Laser Sources Based on Rare-Earth Ion Doped Tellurite Glass Fibers and Microspheres
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Neodymium
2.1. Lasing in Nd-Doped Fibers
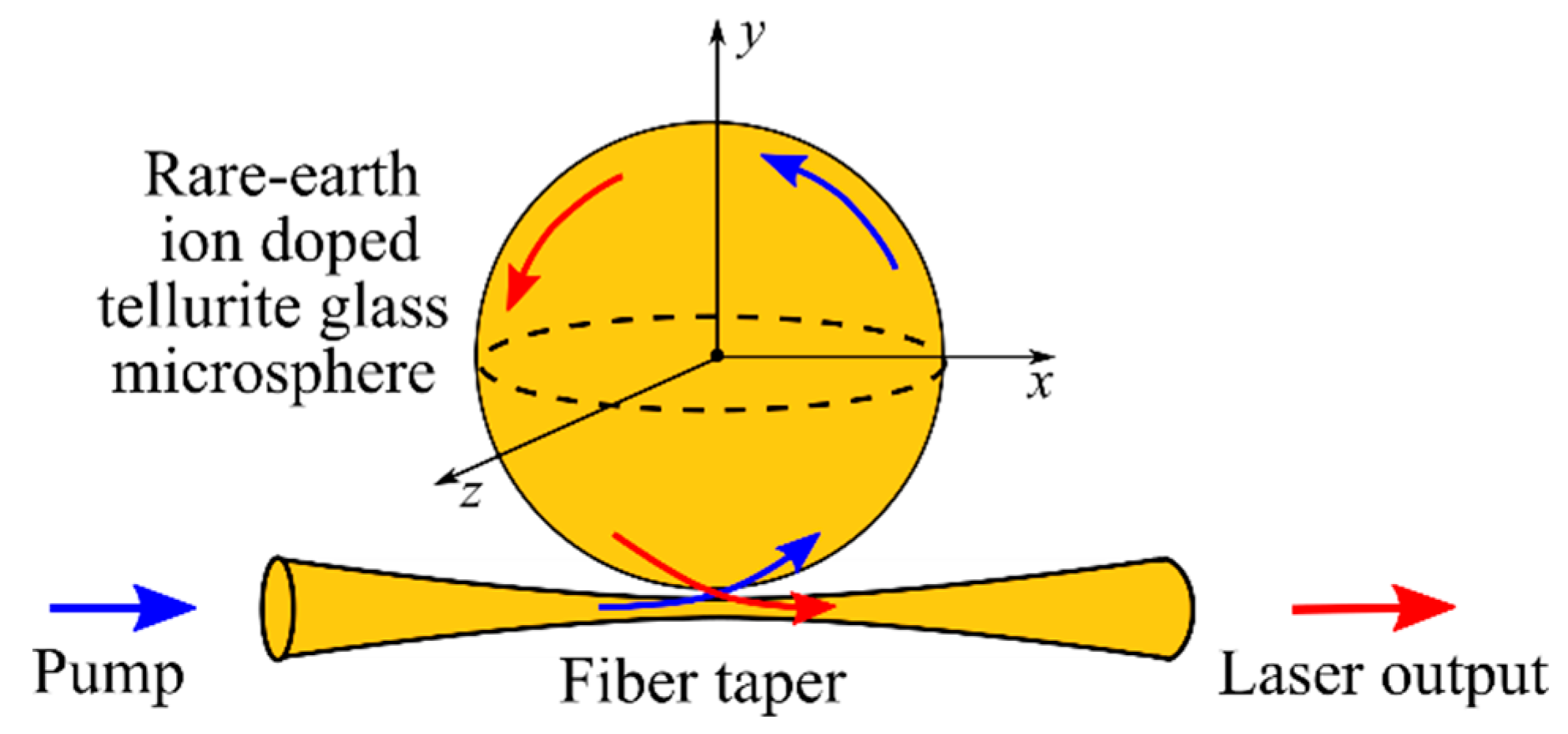
2.2. Lasing in Nd-Doped Microspheres
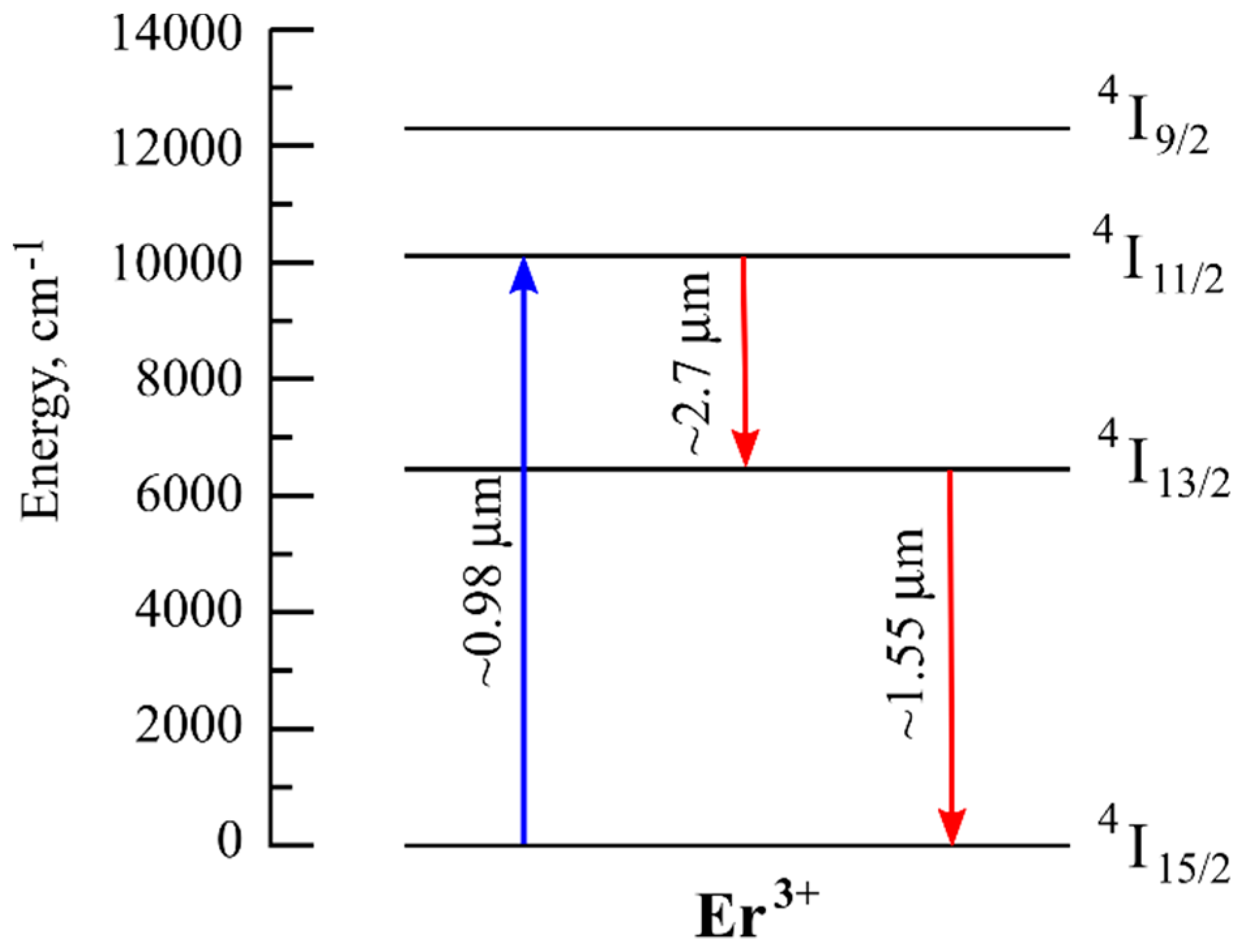
3. Erbium
3.1. Lasing in the 1.5 μm Region in Er-Doped Fibers
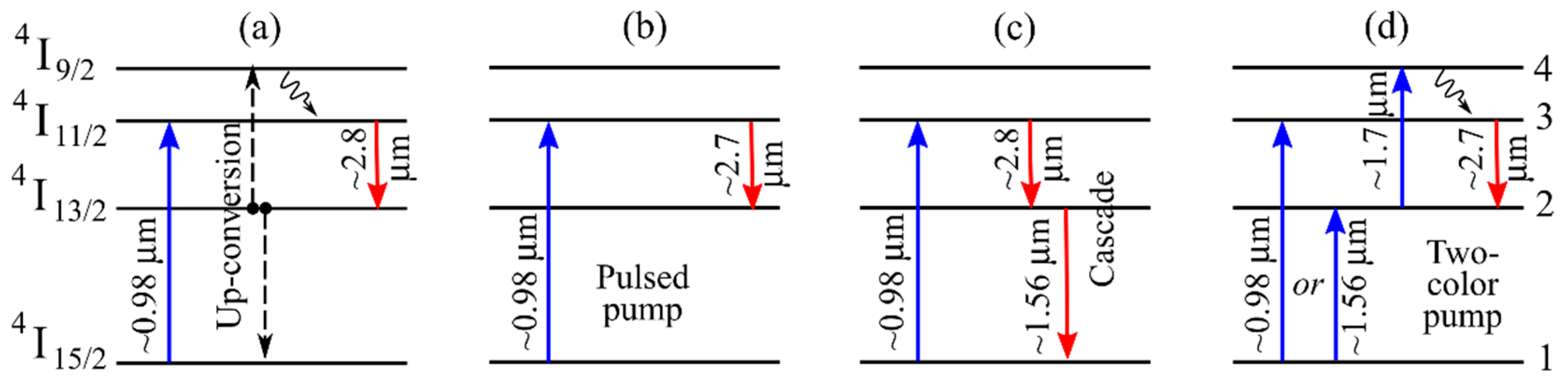
3.2. On the Possibilities of Lasing in the 2.7–2.8 μm Region in Er-Doped Fibers
3.3. Lasing in Er-Doped Microspheres
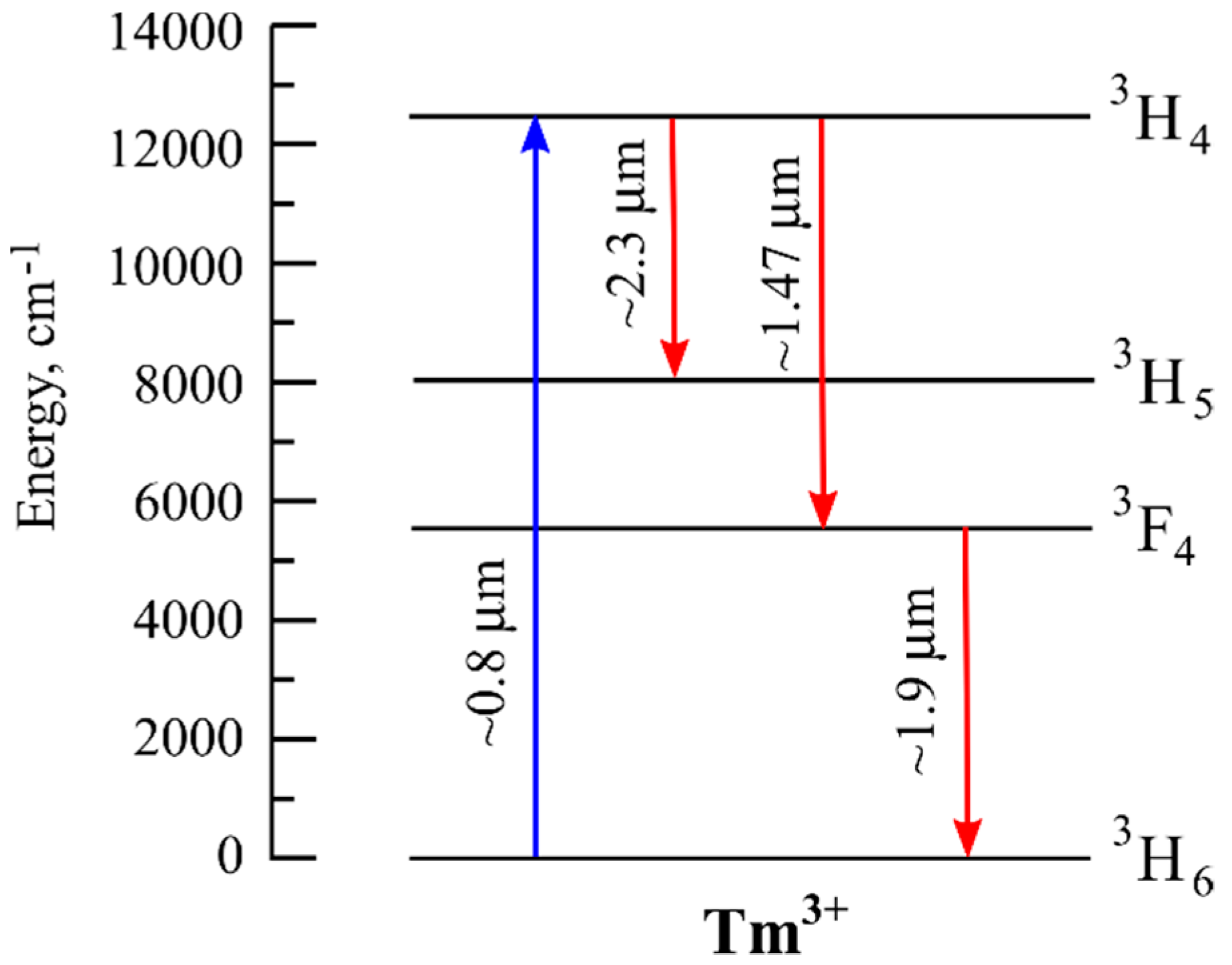
4. Thulium
4.1. Lasing in the 1.9–2 μm Range in Tm-Doped Fibers
4.2. Lasing near 2.3 μm in Tm-Doped Fibers
4.3. Lasing in Tm-Doped Microspheres
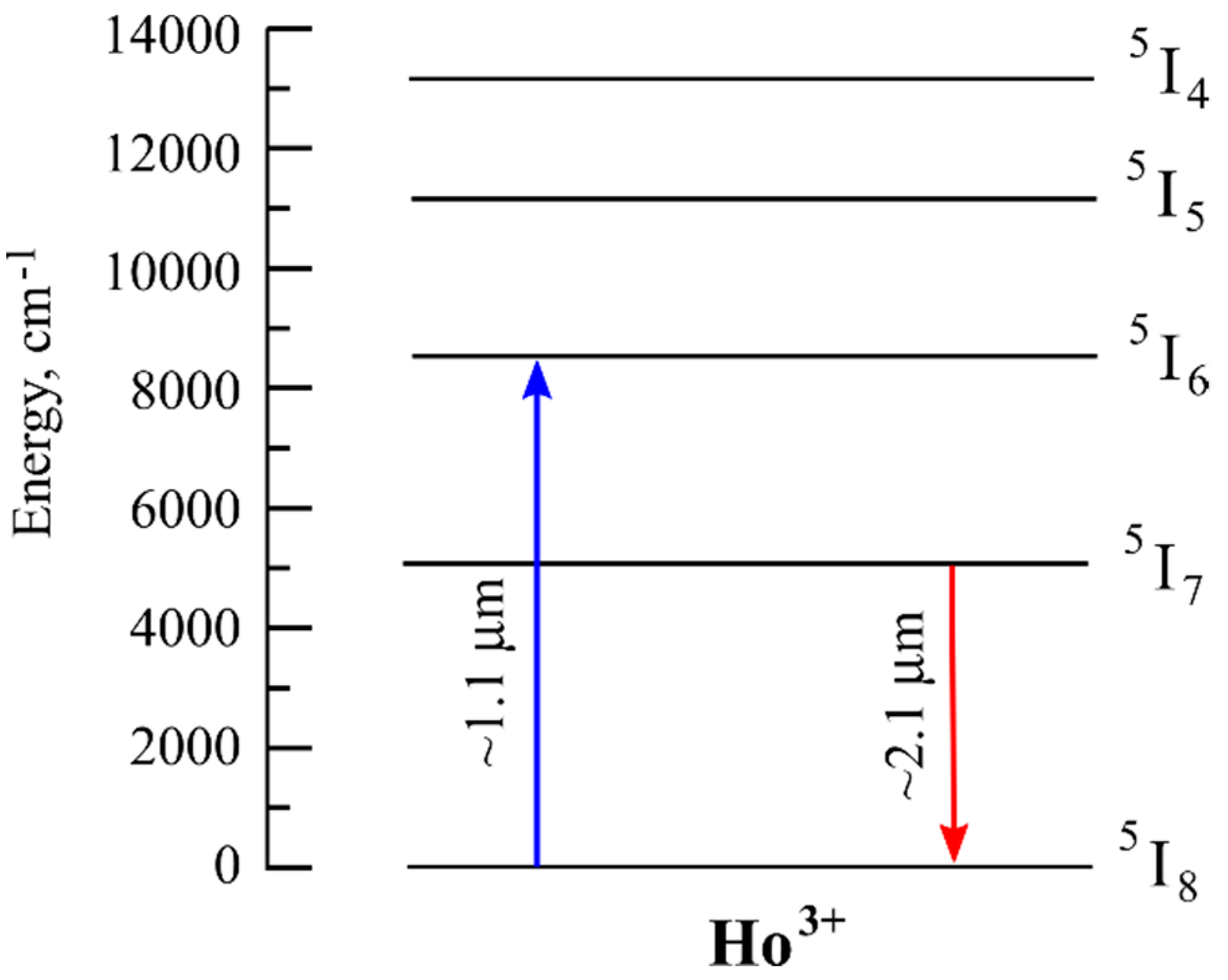
5. Holmium
5.1. Lasing in Ho-Doped Fibers
5.2. Lasing in Ho-Doped Microspheres
6. Opportunities for Other Rare-Earth Ions
7. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Mallawany, R.A.H. Tellurite Glasses Handbook: Physical Properties and Data; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, V.A.G.; Manzani, D. (Eds.) Technological Advances in Tellurite Glasses; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Volume 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H.; Stolyarov, A.M.; Danto, S.; Badding, J.V.; Fink, Y.; Ballato, J.; Abouraddy, A.F. Infrared fibers. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2015, 7, 379–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Richards, B.; Jose, G.; Teddy-Fernandez, T.; Joshi, P.; Jiang, X.; Lousteau, J. Rare-earth ion doped TeO2 and GeO2 glasses as laser materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 1426–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smayev, M.P.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Moiseev, A.N.; Okhrimchuk, A.G. Femtosecond laser writing of a depressed cladding single mode channel waveguide in high-purity tellurite glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 480, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, A.I.; Snetkov, I.L.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Motorin, S.E. Magneto-optical properties of high-purity zinc-tellurite glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 480, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazoumi, S.H.; Aziz, S.A.; El-Mallawany, R.; Aliyu, U.S.; Kamari, H.M.; Zaid, M.H.M.M.; Matori, K.A.; Ushah, A. Optical properties of zinc lead tellurite glasses. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anashkina, E.A.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Koltashev, V.V.; Kim, A.V. Development of Er3+-doped high-purity tellurite glass fibers for gain-switched laser operation at 2.7 μm. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 4337–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorofeev, V.V.; Moiseev, A.N.; Churbanov, M.F.; Kotereva, T.V.; Chilyasov, A.V.; Kraev, I.A.; Pimenov, V.G.; Ketkova, L.A.; Dianov, E.M.; Plotnichenko, V.G.; et al. Production and properties of high purity TeO2−WO3−(La2O3, Bi2O3) and TeO2−ZnO−Na2O− Bi2O3 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 2366–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, B.D.; Jha, A. Lasers utilising tellurite glass-based gain media. In Technological Advances in Tellurite Glasses; Rivera, V.A.G., Manzani, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Volume 254, pp. 101–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muravyev, S.V.; Anashkina, E.A.; Andrianov, A.V.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Motorin, S.E.; Koptev, M.Y.; Kim, A.V. Dual-band Tm3+-doped tellurite fiber amplifier and laser at 1.9 μm and 2.3 μm. