Abstract
Coating, as one of the significant applications in the building and construction sector, is crucial to prevent steel from reaching critical temperature and fire-induced structural collapse. This article reviews the current use of conventional coatings and assesses the potential use of novel geopolymer coatings on the metal substrate, particularly on the steel structure. The conventional passive fireproofing systems, including cement-based coatings and intumescent coatings, exhibit unavoidable limitations either due to the high thickness and weight or poor thermal and chemical resistance of the coating. Thus, innovations in conventional and novel coatings are constantly developing and growing rapidly. In recent years, geopolymer coatings have attracted much attention due to their higher mechanical strength and excellent resistance to chemicals and heat. Moreover, the green and environmentally friendly characteristics make geopolymer an admirable coating material for many applications. The main challenge that lies in the development of geopolymer coating is the interfacial bonding with the metal structure. Therefore, the influencing factors, including precursor materials, alkaline activator, and curing processes on the adhesion and thermal and chemical resistance of the geopolymer coating have been well explored. The performance comparison between these coatings indicates that geopolymer coating offers a superior mechanical and thermal performance, along with a substantially lower environmental impact compared with cement-based coating. This suggests that geopolymer coatings have great potential for fire protection on steel structures.
1. Introduction
Coatings are commonly applied to a substrate’s surface to improve its surface properties, such as appearance, adhesion, abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, roughness, thermal resistance, and wettability [1]. It can also help to maintain or improve the object’s physical and mechanical properties. In addition, coatings allow for an enhancement in the structure or substrate’s service life, which is associated with ease of maintenance and a reduction in refurbishment costs [1,2].
One of the significant applications of coating is to protect steel in the building and construction sectors. The steel structure is one mainstream building structural system due to the high strength–weight ratio and ductility, which enable the design of slim and light structures [3]. In addition, steel structures allow for the reduction of construction costs. However, steel experiences significant strength and stiffness loss at elevated temperatures [3]. It was well proved that 50% of steel’s yield strength could be lost at a temperature above 550 °C [4]. Additionally, an unprotected steel structure may collapse due to a loss in strength and stiffness at high temperatures (greater than 550 °C) during fire [5]. Table 1 lists examples of fire-induced structural-collapse incidents worldwide in the past 25 years. The notable collapse event was the collapse of the World Trade Center on 11 September 2001 [6]. Therefore, a major design factor considering the structural safety of high-rise buildings is to prevent steel from reaching critical temperature and prevent fire-induced structural collapse through an appropriate fireproofing system. It offers sufficient time to evacuate humans and valuables [5].

Table 1.
List of fire-induced structural collapse incidents worldwide in the past 25 years [6,7,8].
Fire-protection systems generally involve an active fire-protection and passive fire-protection system. The former represents the action to control and extinguish the fire by firefighting systems, extinguishers, and sprinklers, and the latter indicates the limits and controls the fire when it occurred, i.e., fire-retarding chemicals, intumescent coatings, thermal insulation panels and cement-based coatings [5,9]. Intumescent coatings are commonly used as a fire-protection coating to prevent structural collapse in buildings and construction sectors [5]. The use of waste-derived compounds in the development of more recent intumescent coating and polymer-based coating systems has also been reported [10,11,12,13,14]. They provide a high-quality finish, lightweight structure, and good fire ratings on buildings. However, the outdoor exposed coatings have poor corrosion resistance due to the presence of water-sensitive ingredients in the formulations [5]. Moreover, the presence of organic binders, such as epoxy resin and polyurethane, emit smoke from combustion and release toxic decomposition products, thus having a negative impact on the environment and human health [10]. Moreover, epoxy-based material exhibits water-absorption phenomena, which could degrade the fire-resistance efficiency over time [15]. Cement-based coatings are more economical and accessible in application but have major limitations in their weight and thickness and poor aesthetics [5]. Thus, innovations in conventional and novel coatings are constantly developing and growing rapidly.
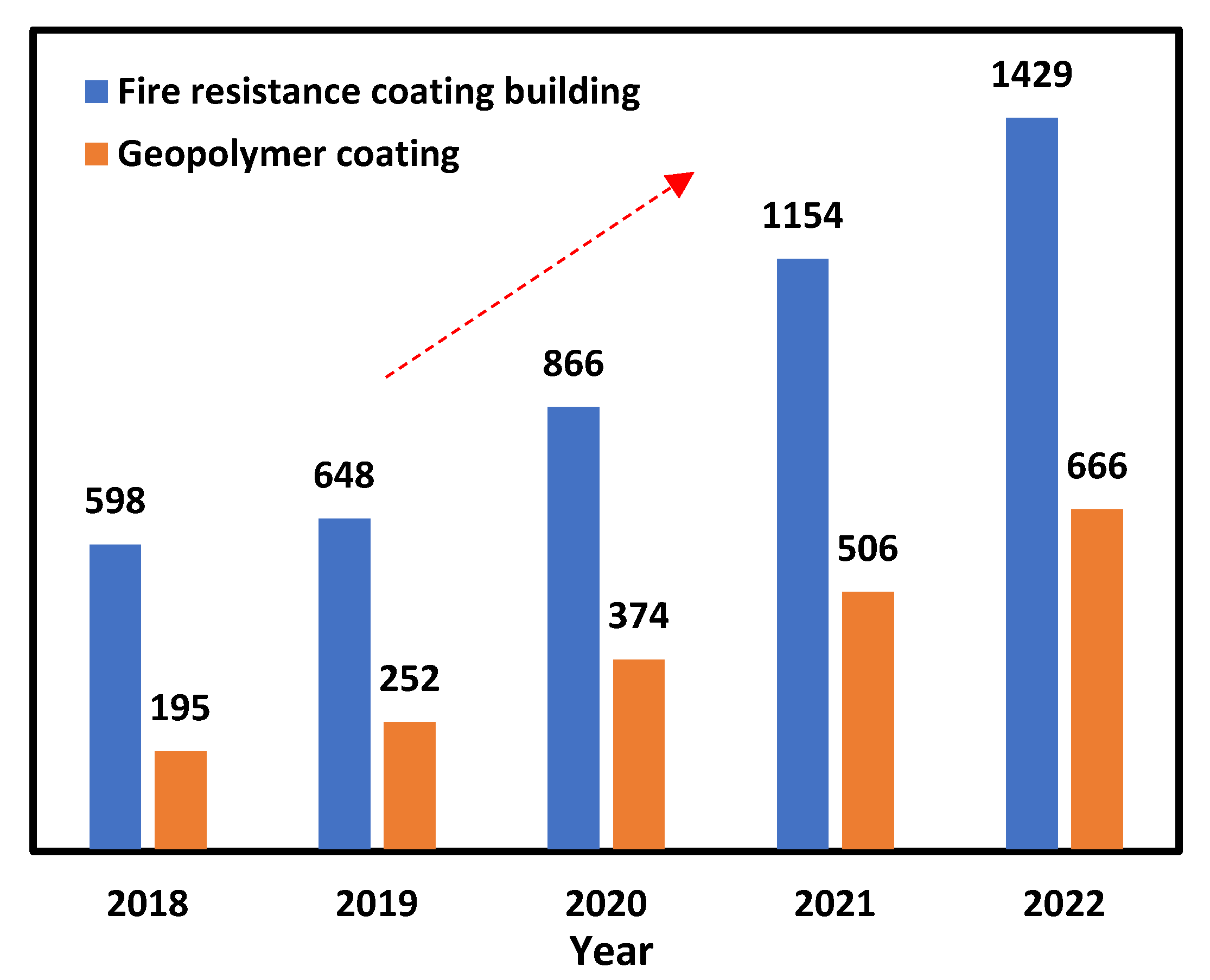
In recent years, extensive research has been carried out to investigate the feasibility of geopolymers as a sustainable substitute for ordinary Portland cement [16]. Figure 1 shows the number of journal articles published on fire resistance coating and geopolymer coating over the last 5 years. These were counted using the keywords ‘fire resistance coating building’ and ‘geopolymer coating’. It was well indicated that geopolymer received more and more attention as coating materials. The growing trend suggests that geopolymer coating exhibits a promising future in the fire protection of buildings. Geopolymer is a three-dimensional inorganic polymer which is derived from the reaction between an aluminosilicate source and alkaline/acidic activators [17,18]. Geopolymer exhibits excellent thermal stability, relatively high strength, and fire and chemical resistance, thus showing great potential in fire-resistance applications. Lach et al. [19] and Sitarz et al. [20] evaluated the thermal and mechanical performance of foamed geopolymer, and it was suggested that the geopolymer offers excellent thermal and mechanical stability at a high temperature (i.e., 600 °C). Geopolymers are also used for protection of polymer material against fire [21].
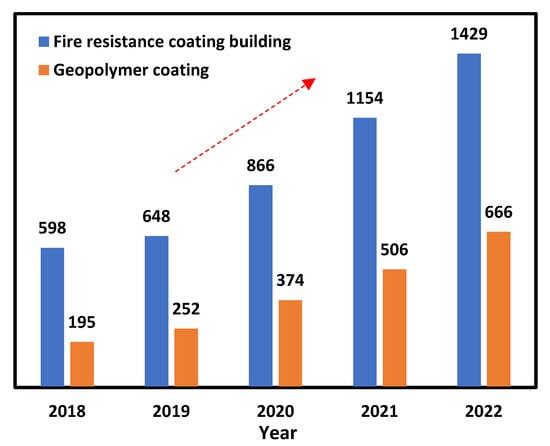
Figure 1.
The number of journal articles published on fire-resistance coating and geopolymer coating over the last 5 years.
More interestingly, geopolymer can be fabricated using industrial solid waste, such as fly ash and slug, it produces less carbon dioxide and consumes less energy during manufacturing than traditional cement [22,23]. It was reported that the estimated CO2 emissions during the production of geopolymer concrete could be reduced by up to 45% more than traditional cement concrete [23]. Apart from the environmental effect, the polymerization reaction speed of geopolymer is rapid, and the three-dimensional network structure can be readily formed. Moreover, fly-ash-based geopolymer can significantly reduce the leaching of toxic and harmful heavy metal ions; therefore, it has attracted more attention and research [24].
The geopolymer paste as a coating material could become an ideal solution to minimize deterioration by protecting the surface and increasing the chemical and thermal resistance of the substrate due to its excellent thermal stability, mechanical properties, and great adhesion to the substrate [25,26]. Despite the fact that a few geopolymer-coating reviews have been conducted, a comprehensive review, including the current conventional coatings and novel geopolymer coating, that is not only focused on the metal substrate but also the comparison between them is rarely reported. Furthermore, the latest fire-induced structural collapse incidents emphasize the necessity of continuous improvement in coatings. Although the number of research studies related to coatings has increased considerably in recent years, there are still issues and knowledge gaps that need to be addressed. This is well discussed in this article, along with some helpful suggestions, which may be beneficial for human lives, economics, and the environment. The review aims to summarize the current use of conventional coating and assess the potential use of novel geopolymer coating on the metal substrate, particularly on the steel structure. The research progress of geopolymer coatings was investigated. A few investigations regarding the comparison between the conventional coating and geopolymer coating are discussed here. The current issues and suggestions regarding the further improvement of coatings are finally stated.
2. The Conventional Coating on Metal Structure
2.1. Passive Coatings
The conventional passive coatings are mainly based on Portland cement, vermiculite, gypsum, and other materials. During the on-site application, they are mixed in water with fillers and binders, which are then applied to substrates via spraying [5]. They offer fire protection through thermal-insulation effects. Cement-based materials exhibit low thermal conductivity, incombustibility, and do not swell under heat, thus making them ideal for the application of fire-resistive materials [27].
Compared to intumescent coatings, Portland cement-based coatings provide superior properties, including anti-ageing and anti-cracking, when exposed to water. In addition, the simple and flexible spraying method significantly shortens the installation time, thus reducing the construction and repair cost [3,28]. Moreover, due to their inorganic nature, they will not produce smoke and release toxic decomposition products [10]. However, the drawback of cement-based coating is also unavoidable. The mechanical properties of cement-based coating deteriorate significantly at high temperatures [27]. More seriously, spalling may occur, meaning that a sudden and rapid brittle failure occurs. To overcome these deteriorations, inorganic porous fillers, such as perlite, hollow glass beads, aerogels, and expanded polystyrene, are typically used to improve the mechanical properties of cement-based materials. The presence of short fibers, such as polypropylene fibers and steel fibers, could enhance the spalling performance, ensuring the structural integrity of the coating during fire. Moreover, the involvement of calcined products, such as fly ash and blast furnace slag, improves the thermal and mechanical properties of cement-based materials [27]. The performance, advantages, and disadvantages of various porous fillers on cement-based materials are summarized in Table 2. It was stated that the filler type needs to be correctly chosen to satisfy the desired thermal and mechanical performance by considering the cost, strength loss, ease of mixing, and complexity of the encapsulation process. For example, the encapsulation process of the phase-change materials is usually performed by mixing the solid (usually powder) form of phase-change materials with cement mortar during the solid–liquid phase-transition process. As the material changed its phase from solid to liquid, it absorbed extra heat so that the insulation property was enhanced [27].

