Impact of Tungsten Incorporation on the Tribomechanical Behavior of AlCrWxSiN Films at Room and Elevated Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
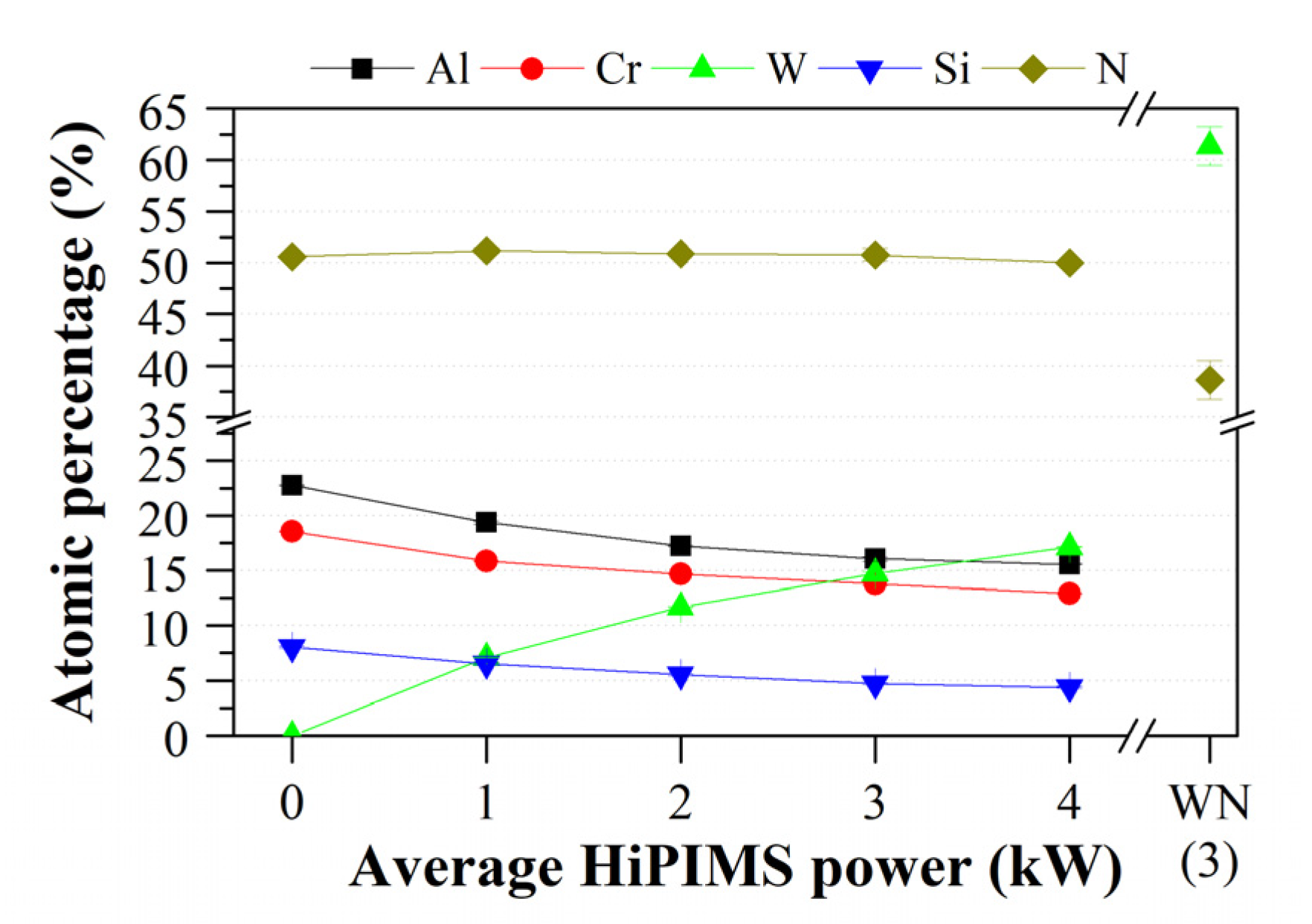
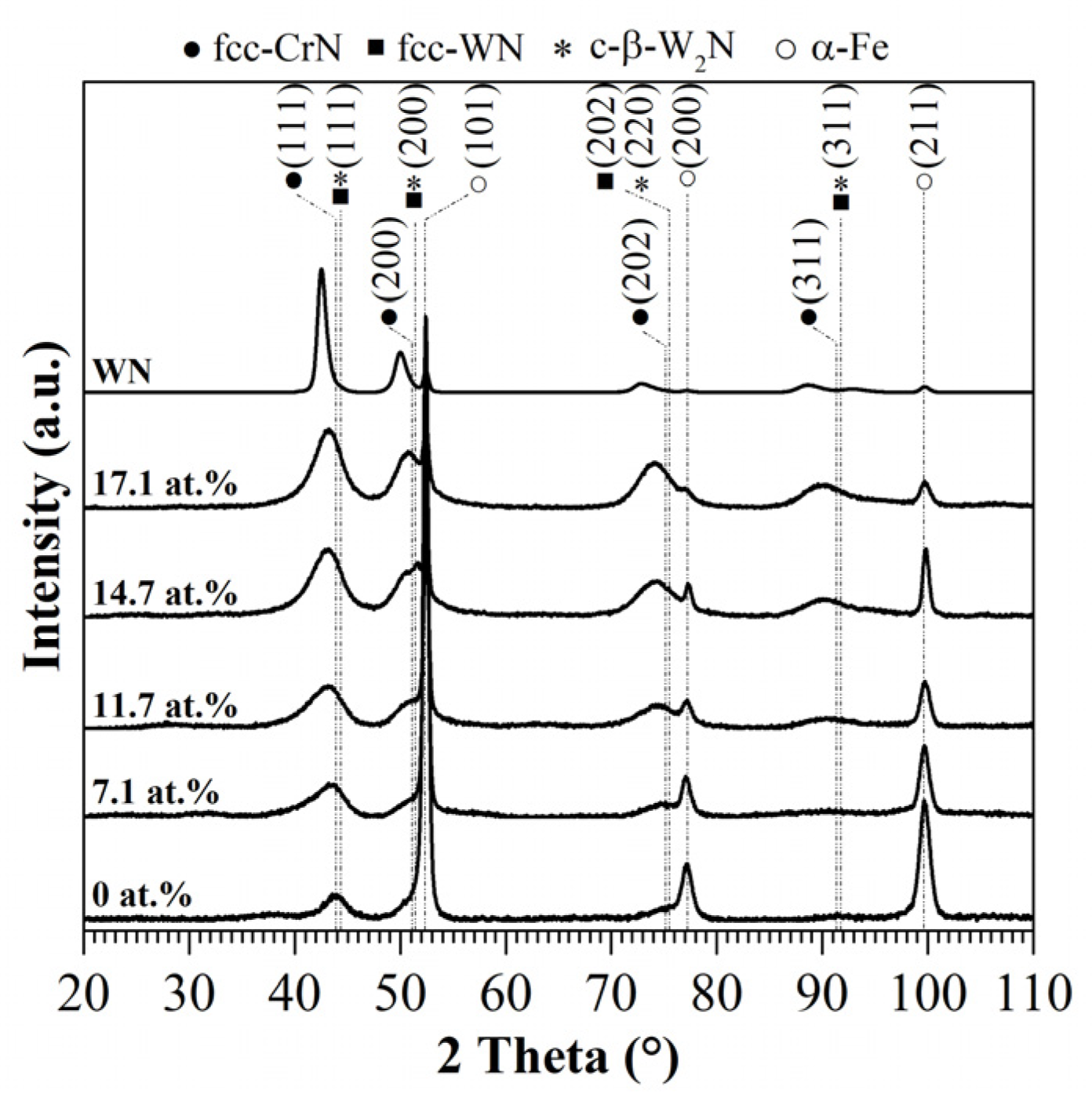
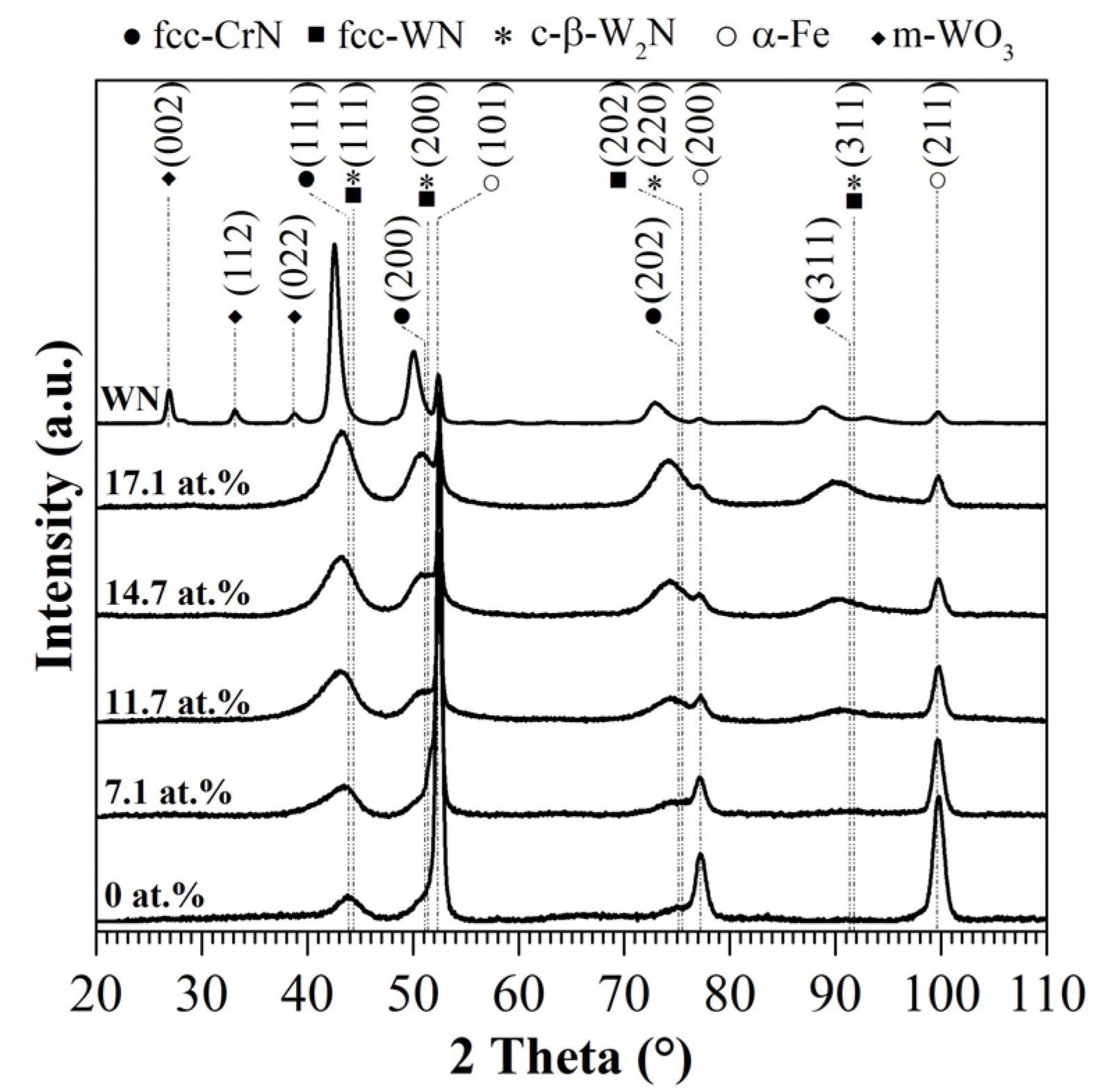
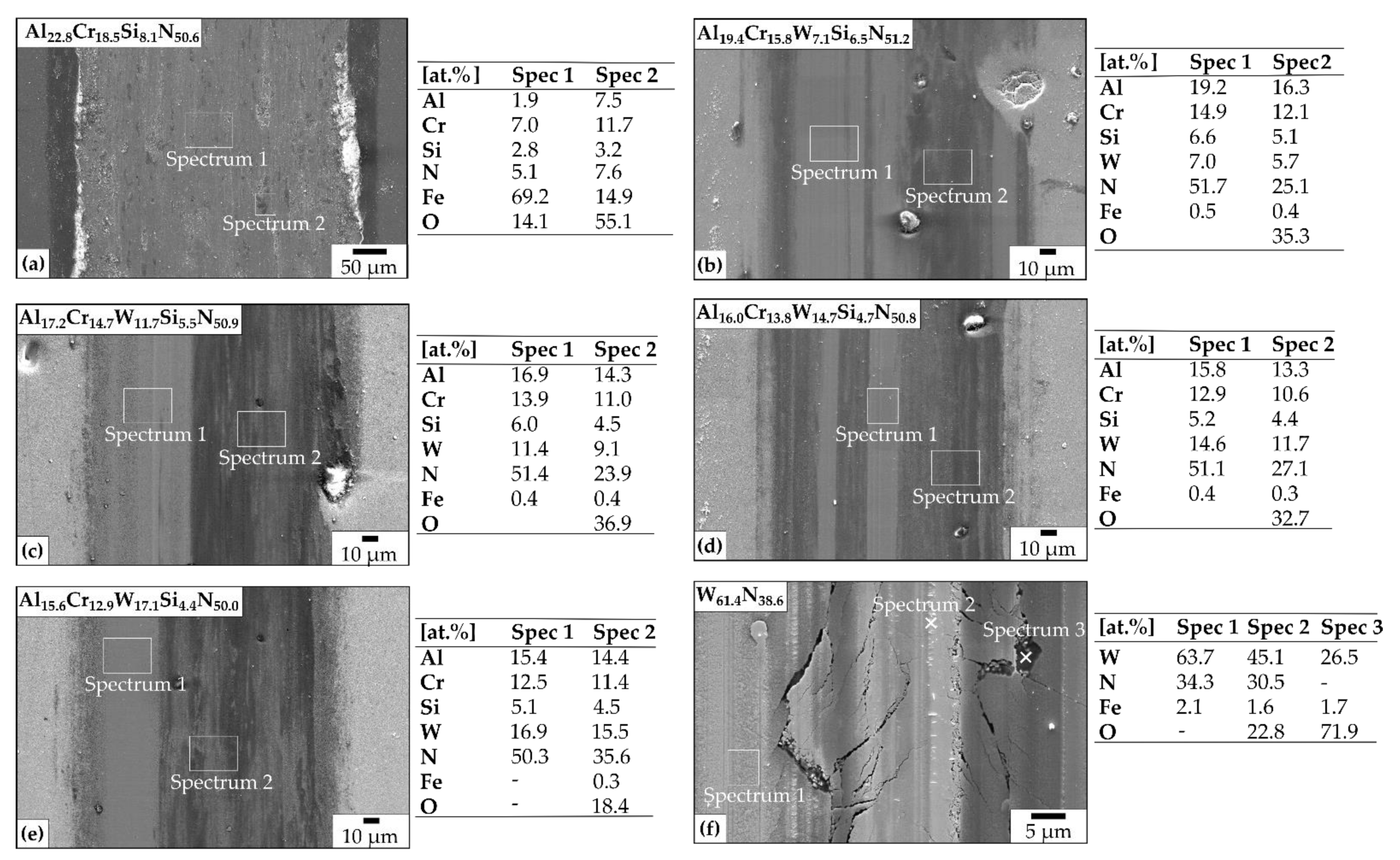
