Abstract
The growing pollution of the environment with slowly decomposing waste, as well as the increasing drug resistance of pathogens, including the antibiotic resistance of bacteria, has led to a search for new solutions based on biodegradable and natural materials, which are known for their potential bacteriostatic properties. This study aimed to produce nanofibers by blowing from a polylactide (PLA) polymer solution containing natural compounds (e.g., beeswax, propolis). As a result of the conducted research, nanofibers were produced from PLA solutions containing various additives. The fibers’ mean diameter ranges from 0.36 to 2.38 µm, depending on the process parameters. To the authors’ knowledge, fibers were produced for the first time by blow spinning from a polymer solution containing propolis and beeswax.
1. Introduction
Nanofibers can be obtained through many techniques. One of the most widely used and relatively straightforward methods, wherein fibers are produced from a polymer solution under the influence of high electric potential forces, is electrospinning. Electrospinning makes it possible to produce nanofiber scaffolds with high porosity and specific surface areas, and it is widely used in biomedical engineering [1]. Electrospinning also allows the production of fibers from solutions of both vegetable proteins (e.g., zein [2], soy protein [3], and gluten [4]) and animal proteins (e.g., casein [5], gelatin [6], and collagen [7]). Nanofibers can be produced from many other proteins and polymers using the proper voltage and suitable solvent and selecting the correct process parameters in electrospinning [8,9]. Fibers fabricated by electrospinning can also be given bacteriostatic properties [10,11,12,13]. However, the disadvantage of electrospinning is the high voltage and low efficiency of the process using a single nozzle, although there are ways to scale up and thus increase efficiency [14]. Blow spinning is a less-known technique that is also capable of obtaining nanofibers. In blow spinning, there is no need to use high voltage. Hence, the method is safer for the operator than electrospinning. The high flexibility of process parameters allows for obtaining fibers from many polymers (e.g., poly(L-lactic acid) (PLA), poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), and poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)), including even proteins [15,16,17], provided that appropriate working conditions are selected. The disadvantage of blow spinning is the formation of irregularly arranged fibers (which can be minimized by choosing the proper collector rotation speed) and their larger diameter than those produced in electrospinning. However, the efficiency of blow spinning is much higher than electrospinning, making it more appropriate to use on an industrial scale, thus gaining utility. The mass of fibers obtained by electrospinning is 0.01–0.1 g/h (single nozzle) [18], while by blow spinning, it is even 0.98 g/h [19]. The most critical process parameters in blow spinning include polymer flow rate from the nozzle, compressed gas flow rate, nozzle diameter, nozzle-to-collector distance, and collector rotational speed [20,21]. Among the physicochemical parameters of the solution, the following are essential: polymer concentration, extensional viscosity, surface tension, and apparent viscosity [22]. The temperature and humidity in which blow spinning is carried out also affect its course. Considering the multitude of parameters that can be controlled to obtain fibers in the blow spinning method, the relatively high efficiency of the process, and the purpose of this study (obtaining fibers from a polymer solution containing non-polymer additives with bacteriostatic potential), it was decided to use blow spinning to produce fibers.
Many natural compounds/products have bacteriostatic, fungicidal, or virucidal properties [23]. For example, Bag and Chattopadhyay [24] showed that the essential oils of coriander, cumin, and mustard have antibacterial activity against Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, Micrococcus luteus, and Staphylococcus aureus. Dias et al. [25] indicated the antibacterial properties of wasabi against Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, S. aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Helicobacter pylori. Hasan et al. [26] proved the antibacterial effect of the ethanol extract of Trigona spp. propolis on Salmonella sp. Watanabe et al. [27] showed that Manuka honey exhibits antiviral properties against the influenza virus. The antibacterial effect of the blend of propolis and beeswax (1:1, v/v) on Candida albicans and S. aureus has also been proven [28]. Such products may become necessary considering increasing antimicrobial resistance, which applies to bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. A report published in 2016 shows that in 2050, nearly 10 million people will die from antimicrobial resistance [29]. Therefore, this study aimed to produce fibers by blow spinning from a polymer solution containing natural additives with bacteriostatic potential.
Propolis is one of five beekeeping products commonly known and widely used in medicinal care. The others are honey, beeswax, bee pollen, and beebread. Propolis is produced by various bee species (including honey worker bees) to prevent intruders from moving inside the hive but also to repair it and obtain stable conditions [30]. It is made by mixing bee saliva with plant extracts. It is composed of resins (60%), waxes (up to 30%), essential oils, pollen, minerals, vitamins, flavonoids, phenolic acids, and terpenoids [30,31].
Since bees produce propolis, its composition strongly depends on the environmental conditions in which the plant extracts were collected and the type of bees and plants from which the extracts were collected [31]. Propolis is a safe and non-toxic substance [30]; its safe dose for humans is 1.4 mg/kg per day or 70 mg/day [30]. However, the cytotoxic activities of propolis have been confirmed against numerous bacteria (B. subtilis, S. aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus viridans, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Corynebacterium diphtheria, E. coli, S. typhi, Salmonella paratyphi-A, Salmonella paratyphi-B, and Shigella flexneri), fungi (Candida, Saccharomyces, Cryptococcus), protozoa (Toxoplasma gondii, Trypanosoma cruzi, Trichomonas vaginalis), and viruses (herpes simplex type 1 (an acyclovir-resistant mutant), herpes simplex type 2, adenovirus type 2, influenza viruses A and B, vaccinia virus, and Newcastle disease virus) [32].
Beeswax was chosen as the second natural additive. Beeswax is produced by Apis mellifera and Apis cerana [28]. It is secreted by the wax glands of 12–18-day-old bees. After production, the wax is enriched with enzymes in the bees’ saliva, and only in this form is it used to build a comb.
Beeswax consists of alkanes (12–16%), wax esters (50–72%), free fatty acids (12–14%), and exogenous substances [28,33]. Due to the presence of exogenous substances, e.g., plant extracts or impurities, its composition, similar to propolis, may depend on the place of occurrence of bees and their species [28]. Beeswax is soluble in chloroform and carbon disulfide but insoluble in water [28].
The cytotoxic activities of crud beeswax have been confirmed against bacteria (S. aureus, Streptococcus epidermidis, S. pyogenes, B. subtilis, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli) and yeast (C. albicans) [28].
The background presented above indicates the need for the efficient and sustainable production of polymer nanofibers containing bacteriostatic additives like beeswax or propolis. We adapted the blow spinning process to produce such materials and investigated how processing parameters and the composition of working solutions affect the process. This is the first attempt to produce fibers in blow spinning from a polymer solution containing propolis and beeswax.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Poly(L-lactic acid) PLA (Ingeo™ 6202D) was supplied by NatureWorks® LLC (Minneapolis, MN, USA). PLA average molecular weight is 44,350 g∙mol−1 [33]. Acetone and chloroform were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Poznań, Poland). Propolis was obtained from Prokit (Kazimierów, Poland), and beeswax (100% natural, pure without additives) from Pallas (Bielsko-Biała, Poland).
