Unveiling the Microstructure Evolution Mechanism of A356 Aluminum Alloy During Squeeze Casting Torsional Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Method
3. Macroscale and Mesoscale Modeling
3.1. Finite Element Modeling
3.2. Material Constitutive for FEM
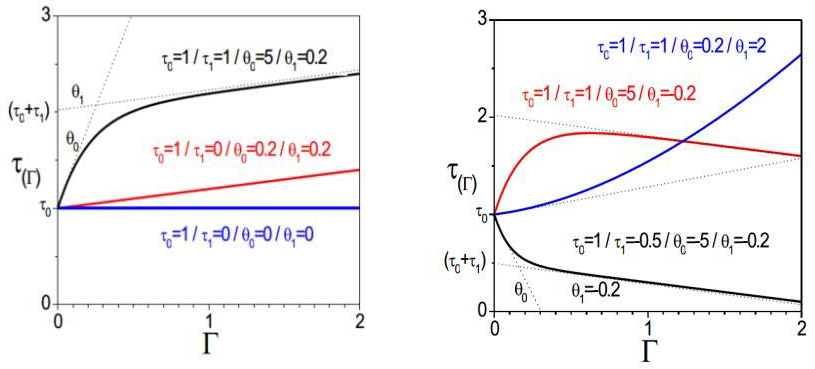
3.3. Velocity Gradient Tensor
3.4. VPSC Modeling
4. Results and Discussion
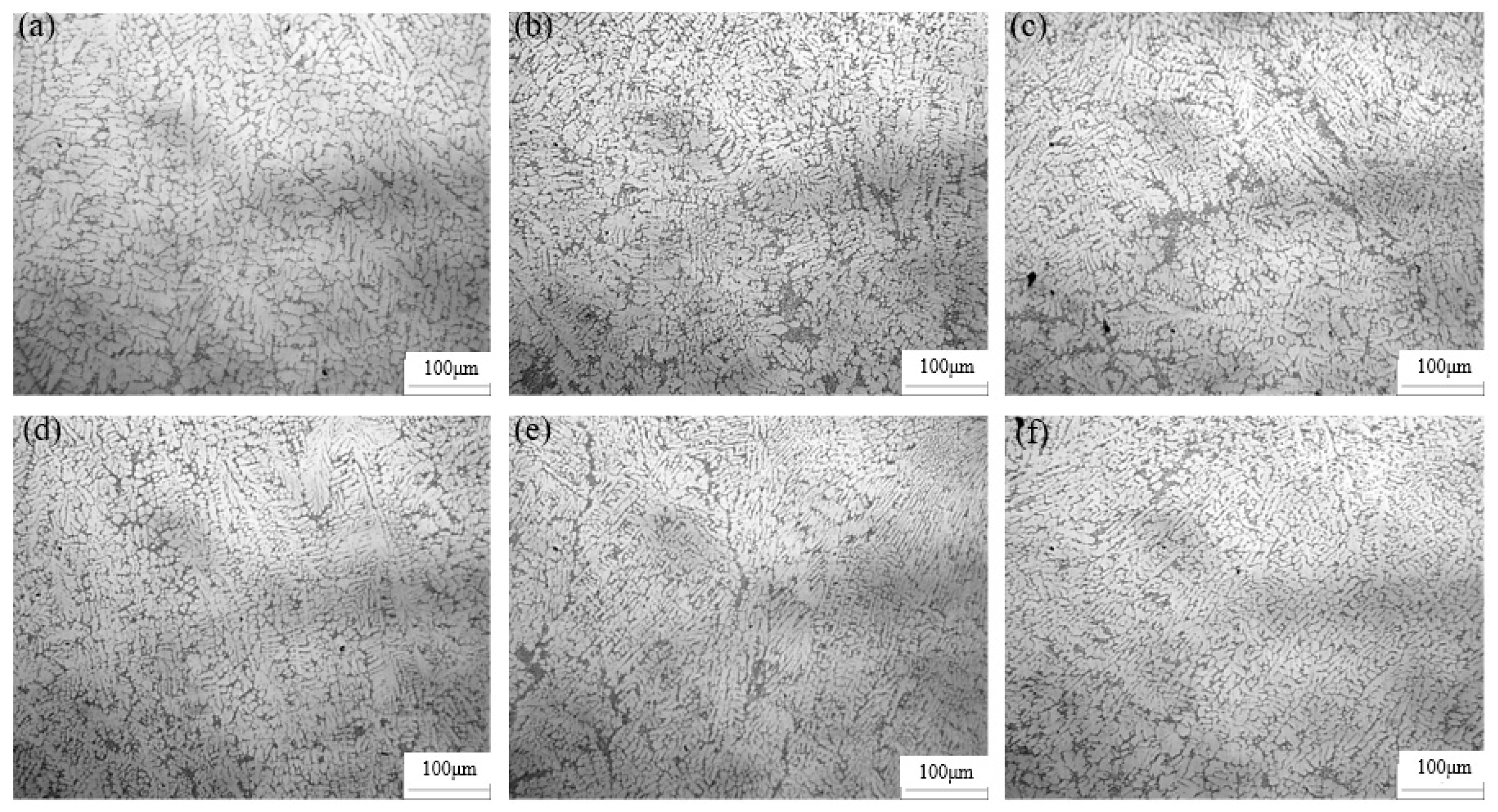
4.1. Microstructure Under SQ and SQT Process
