Abstract
To enhance the high-temperature oxidation resistance of chromium carbide metal ceramic coatings, micro/nanoparticle modification was applied to the alloy binder phase of the typical Cr3C2-NiCr coating. This led to the development of Cr3C2-NiCrCoMo and Cr3C2-NiCrCoMo/nano-CeO2 coatings with superior high-temperature oxidation performance. This study compares the high-temperature oxidation behavior of these coating samples and explores their respective oxidation mechanisms. The results indicate that the addition of CoCrMo improves the compatibility between the oxide film and the coating, enhancing the microstructure and integrity of the oxide film. Compared to Cr3C2-NiCrCoMo coatings, the incorporation of nano-CeO2 promotes the reaction between oxides in the Cr3C2-NiCrCoMo/nano-CeO2 coating, increasing the content of binary spinel phases, reducing thermal stress at the oxide–coating interface, and improving the adhesion strength of the oxide film. As a result, the oxidation rate of the coating is reduced, and its oxidation resistance is improved.
1. Introduction
High-temperature oxidation refers to the corrosion process where materials react with oxygen at elevated temperatures to form oxides. Chromium carbide metal–ceramic composite coatings, consisting of a ceramic hard phase (Cr3C2) and a metallic/alloy binder phase, exhibit high hardness (~1500 HV), a high melting point (1890 °C), and a high elastic modulus (~400 GPa) [1,2,3]. Typical Cr3C2-NiCr coatings are generally suitable for service temperatures below 815 °C, demonstrating excellent oxidation resistance (oxidation rate <0.5 mg/cm2·h), wear resistance (wear rate ~10−6 mm3/N·m), and erosion resistance within this range [4,5]. The higher performance parameters of advanced equipment impose more stringent demands on high-temperature components—including turbine rotors, flow control parts, sealing bearings, fluidized bed combustors, and boiler tubes (service temperatures exceeding 900 °C) [6,7]—thus, these components require protective coatings with enhanced oxidation resistance (target oxidation rate <0.2 mg/cm2·h), wear resistance (wear rate ~10−7 mm3/N·m), and erosion resistance.
The oxidation mechanisms of typical Cr3C2-NiCr coatings have been investigated by domestic and foreign researchers. The high-temperature performance of Cr3C2-NiCr coatings was examined by Matthews and Berger [8], who identified inter-diffusion mechanisms in the 500–900 °C range. It was observed that Cr diffusion facilitates the development of an interfacial oxide film within the coating. The results of Premkumar [9] showed that nanocrystalline Cr3C2-NiCr coatings provide better protection to the substrate, improving the grain boundary diffusion of the nanocrystalline coatings, which promotes the formation of a dense Cr2O3 oxide film, which is conducive to reducing the loss of Cr in the metal-bonded phase of the coating. Matthews [9] analyzed the interdiffusion phenomenon between the Cr3C2-NiCr coating and the Ni625 substrate during the oxidation process at 500–900 °C and found that a stronger interdiffusion occurred at 900 °C, and the depletion of Cr near the interface results from its loss in the substrate. It has been shown that the high-temperature oxidation process leads to the microstructural evolution and elemental diffusion of chromium carbide metal–ceramic coatings, and the formation of oxide film on their surfaces is closely related to the decarburization behavior of chromium carbide in the coatings and the diffusion of Cr elements. In Cr3C2-NiCr coatings, carbides mainly exist in the form of three compounds, Cr3C2, Cr7C3, and Cr23C6, of which Cr7C3 and Cr23C6 are generated due to the decarburization and decomposition of pristine Cr3C2 during powder granulation and spraying, and after decarburization, the elements of Cr and C are dissolved in the metal-bonded phase of the coatings to form the dissolution transition zone [10]. In the first three stages of the decarbonization and oxidation of Cr3C2, Cr7C3, Cr23C6, and CrMET (metallic Cr) are intermediate products of the oxidation process [11]. During the decarbonization and oxidation of Cr3C2, the C element detached from Cr3C2 combines with oxygen and dissipates as CO. In the last stage, the oxidation of CrMET produces Cr2O3.
