Modeling of the Effect of Carrier Gas Injection on the Laminarity of the Plasma Jet Generated by a Cascaded Spray Gun
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation Methods and Investigated Torch Conditions
2.1. Assumptions
- (1)
- The plasma flow is laminar and quasi-steady;
- (2)
- The plasma operates in a local thermal equilibrium (LTE) state and is optically thin to the extent that the radiation is negligible;
- (3)
- The heat and mass transfer properties of the plasma jet are temperature-dependent;
- (4)
- The gravitational effect is negligible inside the plasma torch;
- (5)
- The process gas flows in the radial direction and without a swirl component;
- (6)
- The electric and magnetic fields near the nozzle exit are negligible;
- (7)
- The terms of the viscous dissipation in the energy equation are negligible due to the small Mach number;
- (8)
- The properties of the mixture of ambient air and plasma gas follow the volume and weight mixing law.
2.2. Governing Equations
2.3. Torch Geometry
2.4. Boundary Conditions
2.5. Material Properties
3. Results and Discussions
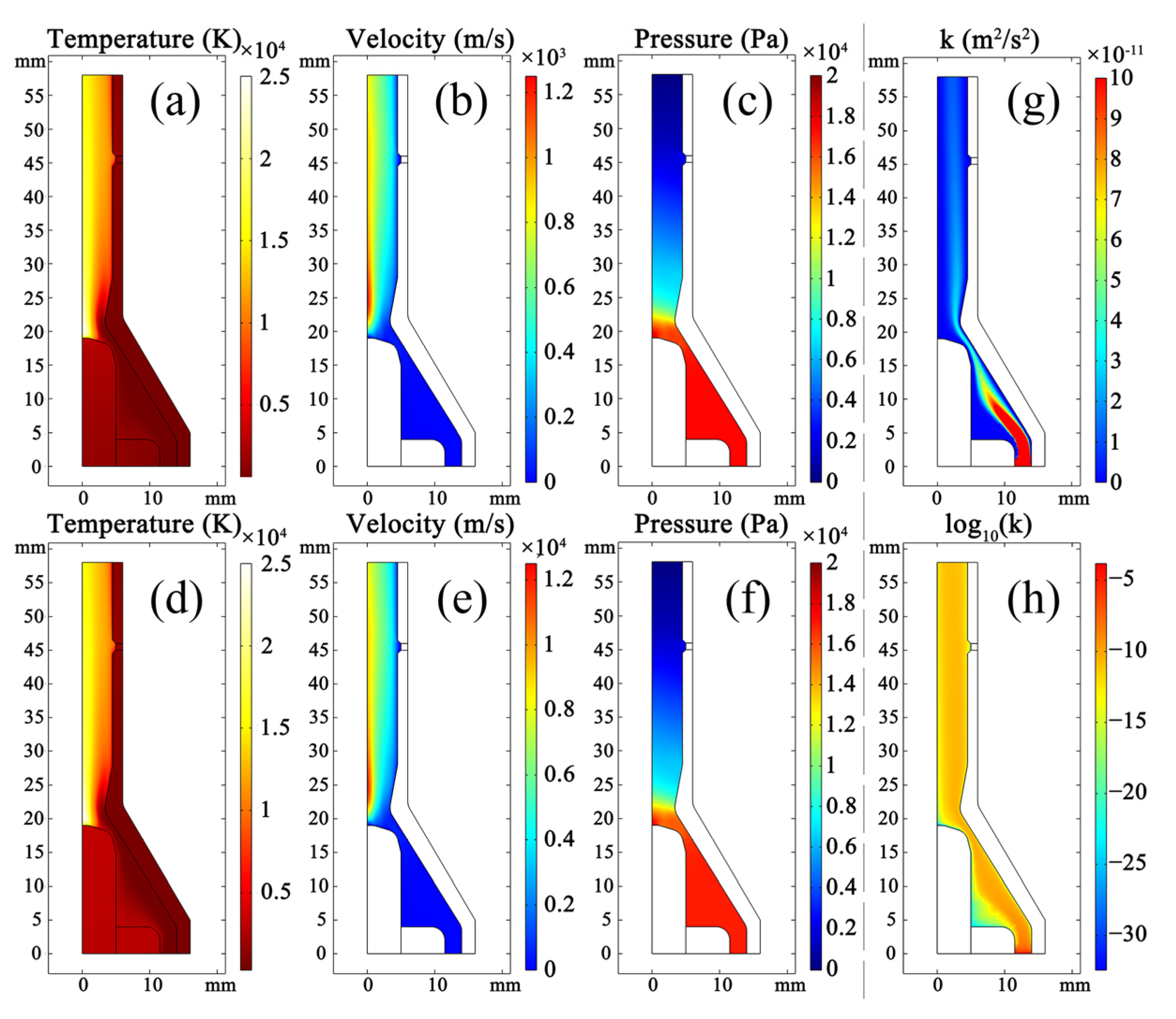
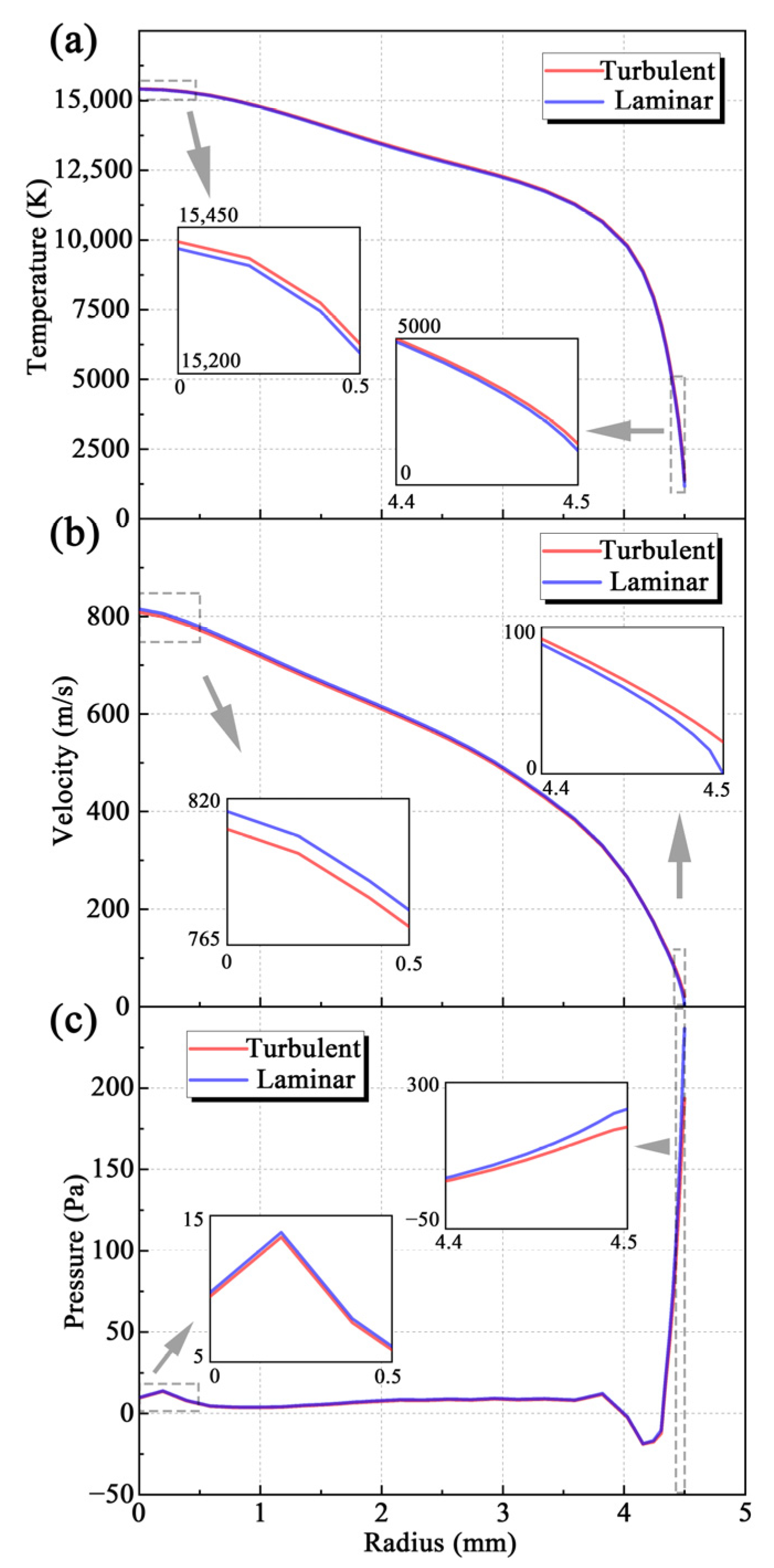
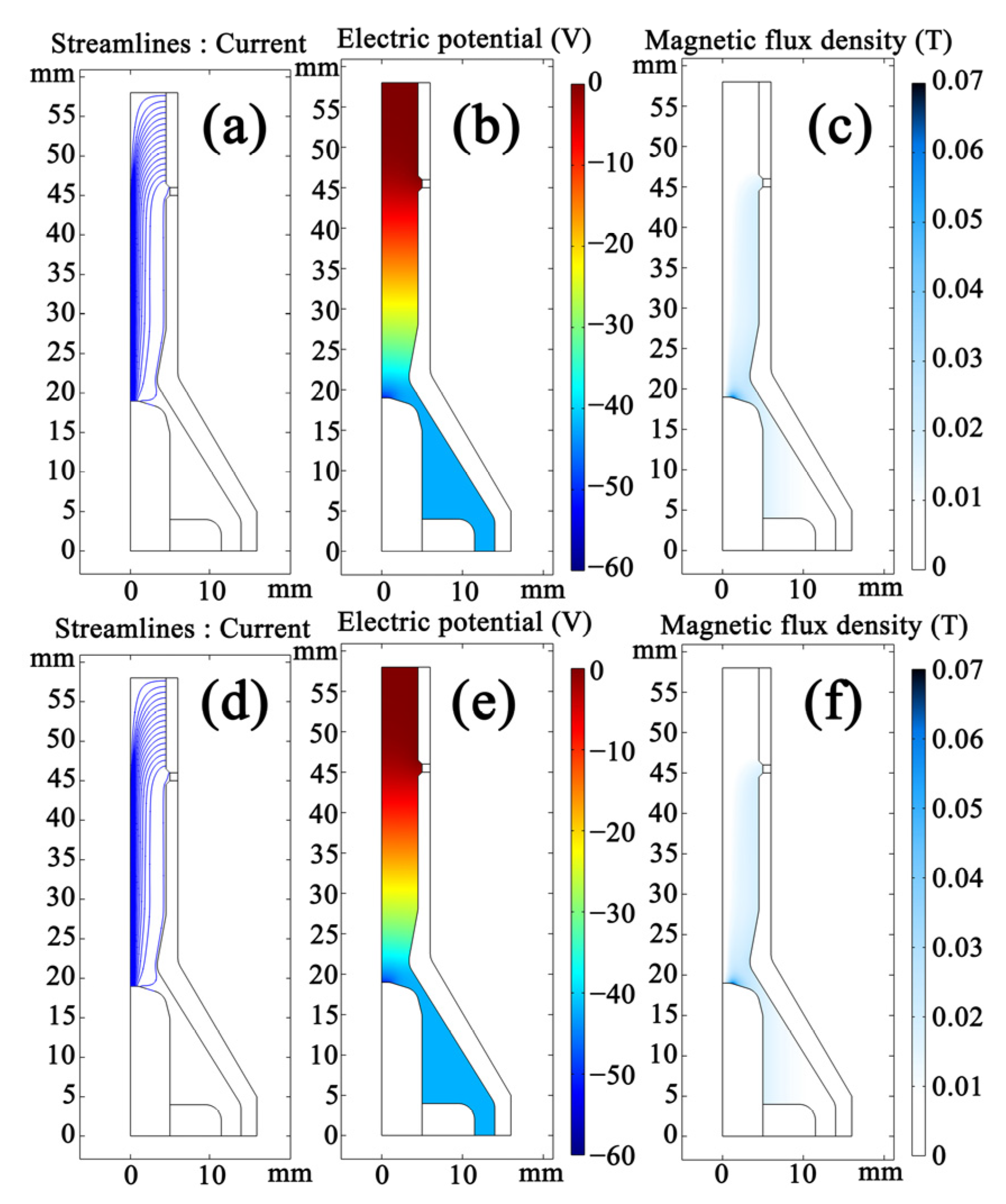
3.1. Simulation of the Arcing Process Inside the SinplexPro™ Plasma Spray Gun
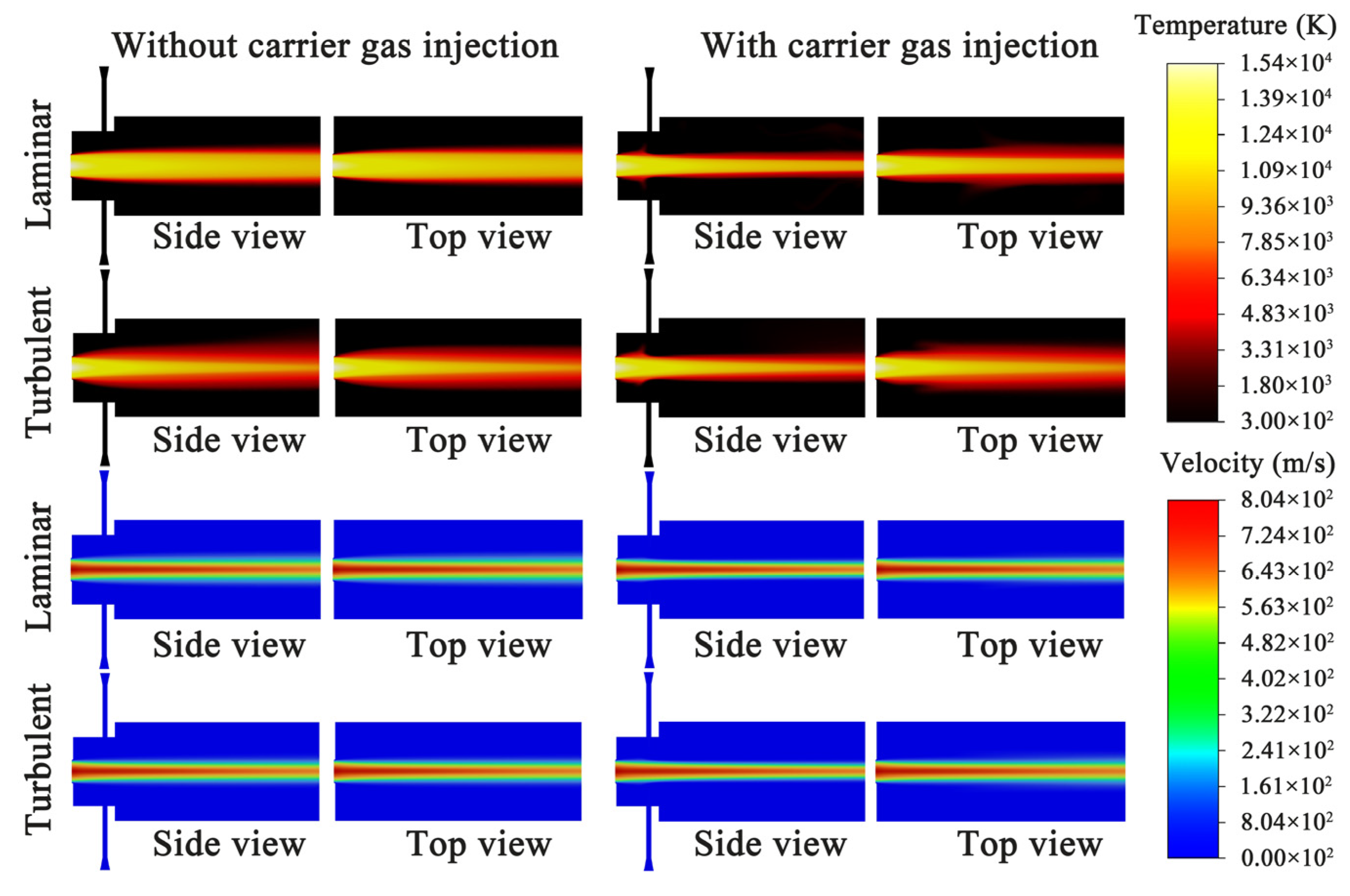
3.2. Simulation of the Plasma Jet Generated by the SinplexPro™ Plasma Spray Gun
