J.A.; Coonrod, S.A. Role for PADI6 and the cytoplasmic lattices in ribosomal storage in oocytes and translational control in the early mouse embryo. Development 2008, 135, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fu, J.; Yu, M.; Feng, R.; Sang, Q.; Liang, B.; Chen, B.; Qu, R.; Li, B.; et al. Mutations in PADI6 Cause Female Infertility Characterized by Early Embryonic Arrest. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Chen, L.; Dai, J.; Dai, C.; Guo, J.; Lu, C.; Gong, F.; Lu, G.; Lin, G. New biallelic mutations in PADI6 cause recurrent preimplantation embryonic arrest characterized by direct cleavage. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020, 37, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisan, E.D.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Lange, S. Putative Roles for Peptidylarginine Deiminases in COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams Waldorf, K.M.; McAdams, R.M. Influence of infection during pregnancy on fetal development. Reproduction 2013, 146, R151–R162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Protein ID Protein Name | Species Name | Phylum | Matches (Sequences) | Total Score (p < 0.05) ⱡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U6GSR1_EIMAC GFP-like fluorescent chromoprotein FP506 | Eimeria acervulina | Apicomplexa | 18 (7) | 378 |
| I1YZZ9_BABBO GFP-BSD | Babesia bovis | Apicomplexa | 18 (7) | |
| B3SHQ6_9CILI Actin (Fragment) | Heterometopus palaeformis | Ciliophora | 2 (2) | 129 |
| Q6 × 407_9SPIT Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit | Strombidium sp. | Ciliophora | 5 (3) | 116 |
| A0A023B6S9_GRENI Histone H4 | Gregarina niphandrodes | Apicomplexa | 3 (2) | 111 |
| A0A0G4HXG8_9ALVE Beta_helix domain-containing protein | Chromera velia | Chromerida | 5 (2) | 102 |
| A0A061DCJ4_BABBI Histone H4 | Babesia bigemina | Apicomplexa | 8 (2) | 83 |
| A0A1Q9DJ14_SYMMI Uncharacterised protein | Symbiodinium microadriaticum | Dinoflagellata | 1 (1) | 65 |
| Q968T9_9SPIT Actin II (Fragment) | Diophrys sp. | Ciliophora | 1 (1) | 61 |
| A0A1R2CHZ0_9CILI AIG1-type G domain-containing protein | Stentor coeruleus | Ciliophora | 7 (1) | 60 |
| A0A0G4EPG2_VITBC Uncharacterised protein | Vitrella brassicaformis | Chromerida | 2 (1) | 59 |
| U6LWU9_EIMMA Cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase, putative | Eimeria maxima | Apicomplexa | 1 (1) | 55 |
| Q5CUG1_CRYPI Uncharacterised protein | Cryptosporidium parvum | Apicomplexa | 2 (2) | 55 |
| A0A0J9SEN8_PLAVI Uncharacterised protein | Plasmodium vivax India VII | Apicomplexa | 7 (2) | 54 |
| A0A139XZM4_TOXGO AP2 domain transcription factor AP2VIIa-6 | Toxoplasma gondii ARI | Apicomplexa | 8 (2) | 53 |
| A0A1J1HE72_PLARL Pep3_Vps18 domain-containing protein | Plasmodium relictum | Apicomplexa | 1 (1) | 53 |
| A0A086JH54_TOXGO CorA family Mg2+ transporter protein | Toxoplasma gondii | Apicomplexa | 8 (1) | 53 |
| A0A1R2C5U2_9CILI Uncharacterised protein | Stentor coeruleus | Ciliophora | 1 (1) | 52 |
| A0A0G4GAZ1_VITBC Phosphoglycerate kinase | Vitrella brassicaformis | Chromerida | 1 (1) | 51 |
| Q22CS8_TETTS Uncharacterised protein | Tetrahymena thermophila (strain SB210) | Ciliophora | 1 (1) | 50 |
| A0A2A9LZE3_9APIC HECT-domain (Ubiquitin-transferase) domain-containing protein | Besnoitia besnoiti | Apicomplexa | 1 (1) | 48 |
| A0A023B8K1_GRENI Protein-serine/threonine phosphatase | Gregarina niphandrodes | Apicomplexa | 2 (1) | 48 |
| A0A2P9DSP9_PLARE Erythrocyte membrane protein 1, PfEMP1 | Plasmodium reichenowi | Apicomplexa | 2 (2) | 48 |
