Characterization of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Thin Films towards Terahertz (THz) Functional Device Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sturcture, Surface Morphology and Composition
3.2. THz Optical and Electrical Properties
3.3. Annealing Effects on UV-VIS-NIR Optical Properties of ITO Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellmer, K. Past achievements and future challenges in the development of optically transparent electrodes. Nat. Photon. 2012, 6, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginley, D.; Hosono, H.; Paine, D. Handbook of Transparent Conductors; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, G.T.; Kim, Y.; Khokhar, M.Q.; Hussain, S.Q.; Cho, E.-C.; Yi, J.; Ahmad, Z.; Rosaiah, P.; Jeon, C.-W. A Brief Review of Transparent Conducting Oxides (TCO): The Influence of Different Deposition Techniques on the Efficiency of Solar Cells. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, M.N.; Bahramy, M.S.; Shida, K.; Sahara, R.; Mizuseki, H.; Kawazoe, Y. Optoelectronic and magnetic properties of Mn-doped indium tin oxide: A first-principles study. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 073105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberg, I.; Granqvist, C.G.; Berggren, K.F.; Sernelius, B.E.; Engström, L. Band-gap widening in heavily Sn-doped In2O3. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 30, 3240–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, M.; Gao, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, T.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Wu, Y. Nanometre-thin indium tin oxide for advanced high-performance electronics. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Perera, I.R.; Daeneke, T.; Makuta, S.; Tachibana, Y.; Jasieniak, J.J.; Mishra, A.; Bäuerle, P.; Spiccia, L.; Bach, U. Indium tin oxide as a semiconductor material in efficient p-type dye-sensitized solar cells. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Ye, C.; Sorger, V.J. Indium-tin-oxide for high-performance electro-optic modulation. Nanophotonics 2015, 4, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhere, R.G.; Gessert, T.A.; Schilling, L.L.; Nelson, A.J.; Jones, K.M.; Aharoni, H.; Coutts, T.J. Electro-optical properties of thin indium tin oxide films: Limitations on performance. Sol. Cells 1987, 21, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Haque, R.R.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, R.; Lu, Z. Broadband electro-optical modulator based on transparent conducting oxide. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4978–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, M.; Andler, J.; Lyu, X.; Niu, C.; Datta, S.; Agrawal, R.; Ye, P.D. Indium-Tin-Oxide Transistors with One Nanometer Thick Channel and Ferroelectric Gating. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 11542–11547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Gilmore, C.M.; Piqué, A.; Horwitz, J.S.; Mattoussi, H.; Murata, H.; Kafafi, J.H.; Chrisey, D.B. Electrical, optical, and structural properties of indium-tin-oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 6451–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Noh, J.H.; Bae, S.-T.; Cho, I.-S.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, J.-K.; Jung, H.S.; Hong, K.S. Indium-tin-oxide-based transparent conducting layers for highly efficient photovoltaic devices. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7443–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janarthanan, B.; Thirunavukkarasu, C.; Maruthamuthu, S.; Manthrammel, M.A.; Shkir, M.; Al Faify, S.; Selvakumar, M.; Reddy, V.R.M.; Park, C. Basic deposition methods of thin films. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laux, S.; Kaiser, N.; Zöller, A.; Götzelmann, R.; Lauth, H.; Bernitzki, H. Room-temperature deposition of indium tin oxide thin films with plasma ion-assisted evaporation. Thin Solid. Film. 1998, 335, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Jeong, I.H.; Kim, W.K.; Kwak, M.G. Deposition of indium-tin-oxide films on polymer substrates for application in plastic-based flat panel displays. Thin Solid. Film. 2001, 397, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, A. Transparent Conducting Oxides—An Up-To-Date Overview. Materials 2012, 5, 661–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.J.; Cameron, D.C. Optical and electrical properties of transparent conductive ITO thin films deposited by sol–gel process. Thin Solid Film. 2000, 377, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, V.; Vickraman, P.; Jayachandran, M.; Sanjeeviraja, C. Structural and optical properties of indium tin oxide (ITO) thin films with different compositions prepared by electron beam evaporation. Vacuum 2010, 84, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, A.J.; Duca, Z.A.; White, N.; Woodell, P.; Ward, P.A. Influence of oxygen on the optical and electrical properties of magnetron-sputtered indium tin oxide thin films at ambient temperature. Thin Solid Film. 2024, 788, 140152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdan, H.I.; Alsahli, F.M.; Bhandari, S.; Mallick, T. Monolithic Use of Inert Gas for Highly Transparent and Conductive Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Guo, R. Optimized sputtering parameters for ITO thin films of high conductivity and transparency. Adv. Appl. Electroceramics II Ceram. Trans. 2012, 235, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Mo, C.; Chen, J.; Ji, P.; Tan, H.; Zhang, X.; CUI, M.; ZHUGE, L.; WU, X.; Huang, T. Effects of power on ion behaviors in radio-frequency magnetron sputtering of indium tin oxide (ITO). Plasma Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 075506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Mo, C.; Cui, M.; Li, M.; Ji, P.; Tan, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhuge, L.; Wu, X. Ion behavior impact on ITO thin film fabrication via DC magnetron sputtering with external anode. Vacuum 2024, 221, 112848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Yan, Y. Effects of Doping Ratio and Thickness of Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering at Room Temperature. Coatings 2023, 13, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, N.; Subrahmanyam, A. Electrical and optical properties of reactively evaporated indium tin oxide (ITO) films-dependence on substrate temperature and tin concentration. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1989, 22, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha, M.; Anusha, S.; Antony, A.; Manoj, R.; Jayaraj, M.K. Effect of substrate temperature on the growth of ITO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.-J.; dos Santos, M.P. Properties of indium tin oxide films prepared by RF reactive magnetron sputtering at different substrate temperature. Thin Solid Film. 1998, 322, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdesau, F.; Khripunov, G.; Cunha, A.F.; Kaelin, M.; Tiwari, A.N. Comparative study of ITO layers deposited by DC and RF magnetron sputtering at room temperature. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 352, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhong, J.; Sun, B.; Zeng, X.; Luo, W.; Zhao, X.; Shu, Y.; Chen, J.; He, J. Influence of base pressure on property of sputtering deposited ITO film. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 13005–13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.J.; Dos Santos, M.P. Properties of indium tin oxide (ITO) films prepared by rf reactive magnetron sputtering at different pressures. Thin Solid Film. 1997, 303, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhou, H.; Sun, H.; Lu, W.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, J. Effect of nitrogen partial pressure on the piezoresistivity of magnetron sputtered ITO thin films at high temperatures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 608, 55292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guileen, C.; Herrero, J. Structure, optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide thin films prepared by sputtering at room temperature and annealed in air or nitrogen. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 073514–073521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, F.; Herth, E.; David, C.; Bayle, F.; Plante, M.P.; Martin, A.; Aassime, A. Electrical and optical properties of sputtered ultra-thin indium tin oxide films using xenon/argon gas. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 8508–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Joo, S.H.; Shin, S.G.; Choi, H.W.; Bark, C.W.; Rim, Y.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S. Effect of Annealing in ITO Film Prepared at Various Argon-and-Oxygen-Mixture Ratios via Facing-Target Sputtering for Transparent Electrode of Perovskite Solar Cells. Coatings 2022, 12, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, A.; Silva, F.; Porteiro, J.; Míguez, J.; Pinto, G. Sputtering physical vapour deposition (PVD) coatings: A critical review on process improvement and market trend demands. Coatings 2018, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donercark, E.; Guler, S.; Ciftpinar, E.H.; Kabacelik, I.; Koc, M.; Ercelebi, A.C.; Turan, R. Impact of oxygen partial pressure during Indium Tin Oxide sputtering on the performance of silicon heterojunction solar cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 281, 115750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.M.; Sabah, F.A.; Abdulgafour, H.I.; Alsadig, A.; Sulieman, A.; Alkhoaryef, M. The effect of post annealing temperature on grain size of indium-tin-oxide for optical and electrical properties improvement. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.; Jung YCh Lee, T.; Park, I.-S.; Ahn, J. Enhanced uniformity in electrical and optical properties of ITO thin films using a wide thermal annealing system. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2018, 79, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak-Bałata, A.; Bodzenta, J.; Dehbashi, M.; Mayandi, J.; Venkatachalapathy, V. Influence of Post Processing on Thermal Conductivity of ITO Thin Films. Materials 2023, 16, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubitidze, T.; Britton, W.A.; Negro, L.D. Enhanced Nonlinearity of Epsilon-Near-Zero Indium Tin Oxide Nanolayers with Tamm Plasmon-Polariton States. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2301669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Chae, M.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.D. Enhanced optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide for solar cell applications via post-microwave treatment. Opt. Mater. 2024, 149, 115093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Seok, H.-J.; Jung, S.H.; Cho, H.K.; Kim, H.-K. Rapid Thermal Annealing Effect of Transparent ITO Source and Drain Electrode for Transparent Thin Film Transistors. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 3149–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T. Transparent conducting oxide semiconductors for transparent electrodes. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Yan, Y. Different Crystallization Behavior of Amorphous ITO Film by Rapid Infrared Annealing and Conventional Furnace Annealing Technology. Materials 2023, 16, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Lin, K.M.; Ho, Y.S. Laser annealing process of ITO thin films using beam shaping technology. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, K.A.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, S.Y. Electrical, structural, and optical properties of ITO thin films prepared at room temperature by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 4834–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prepelita, P.; Stavarache, I.; Craciun, D.; Garoi, F.; Negrila, C.; Sbarcea, B.G.; Craciun, V. Rapid thermal annealing for high-quality ITO thin films deposited by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Xin, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, S. Rapid thermal annealing of ITO films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7061–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-Y.; Jeon, S.-P.; Park, J.B.; Park, H.-B.; Kim, D.-H.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, G.; Jo, J.-W.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, M.; et al. High-performance ITO/a-IGZO heterostructure TFTs enabled by thickness-dependent carrier concentration and band alignment manipulation. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 5905–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniyara, R.A.; Graham, C.; Paulillo, B.; Bi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Herranz, G.; Baker, D.E.; Mazumder, P.; Konstantatos, G.; Pruneri, V. Highly transparent and conductive ITO substrates for near infrared applications. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 021121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.H.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.C. Transparent Conductor-Si pillars heterojunction photodetector. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 064904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberg, I.; Granqvist, C.G. Evaporated Sn-doped In2O3 films: Basic optical properties and applications to energy-efficient windows. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 60, R123–R160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, P.; Junda, M.M.; Salmon, H.; Podraza, N.J. Understanding near infrared absorption in tin doped indium oxide thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 295302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-W.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Yu, P.; Shieh, J.-M.; Pan, C.-L. Frequency-dependent complex conductivities and dielectric responses of indium tin oxide thin films from the visible to the far-infrared. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2010, 46, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, M.H.; Yu, P.; Wada, O.; Pan, C.L. THz conductivities of indium-tin-oxide nanowhiskers as a graded-refractive-index structure. Opt. Express 2012, 20, A441–A451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.S.; Chang, C.M.; Chen, P.H.; Yu, P.; Pan, C.L. Broadband terahertz conductivity and optical transmission of indium-tin-oxide (ITO) nanomaterials. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 16670–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-S.; Lin, M.-H.; Chang, C.-H.; Yu, P.; Shieh, J.-M.; Shen, C.-H.; Wada, O.; Pan, C.-L. Non-Drude behavior in indium-tin-oxide nanowhiskers and thin films investigated by transmission and reflection THz time-domain spectroscopy. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2013, 49, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-L.; Yang, C.-S.; Pan, R.-P.; Yu, P.; Lin, G.-R. Nanostructured Indium Tin Oxides and Other Transparent Conducting Oxides: Characteristics and Applications in the THz Frequency Range. In Terahertz Spectroscopy—A Cutting Edge Technology; Uddin, J., Ed.; InTech Open: London, UK, 2017; Chapter 14; pp. 267–286. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zalkovskij, M.; Iwaszczuk, K.; Lavrinenko, A.V.; Naik, G.V.; Kim, J.; Boltasseva, A.; Jepsen, P.U. Ultrabroadband terahertz conductivity of highly doped ZnO and ITO. Opt. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaForge, J.M.; Cocker, T.L.; Beaudry, A.L.; Cui, K.; Tucker, R.T.; Taschuk, M.T.; Hegmann, F.A.; Brett, M.J. Conductivity control of as-grown branched indium tin oxide nanowire networks. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 035701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.; Kolb, J.; Löffler, T.; Mohler, E.; Roskos, H.; Pernisz, U. Indium–tin–oxide-coated glass as dichroic mirror for far-infrared electromagnetic radiation. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 2210–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, S.A.; Hendry, E.; Isaac, T.H.; Sambles, J.R. Tuneable Fabry–Perot etalon for terahertz radiation. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 033012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubouchi, M.; Kumada, T. Development of high efficiency etalons with an optical shutter for terahertz laser pulses. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 28500–28506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-S.; Tang, T.-T.; Pan, R.-P.; Yu, P.; Pan, C.-L. Liquid crystal terahertz phase shifters with functional indium-tin-oxide nanostructure for biasing and alignment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 141106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Tang, T.T.; Chen, P.H.; Pan, R.P.; Yu, P.; Pan, C.L. Voltage-controlled liquid-crystal terahertz phase shifter with indium–tin–oxide nanowhiskers as transparent electrodes. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2511–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.S.; Kuo, C.; Chen, P.H.; Wu, W.T.; Pan, R.P.; Yu, P.; Pan, C.L. High-Transmittance 2π Electrically Tunable Terahertz Phase Shifter with CMOS-Compatible Driving Voltage Enabled by Liquid Crystals. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Yang, C.-S.; Wada, O.; Pan, C.-L. Twisted nematic liquid crystal based terahertz phase shifter with crossed indium tin oxide finger type electrodes. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cao, H.; Fang, H.; Lai, W.; Shi, G.; Deng, G.; Yin, Z.; Cai, F.; Li, Y. Reflectance-tunable terahertz polarization reflector using indium tin oxide. Opt. Commun. 2020, 460, 25149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Song, L.; Zhang, T. Terahertz reflection and visible light transmission of ITO films affected by annealing temperature and applied in metamaterial absorber. Vacuum 2018, 149, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, C.-Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Lee, C. Resonance enhancement of terahertz metamaterials by liquid crystals/indium tin oxide interfaces. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 6519–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Mei, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Lin, W.; Niu, T. An Ultra-wideband, Wide-angle And Transparent Microwave Absorber Using Indium Tin Oxide Conductive Films. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Kang, S.-Y.; Yu, P.; Pan, C.-L. Enhanced Optically–Excited THz Wave Emission by GaAs Coated with a Rough ITO Thin Film. Coatings 2023, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Jia, W.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, J. Two-Color-Driven Controllable Terahertz Generation in ITO Thin Film. ACS Photonics 2024, 11, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Mai, C.-M.; Pan, C.-L. Enhancement of Indium tin oxide nano-scale films for terahertz device applications treated by rapid thermal annealing. In Proceedings of the 2020 45th International Conference on Infrared Millimeter and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz), Buffalo, NY, USA, 8–13 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, T.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Pan, C.L.; Pan, R.P.; Zhang, X.C. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy studies of the optical constants of the nematic liquid crystal 5CB. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 2372–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.A.; Tani, M.; Pan, C.-L. THz radiation emission properties of multi energy arsenic-ion-implanted GaAs and semi-insulating GaAs based photoconductive antennas. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 2996–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, G.; Lange, B.; Sotier, S. Characterization of sputtered indium tin oxide layers as transparent contact material. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film. 2001, 19, 2514–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzüak, G.D.; Coşkun, D. The effect of annealing on the structural, electrical, optical and electrochromic properties of indium-tin-oxide films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering technique. Optik 2017, 142, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.N.; Tiwari, N. Preparation of optically transparent and conducting radio-frequency sputtered indium tin oxide ultrathin films. Thin Solid Film. 2021, 717, 138471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroescu, H.; Anastasescu, M.; Preda, S.; Nicolescu, M.; Stoica, M.; Stefan, N.; Kampylafka, V.; Aperathitis, E.; Modreanu, M.; Zaharescu, M.; et al. Influence of thermal treatment in N2 atmosphere on chemical, microstructural and optical properties of indium tin oxide and nitrogen doped indium tin oxide rf-sputtered thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2013, 541, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.R.; Reddy, M.S.; Rao, P.K. Effect of rapid thermal annealing on deep level defects in the Si-doped GaN. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Mao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; He, C. Defects evolution and their impacts on conductivity of indium tin oxide thin films upon thermal treatment. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 025304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tesfamichael, T.; Bell, J.; Wang, H. Effect of different thermo-treatment at relatively low temperatures on the properties of indium-tin-oxide thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2017, 636, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergel, D.; Qiao, Z. Correlation of lattice distortion with optical and electrical properties of In2O3: Sn films. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 5608–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, M.; Shigesato, Y.; Takaki, S. Origin of characteristic grain-subgrain structure of tin-doped indium oxide films. Thin Solid Film. 1995, 259, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brintlinger, T.; Chen, Y.F.; Dürkop, T.; Cobas, E.; Fuhrer, M.S.; Barry, J.D.; Melngailis, J. Rapid imaging of nanotubes on insulating substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 2454–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Brinkman, A.W. Preparation and characterization of NiMn2O4 films. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 3, 1215–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumoorthi, M.; Prakash, J.T.J. Structure, optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide ultra-thin films prepared by jet nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2016, 4, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, S.; Sawada, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kagota, Y.; Shida, A.; Ide, M. Highly conducting indium-tin-oxide transparent films prepared by dip-coating with an indium carboxylate salt. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 169, 525–527. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.-S.; Kuo, C.; Tang, C.-C.; Chen, J.C.; Pan, R.-P.; Pan, C.-L. Liquid-Crystal Terahertz Quarter-Wave Plate Using Chemical-Vapor-Deposited Graphene Electrodes. IEEE Photonics J. 2015, 7, 2200808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Au, W.C.; Hong, Y.C.; Pan, C.L.; Zhai, D.; Hérault, E.; Garet, F.; Coutaz, J.L. Dopant profiling of ion-implanted GaAs by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 133, 125705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Hsieh, C.; Pan, R.; Tanaka, M.; Miyamaru, F.; Tani, M.; Hangyo, M. Control of enhanced THz transmission through metallic hole arrays using nematic liquid crystal. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 3921–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, J. Dielectric properties of silicon in terahertz wave region. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2008, 50, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Grischkowsky, D. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy characterization of the far-infrared absorption and index of refraction of high-resistivity, float-zone silicon. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2004, 21, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe-Lavigne, S.; Barret, S.; Garet, F.; Duvillaret, L.; Coutaz, J.L. Far-infrared dielectric constant of porous silicon layers measured by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 6007–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshat, M.; Armitage, N.P. Developments in THz Range Ellipsometry. J. Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 2013, 34, 682–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, L.; Ding, H.F.; Huang, T.Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, B.; Ren, K.; Fu, S. Broadband optical reflection modulator in indium-tin-oxide-filled hybrid plasmonic waveguide with High modulation depth. Plasmonics 2018, 13, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleque, A.; Hattori, H.T. Plasmonic electro-absorption modulator and polarization selector. J. Mod. Opt. 2017, 64, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light, 7th ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Clanget, R. Ionized impurity scattering in degenerate In2O3. Appl. Phys. 1973, 2, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Classical generalization of the Drude formula for the optical conductivity. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 64, 155106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocker, T.L.; Baillie, D.; Buruma, M.; Titova, L.V.; Sydora, R.D.; Marsiglio, F.; Hegmann, F.A. Microscopic origin of the Drude-Smith model. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 205439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němec, H.; Kužel, P.; Sundström, V. Far-infrared response of free charge carriers localized in semiconductor nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 115309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conwell, E.; Weisskopf, V.F. Theory of impurity scattering in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. 1950, 77, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberg, I.; Granqvist, C.G.; Berggren, K.F.; Sernelius, B.E.; Engström, L. Bandgap widening in heavily doped oxide semiconductors used as transparent heat-reflectors. Sol. Energy Mater. 1985, 12, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Kondo, M. Effects of carrier concentration on the dielectric function of ZnO: Ga and In2O3: Sn studied by spectroscopic ellipsometry: Analysis of free-carrier and band-edge absorption. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 075109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.F.J.; Male, J.S.; Cavill, S.A.; Reardon, C.P.; Krauss, T.F. Photonic Characterisation of Indium Tin Oxide as a Function of Deposition Conditions. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.R.; Zhang, W.D.; Chen, H.; Mearini, G.T. THz Behavior of Indium-Tin-Oxide Films on p-Si Substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 091102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valla, A.; Carroy, P.; Ozanne, F.; Muñoz, D. Understanding the role of mobility of ITO films for silicon heterojunction solar cell applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 157, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, B.; Gil, Y.; Kim, H. Highly Transparent Conducting Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering and Thermal Annealing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 19, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y. Influence to Photoelectric Properties of ITO Thin Film by Sputtering Condition and RTA Processing. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 21, 282. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Yang, C.; Zhang, D.; Jin, D.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, H. Effects of ambient high-temperature annealing on microstructure, elemental composition, optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 276, 115534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ederth, J.; Johnsson, P.; Niklasson, G.A.; Hoel, A.; Hultåker, A.; Heszler, P.; Granqvist, C.G.; van Doorn, A.R.; Jongerius, M.J.; Burgard, D. Electrical and optical properties of thin films consisting of tin-doped indium oxide nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 155410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, F.E.M.; Kurcbart, S.M. Hagen-rubens relation beyond far-infrared region. Eur. Phys. Lett. 2010, 90, 44004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naftaly, M.; Dudley, R. Terahertz Reflectivities of Metal-Coated Mirrors. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, R.; Abdel-Hady, K.; Manso-Silván, M.; Torres-Costa, V.; Martín-Palma, R.J.J. Microwave plasma and rapid thermal processing of indium-tin oxide thin films for enhancing their performance as transparent electrodes. J. Photonics Energy 2019, 9, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusayfan, N.M.; El-Nahass, M.M. Study of Structure and Electro-Optical Characteristics of Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2013, 2013, 408182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, S.-C.; Chang, C.-F. Fabrication and Characterization of Indium Tin Oxide Films. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2017, 15, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsianpour, E.; Raoufi, D.; Roostaei, M.; Sohrabi, B.; Samavat, F. Characterization and structural property of indium tin oxide thin films. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2017, 7, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, G.; Kauer, E.; Kostlin, H. Transparent heat-reflecting coatings based on highly doped semiconductors. Thin Solid Film. 1981, 77, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanepoel, R. Determination of the thickness and optical constants of amorphous silicon. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 1983, 16, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacini, A.; Ali, A.H.; Adnan, N.N. Optimization of ITO thin film properties as a function of deposition time using the swanepoel method. Opt. Mater. 2021, 120, 111411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.K.; Raju, R.C.N.; Subrahmanyam, A. Thickness dependent physical and photocatalytic properties of ITO thin films prepared by reactive DC magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3075–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgonos, A.; Mason, T.O.; Poeppelmeier, K.R. Direct optical band gap measurement in polycrystalline semiconductors: A critical look at the Tauc method. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 240, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, E.; Davisson, J.; Bell, E.; Turnre, W.; Lipson, H. Infrared photoconductivity due to neutral impurities in germanium. Phys. Rev. 1954, 93, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, T. The interpretation of the properties of Indium antimonide. Proc. Phys. Soc. B 1954, 67, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.P.; Webb, J.B.; Williams, D.F. Band-gap narrowing in heavily defect-doped ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 1982, 25, 7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elnaiem, A.M.; Hakamy, A. Influence of annealing temperature on structural, electrical, and optical properties of 80 nm thick indium-doped tin oxide on borofloat glass. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 23293–23305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Buurma, C.; Sivananthan, S.; Kodama, R.; Gao, W.; Gessert, T.A. The effect of post-annealing on Indium Tin Oxide thin films by magnetron sputtering method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
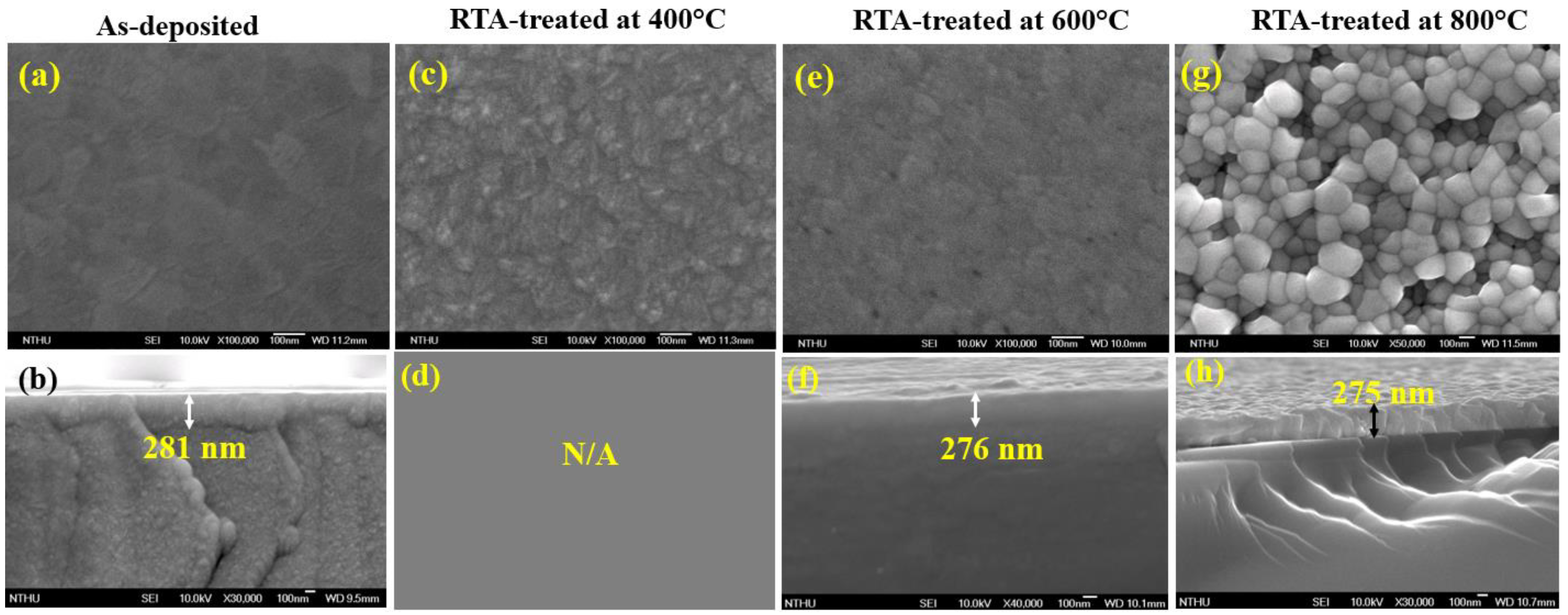
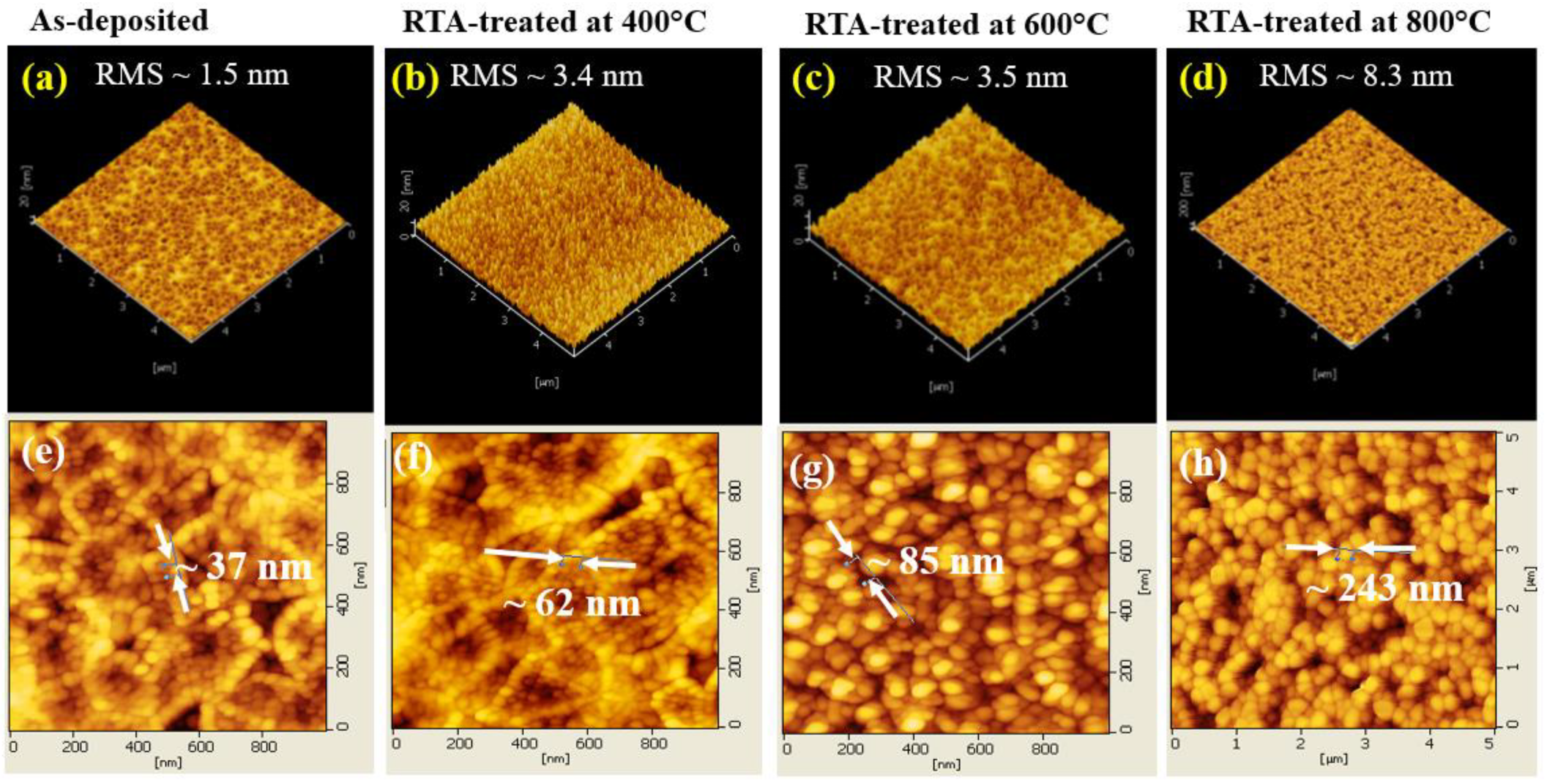

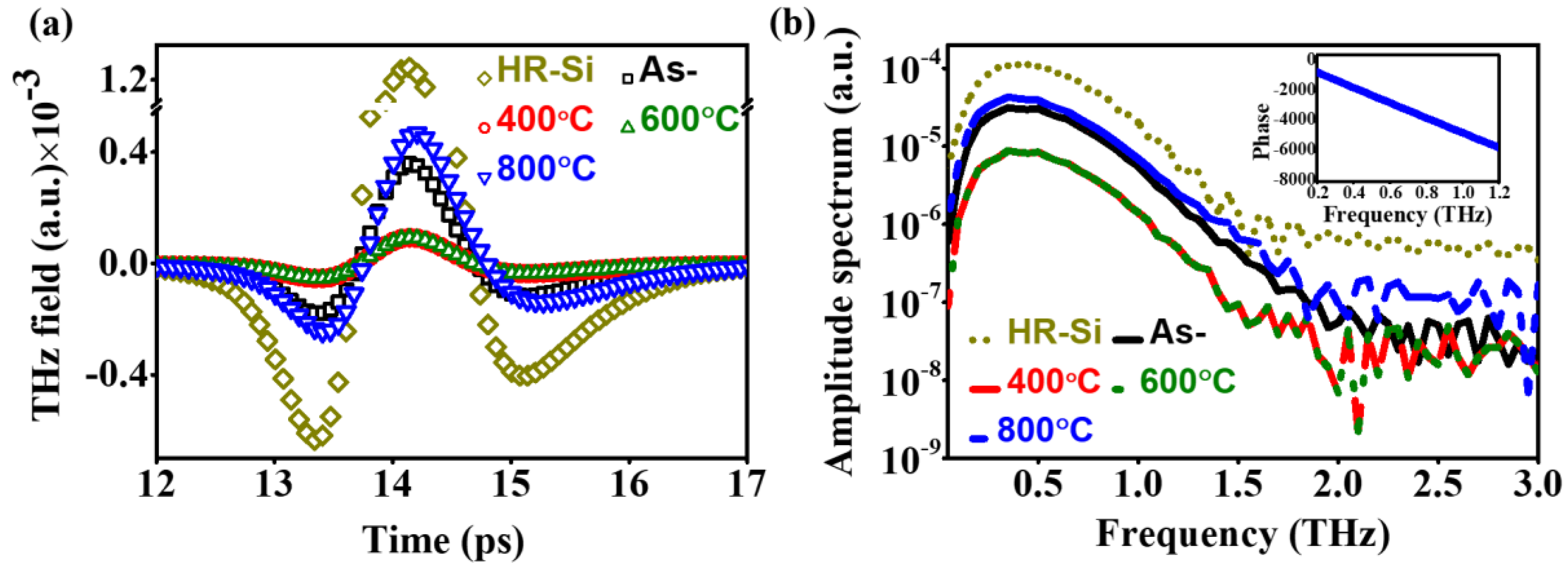
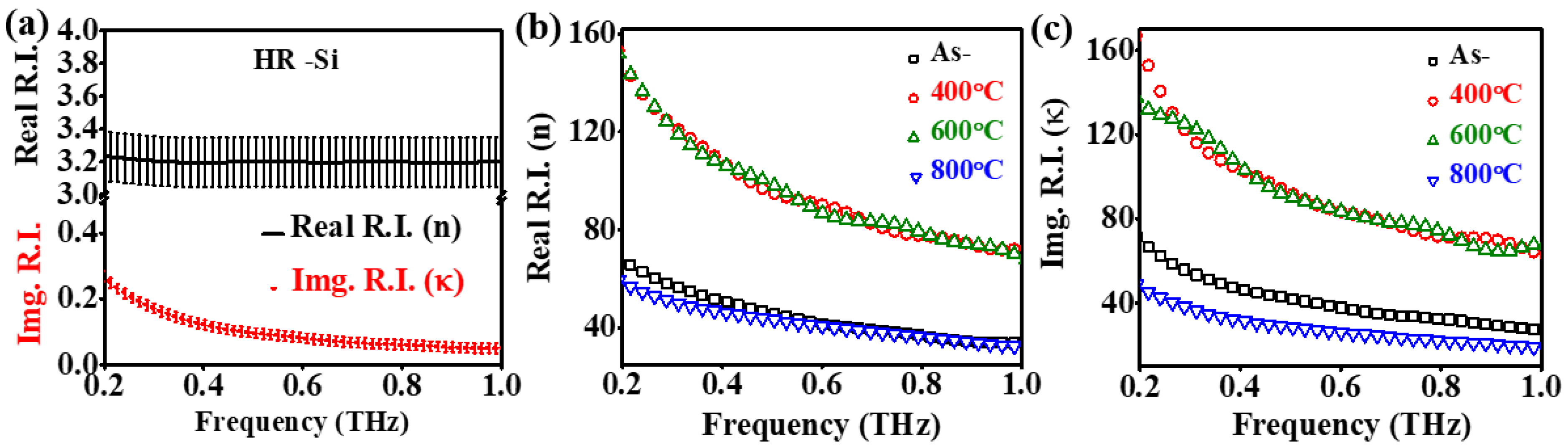
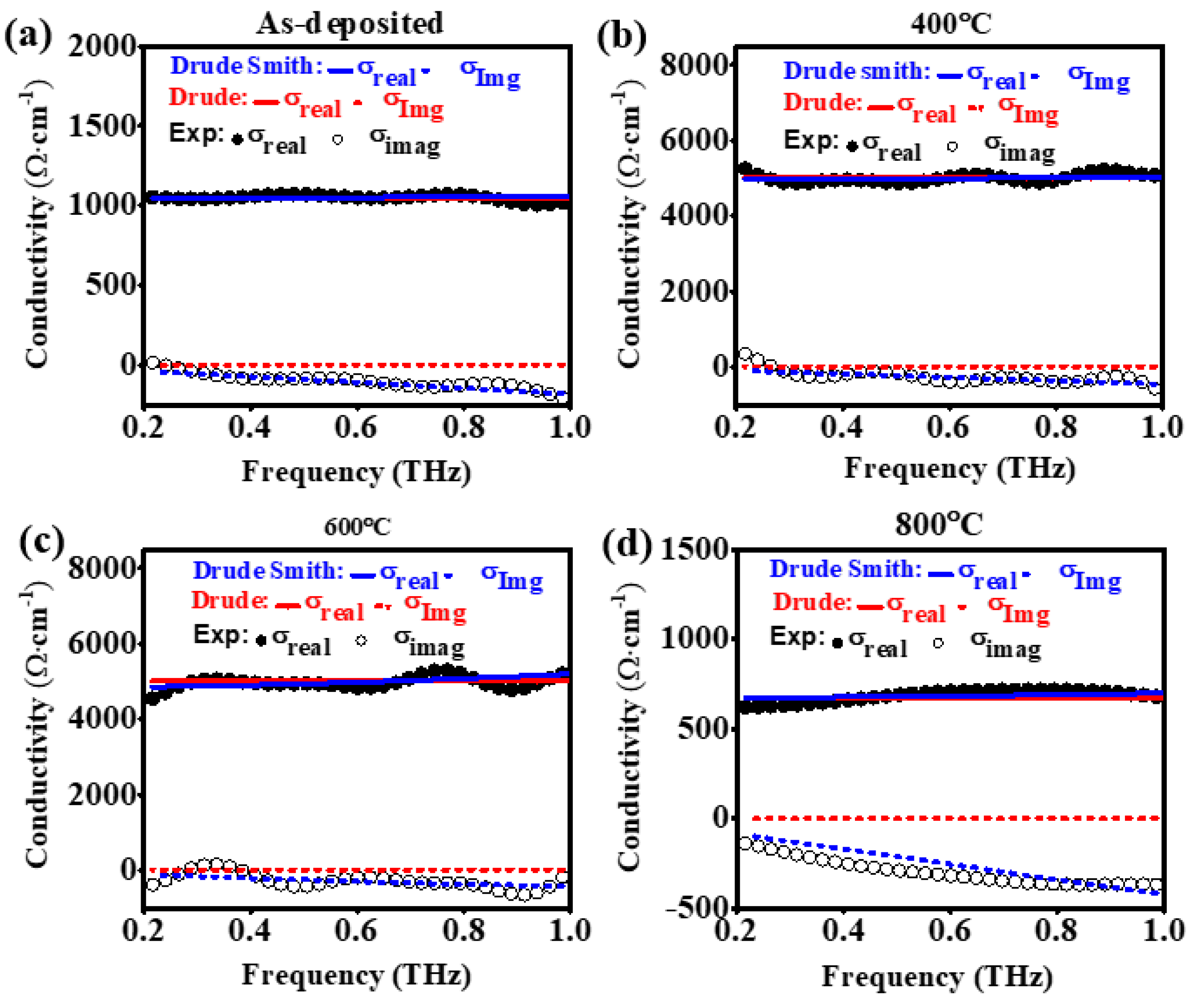
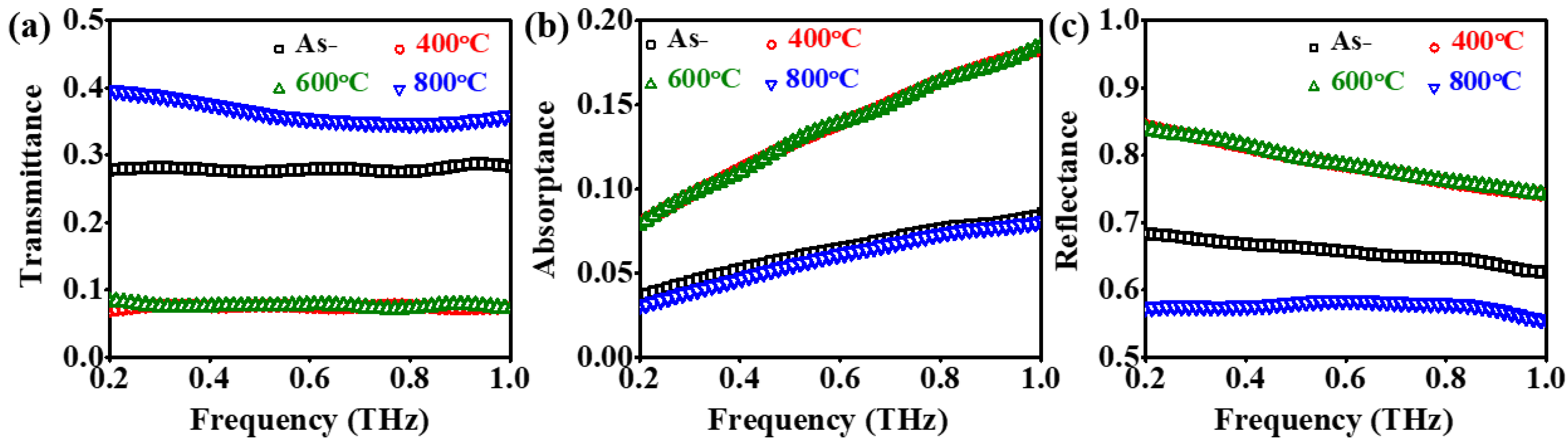

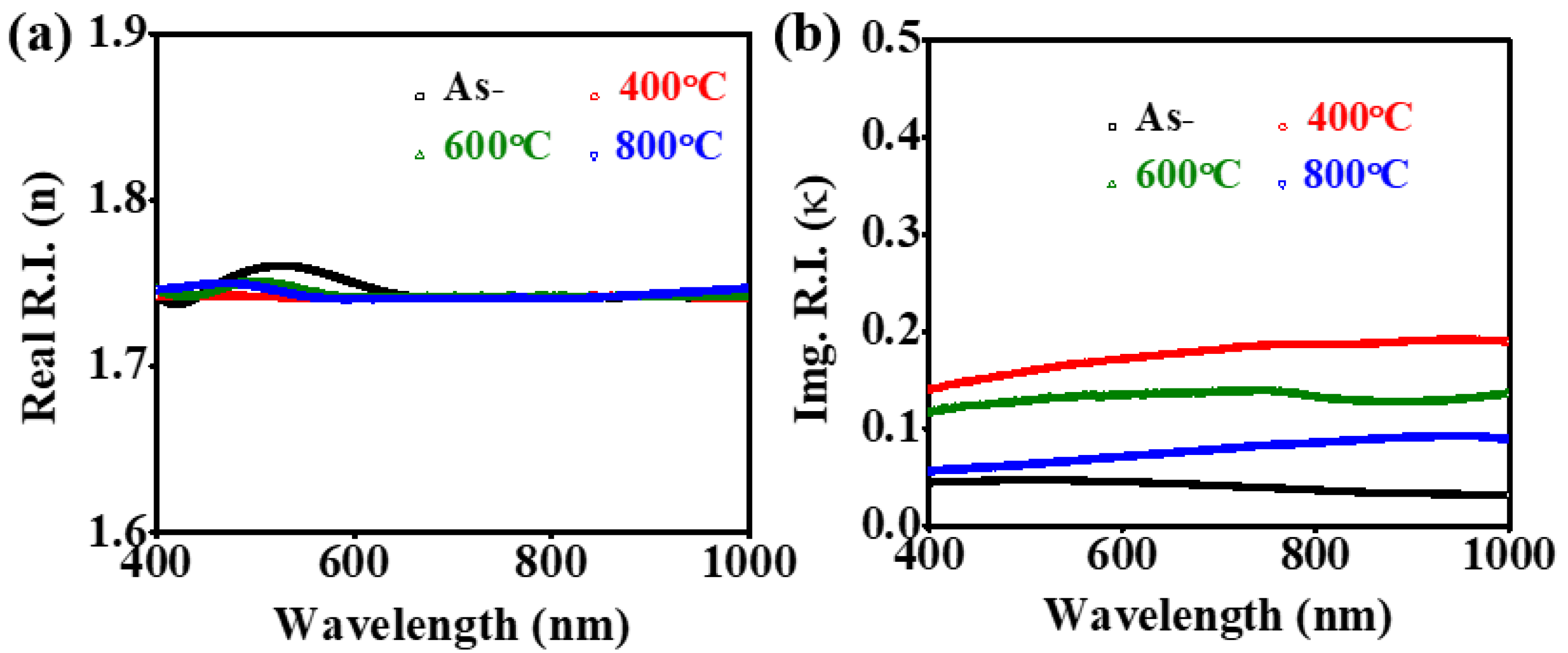
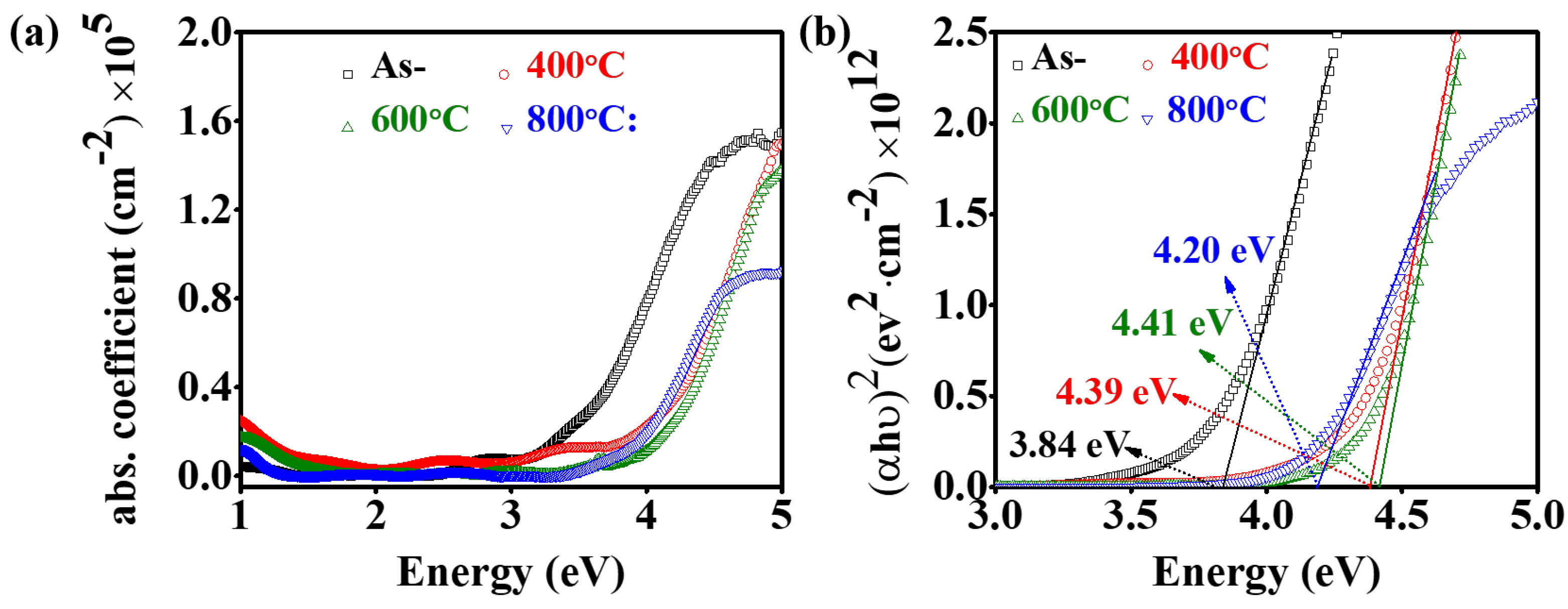
| Sample | O K | In L | Sn L | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (%) | Atomic (%) | Weight (%) | Atomic (%) | Weight (%) | Atomic (%) | |
| As- | 22.78 | 68.01 | 67.44 | 28.05 | 9.77 | 3.93 |
| 600 °C | 22.98 | 68.23 | 69.48 | 28.75 | 7.54 | 3.02 |
| 800 °C | 24.71 | 70.27 | 66.90 | 26.51 | 8.38 | 3.21 |
| Parameters | As- | 400 °C | 600 °C | 800 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| µ (cm2/V∙s) | 5.3 | 22 | 47 | 14 |
| ωp* (rad·THz) | 1784 | 1865 | 1294 | 839 |
| τ (fs) | 6 | 12 | 21 | 20 |
| c | −0.83 | −0.68 | −0.63 | −0.87 |
| Nc (cm−3) | 1.02 × 1021 | 1.31 × 1021 | 6.31 × 1020 | 2.65 × 1019 |
| σdc (Ω−1cm−1) | 1019 | 4815 | 4792 | 628 |
| ρ (Ω‧cm) | 9.8 × 10−4 | 2.0 × 10−4 | 2.0 × 10−4 | 15.9 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahoo, A.K.; Au, W.-C.; Pan, C.-L. Characterization of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Thin Films towards Terahertz (THz) Functional Device Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070895
Sahoo AK, Au W-C, Pan C-L. Characterization of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Thin Films towards Terahertz (THz) Functional Device Applications. Coatings. 2024; 14(7):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070895
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahoo, Anup Kumar, Wei-Chen Au, and Ci-Ling Pan. 2024. "Characterization of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Thin Films towards Terahertz (THz) Functional Device Applications" Coatings 14, no. 7: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070895
APA StyleSahoo, A. K., Au, W.-C., & Pan, C.-L. (2024). Characterization of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Thin Films towards Terahertz (THz) Functional Device Applications. Coatings, 14(7), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070895