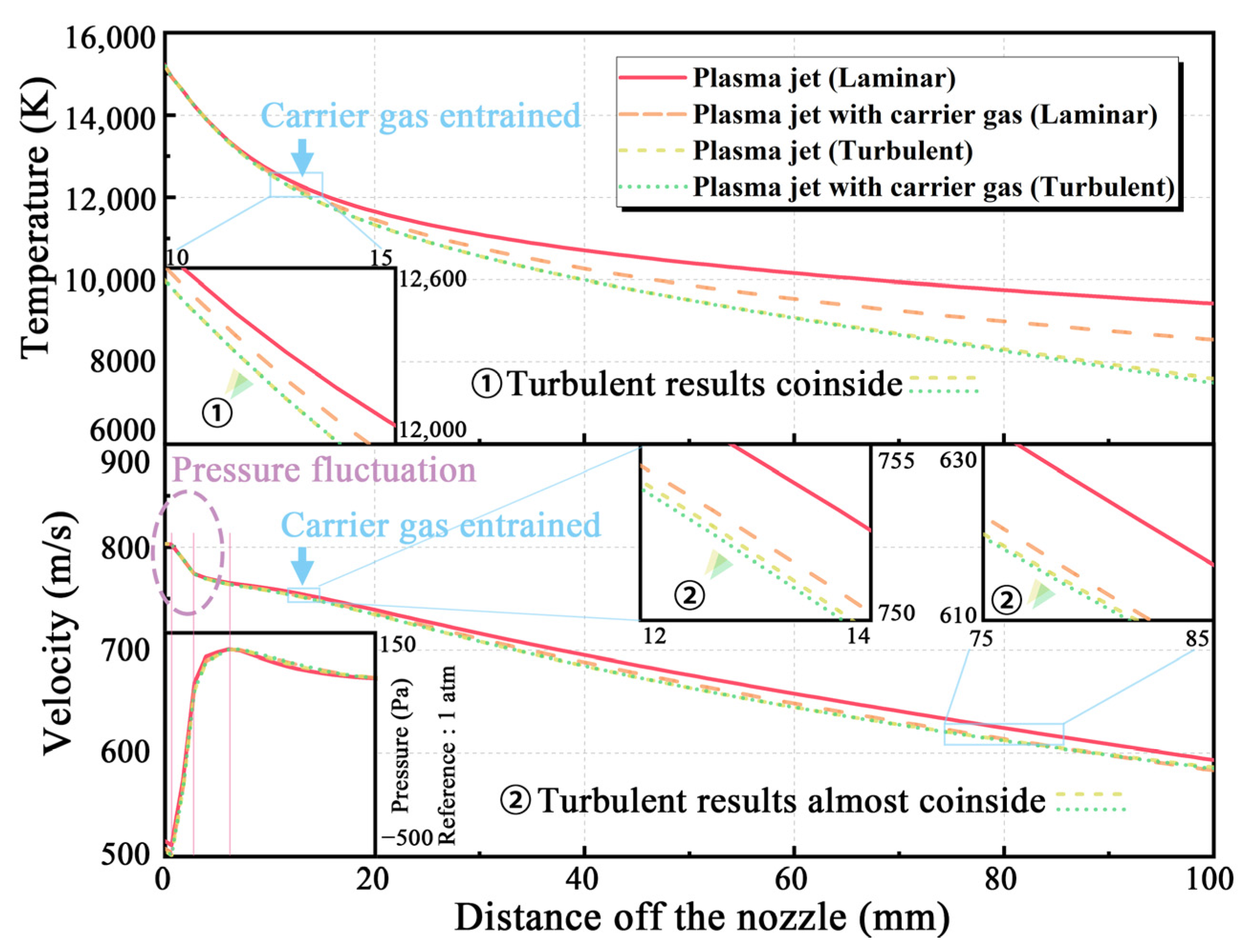
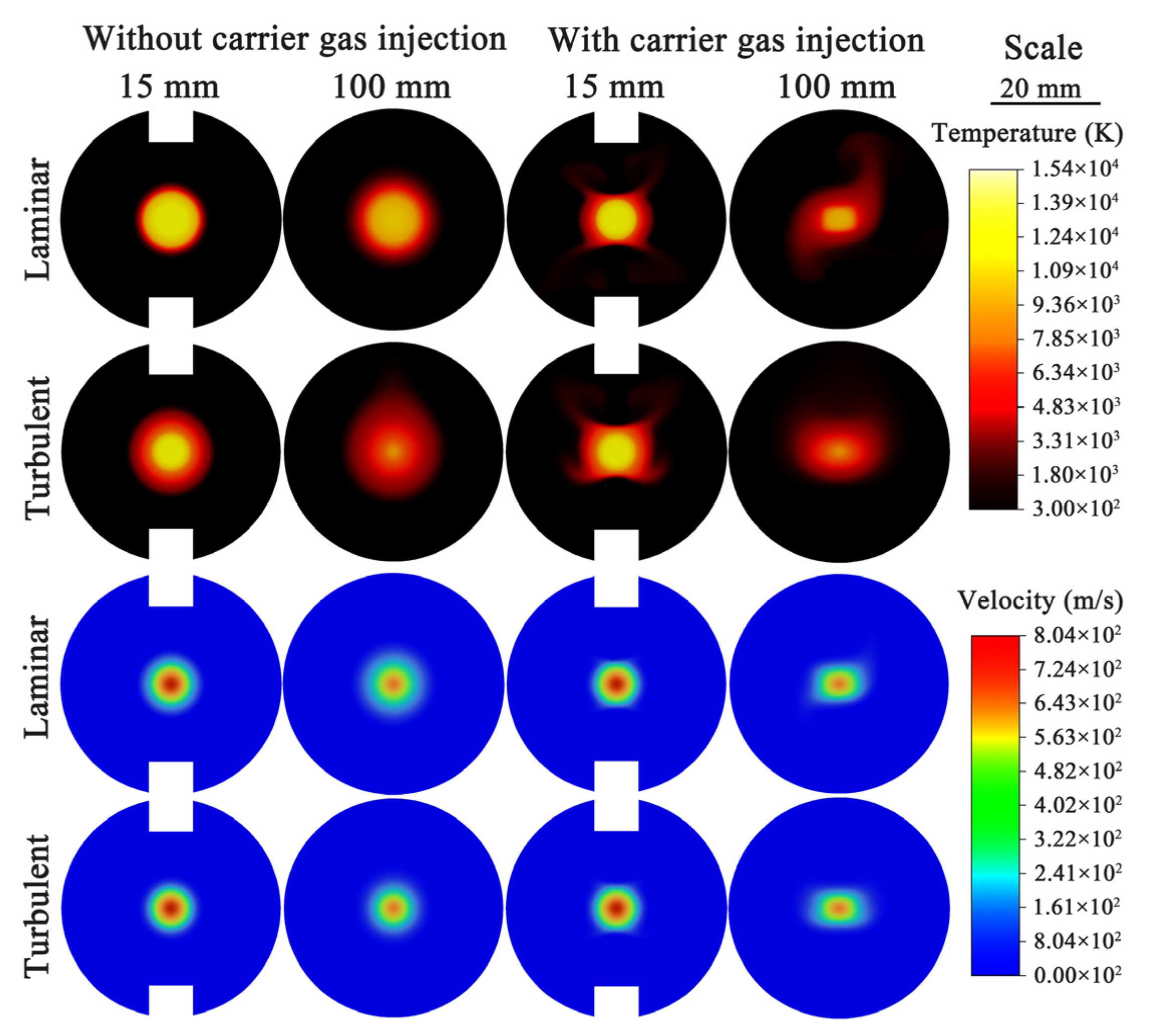
3.3. Simulation of the Plasma Jet with Carrier Gas
4. Conclusions
- The modeling results of the arcing process obtained using the turbulent and laminar models are almost the same. Thus, the plasma flow in the spray gun can be regarded as laminar. The turbulence intensity is the greatest at the gas inlet of the spray gun and gradually decreases to a negligible level in the chamber.