In order to further improve the function of Cr3C2-NiCr materials at high temperatures, problems such as the oxidation of adhesive and bonded phases, the decarburization of hard phases and the oxide layer, and peeling must be resolved [12,13]. One effective method is through coating modification. This can be achieved by modifying the composition of the metal-bonded phase elements such as Co, Cr, Mo, and Ni [14,15]. Reddy et al. [16] applied the HVOF technique to a modified (Cr3C2 + 20NiCr) coating using Ni3Ti and studied the oxidation behavior at elevated temperatures. Additionally, the formation of spinel phases contributed crucially to enhancing the antioxidant properties of the coating. Houdková et al. [17] evaluated and compared three HVOF-sprayed chromium carbide cermet coatings with three different bonding phases, and they found that Cr3C2-50% NiCrMoNb coatings with altered bonding phase compositions are more suitable for use in high-temperature vapor environments and can alleviate the oxidation problems that occur due to the internal carbonization of chromium carbide, and they can also be used in high-temperature steam environments and can mitigate the risk of failure due to oxidation of internal carbides. Luo et al. [18] examined the high-temperature performance of FeMnCrAl/Cr3C2-Ni9Al and FeMnCr/Cr3C2 coatings in an air atmosphere at 800 °C. Their results show that spinel oxides are favorable for the generation of dense oxide layers. Among them, the FeMnCrAl/Cr3C2-Ni9Al coating demonstrated the lowest oxidation rate and proved to be more suitable for high-temperature steam environments, where its oxidation weight gain was notably smaller compared to the mild steel substrate. The increase in oxidation resistance was attributed to the active element content of the coatings inhibiting the formation of FeOx and MnOx oxides. Zhou et al. [19] prepared Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo coatings by using the HVOF spraying technique and conducted thermal corrosion tests under a salt corrosion environment at a temperature of 500 °C. It was found that the Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo coatings showed the same resistance to oxidation as the Cr3C2-NiCr coatings, and the Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo coatings showed better corrosion resistance than the Cr3C2-NiCr coatings. The improvement in the thermal corrosion of the coatings is related to the production of oxide films containing a variety of oxides and spinel during the oxidation process of the coatings. The above study shows that adjusting the alloying elements in the adherent phase is an effective way to improve the composition and densification of the oxide film of chromium carbide coatings in order to enhance the antioxidant performance of the coatings at high temperatures; therefore, the synergistic multi-element modification of the coating bonding phase combined with theoretical oxidation calculations and analyses will help to reduce the number of experiments needed and further boost the oxidation resistance of Cr3C2-based cermet coatings.
The incorporation of rare earth (RE) elements enhances coating performance through their unique physicochemical properties, significantly improving hardness, toughness, and resistance to oxidation, corrosion, and wear [20]. Incorporating rare earth elements into the coating’s binder phase enhances elemental diffusion kinetics, suppresses oxide film growth, and promotes oxide grain refinement while strengthening the oxide–coating interface. Among various rare earth oxides, CeO2 demonstrates particularly high reactivity. Researchers worldwide have consequently employed CeO2 as a modifier in chromium carbide coating matrices to optimize oxide film coherence and overall coating performance. Sun et al. [21] studied NiCr-Cr3C2-MoS2-CeO2 coatings and the results showed that the addition of CeO2 could play a role in the grain refinement and solid solution strengthening of the coatings, and the oxidized film produced on the surface of the coatings had an enhanced inhibition effect on the coatings that were able to undergo further oxidation. Saladi et al. [22] investigated the effect of the second phase (CeO2) on the microstructure and coating properties of Cr3C2-NiCr coatings, which contain the most active rare earth oxides among rare earth materials, and domestic and foreign researchers have attempted to modify the bonding phase of chromium carbide coatings by adding CeO2 to improve both the integrity of the coating oxide film and the coating–substrate interfacial adhesion strength. The above studies show that the modification by trace CeO2 facilitates the generation of a continuous dense oxide film, improves the protective effect of the oxide film on the coating, and contributes to the improvement of the high-temperature performance of chromium carbide coatings.
However, the existing research mainly involves a single modulation of the alloy phase element composition or the introduction of rare earth elements in order to modify the bonding phase of chromium carbide metal–ceramic coatings. There is a lack of composite modification methods combining the characteristics of the two, and both the composition of the alloy phase and the synergistic mechanism of rare earth elements that is involved in modifying the composition and structure of coatings’ oxide films remain unclear, and further research needs to be carried out to rectify this. Based on this, in order to clarify the influence and synergistic mechanisms of both rare earth elements and the multiple alloy bonding phase on the oxidation behavior of the coating, through the regulation of the elemental composition of the bonding phase of chromium carbide composite coatings and the introduction of rare earth elements, a number of micro-nano-particle structures of modified chromium carbide composite coatings are prepared, their high-temperature oxidation performance is compared and analyzed, and the oxidation mechanism is observed and explored.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Powder Feedstock Preparation Followed by Coating Fabrication
C1-2 and E1-2 were prepared with Cr3C2-NiCr. The particle sizes of CoCrMo and commercial nano-CeO2 are shown in Table 1. Before powder preparation, ultrasonic dispersion was used to make the powder uniformly dispersed, the ball milling method was used to ensure that the composite powder was well mixed, and then the resulting composite powder was vacuum-dried and used for the preparation of composite coatings. The ball milling speed was 220 rpm, the ball milling time was 20 min, and the ball–material ratio was 1:3. Subsequently, the composite coatings were deposited on 310S steel substrates using an XM-5000 HVOF (High-Velocity Oxy-Fuel) system (Shanghai Huuma Spraying Equipment Co., Shanghai, China) to prepare the C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings. The coating trajectory was programmed and controlled by a Kawasaki RS020N, origin Kawasaki, Tokyo, Japan (six-axis robotic arm).

Table 1.
Composite powder composition.
