Effects of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Body Composition and Bioelectrical Phase Angle in Serie A Soccer Players: A Comparison of Two Consecutive Seasons
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design and Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Analysis
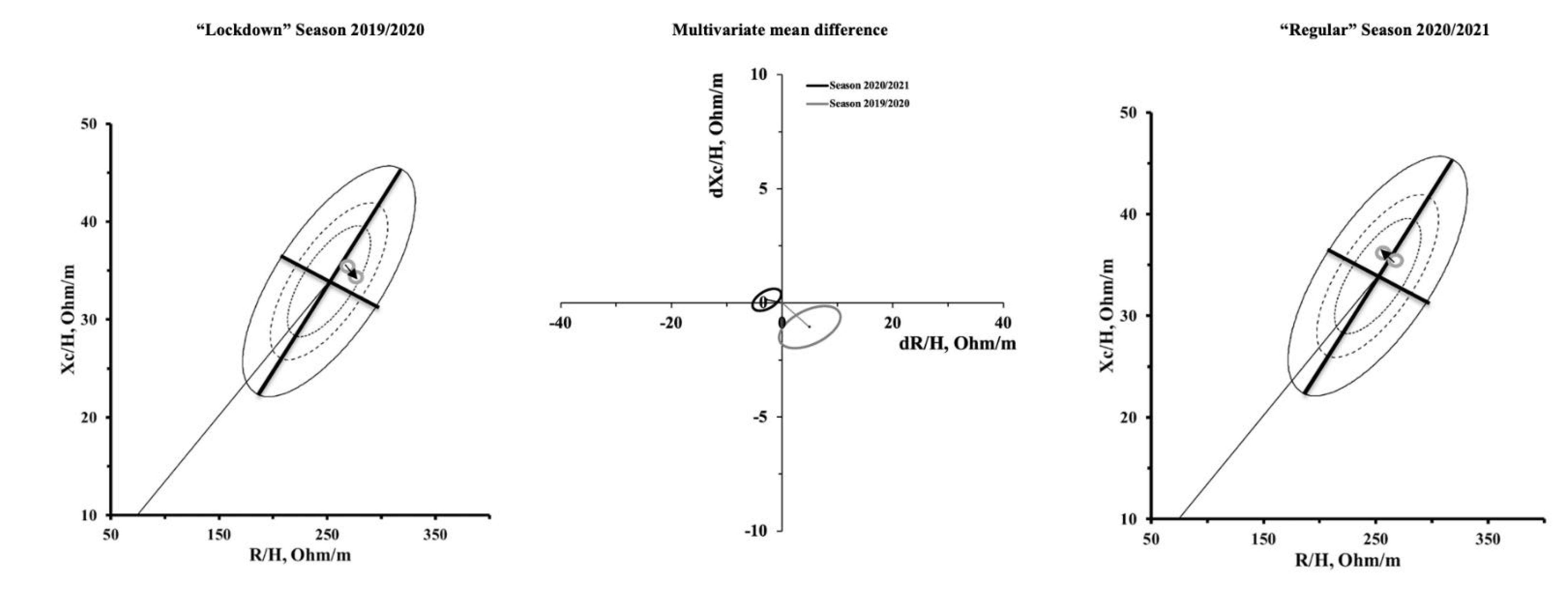
3.2. Qualitative Analysis
3.3. Correlations between Qualitative and Quantitative Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV): Situation Report, 3; World Health Organization, 2020; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330762 (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Mujika, I.; Padilla, S. Detraining: Loss of Training-Induced Physiological and Performance Adaptations. Part I. Sports Med. 2000, 30, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampinini, E.; Donghi, F.; Martin, M.; Bosio, A.; Riggio, M.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Serie A Soccer Players’ Physical Qualities. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazioli, R.; Loturco, I.; Baroni, B.M.; Oliveira, G.S.; Saciura, V.; Vanoni, E.; Dias, R.; Veeck, F.; Pinto, R.S.; Cadore, E.L. Coronavirus Disease-19 Quarantine Is More Detrimental Than Traditional Off-Season on Physical Conditioning of Professional Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 3316–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Arrones, L.; Lara-Lopez, P.; Maldonado, R.; Torreno, N.; De Hoyo, M.; Nakamura, F.Y.; Di Salvo, V.; Mendez-Villanueva, A. The effects of detraining and retraining periods on fat-mass and fat-free mass in elite male soccer players. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koundourakis, N.; Androulakis, N.; Malliaraki, N.; Tsatsanis, C.; Venihaki, M.; Margioris, A.N. Discrepancy between Exercise Performance, Body Composition, and Sex Steroid Response after a Six-Week Detraining Period in Professional Soccer Players. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.R.; Brito, J.; Akenhead, R.; Nassis, G.P. The Transition Period in Soccer: A Window of Opportunity. Sports Med. 2015, 46, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, T.; Rossi, A.; Iaia, F.M.; Alberti, G.; Pasta, G.; Trecroci, A. Association of phase angle and appendicular upper and lower body lean soft tissue with physical performance in young elite soccer players: A pilot study. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2021. Online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiovanni, T.; Mascherini, G.; Genovesi, F.; Pasta, G.; Iaia, F.M.; Trecroci, A.; Ventimiglia, M.; Alberti, G.; Campa, F. Bioimpedance Vector References Need to Be Period-Specific for Assessing Body Composition and Cellular Health in Elite Soccer Players: A Brief Report. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheli, M.L.; Pagani, L.; Marella, M.; Gulisano, M.; Piccoli, A.; Angelini, F.; Burtscher, M.; Gatterer, H. Bioimpedance and Impedance Vector Patterns as Predictors of League Level in Male Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabuco, H.C.G.; Silva, A.M.; Sardinha, L.; Rodrigues, F.B.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Ravagnani, F.C.P.; Cyrino, E.; Ravagnani, C.F.C. Phase Angle is Moderately Associated with Short-term Maximal Intensity Efforts in Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2019, 40, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Teixeira, A.; Guglielmo, L.; Francisco, J.; Silva, D.; Nakamura, F.; Lima, L. Phase Angle Is Related to 10 m and 30 m Sprint Time and Repeated-Sprint Ability in Young Male Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascherini, G.; Gatterer, H.; Lukaski, H.; Burtscher, M.; Galanti, G. Changes in hydration, body-cell mass and endurance performance of professional soccer players through a competitive season. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2014, 55, 749–755. [Google Scholar]
