High-Pressure Aging of Asymmetric Torlon® Hollow Fibers for Helium Separation from Natural Gas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
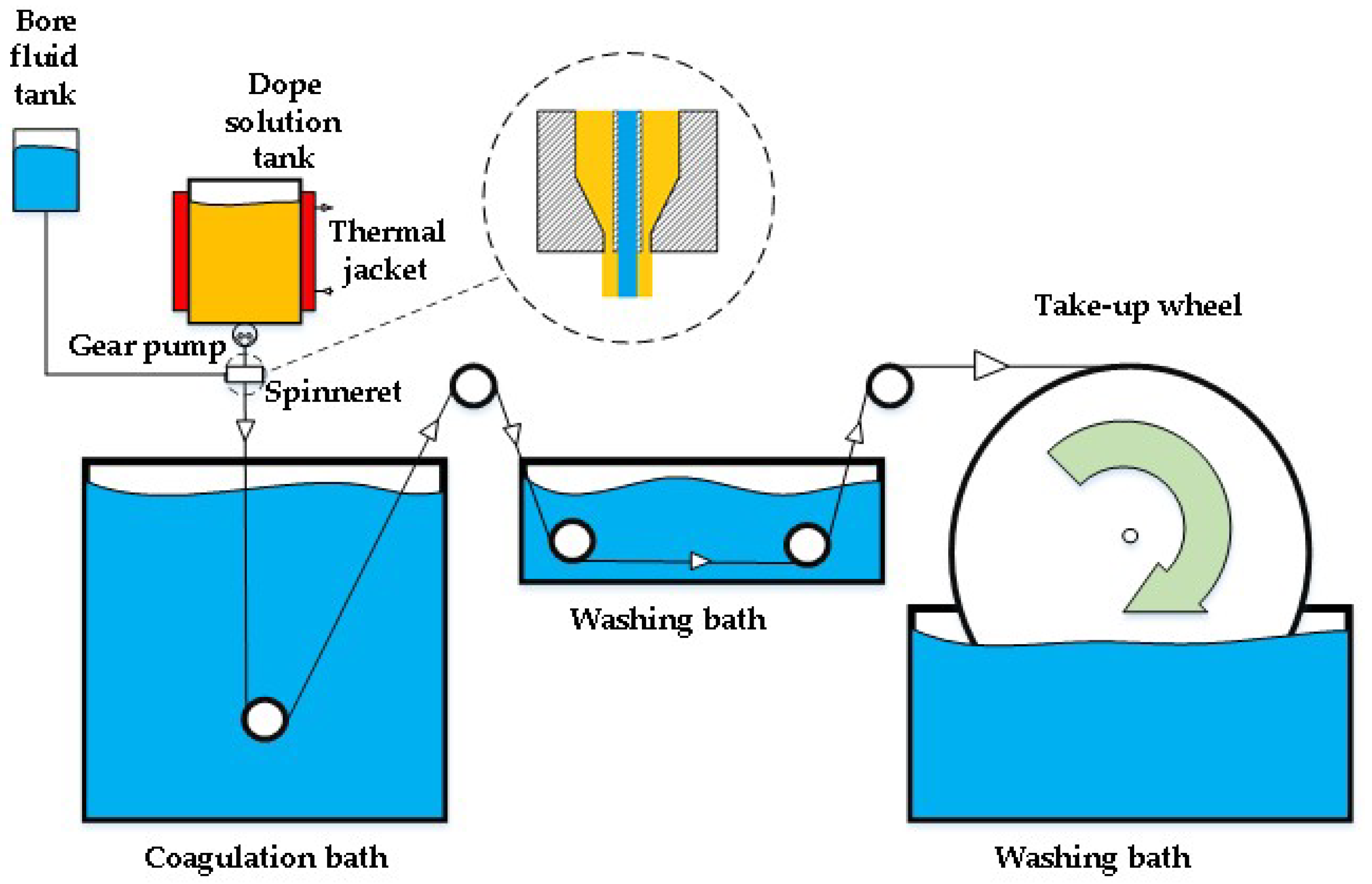
2.2. Asymmetric Hollow-Fiber Spinning and Characterization
2.3. Membrane Element Preparation
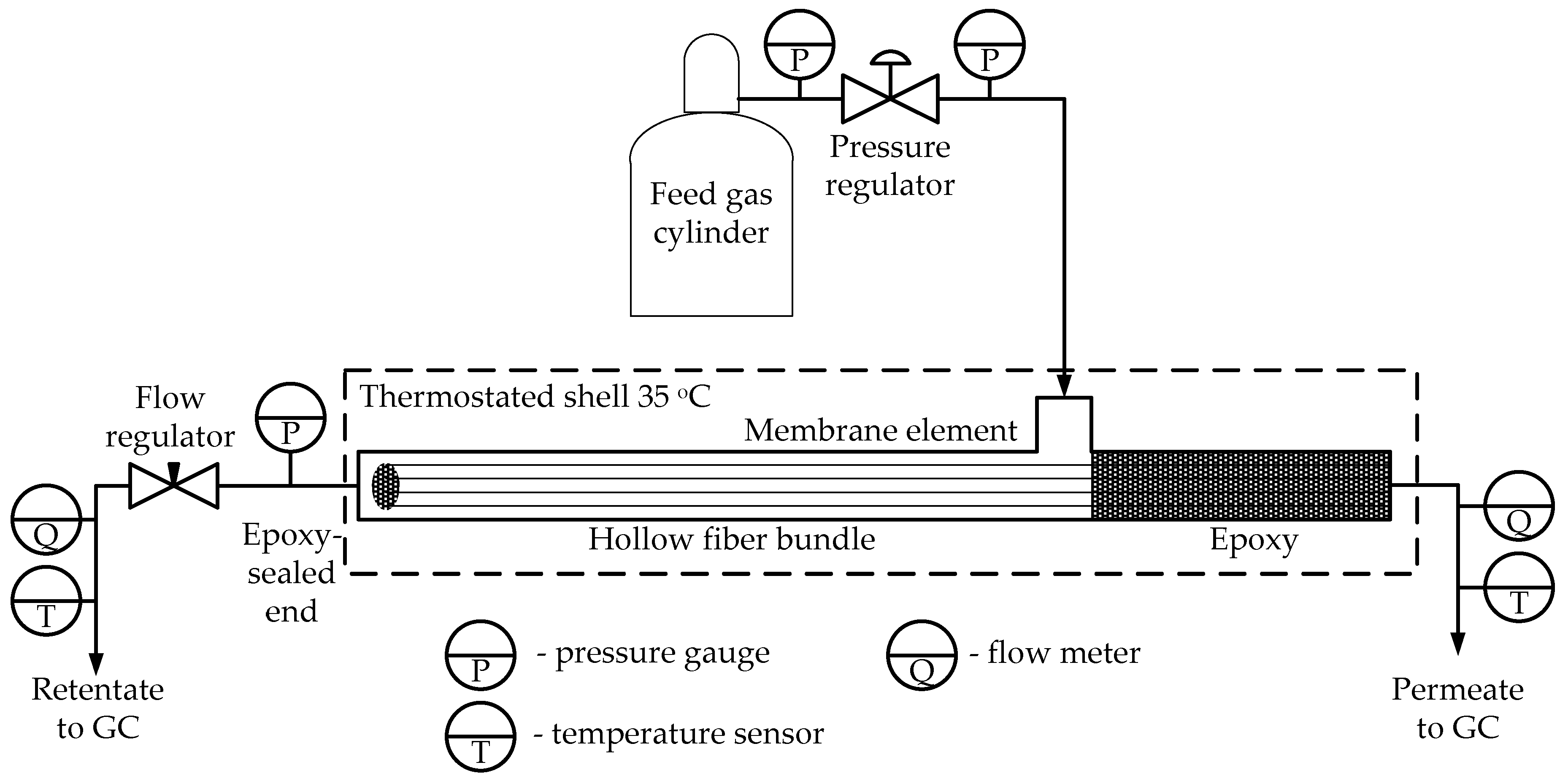
2.4. Mixed-Gas Test
3. Results and Discussion
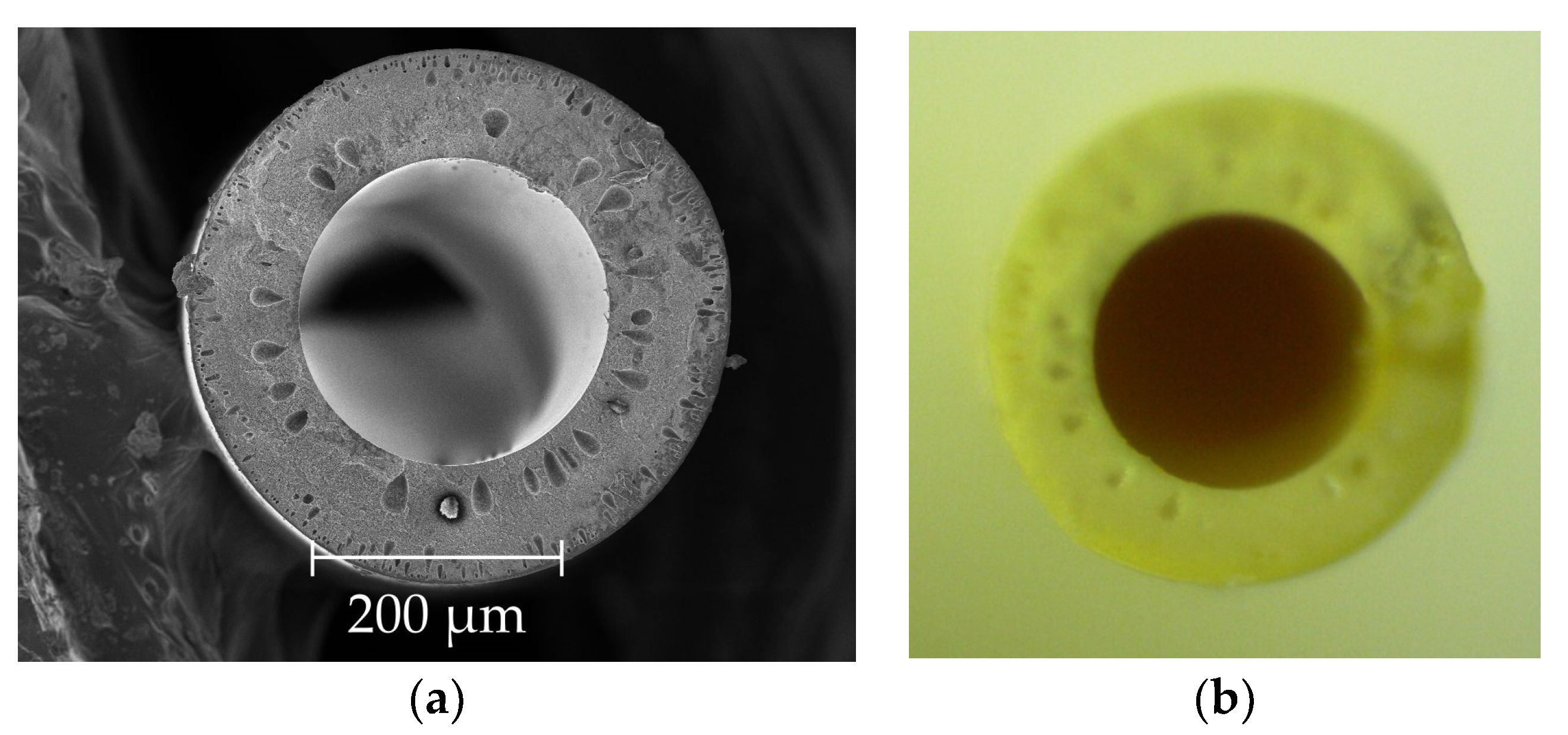
3.1. Hollow Fiber Spinning
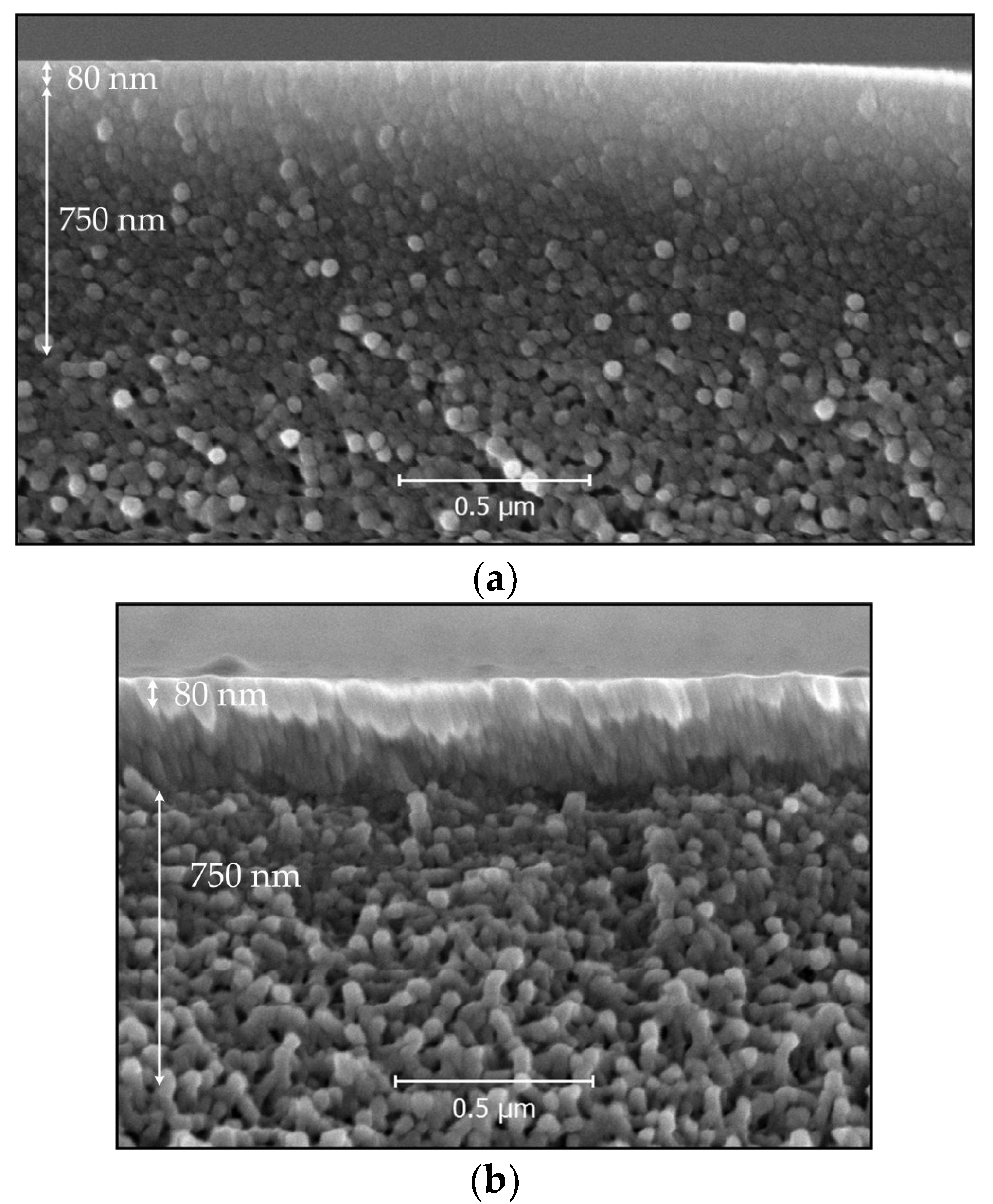
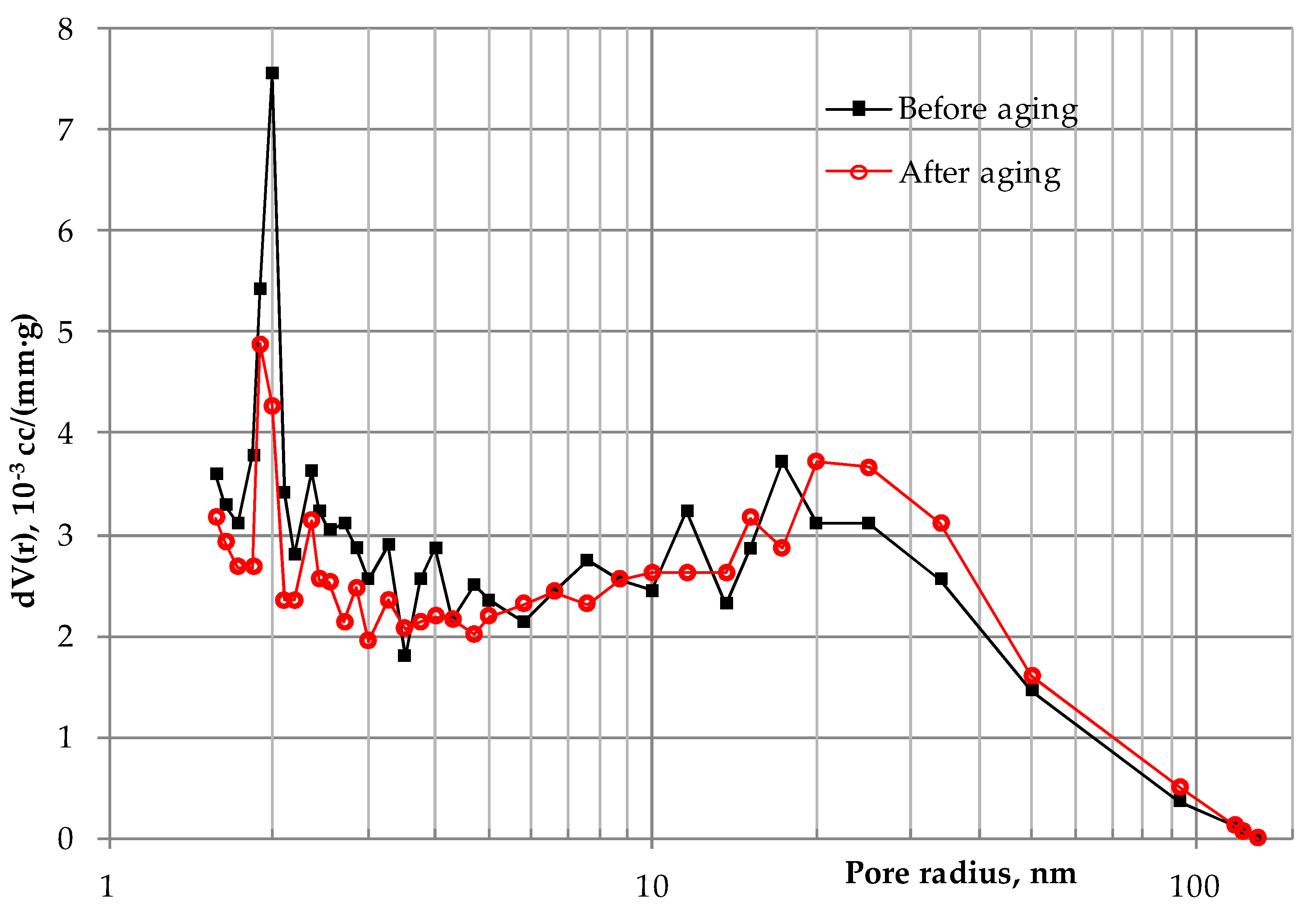
3.2. Scanning Electron and Optical Microscopy
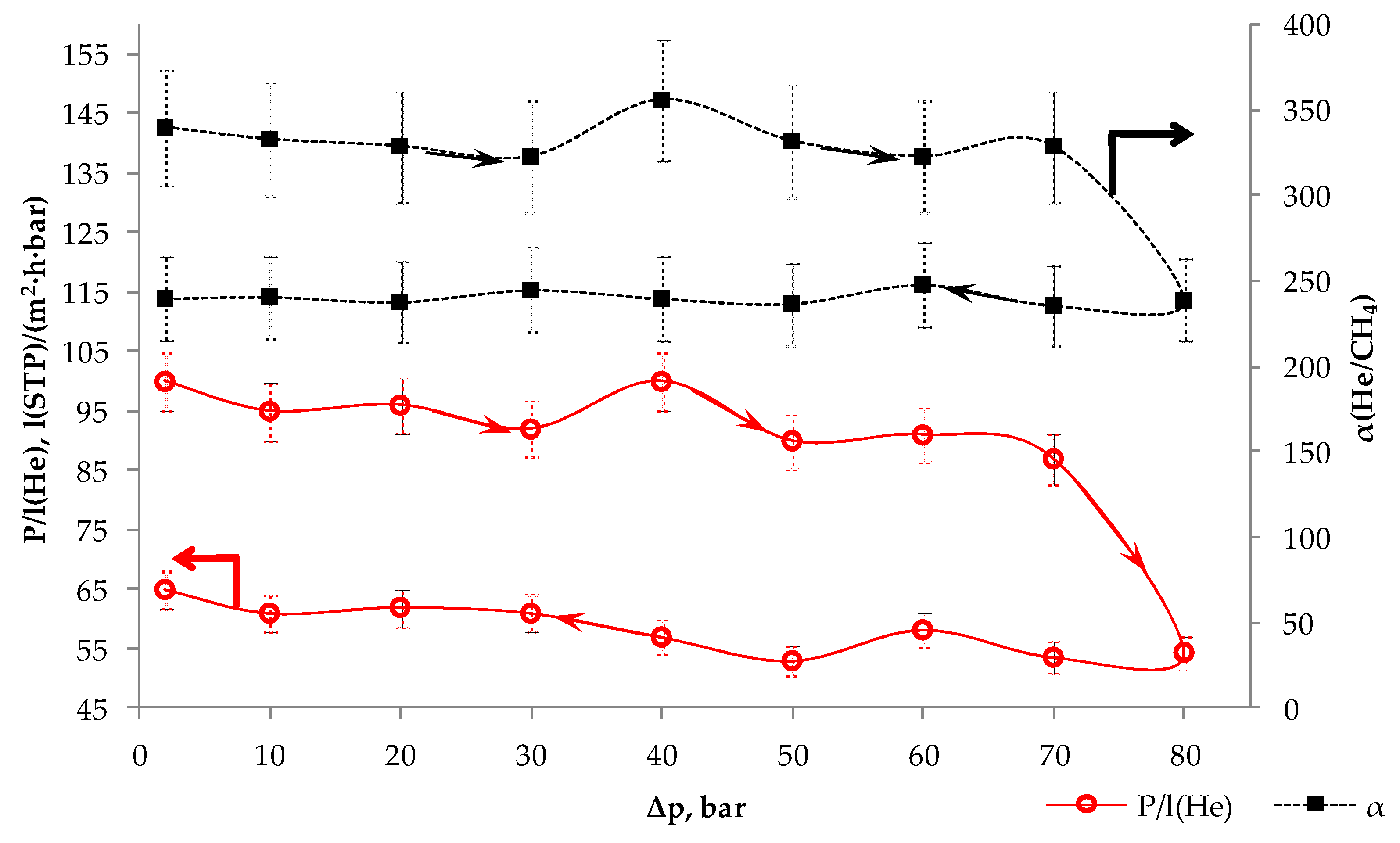
3.3. Membrane-Element Mixed-Gas Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowe, D.J. Helium Recovery and Recycling Makes Good Business Sense. Ind. Heat. 2004, 71, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Scholes, C.; Stevens, G.; Kentish, S. Membrane gas separation applications in natural gas processing. Fuel 2012, 96, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häussinger, P.; Glatthaar, R.; Rhode, W.; Kick, H.; Benkmann, C.; Weber, J.; Wunschel, H.-J.; Stenke, V.; Leicht, E.; Stenger, H. Noble gases. 4.2.1.2. Crude Helium Extraction by Permeation Processes. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 7th ed.; Walter, G., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Baden-Wärttemberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 27, pp. 391–448. ISBN 978-3-527-32943-4. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, S.A.; Sinclair, T.F.; Gareis, P.J.; Vahldieck, N.P.; Mohr, P.H. Helium recovery by permeation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1965, 57, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillman, R. Economics of Gas Separation Membrane Processes. In Membrane Separations Technology; Noble, R., Stern, S., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Eastbourne, UK, 1995; pp. 589–667. ISBN 978-0-444-81633-7. [Google Scholar]
- Laguntsov, N.I.; Kurchatov, I.M.; Karaseva, M.D.; Solomahin, V.I. On the use of membrane technology for helium extraction from high-pressure natural gas. Pet. Chem. 2014, 54, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplyakov, V.V.; Khotimskii, V.S.; Yakovlev, A.V.; Shalygin, M.G.; Gasanova, L.G.; Zen’kevich, V.B.; Netrusov, A.I. Membrane Systems for the Recovery of Energy Carriers from Products of Organic Waste Recycling. Catal. Ind. 2011, 3, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufford, T.E.; Chan, K.I.; Huang, S.H.; May, E.F. A review of conventional and emerging process technologies for the recovery of helium from natural gas. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarso, J.; Hashim, S.S.; Lin, Y.S.; Liuc, S.M. Membranes for helium recovery: An overview on the context, materials and future directions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 176, 335–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, C.A.; Ghosh, U.K. Review of membranes for helium separation and purification. Membranes 