2.2. Microstructural Characterization of Coatings
The cross-sectional samples of the coatings were mechanically polished and subsequently analyzed using a scanning electron microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA: SEM, JEOL JSM-7610F Plus) equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS, Oxford X-max, Oxford, UK). The crystalline phases present on the coating surfaces were identified through X-ray diffraction (Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan: XRD, DMAX-2500PC). Cu-Kα rays were used as the X-ray source, with a scanning speed of 3°/min and a scanning angle of 20°–90°, supplemented by laser Raman spectroscopy (HORIBA Scientific, Tokyo, Japan, LabRAM HR Evolution instrument) employing a 633 nm excitation wavelength. Furthermore, the phase distribution across the coating was investigated using electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD, Oxford Nordly max3 system, Oxford Instruments, Oxford, UK) for microstructural characterization.
2.3. High-Temperature Oxidation Testing
Isothermal oxidation testing was performed at 700–900 °C to characterize the oxidation resistance of the coatings. The cyclic testing protocol consisted of 10 heating–cooling cycles. The coated specimens were placed in a muffle furnace for oxidation testing, with one cycle every 20 h. The heated specimens were then cooled to room temperature before proceeding to the next cycle, and the process was repeated until 200 h had passed. Prior to and following oxidation, the mass of boat-shaped crucibles containing coated specimens was precisely determined using a high-precision electronic balance (Meilen MTW220, ±0.1 mg accuracy). To establish a baseline for oxidation mass gain evaluation, uncoated specimens served as control samples, with measurements specifically focusing on the coated upper surfaces after each thermal cycle.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Oxidation Thermodynamics Calculations
Thermodynamic analysis was performed to evaluate the Gibbs free energy variations during high-temperature oxidation of the coating systems (N0, C1, C2, E1, and E2) according to the established principles [23]. The possible oxidation reactions of the components in the coatings are as follows:
4/13Cr3C2 (s) + O2 (g) = 6/13Cr2O3 (s) + 8/13CO (g),
4/3Cr (s) + O2 (g) = 2/3Cr2O3 (s),
2Ni (s) + O2 (g) = 2NiO (s),
2Co (s) + O2 (g) = 2CoO (s),
Mo (s) + O2 (g) = MoO2 (s).
The coexistence of multiple oxides in each coating’s oxide film may induce interfacial reactions. Previous studies [19,24,25] have demonstrated that Ni-Cr-Co coatings containing alloys tend to develop spinel-structured phases under oxidative conditions. The potential oxide interaction mechanisms include the following:
NiO(s) + Cr2O3 (s) = NiCr2O4(s),
CoO(s) + Cr2O3 (s) = CoCr2O4(s).
Thermodynamic evaluation of coating oxidation was conducted through Gibbs free energy analysis to determine reaction spontaneity and oxide stability in Cr3C2-NiCrCoMo- and CeO2-modified coatings. Figure 1 presents the ΔG variation trends for these coatings during 700–900 °C oxidation. As can be seen in Figure 1, within the temperature range of 700–900 °C, it is suggested that these reactions can proceed spontaneously. This allows for the determination of the priority of oxide formation in the aforementioned oxidation reactions. The order of Gibbs free energy (ΔG) magnitudes for each reaction is |Cr| > |Mo| > |Ni| > |Co|. Based on thermodynamic theory [26], the lower the Gibbs free energy, the more spontaneous and driven the surface reaction with oxygen. Therefore, within the coating, Cr and Cr3C2 preferentially undergo oxidation reactions with oxygen to form Cr2O3, compared to Mo, Ni, and Co elements. The chromium in the oxide Cr2O3 could originate from both the hard phase Cr3C2 and the alloy binder phase NiCrCoMo. By calculating the Gibbs free energy sequence of Cr oxidation in different phases within the coating, which is Gibbs free energy of NiCr2O4 > Gibbs free energy of CoCr2O4, the result shows that Cr from the Cr3C2 hard phase preferentially undergoes oxidation at high temperatures compared to Cr from the alloy binder phase. This indicates that oxidation and decarburization of Cr3C2 occur simultaneously.
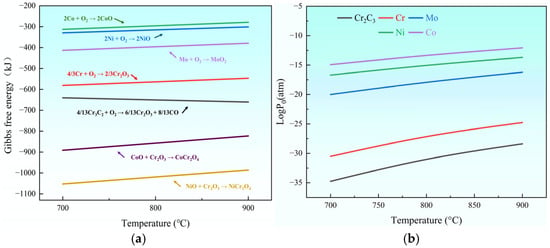
Figure 1.
Gibbs free energy (a) and partial pressure of oxygen (b) of oxidation reactions.
In addition, the Gibbs free energy change and the magnitude of the oxygen partial pressure of the oxide reaction are directly related to the phase stability of the oxide [27]. From a thermodynamic point of view, the lower the Gibbs free energy and the partial pressure of oxygen reacting with oxygen, the higher the thermal stability of the resulting oxides, and the easier it is to generate protective oxides, such as Al2O3, Cr2O3, and spinel oxides, under high-temperature oxidation conditions [26,28]. Therefore, chromium oxide is more stable than other oxides at high temperatures (Figure 1a,b). As shown in Figure 1, at temperatures between 700 and 900 °C, reactions between NiO, CoO, and Cr2O3 oxides produce spinel phases (NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4). At high temperatures ranging from 700 °C to 900 °C, high-temperature thermodynamic calculations indicate parallel formation tendencies for both spinel phases (NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4). This suggests that the affinities of NiO and CoO for Cr2O3 are similar, and the formation of these two spinel phases in the oxidation reaction occurs with comparable priorities. Due to the good stability and low ionic diffusion coefficients of spinel phases, incorporating them into the Cr2O3 oxide film can significantly improve its thermal stability and oxidation resistance and ensure the prevention of metal cation diffusion. During oxidation, the binary spinel phases (NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4) in the coating’s oxide film improve the thermal stability and inhibit ionic diffusion, thereby enhancing the oxidation resistance of the C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings.
