Modular Paradigm for Composites: Modeling Hydrothermal Degradation of Glass Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Environmental Ageing of Glass Fibers and Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites
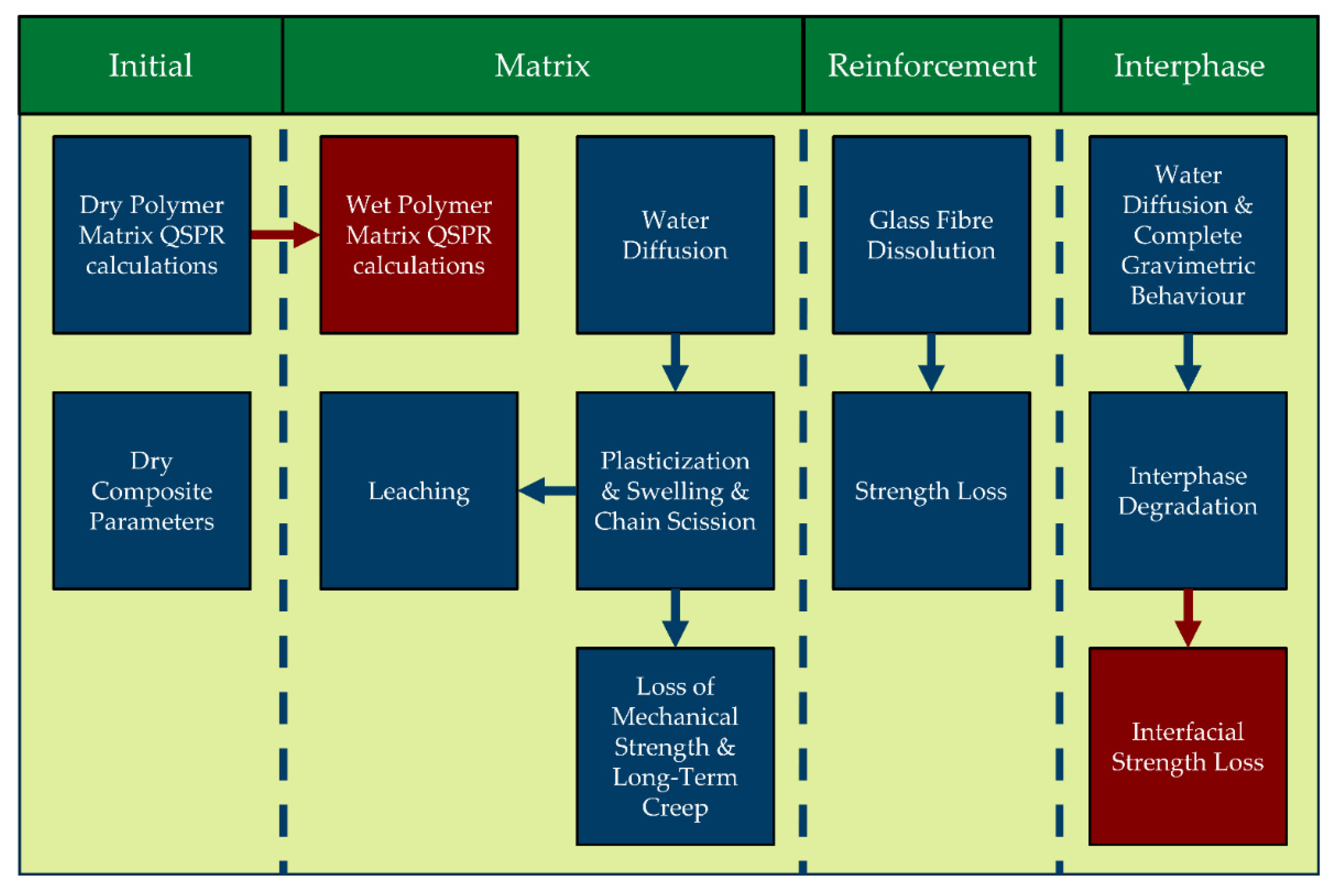
2. Modeling
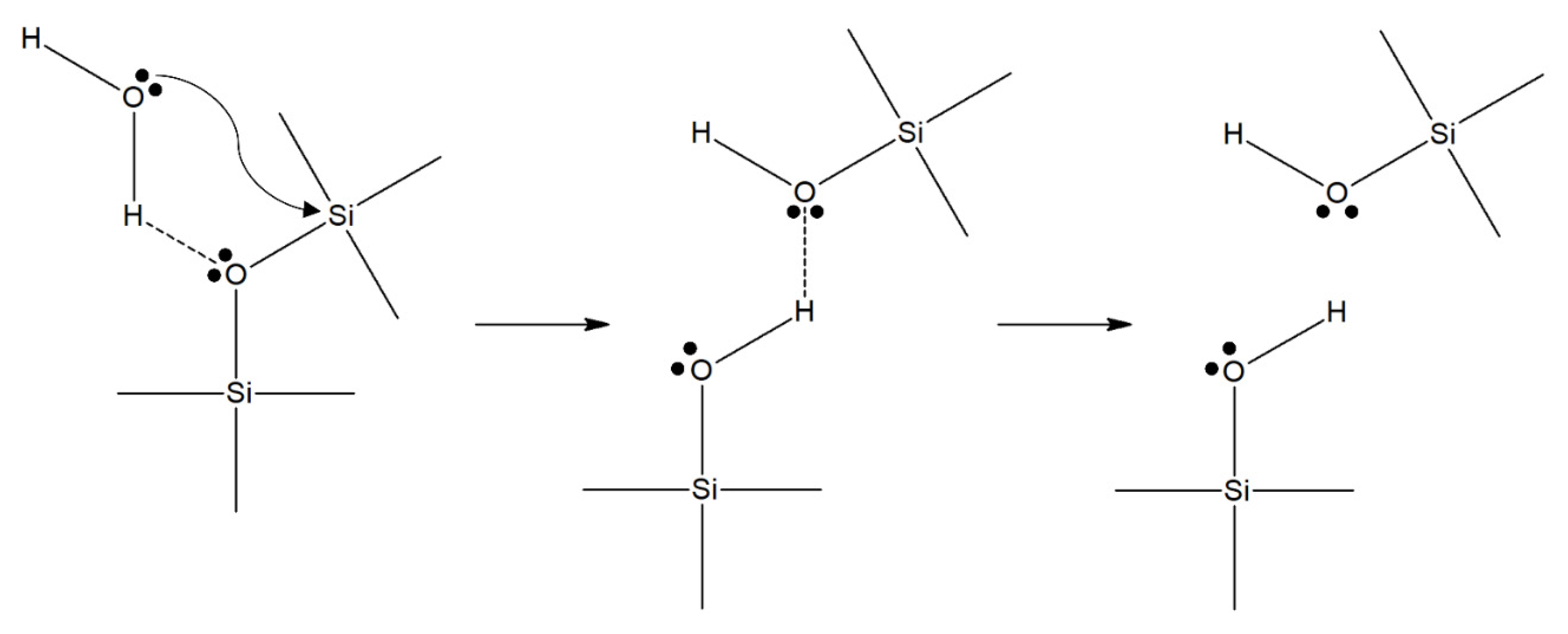
2.1. Molecular Mechanism and Chemical Kinetics of Environmental Ageing
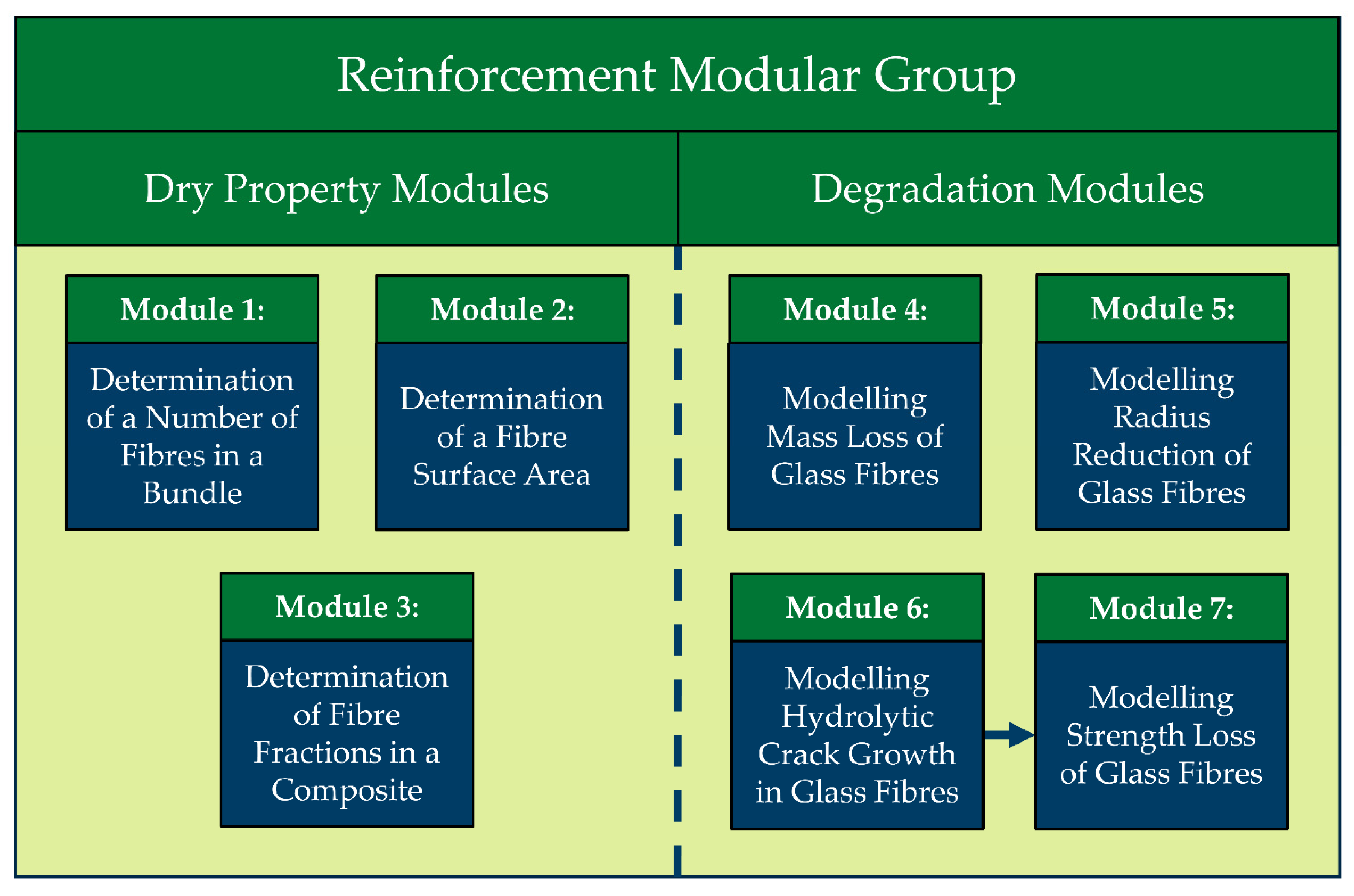
2.2. Module 1: Determination of a Number of Fibers in a Bundle
2.3. Module 2: Determination of a Fiber’s Surface Area
2.4. Module 3: Determination of Fiber Fractions in a Composite
2.5. Module 4: Modeling Mass Loss of Glass Fibers
2.6. Module 5: Modeling Radius Reduction of Glass Fibers
2.7. Module 6: Modeling Hydrolytic Crack Growth in Glass Fibers
2.8. Module 7: Modeling Strength Loss of Glass Fibers
3. Discussion
3.1. Modeling Issues—Extending to Composites
3.2. Future Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, J.; Jones, F.R. The role of sizing resins, coupling agents and their blends on the formation of the interphase in glass fiber composites. Compos. Part A 1998, 29, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E. Environmental Aging of Constituent Materials in Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites. Ph.D. Thesis, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway, 2019; p. 203, ISBN 978-82-326-4027-0. [Google Scholar]
