Research Progress on Polysaccharide Composite Films and Coatings with Antioxidant and Antibacterial Ingredients to Extend the Shelf Life of Animal-Derived Meat
Abstract
1. Introduction
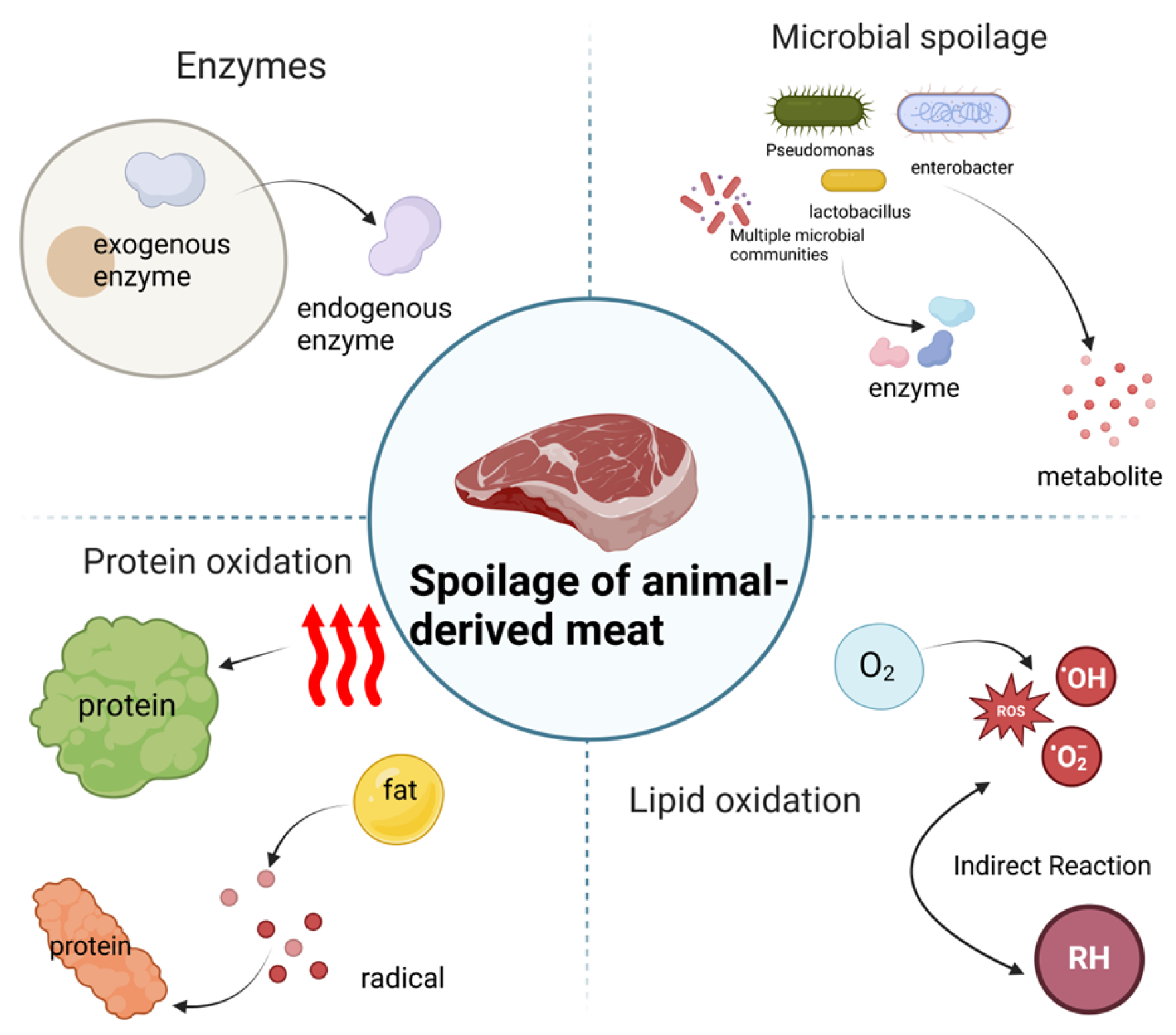
2. Factors Affecting Spoilage of Animal-Derived Meat
2.1. Role of Endogenous Enzymes
2.2. Role of Microorganisms
2.3. Oxidation
2.4. Other Influences
3. The Application of Polysaccharides in Animal-Derived Meat Preservation
3.1. The Animal Polysaccharides
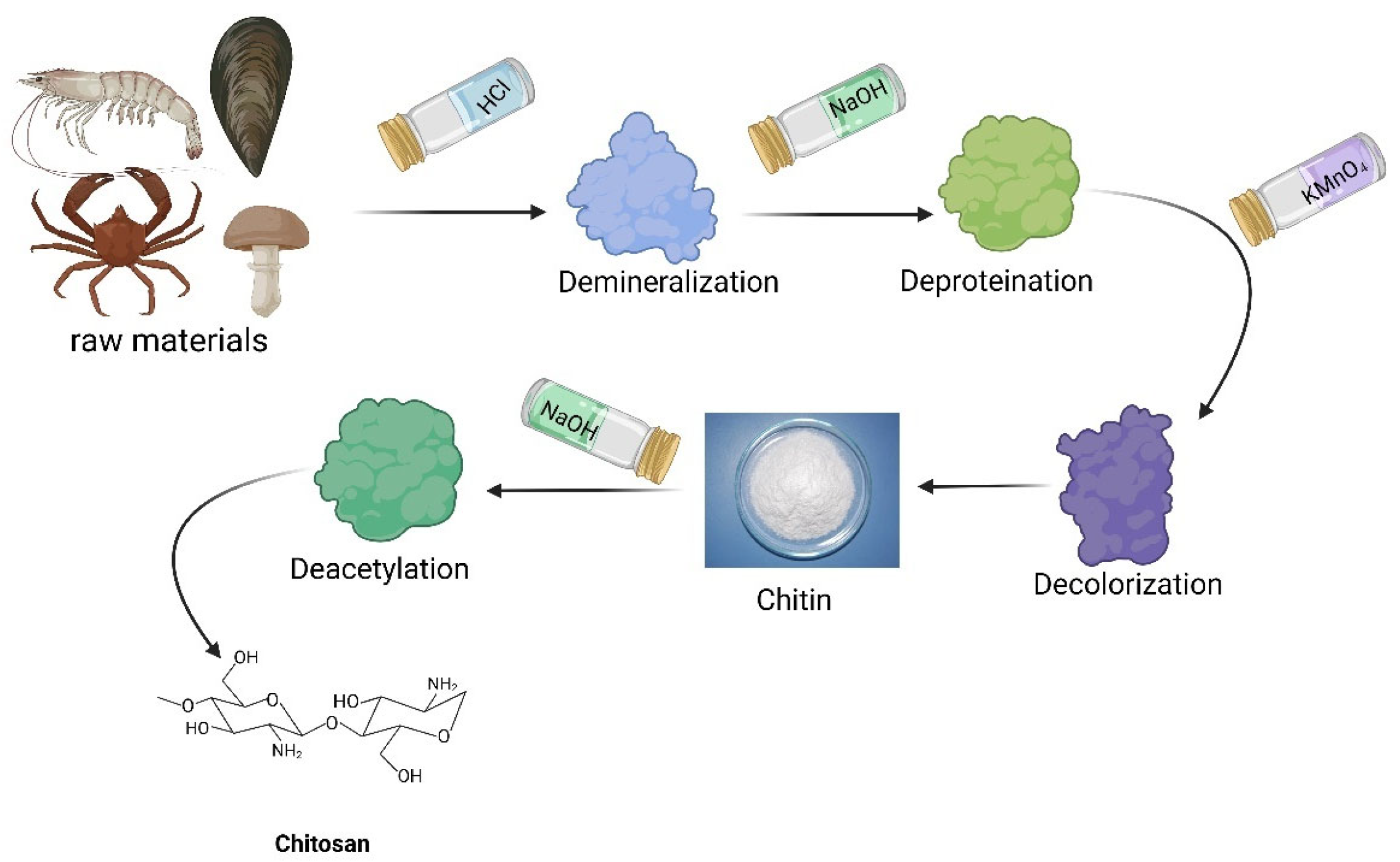
3.1.1. Chitosan
- (1)
- Overview of Chitosan
- (2)
- Application of Chitosan in animal-derived meat
- (a)
- Chitosan derivatization
- (b)
- Chitosan nanoparticles
- (c)
- Chitosan Composite with Other Substances
3.1.2. Hyaluronic Acid
- (1)
- Overview of Hyaluronic acid
- (2)
- Application of Hyaluronic acid in animal-derived meat
3.2. The Plant Polysaccharides
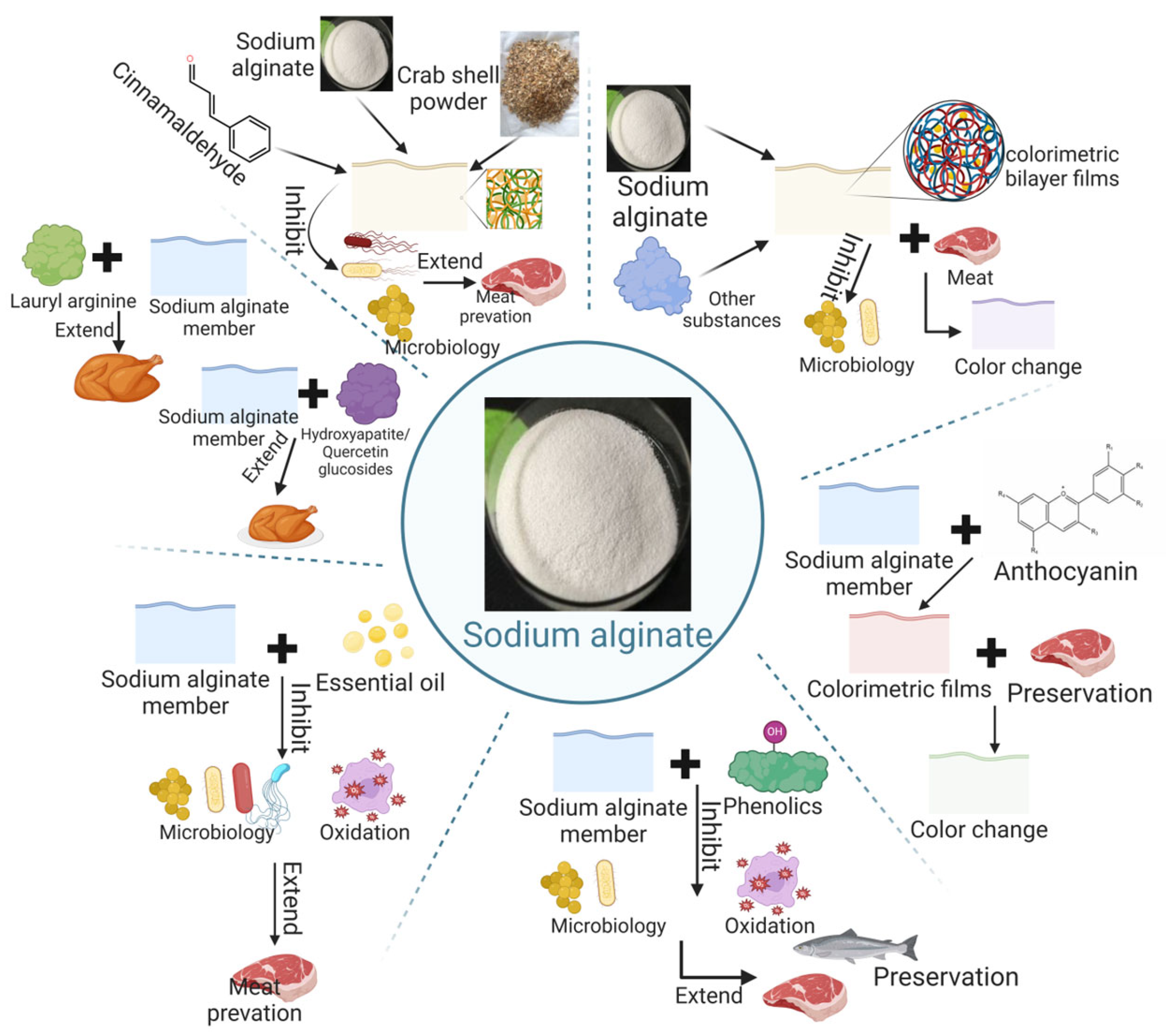
3.2.1. Sodium Alginate
- (1)
- Overview of Sodium Alginate
- (2)
- Application of sodium alginate in animal-derived meat
3.2.2. Carrageenan
- (1)
- Overview of Carrageenan
- (2)
- Application of Carrageenan in animal-derived meat
3.2.3. Starch
- (1)
- Overview of starch
- (2)
- Application of starch in animal-derived meat
3.3. The Microbial Polysaccharides
Pullulan Polysaccharides
- (1)
- Overview of Pullulan Polysaccharides
- (2)
- Application of pullulan polysaccharides in animal-derived meat
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, H.; Karim, N.; Jiang, F.; Hu, H.; Chen, W. Role of temperature fluctuations and shocks during refrigeration on pork and salmon quality. Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, L.; Ma, L.; Lu, X. Impact of lactic acid bacteria on the control of Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, fyac045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, D.; Nadeem, H.; Lin, M.; Dyson, J.M.; Tuck, K.L.; Tanner, J. Application of on-pack pH indicators to monitor freshness of modified atmospheric packaged raw beef. Food Qual. Saf. 2024, 8, fyae021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, K.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Effects of single-, dual-, and multi-frequency ultrasound-assisted freezing on the muscle quality and myofibrillar protein structure in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Effects of multi-frequency ultrasound on the freezing rates, quality properties and structural characteristics of cultured large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Effects of packaging methods and temperature variations on the quality and microbial diversity of grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus) during cold storage. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, P.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X. 3D printing based on meat materials: Challenges and opportunities. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.M.; Oliveira, R.M.; Gehrmann Buchweitz, L.T.; Pereira, J.R.; Cristina dos Santos Hackbart, H.; Nalério, É.S.; Borges, C.D.; Zambiazi, R.C. Encapsulation of olive leaf extract (Olea europaea L.) in gelatin/tragacanth gum by complex coacervation for application in sheep meat hamburger. Food Control 2022, 131, 108426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinarli, C.; Tarlak, F. Microorganisms responsible for deterioration of food products: Review. Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 14, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Tseng, H.J.; Hsiao, H.I.; Chai, H.J.; Shang, K.C.; Pan, C.L.; Tsai, G.J. Applications of Nisin and EDTA in Food Packaging for Improving Fabricated Chitosan-Polylactate Plastic Film Performance and Fish Fillet Preservation. Membranes 2021, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.O.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Gopal, T.K.S. Active Packaging of Fishery Products: A Review. Fish. Technol. 2010, 47, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Conz, A.; Davoli, E.; Franchi, C.; Diomede, L. Seafood loss prevention and waste reduction. Food Qual. Saf. 2024, 8, fyae017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manessis, G.; Kalogianni, A.I.; Lazou, T.; Moschovas, M.; Bossis, I.; Gelasakis, A.I. Plant-Derived Natural Antioxidants in Meat and Meat Products. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.-X.; Hao, Y.; Meng, F.-B.; Li, Y.-C.; Liu, D.-Y. Ice temperature preservation technology and its application in fresh meat preservation. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2023, 14, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Dong, J.; Luo, L.; He, X.; Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Guan, W. Effects of Electromagnetic Field-assisted Low-Temperature Treatment on Meat Quality. Food Res. Dev. 2023, 44, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, D. Research Progress in the Application of Active Functional Water in Preservation of Meat and Meat Products. Food Res. Dev. 2023, 44, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Progress in the application of bioprotective bacteria combined with modified atmosphere packaging for meat preservation. Meat Res. 2022, 36, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Q.; Sharma, M.; Bains, A.; Chawla, P.; Goksen, G.; Zou, J.; Zhang, W.L. Application of seed mucilage as functional biopolymer in meat product processing and preservation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 339, 122228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smaoui, S.; Ben Hlima, H.; Ben Braïek, O.; Ennouri, K.; Mellouli, L.; Khaneghah, A.M. Recent advancements in encapsulation of bioactive compounds as a promising technique for meat preservation. Meat Sci. 2021, 181, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.B.; Li, W.; Chen, C.; Yu, H.Y.; Huang, J.; Lou, X.M.; Tian, H.X. The role of bacterial nanocellulose mats encapsulated with cinnamaldehyde on chilled meat preservation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wang, S.; Tan, M.; Jing, X.; Xiao, M.; Wu, X. Research Progress of Biological Preservatives Combined with Ice-Glazing Technology for Frozen Preservation of Fish. Food Res. Dev. 2023, 44, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, B.K.; Mohite, A.S.; Pathan, D.I.; Desai, A.S.; Wasave, S.M. The use of herbs and spices in fish preservation at chilled temperature storage: Opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 6758–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; You, J.; Ni, L. Application of Bacillus subtilis in Fish Fillets Preservation. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 23, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shang, J.; Yang, X.; Xue, J.; Guo, Y. A review on thickening, gelling and emulsifying properties of polysaccharides. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, D.; Huang, X.Q.; Song, L.J. Effects of different modified atmosphere treatments on lipid oxidation in spiced beef at different storage temperatures. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, X.X.; Wang, X. Research progress of application of polysaccharides, proteins and their composite coatings in preservation of postharvest berries. Storage Process 2022, 22, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, B.S.J.; Venkatachalam, S. Biomass-derived nanoparticles reinforced chitosan films: As high barrier active packaging for extending the shelf life of highly perishable food. J. Food Sci. Technol. Mysore 2024, 61, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Shen, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhang, X.X.; Thakur, K.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Khan, M.R.; Busquets, R.; Wei, Z.J. Fortification of polysaccharide-based packaging films and coatings with essential oils: A review of their preparation and use in meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwatofarati, S.W.; Olayemi, R.A.; Rahman, A. Effects of silver bio-nanoparticle treatment on the wet preservation, technological, and chemical qualities of meat. Food Qual. Saf. 2018, 2, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xing, T.; Huang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, M. Involvement of mu/m-calpain in the proteolysis and meat quality changes during postmortem storage of chicken breast muscle. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, C.; Ren, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G. The postmortem mu-calpain activity, protein degradation and tenderness of sheep meat from Duolang and Hu breeds. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Bian, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W. Changes in actomyosin dissociation and endogenous enzyme activities during heating and their relationship with duck meat tenderness. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Shi, H. Effects of caspase activity of yak meat and internal environment changing during aging. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Pérez-Nevado, F.; Ruiz-Moyano, S.; Serradilla, M.J.; Villalobos, M.C.; Martín, A.; Córdoba, M.G. Spoilage yeasts: What are the sources of contamination of foods and beverages? Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 286, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanur Rahman, S.M.; Islam, S.; Pan, J.; Kong, D.; Xi, Q.; Du, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.-H.; Han, R. Marination ingredients on meat quality and safety—A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Ercolini, D.; Villani, F.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Spoilage microbiota associated to the storage of raw meat in different conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushina, Y.K.; Bataeva, D.S.; Zaiko, E.V.; Machova, A.A.; Velebit, B. Bacterial populations and volatile organic compounds associated with meat spoilage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 333, 012114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenz-García, C.E.; Castañeda-Serrano, P.; Silva, E.M.M.; Alvarado, C.Z.; Nava, G.M. Insights into the Identification of the Specific Spoilage Organisms in Chicken Meat. Foods 2020, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, A.R.; Song, E.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Nam, Y.D.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, D.O.; Seo, D.H.; Nam, T.G. Comparative evaluation of spoilage-related bacterial diversity and metabolite profiles in chilled beef stored under air and vacuum packaging. Food Microbiol. 2019, 77, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci-Goga, B.T.; Sechi, P.; Iulietto, M.F.; Amirjalali, S.; Barbera, S.; Karama, M.; Aly, S.S.; Grispoldi, L. Characterization and Growth under Different Storage Temperatures of Ropy Slime-Producing Leuconostoc mesenteroides Isolated from Cooked Meat Products. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirone, M.; Esposito, L.; D’Onofrio, F.; Visciano, P.; Martuscelli, M.; Mastrocola, D.; Paparella, A. Biogenic Amines in Meat and Meat Products: A Review of the Science and Future Perspectives. Foods 2022, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanborough, T.; Fegan, N.; Powell, S.M.; Singh, T.; Tamplin, M.; Chandry, P.S. Genomic and metabolic characterization of spoilage-associated Pseudomonas species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 268, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Holland, I.B.; Schmitt, L. The Type 1 secretion pathway—The hemolysin system and beyond. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 1629–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bijl, E.; Svensson, B.; Hettinga, K. The Extracellular Protease AprX from Pseudomonas and its Spoilage Potential for UHT Milk: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 834–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeta, G.; Curiel, J.A.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Muñoz, R.; Rivas, B.D.L. Characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from Spanish dry cured meat products. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; Cattivelli, A.; Conte, A.; Tagliazucchi, D. Black, green, and pink pepper affect differently lipid oxidation during cooking and in vitro digestion of meat. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadidi, M.; Orellana-Palacios, J.C.; Aghababaei, F.; Gonzalez-Serrano, D.J.; Moreno, A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Plant by-product antioxidants: Control of protein-lipid oxidation in meat and meat products. LWT 2022, 169, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Zhang, W.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Prieto, M.A.; Bohrer, B.; Lorenzo, J.M. Protein Oxidation in Muscle Foods: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.N.; Heinonen, M.; Baron, C.P.; Estévez, M. Protein oxidation in muscle foods: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 55, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, S.; Xavier, K.A.M.; Devi, S.T.; Nayak, B.B.; Kannuchamy, N. Identification of potential spoilage bacteria in farmed shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei): Application of Relative Rate of Spoilage models in shelf life-prediction. LWT 2018, 97, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhao, X.; Bian, C.; Cheng, H.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. The application of Melissa officinalis L. essential oil nanoemulsions protects sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) against myofibrillar protein and lipid oxidation during refrigeration. Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, M.; Sun, Z. Research progress on fenton reaction-induced meat protein oxidation and its inhibition. Meat Res. 2023, 37, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellenberg, M.A.; Peña, I.; Ibáñez, R.A.; Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E. Effect of dietary vitamin E supplementation on glutathione concentration and lipid and protein oxidation of refrigerated broiler meat. Eur. Poult. Sci. 2019, 83, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovec, J.; Levart, A.; Peric, L.; Stojeic, M.D.; Tomovic, V.; Pirman, T.; Salobir, J.; Rezar, V. Antioxidative effects of supplementing linseed oil-enriched diets with α-tocopherol, ascorbic acid, selenium, or their combination on carcass and meat quality in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6733–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecjak, M.; Leskovec, J.; Levart, A.; Salobir, J.; Rezar, V. Effects of Dietary Vitamin E, Vitamin C, Selenium and Their Combination on Carcass Characteristics, Oxidative Stability and Breast Meat Quality of Broiler Chickens Exposed to Cyclic Heat Stress. Animals 2022, 12, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, E.M.; López, A.; Zimerman, M.; Hernández, O.; Arroquy, J.I.; Nazareno, M.A. Enhanced oxidative stability of meat by including tannin-rich leaves of woody plants in goat diet. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.; Li, S.; Tang, L.; Tang, W.; Zhou, X.; et al. Dietary vitamin A improved the flesh quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) in relation to the enhanced antioxidant capacity through Nrf2/Keap 1a signaling pathway. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspal, M.H.; Badar, I.H.; Amjad, O.B.; Yar, M.K.; Ijaz, M.; Manzoor, A.; Nasir, J.; Asghar, B.; Ali, S.; Nauman, K.; et al. Effect of Wet Aging on Color Stability, Tenderness, and Sensory Attributes of Longissimus lumborum and Gluteus medius Muscles from Water Buffalo Bulls. Animals 2021, 11, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijaz, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Hussain, Z.; Ren, C.