Abstract
A convenient thulium fiber laser source is described with 3 W of output power operating at a wavelength of 2059 nm with a slope efficiency of 49% with respect to input pump power and 60% with respect to absorbed pump power. The laser was applied in an atomic helium spectroscopy experiment to quench 3He (2058.63 nm) and 4He (2058.69 nm) meta-stable singlets (21S0), allowing for further investigation of the helium fine structure. The customized laser effectively eliminates the singlet counts to well below a background level (1%). A simplified analysis describes the basic laser performance with fitted constants in reasonable agreement with previous work.
Keywords:
fiber; laser; fiber laser; thulium; thulium fiber laser; optics; rare-earth elements; spectroscopy 1. Introduction
The key benefits of double clad single transverse mode fiber lasers have been well established, such as efficient and powerful pumping, alignment ease and stability, good heat dissipation due to large surface area to volume ratio, and excellent beam quality [1,2]. For spectroscopic applications, small diameters (typically 250 µm) and long fiber lengths allow for both compact designs and dense mode spacing to conveniently excite very narrow spectral lines. Fiber Bragg gratings are frequently employed to create the laser cavity inside the fiber and select the necessary wavelength and bandwidth. Grating centers can be tuned with temperature for fine control of output wavelength (≈0.02 nm/C for ≈ 2 µm).
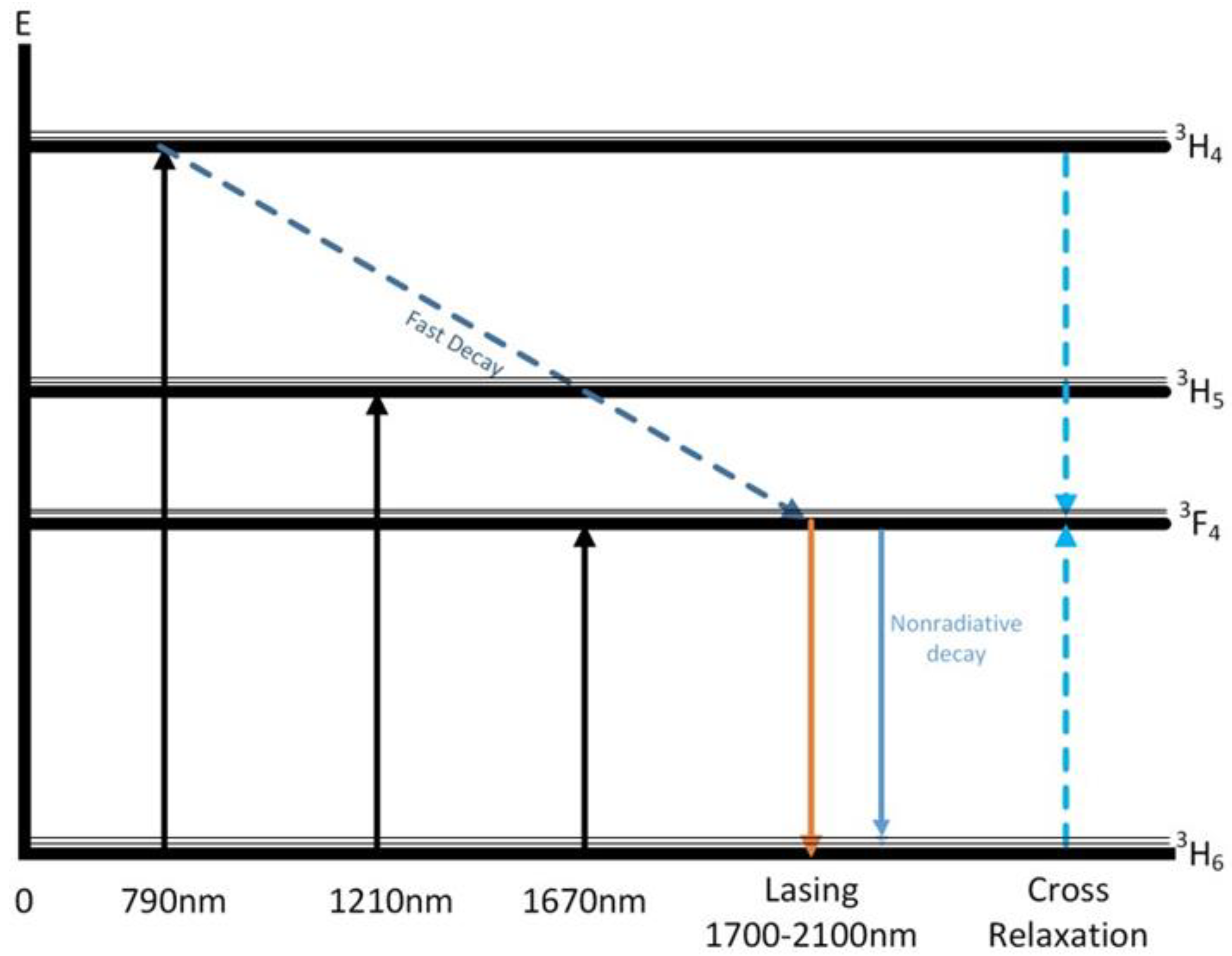
Silica (Si) with rare-earth (RE) do-pants provide very broad homogeneous fluorescent emission. When placed in a silica glass host, thulium (Tm) has several different absorption bands, located at 790 nm, 1210 nm, and 1670 nm [3,4]. The emission spectrum for the 3F4-3H6 transition spans about 400 nm, ranging between 1700 nm to 2100 nm [5]. This emission range extends into the eye-safe regime and has many applications such as laser detection and ranging (LIDAR) for wind shear detection radar, remote sensing, atmospheric pollution monitoring, surgery, range finders, as well as for inducing transitions in atomic spectroscopy experiments [6].