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of PLA Solution
The PLA (4, 6, 8, and 10% w/w) solution in a mixture of chloroform/acetone in a ratio of 3/1 was prepared at room temperature in closed containers on a magnetic stirrer for 24 h.
2.2.2. Preparation of PLA/Beeswax Solution
The beeswax (3, 6, and 12% w/w) was added to the previously prepared PLA solution (10% w/w). The beeswax was ground in a mortar before being poured into the PLA solution. The PLA/beeswax mixture was placed on a magnetic stirrer in a sealed container for one hour. After this time, the PLA/beeswax mixture was transferred to a water bath set at 60 °C for 20 min. After the beeswax had dissolved, the mixture was left on a magnetic stirrer for 22 h at room temperature.
2.2.3. Preparation of PLA/Propolis Solution
The PLA/propolis solution (propolis concentrations of 1.5, 3, and 6% w/w) was prepared at room temperature with continuous agitation for 24 h. The propolis, like beeswax, was ground in a mortar before being added to the previously prepared PLA solution (10% w/w).
2.2.4. Rheological Measurement
The tests were carried out on an oscillatory rheometer (MCR 102, Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) in the plate–plate system with a gap of 1 mm. Due to work with volatile solvents (3/1 chloroform/acetone mixture), the test was carried out on a rheometer equipped with an adapter for rapidly evaporating solvents. The attachment slows down evaporation but does not eliminate it. Therefore, the measurement was shortened to 30 s; such a short measurement time allowed us to obtain repeatable and reliable results. The tests were conducted for PLA/beeswax and PLA/propolis blends at 20 °C and 20, 22, and 24 °C for pure PLA.
The oscillatory rheometer tests were conducted to determine the apparent viscosity as a function of the shear rate of the PLA mixtures used in the polymer blow spinning process. The dependence of apparent viscosity as a function of shear rate characterizes the solution used in blow spinning at the stage of its flow through the syringe and nozzle. However, the extensional viscosity of the blown solution is also essential in the polymer solution blowing process. Extensional viscosity affects stretching the polymer filament and forming the fiber. However, extensional viscosity measurements are challenging due to problems with maintaining constant values of the tensile force acting on the sample, which is why this study focused only on apparent viscosity measurements.
2.2.5. Blow Spinning Process
The apparatus used in the blow spinning method consists of a coaxial nozzle (the inner diameter is 1 mm; the outer diameter is 5 mm), precise infusion pump (Legato270, KDScientific, Holliston, MA, USA), a compressed air source, a mass flow controller (SFC5500–200 slm, Sensirion, Zurich, Switzerland), and a collector.
Compressed air was supplied to the nozzle through a mass flow controller at a 100–200 L/min flow rate. The polymer was fed to the nozzle using a syringe pump with a flow rate of 0.2–3 mL/min. The fibers were collected on a 13 × 21 cm cylindrical collector 37 cm from the nozzle outlet. The collector was covered with a base material (21 × 41 cm). The collector rotated at 18 rpm around its longer axis. Its axis was parallel to the ground and perpendicular to the direction of the airflow. The process was carried out at a constant temperature of 20 °C.
2.2.6. Fibers’ Morphology
The morphology of the obtained fibers was analyzed using a scanning electron microscope (TM-1000, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Fibers from a minimum of three areas were taken from each sample produced. Before taking the SEM image, the fibers were sputtered with a gold layer (K550X EMITECH Quorum, Heathfield, East Sussex, UK). The mean fiber diameter was determined based on a minimum of 50 fibers from all photos taken for a given experiment variant.
2.2.7. Fiber’s Composition
The presence of the specific functional groups of beeswax and propolis within fibers of PLA prepared from PLA/beeswax and PLA/propolis was determined using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy with the Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) mode. We used a Nicolet 6700TM spectrometer with OMNIC 8.3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and recorded spectra ranging from 4000 to 400 cm–1 in the wavenumber range. One spectrum integrated from 32 scans for each tested material was selected for presentation as a representative spectrum.
3. Results and Discussion
When blowing from a polymer solution, the fibers are formed due to the interaction of gas (usually air) with the polymer flowing out of the nozzle. The expansion of the gas to atmospheric pressure (due to the outflow from the nozzle) causes an increase in the polymer flow velocity at the nozzle outlet, which leads to the formation of a polymer droplet. As a result of contact with the flowing gas, which generates high shear forces, the polymer droplet changes its shape to a conical one. When the shear force exceeds the value of the surface tension of the polymer, a polymer stream is formed, from which the solvent evaporates on the way to the collector, and a fiber is formed. The fiber is deposited on the collector [34].
Thus, the fiber formation process will be most affected by three factors: polymer flow, air flow, and the surface tension of the polymer solution. Unfortunately, in the case of polymers dissolved in volatile solvents (such as, for example, the chloroform/acetone solution used in this study), the determination of the surface tension (due to the long test time) is complicated and subject to a significant error. Therefore, when looking for a fiber-forming window (i.e., process parameters at which fibers are generated), one should focus on linking the airflow at the nozzle outlet with the polymer flow. An increase in the polymer flow velocity should lead to a rise in the fibers’ diameter due to a larger volume of polymer droplets accumulating at the nozzle outlet and, thus, a lower value of the air shear force acting per drop area unit [35]. However, too much polymer flow can cause solidification at the exit of the nozzle. In turn, a polymer flow rate that is too low may result in the formation of shorter fibers or their absence due to the lack of continuity in maintaining the droplet at the nozzle outlet. The influence of the gas flow on the fiber formation process results from the shear stresses generated by the gas, which cause the formation of a polymer stream, and from the solvent evaporation taking place on the way to the collector, which is the more intense, the higher the gas flow velocity. It has been observed that increasing the gas flow rate (by increasing the pressure) causes a decrease in the average fiber diameter.
Solution blowing of pure PLA polymer is well described in the literature (e.g., [36]). This process is often carried out at a polymer flow of 0.5 mL/min and an airflow of 200 L/min. However, for new blends, the blowing of which has yet to be described in the literature so far, finding the fiber-forming window boils down to performing a series of experiments with variable values of the polymer and air flow rate. That is why the blow test started with pure PLA’s blowing parameters for each analyzed solution (PLA/beeswax, PLA/propolis). Then, the airflow and polymer flow rates were changed until fiber formation was observed. When fibers were observed, the blowing process was continued for 5 min to collect the appropriate number of fibers for morphological analysis.
Next, another set of parameters was searched for to obtain fibers. For each analyzed solution, three sets of parameters were found at which it was possible to get fibers. The blowing parameters presented in this article are certainly not all possible air and polymer flow rates at which it is possible to obtain fibers from the tested solutions.