Table 2.
The performance, advantages, and disadvantages of various porous lightweight fillers on cement-based materials [27,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44].
The involvement of fiber can reduce spalling under high temperatures, and it is influenced by fiber type, content, and size. At present, polypropylene (PP) fibers are the most widely used fibers to resist the spalling of cement-based materials at high temperatures effectively [45,46,47]. Similarly, the fire-spalling resistance could be improved by adding other polymer fibers with a low-melting point, such as nylon and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber [27]. Although the involvement of polymer fibers can effectively resist concrete spalling, it is not beneficial for increasing the residual strength and elastic modulus of the concrete at high temperatures [45]. Moreover, the PVA has a strong water-retention characteristic; thus, the addition of PVA could reduce the fluidity, resulting in an uneven dispersion of the cement mortar. Consequently, the number of interconnecting holes could increase, thus causing a reduction of the mechanical properties [48]. The use of steel fibers limits the spalling phenomenon while improving the residual strength after heating to some extent, but it could only reduce the degree of spalling severity and duration of the serve spalling. Thus, the combination of polymer and steel fibers was investigated to improve both properties of the cement-based coating [49]. It was stated that the low-melting-point PP fibers will first melt and form a broader channel to release water vapor. As the temperature continues to rise, the steel fibers inside the matrix restrict the expansion of internal cracks during heating. As a result, the compressive strength increased from 120 MPa (single type of fiber) to 200 MPa (combination of PP, nylon and steel fiber) [49].
The use of cement-based materials in steel structural coatings exhibits excellent thermal insulation, spalling resistance, and mechanical properties after elevated temperature. In addition, cement-based coatings are generally more economical and more accessible in application compared to intumescent coating. However, in an actual application, the required thickness of the cement-based coating is significantly larger than that of intumescent coating, and this enormously affects the structural self-weight and aesthetics [27]. The poor bonding properties and brittleness of cement-based coatings lead to delamination of the substrate, resulting in a deterioration of the fire resistance and structural stability. Currently, only a few journal articles related to the mechanism of fire protection, explosion suppression of cement-based coating, and interfacial bonding strength to metal can be found, which needs further investigation. An example of improving the brittleness of cement-based material is reinforcing with pretreated fibers. It was demonstrated that an alkaline treatment and vinyltrimethoxysilane treatment could enhance the fiber–matrix interface [50,51,52,53].
2.2. Reactive Materials
Intumescent coatings have been increasingly used as a fire-protection material for both commercial and industrial applications due to the high-quality finish, lightweight, speed of construction and fair fire ratings [54]. Intumescent coatings are thermally reactive materials and, nowadays, involve both organic and inorganic components that are bound together in a polymer matrix [3,9,12,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62]. They are usually composed of an acid source, e.g., ammonium polyphosphate; a carbonaceous compound, e.g., polymers; a blowing agent, e.g., melamine; binders; and additives. The effect of these compositions on the coating performance has been explored extensively [3]. These types of coatings are insensitive to weather and water compared with alkali-silicate-based coatings, which are generally used for protecting steel-framed structures against fire. In addition, intumescent coatings exhibit a nice surface finish. Therefore, they are increasingly used in modern infrastructure and public facilities [54].
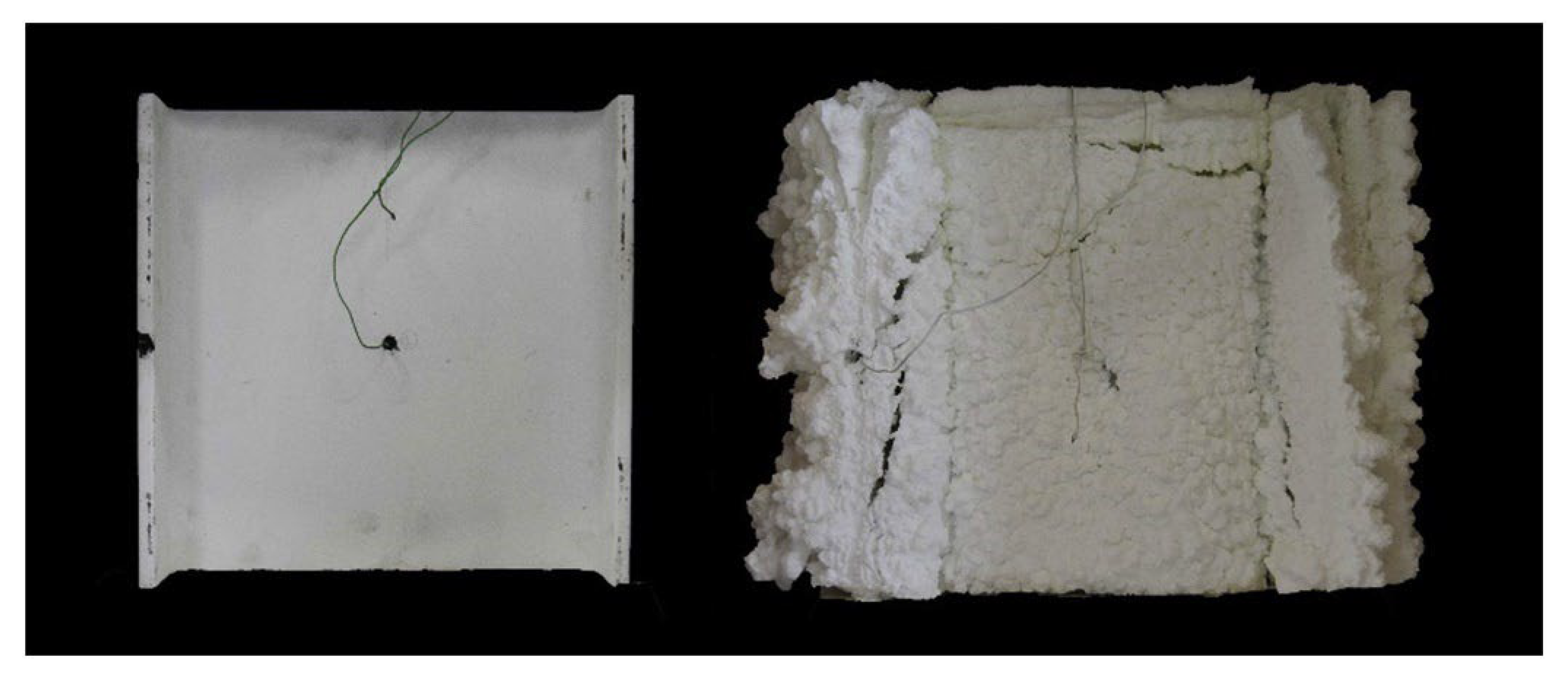
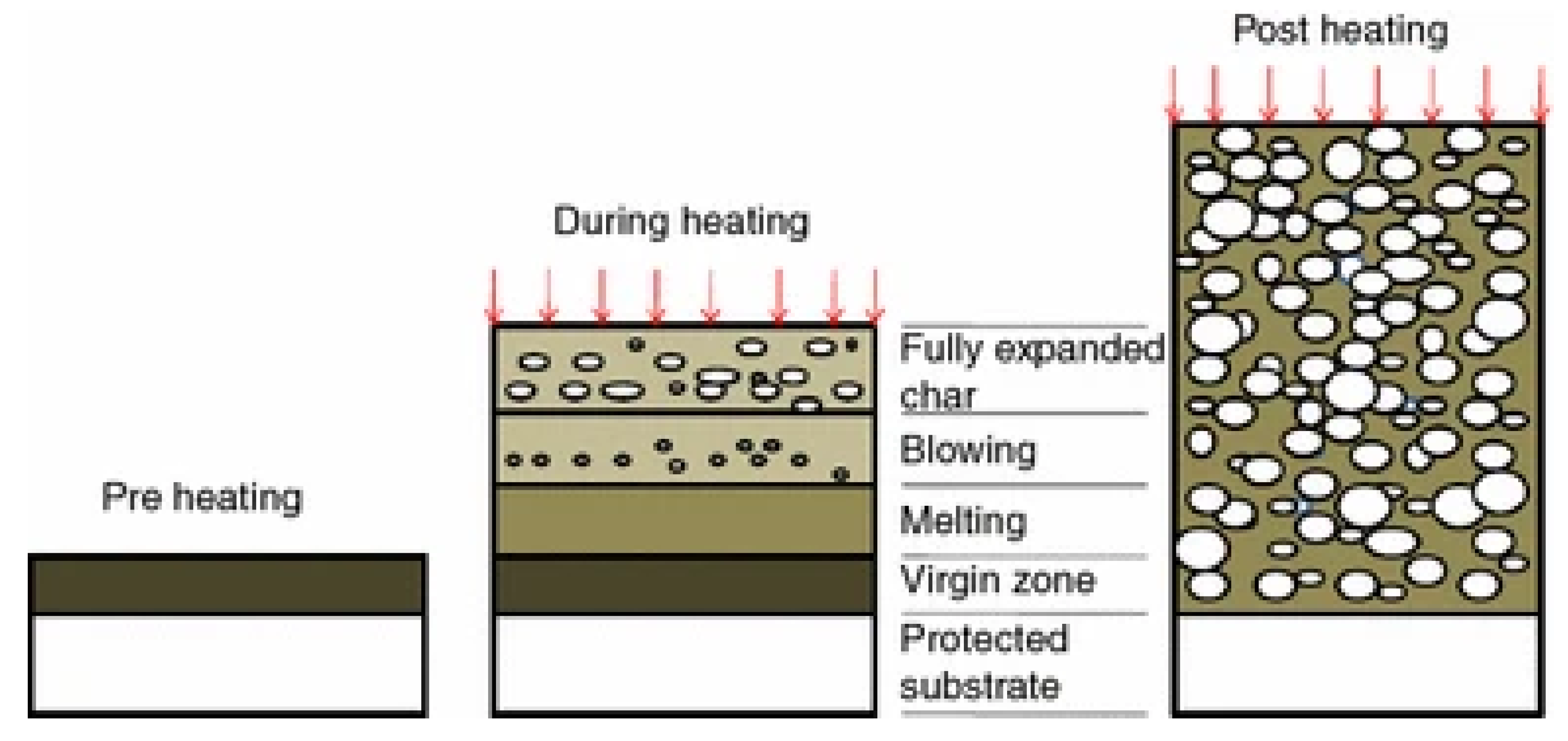
Intumescent coating is reactive because it swells due to heat exposure, increasing its original thickness and decreasing in density many times, producing a porous medium that acts as an insulating layer to protect the substrate (Figure 2) [3,5,63]. The intumescence process generally involves the following steps: A mineral acid is released by breaking the acid source, resulting in dehydration and carbonization of char formers. The blowing agent then decomposes to release gases and is trapped in the melted matrix, making it swell. An insulating multicellular layer is formed to restrict the heat transfer from the source to the substrate and prevents further degradation of the substrate [54,64]. The schematic representation of the intumescence process is shown in Figure 3 [5].

Figure 2.
Steel structure protected with an intumescent coating before (left) and after (right) fire test. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [3]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
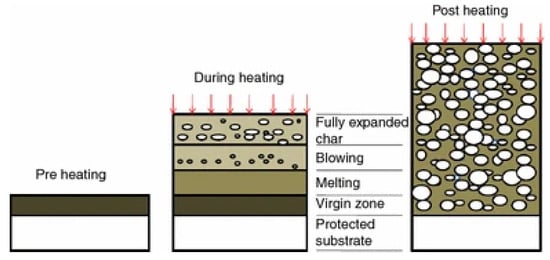
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the intumescence process. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [5]. Copyright 2016, Springer Nature.
As mentioned previously, the main ingredients of intumescent include an acid source, a carbon source, and a blowing agent. The intumescent coating needs to be well designed and formulated to form an efficient protective char, as its structure significantly impacts the heat-barrier properties. A coating should form a large char volume with a thick and continuous inner char structure, while the char should be compact, having a smaller cell size, narrower cell size distribution, and closed solid foam [5].
Ammonium polyphosphate is a commonly used acid source in intumescent formations, and it releases acid above 250 °C during fire. However, the disadvantage is the water sensitivity and poor compatibility with the binder. Other salts, such as melamine phosphate and melamine pyrophosphate, are also widely used in intumescent formations [54]. Melamine pyrophosphate exhibits better water resistance and provides a superior thermal insulation performance than melamine phosphate [5]. It was suggested that the involvement of ammonium and melamine phosphate could form an infusible residue (phosphorus oxynitride), resulting in excellent thermal stability during heating [65].
The presence of char former allows the formation of a carbonaceous char by dehydration in the presence of an acid source [5]. Pentaerythritol is a widely used charring agent, together with ammonium polyphosphate as an acid source, in the intumescent coating due to its low melting point [63]. However, the poor water solubility limits its use, especially for stable weather applications [5]. Starches, sugars, and cellulose that contain pendant hydroxyl groups are also attractive in intumescent formulations due to their low cost and sustainability [66].