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, X. Association between meat color of DFD beef and other quality attributes. Meat Sci. 2020, 161, 107954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspal, M.H.; Badar, I.H.; Usman Ghani, M.; Ijaz, M.; Yar, M.K.; Manzoor, A.; Nasir, J.; Nauman, K.; Junaid Akhtar, M.; Rahman, A.; et al. Effect of Packaging Type and Aging on the Meat Quality Characteristics of Water Buffalo Bulls. Animals 2022, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panea, B.; Ripoll, G. Sex Does Not Affect the Colour, Shear Stress, and Lipid Oxidation of Pork Meat, but Feed-Added Plant-Derived Extracts, Storage Time and Packaging Type Do. Foods 2023, 12, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.C.; Alice, E.J.; Hossain, M.A.; Mehbub, M.F.; Islam, M.T. Effects of vacuum and modified atmosphere packaging on the shelf life of Rohu fish (Labeo rohita) stored at refrigerated temperature (4 °C). Int. Food Res. J. 2021, 28, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemian, M.; Azizi, M.H. The effect of the type of packaging on the physicochemical and microbial characteristics of rainbow salmon (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillets stored at refrigerator temperature. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R.; Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Muzzarelli, C.; Sashiwa, H.; Domb, A.J. Chitosan Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6017–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aider, M. Chitosan application for active bio-based films production and potential in the food industry: Review. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, J.; Yang, Q. A novel edible packaging film based on chitosan incorporated with persimmon peel extract for the postharvest preservation of banana. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, fyac028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hack, M.E.A.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shafi, M.E.; Zabermawi, N.M.; Arif, M.; Batiha, G.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; El-Hakim, Y.M.A.; Al-Sagheer, A.A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of chitosan and its derivatives and their applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2726–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsa, J.; AliSmach, M.; BenMrid, R.; Sobeh, M.; Majdoub, H.; Yasri, A. Functional properties of chitosan derivatives obtained through Maillard reaction: A novel promising food preservative. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, M.S.; Shaaban, H.A.; Hussein, A.M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.M.; El-Massry, K.; El-Ghorab, A. Evaluation of Chitosan/Fructose Model as an Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Agent for Shelf Life Extension of Beef Meat During Freezing. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2016, 66, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatt, S.R.; Chander, R.; Sharma, A. Chitosan glucose complex—A novel food preservative. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmer, R.A.; Williams, A.P.; Townsend, S.; Baker, S.; Jones, D.L. Antibacterial action of chitosan-arginine against Escherichia coli O157 in chicken juice. Food Control 2012, 26, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, N.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Fei, P. Preparation of acylated chitosan with caffeic acid in non-enzymatic and enzymatic systems: Characterization and application in pork preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 194, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondéjar-López, M.; Castillo, R.; Jiménez, A.J.L.; Gómez-Gómez, L.; Ahrazem, O.; Niza, E. Polysaccharide film containing cinnamaldehyde-chitosan nanoparticles, a new eco-packaging material effective in meat preservation. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, L. Mandarin (Citrus reticulata L.) essential oil incorporated into chitosan nanoparticles: Characterization, anti-biofilm properties and application in pork preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Min, S.J.; Biswas, D.; Rhim, J.W. Pullulan/chitosan-based functional film incorporated with curcumin-integrated chitosan nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 660, 130898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Sheng, M.; Lin, Q.; Shi, H.; Tan, Y. Properties of coaxial polycaprolactone cinnamaldehyde chitosan nanoparticles electrospun membrane and its effect on the shelf life of meat. Food Control 2024, 164, 110555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirin, K.; Amirreza, A.-E.; Alireza, M.; Vali Hosseni, S.; Hojjat, A. Physicochemical evaluations of chitosan/nisin nanocapsulation and its synergistic effects in quality preservation in tilapia fish sausage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.A.; Coimbra, M.A. The antioxidant activity of polysaccharides: A structure-function relationship overview. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 314, 120965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, H. Alginate/pectin aerogel microspheres for controlled release of proanthocyanidins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efenberger-Szmechtyk, M.; Nowak, A.; Czyzowska, A. Plant extracts rich in polyphenols: Antibacterial agents and natural preservatives for meat and meat products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Liao, W.Y.; Wang, Q.; Xia, W.S. Chitosan/bacterial cellulose films incorporated with tea polyphenol nanoliposomes for silver carp preservation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Kang, S.; Xue, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.; Yan, B.; Liu, D. Self-assembled carboxymethyl chitosan/zinc alginate composite film with excellent water resistant and antimicrobial properties for chilled meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Feng, X. Incorporating Portulaca oleracea extract endows the chitosan-starch film with antioxidant capacity for chilled meat preservation. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Tseng, H.J.; Hsiao, H.I.; Chai, H.J.; Shang, K.C.; Pan, C.L.; Tsai, G.J. Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan-Polylactate Fabricated Plastic Film and Its Application on the Preservation of Fish Fillet. Polymers 2021, 13, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.H.; Islam, M.N.; Chitrakar, B.; Duan, Z.H.; Xu, W.X.; Zhong, S.Y. Effect of combined chlorogenic acid and chitosan coating on antioxidant, antimicrobial, and sensory properties of snakehead fish in cold storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Kamboj, M.; Ajlouni, S.; Fang, Z. Incorporation of salmon bone gelatine with chitosan, gallic acid and clove oil as edible coating for the cold storage of fresh salmon fillet. Food Control 2021, 125, 107994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qu, S.; Ma, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, K.; Chen, L.; Huang, Q.; Zou, G.; Tang, H. Effects of chitosan coating combined with thermal treatment on physicochemical properties, bacterial diversity and volatile flavor of braised duck meat during refrigerated storage. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filion, M.C.; Phillips, N.C. Pro-Inflammatory Activity of Contaminating DNA in Hyaluronan Preparations. In Hyaluronan; Kennedy, J.F., Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2002; pp. 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, A.; Priefer, R. Hyaluronic acid applications in ophthalmology, rheumatology, and dermatology. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 489, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, M.; Casas, A.; Toubarro, D.; Barros, A.N.; Teixeira, J.A. Microbial Hyaluronic Acid Production: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorana, A.; Pitarresi, G.; Palumbo, F.S.; Catania, V.; Schillaci, D.; Mauro, N.; Fiorica, C.; Giammona, G. Fabrication of silver nanoparticles by a diethylene triamine-hyaluronic acid derivative and use as antibacterial coating. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 295, 119861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, P.