- Campa, F.; Micheli, M.L.; Pompignoli, M.; Cannataro, R.; Gulisano, M.; Toselli, S.; Greco, G.; Coratella, G. The Influence of Menstrual Cycle on Bioimpedance Vector Patterns, Performance, and Flexibility in Elite Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, F.; Matias, C.N.; Marini, E.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Toselli, S.; Sardinha, L.; Silva, A. Identifying Athlete Body Fluid Changes During a Competitive Season With Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020, 15, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Toselli, S.; Mazzilli, M.; Gobbo, L.; Coratella, G. Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes: A Narrative Review of Available Methods with Special Reference to Quantitative and Qualitative Bioimpedance Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coratella, G.; Campa, F.; Matias, C.N.; Toselli, S.; Koury, J.C.; Andreoli, A.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Generalized bioelectric impedance-based equations underestimate body fluids in athletes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.N.; Campa, F.; Santos, D.A.; Lukaski, H.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Fat-free Mass Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Predictive Equation for Athletes using a 4-Compartment Model. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, A.; Rossi, B.; Pillon, L.; Bucciante, G. A new method for monitoring body fluid variation by bioimpedance analysis: The RXc graph. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marini, E.; Campa, F.; Buffa, R.; Stagi, S.; Matias, C.N.; Toselli, S.; Sardinha, L.; Silva, A. Phase angle and bioelectrical impedance vector analysis in the evaluation of body composition in athletes. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.F.; Matias, C.N.; Campa, F.; Morgado, J.P.; Franco, P.; Quaresma, P.; Almeida, N.; Curto, D.; Toselli, S.; Monteiro, C.P. Bioimpedance Vector Patterns Changes in Response to Swimming Training: An Ecological Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Matias, C.; Nunes, C.; Monteiro, C.; Francisco, R.; Jesus, F.; Marini, E.; Sardinha, L.; Martins, P.; Minderico, C.; et al. Specific Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis Identifies Body Fat Reduction after a Lifestyle Intervention in Former Elite Athletes. Biology 2021, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nescolarde, L.; Yanguas, J.; Lukaski, H.; AlOmar, X.; Rosell-Ferrer, J.; Rodas, G. Effects of muscle injury severity on localized bioimpedance measurements. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 36, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nescolarde, L.; Yanguas, J.; Terricabras, J.; Lukaski, H.; AlOmar, X.; Rosell-Ferrer, J.; Rodas, G. Detection of muscle gap by L-BIA in muscle injuries: Clinical prognosis. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, L1–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, U.; Genton, L.; Hans, D.; Pichard, C. Validation of a bioelectrical impedance analysis equation to predict appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASMM). Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stevens, J. Applied Multivariate Statistics for the Social Sciences; Lawrence E.