Blowing agents, typically melamine, are commonly used in intumescent formulations, which decompose to form a considerable amount of gases that cause the carbon-rich mass to bubble and foam, producing a thick insulating layer [54]. The use of binders, such as polymeric resins, in intumescent coatings improves protective performance [5]. The choice of binder depends on the service environment and its expected durability. Waterborne acrylics are mostly used in dry, internal locations, while solvent-borne acrylics are used in an internal or sheltered external location [5].
Inorganic fillers and fibers are also involved in intumescent formulations, which improve the fire-protection performance, as well as the durability of the coating. This could be due to the involvement of fibers improving the heat-shielding effect against fire [67,68,69]. Heat shielding allows the extension of time to reach a high temperature [70]. With the addition of fiber, the char became denser and hard and acted as a thermal barrier to resist heat. In contrast, the char without fibers led to a soft, fluffier structure with large pores, resulting in the heat being penetrated easily to reach the substrate [67]. Fillers such as magnesium hydroxide can increase bonding strength to the metal substrate due to its effective interface adhesion [71]. Inorganic compounds such as borides, nitrides, titanium, or other metals are chemically inert and exhibit a much higher thermal decomposition temperature. They could stabilize char in intumescent formulations [5]. The addition of fibers in the intumescent coating has been well investigated. It was reported that alumina and silica fibers increase the strength of the residual char, thus elongating the fire-protective performance [72]. High-temperature ceramic fibers could enhance the toughness of the char [73]. More recently, the addition of nanoscale additives, such as carbon nanotubes, in intumescent coatings has been widely explored, as it was proved that they could enhance the fire-protection performance of the coatings [5,74].
Thin intumescent coatings are typically solvent- or water-based, with a dry thickness ranging between 400 and 3000 μm, and they are mainly used for cellulosic fire conditions [9]. Cellulosic fire represents the combustion of cellulose material, including timber and paper, and the temperature could reach up to 500 °C in 5 min [75]. This type of fire is classified as class A (ordinary combustible) [76]. In contrast, thick intumescent coatings are usually epoxy-based (two-component systems), with a thickness of a few centimeters. Thick intumescent coatings are mainly applied in industrial applications, such as the oil and gas industry, and they are used for hydrocarbon fire conditions [3,9]. Hydrocarbon fires occur due to the combustion of combustible liquids such as oil and gas, and the temperature could rise to 1000 °C within 5 min [75]. Hydrocarbon fire is classified as class B (flammable liquids and gases) [76]. Intumescent coatings usually consist of a primer, base coat, and top coat. The primer of the coating offers great adhesion to the metal substrate to improve corrosion resistance, while the top coat enhances its durability and appearance when exposed to weathering and an aggressive environment [3,54].
Intumescent coatings offer fire protection for up to several hours, with an aesthetic appearance [9]. Additionally, they could be used in cellulosic fire and hydrocarbon fire, including jet fire, which effectively prolongs fire-induced structural collapse. However, the application usually involves a long drying time, which is sometimes difficult to use on-site. In addition, the outdoor exposed coatings have poor corrosion resistance due to the presence of water-sensitive ingredients in the formulations. Moreover, the formation of carbonaceous char may exhibit poor cohesive strength and fragility, leading to the falling of the coatings during a fire event [5]. Finally, organic binders, such as epoxy resin and polyurethane, emit smoke from combustion and release toxic decomposition products, which negatively impact the environment and human health [10]. Thus, continuous improvement of the intumescent coating is still needed. An example of smoke suppression in the epoxy-based intumescent coating is to introduce of zinc borate and diantimony trioxide. The involvement of these substances leads to a more stable and compact shielding layer; thus, the smoke release and heat generation are limited [77].
3. The Potential of Geopolymer Coating on Metal Structure
In recent years, geopolymer coatings have attracted much attention due to their better workability, higher mechanical strength, excellent resistance to chemicals and heat, and easier handling. In addition, geopolymer coatings offer excellent durability and long-term performance. Moreover, the green and environmentally friendly characteristics make geopolymer an admirable coating material for many applications [78,79].
The effect of the activator solution, binder content, and the curing conditions has a significant influence on the mechanical and durability properties of geopolymer coatings [4,79]. A defect-free and integral coating is essential to provide strong adhesion with the substrate. Therefore, it is required to balance the preparation process of the coating, including water evaporation, geopolymerization, and the techniques used to apply the coating [1].
The common techniques used to apply geopolymer coatings on substrate surfaces are dipping, brushing, spraying, and blading [80]. The dipping method is convenient and simple, but the major drawback is the inability to control the thickness of the applied layer accurately. Similar to the dipping method, the brushing method leaves relatively thick coatings on substrate surfaces. This may limit its use when layers of small thickness are required [1]. Geopolymer coatings can also be manually applied to the surface via a blading method. It usually serves a high shrinkage rate in geopolymer paste, which consequently forms microcracks on the surface in atmospheric conditions [81]. The spray method is a low-cost and efficient method which can precisely control the thickness of the applied layer. In contrast, the disadvantage is that a flowable coating suspension is required [81,82]. Nevertheless, the spraying method still offers the highest application potential for geopolymer coating. The advantages and limitations of these coating techniques are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Advantages and limitations of various coating techniques [1,80,81,82,83].
As a coating material applied on metal surfaces in the building and construction industry, the coating performance, such as adhesion strength, fire resistance, corrosion resistance, and shrinkage, significantly impacts the safety and service life of existing structures.
3.1. Adhesion Strength
Adhesion strength is generally defined as the capability of coating materials to adhere to the substrates [79]. Adhesion to the substrate must tolerate mechanical stress, thermal stress or elastoplastic distortions, and the environment in order to perform its function properly [84]. There are two types of bonding failures: the coating layer debonding from the coating–substrate interface and the substrate or the coating layer failure tears. The system is likely to fail at its weakest spots [85]. The adhesions of geopolymer coatings are typically influenced by the properties of the coating, quality, and state of the substrate, as well as the construction technique of coatings [86].
It was well proved that the effect of Si/Al ratio and Na/Al ratio significantly impacts the adhesive strength [80,87]. Temuujin et al. [87] studied the effect of the Si/Al ratio on adhesion for fly ash (FA)-based geopolymer coating applied to mild steel via the dipping method. The results indicated that the increase in Si/Al ratio led to an increase in the adhesive strength, with a maximum strength of 3.5 MPa at a Si/Al ratio of 3.5. Khan et al. [88] investigated the influence of the Na/Al ratio on the adhesive strength of FA-based coating applied on steel via dipping. The adhesive strength of the prepared samples tends to increase, followed by a reduction as the Na/Al ratio increases from 0.6 to 1.2.
The water content also plays a vital role in forming geopolymer coating and is correlated to the Si/Al and Na/Al ratios [89]. Water is consumed in the dissolution of the aluminosilicate solid through alkaline hydrolysis but released in condensation of the dissolved oligomers. A high-water content is conducive to full hydration of the precursor materials, leading to soft geopolymer binders. This is beneficial for applying geopolymer as adhesive coatings [90,91]. The geopolymerization process is induced at a low water content, resulting in a reduction of porosity in the binder. The workability of the binder decreased, making the coating hard to deposit [92]. It was suggested that the adhesion strength tends to decrease with increasing water content [17].
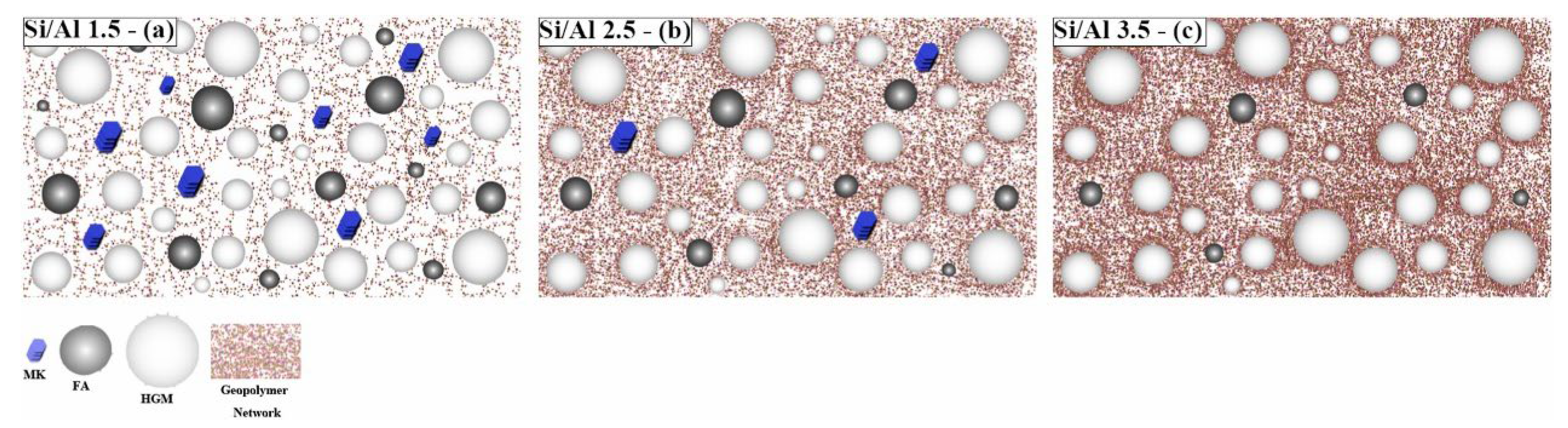
Tatlisu et al. [93] prepared an FA-based geopolymer coating with the addition of hollow glass microspheres (HGMs). The composite coating was applied on hot (300 °C) metal surfaces via the spray deposition technique. The effect of the Si/Al ratio, HGM content, and Na/Al ratio on adhesion strength and thermal conductivity was investigated. As expected, for the samples without HGM, the increase in Si/Al ratio (1.5 to 3.5) resulted in a significant increase in adhesion strength (1 MPa to 6.5 MPa) due to the increasing dissolved geopolymer phase (Figure 4), while the thermal conductivity of the samples decreased slightly. When the HGM was added, the adhesion strength decreased slightly (5.5 MPa to 5.0 MPa at a Si/Al ratio of 2.5) as the wt% of HGM increased from 0 to 10% with a fixed Si/Al ratio. However, as the amount of HGM increased further to 15%, the adhesion strength dropped significantly to 1.0 MPa. The thermal conductivity of the composite coating decreased significantly with the addition of the HGM. Therefore, depending on the application, there should be a trade-off between the adhesion strength and thermal conductivity.
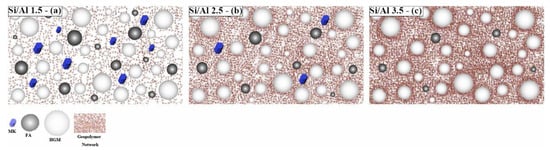
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of dissolution–reorganization mechanism in geopolymer formation at varying Si/Al mole ratios: (a) 1.5, (b) 2.5. and (c) 3.5 in HGM/geopolymer composites. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [93]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
Tomar et al. [94] prepared a geopolymer coating containing fly ash (FA), red mud, metakaolin (MK), and blast furnace slag, and the amount of red mud on the adhesion strength was evaluated. The coating material was applied on mild steel via the spray-coating technique, and the thickness of the coatings was in the range of 240–290 μm. Generally, the adhesion strength increased with the addition of red mud, and the strength of all samples was reported between 10.80 and 12.15 MPa. This may be due to the synergistic effect of red mud and fly ash constituents which emerged as iron that contains inorganic phases. It is worth mentioning that the use of solid waste, including fly ash and furnace slag, enlarges the environmental benefit and sustainability.