3.2. Oxidation Kinetics Analysis
The isothermal oxidation test method [29] was used to measure the mass gain of the N0, C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings. Curves showing the weight gain trend per unit area of each coating with oxidation time are presented in Figure 2. During the oxidation process, the oxidation kinetics of all coatings exhibit a parabolic shape. From this, it can be observed that the oxidation kinetics of the coatings are primarily divided into two stages: In the rapid oxidation stage, the reaction rate between the coating and oxygen is high, causing oxygen to react quickly with the coating material to form oxides. Due to the intense oxidation reaction, significant mass changes may be observed on the coating surface. Typically, during this stage, the oxidation rate has a strong nonlinear dependence on time. In the relatively stable oxidation stage, as the oxidation process progresses, the oxidation rate gradually decreases, and the oxidation of the coating surface stabilizes. The oxide layer becomes denser and more stable, thereby limiting further exposure of the coating to oxygen.
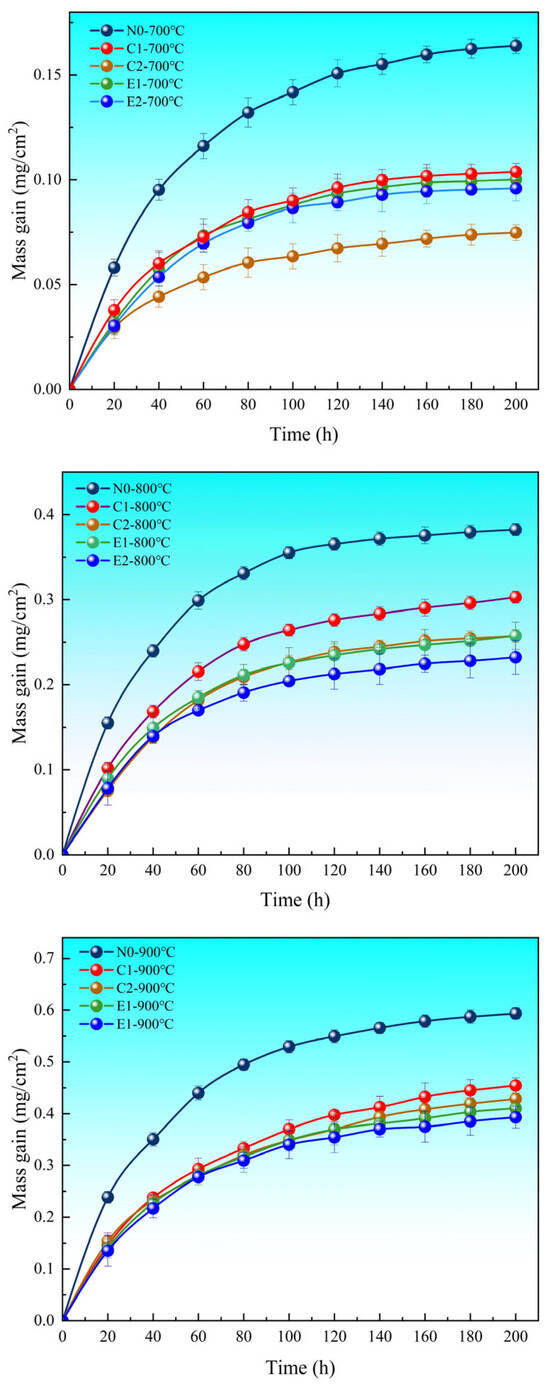
Figure 2.
Oxidation kinetics curves of coatings at 700–900 °C.
The oxidation resistance of coatings C1, C2, E1, and E2 was evaluated through high-temperature testing, with coating N0 serving as the reference. The corresponding weight gain measurements are presented in Figure 2. Based on the oxidation kinetics curves of the coatings at 700–900 °C (Figure 2), it can be seen that compared to N0, the oxidation weight gains of the C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings at 700 °C decreased by 36.7%, 54%, 38.9%, and 41.5%, respectively. The C2 coating showed the greatest reduction in oxidation weight gain, indicating that the C2 coating exhibits more pronounced oxidation resistance at lower temperatures. At 800 °C, the reductions were 20.8%, 32.7%, 32.7%, and 39.3%, with the oxidation weight gain of both the C1 and C2 coatings being higher than that of E1, while the oxidized weight increase was significantly higher for the C1 and C2 coatings than for the E2 coating. At 900 °C, the reductions were 23.5%, 27.8%, 31%, and 33.8%, with the oxidation weight gains of the E1 and E2 coatings being lower than those of the C1 and C2 coatings. These results suggest that the addition of an appropriate amount of CoCrMo improves the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the chromium carbide coatings compared to N0. At lower temperatures (700 °C), the C2 coating exhibits the best oxidation resistance. However, the oxidation rate and oxidation resistance of the E1 and E2 coatings were better than those of the C1 and C2 coatings from 800 °C to 900 °C, suggesting that the addition of nano-CeO2 further limits the outward diffusion of cations and inward diffusion of anions, improving the antioxidant properties of the coating.