3.1. Rheology of Pure PLA and with Additives
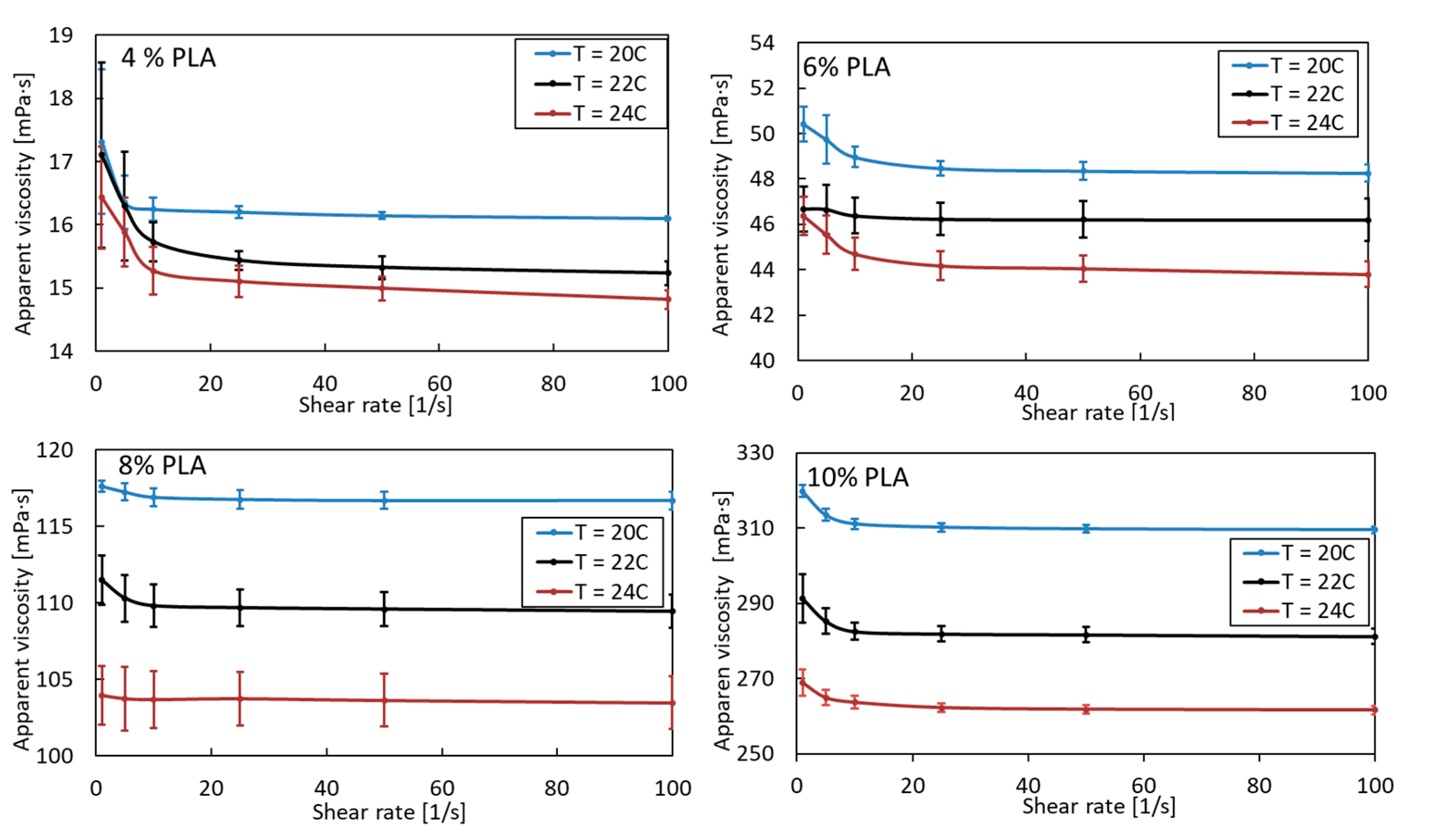
A pure PLA solution is a non-Newtonian shear-thinning fluid. Its apparent viscosity, as expected, increases due to the greater entanglement of polymer chains with increasing concentration and decreasing temperature (Figure 1). As the concentration of PLA increases, the effect of temperature also becomes apparent. The viscosity of 4% PLA at 20 °C and 24 °C differs by 7%. For subsequent PLA solutions (6, 8, and 10%), these values are 9, 11, and 15%, respectively. Such a considerable change in viscosity with a relatively small temperature change can significantly affect the morphology of the obtained fibers. Therefore, the blowing process should be carried out at a constant, uniform ambient temperature, assuming the blown PLA solution is at ambient temperature, especially when the high-concentration PLA solution is blowing.
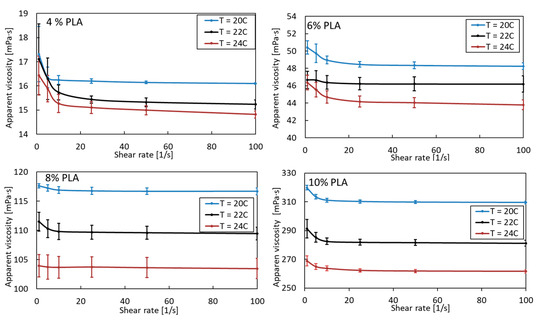
Figure 1.
Apparent viscosity as a function of shear rate for pure PLA in various concentrations and temperature.
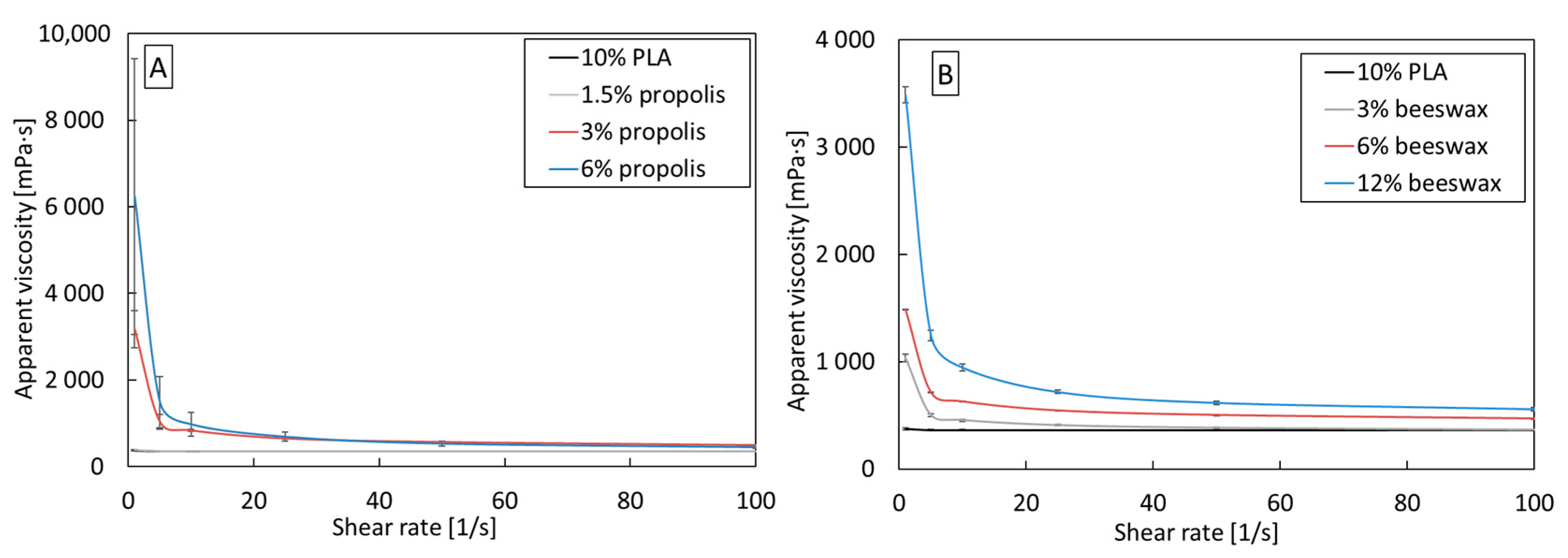
PLA/beeswax and PLA/propolis blends are, like pure PLA, non-Newtonian shear-thinning fluids (Figure 2). Adding beeswax and propolis to each tested concentration increases the apparent viscosity compared to pure 10% PLA. The increase is from three to twenty times at low shear rates, but as the shear rate increases, the differences in viscosity decrease. The increase in viscosity may result from increased entanglement of PLA chains due to additives.