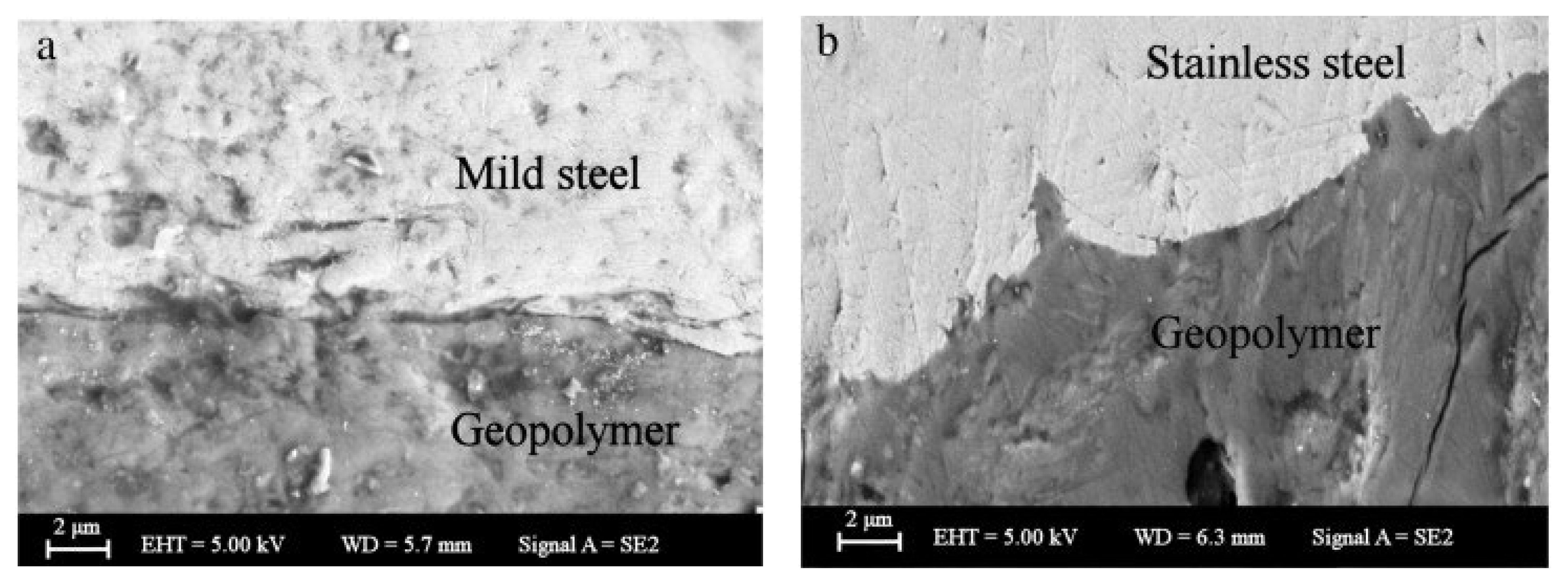
The bonding strength of geopolymer coating to stainless steel and aluminum is generally weak due to only a physical bond being formed [17]. The presence of chromium (Cr) in stainless steel restricted the geopolymerization of the binder on the substrate and formed a weak bond [95]. An excessive reaction with aluminum substrates results in detrimental corrosion. This caused a weak bonding between the coating and substrates being formed [96]. Temuujin [80] studied the adhesion strength of fly-ash-based geopolymer coating on mild steel and stainless steel (Figure 5). The results showed that it exhibits higher adhesion strength on mild steel (2.7 MPa) compared with stainless steel (0.25 MPa). Yong et al. [95] suggested that the growth of synthetic geopolymeric gel is faster when attached to a mild steel substrate due to chemical bonding, while the presence of Cr in stainless steel inhibits the growth of geopolymeric gel. Thus, a weak bonding was formed.

Figure 5.
Interface between geopolymer coating and (a) mild steel and (b) stainless steel. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [80]. Copyright 2009, Elsevier.
High adhesive strength is likely involved in the mechanical interlocking or chemical bonds between the coating and the substrates, apart from the physical bond. This could be achieved by increasing the surface roughness of the substrates, leading to a higher contact area between the coating and substrate [17,97]. Mechanical treatment (sandblasting) and chemical treatment (Nitrophosphoric acid and sanitation) could be carried out on steel and aluminum plates [89]. De Barros et al. [98] suggested that mechanical treatments were more effective than chemical treatments for geopolymer coating applied on steel and aluminum substrates. Wang et al. [99] examined the effect of substrate surface characteristics (relative area) on the adhesion properties of geopolymer coatings. The relative area was determined by an area scale fractal analysis, which can effectively characterize the surface roughness. It was reported that the bond strength reduced with the decreasing relative area. However, Temuujin et al. [80] claimed that the difference in adhesion strength was clearly independent of surface roughness. The surface roughness of each substrate could vary due to the time and power of grinding, although the metal surface was treated in the same way. The relationship between substrate surface roughness and adhesion strength in the coating industry is widely investigated, which provides valuable guidance for geopolymer coatings applied on the metal surface [89].
3.2. Fire Resistance
Steel, as a load-bearing structural component, is widely used in the building and construction industry, and fireproofing is one of the most critical properties. However, steel experiences significant strength and stiffness loss at elevated temperatures [3]. It was well proved that 50% of the steel’s yield strength could be lost at a temperature above 550 °C [4]. Additionally, an unprotected steel structure may collapse due to a loss in strength and stiffness at high temperatures (greater than 550 °C) during fire [5]. Due to their inorganic nature, geopolymer coatings exhibit higher strength, durability, and fire-resistance characteristics compared to conventional coating materials [79,85]. It was well indicated that the effect of composition, additives, and thickness of coatings have a significant influence on the thermal resistance of the geopolymer coating [17].
Temuujin et al. [100] conducted a direct flame test (flame temperature of 1100–1200 °C) for an MK-based geopolymer coating. The results indicated that the coating could withstand the direct flame for 30 min, which denoted high structural integrity. Temuujin et al. [87] also explored the microstructure of the geopolymer coating at elevated temperatures. It was observed that the material exhibited shrinkage with a temperature increase of up to 820 °C. The metal substrates expanded after heating while the geopolymer shrunk, resulting in a loss of adhesion. The formation of cracks during heating due to heat flow directly to the metal substrate caused a loss of strength. Bakharev [101] suggested that KOH-activated FA-based geopolymer coating had better thermal stability than NaOH-activated geopolymer coating. The fire-resistance property was also improved with the increasing K2O and MK content.
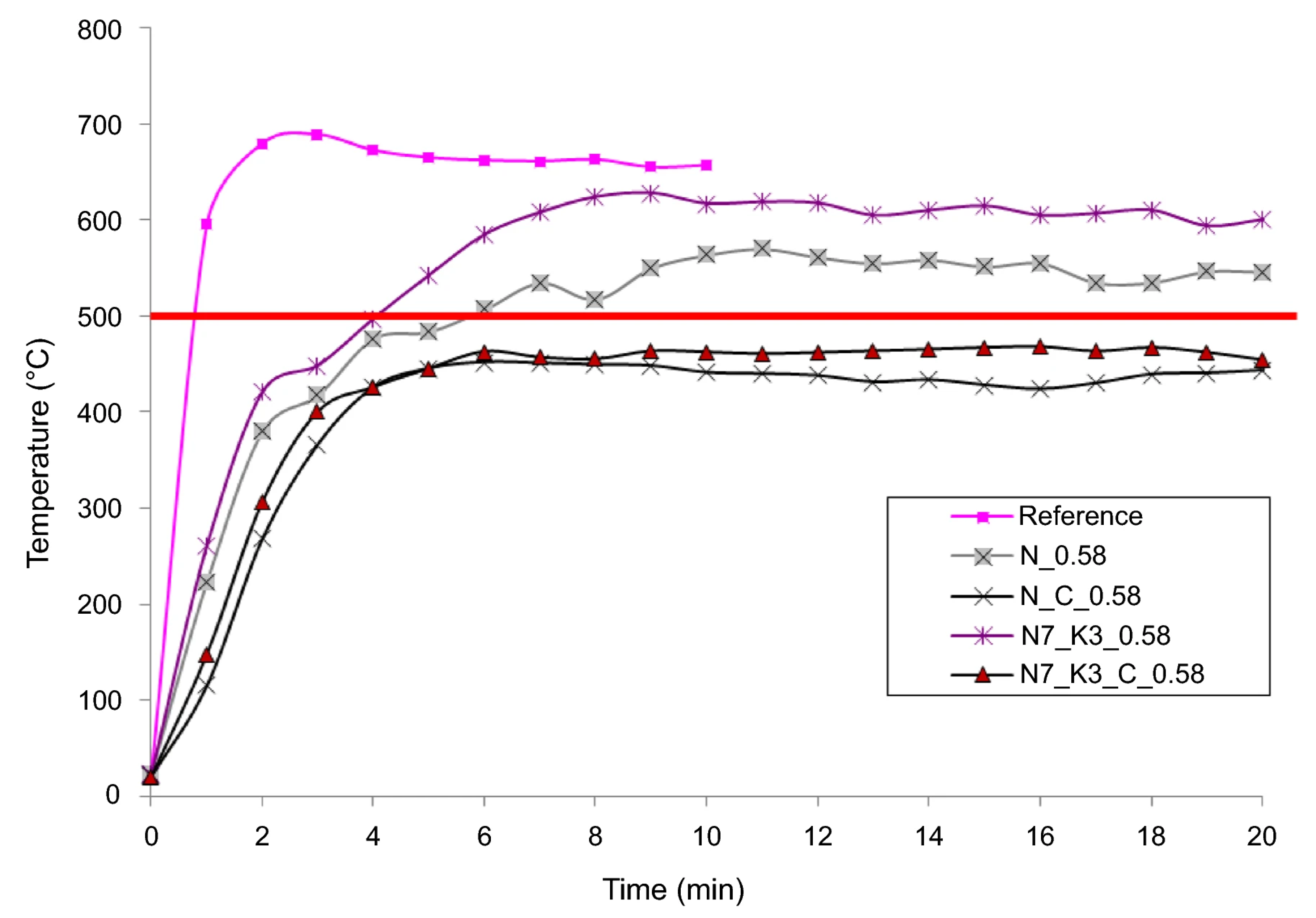
Nicoară et al. [102] prepared a geopolymer coating containing waste glass powder, fly ash, NaOH, KOH, and borax decahydrate (chemical reagents). The coatings were applied on a metal surface via spray technique and tested in direct contact with a propane flame. An uncoated steel plate was used as a reference, and the flame test showed that the back face temperature rose rapidly, reaching the critical value of 500 °C in the first 2 min (Figure 6). This temperature was critical for the structural strength of steel. For the samples containing glass powder, fly ash and borax (N_C_0.58 and N7_K3_C_0.58), the back face temperature remained broadly stable at below 500 °C for more than 1 h, indicating an excellent thermal-resistance property. During the flame test, no exfoliation of the coating layer was observed, indicating excellent adhesion between the coating and substrate. It is also worth mentioning that the addition of glass powder in geopolymer coating improved the thermal performance, which was beneficial to the fire resistance.
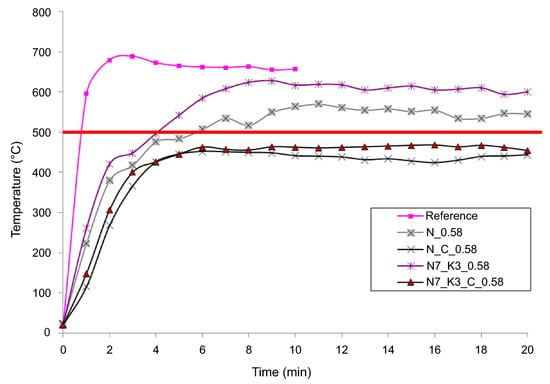
Figure 6.
Evaluation of the back face temperature of the metal plate without coating (reference) and geopolymer coating with various raw ingredients after contact with the propane flame. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [102]. Copyright 2019, Springer Nature.
Sarazin et al. [103] explored the influence of coating thickness on the fire-resistance test by adding a foaming agent and surfactant (CetylTrimethyl Ammonium Bromide, or CTABr). The temperature profiles for three geopolymer coatings were compared during the burn-through tests. Whatever the coating is that is being considered, the temperature rise is lower than for the uncoated steel plates. The maximum decrease in temperature (−251 °C) was obtained for a geopolymer coating modified with both a foaming agent and surfactant, whereas the lowest (−122 °C) was obtained for the reference coating (i.e., without a foaming agent and surfactant) compared to the uncoated steel plate. This means that the foaming structure provided a better thermal barrier than bulk geopolymer, and the addition of foam stabilizer (CTABr) enhanced the thermal barrier effect, as well. This is expected as both additives increase the foam thickness. However, the bromide ions are toxic, which is harmful to the human body and environment [104]. Calcium stearate seems to be an excellent alternative to stabilize the form effectively [105].
Bhardwaj et al. [106] introduced an advanced polymerization process in which water was added to solid precursor powder obtained by co-grinding of raw materials. Amorphous tricalcium phosphate was also added, as it was proved that phosphate-based coatings possessed effective corrosion protection and fire-protective properties. It could also enhance the inhibition efficiency and improve the passivity of the metal surface. At a coating thickness of about 115 μm, the cold side temperature curve showed that the insulation capacity (time required to reach a temperature of 180 °C) was approximately 7 min. This was about three times longer than that of an uncoated steel substrate. It was predicted that the protection efficiency might exceed up to one hour if the thickness of the coating increased to 20 mm. The direct flame test was also carried out, and the results proved that the increased inorganic phosphate content led to superior fire-protective characteristics. The coated sample can withstand a flame for more than 45 min without peeling off. No visual cracks or signs of degradation were observed in the coating after 50 min.
3.3. Chemical Resistance
Corrosion in steel structures is a critical issue, especially for infrastructures exposed to the marine environment. Durability is the major issue caused by corrosion, leading to rust formation, cracking, spalling, delamination, and degradation of structures [107]. In addition, it has nonnegligible impacts on economic losses, human health, and environmental pollution [16]. Geopolymer coating offers higher strength, longer durability, less permeable mix design, and superior chemical resistance, which can be seen as an excellent alternative to conventional coating materials [4].