Fiber coupled laser diodes emitting around 790 nm are capable of generating high signal powers especially when employing cladding pumped schemes [7,8,9].Thulium can be pumped at any of the wavelength bands shown in Figure 1, but the 790 nm band is of particular interest because at high doping (≈4%–6%) it yields a near 2 for 1 cross relaxation process populating the upper lasing level, where the cross relaxation efficiency can be defined as the average number of lasing levels created per pump photon absorbed and increases the overall efficiency that would otherwise be limited to the usual quantum defect between lasing and pump frequencies [10]. Efficiencies have been reported to exceed 60% [3,11].

Figure 1.
Energy Levels of Thulium.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laser Design
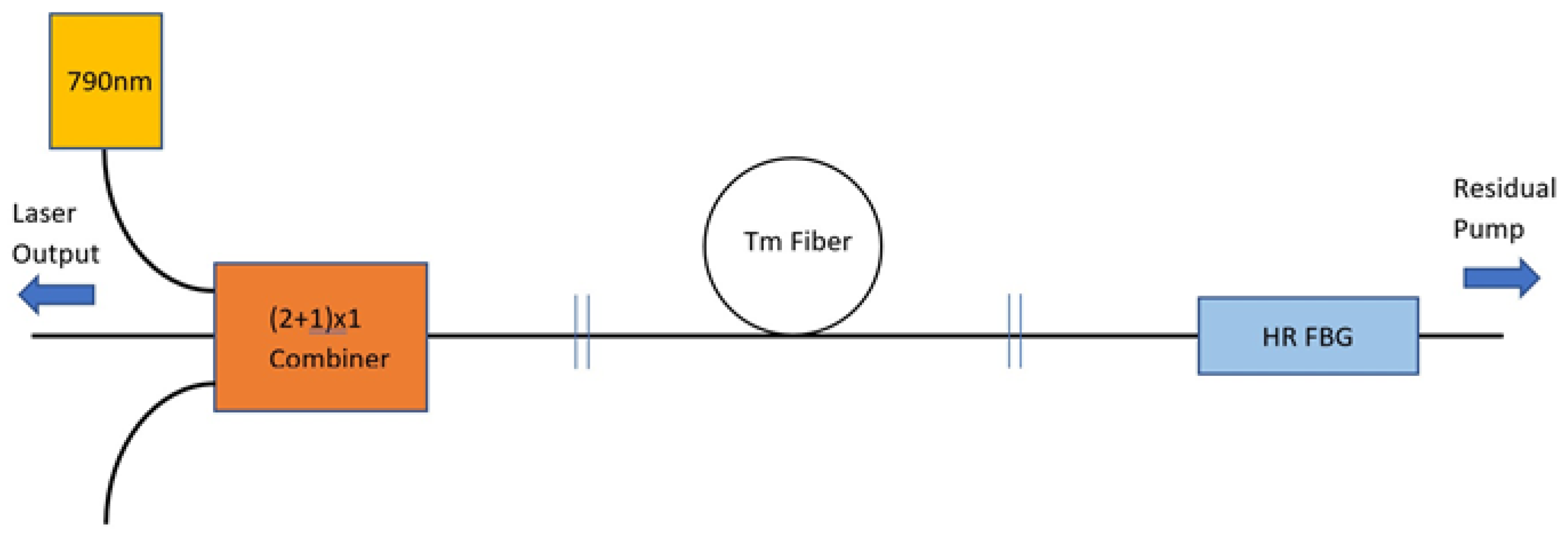
The laser described in this report is pumped with a diode module centered at 793 nm with a maximum output power of 8 W (BWT Beijing), see Figure 2. This pump laser is fiber coupled with 105 µm/125 µm NA = 0.15 fiber and has a bandwidth of 3 nm. It also is built with feedback protection between 1900–2000 nm. The diode module is fused to a (2 + 1) × 1 multi-mode pump combiner (ITF Technologies) to facilitate launching the pump power into the active fiber. For this experiment, only one of the combiner’s input ports was used. The input was designed to match the pump laser fiber and so had 105 µm/125 µm NA = 0.15 fiber on the input pump side. The signal side had 10 µm/125 µm low index double clad NA = 0.46 fiber to match the active fiber. We measured 95% pump beam combiner efficiency and 99% transmission efficiency between the combiner signal ports (called Tc below). Launching the pump power from the combiner into the 10 µm/130 µm low index Tm active fiber was more difficult than we had expected. The ≈3 cm of low index recoat was determined to be responsible for most of the coupling loss. With