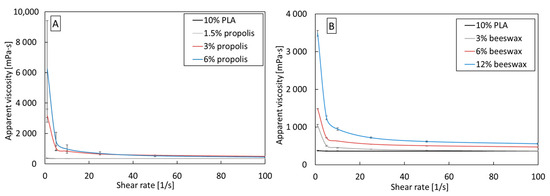
Figure 2.
Apparent viscosity as a function of shear rate for (A) PLA/propolis and (B) PLA/beeswax in various concentrations.
3.2. Solution Blowing of PLA/Beeswax and PLA/Propolis Blends
3.2.1. PLA/Beeswax
Fibers from a PLA solution with the addition of beeswax were obtained for all three analyzed concentrations of beeswax with the parameters listed in Table 1. The table also includes the average fiber diameters obtained with the given blowing parameters. Fibers from a PLA solution containing beeswax are obtained at relatively high values of polymer flow rate from the nozzle (for pure 10% PLA, the fibers are formed at a polymer flow rate of 0.5 mL/min and an airflow of 200 L/min). All analyzed PLA/beeswax blends have a high apparent viscosity value at a low shear rate, which translates into high values of polymer flow resistance and, thus, possibly the need to use a higher polymer flow to produce a drop at the nozzle outlet. Apparent viscosity is only one of the three physicochemical parameters of the solution affecting the blowing process (next to extensional viscosity and surface tension). Therefore, the observed effect is undoubtedly a result of these three quantities; interpreting the observed phenomena is complex without knowing them.

Table 1.
The solution blow parameters for PLA/beeswax blends.
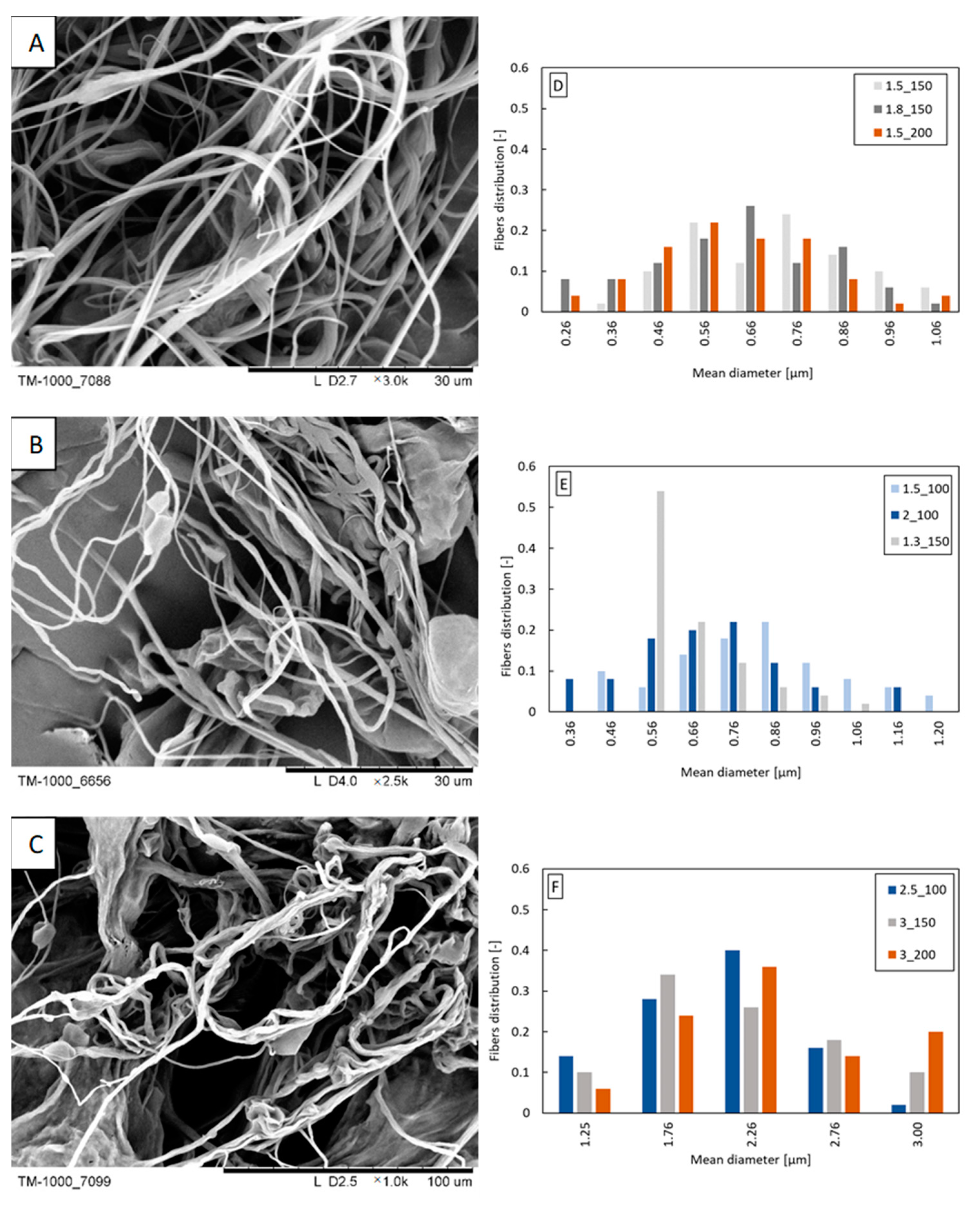
With the increase in the concentration of beeswax in the blend, an increase in the mean fiber diameter and width of the fiber diameter distribution is observed (Figure 3D–F). For the PLA/12% beeswax blend, fibers with a diameter of over 2 μm dominate (Figure 3F), while for the PLA/3% beeswax and PLA/6% beeswax blends (Figure 3D,E), dominate 0.5–0.9 μm fibers. As the beeswax content increases, the fibers become more “twisted” and stick together (Figure 3A–C).