3.3. Microstructure and Phase Composition of Oxide Scale
The thickness growth of the oxide films of the N0, C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings after oxidation from 700 °C to 900 °C was quantitatively analyzed, as shown in Figure 3. After oxidation at 700 °C, the oxide layer thickness of the N0 coating was approximately 8.1 μm, while the oxide films of the C1 and C2 coatings measured 17.2 μm and 19.1 μm, respectively. The E1 and E2 coatings had oxide film thicknesses of about 22.8 μm and 24.5 μm. These findings indicate that the oxide film thickness of the C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings was significantly greater than that of the N0 coating. This resulted in enhanced high-temperature oxidation resistance, as the denser, more complete oxide film formed helped to prevent further oxidation by diffusion. After high-temperature oxidation at 800 °C, the oxide film on the N0 coating surface exhibited a porous and loose structure, with a thickness of 6.4 μm. The sporadic distribution of oxide particles suggested partial exfoliation of the oxide film during oxidation. The oxide film thicknesses of the C1 and C2 coatings were 7.9 μm and 9.0 μm, respectively, while for the E1 and E2 coatings, the thicknesses were 12.5 μm and 14.2 μm. Compared to the N0 coating, the C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings formed a more uniform and dense oxide layer, effectively preventing oxygen intrusion and enhancing the oxidation resistance of the coatings. Compared with the oxide films generated at 700 °C and 800 °C, the thicknesses of the oxide films generated by the coatings at 900 °C were reduced, with the thickness of the oxide film of the N0 coating being about 3.3 μm, the thicknesses of the oxide films of the C1 and C2 coatings being about 5.8 μm and 6.2 μm, respectively, and the thicknesses of the oxide films of the E1 and E2 coatings being about 7.7 μm and 8.9 μm. Considering the fact that the coatings’ mass increased during the course of oxidation, this indicates that some oxide shedding occurs during the oxidation process. The apparent mass gain during oxidation, despite oxide loss through spallation, explains the thinner oxide scales formed at elevated temperatures (800–900 °C). In summary, compared to the original N0 coating, the E1 and E2 coatings with the addition of both CoCrMo and CeO2 form a more complete oxide film during the oxidation process, which reduces the generation of cracks in the coating and in the oxide film, thus improving the integrity of the oxide film.
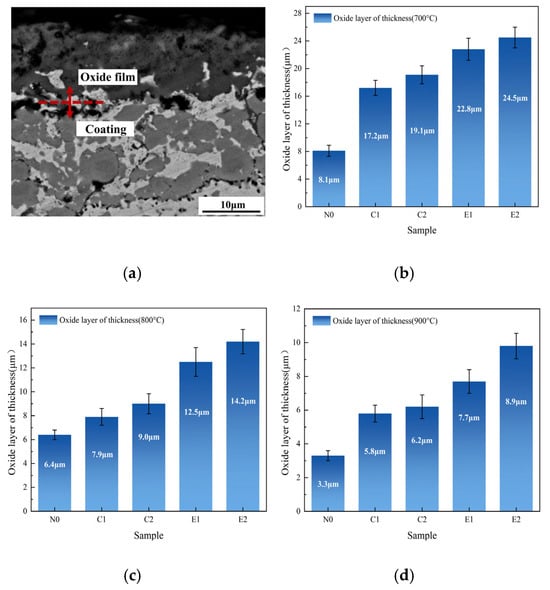
Figure 3.
(a) Example of oxidation scale thickness calculation; (b–d) thickness growth of coatings’ oxide films at (b) 700 °C; (c) 800 °C; (d) 900 °C.
3.4. Phase Composition and Quantitative Analysis of Oxide Film
Figure 4 shows the XRD patterns of the oxide films of five groups of coated specimens at 700–900 °C after high-temperature oxidation for 200 h. Following 200 h of oxidation at temperatures ranging from 700 to 900 °C, the N0 coating surface revealed major phases of Cr2O3 (PDF#85–0730), Cr1.12Ni2.88 (PDF#65–5559), Cr3C2 (PDF#71–2287), and NiCr2O4 (PDF#23–1271). In contrast, the C1 and C2 coatings exhibited additional phases including metallic Co and CoCr2O4 (PDF#35–1321) alongside the aforementioned compounds. Thermodynamic analysis based on Gibbs free energy calculations suggested that CoCr2O4 formation resulted from reactions between cobalt and chromium oxides [30]. For the E1 and E2 coatings, trace amounts of CeO2 (28.6°, PDF#34–0394) were detected in their oxide layers. Quantitative analysis of diffraction peak intensities (Cr2O3 peaks at 24.5°, 33.6°, 36.2°, and 54.9°) demonstrated a temperature-dependent increase in Cr2O3 content, accompanied by progressive depletion of the Cr3C2 (peaks at 39.0° and 40.2°) and Cr1.12Ni2.88 (44.3°) phases. This indicates that the oxidative consumption of chromium in the Cr3C2 and Cr1.12Ni2.88 phases becomes more pronounced at higher temperatures.