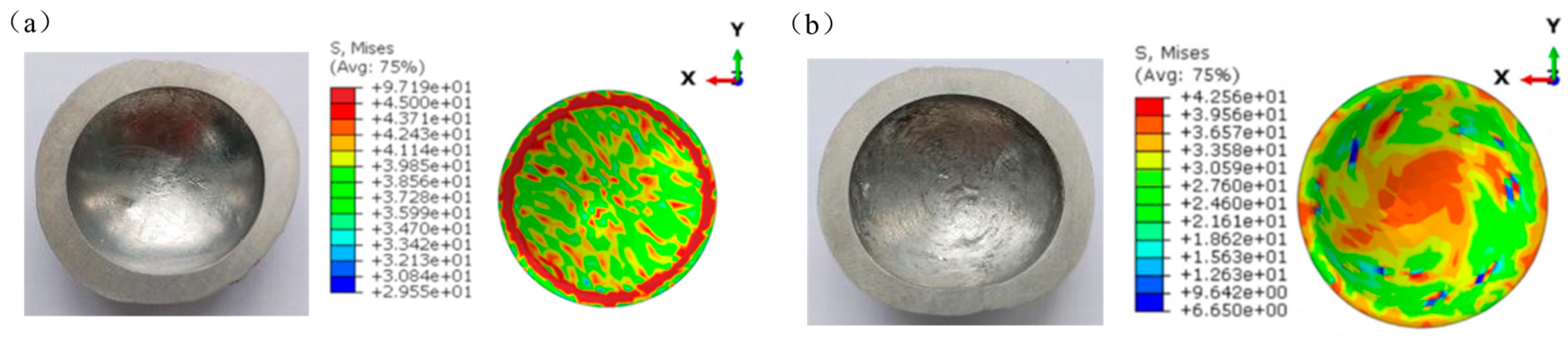
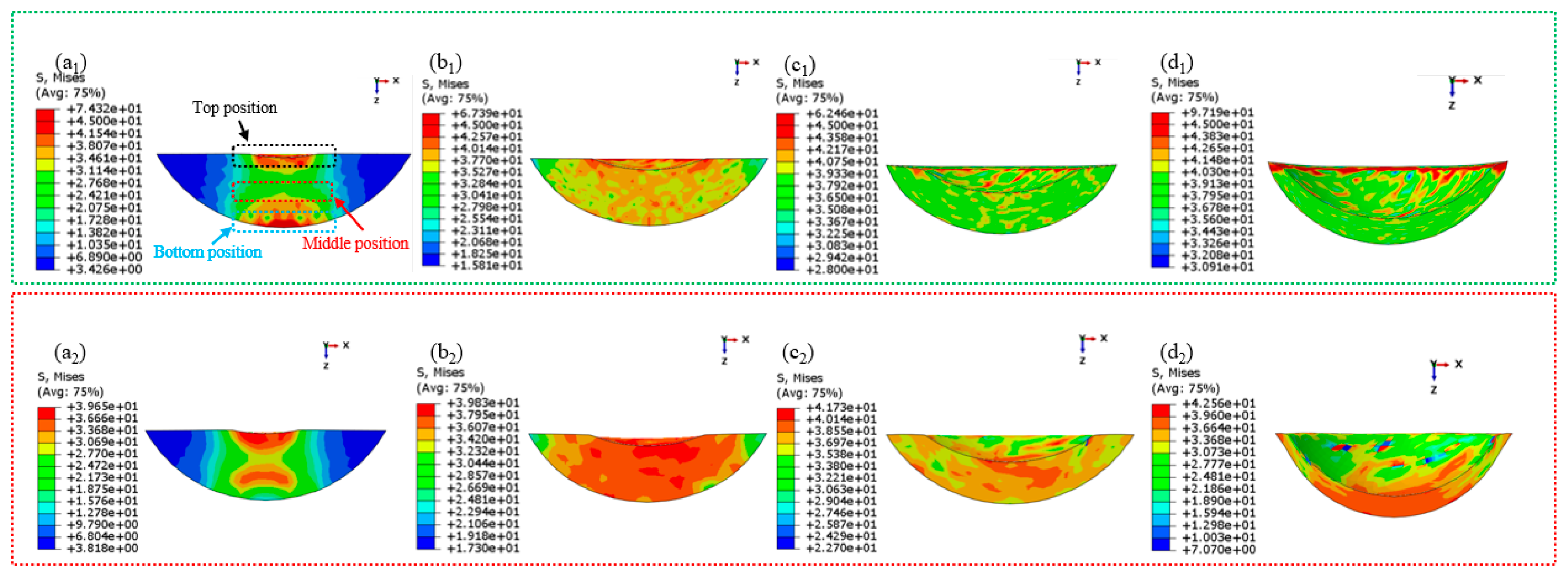
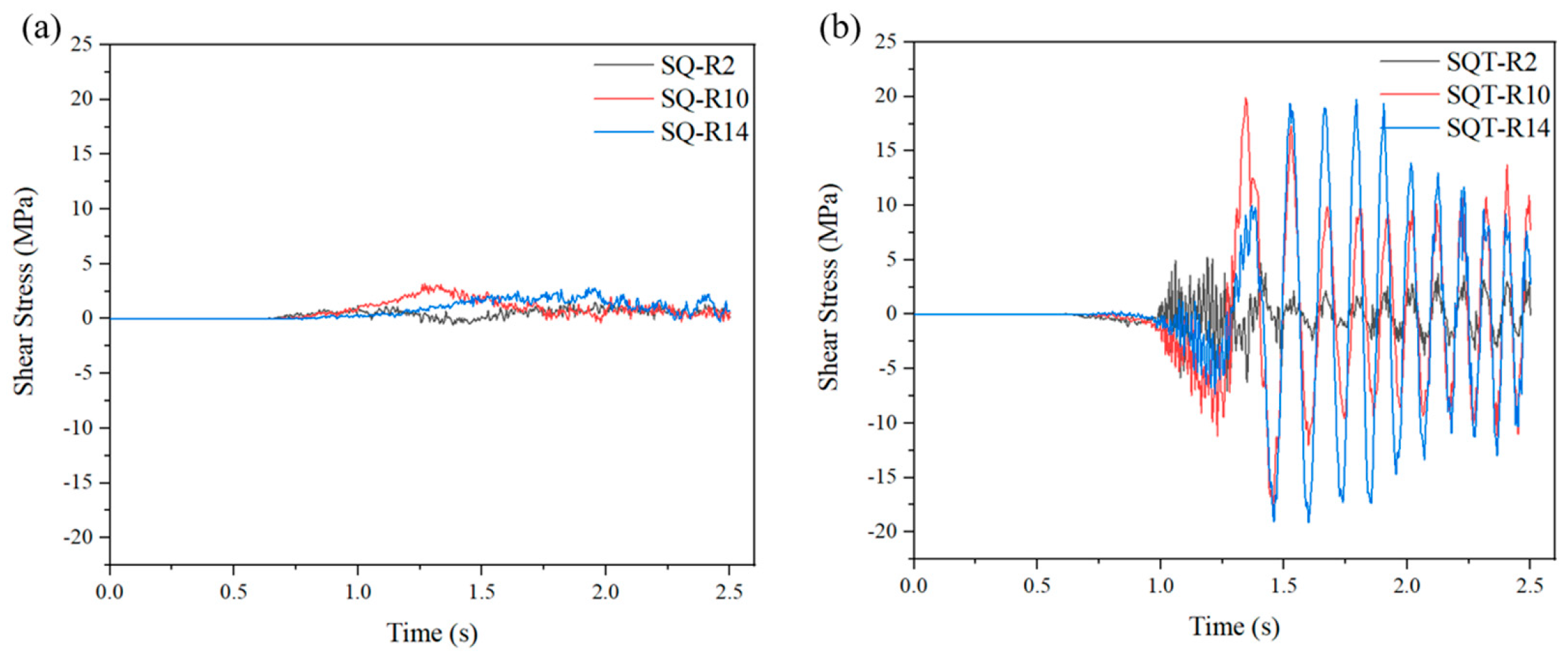
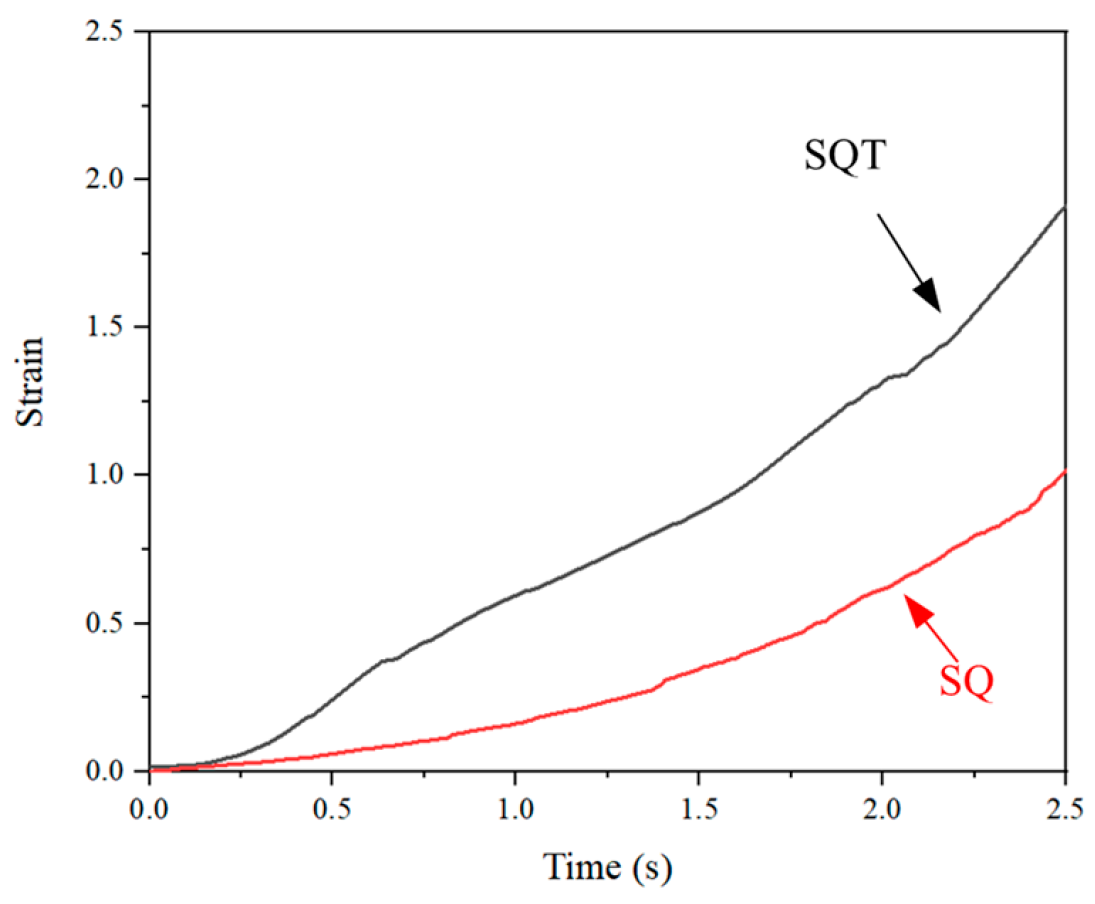
4.2. Evolution of Stress Distribution Under SQ and SQT Process
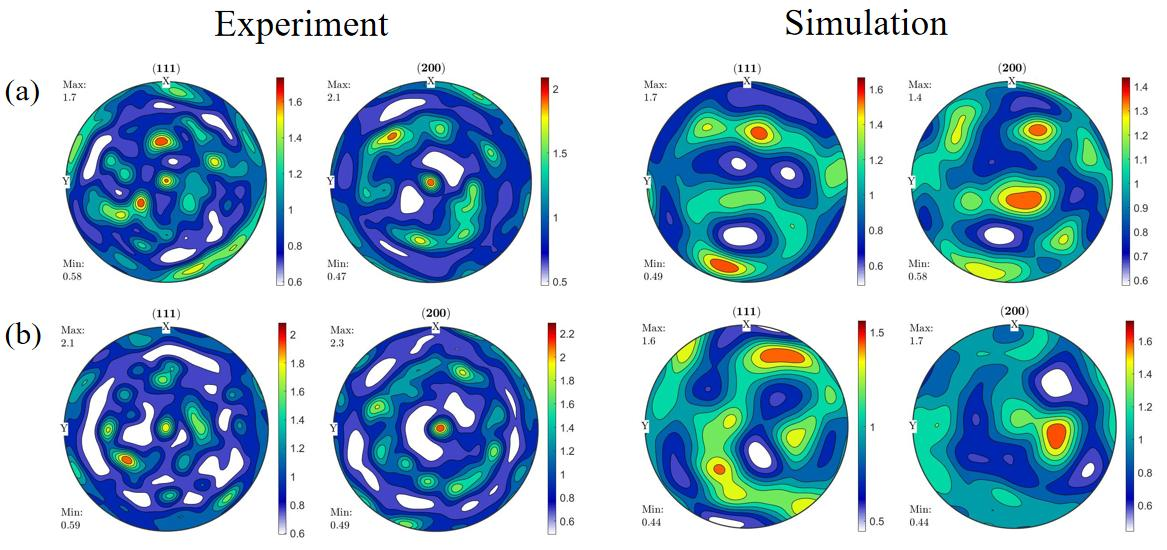
