Surface Modification of Commingled Flax/PP and Flax/PLA Fibres by Silane or Atmospheric Argon Plasma Exposure to Improve Fibre–Matrix Adhesion in Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Fabrics
- Commingled Flax/PP woven fabric (50/50 wt-%); 465 g/m2 area density
- Commingled Flax/PLA woven fabric (50/50 wt-%); 493 g/m2 area density
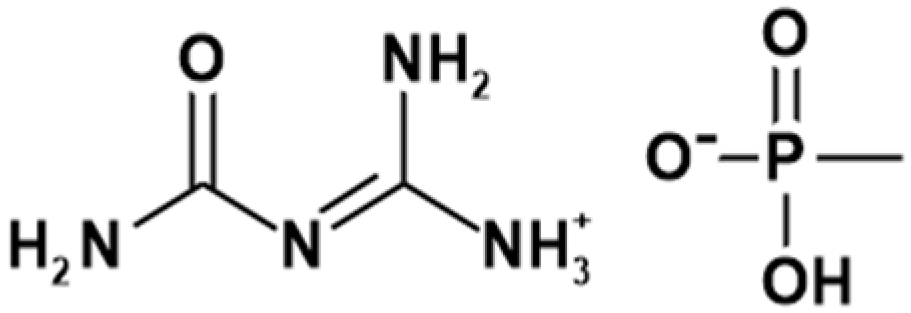
2.1.2. Flame Retardant (FR)
2.1.3. Silane Derivatives
2.2. Fabric Treatments
2.2.1. Flame Retardant Application
2.2.2. Silane Treatment
2.2.3. Plasma Treatment
2.2.4. The Combination of Silane and Plasma Treatments for Flame Retarded Fabrics
2.3. Composite Preparation
2.3.1. Single Layered Laminates for Identifying Optimised Conditions of Silane and Plasma Treatments
2.3.2. Laminates for Fibre/Matrix Interfacial Adhesion Characterisation
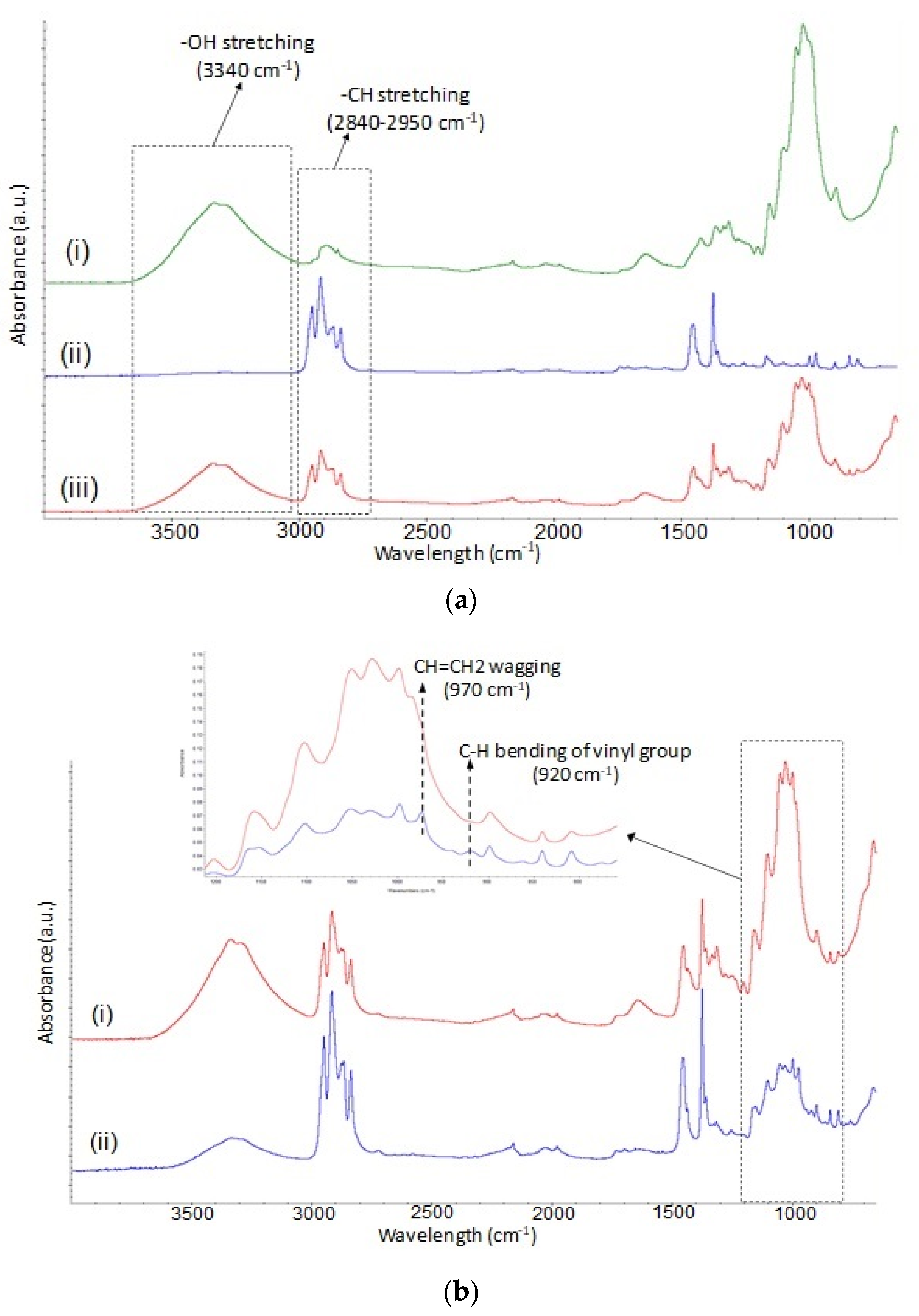
2.4. Surface Characterisation of Flax/PP and Flax/PLA Fabrics
2.5. Mechanical Characterisation of Composite Laminates
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimisation of Silane and Plasma Treatment Conditions
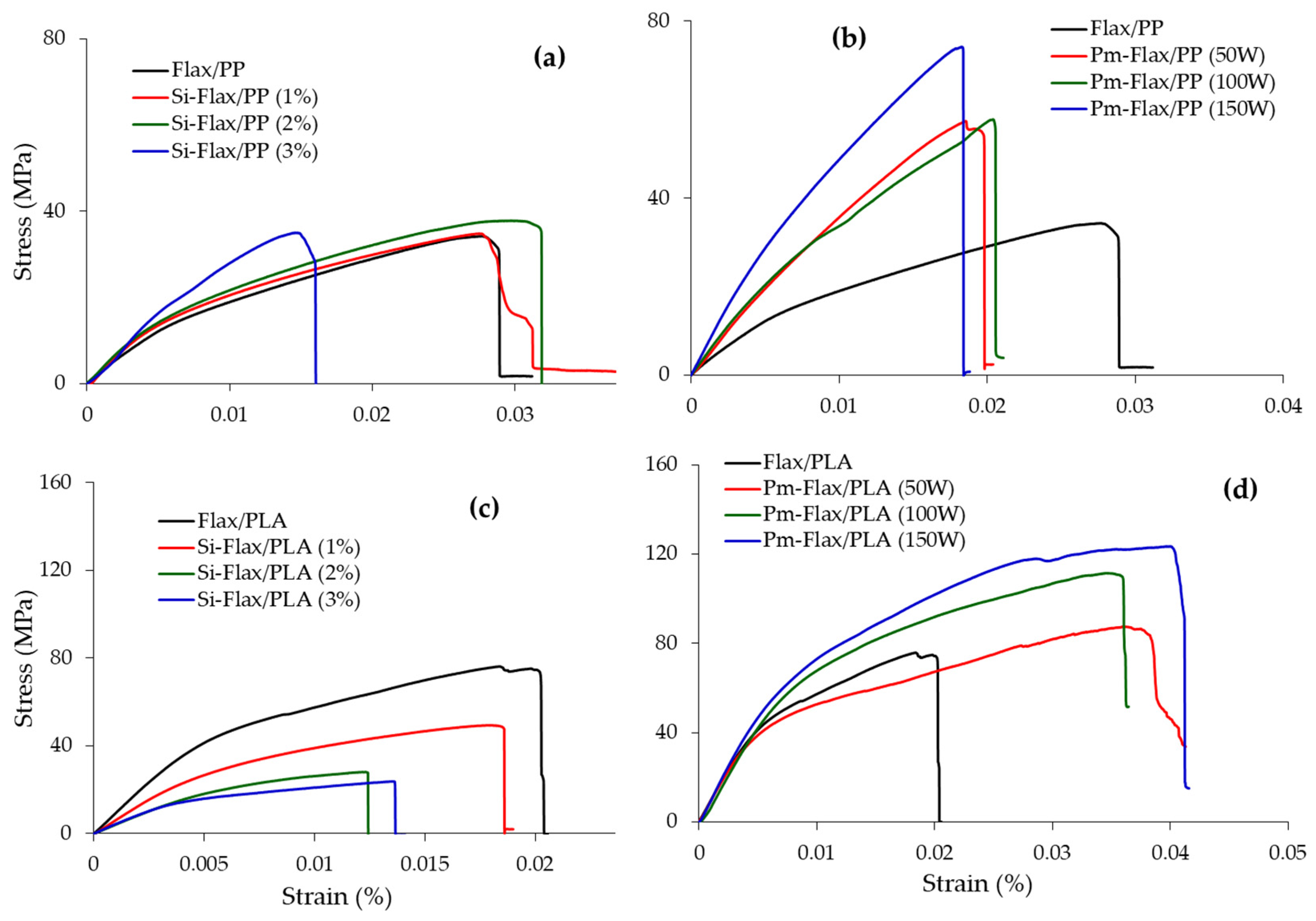
3.1.1. Optimisation of Silane Treatment
Flax/PP Composites
Flax/PLA Composites
3.1.2. Optimisation of Plasma Treatment
Flax/PP Composites
Flax/PLA Composites
3.2. Fibre/Matrix Interfacial Adhesion in FR-Treated Flax/PP and Flax/PLA Laminates
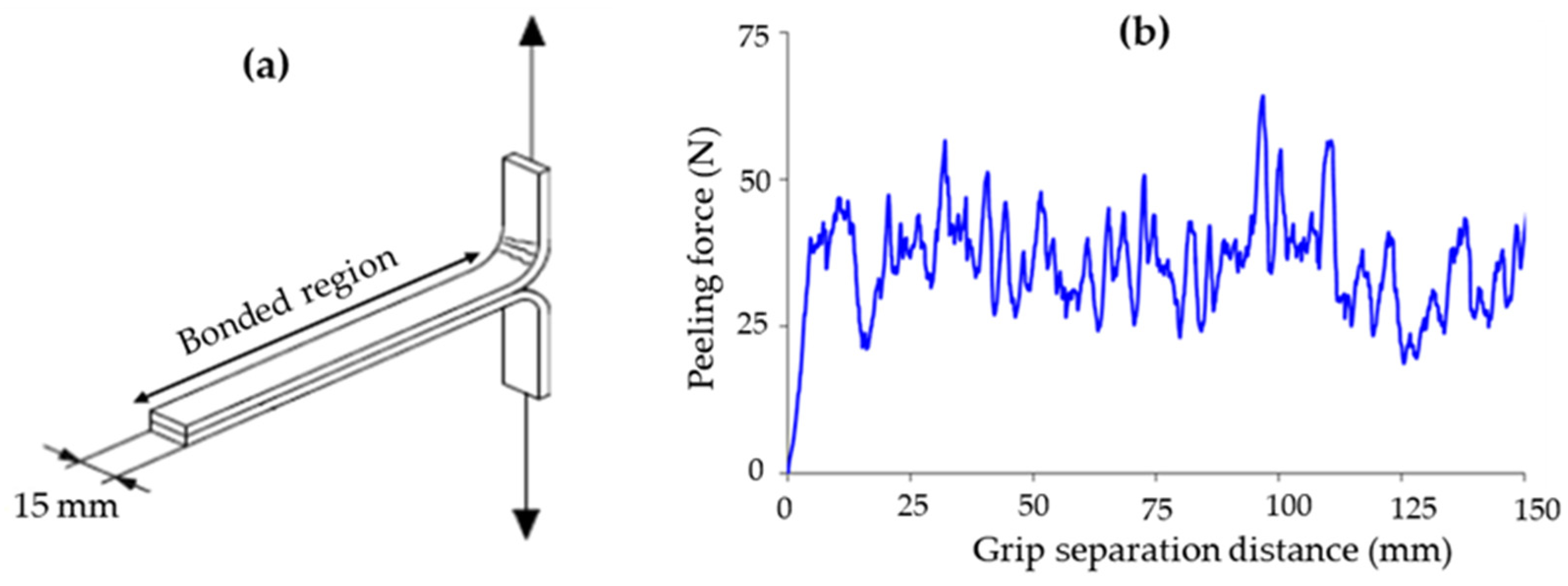
3.2.1. Fibre/Matrix Interfacial Adhesion by Peel Strength Testing
Flax/PP Composites
Flax/PLA Composites
3.2.2. Fibre/Matrix Interfacial Adhesion by Flexural Testing
Flax/PP Composites
Flax/PLA Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, Y.; Hill, C.A.S.; Xiao, Z.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Silane coupling agents used for natural fibre/polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A 2010, 41, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: An overview. Compos. Part B 2012, 43, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salon, M.B.; Abdelmouleh, M.; Boufi, S.; Belgacem, M.N.; Gandini, A. Silane adsorption onto cellulose fibers: Hydrolysis and condensation reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 289, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, B.K.; Mistik, S.I.; Pornwannachai, W.; Horrocks, A.R. Effects of water and chemical solutions ageing on the physical, mechanical, thermal and flammability properties of natural fibre-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Molecules 2021, 26, 4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, R.; Wakeel, S.; Khan, N.Z.; Siddiquee, A.N.; Verma, S.L.; Khan, Z.A. Surface treatments of plant fibers and their effects on mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced composites: A review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2019, 38, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulvel, S.; Reddy, D.M.; Rufuss, D.D.W.; Akinaga, T. A comprehensive review on mechanical and surface characteristics of composites reinforced with coated fibres. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, L.; Krishnaraj, V.; Sathish, S.; Gokulkumar, S.; Karthi, N.; Rajeshkumar, L.; Balaji, D.; Vigneshkumar, N.; Elango, K.S. A review on natural fiber reinforced hybrid composites: Chemical treatments, manufacturing methods and potential applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 8080–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Kaith, B.S.; Kaur, I. Pretreatments of natural fibers and their application as reinforcing material in polymer composites: A Review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1253–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Thapa, A.; Ulven, C.A. Effect of surface treatments on interfacial properties of flax fiber-reinforced composites. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2013, 22, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Ulven, C.; Huo, S. Effect of chemical treatment of flax fiber and resin manipulation on service life of their composites using time-temperature superposition. Polymers 2015, 7, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, U.S.; Dhamarikar, M.; Dharkar, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Kumrawat, A.; Giri, N.; Tiwari, S.; Namdeo, R. Plasma