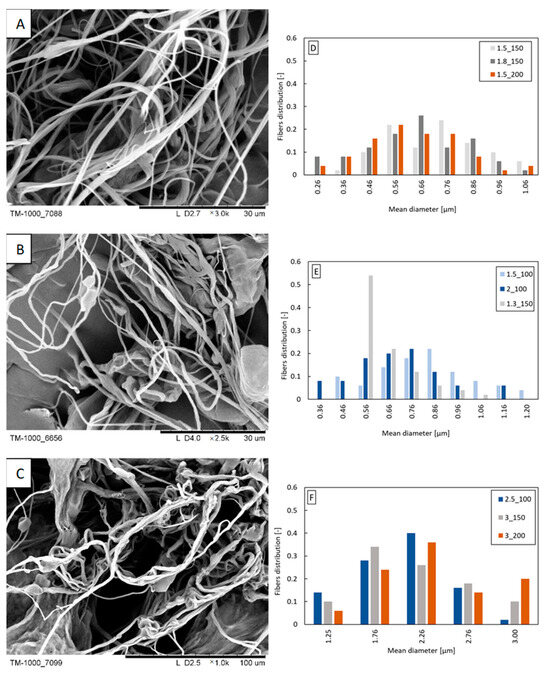
Figure 3.
Exemplary fibers: (A) PLA/3% beeswax (polymer flow 1.5 mL/min; airflow 150 L/min); (B) PLA/6% beeswax (polymer flow 1.5 mL/min; airflow 100 L/min); (C) PLA/12% beeswax (polymer flow 3.0 mL/min; airflow 150 L/min). Fiber diameter distribution obtained from the following: (D) PLA/3% beeswax; (E) PLA/6% beeswax; (F) PLA/12%beeswax. The markings in the legends correspond to the following blowing parameters: polymer flow_airflow (e.g., polymer flow 1.5 mL/min and airflow 150 L/min: 1.5_150).
3.2.2. PLA/Propolis
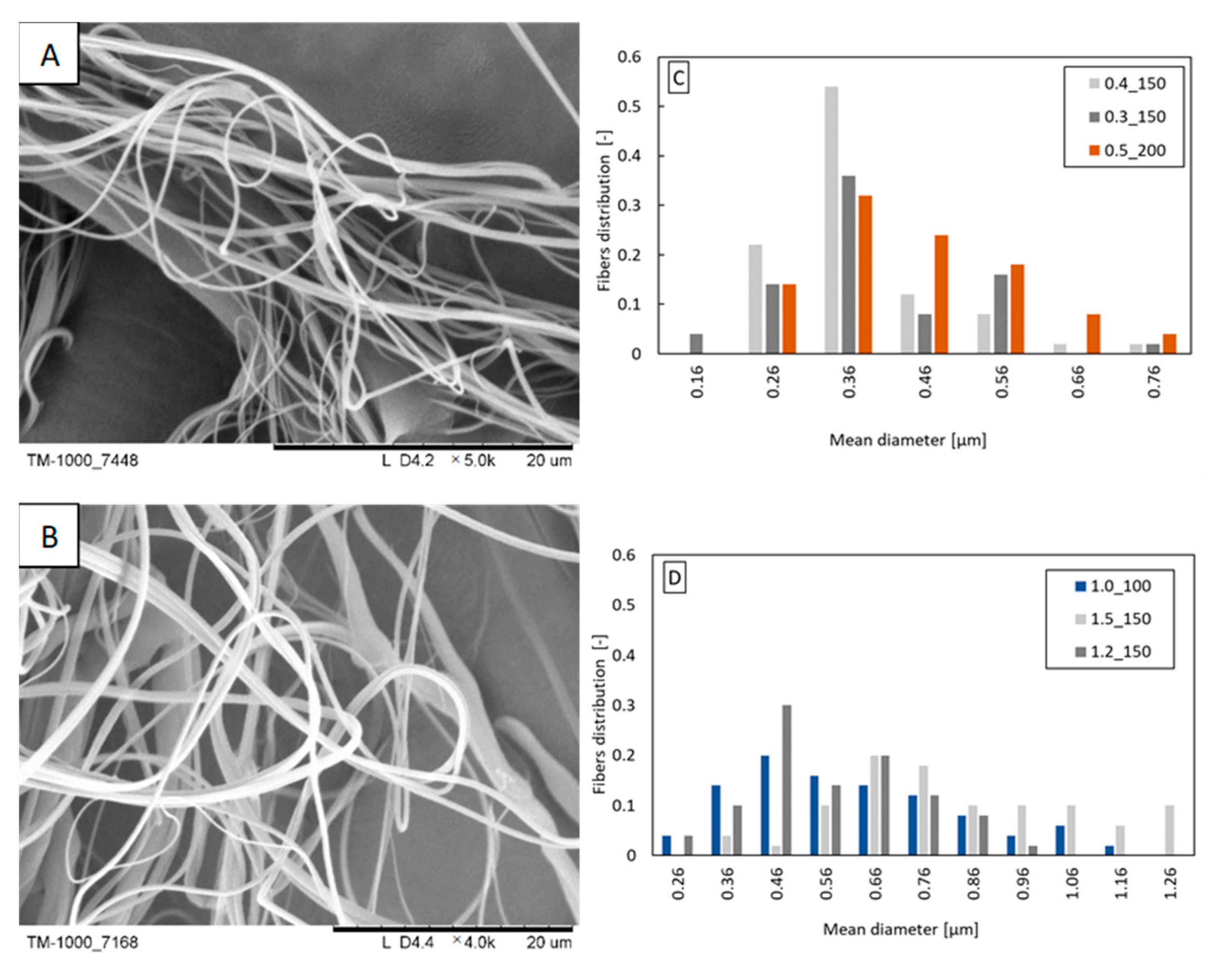
Fibers were obtained from two analyzed concentrations of propolis in PLA solution (1.5 and 3%). Most likely, too high a concentration of propolis (undissolved propolis residues could block the nozzle) was the reason why fibers were not formed from the PLA/6% propolis solution. The blown parameters are shown in Table 2. At a concentration of 1.5% propolis in the PLA/propolis blend, the blow parameters are like those of pure 10% PLA, which may result from similar physicochemical properties of the PLA/1.5% propolis and 10% PLA. Increasing the proportion of propolis in the blend increases the apparent viscosity of the solution, which, as in the case of beeswax, causes an increase in flow resistance and the need to use higher polymer flow rates to be able to form polymer drops at the outlet of the nozzle. Depending on the concentration of propolis, fibers with a diameter in the range of 0.3–0.7 μm dominate the distributions (Figure 4C,D). The width of the distribution is not dependent on the concentration of propolis in the blend. The increase in the concentration of propolis did not affect the appearance of the fibers (Figure 4A,B). The fibers have a smooth, even surface.

Table 2.