improvements in cleanliness and technique, the loss was reduced to 5%, as verified by cutback experiments. Nevertheless, simple observation with an optical microscope indicates the index uniformity of the recoated fiber was not nearly as uniform as the commercial fiber. The active fiber consists of 2.15 m of thulium doped 10 µm/130 µm low index NA = 0.46 fiber (Nufern, East Granby, CT, USA) designed to give a truly single-mode profile (TEM00). The thulium fiber has a cladding absorption of 4.6 dB/m at 793 nm. This fiber is expected to absorb nominally 90% of the pump light launched into the gain fiber (7% was measured exiting the back which is consistent with a 90% absorption and the subsequent losses through grating and recoat sections). The gain length was chosen basically by balancing the cost of lost pump photons versus the cost of additional Tm fiber. The frequency mode spacing of the overall cavity length (c/2nL = 150 MHz) was already dense enough to overlap the broad spectral feature (300 MHz FWHM), so no additional length was needed. The absorbed pump power Pabs in terms of the diode power Pdiode is given by:
with an absorption efficiency ηp of 81%, given by the product of the beam combiner (0.95), launch (0.95), and absorption (0.90) efficiencies.
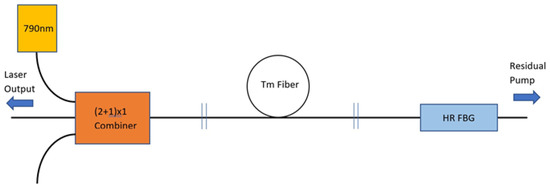
Figure 2.
Thulium Fiber Laser Schematic.
The laser cavity is created by employing a highly reflective fiber Bragg gating (R1 ≈ 99.7% inferred from an optical spectrum analyzer measurement of T1 = 0.3% as supplied by the vendor, O/E Land). It is centered at 2058.45 nm with a bandwidth of 1.2 nm. The grating is fused to the back end of the active fiber and the Fresnel reflection of R2 = 3.3% forms the output coupler at the front end. The fiber Bragg grating (FBG) was designed to insure the laser bandwidth easily overlapped the required transitions even allowing for large grating centering errors and without any grating temperature control.