2017, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosuri, M.R.; Koros, W.J. Defect-free asymmetric hollow fiber membranes from Torlon®, a polyamide–imide polymer, for high-pressure CO2 separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Chung, T.S. The effects of spinneret dimension and hollow fiber dimension on gas separation performance of ultra-thin defect-free Torlon® hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Chung, T.S.; Lai, J.Y. The role of additives on dope rheology and membrane formation of defect-free Torlon® hollow fibers for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 343, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Chung, T.S.; Lai, J.Y. The rheology of Torlon® solutions and its role in the formation of ultra-thin defect-free Torlon® hollow fiber membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Bazzarelli, E.; Tasselli, F.; Clarizia, G.; Mason, C.R.; Maynard-Atem, L.; Budd, P.M.; Lanc, M.; Pilnacek, K.; Vopicka, O.; et al. Effect of physical aging on the gas transport and sorption in PIM-1 membranes. Polymer 2017, 113, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaidan, R.; Ghanem, B.; Litwiller, E.; Pinnau, I. Physical Aging, Plasticization and Their Effects on Gas Permeation in “Rigid” Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 6553–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrov, G.A.; Volkov, V.V.; Vasilevsky, V.P.; Shutova, A.A.; Bazhenov, S.D.; Khotimsky, V.S.; van de Runstraat, A.; Goetheer, E.L.V.; Volkov, A.V. Robust high-permeance PTMSP composite membranes for CO2 membrane gas desorption at elevated temperatures and pressure. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, B.W.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R. Physical aging of ultrathin glassy polymer films tracked by gas permeability. Polymer 2009, 50, 5565–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, N.R.; Paul, D.R. Carbon dioxide sorption and plasticization of thin glassy polymer films tracked by optical methods. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2820–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtin, D.S.; Kulikov, L.A.; Legkov, S.A.; Khotimskiy, V.S.; Levin, I.S.; Borisov, I.L.; Maksimov, A.L.; Volkov, V.V.; Karakhanov, E.A.; Volkov, A.V. Aging of thin-film composite membranes based on PTMSP loaded with porous aromatic frameworks. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, S.; Tena, A.; Shishatskiy, S.; Escolástico, S.; Brinkmann, T.; Serra, J.M.; Abetz, V. Gas Separation Properties of Polyimide Thin Films on Ceramic Supports for High Temperature Applications. Membranes 2018, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, M.V.; Storozhuk, I.P.; Dibrov, G.A.; Semyashkin, M.P.; Pavlukovich, N.G.; Kagramanov, G.G. Elaboration of hollow fiber membrane from polyarylate-polyarylate block-copolymer for air separation. Pet. Chem. 2018, 8, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.V.; Dibrov, G.A.; Loyko, A.V.; Varezhkin, A.V.; Kagramanov, G.G. Techniques to Manage Geometry Characteristics of Hollow Fiber Membranes. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2016, 50, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Singha, N.R. Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes for Next Generation Pervaporation Process: Strategies, Challenges and Future Prospects. Membranes 2017, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henis, J.M.S.; Tripodi, M.K. Compfposite Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation: The Resistance Model Approach. J. Membr. Sci. 1981, 8, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushevenko, E.A.; Borisov, I.L.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Legkov, S.A.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Volkov, A.V. Membrane material based on octyl-substituted polymethylsiloxane for separation of C3/C1 hydrocarbons. Pet. Chem. 2017, 57, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushevenko, E.A; Podtynnikov, I.A.; Golubev, G.S.; Volkov, V.V.; Borisov, I.L. Polyheptylmethylsiloxane—A novel material for removal of oxygenates from water by pervaporation. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.Y. Gas Separation by Permeators with High-Flux Asymmetric Membranes. AIChE J. 1983, 29, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Sandall, O. A Simple Analysis for Gas Separation Membrane Experiments. Chem. Eng. Educ. 2003, 37, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Borisov, I.; Ovcharova, A.; Bakhtin, D.; Bazhenov, S.; Volkov, A.; Ibragimov, R.; Gallyamov, R.; Bondarenko, G.; Mozhchil, R.; Bildyukevich, A.; et al. Development of Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Porous Supports for High Flux Composite Membranes: Air Plasma and Piranha Etching. Fibers 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.V.; Bildukevich, A.V.; Dibrov, G.A.; Usoskiy, V.V.; Kasperchik, V.P.; Vasilevsk, V.P.; Novitsky, E.G. Elaboration of Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes with Selective Layer from Poly [1-(trimethylsylil). 1-propyne] for Regeneration of Aqueous Alkanolamine Solutions. Pet. Chem. 2013, 53, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.J.M.; Smid, J.; Olijslager, J. The resistance towards gas transport of the sublayer of asymmetric PPO hollow fiber membranes determined by plasmaetching. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 57, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, S.D.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Volkov, A.V. Gas-Liquid Hollow Fiber Membrane Contactors for Different Applications. Fibers 2018, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.; Kafchinski, R. The effects of spinning conditions on asymmetric 6FDA/6FDAM polyimide hollow fibers for air separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 65, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D.; An, Q.; Chen, H. Effect of coagulation bath temperature on formation mechanism of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, S.; Galiano, F.; Faccini, M.; Boerrigter, M.E.; Chaumette, C.