modification of natural fiber: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozaci, E.; Sever, K.; Sarikanat, M.; Seki, Y.; Demir, A.; Ozdogan, E.; Tavman, I. Effects of the atmospheric plasma treatments on surface and mechanical properties of flax fiber and adhesion between fiber-matrix for composite materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Fu, Q.; Yan, L.; Kasal, B. Characterization of interfacial properties between fibre and polymer matrix in composite materials—A critical review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 1441–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinaud, C.; Peignon, M.C.; Tessier, P.Y. Plasma etching: Principles, mechanisms, application to micro- and nano-technologies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 164, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weclawski, B.T.; Horrocks, A.R.; Ebdon, J.R.; Mosurkal, R.; Kandola, B.K. Combined atmospheric pressure plasma and UV surface functionalisation and diagnostics of nylon 6.6 fabrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 562, 150090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghini, M.C.; Touchard, F.; Sarasini, F.; Chocinski-Arnault, L.; Tirillò, J.; Bracciale, M.P.; Zvonek, M.; Cech, V. Effects of oxygen and tetravinylsilane plasma treatments on mechanical and interfacial properties of flax yarns in thermoset matrix composites. Cellulose 2019, 27, 511–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornwannachai, W.; Ebdon, J.R.; Kandola, B.K. Fire-resistant natural fibre-reinforced composites from flame retarded textiles. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 154, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornwannachai, W.; Ebdon, J.R.; Kandola, B.K. Fire-resistant flax—Reinforced polypropylene/polylactic acid composites with optimised fire and mechanical performances. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2020, 33, 898–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrocks, A.R.; Nazare, S.; Masood, R.; Kandola, B.K.; Price, D. Surface modification of fabrics for improved flash-fire resistance using atmospheric pressure plasma in the presence of functionalised clay and polysiloxane. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez-Gonzalez, A.; Cervantas-Uc, J.M.; Olayo, R.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Effect of fiber surface treatment on the fiber-matrix bond strength of natural fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part B 1999, 30, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.B.; Shurvell, H.F.; Lightner, D.A.; Cooks, R.G. Introduction to Organic Spectroscopy; MacMillan Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, NH, USA, 2000; pp. 10815–10837. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Goossens, H.; Picchioni, F.; Magusin, P.; Mezari, B.; Duin, M.V. Synthetic aspects and characterisation of polypropylene-silica nanocomposites prepared via solid-state modification and sol-gel reactions. Polymer 2005, 46, 6666–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bengtsson, M.; Oksman, K. The use of silane technology in crosslinking polyethylene/wood flour composites. Compos. Part A 2006, 37, 752–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, G.B.; Fuzail, M.; Anwar, J. Aspects of the crosslinking of polyethylene with vinyl silane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 3796–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.D.; Chowdhury, A.K.; Mowery, D.M.; Esseghir, M.; Cogen, J.M.; Chaudhary, B.I. Structural comparison of products from peroxide-initiated grafting of vinylsilane and silane-functionalised nitroxyl to hydrocarbon and polyolefin substrates. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 4542–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmouleh, M.; Boufi, S.; Belgacem, M.N.; Duarte, A.P.; Salah, A.B.; Gandini, A. Modification of cellulosic fibres with functionalised silanes: Development of surface properties. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2004, 24, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.H.; Ishida, H.; Koenig, J.L. The structure of γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane on glass surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 74, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebnesajjad, S. Plasma treatment of polymeric materials. In Surface Treatment of Materials for Adhesive Bonding, 2nd ed.; Ebnesajjad, S., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2006; Chapter 9. [Google Scholar]
- Put, S.; Bertels, C.; Vanhulsel, A. Atmospheric pressure plasma treatment of polymeric powders. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 234, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolland, J.L.; Gee, G. A review of the role of basic iron III oxide acting as a char forming/smoke suppressing/flame retarding additive in halogenated polymer blends. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1946, 42, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesh, M. Novel Flame-Retardant Treatments for Cotton and Polyester Fabric Using Atmospheric Plasma Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bolton, Bolton, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, E.; Panigrahi, S. Effect of plasma treatment on structure, wettability of jute fibre and flexural strength of its composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Thakur, K.; Celli, A.; Kiechel, M.A.; Schauer, C.L. Surface modification of plant fibers using environment friendly methods for their application in polymer composites, textile industry and antimicrobial activities: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorda-Vilaplana, A.; Fombuena, V.; Garcia-Garcia, D.; Samper, M.D.; Sanchez-Nacher, L. Surface modification of polylactic acid (PLA) by air atmospheric plasma treatment. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 58, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepickova, N.S.; Slepicka, P.; Sajdl, P.; Svorcik, V. Surface changes of biopolymers PHB and PLLA induced by Ar+ plasma treatment and wet etching. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2014, 332, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, B.F.; Shalwan, A.; Chin, C.W.; Ming, K.C. Flexural properties of treated and untreated kenaf/epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, B.K.; Mistik, S.I.; Pornwannachai, W.; Anand, S.C. Natural fibre-reinforced thermoplastic composites from woven-nonwoven textile preforms: Mechanical and fire performance study. Compos. Part B 2018, 153, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; Spinelli, D.; Bose Filho, W.W.; Claro Neto, S.; Chierice, G.O.; Tarpani, J.R. Fracture toughness of natural fibers/castor oil polyurethane composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Franco, P.J.; Valadez-Gonzalez, A. Mechanical properties of continuous natural fibre-reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part A 2004, 35, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keener, T.J.; Stuart, R.K.; Brown, T.K. Maleated coupling agents for natural fibre composites. Compos. Part A 2004, 35, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, M.E.; Robledo-Ortíz, J.R.; Manríquez-González, R.; Silva-Guzmán, J.A.; Pérez-Fonseca, A.A. Polylactic acid functionalization with maleic anhydride and its use as coupling agent in natural fiber biocomposites: A review. Compos. Interfaces 2018, 6440, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
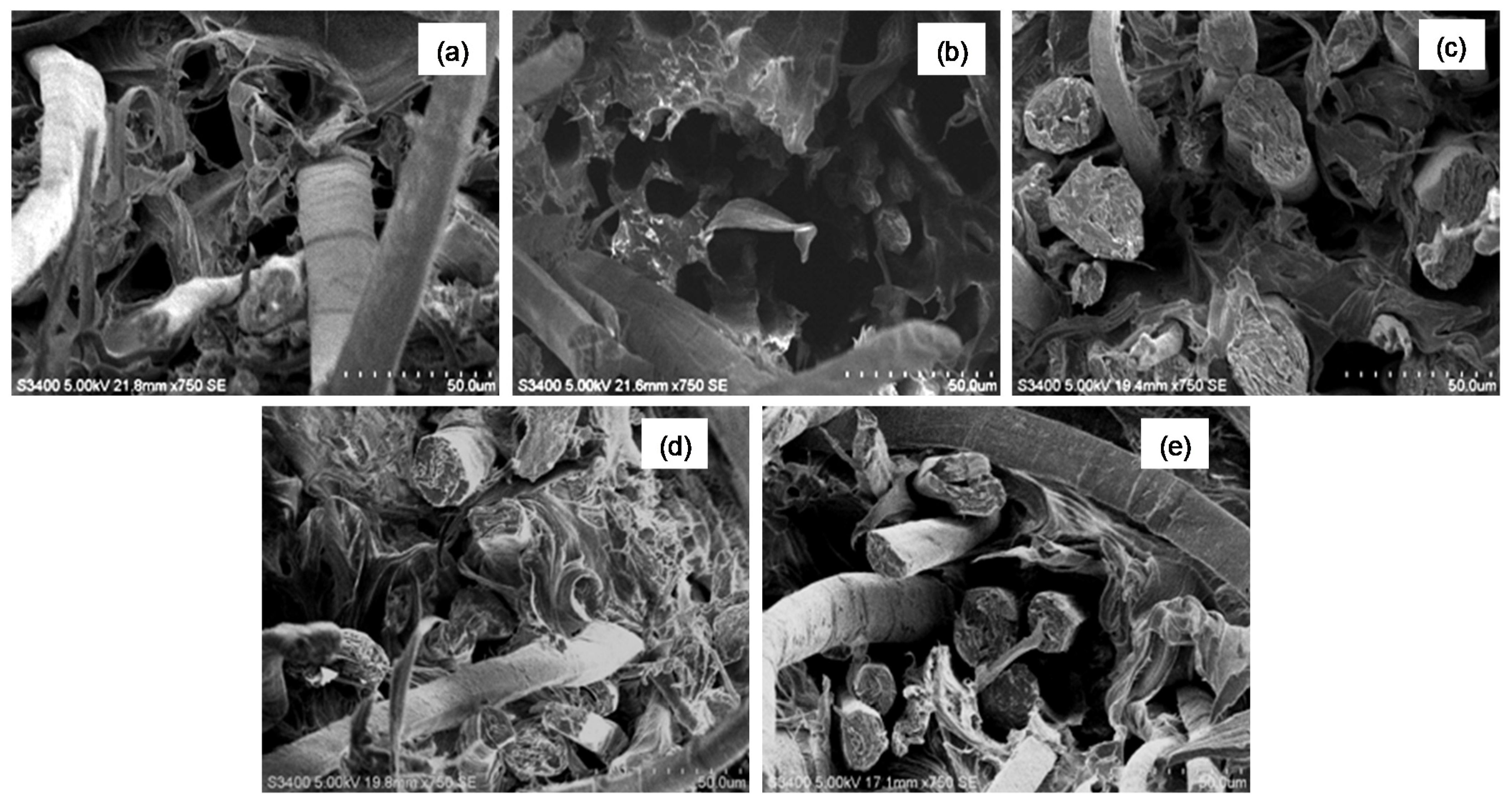
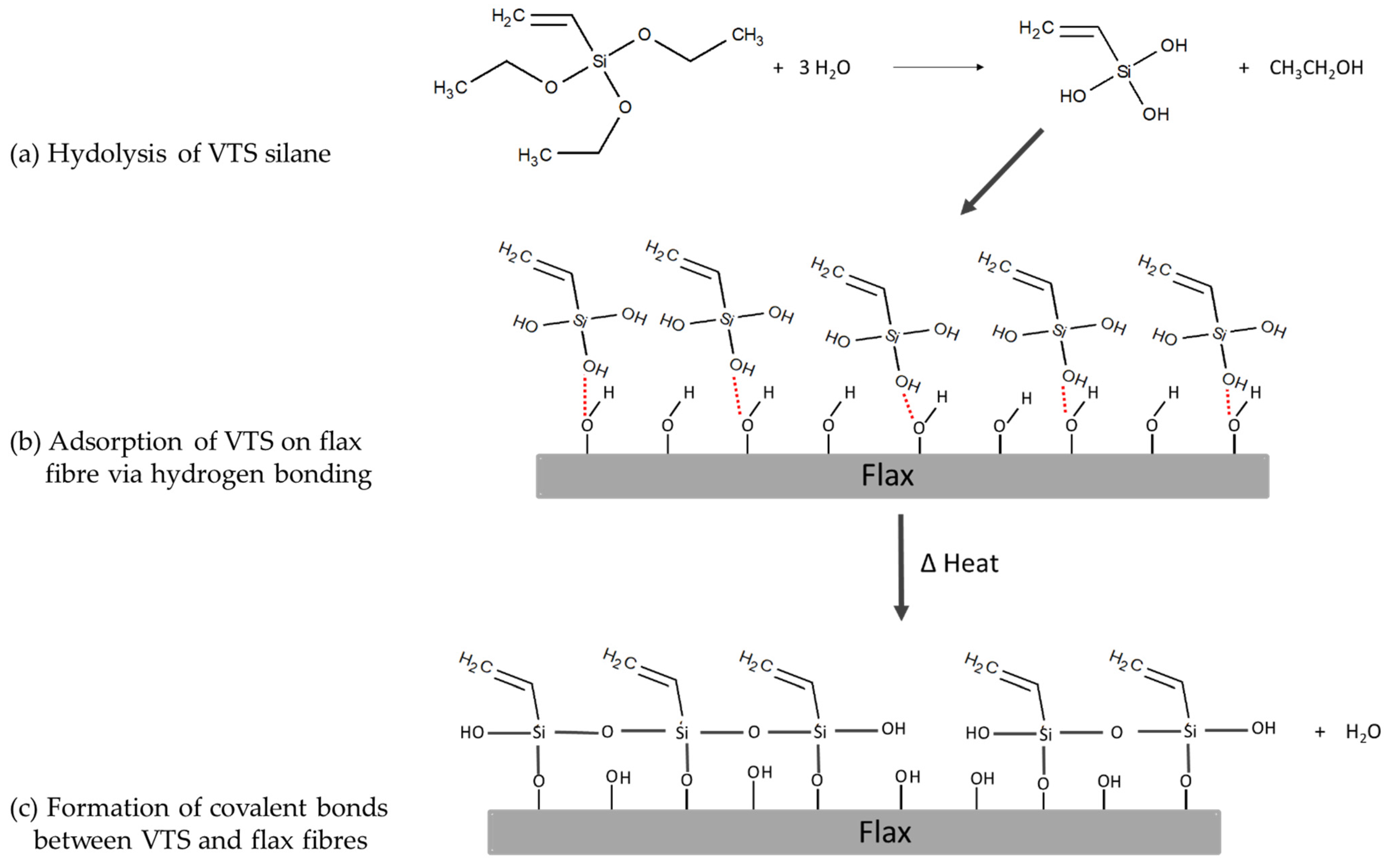
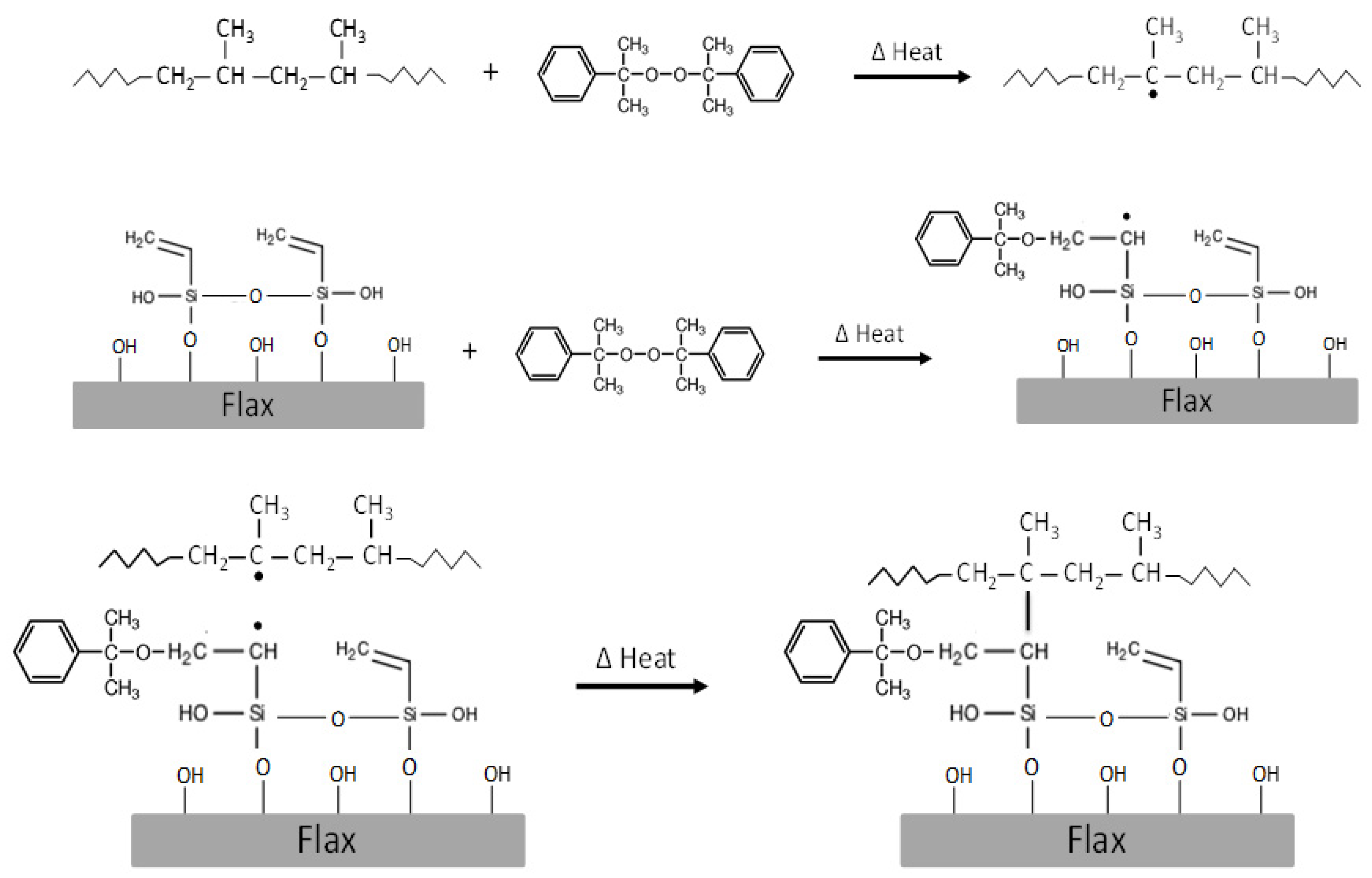
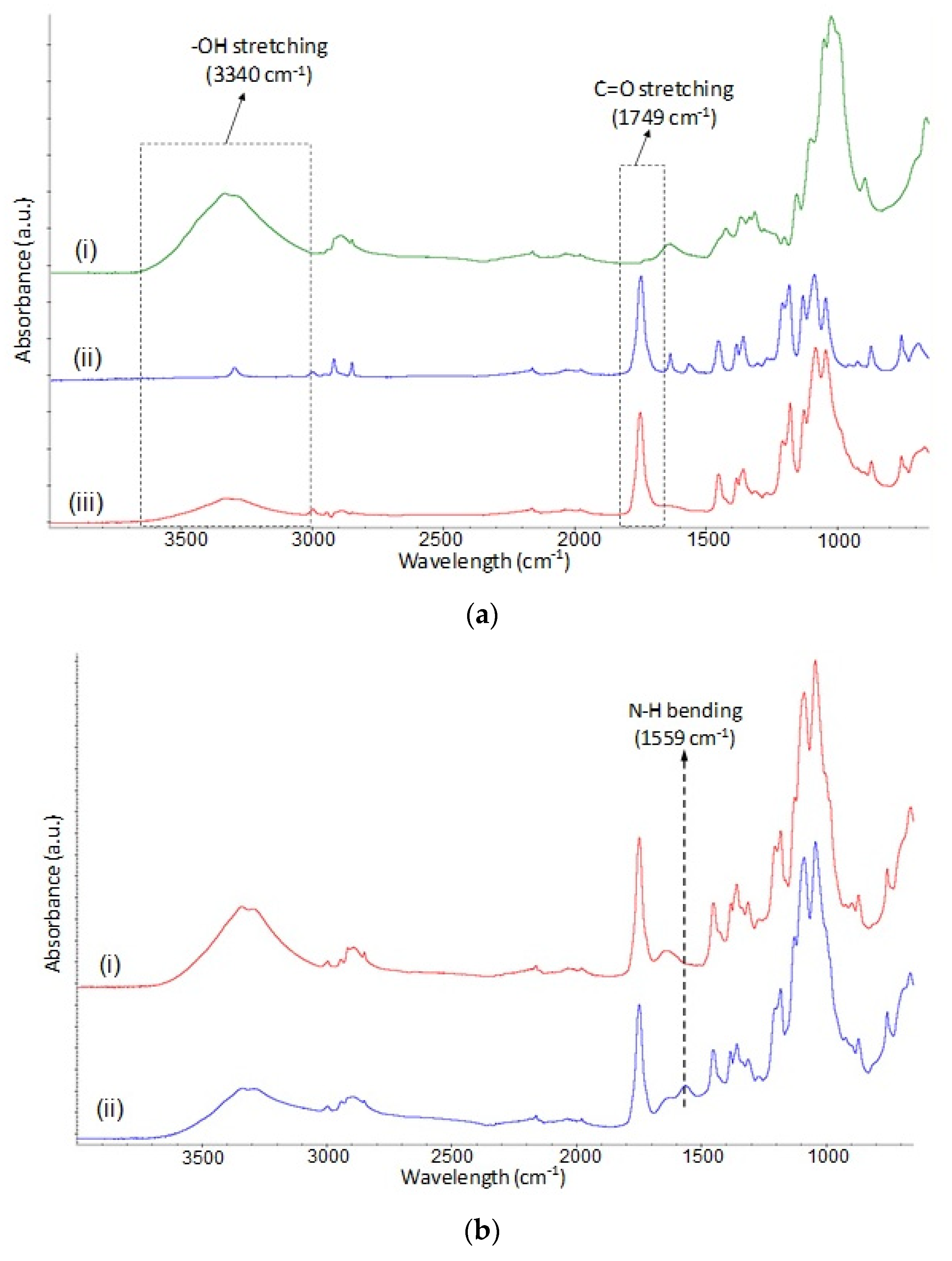
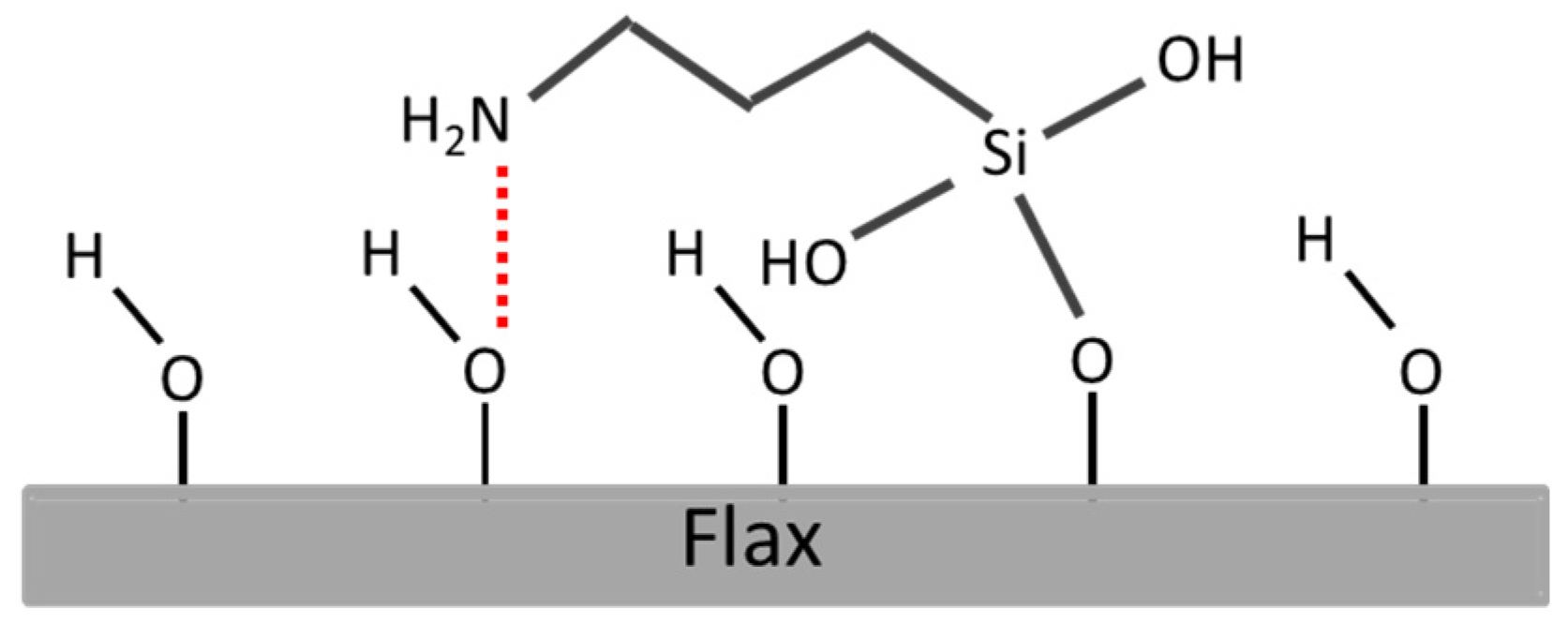
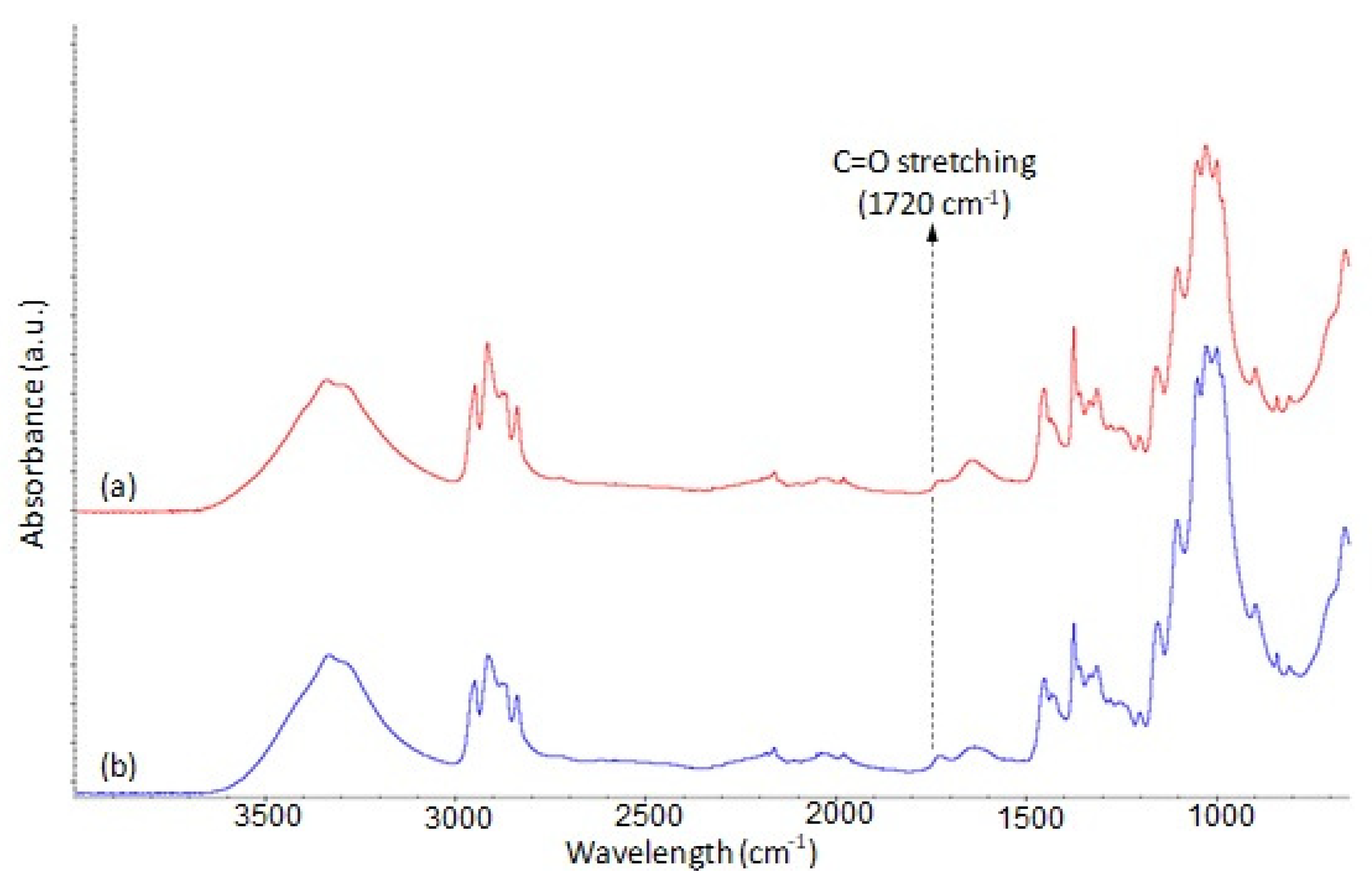

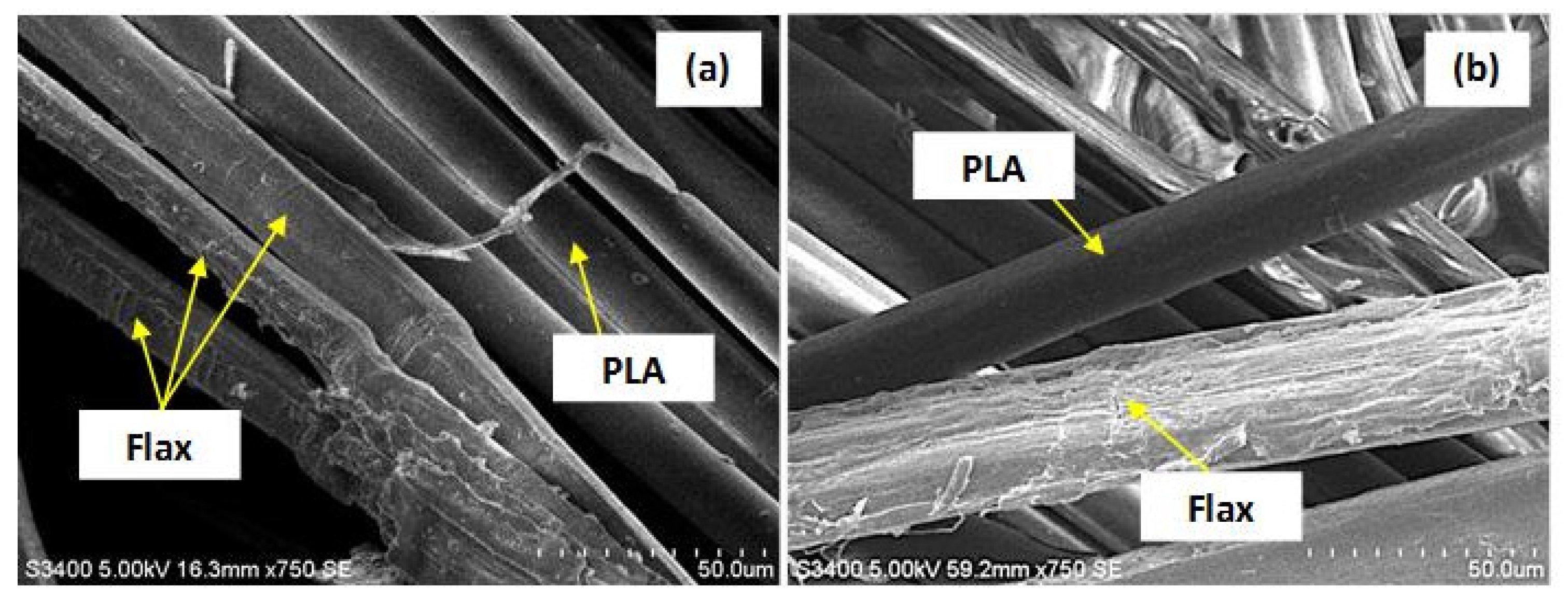
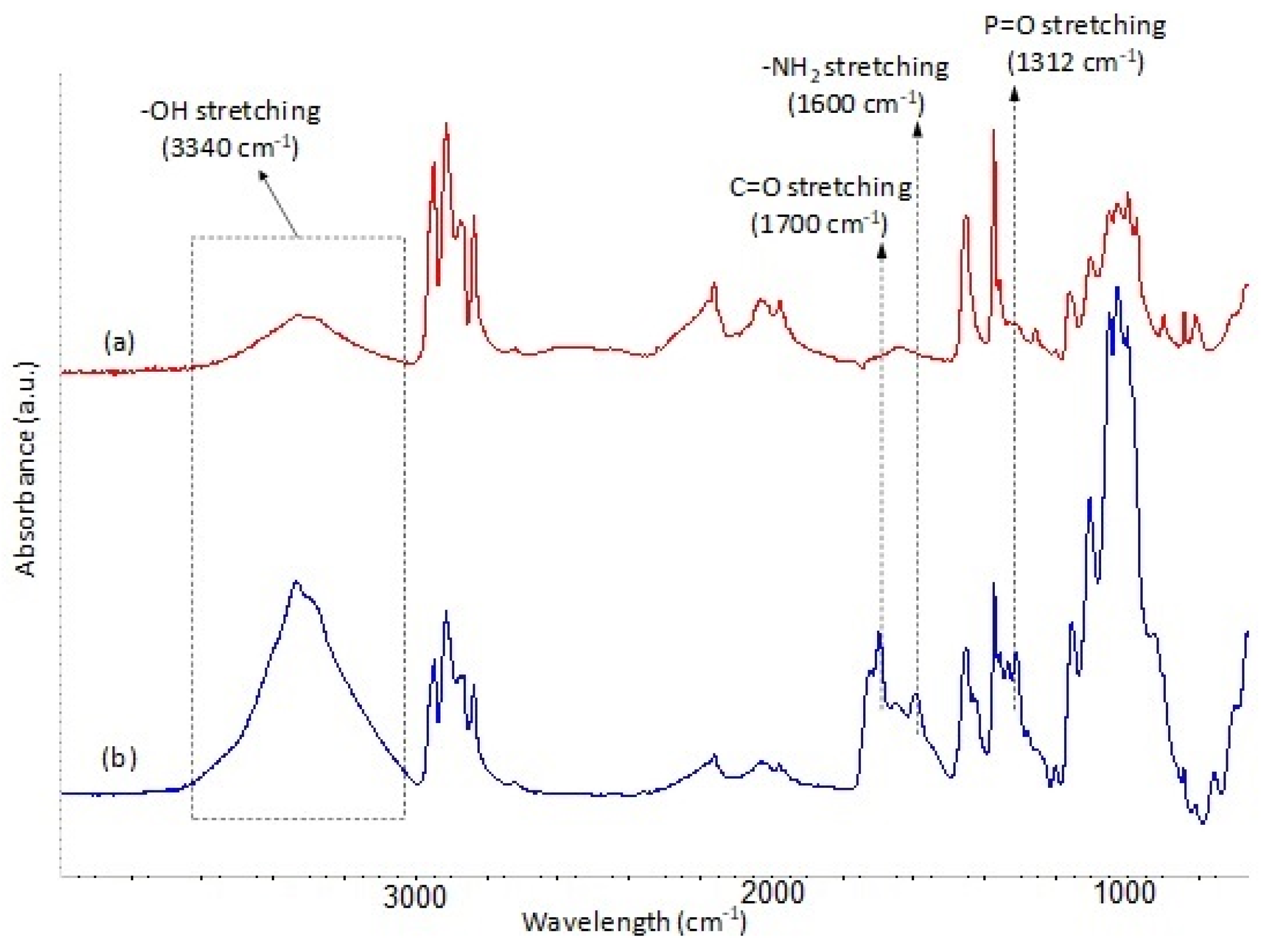

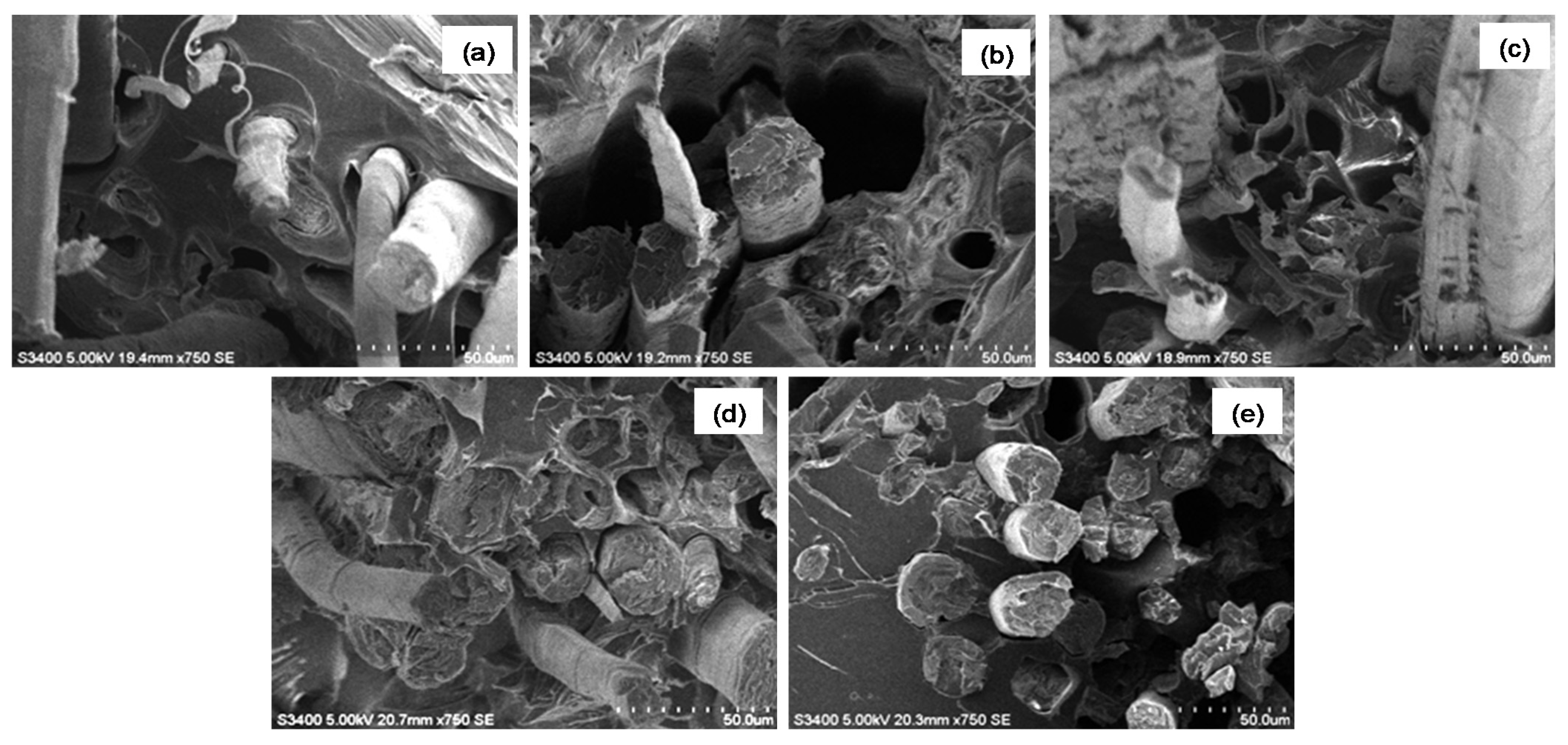
| Sample | Silane Treatment | Silane Content on Fabrics (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Si-Flax/PP (1%) | 1 wt-% VTS solution | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| Si-Flax/PP (2%) | 2 wt-% VTS solution | 2.7 ± 0.1 |
| Si-Flax/PP (3%) | 3 wt-% VTS solution | 4.5 ± 0.1 |
| Si-Flax/PLA (1%) | 1 wt-% APTES solution | 1.2 ± 0.1 |
| Si-Flax/PLA (2%) | 2 wt-% APTES solution | 2.7 ± 0.3 |
| Si-Flax/PLA (3%) | 3 wt-% APTES solution | 4.2 ± 0.1 |