2.2. Atomic Helium Beam
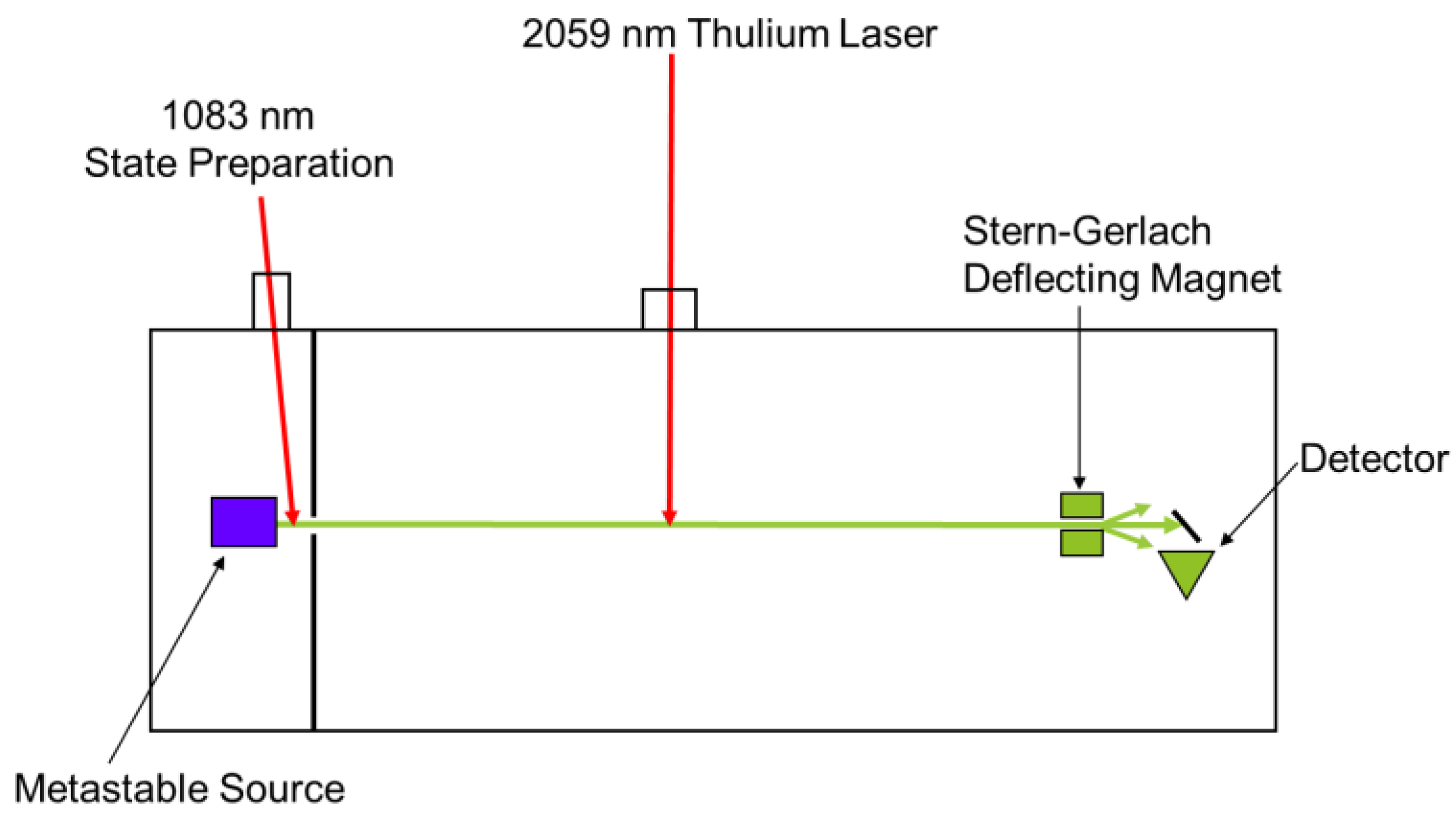
The above laser was designed for use in a high precision measurement of fine and hyper-fine structure in the stable isotopes (3He and 4He) of the helium atom. Metastable helium is created through collisional excitation with electrons produced by thermionic emission from a tungsten filament, see Figure 3. This produces approximately equal sublevel populations in the singlet and triplet states.
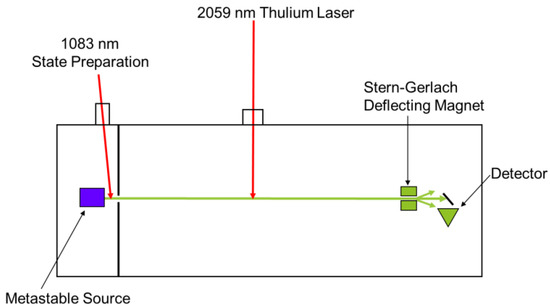
Figure 3.
Helium Atomic Experiment.
The atomic beam is collimated through slits, approximately 4 mils wide, to reduce Doppler broadening. The above laser and a 1083 nm laser depopulate the singlet and the m = 0 magnetic sublevel respectively. Separating the m = 0, +1, and −1 sublevels is done with a set of Stern-Gerlach magnets, which allows for selective detection of the m = 0 state via electron ejection from a gold plated grazing surface (surface Penning ionization or Auger deexcitation). The resulted electrons emit and are collected by a continuous electron multiplier. A signal is detected by using a spectroscopic modulated laser of 1083 nm to allow for observations of the J = 0, 1, 2 states and the comparison of the spacing of these levels allow for measurements of the fine and hyper-fine structure. The remaining gas is circulated through a liquid nitrogen dewar to remove background gas and to reuse the rare and expensive 3He.