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denker, B.I.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Galagan, B.I.; Koltashev, V.V.; Motorin, S.E.; Plotnichenko, V.G.; Sverchkov, S.E. 2.3 µm laser action in Tm3+-doped tellurite glass fiber. Laser Phys. Lett. 2019, 16, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, T.; Riesen, N.; Meldrum, A.; Fan, X.; Hall, J.M.; Monro, T.M.; François, A. Fluorescent and lasing whispering gallery mode microresonators for sensing applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2017, 11, 1600265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Özdemir, Ş.K.; Yang, L. Whispering gallery microcavity lasers. Laser Photonics Rev. 2012, 7, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strekalov, D.V.; Marquardt, C.; Matsko, A.B.; Schwefel, H.G.; Leuchs, G. Nonlinear and quantum optics with whispering gallery resonators. J. Opt. 2016, 18, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Machewirth, D.P.; Wu, F.; Snitzer, E.; Vogel, E.M. Neodymium-doped tellurite single-mode fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 1448–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasagawa, K.; Kusawake, K.; Ohta, J.; Nunoshita, M. Nd-doped tellurite glass microsphere laser. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasagawa, K.; Yonezawa, Z.; Ohta, J.; Nunoshita, M. Control of microsphere lasing wavelength using λ/4-shifted distributed feedback resonator. Electron. Lett. 2003, 39, 1817–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, T.; Kumagai, T.; Yano, T.; Shibata, S. On-chip fabrication of air-bubble-containing Nd3+-doped tellurite glass microsphere for laser emission. AIP Adv. 2012, 2, 042169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, T.; Kumagai, T.; Shibuya, S.; Prudenzano, F.; Yano, T.; Shibata, S. Quasi-single mode laser output from a terrace structure added on a Nd 3+-doped tellurite-glass microsphere prepared using localized laser heating. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 20629–20635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, T.; Kishi, T.; Yano, T. Low threshold lasing of bubble-containing glass microspheres by non-whispering gallery mode excitation over a wide wavelength range. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 113104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Ohishi, Y.; Sudo, S. Erbium-doped tellurite glass fibre laser and amplifier. Electron. Lett. 1997, 33, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wei, Y.Q.; Wonfor, A.; Penty, R.V.; White, I.H.; Lousteau, J.; Jose, G.; Jha, A. Dual-Pumped Tellurite Fiber Amplifier and Tunable Laser Using Er3+/Ce3+ Codoping Scheme. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2011, 23, 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousteau, J.; Boetti, N.G.; Chiasera, A.; Ferrari, M.; Abrate, S.; Scarciglia, G.; Venturello, A.; Milanese, D. Er3+ and Ce3+ Codoped Tellurite Optical Fiber for Lasers and Amplifiers in the Near-Infrared Wavelength Region: Fabrication, Optical Characterization, and Prospects. IEEE Photonics J. 2012, 4, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oermann, M.R.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H.; Ottaway, D.J.; Lancaster, D.G.; Veitch, P.J.; Monro, T.M. Extruded microstructured fiber lasers. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2012, 24, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillcce, E.F.; Narro-García, R.; Menezes, J.W.; Rodriguez, E.; Marconi, D.; Fragnito, H.L.; Barbosa, L.C. Er3+-doped micro-structured tellurite fiber: Laser generation and optical gain. In Optical Components and Materials IX; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8257, p. 82570B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, H.; Meng, X.; Liu, L.; Qin, G.; Qin, W. Broadband amplification and highly efficient lasing in erbium-doped tellurite microstructured fibers. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.X.; Yao, C.F.; Kang, Z.; Qin, G.S.; Ohishi, Y.; Qin, W.P. Self-Q-switching behavior of erbium-doped tellurite microstructured fiber lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 223103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anashkina, E.A.; Andrianov, A.V.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Kim, A.V.; Koltashev, V.V.; Leuchs, G.; Motorin, S.E.; Muravyev, S.V.; Plekhovich, A.D. Development of infrared fiber lasers at 1555 nm and at 2800 nm based on Er-doped zinc-tellurite glass fiber. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 525, 119667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Tong, M.; Zong, J.; Li, M.; Wiersma, K.; Chavez-Pirson, A.; Peyghambarian, N. L-band wavelength-tunable Er3+-doped tellurite fiber lasers. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Song, F.; Jiang, S.; Peyghambarian, N.; Kuwata-Gonokami, M.; Xu, L. Fiber-taper-coupled L-band Er3+-doped tellurite glass microsphere laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1497–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Song, F.; Kuwata-Gonokami, M.; Jiang, S.; Peyghambarian, N. Temperature dependence of the wavelength and threshold of fiber-taper-coupled L-band Er3+-doped tellurite glass microsphere laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 5380–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, B.; Tsang, Y.; Binks, D.; Lousteau, J.; Jha, A. Efficient~ 2 μm Tm3+-doped tellurite fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, B.; Tsang, Y.; Binks, D.; Lousteau, J.; Jha, A. ∼2 μm Tm3+/Yb3+-doped tellurite fibre laser. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electr. 2009, 20, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, G.; Hu, L. Watt-level∼2 μm laser output in Tm3+-doped tungsten tellurite glass double-cladding fiber. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 4136–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Kuan, P.; Chen, D.; Wang, M. Tm3+ and Tm3+-Ho3+ co-doped tungsten tellurite glass single mode fiber laser. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 10115–10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.X.; Liu, L.; Yao, C.F.; Qin, G.S.; Ohishi, Y.; Qin, W.P. Supercontinuum generation and lasing in thulium doped tellurite microstructured fibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 063106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, P.W.; Li, K.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Hasan, T.; Wang, F.; Hu, L. All-Fiber Passively Q-Switched Laser Based on Tm3+-Doped Tellurite Fiber. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Kuan, P.W.; Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Liao, M.; Hu, L. ~2 μm Single-Mode Laser Output in Tm3+-Doped Tellurium Germanate Double-Cladding Fiber. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 1702–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yao, C.; Jia, Z.; Qin, G.; Qin, W. 1887 nm lasing in Tm3+-doped TeO2-BaF2-Y2O3 glass microstructured fibers. Opt. Mater. 2017, 66, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasagawa, K.; Yonezawa, Z.O.; Iwai, R.; Ohta, J.; Nunoshita, M. S-band Tm 3+-doped tellurite glass microsphere laser via a cascade process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 4325–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, S.; Qua, T.; Kuwata-Gonokami, M.; Peyghambarian, N. 2 μm lasing from highly thulium doped tellurite glass microsphere. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 211118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, S.; Peyghambarian, N. 1.5-μm-band thulium-doped microsphere laser originating from self-terminating transition. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 10129–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, F.; Côté, F.; El Amraoui, M.; Messaddeq, Y.; Peter, Y.A.; Rochette, M. Low-threshold lasing at 1975 nm in thulium-doped tellurite glass microspheres. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 5227–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Huang, Y.; Liao, T.; Xu, C.; Ke, C.; Duan, Y. 1.9 μm laser and visible light emissions in Er3+/Tm3+ co-doped tellurite glass microspheres pumped by a broadband amplified spontaneous emission source. J. Opt. 2019, 21, 035401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, A.; Yang, Z.; Lewis, E.; Brambilla, G.; Wang, P. Tm3+-Ho3+ codoped tellurite glass microsphere laser in the 1.47 μm wavelength region. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, Y.; Richards, B.; Binks, D.; Lousteau, J.; Jha, A. A Yb3+/Tm3+/Ho3+ triply-doped tellurite fibre laser. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 10690–10695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, Y.; Richards, B.; Binks, D.; Lousteau, J.; Jha, A. Tm3+/Ho3+ codoped tellurite fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; He, C.; Jia, Z.; Wang, S.; Qin, G.; Ohishi, Y.; Qin, W. Holmium-doped fluorotellurite microstructured fibers for 2.1 μm lasing. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 4695–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, W.; Kuan, P.; Li, W.; Lin, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, C.; Li, K.; Hu, L. Spectroscopic and laser properties of Ho3+ doped lanthanum-tungsten-tellurite glass and fiber. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 10493–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Wang, W.C.; Zhang, C.F.; Yuan, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Q.Y. 2.0 μm Nd3+/Ho3+-doped tungsten tellurite fiber laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 2904–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Bai, X.; Zhou, H. Preparation of Ho3+/Tm3+ co-doped lanthanum tungsten germanium tellurite glass fiber and its laser performance for 2.0 μm. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.P.; Yao, C.F.; Li, Z.R.; Jia, Z.X.; Qin, G.S.; Ohishi, Y.; Qin, W.P. 8.08 W holmium doped fluorotellurite fiber laser at 2067 nm. Laser Phys. Lett. 2019, 16, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yang, K.; Xu, P.; Zhang, W.; Dai, S.; Xu, T. Fabrication and characterization of Tm3+-Ho3+ co-doped tellurite glass microsphere lasers operating at ∼2.1 μm. Opt. Mater. 2017, 72, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Tian, K.; Du, Y.; Nic Chormaic, S.; Wang, P. An experimental and theoretical investigation of a 2 μm wavelength low-threshold microsphere laser. J. Lightwave Technol. 2020, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Dong, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, S.; Brambilla, G.; Wang, P. Infrared-laser and upconversion luminescence in Ho3+-Yb3+ codoped tellurite glass microsphere. J. Lumin. 2020, 218, 116826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, M.; Gholami, A.; Parsanasab, G.