3.1. Chemical Composition and Crystal Structure
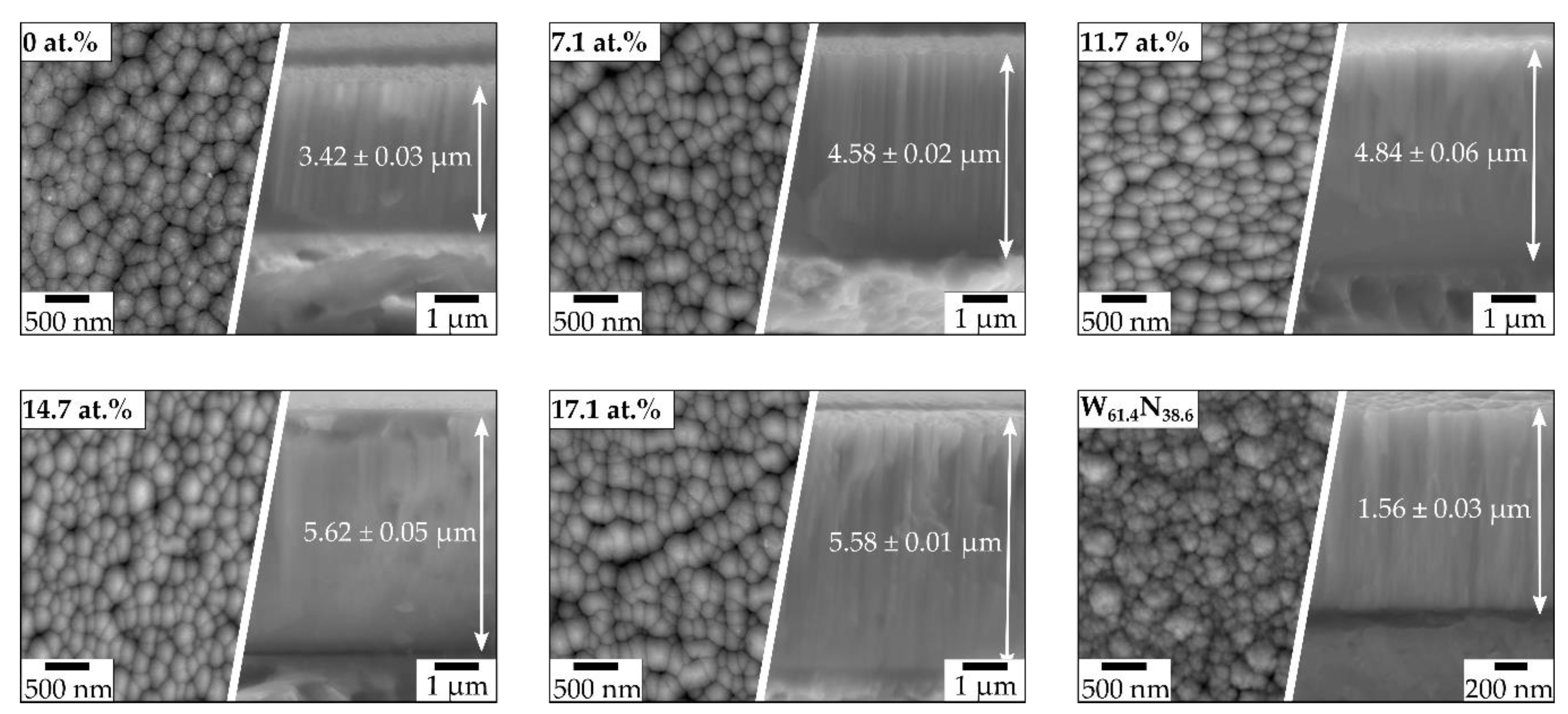
3.2. Microstructure
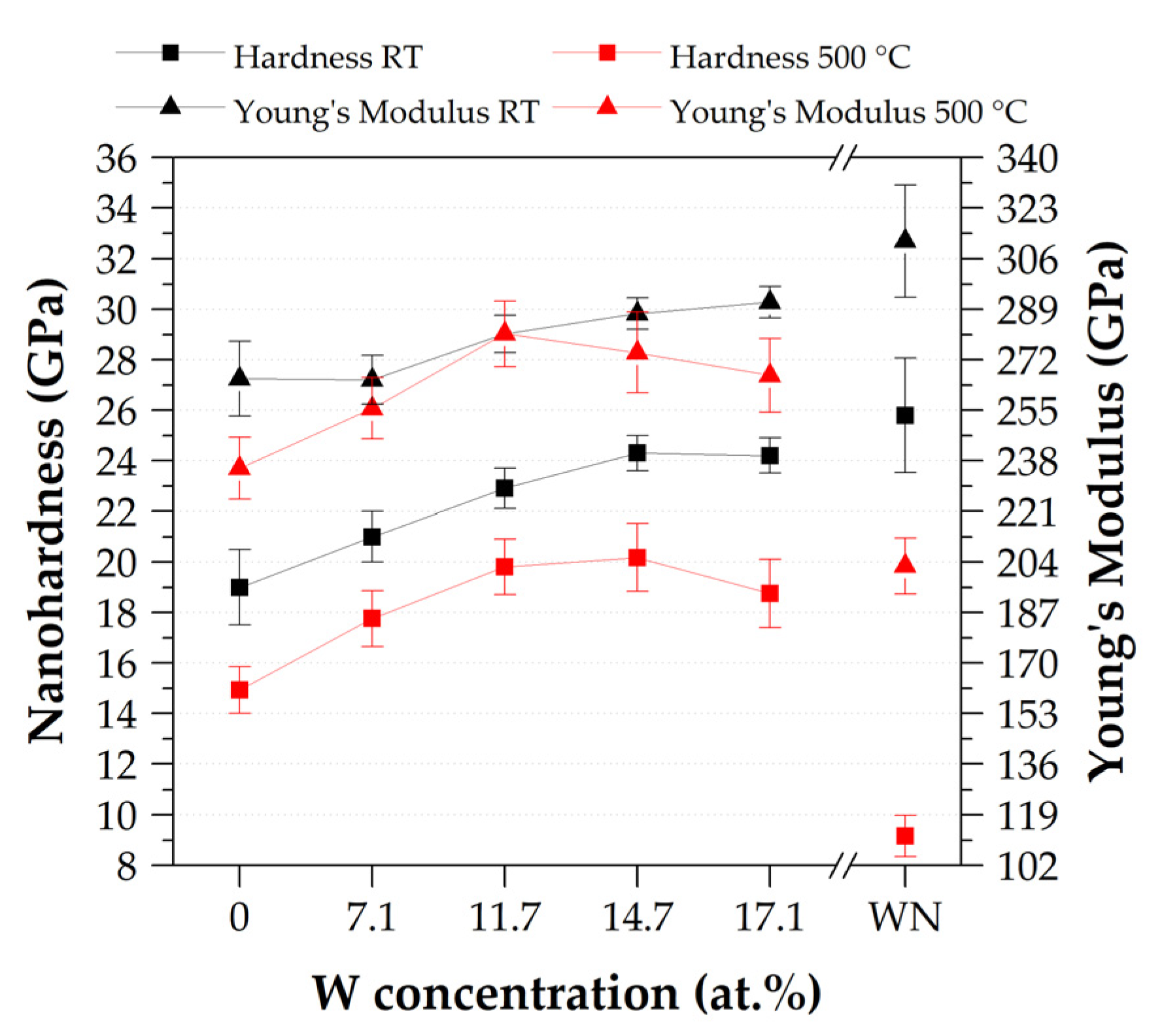
3.3. Mechanical Properties and Adhesion