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kasper, A.; Langan-Evans, C.; Hudson, J.; Brownlee, T.; Harper, L.; Naughton, R.; Morton, J.; Close, G. Come Back Skinfolds, All Is Forgiven: A Narrative Review of the Efficacy of Common Body Composition Methods in Applied Sports Practice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, A.L.; Lago-Peñas, C.; Dunlop, G.; Mehdi, R.; Chtara, M.; Dellal, A. Seasonal Body Composition Variation Amongst Elite European Professional Soccer Players: An Approach of Talent Identification. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 62, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocherie, F.; Girard, O.; Forchino, F.; Al Haddad, H.; Dos Santos, G.A.; Millet, G.P. Relationships between anthropometric measures and athletic performance, with special reference to repeated-sprint ability, in the Qatar national soccer team. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Piras, A.; Raffi, M.; Toselli, S. Functional Movement Patterns and Body Composition of High-Level Volleyball, Soccer, and Rugby Players. J. Sport Rehabil. 2019, 28, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.; Maughan, R.J.; Gleeson, M.; Bilsborough, J.; Jeukendrup, A.; Morton, J.P.; Phillips, S.M.; Armstrong, L.; Burke, L.M.; Close, G.L.; et al. UEFA expert group statement on nutrition in elite football. Current evidence to inform practical recommendations and guide future research. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Pérez, V.; Del Coso, J.; Romero-Rodríguez, D.; Marcé-Hernández, L.; Peñaranda, M.; Madruga-Parera, M. Effects of home confinement due to COVID-19 pandemic on eccentric hamstring muscle strength in football players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 2010–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaseca-Vicuña, R.; Pérez-Contreras, J.; Merino-Muñoz, P.; González-Jurado, J.; Aedo-Muñoz, E. Effects of COVID-19 confinement measures on training loads and the level of well-being in players from Chile women’s national soccer team. Rev. Fac. Med. 2021, 69, e88480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.N.; Monteiro, C.P.; Santos, D.A.; Martins, F.; Silva, A.M.; Laires, M.J.; Sardinha, L.B. Magnesium and phase angle: A prognostic tool for monitoring cellular integrity in judo athletes. Magnes. Res. 2015, 28, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nescolarde, L.; Yanguas, J.; Lukaski, H.; AlOmar, X.; Rosell-Ferrer, J.; Rodas, G. Localized bioimpedance to assess muscle injury. Physiol. Meas. 2013, 34, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaski, H.; Raymond-Pope, C.J. New Frontiers of Body Composition in Sport. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Period | No of Training Weeks | No of Training Sessions/Matches | Weekly Training Contents * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Competitive | 14 | 84 | Monday: rest day. Tuesday and Thursday: sessions based on TT and aerobic training. Wednesday: session based on a combination of strength-related stimuli with a special emphasis on lower limbs. Friday and Saturday: sessions based on a combination of low-intensity TT, attacking and defending maneuvers, and SAQ training. Sunday: match day. |
| Lockdown | 14 | 84 | Monday, Wednesday, and Saturday: sessions based on a combination of aerobic drills suitable for the home-confinement condition. Tuesday and Thursday: sessions based on a combination of aerobic (mainly running/cycling-based MIIT) training and strength-related stimuli suitable for the home-confinement condition. Friday: sessions based on a combination of aerobic drills (mainly running/cycling-based LIT) suitable for the home-confinement condition. Sunday: rest day. |