-M.; Firouzeh, Z.H. Investigation of a High-Power Low-Threshold Single-Mode Microsphere Laser Using a Serially Coupled Double Microsphere Structure. J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 37, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anashkina, E.A.; Leuchs, G.; Andrianov, A.V. Numerical simulation of multi-color laser generation in Tm-doped tellurite microsphere at 1.9, 1.5 and 2.3 microns. Res. Phys. 2020, 16, 102811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anashkina, E.A.; Andrianov, A.V.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Muravyev, S.V.; Koptev, M.Y.; Sorokin, A.A.; Motorin, S.E.; Koltashev, V.V.; Galagan, B.I.; Denker, B.I. Two-color pump schemes for Er-doped tellurite fiber lasers and amplifiers at 2.7–2.8 µm. Laser Phys. Lett. 2019, 16, 025107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, J.C.; Morin, D.; Uzel, F. Propriétés spectroscopiques et effet laser d’un verre tellurite et d’un verre phosphate fortement dopés en néodyme. Revue Phys. Appl. 1978, 13, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Oermann, M.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H.; Ottaway, D.; Monro, T.; Felipe Henriques Librantz, A.; Jackson, S.D. Energy level decay and excited state absorption processes in erbium-doped tellurite glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 083111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oermann, M.R.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H.; Li, Y.; Foo, T.C.; Monro, T.M. Index matching between passive and active tellurite glasses for use in microstructured fiber lasers: Erbium doped lanthanum-tellurite glass. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 15578–15584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, F.; Hu, L.; Zhang, J. Spectroscopic properties in Er3+ doped zinc-and tungsten-modified tellurite glasses for 2.7 μm laser materials. J. Lumin. 2014, 147, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Yuan, J.; Li, L.X.; Chen, D.D.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Q.Y. Broadband 2.7 μm amplified spontaneous emission of Er3+ doped tellurite fibers for mid-infrared laser applications. Opt. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 2964–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wei, T.; Jing, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S. Investigation of mid-infrared emission characteristics and energy transfer dynamics in Er3+ doped oxyfluoride tellurite glass. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anashkina, E.A.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Muravyev, S.V.; Motorin, S.E.; Andrianov, A.V.; Sorokin, A.A.; Koptev, M.Y.; Singh, S.; Kim, A.V. Possibilities of laser amplification and measurement of the field structure of ultrashort pulses in the range of 2.7–3 μm in tellurite glass fibres doped with erbium ions. Quantum Electron. 2018, 48, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denker, B.I.; Dorofeev, V.V.; Galagan, B.I.; Koltashev, V.V.; Motorin, S.E.; Sverchkov, S.E.; Plotnichenko, V.G. Rare-earth ions doped zinc-tellurite glass for 2÷3 µm lasers. Appl. Phys. B 2018, 124, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, Y.O.; Fortin, V.; Maes, F.; Jobin, F.; Jackson, S.D.; Vallée, R.; Bernier, M. Diode-pumped mid-infrared fiber laser with 50% slope efficiency. Optica 2017, 4, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujecki, S.; Sojka, L.; Seddon, A.B.; Benson, T.M.; Barney, E.; Falconi, M.C.; Prudenzano, F.; Marciniak, M.; Baghdasaryan, H.; Peterka, P.; et al. Comparative modeling of infrared fiber lasers. Photonics 2018, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajzl, J.; Peterka, P.; Kowalczyk, M.; Tarka, J.; Sobon, G.; Sotor, J.; Aubrecht, J.; Honzátko, P.; Kašík, I. Thulium-doped