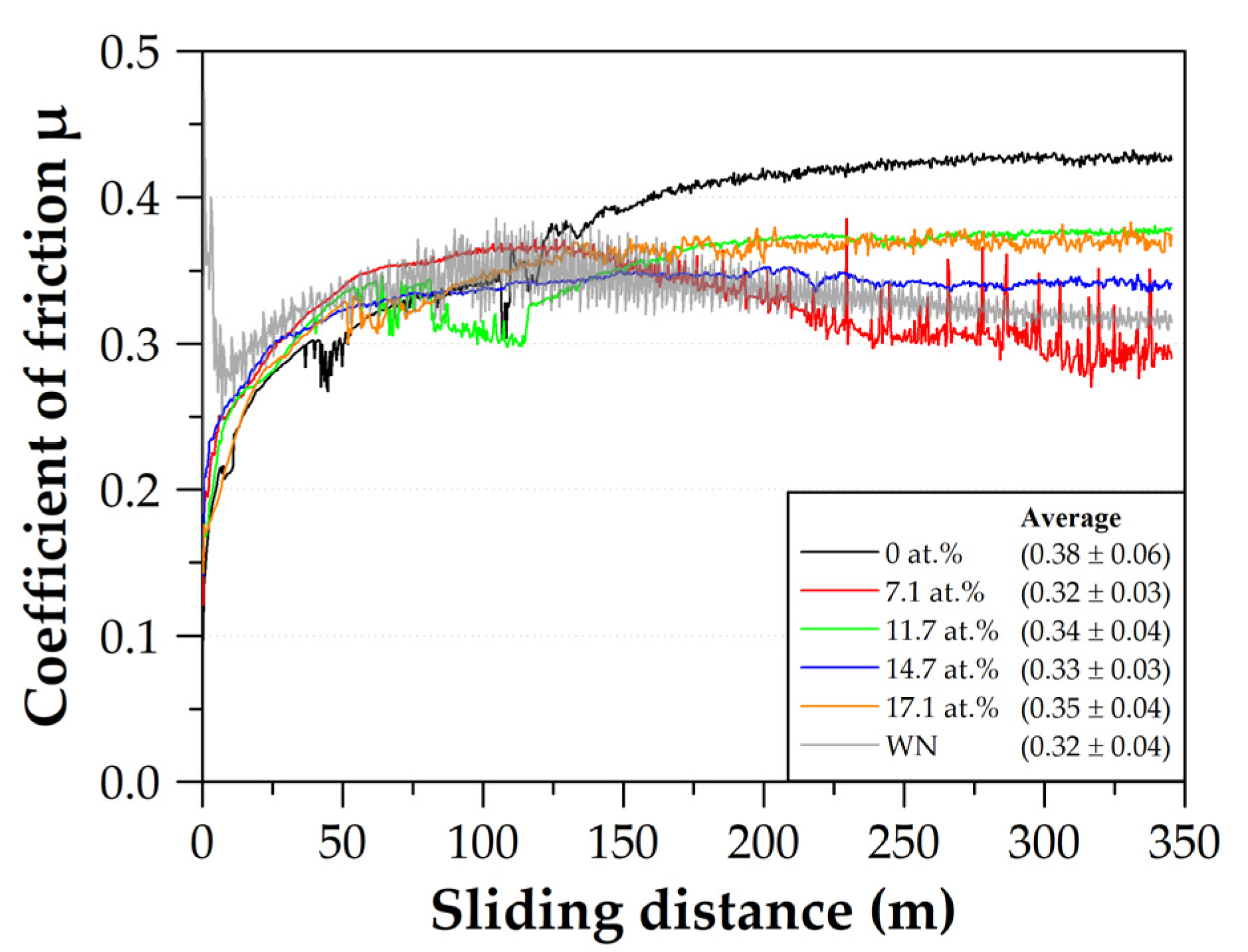
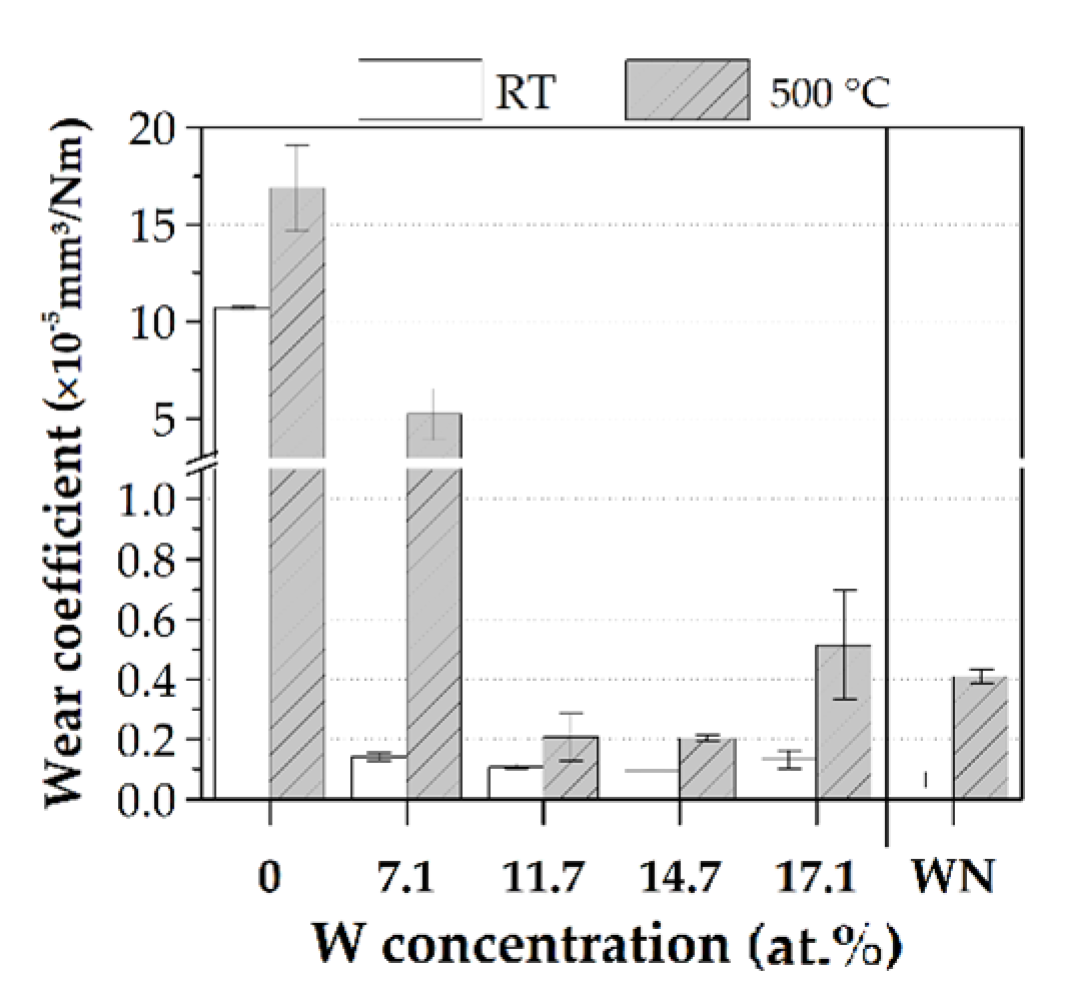
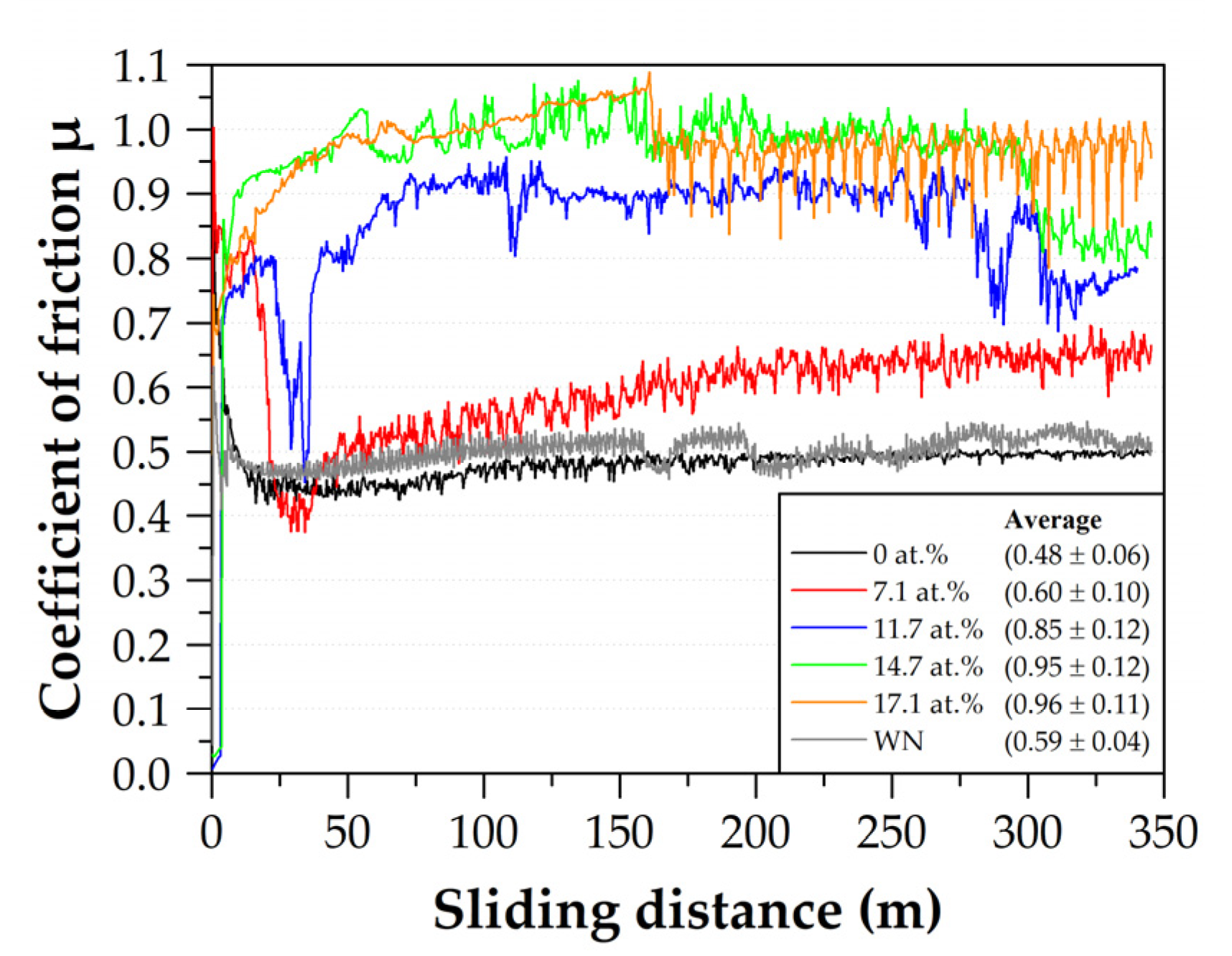
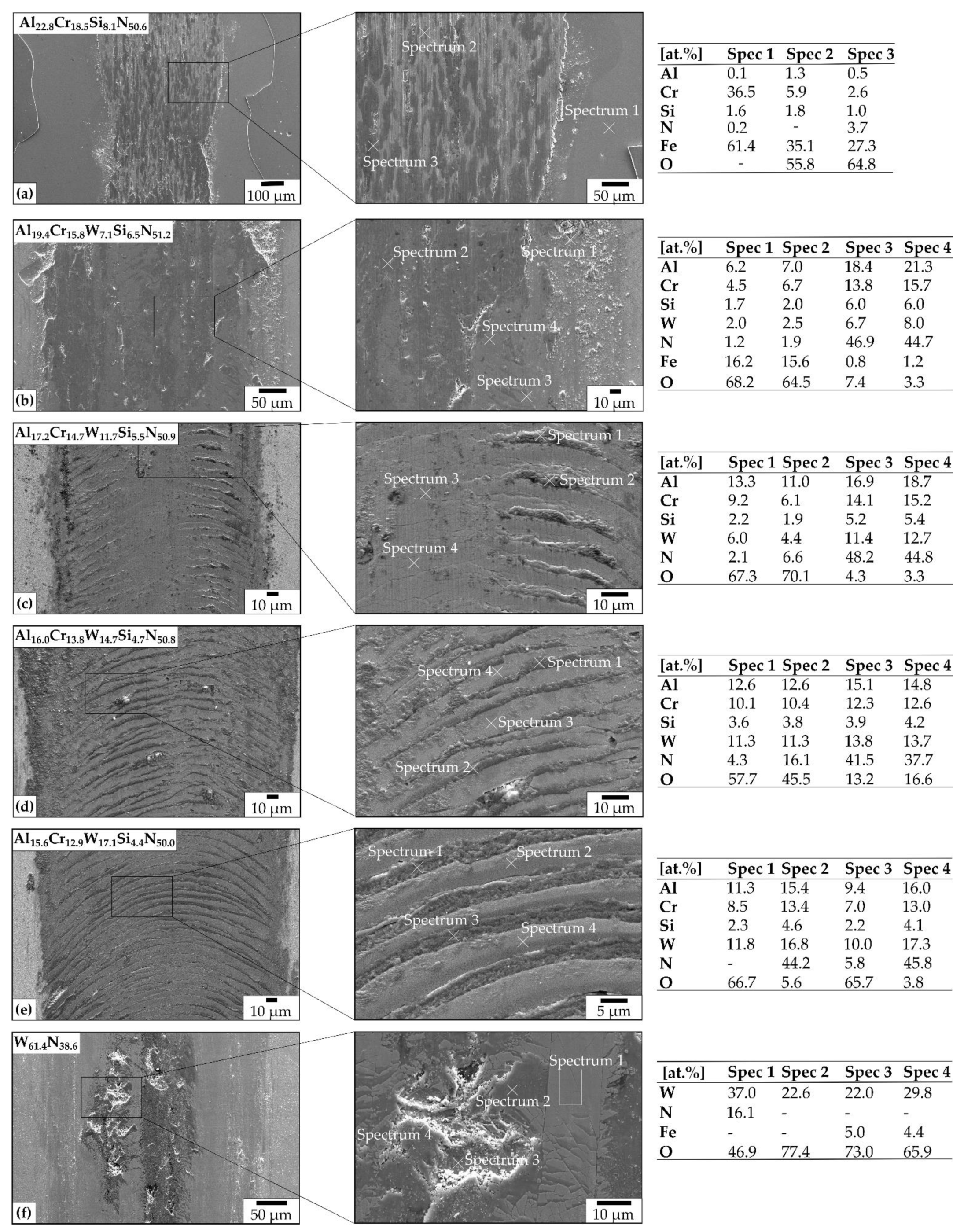
3.4. Tribological Properties
4. Conclusions
- The HiPIMS supply to the W target generated a non-stoichiometric W61.4N38.6, which formed an m-WO3 phase after annealing at 500 °C and deteriorated the mechanical properties. In contrast to this, the AlCrWxSiN film surfaces did not exhibit any crystalline phase transformations after the heat treatment.
