Research on the Synergistic Evolution Law of Microstructure and Properties of Deformed Austenitic Stainless Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
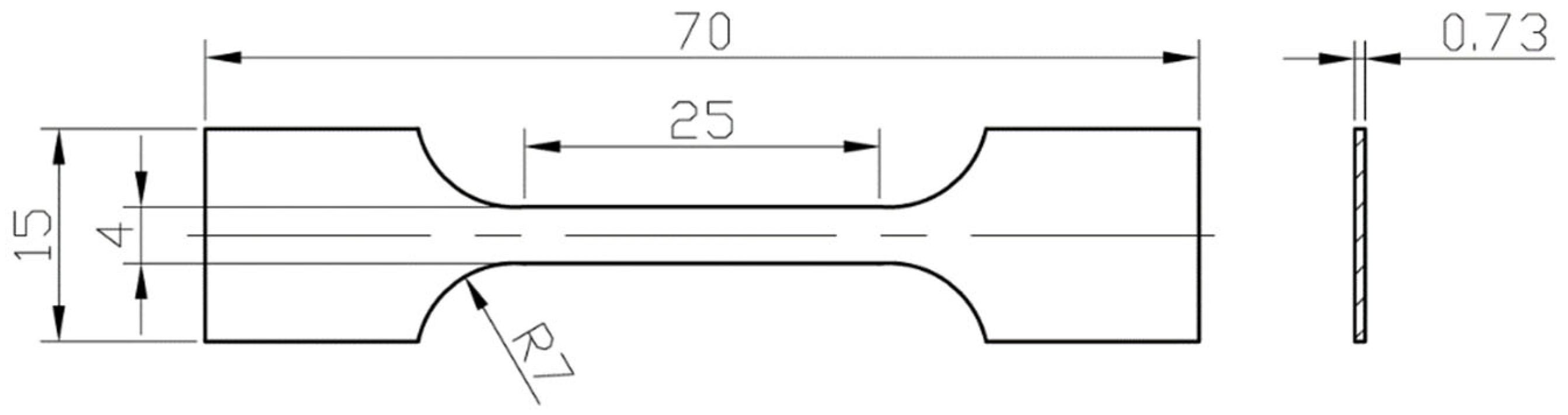
2.1. Material Composition and Plastic Deformation Process
2.2. Microstructure Characterization and Macroscopic Performance Testing
3. Results
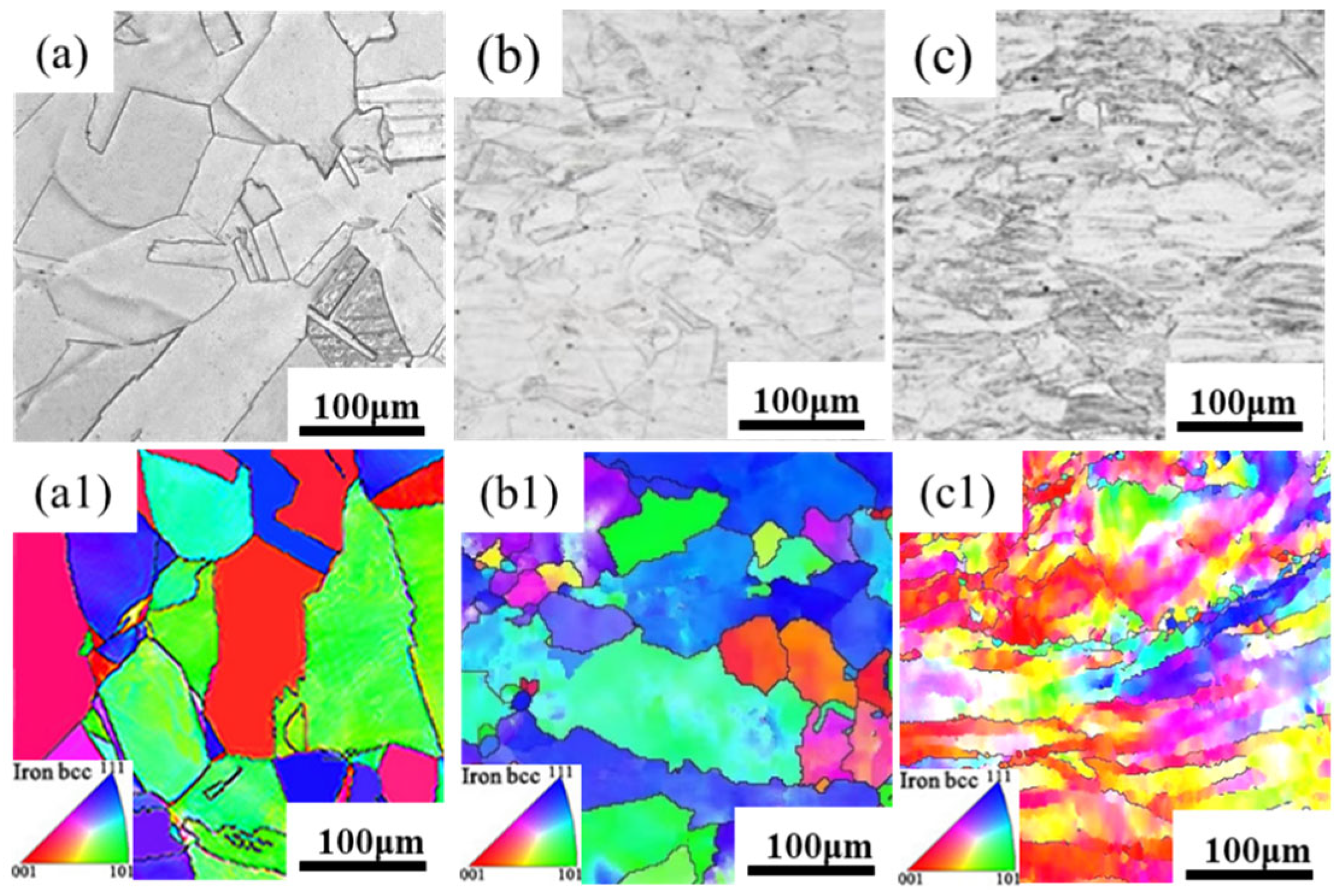
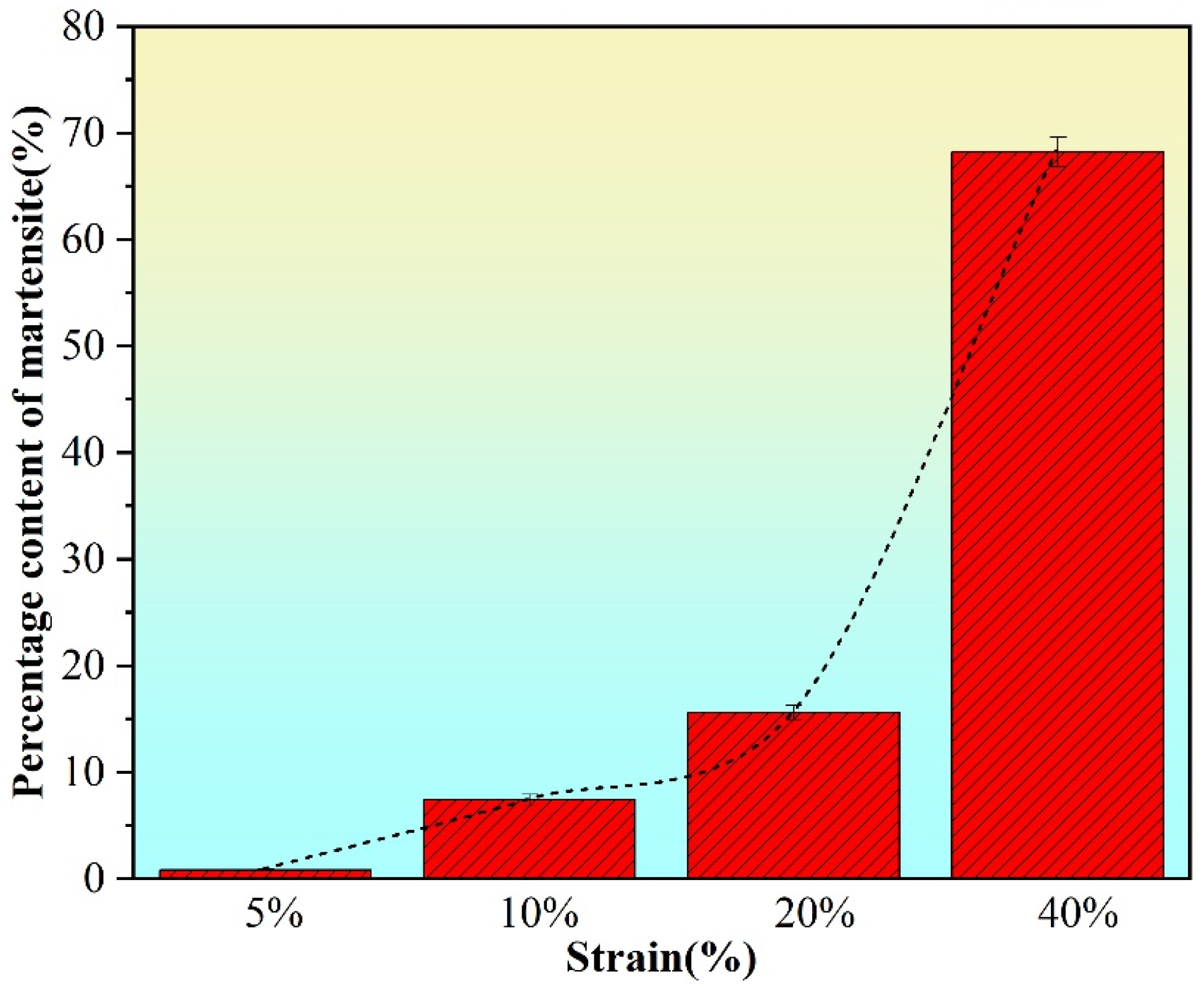
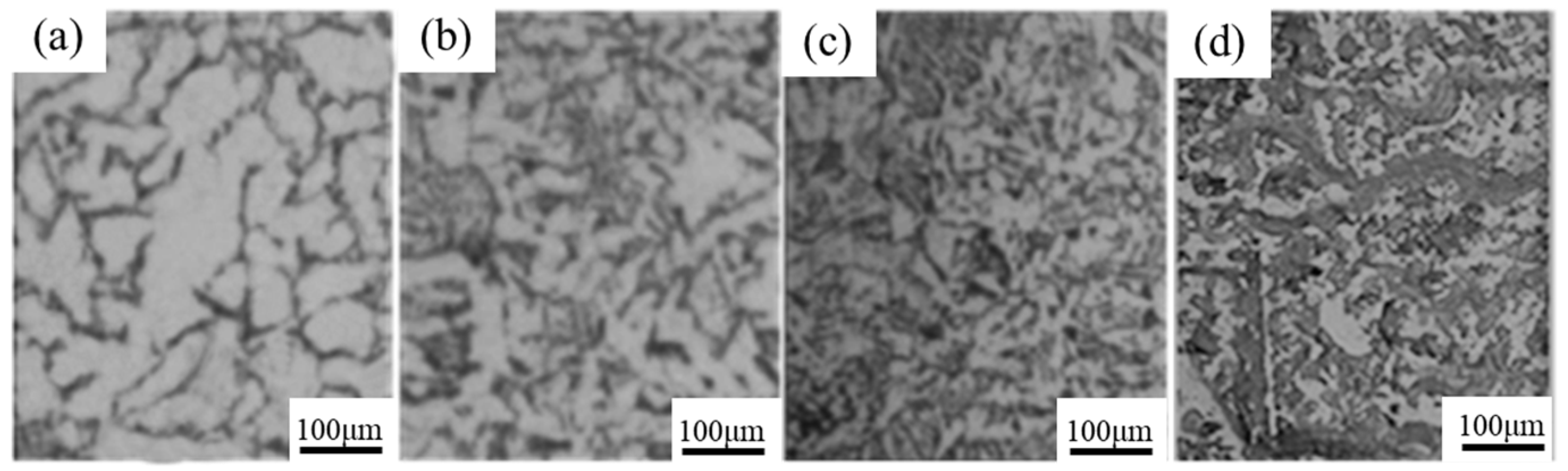
3.1. Microstructural Characterization
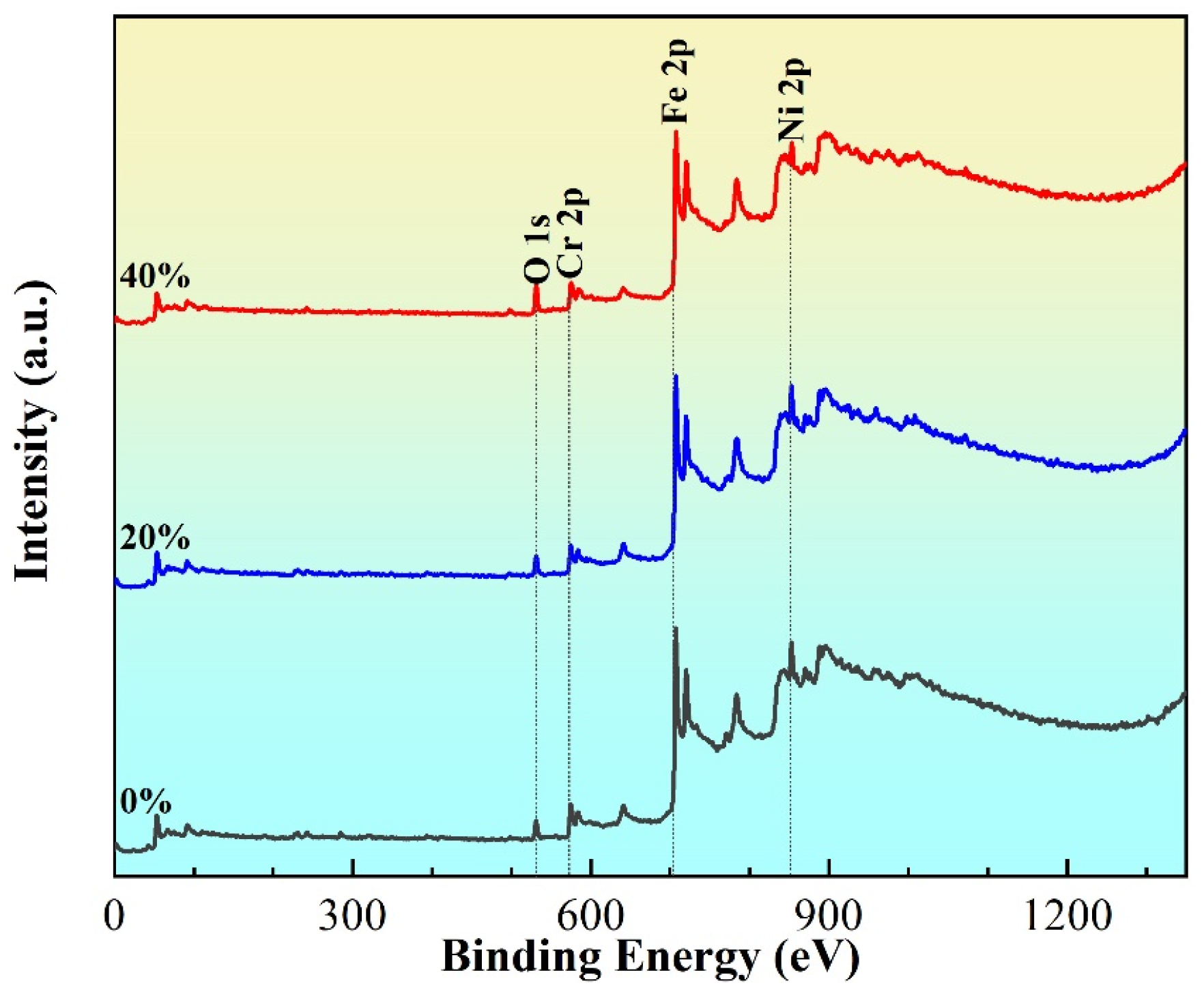
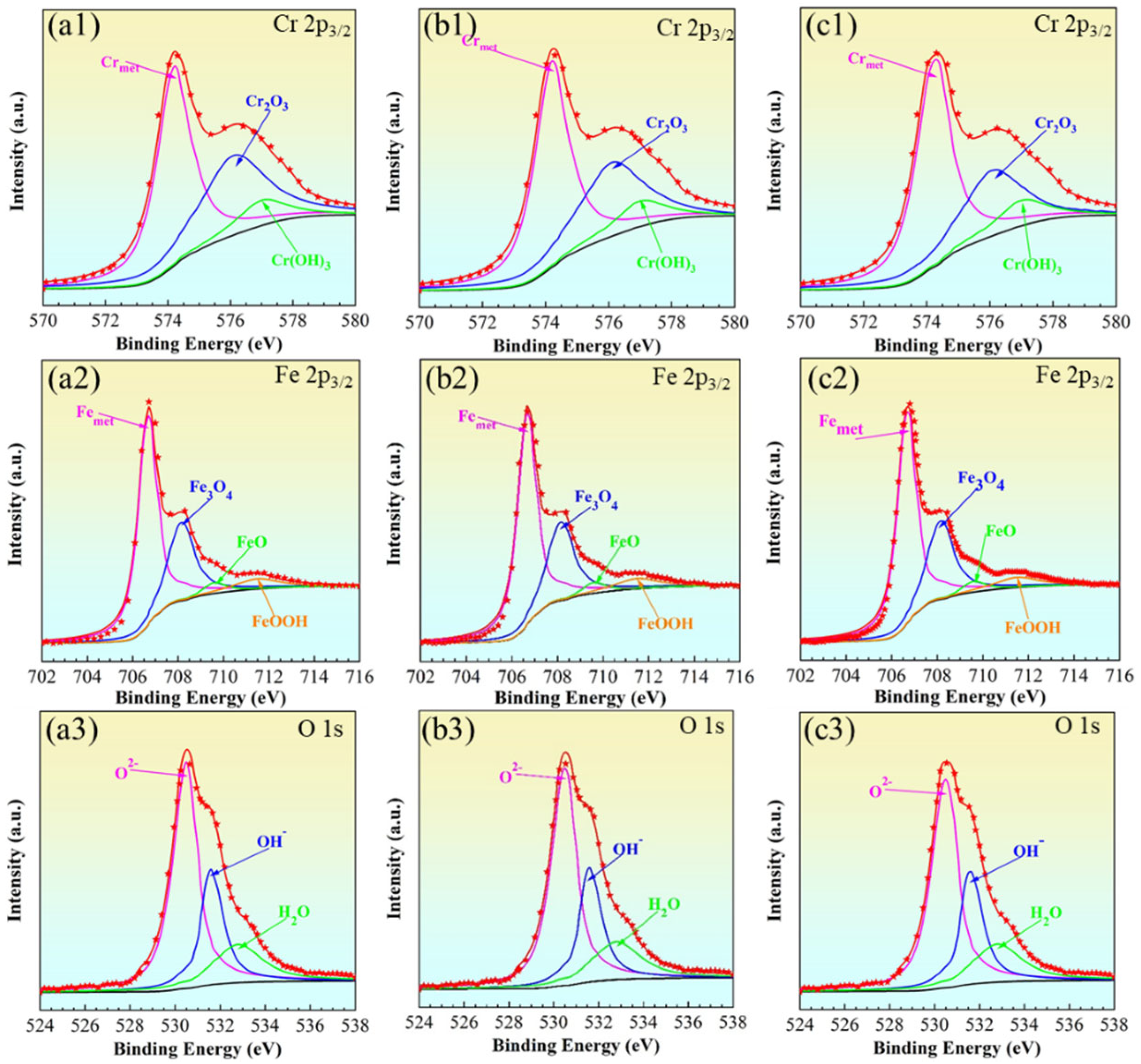
3.2. Surface Passive Film Characteristics
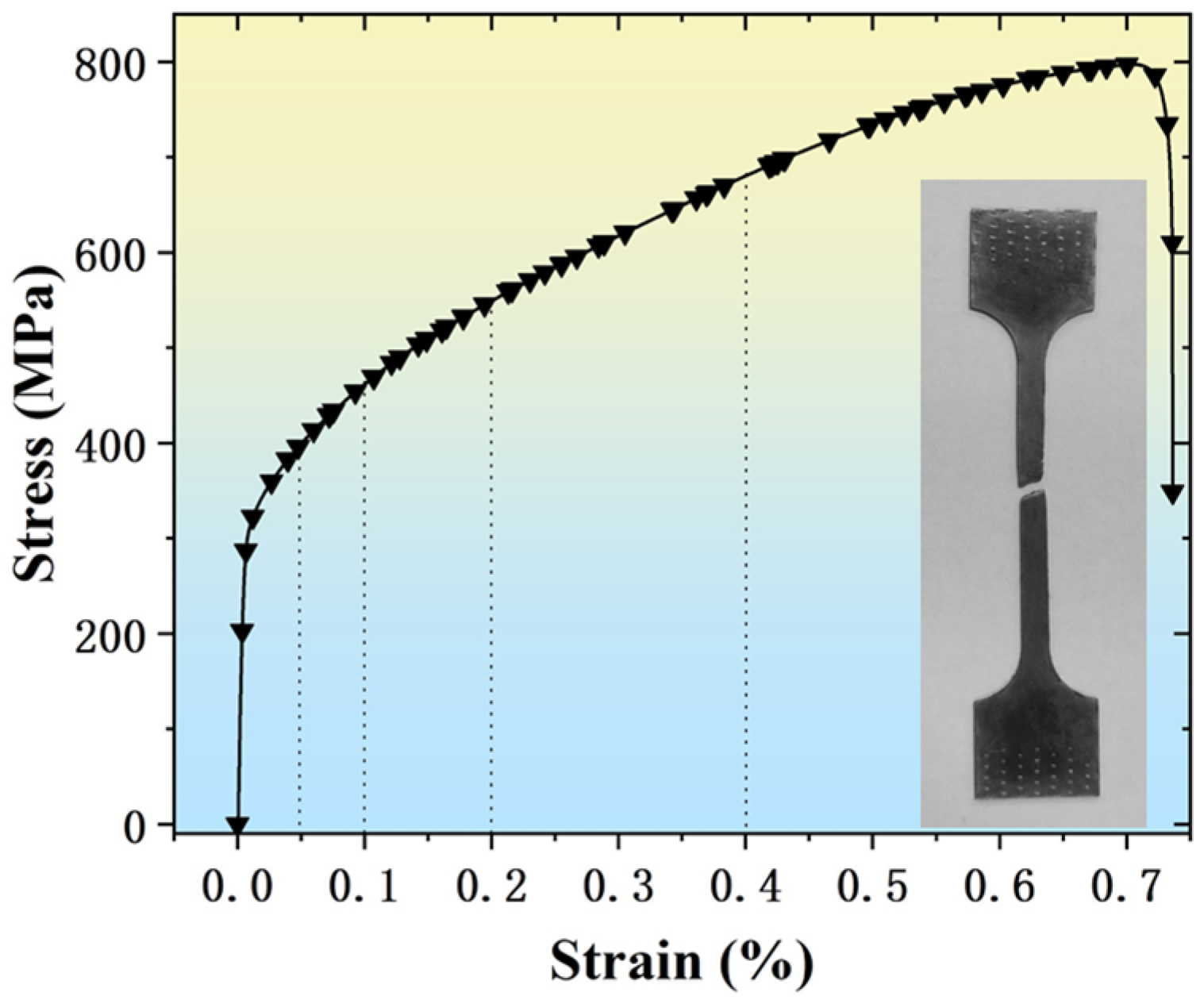
3.3. Mechanical Properties Testing
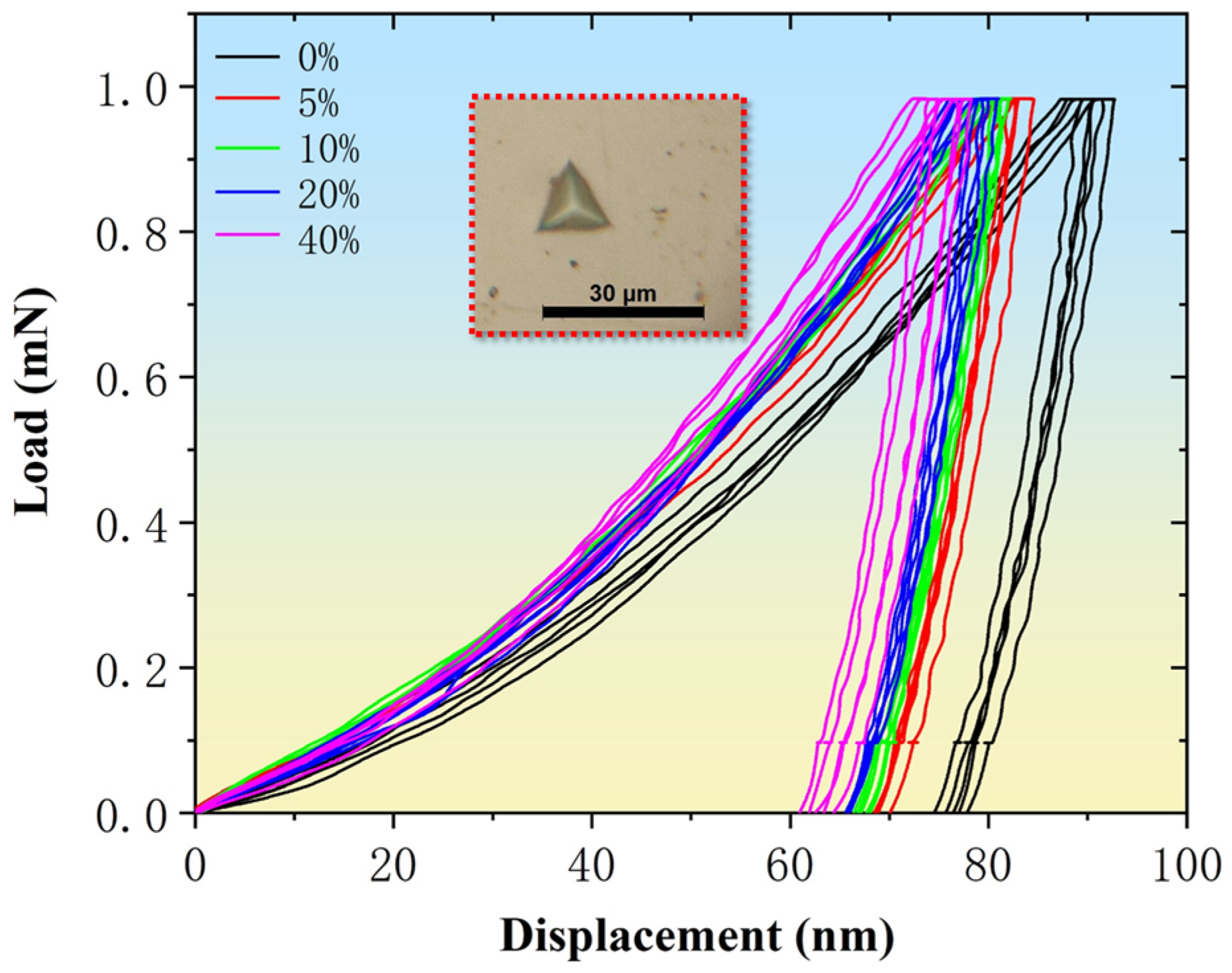
3.3.1. Nanoindentation Testing
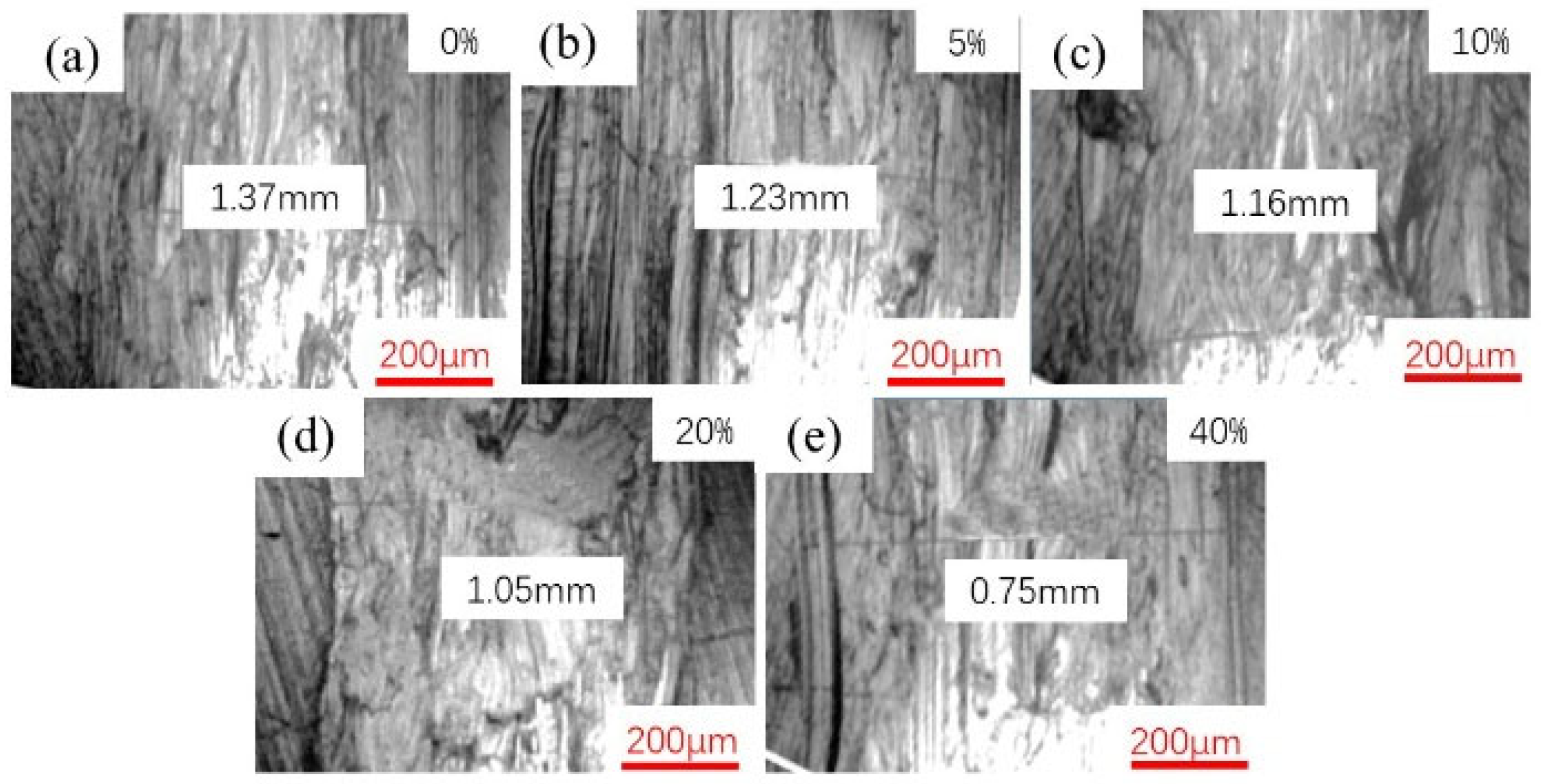
3.3.2. Friction-Wear Testing
3.4. Corrosion Resistance Testing
3.4.1. Salt Spray Corrosion Test
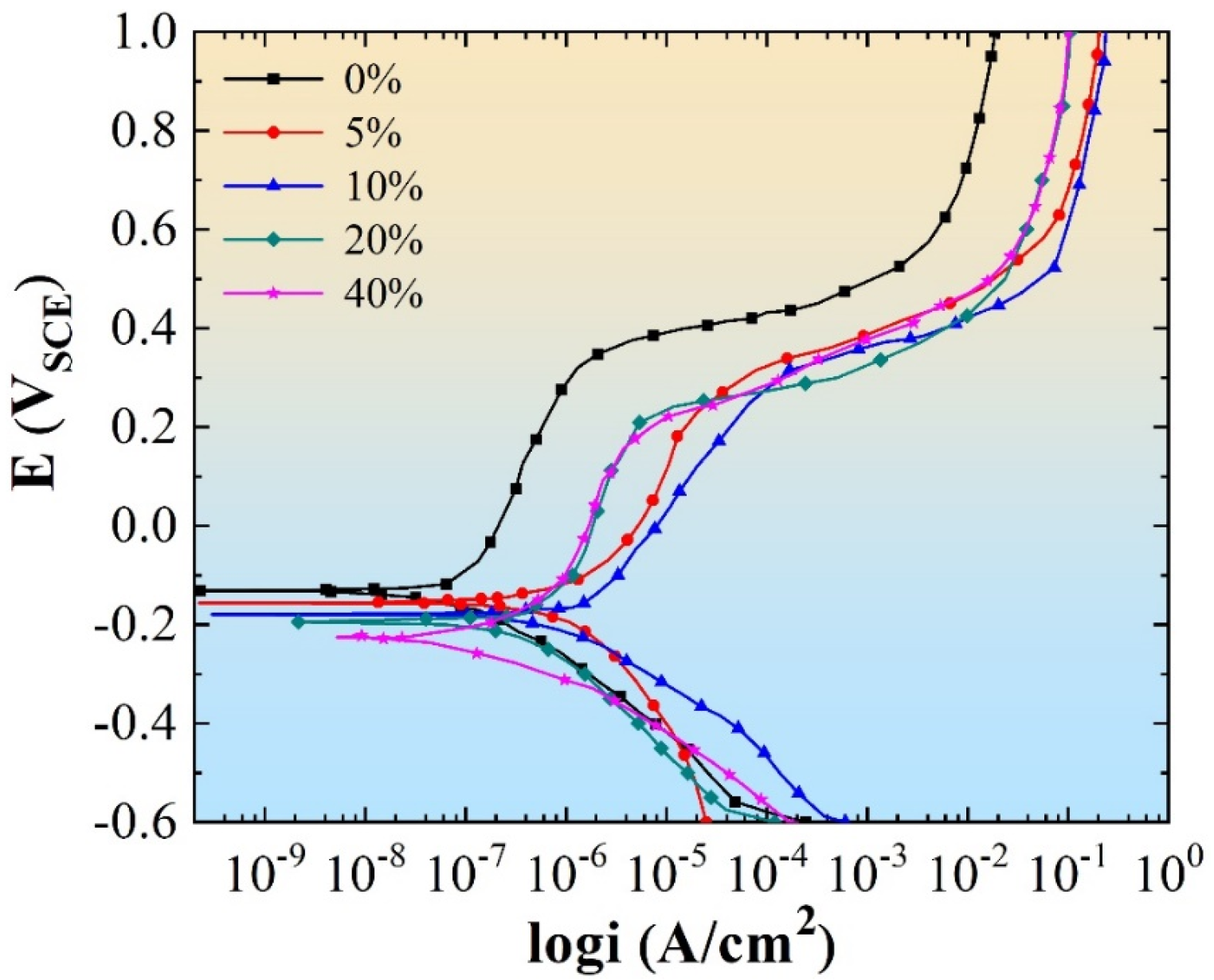
3.4.2. Electrochemical Corrosion Testing
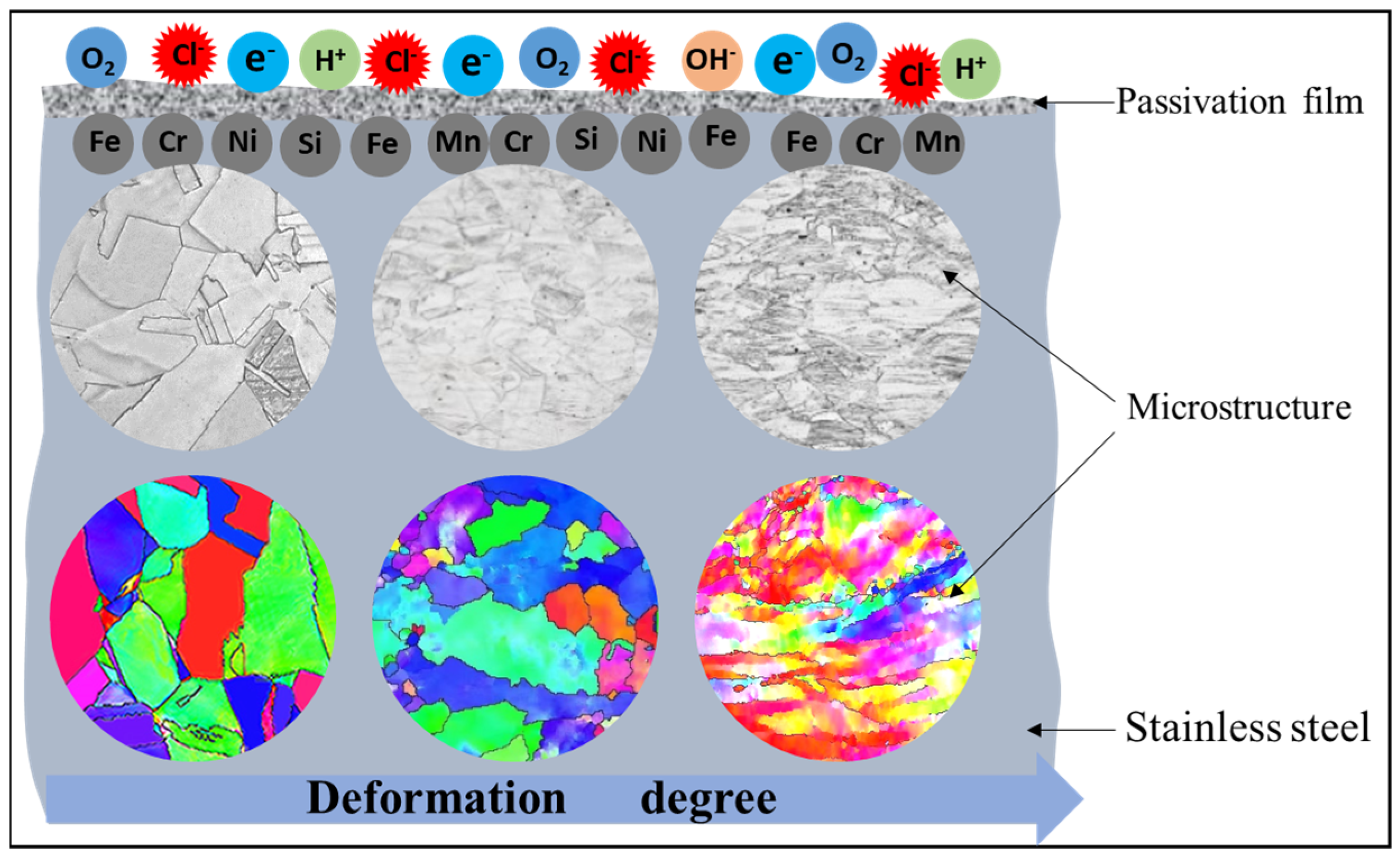
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- With increasing deformation degree in 304 stainless steel, grains are destroyed, generating numerous subgrains internally, grain size significantly decreases, crystal orientations become chaotic, and the content of transformation-induced martensite increases. Additionally, with increasing deformation, the oxide content in the passive film on the stainless steel surface decreases.