silica fibers with enhanced fluorescence lifetime and their application in ultrafast fiber lasers. Fibers 2018, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujecki, S. Modeling and design of lanthanide ion-doped chalcogenide fiber lasers: Progress towards the Practical realization of the first MIR chalcogenide fiber laser. Fibers 2018, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anashkina, E.A.; Kim, A.V. Numerical simulation of ultrashort mid-IR pulse amplification in praseodymium doped chalcogenide fibers. J. Lightwave Technol. 2017, 35, 5397–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianov, A.; Szabo, A.; Sergeev, A.; Kim, A.; Chvykov, V.; Kalashnikov, M. Computationally efficient method for Fourier transform of highly chirped pulses for laser and parametric amplifier modeling. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 25974–25982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Lousteau, J.; Milanese, D.; Scarpignato, G.C.; Jackson, S.D. Energy transfer and energy level decay processes in Tm3+-doped tellurite glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 063105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.N.; Taylor, E.R.; Nilsson, J. 795 nm and 1064 nm dual pump thulium-doped tellurite fibre for S-band amplification. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 1246–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.R.M.; Ng, L.N.; Nilsson, J.; Caponi, R.; Pagano, A.; Potenza, M.; Sordo, B. Thulium-doped tellurite fiber amplifier. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2004, 16, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, R.; Pagano, A.; Potenza, M.; Sordo, B.; Taylor, E.M.; Ng, L.N.; Nilsson, J.; Poli, F. Nearly 10 dB net gain from a thulium-doped tellurite fibre amplifier over the S-band. In Proceedings of the 29th European Conference on Optical Communication—14th International Conference on Integrated Optics and Optical Fibre Communication (ECOC-IOOC 2003), Rimini, Italy, 21–25 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Venkataiah, G.; Babu, P.; Martín, I.R.; Krishnaiah, K.V.; Suresh, K.; Lavín, V.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectroscopic studies on Yb3+-doped tungsten-tellurite glasses for laser applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 479, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzliakov, M.A.; Kouhar, V.V.; Malashkevich, G.E.; Pestryakov, E.V. Spectroscopy of Yb-doped tungsten–tellurite glass and assessment of its lasing properties. Opt. Mater. 2018, 75, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.M.; Jamalaiah, B.C.; Kumar, J.S.; Sasikala, T.; Moorthy, L.R. Spectroscopic and photoluminescence properties of Dy3+-doped lead tungsten tellurite glasses for laser materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridhar, P.; Sailaja, S.; Reddy, B.M.; Raju, V.K.; Raju, N.C.; Reddy, S.B. Spectroscopic studies of RE3+ (RE = Eu, Tb, Sm & Dy): Lithium lead boro tellurite glasses. Ferroelectr. Lett. 2011, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annapurna, K.; Chakrabarti, R.; Buddhudu, S. Absorption and emission spectral analysis of Pr3+: Tellurite glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 6755–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, Ł.; Sobczyk, M. Spectroscopic investigations of Pr3+ ions in Na2O-La2O3-ZnO-TeO2 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 487, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambouli, W.; Elhouichet, H.; Gelloz, B.; Férid, M. Optical and spectroscopic properties of Eu-doped tellurite glasses and glass ceramics. J. Lumin. 