Deshmukh et al. [83] demonstrated that geopolymer coating exhibited strong corrosion resistance via electrochemical measurements by dipping the coated mild steel plate in NaCl electrolyte. The coated mild steel plate showed a significantly lower current density (5 × 10−7 A/cm2) compared to the uncoated mild steel plate (1 A/cm2). After 72 h of dipping, an insignificant increase in current flow was observed, possibly due to the metal oxide/hydroxide formation. Tomar et al. [94] evaluated the effect of red mud amount on the corrosion resistance of the geopolymer coating applied on mild metal. The corrosion test was performed in a salt spray chamber in 3.5% NaCl with 95% RH. The results showed that the rust creepage tends to decrease with the addition of red mud (5%wt to 20%wt). This could be due to the highly dense and intact structure of geopolymer coating with more red mud amount. It was mentioned previously that the adhesion strength also increased with the increasing amount of red mud, indicating that the involvement of red mud improved the overall property of the coating materials.
Bhardwaj [106] discussed the corrosion behavior of phosphatic geopolymer coating applied on mild steel. The results showed that the coated mild steel exhibited strong corrosion-resistance ability even after 20 h of a salt spray test, while the uncoated mild steel corroded within 7 h. A non-electrochemical weight loss method was also performed to determine the corrosion rate of coated mild steel. It was demonstrated that the coating containing tricalcium phosphate and sodium metasilicate provided the highest resistance towards the saline condition. Both of these compounds acted as anodic inhibitors (also known as passivation inhibitors). The addition of phosphate in the geopolymer matrix leads to a denser and less porous structure, so water cannot reach the passivation layer. Thus, the phosphate groups diminish corrosion by promoting the growth of protective iron oxide films and by healing the defects in protective films. Meanwhile, the silicon ion forms negatively charged colloidal particles that migrate to anodic areas and form a passive film. These ensure the corrosion protection efficiency of the coating materials. Besides, phosphatic-based geopolymer offers excellent fire resistance, which can maintain thermally stability as high as 1550 °C [108].
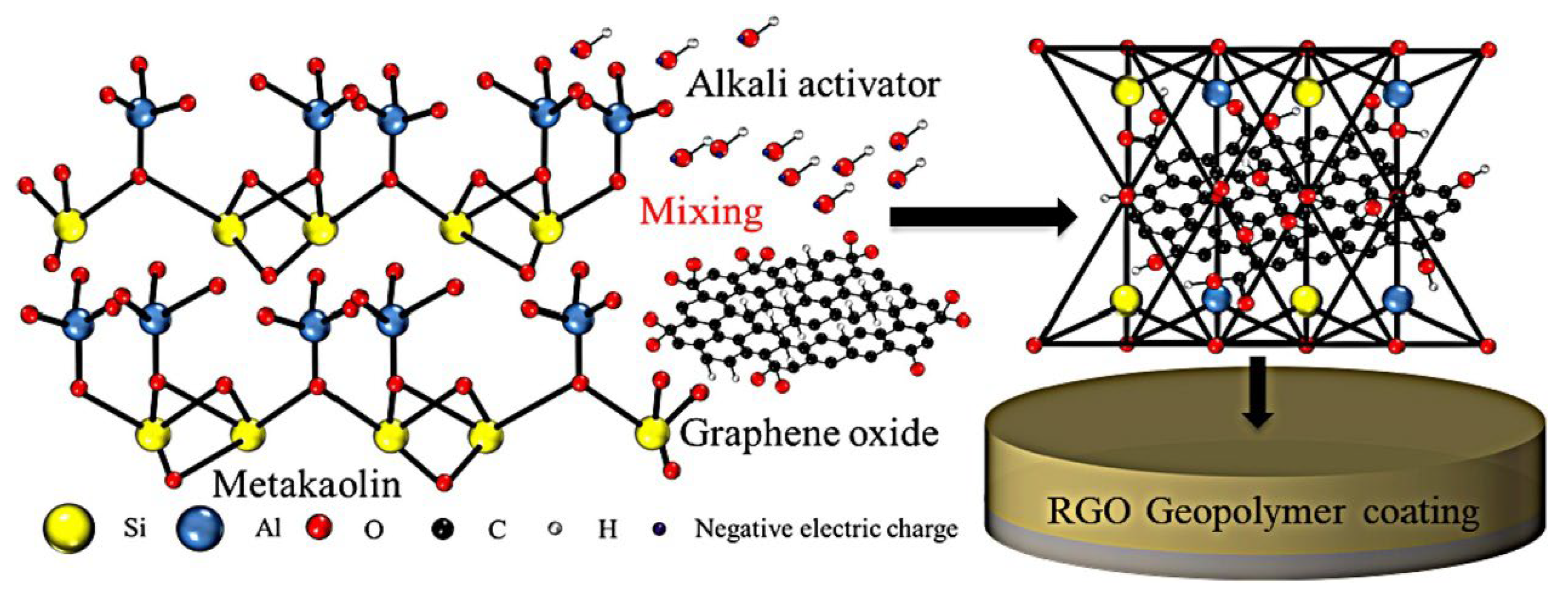
To further improve the corrosion resistance, Yang et al. [16] introduced graphene oxide into the geopolymer coating system (Figure 7), and the influence of graphene oxide contents on the physicochemical and electrochemical properties was investigated. It was indicated that the appearance of graphene oxide showed a noble corrosion potential with very low corrosion density (in the order of 10−7), which shows the effectiveness of graphene oxide geopolymer coating in inhibiting corrosion. In addition, using a graphene oxide content of 0.1% could increase the corrosion resistance of geopolymer-coated steel by more than two orders of magnitude compared to bare carbon steel.
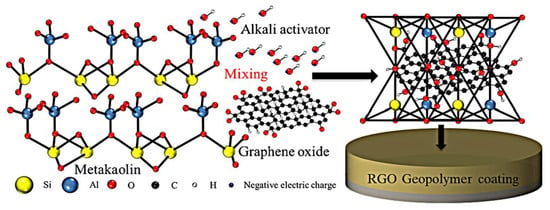
Figure 7.
The schematic illustration of the preparation and coating process for reduced graphene oxide geopolymer coating. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [16]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
The corrosion resistance of geopolymer coating applied on mild steel structures has been investigated widely. However, it was suggested that the geopolymer coatings were not appropriate for aluminum substrate due to the high alkalinity of the geopolymer, leading to the corrosion of aluminum [96].
3.4. Shrinkage
A crack-free coating on substrates is mandatory to sustain fire resistance and anti-corrosive performance. Cracks could occur due to the shrinkage of coatings [2,109]. Therefore, optimizing the preparation process or adjusting the recipe for chosen substrates or applications is necessary.
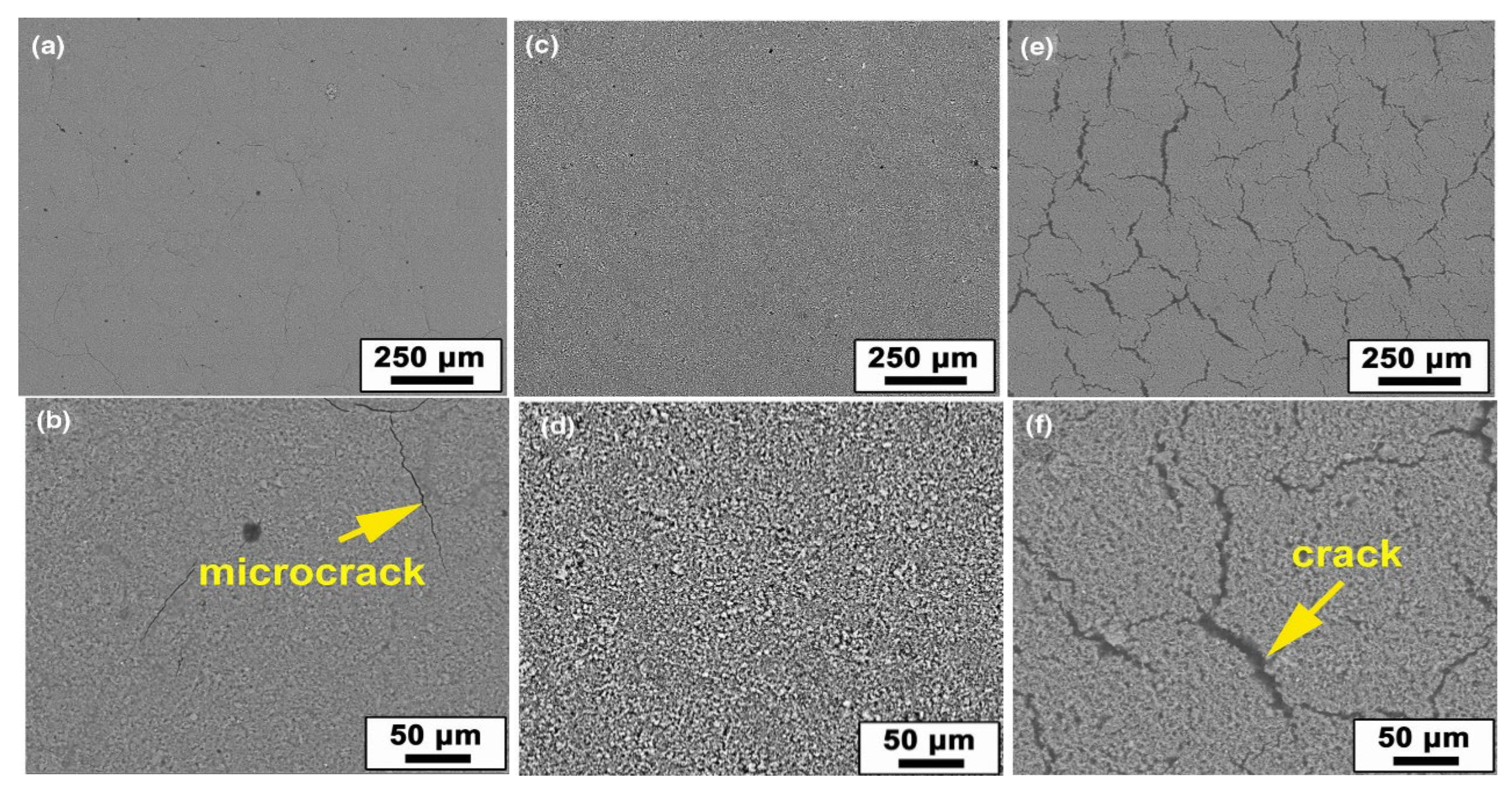
Mao et al. [110] investigated the effect of curing temperature on MK-based geopolymer coating. Results showed that an adequate microstructure was observed at a moderate curing temperature (80 °C). Curing at lower or higher temperatures leads to several or numerous cracks. At low temperatures, several microcracks occurred due to the evaporation of water. At high temperatures, cracks were generally induced by the residual stress between the coating and the substrate (Figure 8). In addition, the performance of geopolymer coating on an aluminum substrate was also explored. As the coating was cured at 40 °C, plastic deformation was observed without cracks in the sample. This could be due to the incomplete polymerization of the coating. Unlike the coating applied on the mild steel, the coating process failed as the coating was cured at 80 °C. As the curing temperature further increased to 150 °C, serve cracks were shown. As a result, the coating was completely removed from the aluminum substrate by a load of 12 N. The authors suggested that chemical adhesion could be involved since large differences in adhesive strength were obtained on mild steel compared to other substrates.
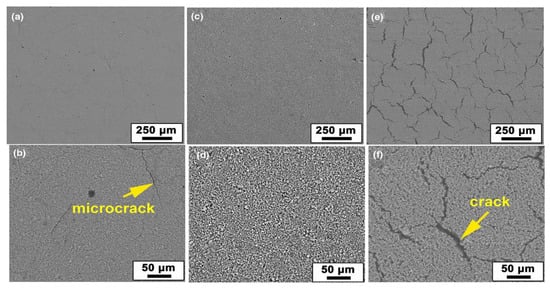
Figure 8.
SEM images of geopolymer coatings on the low carbon steel, with curing at (a,b) 40 °C, (c,d) 80 °C, and (e,f) 150 °C. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [110]. Copyright 2020, Springer Nature.
The water content is also a critical factor influencing the shrinkage of the coating. Temuujin et al. [87] studied the effect of water content on the thermal expansion or shrinkage of the geopolymer coating. With less water content, the initial shrinkage of the samples tends to reduce before 200 °C, while the expansion of the coatings was high thereafter. Zhang et al. [2] demonstrated that the shrinkage of geopolymer coatings could be improved by adding polypropylene fiber and a MgO expansion agent.