The solution blow parameters for PLA/propolis blends.
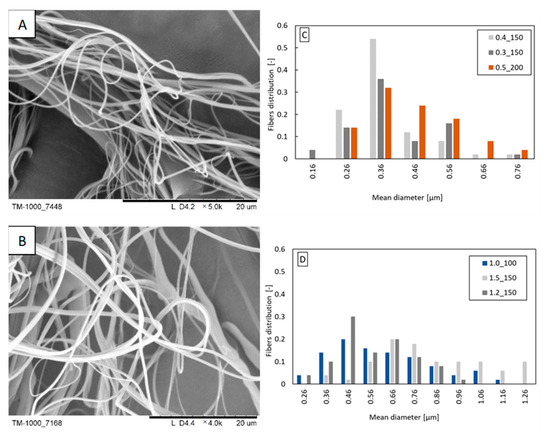
Figure 4.
Exemplary fibers: (A) PLA/1.5% propolis (polymer flow 0.4 mL/min; airflow 150 L/min); (B) PLA/3% propolis (polymer flow 1.5 mL/min; airflow 150 L/min). Fiber diameter distribution obtained from the following: (C) PLA/1.5% propolis; (D) PLA/3% propolis. The markings in the legends correspond to the following blowing parameters: polymer flow_airflow (e.g., polymer flow 0.4 mL/min and airflow 150 L/min: 0.4_150).
3.2.3. Composition of PLA/Beeswax and PLA/Propolis
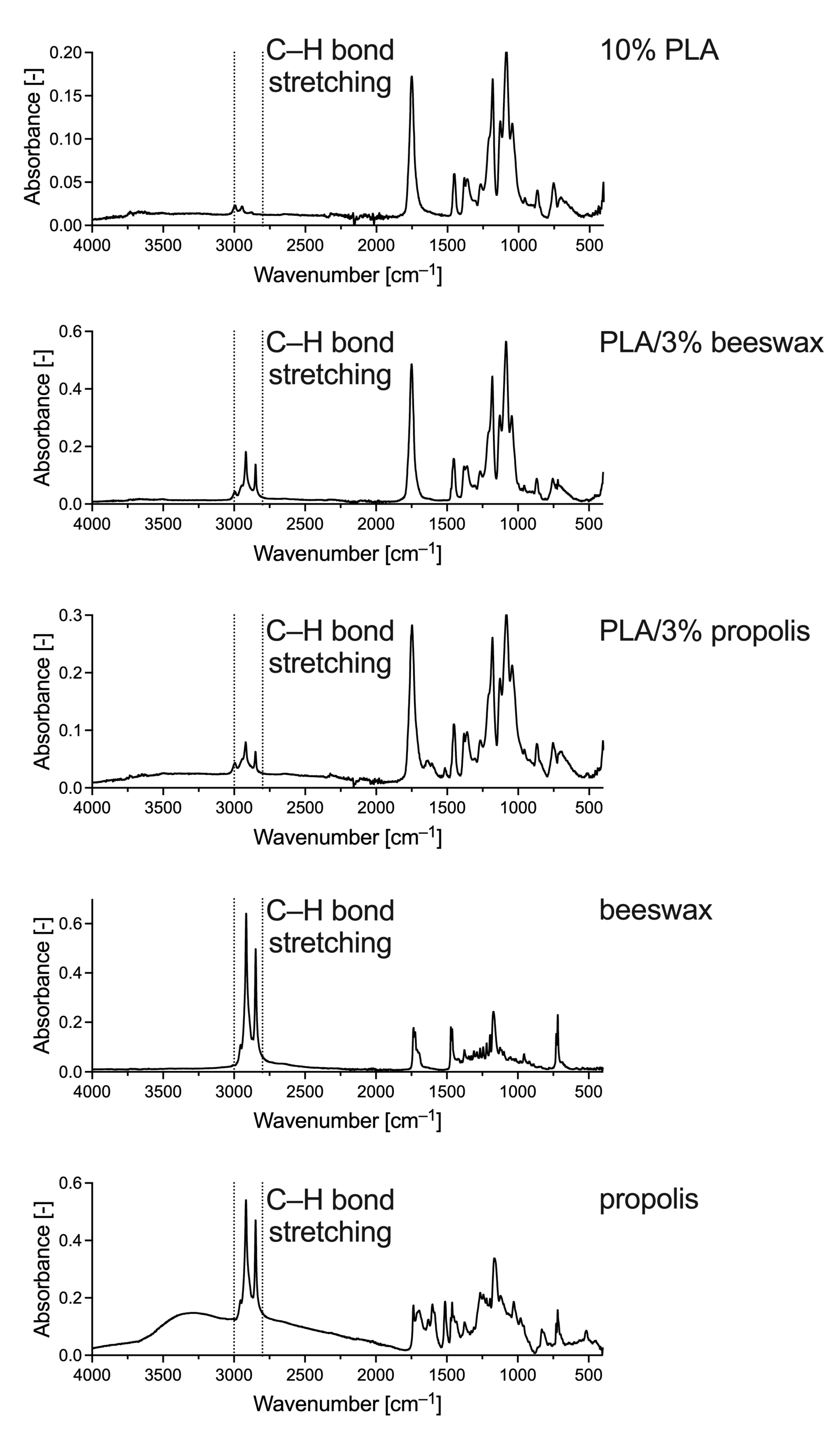
To determine the presence of natural additives in the PLA nanofiber solution blown in the present study, FTIR-ATR was used. This technique detects specific groups of compounds in analyzed samples. The PLA spectrum shows the same characteristic peaks from 1780 to 1760 cm–1 as those for PLA solution blow-spun fibers described by Wojasiński and Ciach and associated with ester bonds in the polyester structure (Figure 5) [37]. Hence, there was no significant change in the composition of PLA during the solution blowing process, as expected. The FTIR spectra changed with the addition of beeswax and propolis. Peaks in the wavenumber range of approximately 1300–1100 cm–1 were also responsible for the characteristic polyester bonds. However, in PLA/beeswax and PLA/propolis samples, they are mixed with signals from alkanes that may appear in the sample. The peaks at 2995 and 2945 cm–1 should also be assigned to alkanes, corresponding to the fatty acid chains in beeswax and propolis (Figure 5). The addition of beeswax to PLA did not change the right side of the spectrum. However, propolis must still have some double or triple bonds because changes in the spectrum appear at 1638 and 1516 cm–1, which are also visible in the spectrum of pure propolis. However, both additions, beeswax and propolis, gave the characteristic signal from stretching vibrations of C–H bonds with peaks in the wavenumber range of 3000–2800 cm–1, that is, peaks associated with longer carbon chains in saturated carbohydrates, most prominently visible in the spectra of pure additives (Figure 5). Thus, we confirmed the presence of the additives in PLA/beeswax and PLA/propolis.