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, F.; Chai, Y. Effect of hyaluronic acid coating on fresh quality of crucian carp (Carassius auratus) during the partial-freezing storage. Food Mach. 2017, 33, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Cong, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, F.; Chai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, Y. Fresh-keeping effect of hyaluronic acid coating combined with super-chilling storage on fresh-cut common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2019, 40, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, M.; Dai, S.; Song, J.; Ni, X.; Fang, Y.; Corke, H.; Jiang, F. Interactions between carboxymethyl konjac glucomannan and soy protein isolate in blended films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Yu, X.; Pilla, S. Mechanical and moisture sensitivity of fully bio-based dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose cross-linked soy protein isolate films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Guo, L.; Yu, W.; Sun, M.; Ma, X.; Chai, Y. Effect of hyaluronic acid-beta-conglycinin composite film on quality of silver carp fillet during preservation by partial freezing. Food Res. Dev. 2023, 44, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Cui, H. Fabrication of a dual-response intelligent antibacterial nanofiber and its application in beef preservation. LWT 2022, 154, 112606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboofetileh, M.; Rezaei, M.; Hosseini, H.; Abdollahi, M. Antimicrobial activity of alginate/clay nanocomposite films enriched with essential oils against three common foodborne pathogens. Food Control 2014, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M.; Hifney, A.F.; Fawzy, M.A.; Abdel-Gawad, K.M. Use of seaweed and filamentous fungus derived polysaccharides in the development of alginate-chitosan edible films containing fucoidan: Study of moisture sorption, polyphenol release and antioxidant properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, H. Development and characterization of starch-sodium alginate-montmorillonite biodegradable antibacterial films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerramathi, B.B.; Kola, M.; Muniraj, B.A.; Aluru, R.; Thirumanyam, M.; Zyryanov, G.V. Structural studies and bioactivity of sodium alginate edible films fabricated through ferulic acid cross linking mechanism. J. Food Eng. 2021, 301, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Guo, Q.; Jiang, C. Effects of sodium alginate coating on the quality and shelf life of large yellow croaker at ice-temperature. Food Ferment. Ind. 2019, 45, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.A.; Abdelrahman, H.A.; Zayed, N.E.R.; Abdel-Naeem, H.H.S. The effects of novel alginate-lauric arginate coatings with temperature on bacterial quality, oxidative stability, and organoleptic characteristics of frozen stored chicken drumsticks. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvano, F.; Montone, A.M.I.; Capuano, F.; Colletti, C.; Roveri, N.; Albanese, D.; Capparelli, R. Effects of active alginate edible coating enriched with hydroxyapatite-quercetin complexes during the cold storage of fresh chicken fillets. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 32, 100847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Yang, J.Y.; Qiao, Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Yang, X.; Li, J.R.; Sun, T. Effect of sandwich-type konjac glucan/sodium alginate/konjac glucan composite coatings on protein oxidation in salmon fillets. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.M.; Pang, D.; Wu, R.Y.; Zou, F.L.; Zhang, B.; Shang, N.; Li, P.L. Development of a Multifunctional Edible Coating and Its Preservation Effect on Sturgeon (Acipenser baeri♀ × Acipenser schrenckii♂) Fillets during Refrigerated Storage at 4 °C. Foods 2022, 11, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ji, F.; Jiang, L.; Li, B.; Luo, Y. Bio-preservative effects of Lactobacillus paracasei H9 in sodium alginate coating on grass carp. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 38, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Fang, S.; Xie, Y.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Preservative Effects of Flaxseed Gum-Sodium Alginate Active Coatings Containing Carvacrol on Quality of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) during Cold Storage. Coatings 2024, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, D.; Ge, S.; Bian, P.; Xue, H.; Lang, Y. Alginate-based edible coating with oregano essential oil/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for chicken breast preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, H.; Cózar, A.; Rubio, N. Lamb meat burgers shelf life: Effect of the addition of different forms of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.). CyTA J. Food 2021, 19, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimifar, P.; Saei-Dehkordi, S.S.; Izadi, Z. Antibacterial, antioxidative and sensory properties of Ziziphora clinopodioides–Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil nanoencapsulated using sodium alginate in raw lamb burger patties. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Peng, H.; Lin, Y.; Cai, K. Effects of ginger essential oil on physicochemical and structural properties of agar-sodium alginate bilayer film and its application to beef refrigeration. Meat Sci. 2023, 198, 109051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Luo, W.; Yang, K.; Li, C. Effects of sodium alginate edible coating with cinnamon essential oil nanocapsules and Nisin on quality and shelf life of beef slices during refrigeration. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Guo, M.; Qiu, W.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Effect of tea polyphenol–trehalose complex coating solutions on physiological stress and flesh quality of marine-cultured Turbot Scophthalmus maximus during waterless transport. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2024, 36, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, M.; He, B.; Yong, Y.; Zhu, J. Composite films of sodium alginate and konjac glucomannan incorporated with tea polyphenols for food preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gao, X.; Xiong, G.; Liang, J. Effect of sodium alginate and carboxymethyl cellulose edible coating with epigallocatechin gallate on quality and shelf life of fresh pork. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, M.; Tabrizad, M.H.A.; Asadi, G.; Ahari, H. Investigating the microbial properties of sodium alginate/chitosan edible film containing red beetroot anthocyanin extract for smart packaging in chicken fillet as a pH indicator. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Lei, J.; Hong, W.; Huang, B.; Zhang, C. Effect of a sodium alginate coating infused with tea polyphenols on the quality of fresh Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicas) fillets. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shancan, W.; Di, Z.; Rui, L.; Zhiyu, L.; Jie, Z. Study on preservation and monitoring effect of sodium alginate-konjac glucomannan films loaded with tea polyphenols and Lycium ruthenicum anthocyanins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendhiran, D.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Encapsulation of Phlorotannin in Alginate/PEO blended nanofibers to preserve chicken meat from Salmonella contaminations. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Huang, X.; Arslan, M.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, Y.; Holmes, M.; Zou, X. High-sensitivity bilayer nanofiber film based on polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/polyvinylidene fluoride for pork spoilage visual monitoring and preservation. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Kong, B.; Wang, H. Effect of Sodium Alginate/Crab Shell Powder Bi-Crosslinked Water Absorbent Pad Added with Cinnamaldehyde on Preservation of Chilled Meat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 40, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, W.-F.; Lin, B.-Y.; Cai, J.-L.; Liang, C.-B. Effect of sodium alginate/Nano-SiO2 coating on preservation of fish. Food Ind. 2015, 10, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, X.