The selection of the geopolymer mixture design, curing conditions, and coating technique significantly impacts the adhesion strength, thermal and chemical resistance, and microstructure. This has been explored extensively. However, the bonding behavior (either physical or chemical or both) needs to be further investigated to fully understand the adhesion mechanism between the coating and the substrate. Moreover, a majority of the investigations are on a lab scale, where an on-site experiment of the geopolymer coating is necessary to promote a large-scale application. Additionally, the fabrication of multifunctional coatings and coatings with photocatalytic properties using geopolymer binder as a precursor could also be investigated to enrich the application [1,111].
4. The Comparison between the Conventional Coating and Geopolymer Coating
As mentioned previously, geopolymer exhibits excellent thermal stability, relatively high strength, and fire and chemical resistance compared with traditional cement. The study indicated that the geopolymeric materials showed only slight and few cracks after exceeding 800 °C, while the cracks are intensive for the samples made of conventional concrete under a fire-resistance test. In addition, no spattering was observed for geopolymers at very high temperatures, indicating excellent thermal stability [1,87,95].
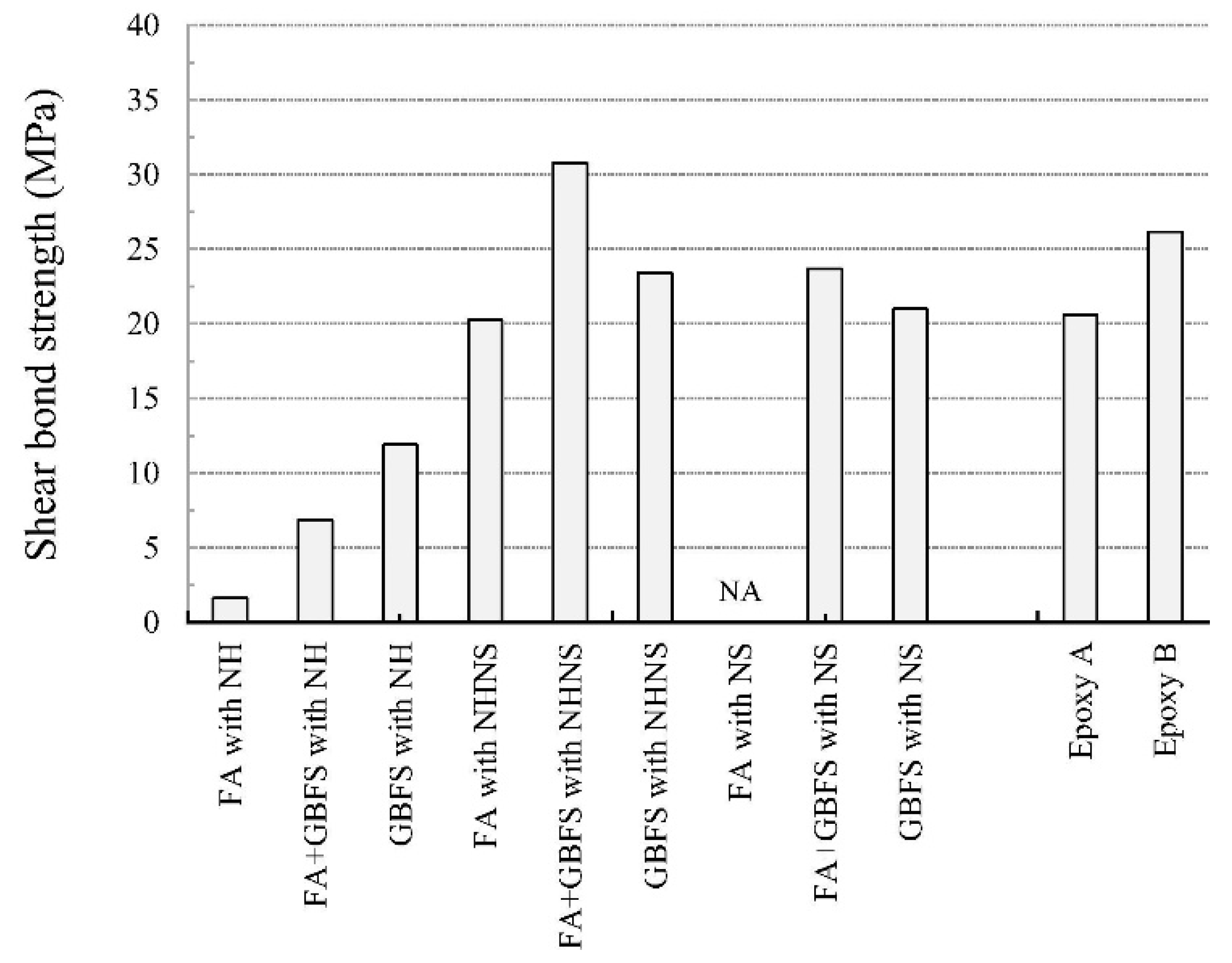
Tanakorn et al. [112] discussed the effect of raw materials’ composition (FA, GGBFS, NaOH, and Na2SiO3) on the adhesion strength. The results indicated that the mixture containing FA and GGBFS activated via a NaOH and Na2SiO3 combined solution possessed the maximum shear bond strength (Figure 9). It is also worth mentioning that the shear bond strength of the geopolymer coating was 19–47% higher than that of the two common organic coatings (Epoxy A and B). Zhang et al. [2] compared the bonding strength between geopolymer coating and cement-based materials at various drying conditions. The results showed that the 1-day bonding strength was equal to or higher than that of cement-based materials at any chosen curing condition (dry–wet cycle curing, air-curing, and seawater-curing).
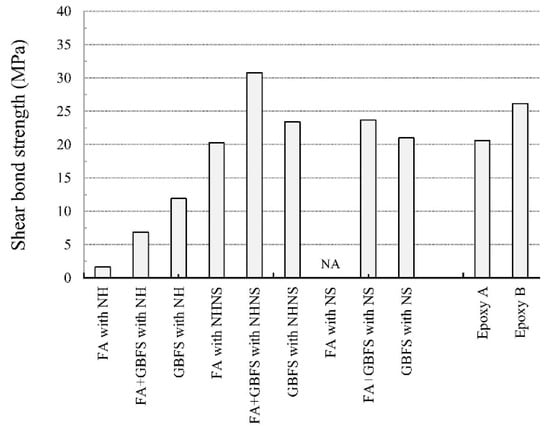
Figure 9.
Shear bond strength between geopolymer paste, epoxy, and substrate with interface line at 45° to the vertical. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [112]. Copyright 2015, Elsevier.
Lahoti et al. [113] compared the fire performance of Portland cement concrete against geopolymer concrete. It was stated that the thermal conductivity of geopolymer (0.2–0.4 W/m·k) is generally much lower than cement concrete (1–4 W/m·K), although both materials are incombustible. Geopolymer concrete also exhibits better spalling resistance compared to OPC concrete due to the interconnected pore structure of geopolymers. More importantly, geopolymer concrete provides excellent fire-resistance properties up to 1200 °C, while a significant strength loss was observed for OPC concrete after 600 °C. At high temperatures, geopolymers maintained microstructural stability, as the chemical bonds in geopolymers do not break down, although a transformation from the amorphous phase to the crystalline phase is generally observed at high temperatures (close to 1000 °C). In contrast, cement paste and aggregates lose their strength above 600 °C, indicating that the concrete is considered structurally failed. Zhao and Sanjayan [114] investigated the spalling behavior of Portland cement concrete and geopolymer via surface exposure test and standard gas furnace fire test. The results indicated that the geopolymer exhibited superior spalling resistance to rapidly rising temperature exposure compared to Portland cement concrete. Nazari [115] studied the thermal shock resistivity of Portland cement and fly-ash-based geopolymer via air-cooling and water-cooling methods. Thermal shock measures the loss of strength in conditions where immediate quenching with water is needed for the building material after exposure to fire. The results indicated that the geopolymer retained more strength (40–72%) compared to cement under the heating temperature of 400 °C, 600 °C, 800 °C, and 1000 °C.
Sarker [116] examined the fire endurance of fly-ash-based geopolymer and Portland cement concrete through the cracking, spalling, and residual strength behaviors. The tests were conducted at different temperatures up to 1000 °C. The results indicated that the Portland cement showed significant spalling at a temperature above 800 °C, whereas this phenomenon was not observed for geopolymer at the same temperature. In addition, serious surface cracking was visualized in the Portland cement specimens after fire exposure above 400 °C, whereas only slight surface cracking was seen in the geopolymer specimens above 800 °C. Moreover, geopolymer retained a higher percentage of residual compressive strength (83–107%) compared to Portland cement (51–90%) within the temperature of 650 °C. As the temperature increased to 1000 °C, both materials exhibited significant strength loss. Finally, the average mass loss of geopolymer was within 4.8% at a temperature of 1000 °C, while no data were obtained for the Portland cement, as significant spalling was shown.
Wang et al. [117] evaluated the environmental impacts of geopolymer coatings against Portland cement coating via life-cycle assessment (LCA). LCA can identify the main contributors to environmental impacts and assist in decision-making by pointing out potential aspects for future improvement. The effect of fabrication parameters, including surface modifier, substitution ratio of slag with metakaolin, and water-to-solid ratio, on the overall environmental performance was also addressed. The environmental performance was evaluated via the cradle-to-gate genre approach, which involves a sector life from the raw material acquisition to the completion of the production process (system boundary). The raw materials considered were limestone orc, iron ore, kaolinite, raw coal, and salt, and the ‘functional unit’ was defined as a coating of equal volume, i.e., 1 m3. All life-cycle inventory was imported into Gabi Professional software via the ReCiPe midpoint method. This method involves twelve categories, such as freshwater eutrophication potential (FEP), global warming potential (GWP), and fossil depletion potential (FDP), which fully cover the environmental impact on the environment, human body, and sustainability.
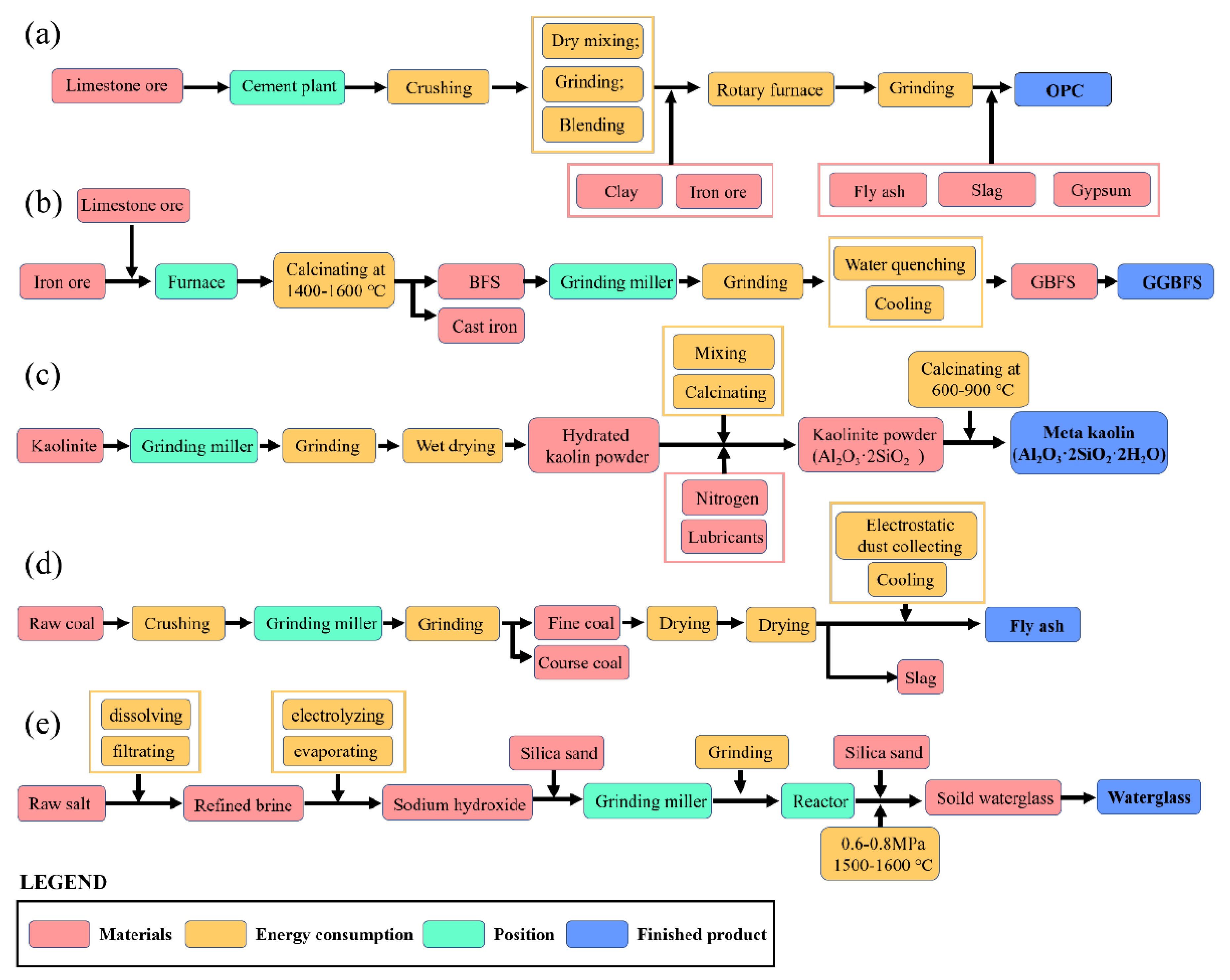
It was concluded that the geopolymer coating exhibited substantially lower environmental impacts (50–80% lower in most impact categories) than ordinary Portland cement coating. For cement-based coating, sand and cement are the two major contributors to the environmental impacts due to the limestone’s calcination and the high temperature needed to heat the raw materials. As a result, the estimated CO2 emissions during cement concrete production could increase up to 45% more than geopolymer concrete [78]. For geopolymer coating, waterglass contributes considerably to the overall environmental impacts, as waterglass production requires heating at high temperatures and emits heavy metal ions into the water environment (Figure 10). In addition, an increase in the W/S ratio decreased the environmental impacts, and slag-based geopolymer coating achieved lower environmental impacts than FA-based and MK-based varieties. These findings provide useful guidance for balancing the performance and environmental impacts of the geopolymer coating [117].