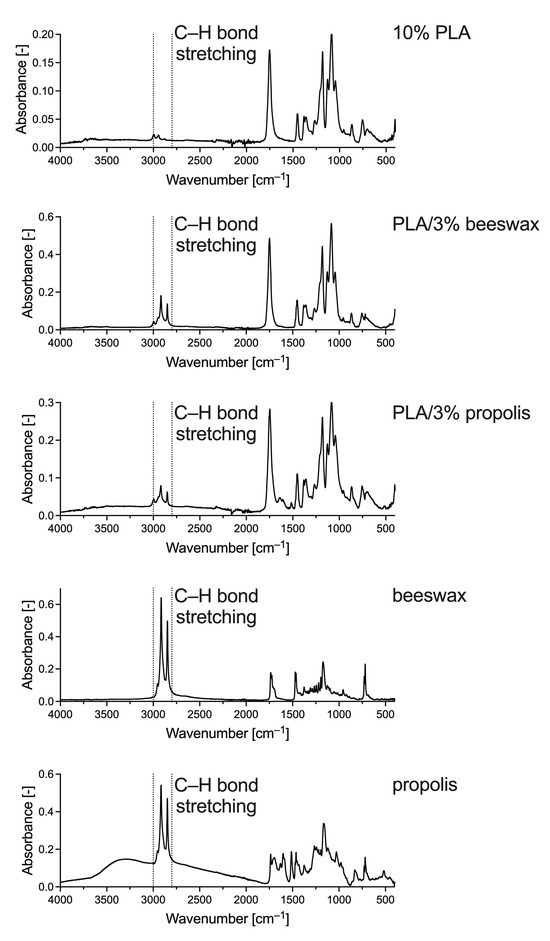
Figure 5.
FTIR-ATR spectra of exemplary samples of 10% PLA, PLA/3% beeswax, PLA/3% propolis, pure beeswax, and pure propolis.
3.2.4. Parameter Analysis
The morphology of fibers obtained in the polymer solution blowing process depends on many parameters. It is known that an increase in the concentration of the polymer should result in the formation of fibers with a larger diameter. An increase in the airflow rate or its pressure should lead to obtaining fibers with a smaller diameter. An increase in the flow rate of the polymer results in an increase in the diameter of the fibers. In the process of blowing from a polymer solution, the distance of the nozzle from the collector and the speed of its rotation will also be critical. Primarily, the efficiency of fiber capture and the degree of their order will depend on these parameters. In the case of solutions containing non-polymer additives, determining the influence of a given parameter on the morphology of the obtained fibers is difficult due to the additional interactions of the additive used with polymer chains.
Since the formation of fibers in the blowing process depends on interactions between the polymer solution flowing out of the nozzle and the gas flowing around them, we decided to use the ratio of Reynolds numbers (Re) for air and polymer solution to describe these quantities. The general relation to the Re number is described as follows:
where u—linear velocity (m/s); d—diameter (m); ρ—density (kg/m3); µ—dynamic viscosity (Pa·s).
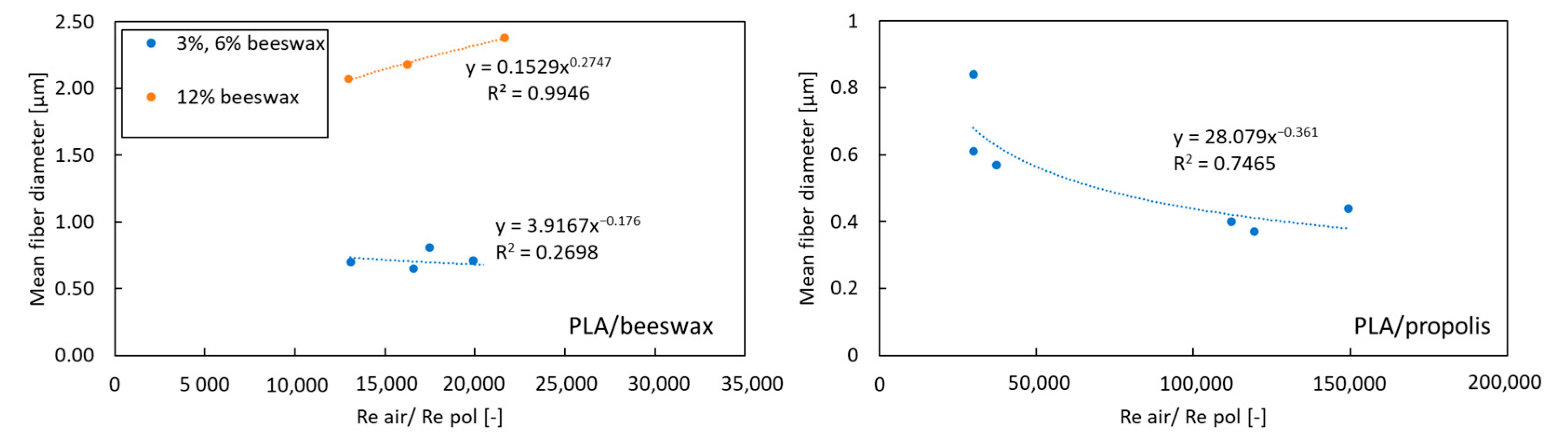
The velocity of air and the polymer solution was determined based on the volumetric flow rate and the known geometry of the system. The equivalent diameter was used to determine Re for the air. The dynamic viscosity of the polymer solution with additives was determined based on the rheological measurements described above in the present paper. All determined values of the Re number for the polymer solution were in the range of 0.012–0.114, and for air, they were in the range of 1235–2470. The mean fiber diameter as a function of Reair/Repol is shown in Figure 6.
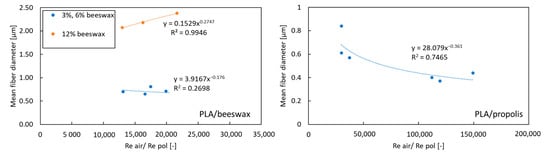
Figure 6.
The mean fiber diameter as a function of Reair/Repol.
The obtained relationships (Figure 6) show that there is no standard key to predicting the size of fibers depending on the process parameters when using non-polymer additives. For propolis, a decrease in the average fiber diameter is observed with an increase in the Reair/Repol ratio. In the case of beeswax, for high concentrations (12%) [orange dots on left chart on Figure 6], an increase in average fiber diameter is observed with an increasing Reair/Repol ratio. In comparison, for lower concentrations (3% and 6%) (blue dots on left chart on Figure 6), the Reair/Repol ratio value does not affect the average fiber diameter.