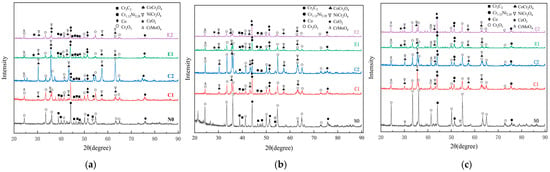
Figure 4.
XRD diffraction spectra of five groups of coated oxide films at different temperatures: (a) 700 °C; (b) 800 °C; (c) 900 °C.
The phase constituent contents of the oxide films on the coatings were quantified using whole-pattern fitting refinement (WPF) based on XRD diffraction patterns, as illustrated in Figure 5. During oxidation, the contents of the Cr1.12Ni2.88 and Cr3C2 phases in the N0, C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings decreased continuously. At elevated temperatures, the oxidative consumption of these Cr1.12Ni2.88 and Cr3C2 phases became more pronounced. Concurrently, the content of the NiCr2O4 spinel phase in these coatings increased with the rising oxidation temperature, which is primarily attributed to the reaction between the Cr2O3 and NiO phases under high-temperature conditions, which promoted the formation of additional spinel phases [31]. In comparison to the N0 coating, both the NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4 spinel phases exhibited higher contents in the oxide films of the oxidized C1 and C2 coatings. The composite oxide films formed by these dual-doped spinel phases in the C1 and C2 coatings improved the integrity, thermal stability, and ion diffusion resistance of the oxide layer, improving the oxidation resistance of the coating [32]. XRD analysis confirmed nano-CeO2’s role in enhancing spinel phase development, with the E1 and E2 coatings containing twice the spinel content of C1 and C2 after thermal exposure. In contrast, the E2 coating with 4 wt.% nano-CeO2 had the highest spinel oxide content. The binary spinel contents of 5.07 wt.%, 8.14 wt.%, and 9.10 wt.% were significantly higher than those of the other coatings at high temperatures of 700–900 °C. The composite coated oxide film has higher thermal stability and oxide film thickness (Figure 3), and the oxidized weight gain was significantly reduced. This effect stemmed from the modification of ion diffusion behavior by Ce4+ doping: under 6-fold coordination, the ionic field strength parameter (r: 0.087, F: 5.29) of Ce4+ exceeded those of Ni2+ (r: 0.072, F: 3.86) and Cr3+ (r: 0.084, F: 4.25) [33]. The Ce4+ cations distributed in the oxide films of the E1 and E2 coatings exerted a stronger attractive force on O2- anions in NiO and Cr3C2, weakening the Ni-O and Cr-O bond strengths in these oxides. Thus, the addition of Ce4+ lowered the temperature at which spinel phases form in the coating’s oxide films, facilitating oxide reactions and promoting the formation of NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4 spinel phases at higher temperatures.
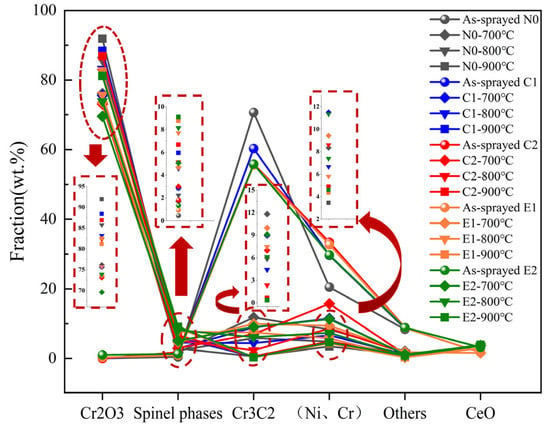
Figure 5.
Temperature-dependent phase composition in coating oxide layers.
3.5. Differences in Oxidation Mechanisms
As the oxidation progresses, elements undergo additional oxidation on the coating surface through diffusion, resulting in the generation of a more developed oxide film. On the one hand, at high temperatures, metal cations (e.g., Ni2+, Co2+, and Cr3+) diffuse outward along the coating interface and form oxides. At the same time, oxygen ions diffuse inward through the oxide film as well as defective areas such as crack spalling, leading to internal oxidation of the coating microstructure. Oxide scale thickening is driven by cation interdiffusion, whereas oxygen ingress through microstructural defects initiates internal oxidation, generating isolated oxide precipitates along defect networks in the coating. During oxidation, the Ni and Co elements in the coating produce oxides such as NiO and CoO, which do not provide protective benefits to the coating. Under high-temperature conditions, NiO and CoO react with Cr2O3, resulting in the formation of two spinel phases (NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4).