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Review for carrageenan-based pharmaceutical biomaterials: Favourable physical features versus adverse biological effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari Maroufi, L.; Ghorbani, M.; Tabibiazar, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Pezeshki, A. Advanced properties of gelatin film by incorporating modified kappa-carrageenan and zein nanoparticles for active food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Haq, M.; Roy, V.C.; Ho, T.C.; Park, J.-S.; Han, J.-M.; Chun, B.-S. Development of fish gelatin/carrageenan/zein bio-nanocomposite active-films incorporated with turmeric essential oil and their application in chicken meat preservation. Colloids Surf. B 2023, 226, 113320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, B.S.; Bai, J.; Chang, Y. Antibacterial κ-carrageenan/konjac glucomannan-based edible hydrogel film containing Salmonella phage PBSE191 and its application in chicken meat. LWT 2023, 180, 114707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Hani, N.M. Active edible films based on semi-refined κ-carrageenan: Antioxidant and color properties and application in chicken breast packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praseptiangga, D.; Widyaastuti, D.; Panatarani, C.; Joni, I.M. Development and Characterization of Semi-Refined Iota Carrageenan/SiO2-ZnO Bionanocomposite Film with the Addition of Cassava Starch for Application on Minced Chicken Meat Packaging. Foods 2021, 10, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, J.A.; Li, Z.L.; Cao, Z.C.; Hao, H.S.; Bi, J.R.; Hou, H.M.; Wu, H.Y.; Zhang, G.L. Antibacterial film based on κ-carrageenan with benzyl isothiocyanate-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex: Characterization and application in chicken preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, P.; Montenegro, G.; Valenzuela, L.M.; Giordano, A.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Martin-Belloso, O. k-carrageenan edible films for beef: Honey and bee pollen phenolic compounds improve their antioxidant capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Yi, J.; Yuan, X.X.; Zhang, Z.L.; Shan, Z.G.; Wang, H.H. Fabrication and characterization of carrageenan-based multifunctional films integrated with gallic acid@ZIF-8 for beef preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Liu, R.; Chi, W.; Liu, W.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, L. Simultaneously flame-retardant and antibacterial films from κ-carrageenan/carboxylated cellulose nanofibril/phytic acid for the preservation of cooked pork. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.K.; Wang, Y.F. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Effects of Kappa-Carrageenan Coatings Enriched with Cinnamon Essential Oil in Pork Meat. Foods 2022, 11, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.X.; Xu, J.X.; Zhang, R.F.; Lin, J.G.; Zhou, M.L.; Qin, X.M.; Wang, K.S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Q.J.; Jin, Y.G.; et al. Development of multi-cross-linking, rapid curing, and easy cleaning, edible hydrogels for meat preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, Z.Y.; Cao, Y.J.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.L.; Han, G.X.; Zhu, X.P. Characterization of sodium alginate-carrageenan films prepared by adding peanut shell flavonoids as an antioxidant: Application in chilled pork preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, T.R.; Raghavan, V.; de Moraes, C.C.; da Rosa, G.S.; Dotto, G.L. Bio-Based Active Packaging: Carrageenan Film with Olive Leaf Extract for Lamb Meat Preservation. Foods 2020, 9, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iswahyuni, H.; Suyatma, N.E.; Wulandari, N.; Irianto, H.E.; Dewi, F.R.; Nurhayati; Sinurat, E.; Nurbayasari, R.; Giyatmi; Fransiska, D. Application of edible coating made from blends of VCO nanoemulsion, iota carrageenan, and alginate for pindang fish preservation by using response surface methodology. Green Mater. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojah, S.M. Bio-based Coating from Fish Gelatin, K-Carrageenan and Extract of Pomegranate Peels for Maintaining the Overall Qualities of Fish Fillet. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2020, 29, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walayat, N.; Wang, X.; Nawaz, A.; Zhang, Z.; Abdullah; Khalifa, I.; Saleem, M.H.; Mushtaq, B.S.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; et al. Ovalbumin and Kappa-Carrageenan Mixture Suppresses the Oxidative and Structural Changes in the Myofibrillar Proteins of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) during Frozen Storage. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; McClements, D.J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Jin, Z.; Tian, Y. Effect of dietary fibers on the structure and digestibility of fried potato starch: A comparison of pullulan and pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Li, L.; Huang, D. Application of starch-based food films in preservation of meat products. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2023, 14, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podshivalov, A.; Zakharova, M.; Glazacheva, E.; Uspenskaya, M. Gelatin/potato starch edible biocomposite films: Correlation between morphology and physical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, L.Y.; Ji, X.Y.; Shen, M.Y.; Chen, X.X.; Qi, X.; Li, Y.L.; Xie, J.H. Characterization of gallic acid-Chinese yam starch biodegradable film incorporated with chitosan for potential use in pork preservation. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Chen, J.W.; Li, S.B.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.K.; Qin, Z.; Wang, H.X.; Su, M.X.; Li, L.; Bai, Z.C. An antibacterial packaging film based on amylose starch with quaternary ammonium salt chitosan and its application for meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Cai, L.F.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, L. Effect of tea polyphenols on sodium alginate/corn starch composite film and its application in freshness preservation. Food Res. Dev. 2022, 43, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Y.X.; Han, P.; Yang, C.C.; Liang, X.B.; Li, L.R.; Cai, S.B. Effect of chitosan-Jicama starch coating on changes in qualities of fresh Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fillets during ice storage. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2220–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Ren, L.; Meng, Y.; Ma, R.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Alamri, A.S.; Alhomrani, M.; et al. Radish residue carbon dots-based novel starch/chitosan film with high antioxidant, biocompatibility, and antibacterial activities for salmon fillets’ active packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.P.; Zhou, J.W.; Yang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhou, C.S.; Wang, L.W.; Xia, G.H.; Yu, X.J.; Yang, H. Preparation and characterization of oregano essential oil-loaded Dioscorea zingiberensis starch film with antioxidant and antibacterial activity and its application in chicken preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 212, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Jia, L.; Tao, H.X.; Hu, W.; Li, C.Z.; Aziz, T.; Al-Asmari, F.; Sameeh, M.Y.; Cui, H.Y.; Lin, L. Fortification of cassava starch edible films with Litsea cubeba essential oil for chicken meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, X.Y.; Chen, Z.J.; Chen, C.W.; Xie, J. Fabrication of polyvinyl alcohol-starch controlled release active film incorporated with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin/lemongrass oil emulsion for large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) preservation. Int. Food Res. J. 2023, 30, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Xiao, L.; Dong, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Sameen, D.E.; Qin, W.; Zhu, B. Preparation of chitosan/curcumin nanoparticles based zein and potato starch composite films for Schizothorax prenati fillet preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekar, C.M.; Nespoli, L.; Bellesia, T.; Ghaani, M.; Farris, S.; Romano, D. Fabrication of double layer nanoparticle infused starch-based thermoplastic food packaging system for meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.S.; Kaur, N.; Rana, V.; Kennedy, J.F. Pullulan: A novel molecule for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Kim, S.