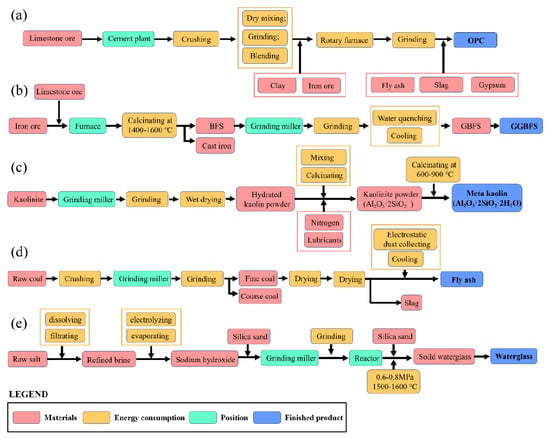
Figure 10.
Life-cycle boundary of (a) ordinary Portland cement, (b) slug, (c) metakaolin, (d) fly ash, and (e) waterglass [117].
Geopolymer coating exhibits superior mechanical and thermal performance compared with a conventional cement-based coating. The life-cycle analysis between these two coatings indicates that the geopolymer coating has a substantially lower environmental impact than the cement-based coating. Apart from these investigations, an economic analysis of geopolymer coating could be carried out and compared with current commercial protective coatings. It was suggested that the benefit-to-cost ratio is a more precise index to utilize in the economic analysis [4].
5. Conclusions
This article reviewed the current use of conventional coating and assessed the potential use of novel geopolymer coating on the metal substrate, particularly on the steel structure. A brief description of the cement-based coating and intumescent coating was first introduced, followed by a detailed discussion of the research and development. The introduction of geopolymer coating was then conducted with the common application techniques described. Moreover, the influencing factors, including precursor materials, the alkaline activator, curing processes, and water contents, on the adhesion and the thermal and chemical resistance of the geopolymer coating were well explored. Finally, the performance comparison between geopolymer coating and the conventional cement-based coating was carried out.
Cement-based coatings exhibit excellent thermal insulation, spalling resistance, and mechanical properties after elevated temperatures. However, the poor bonding properties and brittleness of cement-based coatings lead to the delamination of the substrate, resulting in a deterioration of the fire resistance and structural stability. Intumescent coatings offer fire protection for up to several hours, with an aesthetic appearance. They could be used in cellulosic fire and hydrocarbon fire, including jet fire, effectively prolonging fire-induced structural collapse. However, the outdoor exposed coatings have poor corrosion resistance due to the presence of water-sensitive ingredients in the formulations. Moreover, organic binders, such as epoxy resin and polyurethane, emit smoke from combustion and release toxic decomposition products, which negatively impact the environment and human health.
Geopolymer coatings have attracted much attention due to their better workability, higher mechanical strength, and excellent resistance to chemicals and heat. It is well indicated that the effect of the Si/Al ratio and Na/Al ratio significantly impacts the adhesive strength between the geopolymer coating and the substrates. The water content also plays a vital role in forming geopolymer coating and is correlated to the Si/Al and Na/Al ratios. To examine the fire resistance performance, direct flame tests have been conducted by several researchers. The results show that the geopolymer coating offers excellent thermal stability and fire resistance, without obvious cracks. Various materials, including red mud, phosphate acid, and graphene oxide, have been added to geopolymer coating to investigate the corrosion-resistance behavior. The results indicate that geopolymer coating exhibits strong corrosion resistance with improved mechanical or thermal properties. The comparison between the geopolymer coating and cement-based coating indicates that the geopolymeric materials show only a few slight cracks after exceeding 800 °C, while the cracks are intensive for the samples made of conventional concrete under the fire-resistance test. In addition, no spattering is observed for geopolymers at very high temperatures, thus indicating excellent thermal stability.
In the meanwhile, further study is still required. Although the bonding strength has been widely investigated, the mechanism of adhesion between the coating and the substrate is still unclear. Therefore, the bonding behavior (physical, chemical, or both) needs further investigation. In addition, the required thickness of the fireproof coating is much higher than those of intumescent coating, which increases the structural self-weight. Thus, the trade-off between the weight and the thermal–mechanical performance needs to be identified. Furthermore, the fabrication of multifunctional coatings and coatings with photocatalytic properties using geopolymer binder as a precursor could also be investigated to enrich the application. Moreover, the preparation and production of geopolymer both mainly rely on aluminosilicate precursors and activators. Due to the absence of technical standards and the diversity of constituent materials, the properties of the geopolymer are less controllable compared with cement-based materials. Therefore, further standardization of the raw material and the fabrication process is needed to achieve custom-tailored products for particular performances and applications.
The life-cycle analysis indicates that the geopolymer coating has a substantially lower environmental impact compared to the cement-based coating. Apart from this, an economic analysis of geopolymer coating could also be carried out and compared with current commercial protective coatings. Furthermore, on-site experiments of the geopolymer coating are necessary to verify all the factors investigated. Nevertheless, geopolymer coatings show great potential for fire protection on steel structures, with excellent physical properties, substantially lower environmental impact, and cost savings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L.; methodology, K.W.; formal analysis, K.W.; writing—original draft preparation, K.W.; writing—review and editing, H.L. and K.W.; supervision, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The financial support of Tsinghua—Foshan Advanced Manufacturing Research Institute is acknowledged. The authors are grateful for the support of colleagues at the Future Materials & Design Research Center, The Future Lab, Tsinghua University. The assistance of the technical staff at the School of Materials Science and Engineering Analysis Center, Tsinghua University, is also acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kaczmarski, K.; Pławecka, K.; Kozub, B.; Bazan, P.; Łach, M. Preliminary investigation of geopolymer foams as coating materials. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhu, H. Potential application of geopolymers as protection coatings for marine concrete I. Basic properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, L.; Cristian, M. Intumescent coatings used for the fire-safe design of steel structure A review. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 162, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, L.S.; Liu, M.Y.J.; Yap, S.P.; Mo, K.H.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Goh, Y. The potential of geopolymer in development of green coating materials: A review. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 12289–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, R.G.; Khanna, A.S. Intumescent coatings A review on recent progress. J.Coat.Technol.Res. 2017, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishal, M.; Satyanarayanan, K.S. A review on research of fire-induced progressive collapse on structures. J. Struct. Fire Eng. 2021, 12, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Network, C.R.E. Statistical Analysis of Fire Collapse Accidents of Large Span and Large Space Buildings. Available online: http://www.chinajyzb.com.cn/news_detail-5-4175.html (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Guan, H.; Ying, M. Progressive collapse analysis of a typical super-tall reinforced concrete frame-core tube building exposed to extreme fires. Fire Technol. 2016, 53, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, D.; Nuzzo, I.; Nigro, E.; Occhiuzzi, A. Intumescent coatings for fire resistance of steel structures: Current approaches for qualification and design. Coatings 2022, 12, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowbysz, A.; Samsonowicz, M.; Kukfisz, B. Recent advances in bio-based additive flame retardants for thermosetting resins. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beh, J.H.; Yew, M.K.; Yew, M.C.; Saw, L.H. Characterization and fire protection properties of rubberwood biomass ash formulated intumescent coatings for steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beh, J.H.; Yew, M.C.; Saw, L.H.; Yew, M.K. Fire resistance and mechanical properties of intumescent coating using novel bioAsh for steel. Coatings 2020, 10, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezia, V.; Matta, S.; Lehner, S.; Vitiello, G.; Costantini, A.; Gaan, S.; Malucelli, G.; Branda, F.; Luciani, G.; Bifulco, A. Detailed Thermal, Fire, and Mechanical Study of Silicon-Modified Epoxy Resin Containing Humic Acid and Other Additives. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5969–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huo, S.; Liu, S.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. Recycle of magnesium alloy scrap for improving fire resistance, thermal stability, and water tolerance of intumescent fire-retardant coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020, 18, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Bellayer, S.; Naik, A.; Bachelet, P.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S. Topcoats versus Durability of an Intumescent Coating. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9625–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Das, C.S.; Xue, X.; Li, W.; Dai, J.-G. Geopolymer coating modified with reduced graphene oxide for improving steel corrosion resistance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Wang, S.; Sui, Y.; Lv, Z. Alkali-activated materials as coatings deposited on various substrates: A review. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 110, 102934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Liu, Y.; Le, H. Mechanical and thermal properties of phosphoric acid activated geopolymer materials reinforced with mullite fibers. Materials 2022, 15, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łach, M.; Mierzwiński, D.; Korniejenko, K.; Mikuła, J.; Walczak, A.; Polańczyk, A. Geopolymer foam as a passive fire protection. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 247, 00031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarz, M.; Figiela, B.; Łach, M.; Korniejenko, K.; Mróz, K.; Castro-Gomes, J.; Hager, I. Mechanical response of geopolymer foams to heating—Managing coal gangue in fire-resistant materials technology. Energies 2022, 15, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.S.; Nguyen, V.V.; Sharko, A.; Ercoli, R.; Nguyen, T.X.; Tran, D.H.; Los, P.; Buczkowska, K.E.; Mitura, S.; Spirek, T.; et al. Fire Resistance of Geopolymer Foams Layered on Polystyrene Boards. Polymers 2022, 14, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, A.; He, K.; Pan, H.; Liao, J.; Ding, Z.; Xing, F.; Le, H.; Wang, X. Property evolution of geopolymer composites with SiC whiskers loaded with BN coating at elevated temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.K.; Collins, F.G. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions: A comparison between geopolymer and OPC cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, X. Study on the solidication of heavy metals by fly ash based geopolymers. Jianzhu Cailiao Xuebao J. Build. Mater. 2006, 9, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Zainal, F.F.; Fazill, M.F.; Hussin, K.; Rahmat, A.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Wazien, W. Effect of geopolymer coating on mild steel. Solid State Phenom. 2018, 273, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R.E.; Balaguru, P.N.; Foden, A.; Sorathia, U.; Davidovits, J.; Davidovics, M. Fire-resistant aluminosilicate composites. Fire Mater. 1997, 21, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Pan, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J. A review on cement-based materials used in steel structures as fireproof coating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Wu, C.; Hou, D.; Li, S.; Jin, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Research and application progress of nano-modified coating in improving the durability of cement-based materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 161, 106529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.; García, P.; Mateos, P.; Ayala, J. Characteristics and properties of lightweight concrete manufactured with cenospheres. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; Zhang, M.-H. Development of ultra-lightweight cement composites with low thermal conductivity and high specific strength for energy efficient buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 87, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinheimer, V.; Wu, Y.; Wu, T.; Celik, K.; Wang, J.; De Lorenzis, L.; Wriggers, P.; Zhang, M.-H.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Multi-scale study of high-strength low-thermal-conductivity cement composites containing cenospheres. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ranade, R.; Zhang, Q.; Ni, W.; Li, V.C. Mechanical and thermal properties of green lightweight engineered cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, A.; Lu, Z.; Diao, S.; Zeng, X.; Li, Z. Properties investigation of fiber reinforced cement-based composites incorporating cenosphere fillers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q. Research on properties of foamed concrete reinforced with small sized glazed hollow beads. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancar, E.B.; Akpınar, M.V. Temperature reduction of concrete pavement using glass bead materials. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2016, 10, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Han, T.-S.; Youm, K.-S. Evaluation of thermal conductivity for thermally insulated concretes. Energy Build. 2013, 61, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-Y.; Han, T.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Jay Kim, J.-H.; Youm, K.S.; Lim, J.-H. Evaluation of effect of glass beads on thermal conductivity of insulating concrete using micro CT images and probability functions. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 65, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J. Experimental investigation on thermal conductivity of aerogel-incorporated concrete under various hygrothermal environment. Energy 2019, 188, 115999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Jelle, B.P.; Gustavsen, A.; Jacobsen, S. Aerogel-incorporated concrete: An experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Seo, J.; Cha, J.; Kim, S. Chemical retreating for gel-typed aerogel and insulation performance of cement containing aerogel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, M.; Entrop, A.G.; Mandilaras, I.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Founti, M. The behavior of self-compacting concrete containing micro-encapsulated Phase Change Materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddhahak-Ouni, A.; Drissi, S.; Colin, J.; Neji, J.; Care, S. Experimental and multi-scale analysis of the thermal properties of Portland cement concretes embedded with microencapsulated Phase Change Materials (PCMs). Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 64, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, G.; Wang, S.; Fang, X.; Liu, X. Thermal energy storage cement mortar containing n-octadecane/expanded graphite composite phase change material. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xing, F.; Cui, H.-Z.; Chen, D.-Z.; Ouyang, X.; Xu, S.-Z.; Wang, J.-X.; Huang, Y.-T.; Zuo, J.-D.; Tang, J.