The Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on the Compressive Strength of Cement Mortars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dispersion of MWCNTs
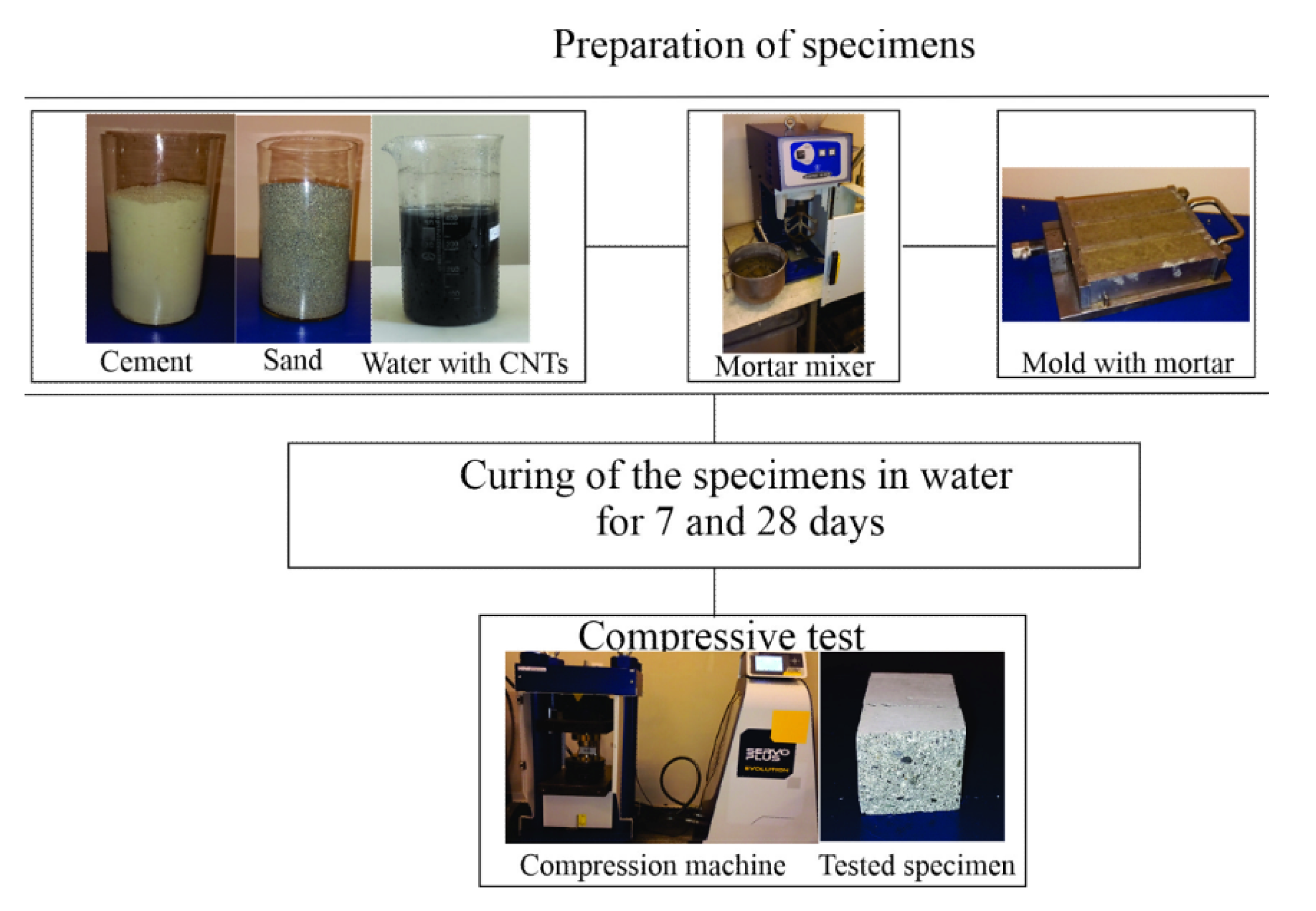
2.3. Mixing and Sample Preparation
2.4. Compressive Strength Testing
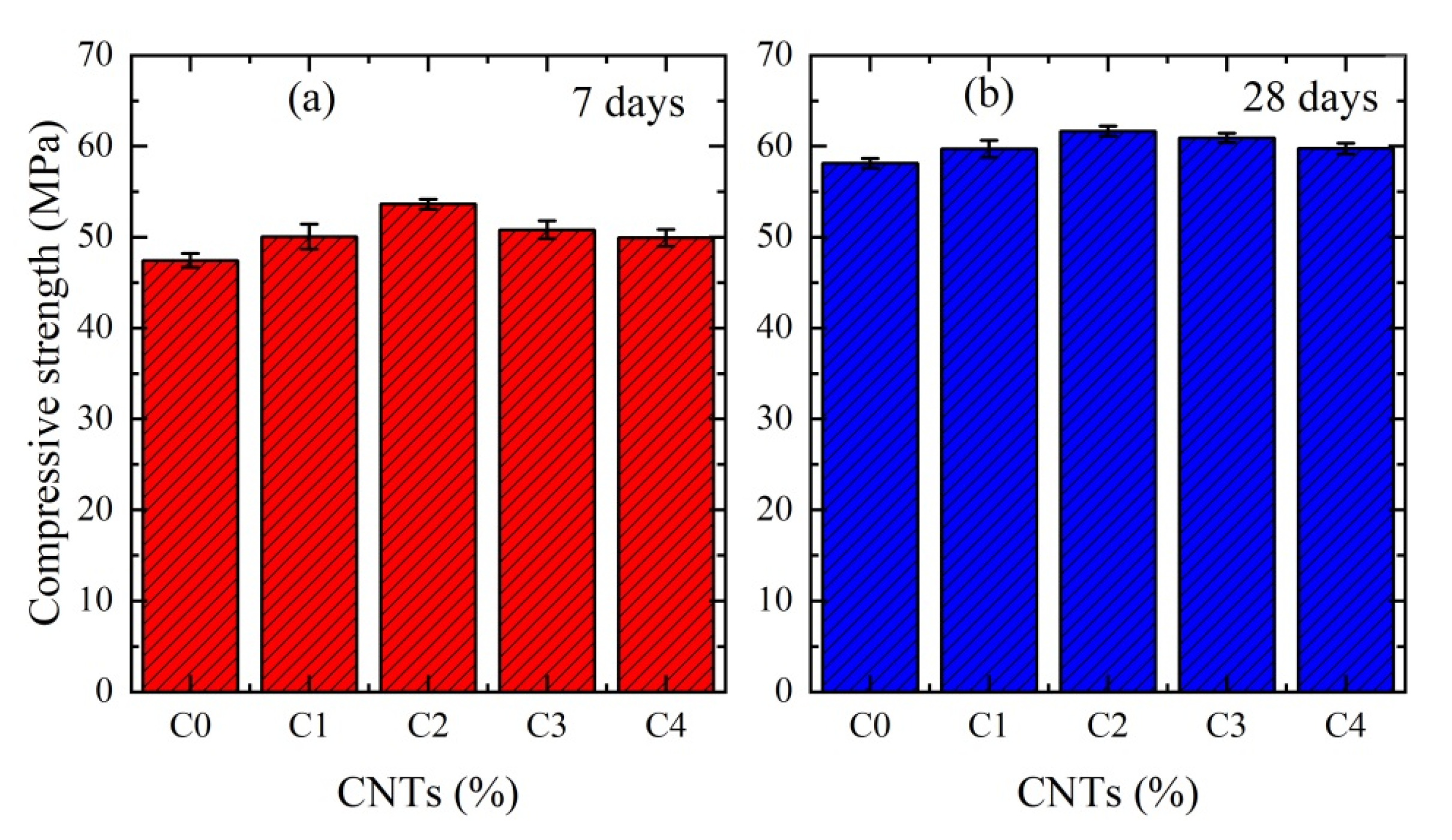
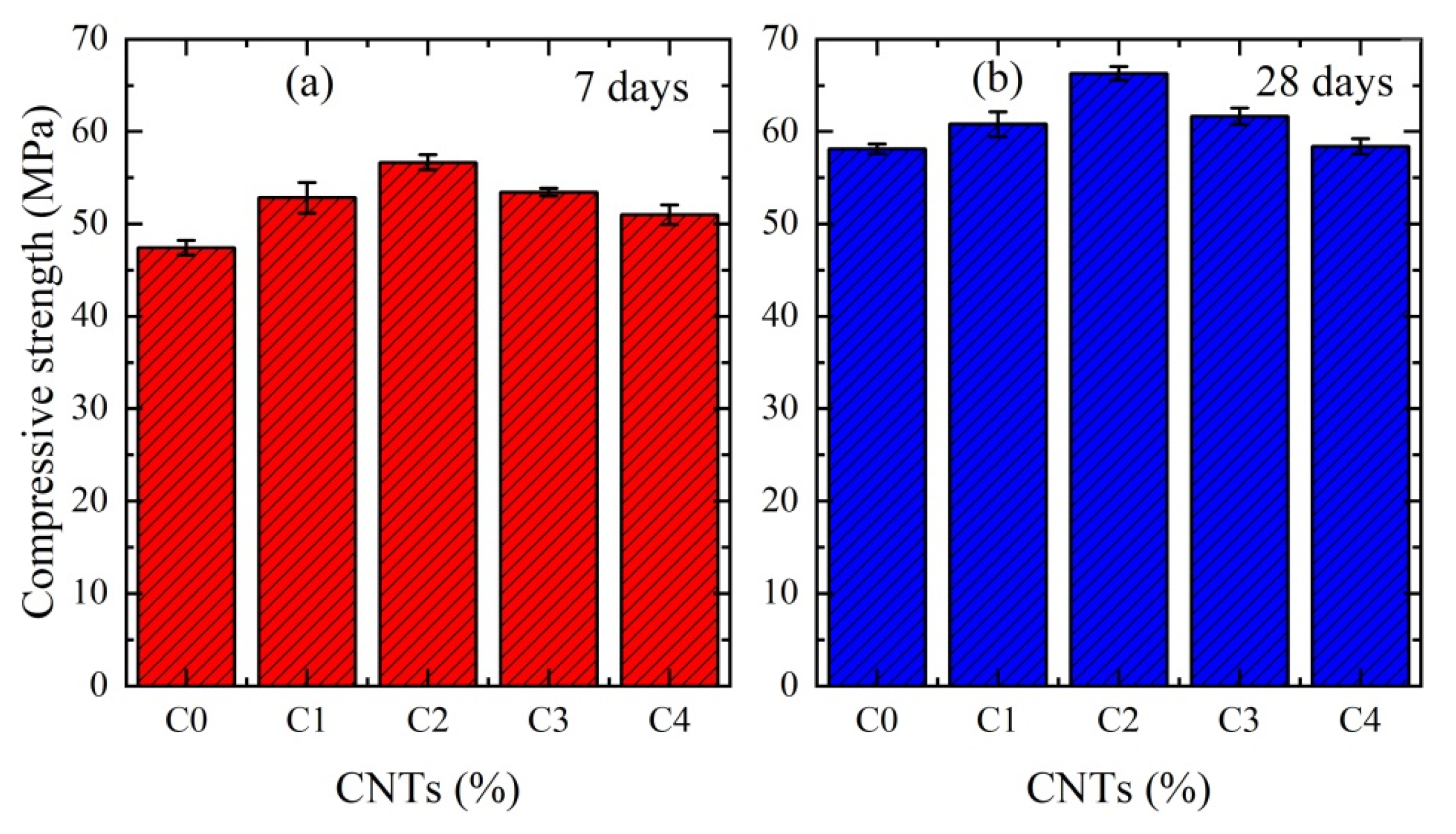
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, J.; Han, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Shah, S.P. Review of recent developments in cement composites reinforced with fibers and nanomaterials. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2021, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Al-Kutti, W. Performance of Date Palm Ash as a Cementitious Material by Evaluating Strength, Durability, and Characterization. Buildings 2019, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasir, M.; Al-Kutti, W.; Kayed, T.S.; Adesina, A.; Chernykh, T. Synthesis and SWOT analysis of date palm frond ash–Portland cement composites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 45240–45252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Nasir, M.; Baghabra Al-Amoudi, O.S.; Maslehuddin, M. Influence of in-situ casting temperature and curing regime on the properties of blended cement concretes under hot climatic conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 12186. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, M.; Johari, M.A.; Maslehuddin, M.; Yusuf, M. Sodium sulfate resistance of alkali/slag activated silicomanganese fume-based composites. Struct. Concr. 2020, 79, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.; Salami, B.A.; Algaifi, H.A.; Rahman, M.K.; Nasir, M.; Ewebajo, A.O. Assessment of acid resistance of natural pozzolan-based alkali-activated concrete: Experimental and optimization modelling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Aziz, M.A.; Zubair, M.; Ashraf, N.; Hussein, T.N.; Allubli, M.K.; Manzar, M.S.; Al-Kutti, W.