-M.; Rhim, J.-W. Pectin/pullulan blend films for food packaging: Effect of blending ratio. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraśniewska, K.; Pobiega, K.; Gniewosz, M. Pullulan—Biopolymer with Potential for Use as Food Packaging. Int. J. Food Eng. 2019, 15, 20190030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Vishwasrao, C.; Singhal, R.S.; Ananthanarayan, L. n-Octenyl succinylation of pullulan: Effect on its physico-mechanical and thermal properties and application as an edible coating on fruits. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xiong, X.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, Q. Effect of lactoferrin on physicochemical properties and microstructure of pullulan-based edible films. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4150–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.K.; Khalaf, H.H.; Sharoba, A.M.; El-Tanahi, H.H.; Cutter, C.N. Incorporation of Essential Oils and Nanoparticles in Pullulan Films to Control Foodborne Pathogens on Meat and Poultry Products. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M675–M684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Kumari, S.; Shameli, K.; Selamat, J.; Sazili, A.Q. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Pullulan Mediated Silver Nanoparticles through Ultraviolet Irradiation. Materials 2019, 12, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, Y.M.; Chen, Z.; Jia, Y.M.; Han, P.; Cheng, C.S. Effect of pullulan hydrolysates on the quality of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fillets during ice storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.-G.; Shen, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhang, X.-X.; Thakur, K.; Khan, M.R.; Wei, Z.-J. Preparation and Characterization of Eugenol Incorporated Pullulan-Gelatin Based Edible Film of Pickering Emulsion and Its Application in Chilled Beef Preservation. Molecules 2023, 28, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishva, R.M.; Sumit, G.; Vaijayanti, R.; Prasad, S.V. Pullulan or chitosan based active coating by incorporating polyphenols from lemon peel in raw poultry meat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3807–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Kang, S.; Lapu, M.; Jiang, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Liu, M. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/pullulan film loading carvacrol for targeted antibacterial packaging of chilled meat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 211, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.J.; Riahi, Z.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Development of innovative active packaging films using gelatin/ pullulan-based composites incorporated with cinnamon essential oil-loaded metal-organic frameworks for meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighatpanah, N.; Omar-Aziz, M.; Gharaghani, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Hosseini, S.S.; Kennedy, J.F. Effect of mung bean protein isolate/pullulan films containing marjoram (Origanum majorana L.) essential oil on chemical and microbial properties of minced beef meat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 201, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasti, T.; Dixit, S.; Hiremani, V.D.; Chougale, R.B.; Masti, S.P.; Vootla, S.K.; Mudigoudra, B.S. Chitosan/pullulan based films incorporated with clove essential oil loaded chitosan-ZnO hybrid nanoparticles for active food packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 227, 118866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; Ge, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, T. Preparation of pullulan polysaccharide/thermoplastic polyurethane coaxial electrospinning film with oregano essential oil as core material and its preservative effect on the quality of Lateolabrax japonicus fillets. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, J. The effect of grape seed extract nanoparticles/pullulan coatings on the quality of salmon fillets. Food Mach. 2023, 39, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Priyadarshi, R.; Rhim, J.W. Development of Multifunctional Pullulan/Chitosan-Based Composite Films Reinforced with ZnO Nanoparticles and Propolis for Meat Packaging Applications. Foods 2021, 10, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.Q.; Xiong, X.; Cheng, A.W.; Zhao, Z.T.; Xiao, Q. Development of pullulan-based nanocomposite films reinforced with starch nanocrystals for the preservation of fresh beef. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 1981–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Du, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xue, J.; Shi, J.; Tingting, S.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, J.; Capanoglu, E.; et al. Lactobacillus bulgaricus-loaded and chia mucilage-rich gum arabic/pullulan nanofiber film: An effective antibacterial film for the preservation of fresh beef. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhuang, W.; Gong, X.; Huang, K.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Cheng, Q.; Bao, J. Preparation and preservation effect of pullulan polysaccharide/chitosan/xanthan gum/collagen composite coating. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriana, Z.; Mohammad, A.; Masoud, H.; Leila, G.; Ayoub, F. Preservation effect of ice-glazing using pullulan and bay laurel extract on the quality characteristics of Caspian trout (Salmo trutta caspius) during frozen storage. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2022, 31, 853–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Handling Method | Meat | Effects | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan derivatives | Chitosan fructose MRPs | Beef | Prolong the shelf life of beef during freezing through excellent antioxidant properties | [69] |
| Chitosan glucose complex | Lamb | Prolong the shelf life of lamb Increase the shelf life of pork cocktail Italian sausages | [70] | |
| A novel chitosan with arginine functionalization | Pork cocktail Italian sausages | Inhibit pathogenic E. coli O157 in chicken juice Reduce the odor of the treated chicken juice | [71] | |
| A composite nano-film made from 0.6% chitosan and 0.1% nisin | Fish sausage | Reduce TVB-N, TBARS, and pH Maintain the color | [77] | |
| Chitosan nanoparticles | Citrus essential oil incorporated into chitosan nanoparticles | Chicken | Inhibit S. aureus and E. coli and the formation of biofilm Change the morphology of the cell membrane Destroy mature biofilm | [74] |
| Biomass-derived nanoparticle (nanocellulose, nanohemicellulose, and nanolignin)-reinforced chitosan films | Goat | Improve tensile strength, elongation properties, water, and UV barrier properties, as well as enhanced antioxidant and antimicrobial activities | [27] | |
| Polycaprolactone-based electrospun membranes, combined with cinnamaldehyde chitosan nanoparticles | Pork | Reduce the microbial content, TBA, TVB-N, and pH Prolong the shelf life | [76] | |
| Cinnamaldehyde, chitosan nanoparticles, and 2% chitosan film | Burgers | Inhibit the growth of Listeria | [73] | |
| Chitosan Composite with Other Substances | The zinc ion chelation is evenly distributed on the surface of the sodium alginate and carboxymethyl chitosan composite film | Chicken | Have good antibacterial and waterproof properties | [82] |
| Chitosan starch composite film with purslane added | Duck | Reduce the content of TBA reactants and volatile base nitrogen Inhibit the oxidation of meat | [83] | |
| Chitosan coatings with physical treatments | Pork | Decrease carbonyl concentration, Enterobacteriaceae bacteria, total viable bacteria and, the proportion of four main spoilage organisms | [87] | |