2016, 138, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ramos, M.E.; Alvarado-Rivera, J.; Zayas, M.E.; Caldiño, U.; Hernández-Paredes, J. Yellow to orange-reddish glass phosphors: Sm3+, Tb3+ and Sm3+/Tb3+ in zinc tellurite-germanate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2018, 75, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rai, D.K.; Rai, S.B. Optical properties of Sm3+ ions doped in tellurite glass. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 59, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dopant | Glass Composition | Fiber Length, cm | Pump Laser, Pump Wavelength, nm | CW or Pulsed | Laser Wavelength, nm | Maximum Output Power (or Energy) | Year, Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nd3+ | 76.9TeO2-6.0Na2O-15.5ZnO-1.5Bi2O3-0.1Nd2O3 | 60 | Ti: sapphire, 818 | CW | 1061 | 4.2 mW | 1994 [16] |
| Er3+ | Not reported | 85 | Ti: sapphire, 978 | CW | 1560 | 2.5 mW | 1997 [22] |
| Er3+, 0.9·1020 cm−3, Ce3+, 2.1·1020 cm−3 | 80TeO2-10ZnO-10Na2O | 22 | Laser diodes, 980&1480 | CW | 1527–1610 | 0 dBm (1 mW) @1558 nm | 2011 [23] |
| Er3+, 8.12·1019 cm−3, Ce3+, 1.92·1019 cm−3 | 79TeO2-13ZnO-8Na2O | 10 | Laser diodes, 980&1480 | CW | ~1550 | 2.6 mW | 2012 [24] |
| Er3+, 1019 cm−3 | TeO2-ZnO-La2O3-Na2O | ~220 | Laser diode, 974 | CW | ~1550 | <1 mW | 2012 [25] |
| Er3+, (7500 ppm Er2O3) | 71TeO2-22.5WO3-5Na2O-1.5Nb2O5 | 5–16 | Laser diode, 980 | CW | 1530–1565 | ≤−24.39 dBm (≤3.6 μW) | 2012 [26] |
| Er3+, (Er2O3 5000 ppm) | 78TeO2-5ZnO-12Na2CO3-5Bi2O3 | 17 | Laser diode, 1480 | CW | 1561 | 140 mW | 2013 [27] |
| Er3+, 10000 ppm | 76.5TeO2-6Bi2O3-6ZnO-11.5Li2O | 14 | Fiber Raman laser, 1480 | Pulsed (self-Q-switch) | 1558 | 316 mW | 2014 [28] |
| Er3+, 1020 cm−3 | TeO2-ZnO-La2O3-Na2O | 20 | Laser diode, 975 | CW | 1555 | >100 μW | 2019 [29] |
| Er3+, 1 wt % | (50–80) TeO2-(10–40) ZnO-(10 − x) La2O3-xEr2O3 | ~300 | Fiber laser, 1570 | CW | 1589–1627 | 52.4 mW @ 1614 nm | 2019 [30] |
| Tm3+/Yb3+ (1.5/1.0 wt % Yb2O3/Tm2O3) | 80TeO2-10ZnO-10Na2O | 32 | Fiber laser, 1568–1610 | CW | 1880–1990 | 280 mW | 2008 [33] |
| Tm3+/Yb3+ (1.5/1.0 wt % Yb2O3/Tm2O3) | 80TeO2-10ZnO-10Na2O | 22 | Fiber laser, 1088 | CW | 1910–1994 | 67 mW | 2009 [34] |
| Tm3+ 3.76 × 1020 cm−3 | 60TeO2-30WO3-10La2O3 | 40 | Laser diode, 800 | CW | 1937 | 1.12 W | 2010 [35] |
| Tm3+, 1 mol % | 60TeO2-30WO3-10La2O3 | 20 | Laser diode, 793 | CW | ~1900 | 494 mW | 2012 [36] |
| Tm3+, 5000 ppm | 78TeO2-5ZnO-12Na2CO3-5Bi2O3 | 20 | Femto-second fiber system, 1560 | CW | 1887 | >6.5 mW | 2014 [37] |
| Tm3+, 3.76 × 1020 cm−3 | Not reported | 9 | Fiber laser, 1590 | Pulsed (Q-switch) | 1860 | 84 mW, 736 nJ | 2015 [38] |
| Tm3+, 1 mol % Tm2O3 | 45GeO2-25TeO2-15PbO-10(La2O3+ Al2O3)-5(CaO+ SrO+ Li2O) | 26 | Laser diode, 793 | CW | 1968 | 0.75 W | 2015 [39] |
| Tm3+, 0.5% Tm2O3 | 70TeO2-10BaF2-9.5Y2O3-0.5Tm2O3 | 42.5 | Fiber laser, 1570 | CW | 1887 | 408 mW | 2017 [40] |
| Tm3+, 5 × 1019 cm−3 | TeO2-ZnO-La2O3-Na2O | ~220 | Laser diode, 792 | CW | 2300&1950 | 1.7 mW @2300 nm, ~40 mW @1950 nm | 2018 [11] |
| Tm3+, 5 × 1019 cm−3 | (86 − x) TeO2-xZnO-4La2O3-10Na2O | 30 | Laser diode, 794 | Pulsed | 2300; 2300&1900 | A few μW | 2019 [12] |
| Tm3+/Ho3+/Yb3+, (1.5/1.0/1.0 wt % Yb2O3/Tm2O3/Ho2O3) | 80TeO2–10ZnO–10Na2O | 17 | Fiber laser, 1088 | CW | ~2100 | 60 mW | 2008 [47] |
| Tm3+/Ho3+/Yb3+, (1.5/1.0/1.0 wt % Yb2O3/Tm2O3/Ho2O3) | 80TeO2–10ZnO–10Na2O | 76 79 | Fiber laser, 1600 Fiber laser, 1600 | CW Pulsed (Q-switch) | 2051–2096 ~2100 | 160 mW 26 mW, 1.3 μJ (train), 0.65 μJ (main pulse) | 2008 [48] |
| Tm3+/Ho3+, 1 mol %/0.5 mol % | 60TeO2-30WO3-10La2O3 | 7 | Laser diode, 793 | CW | 2046 | 35 mW | 2012 [36] |