- Krauklis, A.; Echtermeyer, A. Mechanism of Yellowing: Carbonyl Formation during Hygrothermal Aging in a Common Amine Epoxy. Polymers 2018, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, G.Z.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Swelling of DGEBA/DDA epoxy resin during hygrothermal ageing. Polymer 1998, 39, 3253–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, A.; Pitarresi, G.; Scafidi, M.; Di Filippo, M.; Spadaro, G.; Alessi, S. Water diffusion and swelling stresses in highly crosslinked epoxy matrices. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 133, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabovac, I.; Whittaker, D. Application of bonded composites in the repair of ships structures—A 15-year service experience. Compos. Part A 2009, 40, 1381–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeorge, D.; Echtermeyer, A.T.; Leong, K.H.; Melve, B.; Robinson, M.; Fischer, K.P. Repair of floating offshore units using bonded fibre composite materials. Compos. Part A 2009, 40, 1364–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, C.G.; Echtermeyer, A. Long-term properties of carbon fibre composite tethers. Int. J. Fatigue 2006, 28, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, M.M.; Stjern, G.; Storhaug, T.; Spencer, B.; Echtermeyer, A. The First Offshore Field Installation for a Composite Riser Joint; OTC-14018-MS; Offshore Technology Conference: Houston, TX, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echtermeyer, A.T.; Gagani, A.I.; Krauklis, A.E.; Mazan, T. Multiscale