| Chitosan/bacterial cellulose-based films loaded with tea polyphenol-loaded chitosan-coated nanoliposomes | Chub | Improve elongation at break, thermal stability, and tea polyphenol stability | [81] | |
| Chitosan-PLA plastic films | Grouper fillets | Increase in water vapor transmission rate and moisture content Decrease in bacterial content and TVB-N Extended the shelf life | [84] | |
| Nisin and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid to chitosan-polylactic acid composite film | Grouper fillets | Improve the antimicrobial activity and inhibit the number of thermophilic bacteria and spoilage bacteria, as well as TVB-N Extended the freshness of grouper fillets | [10] | |
| Chlorogenic acid and chitosan coating composite film | Snakehead fish fillets | Retard the oxidation of TCA, TBARS, and proteins in the fillets Better preserves the odor and color of the fillets | [85] | |
| Gelatine from salmon fish bone, chitosan, gallic acid, and clove oil composite film | Salmon fish fillets | Have good antibacterial and antioxidant activity Extend the shelf life by at least 5 days | [86] | |
| Handling Method | Meat | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9% Hyaluronic acid | Crucian carp | Slow down the degradation of fish quality Inhibit the production of TVB-N and TBA, and extend the shelf life | [92] |
| 0.9% Hyaluronic acid | Carp (Cyprinus carpio) | Delay the increase in conductivity, TBARS, TVB-N, and pH Maintain meat water-holding capacity Prolong shelf life | [93] |
| 0.9% Hyaluronic acid and 2% β-conglycinin | Silver carp fillet | Delay the increase of TBARS, TVB-N, pH, conductivity, and TCA soluble peptide content of silver carp meat Reduce the loss of water holding capacity of the fish | [96] |
| Hyaluronic acid smart antimicrobial nanofiber treatment | Beef | Decay the growth of E. coli Prolong the shelf life | [97] |
| Handling Method | Meat | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5% Sodium alginate | Large yellow croaker | Lower pH, TVB-N, and TBA, and good sensory properties Extend shelf life up to 29 days | [102] |
| Alginate coating | Frozen chicken legs | Hinder the number of microorganisms Improve oxidative stability | [103] |
| Alginate coating with lauryl arginine | Frozen chicken legs | Reduce the number of microorganisms Improve oxidative stability Improve the antibacterial efficiency | [103] |
| Alginate coatings with hydroxyapatite/quercetin glucoside complexes | Fresh chicken fillet | Inhibit the growth of spoilage bacteria Inhibit TVB-N | [104] |
| Konjac glucan and sodium alginate, loaded with thymol and epsilon-poly-L-lysine hydrochloride, formed composite films. | Salmon fillets | Increase Ca2+-ATPase activity, myofibrillar protein solubility, and sulfhydryl content Decrease myofibrillar protein carbonyl content, surface hydrophobicity, and prolong shelf life | [105] |
| 2% sodium alginate/antimicrobial 1:10 protein solution | Sturgeon | Inhibit microbial growth, reduce TVB-N Reduce nucleotide catabolism Retard lipid oxidation and protein degradation in fish fillets Maintain sensory quality | [106] |
| The grass carps were treated by L. paracasei H9 and then coated with 1% sodium alginate | Grass carp | Reduce TVB-N, TBA, and total bacterial counts Maintain a better sensory evaluation of grass carp | [107] |
| Oregano essential oil and β-cyclodextrin of Sodium alginate edible coating | Chicken breast meat | Extend the shelf life | [108] |
| Sodium alginate-loaded rosemary essential oil | Mutton burgers | Inhibit Pseudomonas, Enterobacteriaceae, and lactic acid bacteria Delay lipid oxidation Extend the shelf life | [110] |
| Rosemary essential oil loaded with sodium alginate | Mutton burger patties | Extend the shelf life Maintain sensory properties Improve the antibacterial and antioxidant activities | [111] |
| Agar sodium alginate double layer antibacterial film mixed with ginger essential oil | Beef | Delay the protein breakdown and lipid oxidation of beef Inhibit the growth of S. aureus, E. coli, and fungi Maintain the freshness of beef Extend the shelf life | [112] |
| Loading cinnamon essential oil and nisin into edible sodium alginate coating | Beef | Delay bacterial growth and protein degradation Result in the lowest pH value and low volatile base nitrogen value Reduce the growth of microorganisms Extend the shelf life A coating with low permeability to water vapor, low water loss, stable color brightness, and good sensory value | [113] |
| Adding tea polyphenols to the network formed by sodium alginate konjac glucomannan | Beef | Improve the mechanical properties of the film Improve resistance to water vapor and light Improve antibacterial and antioxidant activities and stability Inhibit the growth of S. aureus | [115] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate ester was added to sodium alginate | Fresh pork | Inhibit microbial growth and lipid oxidation Reduce weight loss in pork samples Protect their color Improve the odor, color, and overall acceptance of the meat Extend the storage period of pork | [116] |
| Sodium alginate with anthocyanins | Chicken willow | Decrease nitrogen content, pH value, and TBA index Inhibit the number of coagulase-positive S. aureus and the total number of microorganisms Improve the chemical, microbial, and texture characteristics | [117] |
| Sodium alginate-konjac glucomannan films with anthocyanins | Beef and fish | Extend the shelf life | [119] |
| Root bark tannins in sodium alginate/polyethylene oxide mixed nanofibers | Chicken | Decrease the number of S. enteritidis Extend the shelf life without affecting sensory quality | [120] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol-sodium alginate-alizarin and a layer with polyvinylidene fluoride-vanillin | Pork | Indicating color changes from yellow to purple with the naked eye and the color changes check pork freshness Decrease E. coli and S. aureus Extend the pork shelf life | [121] |
| The double cross-linked water gel adsorption pad formed by sodium alginate and crab shell powder has good compatibility with cinnamaldehyde | Pork | Have good antibacterial ability Absorb the exudates from the meat inside the substrate Avoid reverse osmosis caused by compression or dumping Slow down the rise of pork pH, protein oxidation, Inhibit microbial growth Reduce juice loss rate Seal the exuded juice Reduce the production of specific volatile substances. Extend the shelf life | [122] |
| A composite film composed of alginate and nano-SiO2 | Grass carp | Reduce the production of malondialdehyde and TBARS Reduce the increase in pH, and the total bacterial count Extend the shelf life of grass carp fish | [123] |
| Handling Method | Meat | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin/carrageenan/corn protein/turmeric essential oil composite film | Chicken | Extend the shelf life Improve the biological activity Demonstrate strong antibacterial activity | [126] |
| k-carrageenan/konjac glucomannan hydrogel film loaded with Salmonella bacteriophage | Chicken | Improve food safety Prevent Salmonella contamination | [127] |
| Semi-refined k-carrageenan and germinated fenugreek seed water extraction | Chicken breast meat | Inhibit reproduction of microorganisms Have great potential for application in active food packaging | [128] |
| Semi-refined iota-carrageenan/cassava starch incorporated with SiO2-ZnO nanoparticles | Chicken | Keep minced chicken fresh for longer | [129] |
| Encapsulating benzyl isothiocyanate in the carrier beta-cyclodextrin/k-carrageenan | Chicken breasts | Lower the total viable count | [130] |
| k-carrageenan composite honey extract film, water-alcohol extract of honey, and bee pollen | Beef | Have antibacterial and antioxidant activities Inhibit lipid oxidation and microbial growth and reproduction | [131] |
| ZIF-8/Carrageenan | Beef | Reduce the growth of microorganisms and oxidation of lipids | [132] |
| k-carrageenan/carboxymethyl cellulose nanofibers/phytic acid | Pork | Delay browning and dehydration, reduce oxidation, inhibit bacterial growth, and completely inhibit the antibacterial rate of S. aureus and E. coli | [133] |