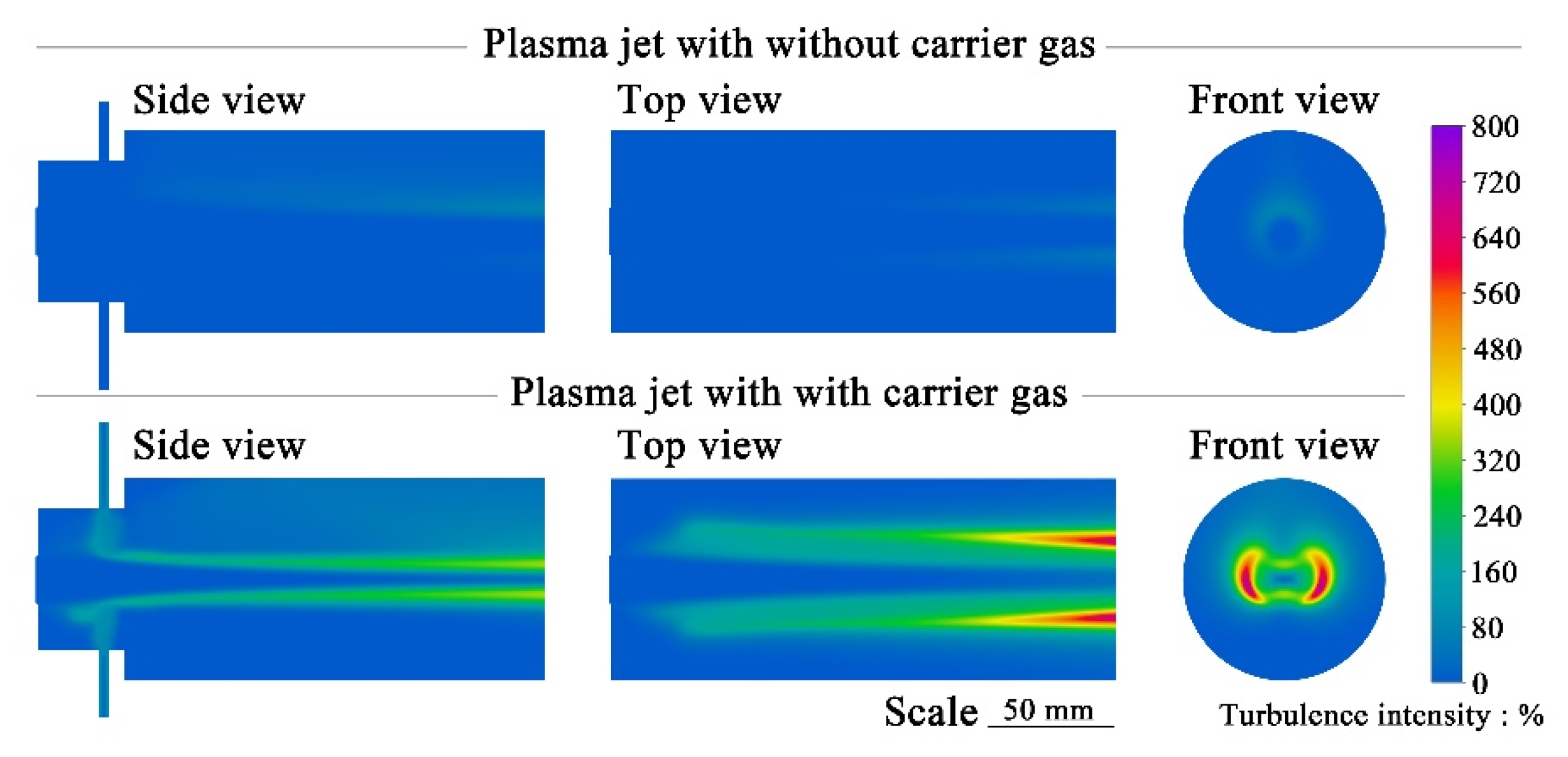
- The results obtained by the turbulent model are closer to the experimental results. The turbulence of the plasma jet is mainly generated at the edge and gradually gathers toward the center as the plasma jet develops. Affected by air buoyancy, the plasma tends to slightly float upward. The convection with the surrounding air results in the area of maximum turbulence intensity right above the plasma jet.