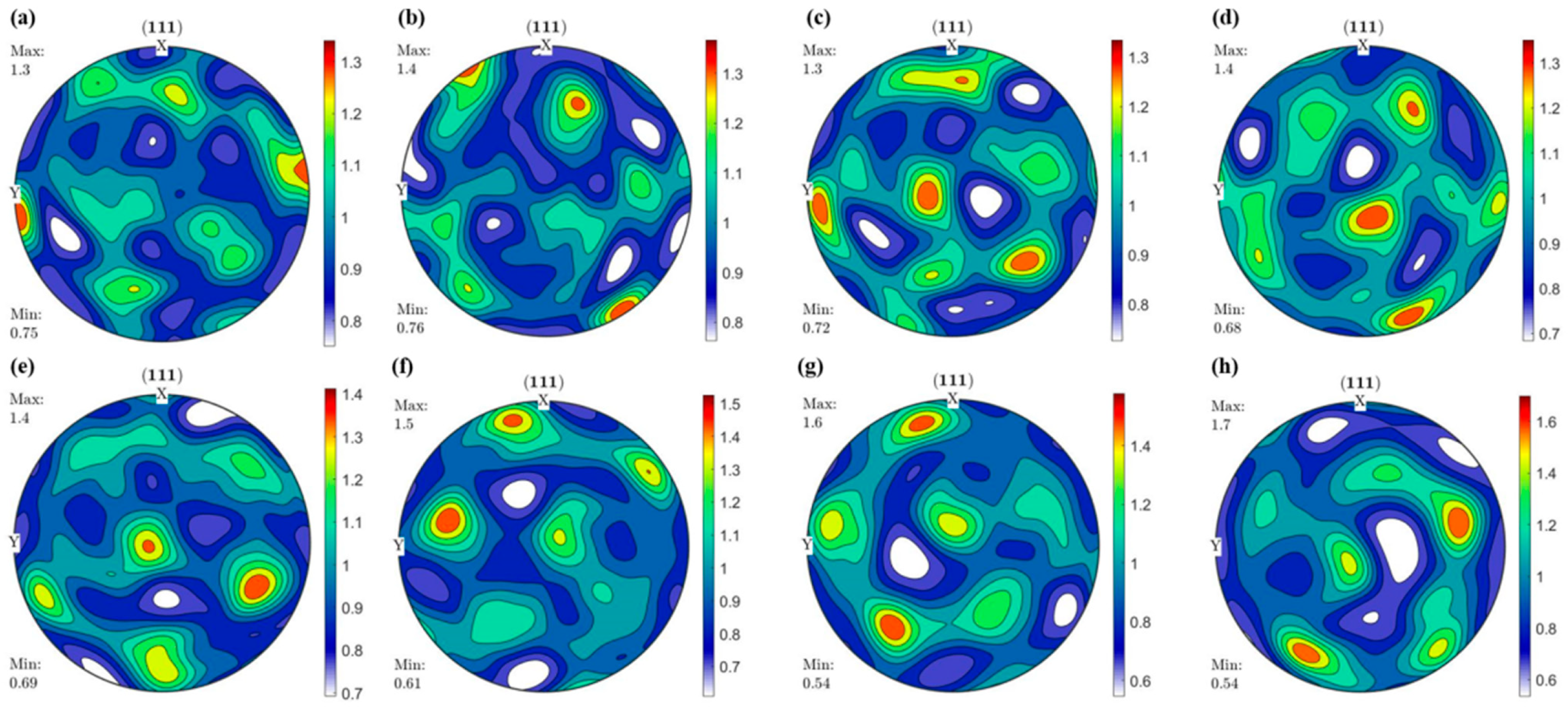
4.3. Texture Under SQ and SQT Process
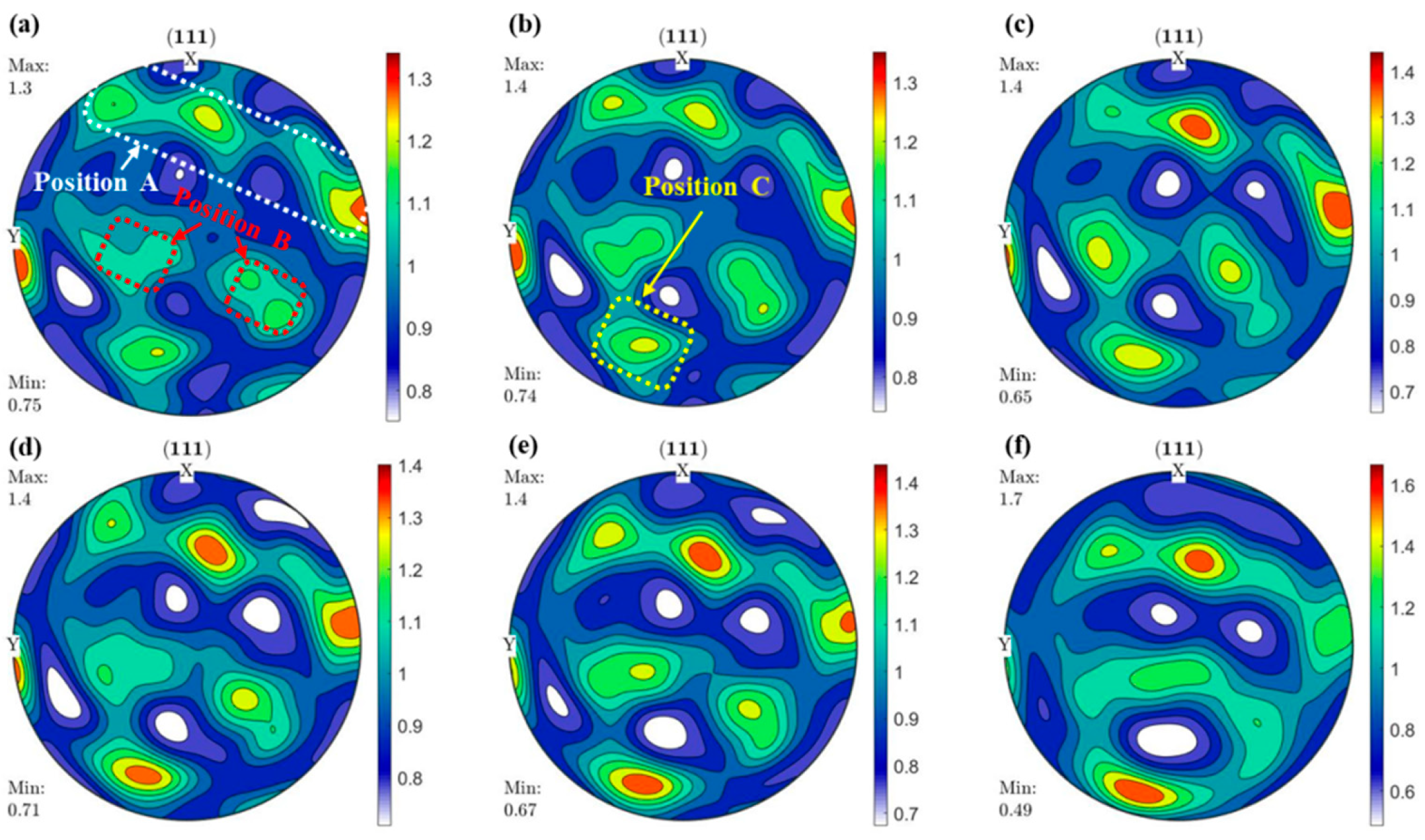
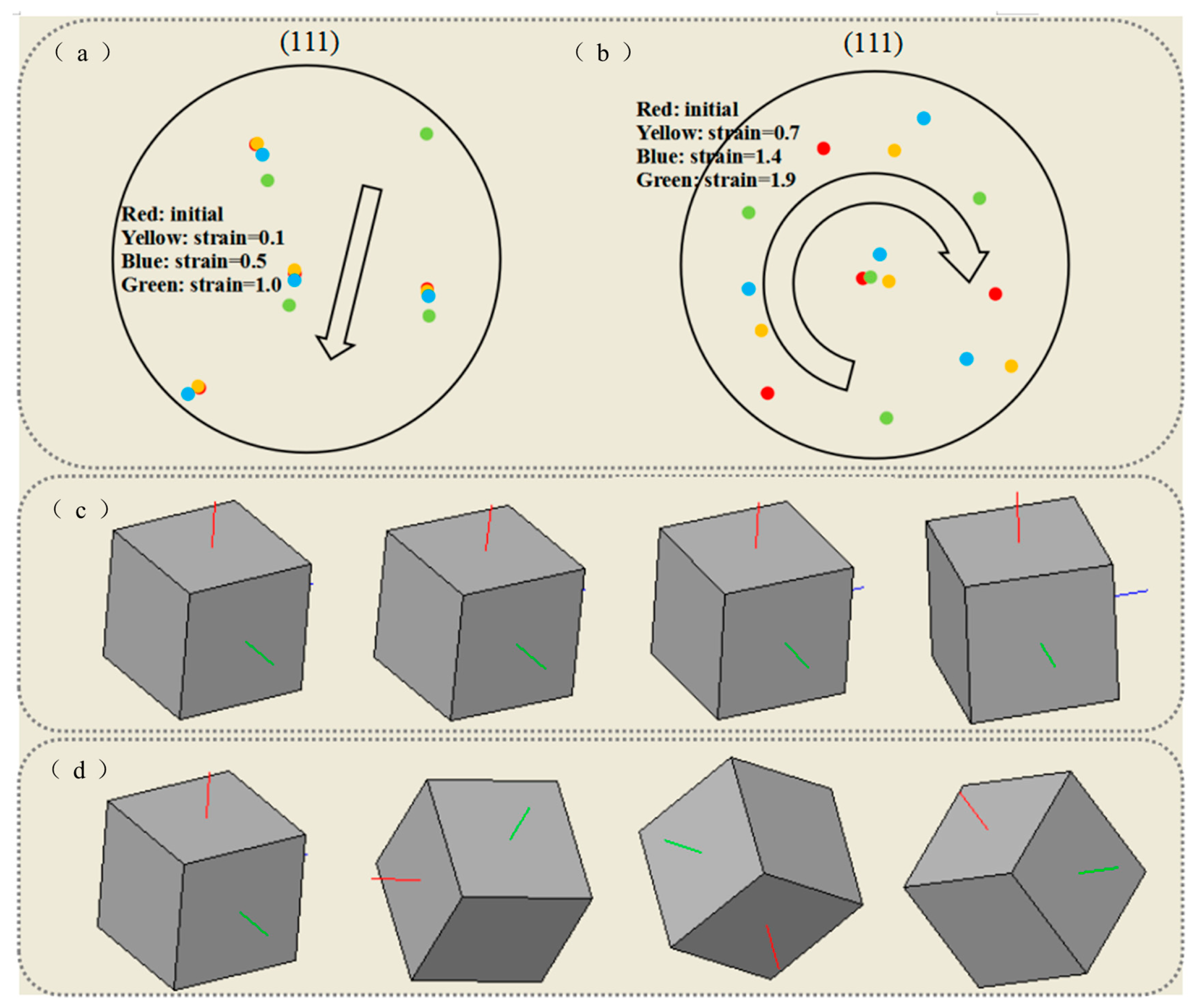
4.4. The Role of Shear Stress in the Texture Evolution SQT Process
4.5. Evolution of Deformation Mode Under SQ and SQT Process
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- After the introduction of torsion shear in SQ, the stress concentration during the forming process is reduced, and low and uniform distributed equivalent stresses are obtained, reducing deformation resistance. Consequently, plastic deformation and forming efficiency is enhanced, ultimately producing thinner-walled workpieces with finer secondary dendrites and eutectic silicon.