| Method | The Order of Fabric Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| FR | FR solution (Pad/Dry) | |||
| FR-Si | FR solution (Pad/Dry) | Silane (Spray) | ||
| FR-Pm | Plasma | FR solution (Pad/Dry) | Plasma | |
| FR-Pm-Si | Plasma | FR solution (Pad/Dry) | Plasma | Silane (Spray) |
| Fabric Sample | FR Content (%) | P Content (%) * | Silane Content (%) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR-Flax/PP | 10.9 | 1.0 | - |
| FR-Si-Flax/PP | 10.9 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| FR-Pm_Flax/PP | 12.2 | 1.1 | - |
| FR-Pm-Si_Flax/PP | 12.2 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
| FR-Flax/PLA | 7.2 | 0.6 | - |
| FR-Si-Flax/PLA | 7.2 | 0.6 | 2.1 |
| FR-Pm-Flax/PLA | 9.4 | 0.8 | - |
| FR-Pm-Si-Flax/PLA | 9.4 | 0.8 | 3.2 |
| Sample | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Strain-at-Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flax/PP | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 42 ± 5 | 3.2 ± 0.7 |
| Flax/PLA | 7.7 ± 0.7 | 61 ± 6 | 2.0 ± 0.9 |
| Silane pretreatment | |||
| Si-Flax/PP (1%) | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 40 ± 1 | 3.1 ± 0.1 |
| Si-Flax/PP (2%) | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 44 ± 4 | 3.1 ± 0.4 |
| Si-Flax/PP (3%) | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 41 ± 2 | 2.0 ± 0.4 |
| Si-Flax/PLA (1%) | 4.8 ± 0.9 | 36 ± 7 | 1.4 ± 0.4 |
| Si-Flax/PLA (2%) | 3.9 ± 0.4 | 21 ± 4 | 0.9 ± 0.3 |
| Si-Flax/PLA (3%) | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 17 ± 5 | 1.0 ± 0.4 |
| Plasma pretreatment | |||
| Pm-Flax/PP (50 W) | 4.6 ± 0.3 | 60 ± 6 | 1.8 ± 0.3 |
| Pm-Flax/PP (100 W) | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 68 ± 6 | 2.0 ± 0.3 |
| Pm-Flax/PP (150 W) | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 84 ± 2 | 1.7 ± 0.1 |
| Pm-Flax/PLA (50 W) | 7.8 ± 0.9 | 85 ± 14 | 3.5 ± 0.3 |
| Pm-Flax/PLA (100 W) | 8.6 ± 0.6 | 91 ± 7 | 3.1 ± 0.8 |
| Pm-Flax/PLA (150 W) | 9.1 ± 0.5 | 102 ± 5 | 3.3 ± 0.7 |
| Sample | Peeling Strength | % Change in Peeling Strength | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N) | (w.r.t. Flax/Polym) | (w.r.t. FR-Flax/Polym) | |