Modelling of Environmental Degradation—First Steps. In Durability of Composites in a Marine Environment 2. Solid Mechanics and Its Applications; Davies, P., Rajapakse, Y.D.S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 245, pp. 135–149. ISBN 978-3-319-65145-3. [Google Scholar]
- Thomason, J.L. Glass Fiber Sizings: A Review of the Scientific Literature; Create Space Independent Publishing Platform: Middletown, DE, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-9573814-1-4. [Google Scholar]
- Weitsman, Y. Coupled damage and moisture-transport in fiber-reinforced, polymeric composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1987, 23, 1003–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitsman, Y.J.; Elahi, M. Effects of fluids on the deformation, strength and durability of polymeric composites—An overview. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2000, 4, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S. Moisture-Induced Degradation. In Long-Term Durability of Polymeric Matrix Composites; Pochiraju, V.K., Tandon, P.G., Schoppner, A.G., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 181–236. ISBN 978-1-4419-9307-6. [Google Scholar]
- Apicella, A.; Nicolais, L. Effect of Water on the Properties of Epoxy Matrix and Composite. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1985, 72, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, D.R.; Elliker, P.R.; Takahashi, K.M.; Raju, V.R.; Kaplan, M.L. The Critical Humidity Effect in the Adhesion of Epoxy to Glass: Role of Hydrogen Bonding. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2000, 14, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guermazi, N.; Elleuch, K.; Ayedi, H.F. The Effect of Time and Aging Temperature on Structural and Mechanical Properties of Pipeline Coating. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2006–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F.; Xu, W.J. Atomistic Simulation Study of Absorbed Water Influence on Structure and Properties of Crosslinked Epoxy Resin. Polymer 2007, 48, 5440–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Karl, C.W.; Gagani, A.I.; Jørgensen, J.K. Composite Material Recycling Technology—State-of-the-Art and Sustainable Development for the 2020s. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Ji, J.; Yang, Y.; Shen, J.; Ye, M. The hygrothermal aging process and mechanism of the novolac epoxy resin. Compos. Part B 2016, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, J.C. Effects of Environmental Factors on Composite Materials; Technical Report AFML-TR-67–423; Air Force Materials Laboratory: Dayton, OH, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Karl, C.W.; Rocha, I.B.C.M.; Burlakovs, J.; Ozola-Davidane, R.; Gagani, A.I.; Starkova, O. Modelling of Environmental Ageing of Polymers and Polymer Composites—Modular and Multiscale Methods. (soon to be submitted).