- The introduction of carrier gas significantly affects the laminarity of the plasma jet. Turbulence still occurs at the edge of the plasma jet, but the areas of the highest turbulence intensity are on the right and left sides of the plasma jet. This intensity distribution is mainly attributed to the effect of buoyancy on the carrier gas from the bottom injector. Therefore, during the spraying process, the plasma jet will also be affected by the gravity, which may also affect the particles with small diameters.
- Only a small part of the carrier gas can directly enter the plasma jet. Part of the carrier gas that cannot directly enter the jet leaves the computational domain due to heating and buoyancy. Another part will continue to be entrained from the edge into the plasma jet. This helps to make the particles move toward the center of the plasma jet during the plasma-spraying process.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y. Study on Preparation Technologies of Thermal Barrier Coatings. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2017, 24, 1730004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Shan, X.; Lu, J.; Zhao, X. Progress Update on Extending the Durability of Air Plasma Sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18021–18034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutter, M.; Mauer, G.; Mücke, R.; Guillon, O.; Vaßen, R. Correlation of Splat Morphologies with Porosity and Residual Stress in Plasma-Sprayed YSZ Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 318, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ye, Z.; Xiao, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. Numerical Simulation of Temperature Field and Temperature Control of DC Arc Plasma Torch. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2005, 012134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.H.; Hsu, C.M.; Hsu, C.C. Numerical Simulation of Downstream Kinetics of an Atmospheric Pressure Nitrogen Plasma Jet Using Laminar, Modified Laminar, and Turbulent Models. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2013, 33, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Sun, S.R.; Zhang, L.H.; Wang, H.X. Two-Temperature Chemical Non-Equilibrium Modeling of Argon DC Arc Plasma Torch. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2020, 40, 1383–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-H.; Sun, S.-R.; Niu, C.; Wang, H.-X. Non-Equilibrium Modeling on the Plasma–Electrode Interaction in an Argon DC Plasma Torch. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 465202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelles, J.P.; Pfender, E.; Heberlein, J. Multiscale Finite Element Modeling of Arc Dynamics in a DC Plasma Torch. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2006, 26, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvan, B.; Ramachandran, K.; Sreekumar, K.P.; Thiyagarajan, T.K.; Ananthapadmanabhan, P.V. Numerical and Experimental Studies on DC Plasma Spray Torch. Vacuum 2009, 84, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Trelles, J.P.; Murphy, A.B.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.L.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.X.; Li, C.J. Numerical Simulation of the Flow Characteristics inside a Novel Plasma Spray Torch. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 335203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Fukanuma, H.; Uesugi, Y.; Tanaka, Y. Comparisons of Two Models for the Simulation of a DC Arc Plasma Torch. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sheng, H. Numerical Simulation of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a DC Non-Transferred Arc Plasma Torch Operating under Laminar and Turbulent Conditions. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2011, 13, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram Seshadri, R.; Sampath, S. Characteristics of Conventional and Cascaded Arc Plasma Spray-Deposited Ceramic Under Standard and High-Throughput Conditions. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2019, 28, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelles, J.P.; Heberlein, J.V.R. Simulation Results of Arc Behavior in Different Plasma Spray Torches. Proc. Int. Therm. Spray Conf. 2006, 15, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, K.; Marqués, J.L.; Vaßen, R.; Stöver, D. Modelling of Arc Behaviour inside a F4 APS Torch. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, 3323–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rat, V.; Mavier, F.; Coudert, J.F. Electric Arc Fluctuations in DC Plasma Spray Torch; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 37, ISBN 1109001797977. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Fukanuma, H.; Uesugi, Y.; Tanaka, Y. Simulation of Arc Root Fluctuation in a DC Non-Transferred Plasma Torch with Three Dimensional Modeling. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2012, 21, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaya, M.; Chazelas, C.; Mariaux, G.; Vardelle, A. Arc-Cathode Coupling in the Modeling of a Conventional DC Plasma Spray Torch. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2014, 24, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovskii, R.; Chazelas, C.; Vardelle, A.; Rat, V. Control of the Arc Motion in DC Plasma Spray Torch with a Cascaded Anode. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2020, 29, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovskii, R.; Chazelas, C.; Vardelle, A.; Rat, V.; Distler, B. Effect of Electromagnetic Boundary Conditions on Reliability of Plasma Torch Models. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2020, 29, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, L. Design and Characteristics of a New Type Laminar Plasma Torch for Materials Processing. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 015402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Ramshaw, J.D. Numerical Simulations of Argon Plasma Jets Flowing into Cold Air. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 1993, 13, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Ramshaw, J.D. Modeling of Nonequilibrium Effects in a High-Velocity Nitrogen-Hydrogen Plasma Jet. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 1995, 16, S5–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hadj, A.A.; Ait-Messaoudene, N. Comparison between Two Turbulence Models and Analysis of the Effect of the Substrate Movement on the Flow Field of a Plasma Jet. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2005, 25, 699–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yu, D.; Xiao, M.; Miao, J.; Xiang, Y.; Yao, J. Design and Characteristics of a Laminar Plasma Torch for Materials Processing. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2016, 36, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, C.; He, R.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Huang, B. Study on the Influences of the Anode Structures on the Jet Characteristics of a Laminar Plasma Torch. Plasma Res. Express 2020, 2, 018001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.X.; Pan, W. Modeling Study of Shrouding Gas Effects on a Laminar Argon Plasma Jet Impinging upon a Flat Substrate in Air Surroundings. Thin Solid Film. 2006, 506–507, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.X.; Meng, X.; Li, G.; Fei, Q.X.; Wu, C.K. Feasibility of Laminar Plasma-Jet Hardening of Cast Iron Surface. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 197, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Li, C.J.; Li, C.X. In-Situ Heating Effect of Laminar Plasma Jet during Mo Coatings Deposition. Mater. Lett. 2021, 305, 130743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Ji, G.; Li, L.; Xu, P.; Huang, J.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, C.X.; Li, C.J. Microstructural Evolution of Alumina Coatings by a Novel Long Laminar Plasma Spraying Method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 363, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Li, C.X.; Li, L.; Huang, J.H.; Xu, P.; Hu, Y.Z.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.J. Development of Long Laminar Plasma Jet on Thermal Spraying Process: Microstructures of Zirconia Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 337, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solonenko, O.P.; Ando, Y.; Nishiyama, H.; Kindole, D.; Smirnov, A.V.; Golovin, A.A.; Uehara, S.; Nakajima, T. Synthesis of Thick Photocatalytic Titania Surface Layers by Solution Plasma Spraying and Subsequent Treatment by Pulsed Laminar Plasma Jet. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 333, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutsishvili, M.; Kikvadze, L. Spraying Powder Materials by the High-Enthalpy Laminar Plasma Flow. AIP Conf. Proc. 2008, 993, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Li, C.-X.; Liu, S.-H.; Li, L.; Yang, G.-J.; Li, C.-J.; Zhang, S.-L. Splash Involved Deposition Behavior and Erosion Mechanism of Long Laminar Plasma Sprayed NiCrBSi Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 395, 125939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Liu, S.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, S.L.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.J. Structured La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ Cathode with Large-Scale Vertical Cracks by Atmospheric Laminar Plasma Spraying for IT-SOFCs. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 825, 153865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Pan, W.X.; Wu, C.K. Preliminary Investigations on Low-Pressure Laminar Plasma Spray Processing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 191, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Trelles, J.P.; Li, C.J.; Guo, H.B.; Li, C.X. Numerical Analysis of the Plasma-Induced Self-Shadowing Effect of Impinging Particles and Phase Transformation in a Novel Long Laminar Plasma Jet. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 375202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, L.; Xu, P.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.J. A Novel Structure of YSZ Coatings by Atmospheric Laminar Plasma Spraying Technology. Scr. Mater. 2018, 153, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Li, C.J.; Li, C.X. Deposition and Oxidation Behavior of Atmospheric Laminar Plasma Sprayed Mo Coatings from 200 Mm to 400 Mm under 20 KW: Numerical and Experimental Analyses. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 400, 126245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovskii, R.; Chazelas, C.; Rat, V.; Vardelle, A.; Molz, R. Predicted Anode Arc Attachment by LTE (Local Thermodynamic Equilibrium) and 2-T (Two-Temperature) Arc Models in a Cascaded-Anode DC Plasma Spray Torch. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 31, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinè, B. A 2D Model of a Plasma Torch. 2016 COMSOL Conf. 2016, 7, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS Inc. ANSYS FLUENT Theory Guide. Available online: https://ansyshelp.ansys.com/account/secured?returnurl=/Views/Secured/corp/v201/en/flu_th/flu_th.html?q=ansysfluenttheoryguide (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- COMSOL Inc. The SST Turbulence Model. Available online: https://doc.comsol.com/5.5/doc/com.comsol.help.cfd/cfd_ug_fluidflow_single.06.091.html (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Metco, O. Product Data Sheet SinplexProTM Universal Plasma Spray Guns Oerlikon. Available online: https://www.oerlikon.com/ecomaXL/files/metco/oerlikon_DSE-0061.5_SinplexPro_series_EN.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2015).
- Boulos, M.I.; Fauchais, P.; Pfender, E. Thermal Plasmas Fundamentals and Applications; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 1, ISBN 9781489913395. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, Y.; Tobe, S.; Tahara, H. TiO2 Film Deposition by Atmospheric Thermal Plasma CVD Using Laminar and Turbulence Plasma Jets. AIP Conf. Proc. 2008, 982, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.X.; Li, G.; Meng, X.; Ma, W.; Wu, C.K. Laminar Plasma Jets: Generation, Characterization, and Applications for Materials Surface Processing. Pure Appl. Chem. 2005, 77, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Wu, C. Generation of Long, Laminar Plasma Jets at Atmospheric Pressure and Effects of Flow Turbulence. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2001, 21, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yu, D.; Xiang, Y.; Yao, J.; Miao, J. Influence of the Laminar Plasma Torch Construction on the Jet Characteristics. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2016, 18, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
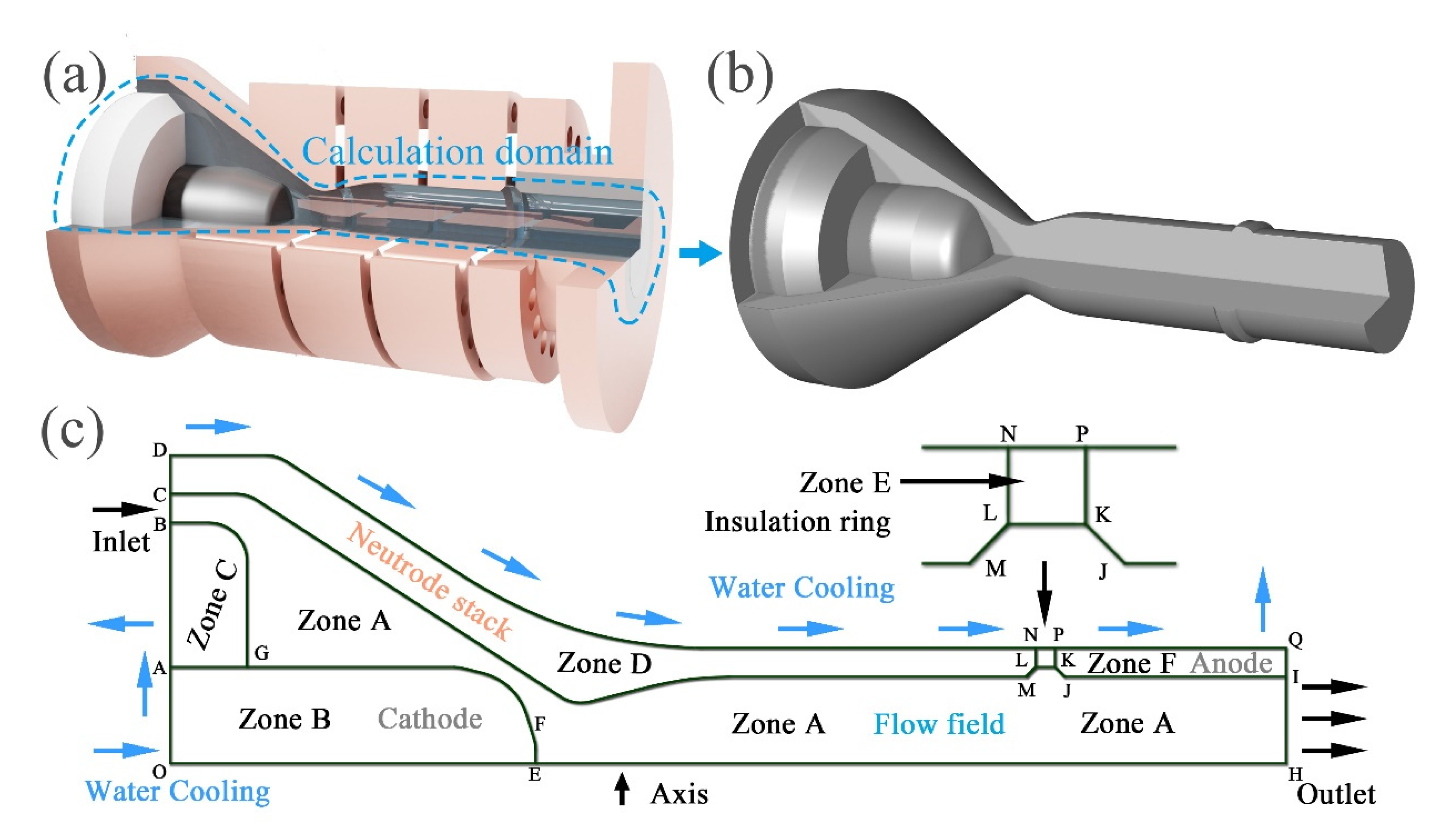



| No. | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inside the torch | × | × | × | × | × | |||
| Outside the torch | × | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| Boundary | Definition | Length (mm) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC | Gas inlet | 2.5 | Vertical (radius) |
| HI | Outflow | 4.5 | Vertical |
| EF | Cathode tip | ≈1.5 | Vertical |
| KJI | Anode (tungsten) | 12 | Horizontal (=PQ) |
| OB | Wall (water cooling) | 11.5 | Vertical |
| JK | Anode | 0.5 | Horizontal (45°) (=LM) |
| LK | Insulation ring | 1 | Horizontal (=NP) |
| AG | Interface | 4 | Horizontal |
| OE | Axis (cathode) | 19 | Horizontal |
| OH | Axis | 58 | Horizontal |
| Boundary | Definition | Length (mm) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| OA | Nozzle exit | 4.5 | Vertical (radius) |
| AB | Chamfer | 0.5 | Vertical (45°) |
| BC | Wall | 7 | Vertical |
| CD | Anode | 12 | Horizontal |
| DF | Wall | 28 | Vertical |
| EF | Wall | 5 | Vertical |
| FG | Carrier gas inlet | 4 | Horizontal |
| CI | Wall | 14 | Horizontal |
| CJ | Wall | 18 | Horizontal |
| JK | Wall | 8 | Vertical |
| LM | Outlet | 20 | Vertical |
| OM | Axis | 58 | Horizontal |
| Boundary | Definition | Heat Transfer | Fluid Flow | Electric Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | Gas inlet | 300 K | 40 SLPM | - |
| HI | Outflow | - | ||
| EF | Cathode tip | 3500 K | - | 450 A |
| KJI | Anode | Interface | - | 0 V |
| OAB | Wall | - | - | |
| DNPQ | Wall | - | - | |
| OEH | Axis | - | - | - |
| Boundary | Definition | Heat Transfer | Fluid Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| OA | Gas inlet | From simulation | From simulation |
| KLM | Outflow | 300 K | |
| FG | Cathode tip | 300 K | 2 SLPM |
| ABCDEF | Wall | - | |
| GHIJK | Wall | - | |
| OM | Axis | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Mauer, G.; Liu, S.; Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Vaßen, R. Modeling of the Effect of Carrier Gas Injection on the Laminarity of the Plasma Jet Generated by a Cascaded Spray Gun. Coatings 2022, 12, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101416
Zhang H, Mauer G, Liu S, Liu M, Jia Y, Li C, Li C, Vaßen R. Modeling of the Effect of Carrier Gas Injection on the Laminarity of the Plasma Jet Generated by a Cascaded Spray Gun. Coatings. 2022; 12(10):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101416
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huiyu, Georg Mauer, Senhui Liu, Meng Liu, Yunjie Jia, Changjiu Li, Chengxin Li, and Robert Vaßen. 2022. "Modeling of the Effect of Carrier Gas Injection on the Laminarity of the Plasma Jet Generated by a Cascaded Spray Gun" Coatings 12, no. 10: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101416
APA StyleZhang, H., Mauer, G., Liu, S., Liu, M., Jia, Y., Li, C., Li, C., & Vaßen, R. (2022). Modeling of the Effect of Carrier Gas Injection on the Laminarity of the Plasma Jet Generated by a Cascaded Spray Gun. Coatings, 12(10), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101416