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Preparation and Characterization of Polymeric-Hybrid PES/TiO2 Hollow Fiber Membranes for Potential Applications in Water Treatment. Fibers 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Chung, T.-S.; Wang, K.Y. Macrovoid evolution and critical factors to form macrovoid-free hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvey, S.A.; Koros, W.J. Phase separation, vitrification, and the manifestation of macrovoids in polymeric asymmetric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 112, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M.; Harlacher, T.; Melin, T.; Wessling, M. Modeling Gas Permeation by Linking Nonideal Effects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
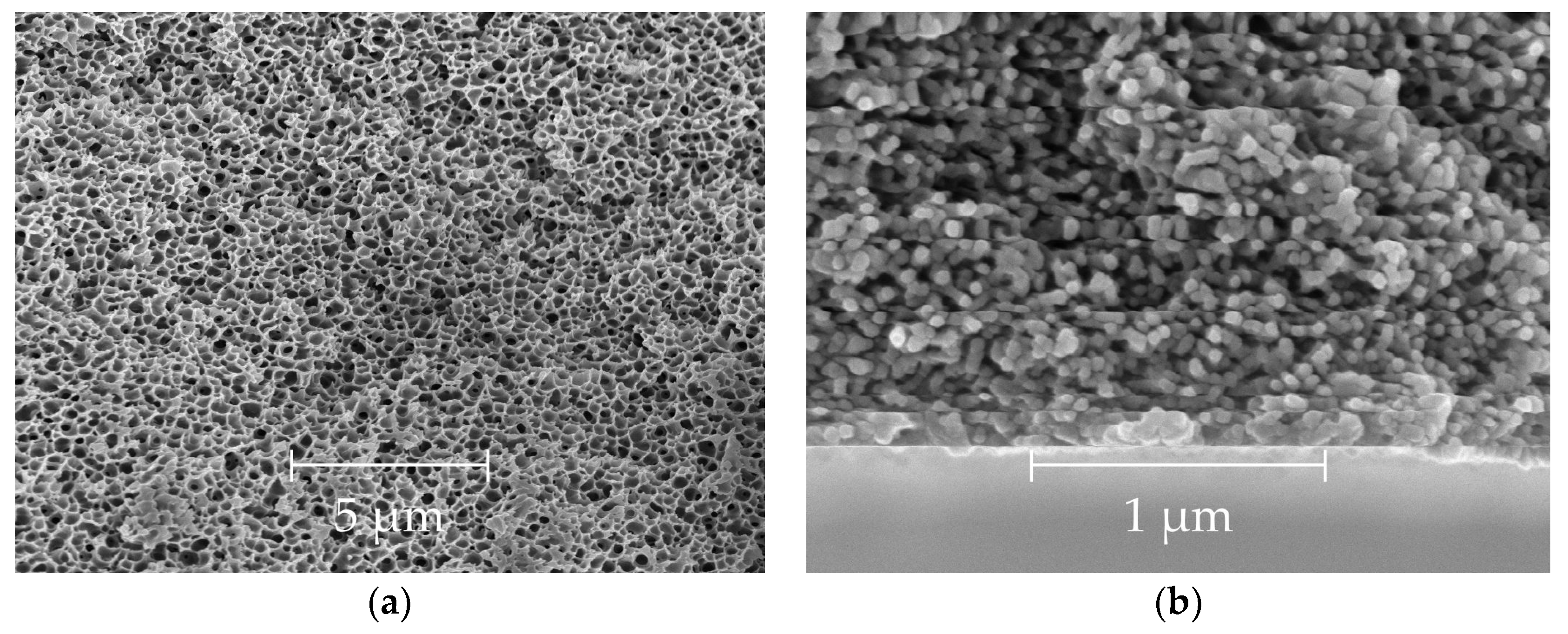
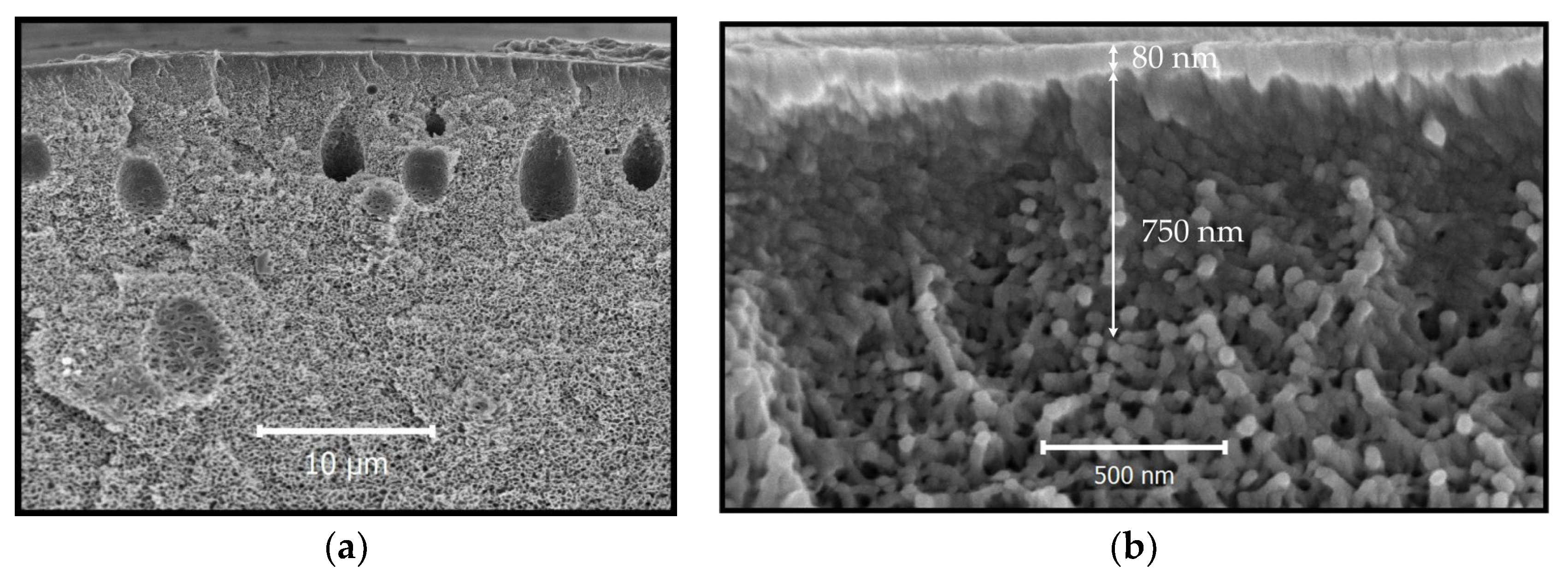
| # | Air Gap, cm | υ 1, m/min | Draw Ratio | T 2, °C | OD, μm | ID, μm | P/l(He) 3 | α(He/CH4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 7 | 2.7 | 40 | 420 | 240 | 105 | 360 |
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 2.7 | 40 | 420 | 240 | 106 | 345 |
| 3 | 9 | 9 | 3.5 | 40 | 370 | 220 | 100 | 320 |
| 4 | 9 | 7 | 2.7 | 27 | 420 | 240 | 63 | 260 |
| Parameter | Before Aging | After Aging |
|---|---|---|
| P/l(He)t, l(STP)/(m2·h·bar) | 100 | 60 |
| P/l(CH4)t, l(STP)/(m2·h·bar) | 0.29 | 0.25 |
| α(He/CH4)t | 340 | 240 |
| P/l(He)1, l(STP)/(m2·h·bar) | 144.38 | 123.03 |
| P/l(CH4)1, l(STP)/(m2·h·bar) | 0.29 | 0.25 |