| Protein ID Protein Name | Species Name Common Name | Phylum | Matches (Sequences) | Total Score (p < 0.05) ⱡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U6GSR1_EIMAC GFP-like fluorescent chromoprotein FP506, related | Eimeria acervulina | Apicomplexa | 39 (16) | 809 |
| A0A023B6S9_GRENI Histone H4 | Gregarina niphandrodes | Apicomplexa | 3 (2) | 136 |
| B3SHQ6_9CILI Actin (Fragment) | Heterometopus palaeformis | Ciliophora | 3 (3) | 128 |
| A0A0G4EA45_VITBC Histone H4 | Vitrella brassicaformis | Chromerida | 3 (2) | 127 |
| A0A061DCJ4_BABBI Histone H4 | Babesia bigemina | Apicomplexa | 4 (2) | 121 |
| A0A0D9QNG9_PLAFR Elongation factor 1-alpha | Plasmodium fragile | Apicomplexa | 4 (3) | 105 |
| C5LYZ2_PERM5 Alternative oxidase, putative | Perkinsus marinus | Perkinsozoa | 2 (2) | 82 |
| A0A0F7R4L8_LEPCH Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain | Lepidodinium chlorophorum | Dinoflagellata | 6 (2) | 77 |
| Q9GRE8_TOXGO Hsp70 protein | Toxoplasma gondii | Apicomplexa | 18 (1) | 64 |
| A0A0V0QLA9_PSEPJ Uncharacterised protein | Pseudocohnilembus persalinus | Ciliophora | 2 (2) | 64 |
| A0A1R2CHZ0_9CILI AIG1-type G domain-containing protein | Stentor coeruleus | Ciliophora | 5 (1) | 60 |
| A0A086JH54_TOXGO CorA family Mg2+ transporter protein | Toxoplasma gondii | Apicomplexa | 6 (1) | 58 |
| A0A2C6KZC4_9APIC Uncharacterised protein | Cystoisospora suis | Apicomplexa | 2 (2) | 58 |
| Q968T9_9SPIT Actin II (Fragment) | Diophrys sp. | Ciliophora | 1 (1) | 57 |
| A0A0F7UJI8_NEOCL DNA-directed DNA polymerase | Neospora caninum (strain Liverpool) | Apicomplexa | 2 (2) | 56 |
| A0A2P9CCB1_9APIC P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase | Plasmodium gaboni | Apicomplexa | 2 (2) | 54 |
| A0A2C6LD60_9APIC Chromosome condensation regulator repeat protein | Cystoisospora suis | Apicomplexa | 3 (2) | 53 |
| G0QSP8_ICHMG Uncharacterised protein | Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (strain G5) | Ciliophora | 2 (1) | 53 |
| A0A060BG26_9CILI Tubulin beta chain | Stentor coeruleus | Ciliophora | 2 (2) | 52 |
| A0A1Q9C0L9_SYMMI Uncharacterised protein | Symbiodinium microadriaticum | Dinoflagellata | 4 (1) | 51 |
| U6LWU9_EIMMA Cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase, putative | Eimeria maxima | Apicomplexa | 1 (1) | 50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kristmundsson, Á.; Erlingsdóttir, Á.; Lange, S. Peptidylarginine Deiminase (PAD) and Post-Translational Protein Deimination—Novel Insights into Alveolata Metabolism, Epigenetic Regulation and Host–Pathogen Interactions. Biology 2021, 10, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030177
Kristmundsson Á, Erlingsdóttir Á, Lange S. Peptidylarginine Deiminase (PAD) and Post-Translational Protein Deimination—Novel Insights into Alveolata Metabolism, Epigenetic Regulation and Host–Pathogen Interactions. Biology. 2021; 10(3):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030177
Chicago/Turabian StyleKristmundsson, Árni, Ásthildur Erlingsdóttir, and Sigrun Lange. 2021. "Peptidylarginine Deiminase (PAD) and Post-Translational Protein Deimination—Novel Insights into Alveolata Metabolism, Epigenetic Regulation and Host–Pathogen Interactions" Biology 10, no. 3: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030177
APA StyleKristmundsson, Á., Erlingsdóttir, Á., & Lange, S. (2021). Peptidylarginine Deiminase (PAD) and Post-Translational Protein Deimination—Novel Insights into Alveolata Metabolism, Epigenetic Regulation and Host–Pathogen Interactions. Biology, 10(3), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030177