Due to the stability and low ion diffusion coefficients of spinel phases, compared to the oxide film formed on the N0 coating, which mainly consists of Cr2O3, the oxide films formed on the C1 and C2 coatings primarily comprise Cr2O3 and CoO. Cr2O3, NiO, and CoO are oxides that exhibit p-type semiconducting properties, and the formation of spinel phases can be explained by the ion transport mechanism in p-type semiconductors. The substitution of Co2+ and Ni2+ ions for Cr3+ ions reduces the number of cation vacancies. The growth rate of p-type semiconductor oxides is influenced by the diffusion rate of cation vacancies. As the number of cation vacancies decreases, cation diffusion is suppressed. Since the oxidation rate is mainly controlled by diffusion, the reduction in cation vacancies improves the oxidation resistance of the coating. Additionally, the substitution of Co2+ and Ni2+ ions for Cr3+ leads to the formation of binary spinel phases (NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4) in the oxide film. A higher concentration of spinel phases results in more ion substitution and fewer cation vacancies. A composite oxide film with a higher content of NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4 spinel phases is more prone to forming eutectic mixtures or solid solutions, leading to a denser structure and improved high-temperature stability compared to a single Cr2O3 oxide film. This reduces ion diffusion and raises the activation energy needed for ion diffusion, thereby strengthening the oxide film’s protective function.
The inclusion of CeO2 in the oxide films of the E1 and E2 coatings promotes high-temperature reactions between different oxides. The presence of Ce4+ ions effectively reduces the temperature required to form NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4 in the oxide film. This increased concentration of spinel phases helps inhibit the diffusion of Cr3+ and O2− ions during oxidation. Moreover, the addition of nano-sized CeO2 enhances the overall density and adhesion of the oxide film, and inhibits the external diffusion of metal ions and internal diffusion of oxygen ions.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Incorporating CoCrMo enhances the high-temperature oxidation resistance of Cr3C2-NiCr coatings. At lower temperatures (700 °C), the C2 coating shows the best oxidation resistance. At higher temperatures (800–900 °C), the E1 and E2 coatings exhibit better oxidation resistance than the C1 and C2 coatings, with the incorporation of nano-CeO2 further enhancing antioxidant performance.
- (2)
- The addition of CoCrMo and nano-CeO2 significantly enhances the high-temperature oxidation resistance of chromium carbide coatings. The C2 coating exhibited the best oxidation resistance at lower temperatures (700 °C), while the E1 and E2 coatings outperformed the C1 and C2 coatings at higher temperatures (800–900 °C). The oxide films formed on the C1, C2, E1, and E2 coatings were denser and more complete compared to the N0 coating, effectively inhibiting oxygen infiltration and improving oxidation resistance. Additionally, the E1 and E2 coatings, with the incorporation of CeO2, exhibited superior performance due to their enhanced oxide film formation, leading to improved integrity and reduced oxidation rates at high temperatures.
- (3)
- In the case of Ni and Co elements, oxides such as NiO and CoO do not provide protective effects, while reactions between these oxides and Cr2O3 at high temperatures generate stable spinel phases like NiCr2O4 and CoCr2O4. These spinel phases, characterized by good stability and high melting points, improve oxidation resistance by reducing ion diffusion. The addition of CeO2 to the E1 and E2 coatings promotes the formation of these spinel phases by lowering the synthesis temperature, further improving oxidation resistance by reducing ion diffusion rates and increasing the activation energy required for diffusion. Consequently, the incorporation of Co2+, Ni2+, and CeO2 into the coatings results in enhanced high-temperature oxidation resistance.
Author Contributions
L.W.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing. J.W.: methodology, supervision. H.L.: methodology, investigation. J.D.: investigation, writing—review and editing, supervision. X.Q.: investigation, writing—review and editing. L.L.: investigation. Z.L.: investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52305542) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant Nos. ZR2023QE320, ZR2023ME153, ZR2021ME157).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Haiyang Lu was employed by the company Inspur Genersoft Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Chatha, S.S.; Sidhu, H.S.; Sidhu, B.S. The Effects of Post-Treatment on the Hot Corrosion Behavior of the HVOF-Sprayed Cr3C2–NiCr Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 4212–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Shan, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Gong, K.; Li, C. Effect of Cr3C2 Content on the Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Fe3Al/Cr3C2 Composites. Coatings 2022, 12, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z. Influential Mechanism of Cr3C2 Content and Process Parameters on Crack Generation of Fe3Al/Cr3C2 Composites. Coatings 2023, 13, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhou, M.; Gao, Y.; Gan, B.; Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; Song, C.; Hua, L.; Zhang, G. Microstructure, Hardness, and Wear Properties of Hot-Press Sintered Cr3C2/Ni3Al Composites Containing Cr3C2 Particles of Different Sizes. Intermetallics 2024, 175, 108503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Nan, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Preparation, Microstructure, and Interface Quality of Cr3C2-NiCr Cladding Layer on the Surface of Q235 Steel. Coatings 2023, 13, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, S.; Irfan; Gong, Q.; Wang, H.; Hu, M. Deposition Mechanisms and Characteristics of Nano-Modified Multimodal Cr3C2–NiCr Coatings Sprayed by HVOF. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2022, 61, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Du, Y.; Cao, H.; Peng, Y.; He, G.; Liang, Q.; Tu, J. Effects of Cr3C2 Addition on Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Cr3C2/15–5PH Composite Coatings on 12Cr13 by Laser Cladding. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; Berger, L.-M. Inter-Diffusion between Thermally Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings and an Alloy 625 Substrate during Long-Term Exposure at 500 °C, 700 °C and 900 °C. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 770, 1078–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, K.; Balasubramanian, K.R. Evaluation of Cyclic Oxidation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline Composite HVOF Coatings on SA 210 Grade C Material. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 97, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubière, S.; Laurent, C.; Bonino, J.P.; Rousset, A. Elaboration, Microstructure and Reactivity of Cr3C2 Powders of Different Morphology. Mater. Res. Bull. 1995, 30, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.-C.; Li, C.-J.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, W.-Y. Microstructural Characterization and Abrasive Wear Performance of HVOF Sprayed Cr3C2–NiCr Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 6749–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, D. Structural Characteristics and Wear, Oxidation, Hot Corrosion Behaviors of HVOF Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Hardmetal Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 457, 129319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Alam, M.S.; Mishra, N.K.; Kumar, S.; Giri, J.; Aly, A.A.; Gupta, G.K. Cyclic Oxidation of 304L and 316L Stainless Steel Coated and Uncoated with Cr3C2–NiCr at Elevated Temperatures. Mater. Sci. 2025, 43, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Lin Peng, R.; Li, X.-H.; Johansson, S. Hot Corrosion Behavior of HVOF-Sprayed CoNiCrAlYSi Coatings in a Sulphate Environment. Vacuum 2015, 122, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, V.; Manikandan, M. High-Temperature Corrosion Behaviour of Air Plasma Sprayed Cr3C2-25NiCr and NiCrMoNb Powder Coating on Alloy 80A at 900 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 337, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.C.; Kumar, B.S.A.; Reddappa, H.N.; Ramesh, M.R.; Koppad, P.G.; Kord, S. HVOF Sprayed Ni3Ti and Ni3Ti+ (Cr3C2+20NiCr) Coatings: Microstructure, Microhardness and Oxidation Behaviour. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 736, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdková, Š.; Česánek, Z.; Smazalová, E.; Lukáč, F. The High-Temperature Wear and Oxidation Behavior of CrC-Based HVOF Coatings. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2018, 27, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Yucheng, W. Oxidation Behavior of Arc-Sprayed FeMnCrAl/Cr3C2–Ni9Al Coatings Deposited on Low-Carbon Steel Substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3411–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhou, K.; Deng, C.; Zeng, K.; Li, Y. Hot Corrosion Behavior of HVOF-Sprayed Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo Coating. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 9390–9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Liu, G.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J.; Yan, F. Microstructures and Properties of Plasma Sprayed FeAl/CeO2/ZrO2 Nano-Composite Coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4176–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Tong, Z.; Fang, X.; Liu, X.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, W. Effect of Scanning Speeds on Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Laser-Processed NiCr–Cr3C2–MoS2–CeO2 on 38CrMoAl Steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 77, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladi, S.; Menghani, J.; Prakash, S. Effect of CeO2 on Cyclic Hot-Corrosion Behavior of Detonation-Gun Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings on Ni-Based Superalloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, N.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, H. High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior and Corrosion Resistance of in-Situ TiC and Mo Reinforced AlCoCrFeNi-Based High Entropy Alloy Coatings by Laser Cladding. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 10151–10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, X. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of TiC/Inconel 625 Nanocomposites Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Corros. Sci. 2020, 169, 108606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Yan, S.; Yu, G.; Chen, J.; Yin, F. High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Atmosphere Plasma Sprayed AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 282, 125939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, K.; Li, H.; Ju, J.; Dong, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Q.; Ding, W. In Situ Nanoparticle-Induced Anti-Oxidation Mechanisms: Application to FeCrB Alloys. Corros. Sci. 2021, 190, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, S.; Ye, F.; Ren, X.; Feng, P. Recycling of MoSi2-Based Industrial Solid Wastes for the Fabrication and High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of MoSi2–ZrSi2–SiC Composite Coating. Compos. B Eng. 2024, 274, 111281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, K.; Li, H.; Ju, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Q. In Situ Nanoparticle-Induced Anti-Oxidation of FeCr Alloys. Mater. Charact. 2021, 179, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Long, X.; Zhou, L.; Deng, H.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, W.; Yin, M.; Yin, G.; Chen, L. Effect of Ti Addition on High-Temperature Properties of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Coating Prepared on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Corros. Sci. 2023, 217, 111105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, N.; Tunthawiroon, P.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A. Characterisation of Oxide Films Formed on Co–29Cr–6Mo Alloy Used in Die-Casting Moulds for Aluminium. Corros. Sci. 2013, 73, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Gao, Y.; Sun, L.; He, L.; Wang, Y. Improvement of High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Cr3C2-20 Wt % Ni Cermets by Adding 1 Wt % Mo. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 731, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Gan, J.; Li, W.; Tian, H.; Luo, X.; Ju, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Yao, H.; Chen, Z.; et al. Exceptional High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance and Mechanisms of a Novel Chemically Complex Intermetallic Alloy. Corros. Sci. 2023, 225, 111607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Elabyouki, M.; Zhang, W. Theoretical Study of the Structure and Properties of Ni/V Porphyrins under Microwave Electric Field: A DFT Study. Fuel 2020, 278, 118305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).