3. Results
3.1. Laser Characterization
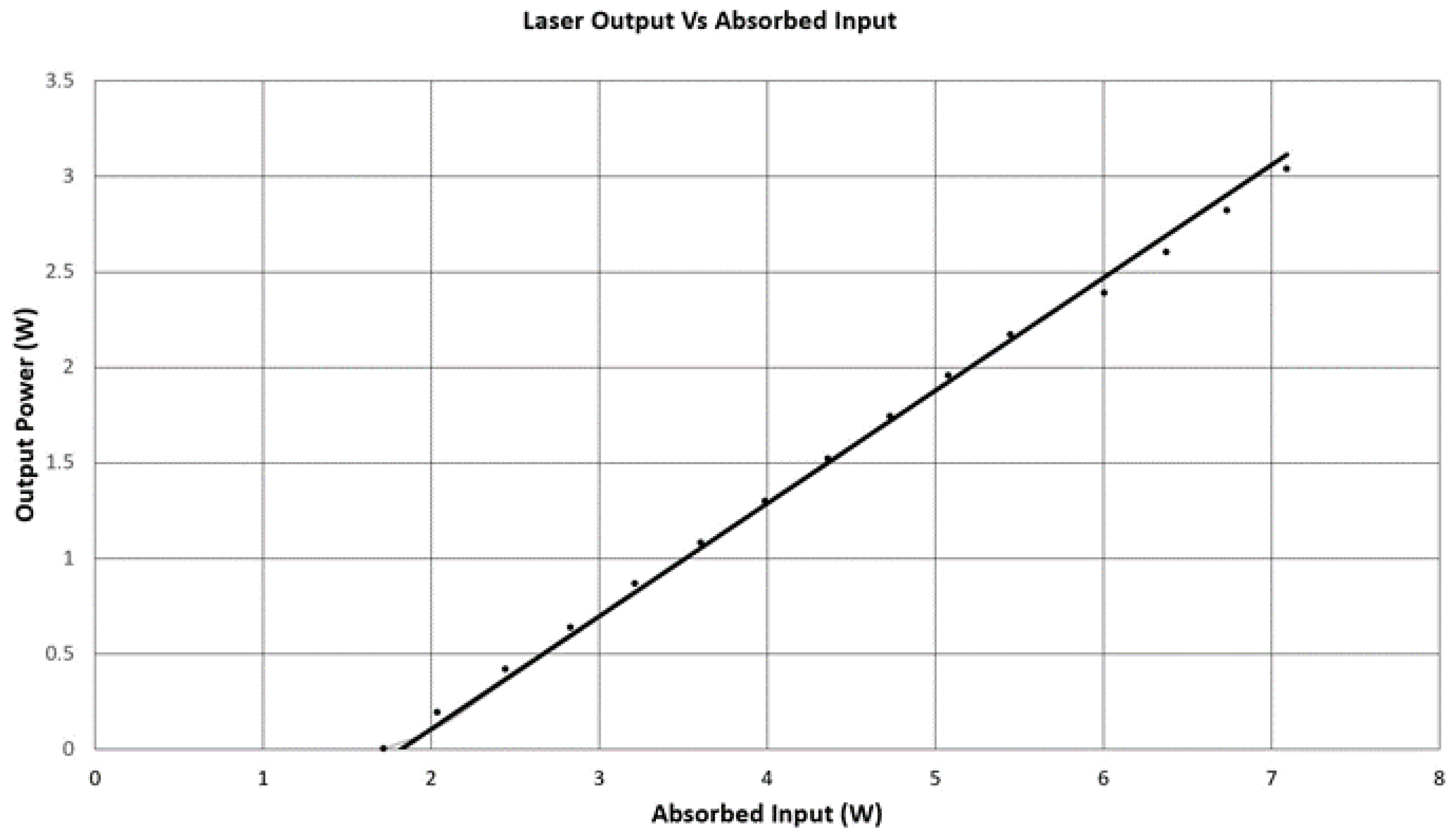
Upon testing the laser, the threshold was found to be 1.7 W with a bandwidth of 70 GHz (50 °C). The laser produces an output of over 3 W corresponding to a slope efficiency of 60% with respect to absorbed power and follows a TEM00 profile.