- The successive increase of W in AlCrSiWxN resulted in a denser film growth and steadily increased the film hardness, thus further enhancing the film adhesion.
- Based on the denser film growth, tungsten additions to AlCrWxSiN resulted in slight decrease of the COF at room temperature. In particular, the formation of cracks in the WN wear track fostered oxygen diffusion at room temperature. Thus, a preliminary stage in the formation of friction-reducing tungsten oxides begun, which is of interest for further research.
- It was shown that at 500 °C higher tungsten proportions led to a significantly increased and alternating friction behavior due to scaly oxidations in the wear tracks, which locally increased the surface roughness in the wear track. Furthermore, the WN film exhibited a fracturing in the wear track, which increased the friction. Additionally, the partial transformation of WN to m-WO3 did not induce a self-lubricating effect. Therefore, the friction was generally increased at 500 °C for all systems.
- Although the friction and oxidation in the wear track were intensified at high temperatures, the wear coefficient was significantly decreased for films with a balanced W/Cr ratio. This finding offers great potential for tungsten as an alloying element in chromium-based systems for use as wear resistant film.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, W.-Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Xiao, B.-H.; Yang, T.-X.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, P.-H.; Chang, C.-L. Microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of CrWN films deposited by DC magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2013, 87, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-N.; Han, S.; Weng, K.-W.; Lee, C.-T. Investigation on the structural and mechanical properties of anti-sticking sputtered tungsten chromium nitride films. Thin Solid Films 2013, 529, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.H.; Su, Y.L.; Kao, W.H. Effect of Ag/W addition on the wear performance of CrN coatings prepared by RF unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 398, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hones, P.; Consiglio, R.; Randall, N.; Lévy, F. Mechanical properties of hard chromium tungsten nitride coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 125, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-I.; Cheng, Y.-R.; Chang, L.-C.; Lee, J.-W. Chemical inertness of Cr–W–N coatings in glass molding. Thin Solid Films 2015, 593, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-C.; Zheng, Y.-Z.; Gao, Y.-X.; Chen, Y.-I. Mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of sputtered Cr–W–N coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 320, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcar, T.; Cavaleiro, A. High-temperature tribological properties of CrAlN, CrAlSiN and AlCrSiN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, S.-K.; Lin, C.-H.; Tsai, Y.-Z.; Duh, J.-G. Effect of nitrogen flow on the properties of quaternary CrAlSiN coatings at elevated temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Chen, H.-W.; Lee, J.-W.; Duh, J.-G. Development of Si-modified CrAlSiN nanocomposite coating for anti-wear application in extreme environment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 284, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.Z.; Duh, J.G. Enhanced hardness of CrAlSiN/W2N superlattice coatings deposited by direct current magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 2325–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-Z.; Duh, J.-G. Tribological behavior of CrAlSiN/W2N multilayer coatings deposited by DC magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 7523–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-W.; Tsai, Y.-Z.; Duh, J.-G.; Lee, J.-W. Texture, microstructure and anti-wear characteristics in isostructural CrAlSiN/W2N multilayer coatings. Thin Solid Films 2013, 544, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Fehr, A.; Stangier, D. Microstructural and tribological properties of sputtered AlCrSiWN films deposited with segmented powder metallurgic target materials. Thin Solid Films 2019, 687, 137465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Fehr, A.; Stangier, D. Powder metallurgic fabricated plug targets for the synthesis of AlCrSiWN multicomponent coating systems. Int J. Refract. Met. H. 2019, 85, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hones, P.; Martin, N.; Regula, M.; Lévy, F. Structural and mechanical properties ofchromium nitride, molybdenum nitride, and tungsten nitride thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velicu, I.-L.; Tiron, V.; Porosnicu, C.; Burducea, I.; Lupu, N.; Stoian, G.; Popa, G.; Munteanu, D. Enhanced properties of tungsten thin films deposited with a novel HiPIMS approach. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 424, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Tengstrand, O.; Bakhit, B.; Lu, J.; Greene, J.E.; Hultman, L.; Petrov, I.; Greczynski, G. Growth of dense, hard yet low-stress Ti 0.40 Al 0.27 W 0.33 N nanocomposite films with rotating substrate and no external substrate heating. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2020, 38, 23006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiron, V.; Velicu, I.-L.; Porosnicu, C.; Burducea, I.; Dinca, P.; Malinský, P. Tungsten nitride coatings obtained by HiPIMS as plasma facing materials for fusion applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Prakash, B.; Yuan, Z.G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.P.; Fang, Q.F. Influence of sputtering target power on microstructure and mechanical properties of W-N and Ta-N coatings. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2012, 4, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.-P.; Zhang, L.; Ke, R.-L.; Wan, Q.-L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z.-H. Thermal stability and oxidation behavior of AlTiN, AlCrN and AlCrSiWN coatings. Int J. Refract. Met. H. 2014, 43, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Kokalj, D.; Stangier, D.; Paulus, M.; Sternemann, C.; Tolan, M. Investigation of the influence of the vanadium content on the high temperature tribo-mechanical properties of DC magnetron sputtered AlCrVN thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 328, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Fehr, A.; Stangier, D.; Dildrop, M. Influences of substrate pretreatments and Ti/Cr interlayers on the adhesion and hardness of CrAlSiN and TiAlSiN films deposited on Al2O3 and ZrO2-8Y2O3 thermal barrier coatings. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Fehr, A.; Stangier, D.; Dildrop, M.; Homberg, W.; Lossen, B.; Hijazi, D. Al2O3/ZrO2-8Y2O3 and (Cr,Ti)AlSiN tool coatings to influence the temperature and surface quality in friction-spinning processes. Prod. Eng. 2019, 13, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1624–05 Standard Test Method for Adhesion Strength and Mechanical Failure Modes of Ceramic Coatings by Quantitative Single Point Scratch Testing; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005.