| k-carrageenan coating with cinnamon essential oil | Pork | Retard the growth of total viable count, reduce lipid oxidation, and maintain the color of the sample | [134] |
| Gelatin/k-carrageenan/triple-helix/tannic acid with phenolic hydroxyl groups | Pork | Maintaining the temperature of refrigerated meat during brief periods of high temperatures | [135] |
| Sodium alginate and carrageenan composite films incorporated with peanut shell flavonoids | Pork | Keep pork fresh longer | [136] |
| Add olive leaf extract to carrageenan-based active packaging film | Lamb | Have an antimicrobial capacity and increase the shelf life | [137] |
| Virgin coconut oil nanoemulsion, iota carrageenan, and alginatex formed a composite film | Pindang (mildly salted cooked) fish products | No change in the number of bacteria and molds present Improve the quality of the product Extend the shelf life | [138] |
| Fish gelatin, k-carrageenan, and extract of pomegranate peels formed a composite emulsion | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fillets | Reduce the microbial populations of Cryptophilus, molds, yeasts, and Enterobacteriaceae | [139] |
| A 6% ovalbumin and k-carrageenan mixture | Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) | Maintain the SH content and Ca2+-ATPase activity Stabilize the myofibrillar protein structure Have better antioxidant properties | [140] |
| Handling Method | Meat | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid-induced Chinese yam starch and chitosan | Pork | Have excellent mechanical, oxidation resistance, and antibacterial properties Extend the preservation | [144] |
| Amylose starch and 2-hydroxypropyl-trimethylammonium chloride chitosan (HTCC) | Meat | Have significant bacteriostatic properties, relatively low cytotoxicity, and low UV transmittance Enhance the freshness of fresh meat | [145] |
| Portulaca oleracea extract is mixed with chitosan/starch to form a composite film | Meat | Have good antioxidant activity Inhibit lipid oxidation Have better preservation and prolong the shelf life | [83] |
| 1.25% Tea polyphenol added to sodium alginate and corn-starch | Chicken meat | Inhibited the elevation of TVB-N, TBARS, and pH of the stored chicken meat Prolong the shelf life | [146] |
| 0.5% Chitosan/1% Jicama starch/0.25% glycerol | Nile tilapia fillets | Reduce water loss, TBA, and TCA of meat Keep the fillets fresh longer | [147] |
| Radish residues with starch and chitosan | Salmon fillets | Inhibit lipid oxidation, proteolysis, and growth of spoilage bacteria Extend the shelf life by 4 days | [148] |
| A composite film treated by 3% OEO and starch film | Fresh chicken | Have antimicrobial activity against Bacillus subtilis, E. coli, and S. aureus Reduce the total viable bacterial count at 4 °C storage condition | [149] |
| Cassava starch/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose edible films fortified with Litsea cubeba essential oil | Chicken meat | Have better barrier, texture, and mechanical properties Improve biodegradability, thermal stability, hydrophobicity, biodegradability, and strong antimicrobial properties Extend the shelf life | [150] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol-starch active films incorporated with lemongrass oil | Large yellow croaker | Inhibit the growth of fish microorganisms and lipid oxidation Delay protein breakdown and freshness reduction | [151] |
| A zein/potato starch film based on chitosan nanoparticles incorporated with curcumin | Schizothorax Prenati fillets | Extend the shelf by 15 days | [152] |
| Mixing ZnO-40 μg/mL; FeO-60 μg/mL nanoparticles with the tamarind seed starch-based bio-thermoplastic packaging films | Mutton and chicken meat | Reduce the L. lactis, Enterobacteriaceae, and P. aeruginosa Reduce the total viable bacteria counts Extend the shelf life | [153] |
| Handing Methods | Meat | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| The hydrolysate of pullulan polysaccharide | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Reduce TBA, TVB-N, conductivity, and pH Maintain moisture and color Inhibit bacterial growth | [161] |
| Pullulan–gelatin and Eugenol Pickering emulsion | Beef | Inhibit protein degradation, lipid oxidation, and microbial propagation | [162] |
| The pullulan/chitosan/lemon peel polyphenols | Meat | Increase bacterial lag phase Reduce lipid peroxidation Extend the shelf life | [163] |
| Chitosan/pullulan/carvacrol film | Goat | Exhibit satisfying antibacterial activity against the common bacteria in chilled meat Extend the shelf life of goat meat by more than 15 days | [164] |
| The incorporation of cinnamon essential oil-loaded metal-organic frameworks into gelatin/pullulan films | Meat | Inhibit bacterial growth Reduce moisture loss and maintain the pH Extend the shelf life of meat preserved | [165] |
| Adding marjoram essential oil (MEO) into mung bean protein isolate (MPI)/pullulan (PU) composite films | Beef | Facilitate DPPH radical scavenging Improve antimicrobial activity Increase the oxidative stability of minced meat | [166] |
| The eugenol oil-loaded chitosan zinc oxide hybrid nanoparticles mix with chitosan pullulan polysaccharide | Chicken meat | Improve the UV line barrier ability, reduce its water vapor and oxygen permeability, and increase its tensile strength and hydrophobicity Exhibit excellent antioxidant ability against DPPH free radicals Have high sensitivity to P. aeruginosa and S. aureus Extend the shelf life | [167] |
| Oregano essential oil, pullulan, and thermoplastic polyurethane formed coaxial electrospinning films by electrospinning | Fish fillets | Have low tensile strength and dissolution, and are effective in retarding the films Keep the fish fillets fresh longer | [168] |
| GSE nanoparticles, gamma-polyglutamic acid, and PUL coating solution | Salmon fillets | Inhibit proteolysis, total bacterial counts, and lipid oxidation in the fish Increase protein solubility Improve the shelf life | [169] |
| Pullulan/chitosan/ZnONPs/propolis film | Pork | Exhibit good antioxidant activity and excellent antibacterial activity against foodborne pathogens Reduce peroxide value and the total number of aerobic microorganisms | [170] |
| Pullulan-starch nanocrystals films | Beef | Reduce the production of undesirable substances | [171] |
| Chia mucilage protection solution/gum Arabic/pullulan/L. bulgaricus | Beef | Inhibit E. coli and S. aureus Extend the shelf life | [172] |
| The pullulan polysaccharide/carboxymethyl chitosan/xanthan gum solution with 3 g/100 mL fish skin collagen solution formed a composite film | Salmon fillets | Reduce the total viable bacterial count, TVB-N, K, and pH Reduce actinomycin, total sulfhydryl groups, and Ca2+-ATPase activity Extend the shelf life | [173] |
| Ice-glazing using pullulan and bay laurel extract | Caspian trout (Salmo trutta caspius) | Inhibit oxidation and the growth of spoilage microorganisms Maintain color and texture | [174] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, M.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Research Progress on Polysaccharide Composite Films and Coatings with Antioxidant and Antibacterial Ingredients to Extend the Shelf Life of Animal-Derived Meat. Coatings 2024, 14, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14101338
Yuan M, Mei J, Xie J. Research Progress on Polysaccharide Composite Films and Coatings with Antioxidant and Antibacterial Ingredients to Extend the Shelf Life of Animal-Derived Meat. Coatings. 2024; 14(10):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14101338
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Ming, Jun Mei, and Jing Xie. 2024. "Research Progress on Polysaccharide Composite Films and Coatings with Antioxidant and Antibacterial Ingredients to Extend the Shelf Life of Animal-Derived Meat" Coatings 14, no. 10: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14101338
APA StyleYuan, M., Mei, J., & Xie, J. (2024). Research Progress on Polysaccharide Composite Films and Coatings with Antioxidant and Antibacterial Ingredients to Extend the Shelf Life of Animal-Derived Meat. Coatings, 14(10), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14101338