-N. A novel phase-change cement composite for thermal energy storage: Fabrication, thermal and mechanical properties. Appl. Energy 2016, 170, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noumowe, A. Mechanical properties and microstructure of high strength concrete containing polypropylene fibres exposed to temperatures up to 200 °C. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2192–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvaranta, L.; Mikkola, E. Fibre mortar composites in fire conditions. Fire Mater. 1994, 18, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, K.; Gre´goire, C.n.; Christophe, G. High-temperature behaviour of HPC with polypropylene fibres From spalling to microstructure. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Li, G.; Deng, S.; Wang, Z. Mechanical properties and microstructure of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) modified cement mortar. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Sohn, Y.S.; Lee, S.H. Fire resistance of hybrid fibre-reinforced, ultra-high-strength concrete columns with compressive strength from 120 to 200 MPa. Mag. Concr. Res. 2012, 64, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Iqbal Khan, M. Fiber–matrix interactions in fiber-reinforced concrete: A Review. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.T.; Yang, L.; Liggat, J.J.; Thomason, J.L. Kinetics of dissolution of glass fibre in hot alkaline solution. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 53, 1710–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaibi, N.; Benzerzour, M.; Abriak, N.E.; Binetruy, C. Mechanical properties of concrete-reinforced fibres and powders with crushed thermoset composites: The influence of fibre/matrix interaction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedan, D.; Pagnoux, C.; Smith, A.; Chotard, T. Mechanical properties of hemp fibre reinforced cement: Influence of the fibre/matrix interaction. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, T. Recent developments of intumescent fire protection coatings for structural steel: A review. J. Fire Sci. 2016, 34, 120–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D. Experimental study of heat transfer in intumescent coatings exposed to non-standard furnace curves. Fire Technol. 2015, 51, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.L.; Huang, Y.T.; Gu, L.; Shen, J.C.; Cheng, X.W.; Guan, J.P. Fabrication of P/N/B-based intumescent flame-retardant coating for polyester/cotton blend fabric. Materials 2022, 15, 6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, L. Synergistic effect between piperazine pyrophosphate and melamine polyphosphate in flame retardant coatings for structural steel. Polymers 2022, 14, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperopoulos, E.; Grifò, G.; Scionti, G.; Atria, M.; Calabrese, L.; Consolo, G.; Proverbio, E. Study of intumescent coatings growth for fire retardant systems in naval applications: Experimental test and mathematical model. Coatings 2022, 12, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, M. Research on thermal response behavior of the intumescent coating at high temperature: An experimental and numerical study. Buildings 2022, 12, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qu, W.; Zhang, J. Crack-resistant amino resin flame-retardant coatings using waterborne polyurethane as a co-binder resin. Materials 2022, 15, 4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.N.; Mustapha, F.; Ahmad, K.A.; Mustapha, M.; Khan, T.; Singh, B.; Sebaey, T.A. Effect of different pre-treatment on the microstructure and intumescent properties of rice husk ash-based geopolymer hybrid coating. Polymers 2022, 14, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Yan, L. Fabrication of polypyrrole-decorated tungsten tailing particles for reinforcing flame retardancy and ageing resistance of intumescent fire-resistant coatings. Polymers 2022, 14, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anees, S.M.; Dasari, A. A review on the environmental durability of intumescent coatings for steels. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 53, 124–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Chow, W.K. A brief review of intumescent fire retardant coatings. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2003, 46, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, E.D.; Choudhary, V. Flame-retarding plastics and elastomers with melamine. J. Fire Sci. 1995, 13, 104–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réti, C.; Casetta, M.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S.; Delobel, R. Flammability properties of intumescent PLA including starch and lignin. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Ahmad, F.; Yusoff, P.S.M.M.; Ullah, S.; Jimenez, M. Latest trends for structural steel protection by using intumescent fire protective coatings: A review. Surf. Eng. 2019, 36, 334–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, R.G.; Khanna, A.S. Influence of heat-stable filler on the thermal shielding performance of water-based intumescent fire-resistive coating for structural steel applications. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 14, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Fina, A.; Malucelli, G. Thermal shielding performances of nano-structured intumescent coatings containing organo-modified layered double hydroxides. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 78, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, E. Secondary batteries-lead-acid systems automotive batteries: Conventional. In Encyclopedia of Electrochemical Power Sources; Garche, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 829–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, M.C.; Ramli Sulong, N.H.; Yew, M.K.; Amalina, M.A.; Johan, M.R. Influences of flame-retardant fillers on fire protection and mechanical properties of intumescent coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 78, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, G. Intumescent Fire-Retardant Composition for High Temperature and Long Duration Protection. US5723515A, 3 March 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, H.K.; Peter, S.N.; Fan-Bill, C. Effect of high temperature additives in fire resistant materials. Fire Sci. 1997, 15, 427–504. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.; Fang, Z. Effects of carbon nanotubes on the thermal stability and flame retardancy of intumescent flame-retarded polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permax. Differences between Cellulosic and Hydrocarbon Fires. Available online: https://permax.com.au/ (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Chris, H. The 5 Classes of Fire Explained (A to E). Available online: https://firefightergarage.com/classes-of-fire/ (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Zhang, F.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Smoke suppression and synergistic flame retardancy properties of zinc borate and diantimony trioxide in epoxy-based intumescent fire-retardant coating. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 123, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Novel Development of Eco-Friendly Porous Thermal Insulation Materials and the Application. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, A.; Bao, X.; Ni, T.; Ling, J. A review on geopolymer in potential coating application: Materials, preparation and basic properties. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temuujin, J.; Minjigmaa, A.; Rickard, W.; Lee, M.; Williams, I.; van Riessen, A. Preparation of metakaolin based geopolymer coatings on metal substrates as thermal barriers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, X.; Wang, H. Potential application of geopolymers as protection coatings for marine concrete III. Field experiment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 67–68, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Zhu, W.; Weng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, E.-H.; Leong, K.F.; Tan, M.J.; Wong, T.N.; Qian, S. Study of MgO-activated slag as a cementless material for sustainable spray-based 3D printing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumud, D.; Richa, P.; Avneesh, A.; Archana, S.; Pooja, B.; Rainy, G.; Deepti, M.; Sudhir Sitaram, A. Studies on fly ash based geopolymeric material for coating on mild steel by paint brush technique. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 75, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyana, J.; Kamarudin, H.; Al Bakri, A.M.; Binhussain, M.; Ruzaidi, C.M.; Izzat, A.M. Reviews on fly ash based geopolymer materials for protective coating field implementations. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2013, 7, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Fahim Huseien, G.; Mirza, J.; Ismail, M.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Abdulameer Hussein, A. Geopolymer mortars as sustainable repair material: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoying, P.; Zhenguo, S.; Caijun, S.; Tung-Chai, L.; Ning, L.a. A review on concrete surface treatment Part I Types and mechanisms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temuujin, J.; Minjigmaa, A.; Rickard, W.; Lee, M.; Williams, I.; van Riessen, A. Fly ash based geopolymer thin coatings on metal substrates and its thermal evaluation. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 180, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan Khan, M.; Azizli, K.; Sufian, S.; Man, Z. Sodium silicate-free geopolymers as coating materials: Effects of Na/Al and water/solid ratios on adhesion strength. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 2794–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Wang, Z.; Xing, X.; Zhao, L. Review on the adhesion of geopolymer coatings. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5108–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Cui, X. A green drying powder inorganic coating based on geopolymer technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer technology: The current state of the art. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwa, M.S.; Al Bakri, A.M.; Kamarudin, H.; Ruzaidi, C.M.; Binhussain, M.; Zaliha, S.S. Review on current geopolymer as a coating material. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2013, 5, 246–257. [Google Scholar]
- Tatlisu, G.C.; Aciksari, C.; Celebi, S.; Turan, S. Developing a hollow glass microsphere/geopolymer thermal insulation composite for hot metal surface coating. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 11924–11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Tomar, A.; Gupta, R.; Singh, A.; Thankaraj Salammal, S.; Akram Khan, M.; Mishra, D. Evaluation of corrosion protective properties of fly ash-red mud based geopolymer coating material for mild steel. Mater. Today: Proc. 2022, 68, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.L.; Feng, D.W.; Lukey, G.C.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Chemical characterisation of the steel–geopolymeric gel interface. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 302, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonathan, B.; Matthew, G.; Waltraud, K. Use of Geopolymeric Cements as a Refractory Adhesive for Metal and Ceramic Joins; The American Ceramic Society: Franklin County, OH, USA, 2005; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Latella, B.A.; Perera, D.S.; Escott, T.R.; Cassidy, D.J. Adhesion of glass to steel using a geopolymer. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros, S.; De Souza, J.R.; Gomes, K.C.; Sampaio, E.M.; Barbosa, N.P.; Torres, S.M. Adhesion of geopolymer bonded joints considering surface treatments. J. Adhes. 2012, 88, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Rong, X.; Zhao, L.; Xing, X.; Ma, H. Effects of substrate surface characteristics on the adhesion properties of geopolymer coatings. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11988–11994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temuujin, J.; Rickard, W.; Lee, M.; van Riessen, A. Preparation and thermal properties of fire resistant metakaolin-based geopolymer-type coatings. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T. Thermal behaviour of geopolymers prepared using class F fly ash and elevated temperature curing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoară, A.I.; Bădănoiu, A.I.; Voicu, G.; Dinu, C.; Ionescu, A. Intumescent coatings based on alkali-activated borosilicate inorganic polymers. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 17, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarazin, J.; Davy, C.A.; Bourbigot, S.; Tricot, G.; Hosdez, J.; Lambertin, D.; Fontaine, G. Flame resistance of geopolymer foam coatings for the fire protection of steel. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 222, 109045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoey, S. Bromide ion toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts. Available online: https://naturalpedia.com/bromide-ion-toxicity-side-effects-diseases-and-environmental-impacts.html (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Cui, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Ng, S.; Rui, Y. Effect of calcium stearate based foam stabilizer on pore characteristics and thermal conductivity of geopolymer foam material. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Gupta, R.; Mishra, D.; Sanghi, S.K.; Verma, S.; Amritphale, S.S. Corrosion and fire protective behavior of advanced phosphatic geopolymeric coating on mild steel substrate. Silicon 2019, 12, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Pouya, H.S.; Ganjian, E.; Claisse, P. A review of corrosion and protection of steel in concrete. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 5035–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X. Comprehensive understanding of aluminosilicate phosphate geopolymers: A critical review. Materials 2022, 15, 5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhu, H. Potential application of geopolymers as protection coatings for marine concrete II. Microstructure and anticorrosion mechanism. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Biasetto, L.; Colombo, P. Metakaolin-based geopolymer coatings on metals by airbrush spray deposition. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020, 17, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, L.; Razak, R.A.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Vizureanu, P.; Bras, A.; Imjai, T.; Sandu, A.V.; Abd Rahim, S.Z.; Yong, H.C. The suitability of photocatalyst precursor materials in geopolymer coating applications: A Review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoo-ngernkham, T.; Maegawa, A.; Mishima, N.; Hatanaka, S.; Chindaprasirt, P. Effects of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate solutions on compressive and shear bond strengths of FA–GBFS geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoti, M.; Tan, K.H.; Yang, E.-H. A critical review of geopolymer properties for structural fire-resistance applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Sanjayan, J.G. Geopolymer and Portland cement concretes in simulated fire. Mag. Concr. Res. 2011, 63, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, A.; Bagheri, A.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Dao, M.; Mallawa, C.; Zannis, P.; Zumbo, S. Thermal shock reactions of Ordinary Portland cement and geopolymer concrete: Microstructural and mechanical investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, P.K.; Kelly, S.; Yao, Z. Effect of fire exposure on cracking, spalling and residual strength of fly ash geopolymer concrete. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, B.; Chen, C. Green protective geopolymer coatings: Interface characterization, modification and life-cycle analysis. Materials 2022, 15, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).