- Tillmann, W.; Lopes Dias, N.F.; Stangier, D. Effect of Hf on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and oxidation behavior of sputtered CrAlN films. Vacuum 2018, 154, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, A.; Andersson, J.; Ehiasarian, A. High power impulse magnetron sputtering: Current-voltage-time characteristics indicate the onset of sustained self-sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.C.; Shah, S.I. Reactive sputter deposition of tungsten nitride thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film. 2002, 20, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawate, M.; Kimura, A.; Suzuki, T. Microhardness and lattice parameter of Cr1−xAlxN films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2002, 20, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-Z.; Duh, J.-G. Thermal stability and microstructure characterization of CrN/WN multilayer coatings fabricated by ion-beam assisted deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, L.; Ye, F. Comparison study on the oxidation behavior of WN and WCN ceramic coatings during heat treatment. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 206, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hones, P.; Diserens, M.; Sanjinés, R.; Lévy, F. Electronic structure and mechanical properties of hard coatings from the chromium–tungsten nitride system. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2000, 18, 2851–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrino, J.L.; Derflinger, V. The influence of alloying elements on the phase stability and mechanical properties of AlCrN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Barnett, S.A. Model of superlattice yield stress and hardness enhancements. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 4403–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drnovšek, A.; Rebelo de Figueiredo, M.; Vo, H.; Xia, A.; Vachhani, S.J.; Kolozsvári, S.; Hosemann, P.; Franz, R. Correlating high temperature mechanical and tribological properties of CrAlN and CrAlSiN hard coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 372, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayrhofer, P.H.; Mitterer, C.; Hultman, L.; Clemens, H. Microstructural design of hard coatings. Prog. Mater Sci. 2006, 51, 1032–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, B.-S.; Chu, C.-W.; Lin, D.; Lee, W.; Duh, J.-G.; Lin, C.-H. Tungsten doped chromium nitride coatings. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, Z.; Li, K.; Chen, Q.; Gong, F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, B.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Han, B.; et al. Microstructure, wear and oxidation resistance of CrWN glass molding coatings synthesized by plasma enhanced magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2020, 174, 109206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeswinkel, T.; Music, D.; Schneider, J.M. Coulomb-potential-dependent decohesion of Magnéli phases. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 292203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Ding, N.; Xu, J.; Yu, L.; Asempah, I.; Xu, J.; Yi, G.; Ma, B. Crystal structure and the improvement of the mechanical and tribological properties of tungsten nitride films by addition of titanium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 345, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayrhofer, P.H.; Hovsepian, P.E.; Mitterer, C.; Münz, W.-D. Calorimetric evidence for frictional self-adaptation of TiAlN/VN superlattice coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 177, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Bagcivan, N.; Ewering, M.; Brugnara, R.H.; Theiß, S. DC-MSIP/HPPMS (Cr,Al,V)N and (Cr,Al,W)N thin films for high-temperature friction reduction. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugscheider, E.; Knotek, O.; Bobzin, K.; Bärwulf, S. Tribological properties, phase generation and high temperature phase stability of tungsten- and vanadium-oxides deposited by reactive MSIP-PVD process for innovative lubrication applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 133–134, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Duh, J.-G.; Yau, B.-S. Processing of chromium tungsten nitride hard coatings for glass molding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, G.; Mayrhofer, P.H.; Kutschej, K.; Mitterer, C.; Kathrein, M. Magnéli phase formation of PVD Mo–N and W–N coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 3335–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.38 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 5.3 | 1.3 | 0.4 | rest |
| Ar/Kr Flow | 120 sccm/80 sccm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure | 500 mPa, N2 Controlled (N2 Flow: ~320 sccm) | ||||||
| Heating Power | 5 kW (Substrate Temperature: ~400 °C) | ||||||
| Bias | −120 V | ||||||
| Target | Mode | (Average) Cathode Power [kW] | |||||
| 2 × AlCr24 | DC | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| 1 × Cr | DC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 × Si | DC | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 1 × W | HiPIMS | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| W-HiPIMS Power (kW) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al/Cr | 1.23 | 1.22 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.21 |
| W/Cr | 0 | 0.45 | 0.80 | 1.07 | 1.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tillmann, W.; Fehr, A.; Stangier, D. Impact of Tungsten Incorporation on the Tribomechanical Behavior of AlCrWxSiN Films at Room and Elevated Temperature. Coatings 2021, 11, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11091033
Tillmann W, Fehr A, Stangier D. Impact of Tungsten Incorporation on the Tribomechanical Behavior of AlCrWxSiN Films at Room and Elevated Temperature. Coatings. 2021; 11(9):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11091033
Chicago/Turabian StyleTillmann, Wolfgang, Alexander Fehr, and Dominic Stangier. 2021. "Impact of Tungsten Incorporation on the Tribomechanical Behavior of AlCrWxSiN Films at Room and Elevated Temperature" Coatings 11, no. 9: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11091033
APA StyleTillmann, W., Fehr, A., & Stangier, D. (2021). Impact of Tungsten Incorporation on the Tribomechanical Behavior of AlCrWxSiN Films at Room and Elevated Temperature. Coatings, 11(9), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11091033