| Flax/PP | 35 ± 10 | - | - |
| FR-Flax/PP | 19 ± 6 | −46 | - |
| FR-Si-Flax/PP | 24 ± 7 | −31 | +26 |
| FR-Pm-Flax/PP | 23 ± 7 | −34 | +21 |
| FR-Pm-Si-Flax/PP | 25 ± 7 | −29 | +31 |
| Flax/PLA | 50 ± 6 | - | - |
| FR-Flax/PLA | 35 ± 4 | −30 | - |
| FR-Si-Flax/PLA | 34 ± 3 | −32 | −3 |
| FR-Pm-Flax/PLA | 39 ± 9 | −22 | +11 |
| FR-Pm-Si-Flax/PLA | 39 ± 5 | −22 | +11 |
| Sample | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Flax/PP | 8.8 ± 0.5 | 80 ± 1 |
| FR-Flax/PP | 10.8 ± 0.6 | 92 ± 4 |
| FR-Si-Flax/PP | 12.7 ± 1.7 | 80 ± 4 |
| FR-Pm-Flax/PP | 13.1 ± 0.7 | 85 ± 9 |
| FR-Pm-Si-Flax/PP | 14.9 ± 1.4 | 114 ± 10 |
| Flax/PLA FR-Flax/PLA | 12.4 ± 0.7 12.3 ± 1.0 | 135 ± 1 109 ± 6 |
| FR-Si-Flax/PLA | 12.5 ± 0.2 | 105 ± 11 |
| FR-Pm-Flax/PLA | 16.0 ± 0.2 | 125 ± 1 |
| FR-Pm-Si-Flax/PLA | 16.0 ± 1.1 | 110 ± 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pornwannachai, W.; Horrocks, A.R.; Kandola, B.K. Surface Modification of Commingled Flax/PP and Flax/PLA Fibres by Silane or Atmospheric Argon Plasma Exposure to Improve Fibre–Matrix Adhesion in Composites. Fibers 2022, 10, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10010002
Pornwannachai W, Horrocks AR, Kandola BK. Surface Modification of Commingled Flax/PP and Flax/PLA Fibres by Silane or Atmospheric Argon Plasma Exposure to Improve Fibre–Matrix Adhesion in Composites. Fibers. 2022; 10(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10010002
Chicago/Turabian StylePornwannachai, Wiwat, A. Richard Horrocks, and Baljinder K. Kandola. 2022. "Surface Modification of Commingled Flax/PP and Flax/PLA Fibres by Silane or Atmospheric Argon Plasma Exposure to Improve Fibre–Matrix Adhesion in Composites" Fibers 10, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10010002
APA StylePornwannachai, W., Horrocks, A. R., & Kandola, B. K. (2022). Surface Modification of Commingled Flax/PP and Flax/PLA Fibres by Silane or Atmospheric Argon Plasma Exposure to Improve Fibre–Matrix Adhesion in Composites. Fibers, 10(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10010002