- (2)
- After the introduction of torsion shear in SQ, the shear forces during the forming process is increased. As the distance from the torsion axis increases, shear forces increase and the maintained time of shear forces increases. This causes more a pronounced refinement effect on secondary dendrites and eutectic silicon, leading to the formation of a finer microstructure.
- (3)
- After the introduction of torsion shear in SQ, a slip system is introduced. At the early deformation stage, and are the dominant slip systems. In the later deformation stages, , , , and become the prevalent slip systems. This change in slip systems results in a noticeable alteration in the direction of grain rotation, leading to an increase in the grain rotation angle. Ultimately, this process leads to the development of a distinct texture.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Xing, S.M.; Ao, X.H.; Wang, T.Y. Microstructure evolution of A380 aluminum alloy during rheological process under applied pressure. China Foundry 2019, 16, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Li, J.K.; Sun, H.W.; Cheng, J.X.; Ren, X.P.; Jiang, P. Improving ductility of AlSi7Mg alloy by casting-forging process: Effect of deformation degree. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Song, D.F.; Xu, J.; Zheng, K.H. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-1.1Mg-0.6Si-0.4Cu Alloy Manufactured by Casting-Forging Integrated Technology. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2016, 850, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.F.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.Z.; Hu, G.Q.; Wang, Y.; Ding, C.J.; Zou, D.C. Investigation on heat treatment of large-sized and complex AlSi9Mg aluminum alloy components formed by squeeze casting. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 924, 166504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, W.W.; Jiang, J.F.; Huang, M.J.; Li, M.X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, C.J.; Zou, D.C. Effect of T6 heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of large-weight aluminum alloy flywheel housing parts formed by local-loading squeeze casting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 1612–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Naghdy, S.; Kestens, L.; Hertelé, S.; Verleysen, P. Evolution of microstructure and texture in commercial pure aluminum subject to high pressure torsion processing. Mater. Charact. 2016, 120, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocich, R.; Kunčická, L.; Král, P.; Macháčková, A. Sub-structure and mechanical properties of twist channel angular pressed aluminum. Mater. Charact. 2016, 119, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhang, X.L.; Wu, X.Y.; Fu, H.W.; Jia, L.N.; Zhang, H. Rheological behaviour of partially solidified A356 alloy: Experimental study and constitutive modelling. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 803, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostad, S.M.; Baghani, A.; Rahimipour, M.R.; Razavi, M.; Zakeri, M.; Heydari, F. Effect of temperature, time, and shear force on the morphology and size of dendrites in A356-Al2O3 composites. J. Compos Mater. 2022, 56, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MartinRaya, O.; Menargues, S.; Martin, E.; Baile, M.T.; Picas, J.A. Rheological Behavior of the A356 Alloy in the Semisolid State at Low Shear Rates. Materials 2023, 16, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebensohn, R.A.; Tomé, C.N. A self-consistent anisotropic approach for the simulation of plastic deformation and texture development of polycrystals-Application of zirconium alloys. Acta Metal. Mater. 1993, 41, 2611–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; He, J.M.; Zhu, B.W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.F.; Shu, X.D.; Fang, Q.H. Transition of dynamic recrystallization mechanisms of as-cast AZ31 Mg alloys during hot compression. Int. J. Plast. 2018, 111, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, H.; Hu, M.Y.; Zhu, B.W.; Xie, C.; Zhang, X.F.; Liu, W.H. Effect of deformation mode on double-peak texture evolution in pre-twinning Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy during high-speed impacting loading. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 172122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Khan, A.S.; Kim, E.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Herold, T.G. Experimental and numerical investigations of yield surface, texture, and deformation mechanisms in AA5754 over low to high temperatures and strain rates. Int. J. Plast. 2013, 41, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabei, A.; Shih, D.S.; Garmestani, H.; Liang, S.Y. Derivation of Process Path Functions in Machining of Al Alloy 7075. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 4503–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Sharma, A.; Morea, A.M.; Kalsar, R.; Bisht, A.; Nayan, N.; Suwas, S. Effect of equal channel angular pressing (ECAP)on the evolution of texture, microstructure and mechanical properties in the Al-Cu-Li alloy AA2195. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 785, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitish, R.; Atul, K.; Premanand, S.C.; Anupma, A. Finite element modelling and microstructural correlation of hot forged Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy (T6) using DEFORM-3D. Mater Today Proceed 2024, 103, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.; Liu, Z.W.; Zeng, W.Q. Isothermal extrusion speed curve design for porthole dieextrusion of hollow aluminum profile based on PID algorithm and finite element simulations. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 2021, 31, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cui, S.S. Grain modeling and finite element simulation of damage evolution for AA5182-O aluminum alloy sheet. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10559–10575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.P.; Tu, Y.Y.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, Y.H. Size effects on mechanical properties of pure industrial aluminum sheet for micro/meso scale plastic deformation: Experiment and modeling. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 859, 157752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Song, H.W.; Zhang, S.H.; Cheng, M.; Lee, M.G. Effect of shear deformation on plasticity, recrystallization mechanism and texture evolution of Mg–3Al–1Zn alloy sheet: Experiment and coupled finite element-VPSC simulation. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 805, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Pang, J.M.; Zhao, J.; Zang, J.; Wang, F.Z. FEM-simulation of machining induced surface plastic deformation and microstructural texture evolution of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 123, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Pang, J.M.; Zhao, J. Crystallographic texture evolution and tribological behavior of machined surface layer in orthogonal cutting of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4598–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Hu, Z.J.; Zhu, B.W.; Chen, Y.Q.; Liu, W.H.; Li, Y.X.; Li, N.B. High temperature flow behavior of A356 aluminum alloy based on modified Johnson-Cook model and recrystallization model. J. Plast. Eng. 2021, 28, 115–124. [Google Scholar]


| Si | Mg | Ti | Sr | Fe | Cu | Zn | Mn | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.43 | 0.41 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.05 | Bal. |
| Slip | Schmidt Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strain = 0 | Strain = 0.4 | Strain = 0.7 | |
| 0.0701 | 0.0686 | 0.0921 | |
| 0.2840 | 0.2784 | 0.3137 | |
| 0.3541 | 0.3470 | 0.4059 | |
| 0.1672 | 0.1679 | 0.1826 | |
| 0.0076 | 0.0173 | 0.0554 | |
| 0.1597 | 0.1507 | 0.2380 | |
| 0.3617 | 0.3643 | 0.3505 | |
| 0.2927 | 0.2983 | 0.2535 | |
| 0.0690 | 0.0660 | 0.0970 | |
| 0.1243 | 0.1278 | 0.0757 | |
| 0.0011 | 0.0027 | 0.0049 | |
| 0.1254 | 0.1304 | 0.0709 | |
| Slip | Schmidt Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strain = 0 | Strain = 0.7 | Strain = 1.4 | |
| 0.0701 | 0.0757 | 0.0371 | |
| 0.2840 | 0.2495 | 0.2843 | |
| 0.3541 | 0.3252 | 0.3214 | |
| 0.1672 | 0.2024 | 0.0971 | |
| 0.0076 | 0.0654 | 0.0038 | |
| 0.1597 | 0.1370 | 0.0932 | |
| 0.3617 | 0.3906 | 0.3253 | |
| 0.2927 | 0.3240 | 0.2890 | |
| 0.0690 | 0.0666 | 0.0363 | |
| 0.1243 | 0.1125 | 0.1911 | |
| 0.0011 | 0.0092 | 0.0008 | |
| 0.1254 | 0.1217 | 0.1919 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Xiong, S.; Liu, W.; Qin, G.; Xu, C.; Li, L. Unveiling the Microstructure Evolution Mechanism of A356 Aluminum Alloy During Squeeze Casting Torsional Formation. Coatings 2025, 15, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091099
Wang Z, Zhu B, Li H, Liu X, Chen G, Xiong S, Liu W, Qin G, Xu C, Li L. Unveiling the Microstructure Evolution Mechanism of A356 Aluminum Alloy During Squeeze Casting Torsional Formation. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091099
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhenhu, Biwu Zhu, Heng Li, Xiao Liu, Guoqiang Chen, Shengkai Xiong, Wenhui Liu, Ganlin Qin, Congchang Xu, and Luoxing Li. 2025. "Unveiling the Microstructure Evolution Mechanism of A356 Aluminum Alloy During Squeeze Casting Torsional Formation" Coatings 15, no. 9: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091099
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhu, B., Li, H., Liu, X., Chen, G., Xiong, S., Liu, W., Qin, G., Xu, C., & Li, L. (2025). Unveiling the Microstructure Evolution Mechanism of A356 Aluminum Alloy During Squeeze Casting Torsional Formation. Coatings, 15(9), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091099