- (2)
- With increasing deformation degree, the nanohardness of 304 stainless steel gradually increases, and its wear resistance gradually improves.
- (3)
- With increasing deformation degree, the resistance of 304 stainless steel to salt spray corrosion and pitting corrosion gradually decreases.
- (4)
- The destruction of grains, martensitic transformation, dislocation accumulation, and changes in surface passive film characteristics caused by plastic deformation lead to the increase in nanohardness and wear resistance of 304 austenitic stainless steel but cause the deterioration of its corrosion resistance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kariksiz, M.; Kirkik, D. Antibacterial evaluation of antibiotic-coated titanium and stainless steel implants in orthopaedic application: A dip-coating approach. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2025, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaddam, S.; Haridas, R.S.; Tammana, D.; Sanabria, C.; Lammi, C.J.; Berman, D.; Mishra, R.S. Double-sided friction stir welding of Nitronic-40 stainless steel for application in tokamak devices. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 159, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiao, H.; Shao, P.; Huang, S.; Shi, Y.; Liu, K. Microstructure evolution and deformation behavior of high strength titanium clad steel plate in the thermal compression. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 2300834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zergani, H.M.R. Unraveling the effect of deformation temperature on the mechanical behavior and transformation-induced plasticity of the sus304l stainless steel. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 2000114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, M.; Jiang, K. Effect of deformation on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of bismuth-containing austenitic stainless steels: A molecular dynamics study. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2025, 126, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, S.; Bahanan, S.; Kang, J.-H.; Widiantara, I.P.; Ko, Y.G. Deep penetration of shear deformation in ferritic stainless steel via differential speed rolling considering contact condition. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, M.J.; Mirzadeh, H.; Sadeghpour, S.; Mahmudi, R. Dependency of work-hardening behavior of a metastable austenitic stainless steel on the nucleation site of deformation-induced martensite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 868, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhyasankari, N.; John, R.R.; Senthilmurugan, P.R.; Vishnupriya, V. Comparative evaluation on surface nanohardness, surface microhardness, surface roughness, and wettability of plant-based organic nanoparticle reinforced polyetheretherketone as an implant material-An in vitro study. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2024, 24, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Lei, H.; Jiao, F.; Niu, W.; Xu, X.; Lin, X. Influence of citric acid passivation treatment on the marine atmospheric corrosion resistance of L80-13Cr stainless steel. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Xie, Y. Effect of pre-filming potential on the electrochemical characteristics of 2205 duplex stainless steel in NaCl solution. 2024 International Conference on Corrosion Protection and Application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2821, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Kelly, R.G.; Birbilis, N. On the origin of passive film breakdown and metastable pitting for stainless steel 316L. Sci. C. 2024, 230, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pshyk, O.V.; Patidar, J.; Cancellieri, C.; Siol, S. Auger parameter analysis for TiN and AlN thin films via combined in-situ XPS and HAXPES Empa. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.20145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Lin, D.; Qin, L.; Sun, M.; Liao, K.; Du, X.; Chen, Y. Passivation film characteristics of 2205 duplex stainless steel in reboiler tubes under the combined effects of dissolved oxygen and applied stress. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 5007–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, Y.; Lu, D.; Yu, Y.; Yang, H.; Qiao, Y. Passivation behavior of different building planes of selective laser melting 316l stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl solution. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 94, 2200759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, X.-Q.; Wang, L.-W.; Yang, Q.-R.; Cheng, L.-J.; Cui, Z.-Y. Passivation behavior of 2507 super duplex stainless steel in hot concentrated seawater: Influence of temperature and seawater concentration. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 35, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Li, K. Semiconducting Behaviour and corrosion resistance of passive film on corrosion-resistant steel rebars. Materials 2022, 15, 7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralls, A.M.; Leong, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Unraveling the friction and wear mechanisms of surface nanostructured stainless-steel. Wear 2024, 538–539, 205185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.; Tang, J.; Yu, W.; Tang, Z.; Qin, R. Effect of aging treatment on long-term salt spray corrosion resistance of 15-5pH stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2025, 56, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gong, F.; Zhang, X.; Xia, J.; Liu, X. Effect of cutting parameters on pitting corrosion resistance of S32760 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Corros. Werkst. Und Korros. 