The laser shows a fairly abrupt threshold and a fairly uniform slope efficiency, see Figure 4. Under such conditions a simplified analysis may be adequate to determine if the laser is operating as expected, see for example [12]. It is important to point out that more detailed and complete laser models have been developed and reported in literature [4,9], and they help motivate the simplifications taken below. To estimate the slope efficiency, a homogeneously broadened lasing transition is assumed with no parasitic pump or laser absorption, no excited state absorption, hole burning, etc. In steady state, any attempt at additional population in the lasing level above threshold results in a shortened lifetime through stimulated emission. Hence, the slope efficiency ηslope is written as
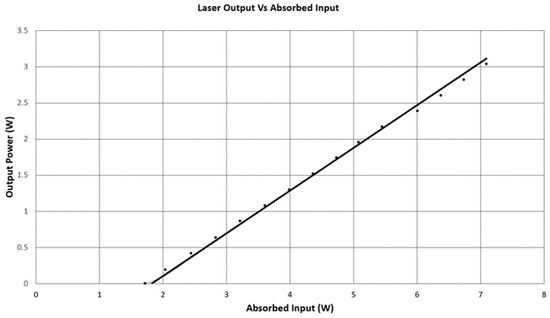
Figure 4.
Laser Output vs. Absorbed Input.
In addition to the cross relaxation efficiency (CR) and the quantum defect, the extraction efficiency (ηex) indicates the fraction of the stimulated photons that exit the cavity and form the laser output. Because the output coupling of 96.7% is so large, the additional internal 2.4% loss has only a small effect of laser operation (note the nonuniform laser intensity within the cavity reduces sensitivity to losses from the back side of the laser in contrast to the threshold estimate below). With ηex = 0.974, the CR term, which was not independently determined, was simply adjusted to 1.6 to yield the measured slope efficiency. This value of 1.6 is composition dependent (particularly the Al and Tm concentrations) [7], and is less than the best reported values of approximately 1.8 [3,9].
The threshold of the laser occurs when the round trip gain G from inversion equals the round trip losses. The gain is found using the absorption (σa = 2.8 × 10−28 m2) and emission (σe = 9 × 10−26 m2) cross sections at 2059 nm taken from published data on similar fibers [13,14,15,16]. The data agreed to ±10%. The variation could be partially attributed to composition dependence. The value for σa was verified to within 7% by measuring the fiber absorption at 2059 nm (assuming negligible parasitic absorption). Also the modal overlap with the core (Γ = 0.75), the fiber core area A, and the Tm concentration density (3 × 1026 m3) are required. To good approximation, the population is primarily only in the ground and lasing levels, nt = n1 + n2. The round trip loss is determined by the refectivities, the coupler transmission and the typical splice transmission Ts, experimentally measured through the cut back technique to be approximately 99%. At threshold the gain is fixed by R1R2Ts4Tc2G = 1, and the upper state population N2 is then determined by
Notably, G is better expressed in terms of the total level populations, since the pumping and resulting populations are not uniform along the fiber length. The threshold is determined by finding the pump power at threshold, Pth, required to balance the sum of the density dependent decay rates from the excited levels:
The standard definition for the thulium cross relaxation coefficient (k = k1310) has been used [4]. To simplify the expression, we used the fact that n2 is small compared to n1 and that n2 is approximately determined by the local pump power (n2 = n0e−αz). The integration factor of 1.2 would be 1.0 in the limit of long fiber length compared to absorption length. The low density lifetime (τ0 = 1/γ0) was measured by electrical pulse pumping and fluorescent monitoring of the decay at long time scales. For times greater than about 500 µs, the decay rate was a simple exponential and gave a lifetime of 480 µs. This is approximately consistent with the range and composition dependent values for the lifetime reported in the literature [17]. The parameters in Equations (3) and (4) that were not measured by us for this fiber were σe and k. To fit our measured values for threshold, σe has to be reduced by 40%, assuming the fitted value of k (1.5 × 10−23 m3s−1) taken from [4] is correct for our fiber. This k value gives an effective lifetime τeff of 380 µs for our fiber at threshold.