| Effective selective-layer thickness, nm | 82.3 | 96.6 |
| P/l(He)2, l(STP)/(m2·h·bar) | 325.33 | 117.12 |
| P/l(CH4)2, l(STP)/(m2·h·bar) | 162.67 | 58.56 |
| Δp, bar | qf, 10−3 m3(STP)/h | yp(He), % | θ, % | P/l(He), l(STP)/(m2·h·bar) | α(He/CH4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 66 | 10.6 | 3.3 | 100 | 356 |
| 50 | 93 | 12.1 | 2.9 | 90 | 332 |
| 60 | 130 | 13.4 | 2.6 | 91 | 323 |
| 70 | 160 | 14.7 | 2.4 | 87 | 329 |
| 80 | 150 | 14.1 | 2.5 | 55 | 239 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dibrov, G.; Ivanov, M.; Semyashkin, M.; Sudin, V.; Kagramanov, G. High-Pressure Aging of Asymmetric Torlon® Hollow Fibers for Helium Separation from Natural Gas. Fibers 2018, 6, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040083
Dibrov G, Ivanov M, Semyashkin M, Sudin V, Kagramanov G. High-Pressure Aging of Asymmetric Torlon® Hollow Fibers for Helium Separation from Natural Gas. Fibers. 2018; 6(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040083
Chicago/Turabian StyleDibrov, George, Mikhail Ivanov, Mikhail Semyashkin, Vladislav Sudin, and Georgy Kagramanov. 2018. "High-Pressure Aging of Asymmetric Torlon® Hollow Fibers for Helium Separation from Natural Gas" Fibers 6, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040083
APA StyleDibrov, G., Ivanov, M., Semyashkin, M., Sudin, V., & Kagramanov, G. (2018). High-Pressure Aging of Asymmetric Torlon® Hollow Fibers for Helium Separation from Natural Gas. Fibers, 6(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040083