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Engineered cellulose nanocrystals-based cement mortar from office paper waste: Flow, strength, microstructure, and thermal properties. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104345. [Google Scholar]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Eklund, P.C.; Rao, A.M. Carbon nanotubes. In The Physics of Fullerene-Based and Fullerene-Related Materials; Andreoni, W., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 23, pp. 331–374. [Google Scholar]
- Tasis, D.; Tagmatarchis, N.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M. Chemistry of carbon nanotubes. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1105–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Research Nanomaterials, Inc. Layers of Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes, MWNTs, MWCNTs, Short MWNTs, Short MWCNTs. Available online: https://www.us-nano.com/layers (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Makar, J.M.; Beaudoin, J.J. Carbon Nanotubes and Their Application in the Construction Industry; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestro, L.; Gleize, P.J.P. Effect of carbon nanotubes on compressive, flexural and tensile strengths of Portland cement-based materials: A systematic literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yu, X.; Kwon, E.; Ou, J. Effects of CNT concentration level and water/cement ratio on the piezoresistivity of CNT/cement composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Gong, H.; Gu, C. Research progress on CNTs/CNFs-modified cement-based composites—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.C.; Bassem, A. Finite element analysis of carbon nanotube/cement composite with degraded bond strength. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 47, 994–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Shah, S.P. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Jeevanagoudar, Y.V.; Krishna, R.H.; Gowda, R.; Preetham, R.; Prabhakara, R. Improved mechanical properties and piezoresistive sensitivity evaluation of MWCNTs reinforced cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, L.; Alsalman, A.; Bianco, D.; Ziehl, H.; El-Khatib, J.; Bayat, M.; Hussein, F.H. Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) Dispersion & Mechanical Effects in OPC Mortar & Paste: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102512. [Google Scholar]
- Hilding, J.; Grulke, E.A.; Zhang, Z.G.; Lockwood, F.J. Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Liquids. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2003, 24, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Elkashef, M.; Wang, K.; Abou-Zeid, M.N. Acid-treated carbon nanotubes and their effects on mortar strength. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2016, 10, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrekabi, S.; Cundy, A.; Lampropoulos, A.; Savina, I. Experimental investigation on the effect of ultrasonication on dispersion and mechanical performance of multi-wall carbon nanotube-cement mortar composites. Int. J. Civil Environ. Struct. Constr. Archit. Eng. 2016, 111, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Metaxa, Z.S.; Boutsioukou, S.; Amenta, M.; Favvas, E.P.; Kourkoulis, S.K.; Alexopoulos, N.D. Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes into White Cement Mortars: The Effect of Concentration and Surfactants. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolkina, A.; Mechtcherine, V.; Khavrus, V.; Maier, D.; Mende, M.; Ritschel, M.; Leonhardt, A. Dispersion of carbon nanotubes and its influence on the mechanical properties of the cement matrix. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, Y.; Roudi, M.R.R.; Korayem, A.H.; Shamsaei, E. Investigation of ultrasonication energy effect on workability, mechanical properties and pore structure of halloysite nanotube reinforced cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avakyan, L.; Manukyan, A.; Bogdan, A.; Gyulasaryan, H.; Coutinho, J.; Paramonova, E.; Sukharina, G.; Srabionyan, V.; Sharoyan, E.; Bugaev, L. Synthesis and structural characterization of iron-cementite nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon matrix. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2020, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manukyan, A.; Gyulasaryan, H.; Ginoyan, A.; Kaniukov, E.; Petrov, A.; Yakimchuk, D.; Shashov, S.; Nurijanyan, M.; Mirzakhanyan, A. Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of nickel-carbon nanocomposites prepared by solid-phase pyrolysis of Ni phthalocyanine. In Fundamental and Applied Nano-Electromagnetics; Maffucci, A., Maksimenko, S.A., Eds.; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series B: Physics and Biophysics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Arzumanyan, A.A.; Tadevosyan, V.G.; Muradyan, N.G.; Navasardyan, H.V. Study of “Saralsk” Deposit for Practical Applications in Construction. J. Arch. Eng. Res. 2021, 1, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
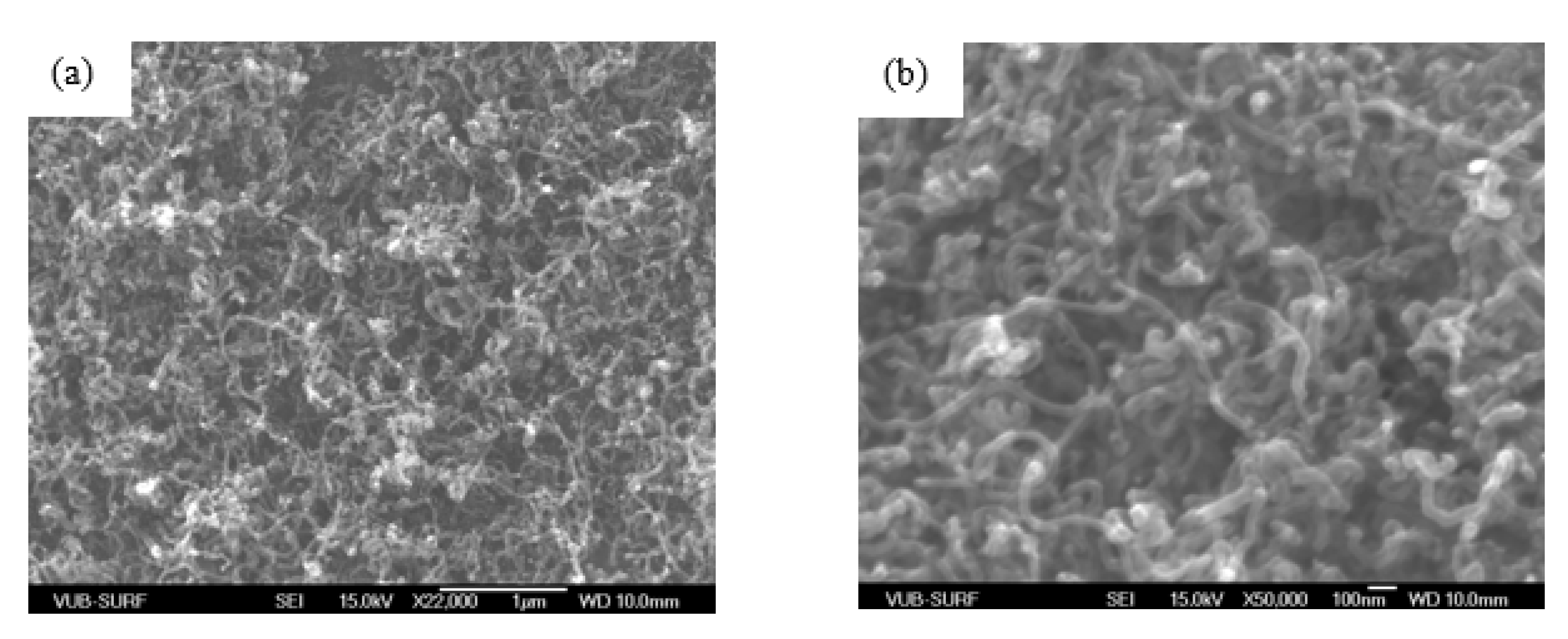

| Characteristics | Days | Results Obtained | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard consistency (%) | - | 31 | ||||||
| Specific gravity (g/sm3) | - | 3.1 | ||||||
| Blain’s fineness (m2/kg) | - | 354.8 | ||||||
| Compressive strength (MPa) (EN 196-1) | 3 days | 23 | ||||||
| 7 days | 38 | |||||||
| 28 days | 52 | |||||||
| Setting time (min) | Initial | 60 | ||||||
| Final | 330 | |||||||
| Chemical composition of cement (wt.%) | ||||||||
| Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | Loss of Ignition | Insol. Resid. | Free CaO |
| 3.21 | 23.2 | 1.25 | 57.5 | 5.1 | 2.9 | 3.7 | 2.1 | 1.13 |
| Sand | Fineness Modulus 2.43 | Specific Gravity 2.17 | Zone II | Bulk Density in Compact State (kg/m3) 1829 | Bulk Density in Loose State (kg/m3) 1609 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNTS | Outer diameter 40–50 nm | Length < 1 μm | Purity > 90% | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muradyan, N.G.; Gyulasaryan, H.; Arzumanyan, A.A.; Badalyan, M.M.; Kalantaryan, M.A.; Vardanyan, Y.V.; Laroze, D.; Manukyan, A.; Barseghyan, M.G. The Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on the Compressive Strength of Cement Mortars. Coatings 2022, 12, 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121933
Muradyan NG, Gyulasaryan H, Arzumanyan AA, Badalyan MM, Kalantaryan MA, Vardanyan YV, Laroze D, Manukyan A, Barseghyan MG. The Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on the Compressive Strength of Cement Mortars. Coatings. 2022; 12(12):1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121933
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuradyan, Nelli G., Harutyun Gyulasaryan, Avetik A. Arzumanyan, Maria M. Badalyan, Marine A. Kalantaryan, Yeghiazar V. Vardanyan, David Laroze, Aram Manukyan, and Manuk G. Barseghyan. 2022. "The Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on the Compressive Strength of Cement Mortars" Coatings 12, no. 12: 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121933
APA StyleMuradyan, N. G., Gyulasaryan, H., Arzumanyan, A. A., Badalyan, M. M., Kalantaryan, M. A., Vardanyan, Y. V., Laroze, D., Manukyan, A., & Barseghyan, M. G. (2022). The Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on the Compressive Strength of Cement Mortars. Coatings, 12(12), 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121933