| Ho3+, 0.75% Ho2O3 | 70TeO2–20BaF2–9.25Y2O3–0.75Ho2O3 | 27 | Fiber laser, 1992 | CW | 2077 | 161 mW | 2015 [49] |
| Ho3+, 0.5% Ho2O3 | 60TeO2–30WO3–9.5La2O3–0.5Ho2O3 | 9 | Fiber laser, 1940 | CW | 2040 | 34 mW | 2016 [50] |
| Nd3+/Ho3+, 0.5% Nd2O3/0.5% Ho2O3 | 60TeO2–30WO3–3ZnO–6La2O3–0.5Ho2O3–0.5Nd2O3 | 5 | Laser diode, 975 | CW | 2052 | 12 mW | 2016 [51] |
| Tm3+/Ho3+, Ho2O3: 0.3%mol, Tm2O3: 0.3%mol | 50TeO2-25GeO2-3WO3-5La2O3-3Nb2O5-5Li2O-9BaF2 | 50 | Fiber laser, 1560 | CW | 2051 | 0.993 | 2017 [52] |
| Ho3+, 0.75% Ho2O3 | 70TeO2-20BaF2-9.25Y2O3-0.75Ho2O3 | 30 | Fiber laser, 1980 | CW | 2067 | 8.08 W | 2019 [53] |
| Dopant | Glass Composition | Sphere Diameter, μm | Pump Laser, Pump Wavelength, nm | Single-Mode (SM) or Multi-Mode (MM) | Laser Wavelength, nm | Year, Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nd3+, (1 wt % Nd2O3) | 70TeO2-20ZnO-10Li2O | 201 (50-a few hundred) | Ti: sapphire, 800 | MM | ~1060 (1061–1067) | 2002 [17] |
| Nd3+, (0.2 wt % Nd2O3) | 75TeO2-20ZnO-5Na2O | ~70–180 | Ti: sapphire, 800 | SM and MM | ~1058–1075 | 2003 [18] |
| Nd3+, (1 mol % Nd2O3) | 80TeO2-10K2O-10WO3 air-bubble-containing or solid | ~20–50 | Ti: sapphire, 810 | MM | ~1060–1070 | 2012 [19] |
| Nd3+, (1 mol % Nd2O3) | 80TeO2-10K2O-10WO3 | 29 | Ti: sapphire, 800–810 | SM and MM | ~1060–1070 | 2015 [20] |
| Nd3+, (1 mol % Nd2O3) | 80TeO2-10K2O-10WO3 air-bubble-containing or solid | ~4-200 | Ti: sapphire, 790–817 | MM | ~1060–1070 | 2015 [21] |
| Er3+, (1.7 × 1020 cm−3) | Not reported | 33 | 975 | SM and MM | 1560–1610 | 2003 [31] |
| Er3+ | Not reported | 31 | 1480 | SM | ~1606–1608 | 2003 [32] |
| Tm3+, (0.15% Tm2O3) | 74.85TeO2-20ZnO-5Na2O-0.15Tm2O3 | 104 | Ti: sapphire, 800 | MM | ~1500&1900 | 2004 [41] |
| Tm3+, (5 wt %) | Not reported | 25 | Ti: sapphire, 793 | SM | ~2000 | 2005 [42] |
| Tm3+, 0.5 wt % Tm2O3 | Not reported | Not reported | Ti: sapphire, 793 | MM | ~1500&1900 | 2005 [43] |
| Tm3+, (4.2 × 1020 cm−3) | 74TeO2-15ZnO-5Na2O-5ZnCl2-1Tm2O3 (mol. %) | 30 | 1504–1629 | MM | Centered at ~1975 | 2015 [44] |
| Er3+/Tm3+ (0.1/0.2% Er2O3/Tm2O3) | 68.7TeO2-23WO3-8La2O3-0.1Er2O3-0.2Tm2O3 (mol %) | 110 | Amplified spontaneous emission source, 1527–1603 | SM and MM | ~1900 | 2019 [45] |
| Tm3+/Ho3+ (0.2/0.8% Tm2O3/Ho2O3) | 72TeO2-20ZnO-5.0Na2CO3-2.0Y2O3-0.8Ho2O3-0.2Tm2O3 | ~100 | Laser diode, 802 | SM and MM | ~1470 | 2019 [46] |
| Tm3+/Ho3+ (1.0/0.7% Tm2O3/Ho2O3) | 75TeO2-18.3ZnO-5Na2O-1.0Tm2O3-0.7Ho2O3 | ~60 | Laser diode, 808 | SM and MM | ~2100 | 2017 [54] |
| Ho3+, (1 mol % HoF3) | 72TeO2-20ZnO-5Na2CO3-2Y2O3-1HoF3 (in mol %) | ~42 | Fiber laser, 1150 | SM | ~2080 | 2020 [55] |
| Ho3+/Yb3+ (0.2/0.8% Ho2O3/Yb2O3) | 72TeO2-20ZnO-5Na2CO3-2Y2O3-0.8Yb2O3-0.2Ho2O3 | 80 | Laser diode, 980 | SM and MM | ~2065–2072 | 2020 [56] |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anashkina, E.A. Laser Sources Based on Rare-Earth Ion Doped Tellurite Glass Fibers and Microspheres. Fibers 2020, 8, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8050030
Anashkina EA. Laser Sources Based on Rare-Earth Ion Doped Tellurite Glass Fibers and Microspheres. Fibers. 2020; 8(5):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8050030
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnashkina, Elena A. 2020. "Laser Sources Based on Rare-Earth Ion Doped Tellurite Glass Fibers and Microspheres" Fibers 8, no. 5: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8050030
APA StyleAnashkina, E. A. (2020). Laser Sources Based on Rare-Earth Ion Doped Tellurite Glass Fibers and Microspheres. Fibers, 8(5), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8050030