2024, 75, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, B.; Yan, B. Effect of arc remelting on microstructure and pitting corrosion resistance of 441 ferritic stainless steel. Kov. Mater. 2023, 61, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Zou, Z.; Jin, M.; Cui, Z.; Wang, T. Constitutive model of trip-type duplex stainless steel under symmetrical strain cyclic loading considering the effect of martensitic transformation. Metall. Mater. Trans. Part A 2025, 56, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P. Effect of silicon on the martensitic nucleation and transformation of 301 stainless steel under various cold-rolling deformations. Metals 2024, 14, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Xie, L.; Shen, F.; Xin, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, W.; Li, L. Mechanical properties and martensitic transformation behavior of 316ln stainless steel under cryogenic deformation. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, j.; Li, j.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Niu, G.; Feng, G.; Pang, Q. Strengthening mechanism of antibacterial stainless steel based on heterogeneous nano/ultrafine austenite with high dislocation density. JOM 2025, 77, 2698–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Luan, J.; Jiao, Z.; Liu, C.T.; Zhang, Z. Formation of core-shell nanoprecipitates and their effects on work hardening in an ultrahigh-strength stainless steel. Int. J. Plast. 2025, 184, 104184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, G.; Song, Y.; Xu, H. Effect of recrystallization degree on properties of passive film of super ferritic stainless steel S44660. Corros. Rev. 2024, 42, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assumpo, R.F.; Georges, M.; Guo, X.; Farias, F.W.C.; Santos, D.B.; Frankel, G.S.; Sicupira, D.C. Reverse martensitic transformation on the corrosion behavior of a 2304 lean duplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2025, 245, 112690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, A.; Iswanto, P.T.; Irfanuddin, F. Effect of cold rolling and shot peening on physical and mechanical properties of 316L stainless steel. AIP Conf. Proc. 2025, 3120, 020010. [Google Scholar]
| Material | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 1.13 | 0.039 | 0.022 | 18.09 | 8.06 |
| Material | Deformation Degree (%) | Nanohardness Value (GPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | 0% | 4.0 ± 0.1–5.0 ± 0.2 |
| 5% | 4.0 ± 0.1–5.5 ± 0.2 | |
| 10% | 4.5 ± 0.1–5.5 ± 0.2 | |
| 20% | 5.0 ± 0.2–7.5 ± 0.3 | |
| 40% | 6.0 ± 0.3–7.5 ± 0.3 |
| Material | Deformation Degree (%) | Average Mass Loss/g | Average Corrosion Rate/(g/m2·h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 0% | 0.0021 ± 0.0002 | 0.0125 ± 0.001 |
| 5% | 0.0023 ± 0.0002 | 0.0140 ± 0.001 | |
| 10% | 0.0027 ± 0.0003 | 0.0161 ± 0.002 | |
| 20% | 0.0029 ± 0.0003 | 0.0173 ± 0.002 | |
| 40% | 0.0032 ± 0.0003 | 0.0190 ± 0.002 |