4. Conclusions
As a result of the conducted research, nanofibers were produced from PLA solutions containing propolis and beeswax. The fibers’ mean diameter ranges from 0.36 to 2.38 µm, depending on the process parameters. The blowing parameter range was 100–200 L/min for airflow and 0.3–3 L/min for polymer flow. The fibers obtained by blowing from the PLA/propolis solution had a smaller diameter than the fibers obtained from PLA/beeswax. FTIR tests of the obtained fibers confirmed the presence of functional groups characteristic of beeswax and propolis. To the authors’ knowledge, fibers were produced for the first time from a solution containing propolis and beeswax. The propolis and beeswax used in the research have yet to be analyzed for composition, which may vary depending on the species of bees, their diet, and their living environment. However, considering that propolis and beeswax tested by scientists from different parts of the world showed bacteriostatic properties, it can be assumed that the variability of the composition does not significantly affect the cytotoxic properties. In the following study, we plan to evaluate the bacteriostatic effect of fibers containing beeswax and propolis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P. and A.M.; methodology, A.P. and A.M.; investigation, M.K., A.S., M.W. and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P.; writing—review and editing, A.P., M.K., A.S., M.W. and A.M.; supervision, A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mirbagheri, M.S.; Akhavan-Mahdavi, S.; Hasan, A.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Jafari, S.M. Propolis-loaded nanofiber scaffolds based on polyvinyl alcohol and polycaprolactone. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 642, 123186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, T.I.; Toyohara, K.; Minematsu, H. Preparation of ultrafine fibrous zein membranes via electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. Preparation and properties of electrospun soy protein isolate/polyethylene oxide nanofiber membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2012, 4, 4331–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.M.; Patzer, V.L.; Dersch, R.; Wendorff, J.; da Silveira, N.P.; Pranke, P. A novel globular protein electrospun fiber mat with the addition of polysilsesquioxane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Hsieh, Y.L. Ultra-high surface fibrous membranes from electrospinning of natural proteins: Casein and lipase enzyme. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Chi, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chen, K.-Y.; Chen, P.-L.; Yao, C.-H. Evaluation of proanthocyanidin-crosslinked electrospun gelatin nanofibers for drug delivering system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.P.; Shanmugasundaram, S.; Masih, P.; Pandya, D.; Amara, S.; Collins, G.; Arinzeh, T.L. An investigation of common crosslinking agents on the stability of electrospun collagen scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 103, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babitha, S.; Rachita, L.; Karthikeyan, K.; Shoba, E.; Janani, I.; Poornima, B.; Sai, K.P. Electrospun protein nanofiber in Healthcare: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 52–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Gulino, E.F.; Citarrella, M.C. Biodegradable Membrane with High Porosity and Hollow Structure Obtained via Electrospinning for Oil Spill Clean-up Application. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewska, I.; Czapka, T. Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers with Antimicrobial Activity. Polymers 2022, 14, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, M.D.; Simin, S.; Azin, J. Electrospun nanofibers as versatile platform in antimicrobial delivery: Current state and perspectives. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.M.; Hassanin, A.H.; El-kaliuoby, M.I.; Omran, N.; Gamal, M.; El-Khatib, A.M.; Kandas, I.; Shehata, N. Innovative antibacterial electrospun nanofibers mats depending on piezoelectric generation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaffaro, R.; Settanni, L.; Gulino, E.F. Release Profiles of Carvacrol or Chlorhexidine of PLA/Graphene Nanoplatelets Membranes Prepared Using Electrospinning and Solution Blow Spinning: A Comparative Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, P.; Szabó, E.; Domokos, A.; Hirsch, E.; Galata, D.; Farkas, B.; Démuth, B.; Andersen, S.K.; Vigh, T.; Verreck, G.; et al. Scale-up of electrospinning technology: Applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha-Ray, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yarin, A.L.; Davis, S.C.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Solution blowing of soy protein fibers. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha-Ray, S.; Khansari, S.; Yarin, A.L.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Effect of Chemical and Physical Cross-Linking on Tensile Characteristics of Solution-Blown Soy Protein Nanofiber Mats. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 15109–15121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penconek, A.; Kasak, D.; Moskal, A. Soy Protein Nanofibers Obtained by Solution Blow Spinning. Processes 2023, 11, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abduljabbar, A.; Farooq, I. Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers: Processing, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penconek, A.; Jackiewicz-Zagórska, A.; Przekop, R.; Moskal, A. Fibrous Structures Produced Using the Solution Blow-Spinning Technique for Advanced Air Filtration Process. Materials 2023, 16, 7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Orts, W.J.; Mattoso, L.H. Solution blow spinning: A new method to produce micro- and nanofibres from polymer solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Systematic investigation on parameters of solution blown micro/nanofibers using response surface methodology based on box-Behnken design. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 2, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojasiński, M.; Ciach, T. Shear and Elongational Rheometry for Determination of Spinnability Window of Polymer Solutions in Solution Blow Spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, D.; Enciu, A.M.; Mateescu, A.L.; Ion, A.C.; Brezeanu, A.C.; Stan, D.; Tanase, C. Natural Compounds with Antimicrobial and Antiviral Effect and Nanocarriers Used for Their Transportation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 723233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bag, A.; Chattopadhyay, R.R. Evaluation of Synergistic Antibacterial and Antioxidant Efficacy of Essential Oils of Spices and Herbs in Combination. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, C.; Aires, A.; Saavedra, M.J. Antimicrobial activity of isothiocyanates from cruciferous plants against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19552–19561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, Z.; Artika, I.M.; Fatoni, A.; Kuswandi; Haryanto, B. Antimicrobial Activity of Propolis Trigona Spp. from Bukittinggi West Sumatera against Salmonella Spp. Chem. Progr. 2011, 4, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Rahmasari, R.; Matsunaga, A.; Haruyama, T.; Kobayashi, N. Anti-influenza viral effects of honey in vitro: Potent high activity of manuka honey. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, F.; Cilia, G.; Turchi, B.; Felicioli, A. Beeswax: A minireview of its antimicrobial activity and its application in medicine. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations: Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Government of the United Kingdom: London, UK, 2016. Available online: https://apo.org.au/node/63983 (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Wieczorek, P.P.; Hudz, N.; Yezerska, O.; Horčinová-Sedláčková, V.; Shanaida, M.; Korytniuk, O.; Jasicka-Misiak, I. Chemical Variability and Pharmacological Potential of Propolis as a Source for the Development of New Pharmaceutical Products. Molecules 2022, 27, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, Z.; Naseem, M.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S.; Zohaib, S. Propolis: A natural biomaterial for dental and oral healthcare. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2017, 11, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Burdock, G.A. Review of the biological properties and toxicity of bee propolis (propolis). Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchwald, R.; Breed, M.D.; Greenberg, A.R.; Otis, G. Interspecific variation in beeswax as a biological construction material. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 3984–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.-X.; Huang, L.-P.; Yu, M.; Long, Y.-Z. Recent progress and challenges in solution blow spinning. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhuang, X.; Tao, X.; Cheng, B.; Kang, W. Solution blowing nylon 6 nanofiber mats for air filtration. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackiewicz-Zagórska, A.; Mika, K.; Penconek, A.; Moskal, A. Non-Woven Filters Made of PLA via Solution Blowing Process for Effective Aerosol Nanoparticles Filtration. Processes 2022, 10, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojasiński, M.; Ciach, T. Solution Blow Spun Poly-L-Lactic Acid/Ceramic Fibrous Composites for Bone Implant Applications. Chem. Proc. Eng. 2021, 42, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).