3.2. Atomic Spectroscopy
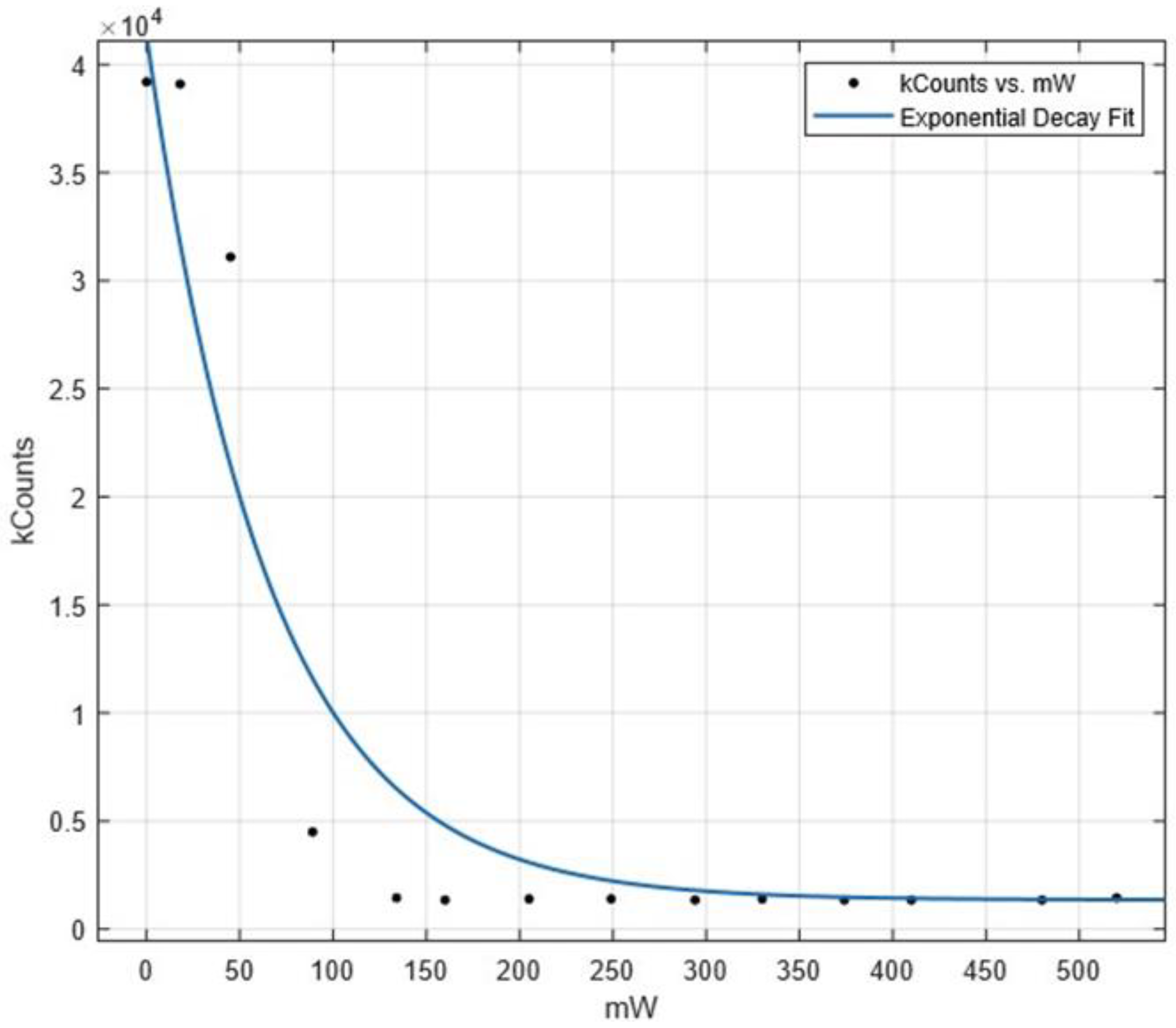
The above laser was designed for convenient optical quenching in an atomic spectroscopy experiment in helium [18]. The fiber laser operating at 2058.65 nm is used for quenching transitions in 3He (2058.63 nm) and 4He (2058.69 nm) singlets (21S0). The atomic beam of meta-stable helium is created by electron collisions and has an approximately room temperature thermal distributions of velocities (vavg ≈ 1500 m/s). The quenching is accomplished when the atoms cross the ≈3 mm diameter laser beam and undergo laser transitions to the fast decaying 21P0 state (Figure 5). With high-power (>0.5 W), the broad emission spectrum is sufficiently stable and continuous to allow for efficient quenching of 3He and 4He simultaneously, insensitive to temperature and alignment fluctuations and drifts. At low power, the inefficient quenching of the states leads to sensitivity to the size of the beam, the power applied, and the transit time of atoms across the laser beam. Also, near threshold, the laser does not produce a uniform and stable frequency spectrum. Thus, the atomic quenching does not follow a simple exponential decay versus overall applied laser power, see Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Quenching of the Singlet States.