| Variable | “Lockdown” 2019/2020 Season | “Regular” 2020/2021 Season | Time Effect | Condition x Time Interaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body mass (kg) | PRE | 79.6 ± 7.6 | 79.7 ± 7.9 | F = 4.40, p = 0.045, ηp2 = 0.136 | F = 8.26, p = 0.008, ηp2 = 0.228 |
| POST | 78.6 ± 7.8 * | 79.8 ± 7.9 | |||
| 95% CI | −1.66/−0.22 | −0.21/0.51 | |||
| Effect size | −0.72 | 0.22 | |||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | PRE | 23.7 ± 1.0 | 23.7 ± 1.1 | F = 1.43, p = 0.242, ηp2 = 0.049 | F = 9.66, p = 0.004, ηp2 = 0.257 |
| POST | 23.4 ± 1.1 * | 23.8 ± 1.1 | |||
| 95% CI | −0.06/−0.49 | −0.05/0.30 | |||
| Effect size | −0.73 | 0.38 | |||
| R/H (Ohm/m) | PRE | 258.9 ± 22.4 | 253.7 ± 19.7 | F = 1.09, p = 0.305, ηp2 = 0.038 | F = 13.11, p = 0.001, ηp2 = 0.319 |
| POST | 263.9 ± 23.5 * | 250.9 ± 19.3 * | |||
| 95% CI | 0.83/9.15 | −4.69/−0.81 | |||
| Effect size | 0.66 | −0.78 | |||
| Xc/H (Ohm/m) | PRE | 35.6 ± 3.6 | 35.4 ± 3.1 | F = 6.53, p = 0.016, ηp2 = 0.189 | F = 10.88, p = 0.003, ηp2 = 0.028 |
| POST | 34.6 ± 3.5 * | 35.6 ± 3.1 | |||
| 95% CI | −1.75/−0.37 | −0.22/0.49 | |||
| Effect size | −0.85 | 0.20 | |||
| PhA (degree) | PRE | 8.0 ± 0.5 | 7.9 ± 0.5 | F = 10.74, p = 0.003, ηp2 = 0.277 | F = 39.24, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.584 |
| POST | 7.5 ± 0.5 * | 8.1 ± 0.5 * | |||
| 95% CI | −0.51/−0.24 | 0.01/0.22 | |||
| Effect size | −1.56 | 0.63 | |||
| Fat mass (%) | PRE | 14.1 ± 1.7 | 13.6 ± 1.5 | F = 0.51, p = 0.823, ηp2 = 0.002 | F = 1.31, p = 0.261, ηp2 = 0.045 |
| POST | 14.3 ± 1.9 | 13.4 ± 1.3 | |||
| 95% CI | 0.69/−0.41 | −0.51/0.10 | |||
| Effect size | 0.13 | −0.35 | |||
| Muscle mass (kg) | PRE | 28.2 ± 2.3 | 28.1 ± 2.3 | F = 29.54, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.513 | F = 16.29, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.368 |
| POST | 27.4 ± 2.7 * | 27.9 ± 2.7 | |||
| 95% CI | −1.12/−0.64 | −0.45/0.19 | |||
| Effect size | −2.04 | −0.22 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campa, F.; Bongiovanni, T.; Trecroci, A.; Rossi, A.; Greco, G.; Pasta, G.; Coratella, G. Effects of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Body Composition and Bioelectrical Phase Angle in Serie A Soccer Players: A Comparison of Two Consecutive Seasons. Biology 2021, 10, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111175
Campa F, Bongiovanni T, Trecroci A, Rossi A, Greco G, Pasta G, Coratella G. Effects of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Body Composition and Bioelectrical Phase Angle in Serie A Soccer Players: A Comparison of Two Consecutive Seasons. Biology. 2021; 10(11):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111175
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampa, Francesco, Tindaro Bongiovanni, Athos Trecroci, Alessio Rossi, Gianpiero Greco, Giulio Pasta, and Giuseppe Coratella. 2021. "Effects of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Body Composition and Bioelectrical Phase Angle in Serie A Soccer Players: A Comparison of Two Consecutive Seasons" Biology 10, no. 11: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111175
APA StyleCampa, F., Bongiovanni, T., Trecroci, A., Rossi, A., Greco, G., Pasta, G., & Coratella, G. (2021). Effects of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Body Composition and Bioelectrical Phase Angle in Serie A Soccer Players: A Comparison of Two Consecutive Seasons. Biology, 10(11), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111175