- Krauklis, A. Predicting environmental ageing of composites: Modular approach & multiscale modelling. In Proceedings of the 1st Corrosion and Materials Degradation Web Conference, Online, 17–19 May 2021; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feih, S.; Wei, J.; Kingshott, P.; Sørensen, B.F. The influence of fiber sizing on the strength and fracture toughness of glass fiber composites. Compos. Part A 2005, 36, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, K.L. Glass Science and Technology (Book 6), The Manufacturing Technology of Continuous Glass Fibres; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; ISBN 978-0444893468. [Google Scholar]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Gagani, A.I.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Long-Term Hydrolytic Degradation of the Sizing-Rich Composite Interphase. Coatings 2019, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krauklis, A.E. Environmental Durability of Composite Materials: Analytical Modelling Toolbox. In Aachen Reinforced! Symposium 2021; RWTH: Aachen, Germany, 2021; pp. 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gagani, A.I. Environmental Effects on Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites—Fluid and Temperature Effects on Mechanical Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway, 2019. ISBN 978-82-326-3839-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gagani, A.I.; Fan, Y.; Muliana, A.H.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Micromechanical modeling of anisotropic water diffusion in glass fiber epoxy reinforced composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 52, 2321–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagani, A.I.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Influence of delaminations on fluid diffusion in multidirectional composite laminates—Theory and experiments. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 158, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagani, A.; Krauklis, A.; Echtermeyer, A. Orthotropic fluid diffusion in composite marine structures. Experimental procedure, analytical and numerical modelling of plates, rods and pipes. Comp. Part A 2018, 115, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Gagani, A.I.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Method for Monitoring Water Content in Epoxy Resins and Fiber-Reinforced Composites. Materials 2018, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Gagani, A.I.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Hygrothermal Aging of Amine Epoxy: Reversible Static and Fatigue Properties. Open Eng. 2018, 8, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Gagani, A.I.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Prediction of Orthotropic Hygroscopic Swelling of Fiber-Reinforced Composites from Isotropic Swelling of Matrix Polymer. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction. Open Chem. 2018, 16, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Gagani, A.I.; Vegere, K.; Kalnina, I.; Klavins, M.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Dissolution Kinetics of R-Glass Fibres: Influence of Water Acidity, Temperature and Stress Corrosion. Fibers 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Echtermeyer, A.T.; Krauklis, A.E.; Gagani, A.I.; Sæter, E. Zero Stress Aging of Glass and Carbon Fibers in Water and Oil—Strength Reduction Explained by Dissolution Kinetics. Fibers 2019, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Akulichev, A.G.; Gagani, A.I.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Time–Temperature–Plasticization Superposition Principle: Predicting Creep of a Plasticized Epoxy. Polymers 2019, 11, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gagani, A.; Krauklis, A.; Echtermeyer, A. Anisotropic fluid diffusion in carbon fiber reinforced composite rods: Experimental, analytical and numerical study. Mar. Struct. 2018, 59, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Gagani, A.I.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Hygrothermal aging of fiber-reinforced composites: Introduction to phenomenological perspective and mass balance approach. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Composite Structures (ICCS21), Bologna, Italy, 4–7 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model for Predicting Hygrothermal Aging of Glass Fiber Bundles and Fiber-Reinforced Composites. In Proceedings of the 4th International Glass Fiber Symposium, Aachen, Germany, October 2018; Gries, T., Pico, D., Lüking, A., Becker, T., Eds.; pp. 66–72, ISBN 978-3-95886-249-4. [Google Scholar]