The bandwidth of the laser is an important design parameter which is approximately given by the FWHM of the output grating given sufficient high input pumping above threshold. When applied to the atomic beam, the laser can quench the singlet states down to a background level (<1%) as shown (Separate experiments indicate the residual signal is from UV background photons) [19].
4. Discussion
This paper describes the use of a thulium fiber laser operating at 2059 nm in an atomic spectroscopy experiment. The laser effectively quenches the singlet states of atomic helium, while being very insensitive to laboratory temperature and alignment changes, making it a very convenient and reliable solution. These results indicate that customized Tm double clad fiber lasers might provide effective solutions in similar optical pumping and spectroscopy applications. The simplified analysis and published cross-sections support readily feasible laser designs between 1900 and 2100 nm. The paper shows a simple and effect fiber laser source that utilizes readily available materials to accomplish scientific experiments.
Author Contributions
This article was supported by D.S. through writing—review and editing, supervision, resources, and validation. A.K. contributed through validation and conceptualization. R.C. was responsible for writing-original draft preparation, formal analysis, data curation, methodology. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by NSF award number 1404498.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Richardson, D.J.; Nilsson, J.; Clarkson, W.A. High power fiber lasers: Current status and future perspectives. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2010, 27, B63–B92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervas, M.N.; Codemard, C.A. High power fiber lasers: A review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, P.F.; Rines, G.A.; Slobodtchikov, E.V.; Wall, K.F.; Frith, G.; Samson, B.; Carter, A.L.G. Tm-doped fiber lasers: Fundamentals and power scaling. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2009, 15, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.D.; King, T.A. Theoretical modeling of tm-doped silica fiber lasers. J. Light. Technol. 1999, 17, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, D.; Percival, R.M.; Smart, R.G.; Tropper, A.C. Efficient and tunable operation of a tm-doped fibre laser. Opt. Commun. 1990, 75, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jivraj, J.; Zhou, J.; Ramjist, J.; Wong, R.; Gu, X.; Yang, V.X.D. Pulsed and cw adjustable 1942 nm single-mode all-fiber tm-doped fiber laser system for surgical laser soft tissue ablation applications. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 16674–16686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.D.; King, T.A. High-power diode-cladding-pumped tm-doped silica fiber laser. Opics Lett. 1998, 23, 1462–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walbaum, T.; Heinzig, M.; Schreiber, T.; Eberhardt, R.; Tunnermann, A. Monolithic thulium fiber laser with 567 w output power at 1970 nm. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2632–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frith, G.; Carter, A.; Farroni, J.; Farley, K.; Tankala, K. Efficient and reliable 790nm-pumped Tm lasers from 1.91 to 2.13 µm. In Proceedings of the SSDLTR, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 4 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, S. Cross relaxation and energy transfer up-conversion processes relevant to the functioning of 2 µm tm3+-doped silica fibre lasers. Opt. Commun. 2004, 14, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, G.F.S.; Samson, B. Developments in thulium-doped fiber lasers offer higher powers. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual Meeting LEOS, IEEE Lasers Electro-Optics Society, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 9–13 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Siegman, A. Lasers; Chapter 12; University Science Books: Mill Valley, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, B.; Barnes, N. Comparison of tm: Zblan and tm: Silica fiber lasers; spectroscopy and tunable pulsed laser operation around 1.9 µm. Appl. Phys. B 2004, 78, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agger, S.D.; Povlsen, J.H. Emission and absorption cross section of thulium doped silica fibers. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, C.; Tench, R.; Jaouen, Y.; Williams, G. Simulation and design of a multistage 10w thulium-doped double clad silica fiber amplifier at 2050 nm. In Fiber Lasers XIV: Technology and Systems; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017; p. 10083. [Google Scholar]
- Peterka, P.; Kasik, I.; Dhar, A.; Dussardier, B.; Blanc, W. Theoretical modeling of fiber laser at 810 nm based on thulium-doped silica fibers with enhanced 3h4 level lifetime. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajzl, J.; Paterka, P.; Kowalczyk, M.; Tarka, J.; Sobon, G.; Sotor, J.; Aubrecht, J.; Honzatko, P.; Kasik, I. Thuliumdoped silica fibers with enhanced fluorescence lifetime and their application in ultrafast fiber lasers. Fibers 2018, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiciklas, M.; Shiner, D. Determination of the fine structure constant using helium fine structure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeian, N.H. A Precise Few-Nucleon Size Difference by Isotope Shift Measurements of Helium; University of North Texas: Denton, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).