| Deformation Degree | Ep (mVSCE) | Ec (mVSCE) | ic (nAcm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 398.7 ± 2.2 | −131.4 ± 2.5 | 23.04 ± 0.14 |
| 5% | 360.4 ± 1.9 | −156.6 ± 2.1 | 22.01 ± 0.11 |
| 10% | 315.1 ± 1.7 | −179.1 ± 2.3 | 29.55 ± 0.08 |
| 20% | 252.9 ± 1.2 | −194.1 ± 1.7 | 21.74 ± 0.04 |
| 40% | 221.7 ± 2.3 | −225.6 ± 1.5 | 52.58 ± 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, H.; Cai, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiu, H.; Tong, Z.; Ding, M. Research on the Synergistic Evolution Law of Microstructure and Properties of Deformed Austenitic Stainless Steel. Coatings 2025, 15, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070845
Tao H, Cai Y, Li Z, Xiu H, Tong Z, Ding M. Research on the Synergistic Evolution Law of Microstructure and Properties of Deformed Austenitic Stainless Steel. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070845
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Huimin, Yafang Cai, Zi Li, Haiteng Xiu, Zeqi Tong, and Mingming Ding. 2025. "Research on the Synergistic Evolution Law of Microstructure and Properties of Deformed Austenitic Stainless Steel" Coatings 15, no. 7: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070845
APA StyleTao, H., Cai, Y., Li, Z., Xiu, H., Tong, Z., & Ding, M. (2025). Research on the Synergistic Evolution Law of Microstructure and Properties of Deformed Austenitic Stainless Steel. Coatings, 15(7), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070845