- Echtermeyer, A.T.; Gagani, A.I.; Krauklis, A.E.; Moslemian, R. Long Term Fatigue Degradation—Superposition of Dry and Wet Properties. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Composite Materials (ICCM22), Melbourne, Australia, 11–16 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gagani, A.I.; Krauklis, A.E.; Sæter, E.; Vedvik, N.P.; Echtermeyer, A.T. A novel method for testing and determining ILSS for marine and offshore composites. Comp. Struct. 2019, 220, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagani, A.I.; Monsås, A.B.; Krauklis, A.E.; Echtermeyer, A.T. The effect of temperature and water immersion on the interlaminar shear fatigue of glass fiber epoxy composites using the I-beam method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 181, 107703–107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Krauklis, A.E.; Gagani, A.; Sæter, E.; Echtermeyer, A.T.; Muliana, A. Predicting Multi-axial Diffusion of Water in Laminated Composite Structural Components. Comp. Struct. 2021, 261, 113551–113562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagani, A.I.; Mialon, E.P.V.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Immersed interlaminar fatigue of glass fiber epoxy composites using the I-beam method. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 119, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagani, A.I.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Fluid diffusion in cracked composite laminates–Analytical, numerical and experimental study. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 160, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WindEurope—Cefic—EuCIA. Accelerating Wind Turbine Blade Circularity. White Paper. May 2020. Available online: https://windeurope.org/wp-content/uploads/files/about-wind/reports/WindEurope-Accelerating-wind-turbine-blade-circularity.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Van der Woude, J. (EuCIA) Recycling, Status and Developments in Europe. In International Glass Fiber Symposium; RWTH: Aachen, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tournié, A.; Ricciardi, P.; Colomban, P. Glass Corrosion Mechanisms: A Multiscale Analysis. Solid State Ion. 2008, 179, 2142–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grambow, B.; Müller, R. First-order dissolution rate law and the role of surface layers in glass performance assessment. J. Nucl. Mater. 2001, 298, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grambow, B. A General Rate Equation for Nuclear Waste Glass Corrosion. Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1985, 44, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, F.M.I.; Hoch, A.R.; Heath, T.G.; Baston, G.M.N. Report RWM005105, AMEC/103498/02 Issue 2: Review of Glass Dissolution Models and Application to UK Glasses; AMEC: Didcot, Oxfordshire, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Michalske, T.A.; Freiman, S.W. A Molecular Mechanism for Stress Corrosion in Vitreous Silica. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1983, 66, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iler, R.K. The Chemistry of Silica: Solubility, Polymerization, Colloid and Surface Properties and Biochemistry of Silica; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; p. 896. ISBN 978-0-471-02404-0. [Google Scholar]
- Putnis, C.V.; Ruiz-Agudo, E. The mineral–water interface: Where minerals react with the environment. Elements 2013, 9, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A. The Effect of Strong Acids on Glass Fibre Reinforced Composites; SINTEF Report 102017059-3-12; SINTEF: Oslo, Norway, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D3171/D3171-15. Standard Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite Materials; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wierderhorn, S.M.; Bolz, L.H. Stress corrosion and static fatigue of glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1970, 53, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiman, S.W.; Wiederhorn, S.M.; Mecholsky, J.J., Jr. Environmentally Enhanced Fracture of Glass: A Historical Perspective. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, D.; Yvonnet, J. Topology Optimization for Maximizing the Fracture Resistance of Periodic Quasi-Brittle Composites Structures. Materials 2020, 13, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, D.; Cui, X.; Long, K.; Cai, Y.; Li, G. Multiscale concurrent topology optimization of structures and microscopic multi-phase materials for thermal conductivity. Eng. Comput. 2019, 36, 126–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, D.; Qian, X. Fracture resistance design through biomimicry and topology optimization. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2020, 40, 100890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, D. Topology Optimization Design of Heterogeneous Materials and Structures; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1786305589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krauklis, A.E. Modular Paradigm for Composites: Modeling Hydrothermal Degradation of Glass Fibers. Fibers 2021, 9, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9120083
Krauklis AE. Modular Paradigm for Composites: Modeling Hydrothermal Degradation of Glass Fibers. Fibers. 2021; 9(12):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9120083
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrauklis, Andrey E. 2021. "Modular Paradigm for Composites: Modeling Hydrothermal Degradation of Glass Fibers" Fibers 9, no. 12: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9120083
APA StyleKrauklis, A. E. (2021). Modular Paradigm for Composites: Modeling Hydrothermal Degradation of Glass Fibers. Fibers, 9(12), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9120083





