The Effect of Match between High Power Impulse and Bias Voltage: TiN Coating Deposited by High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering
Abstract
1. Introduction
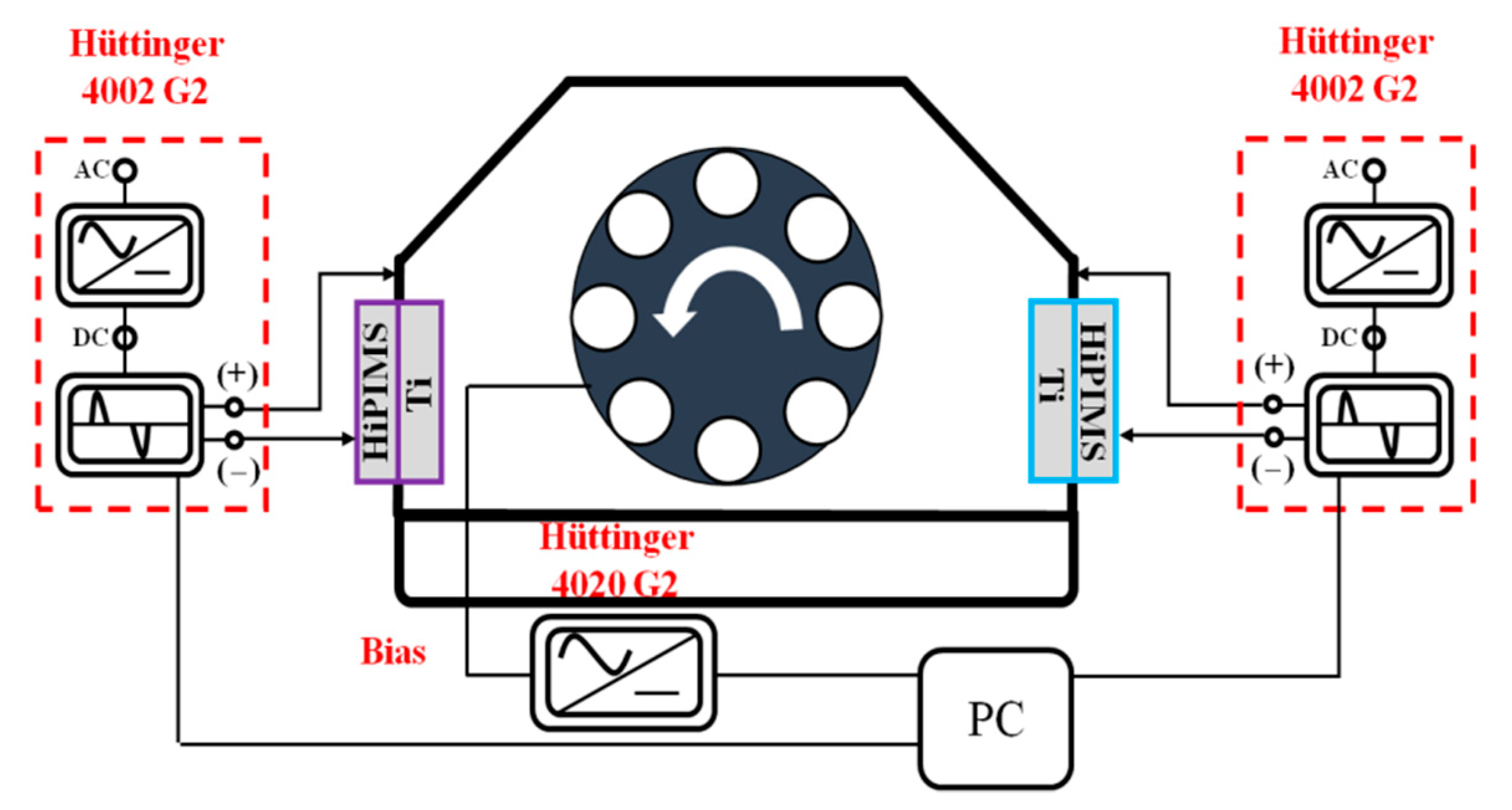
2. Experiment Details
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
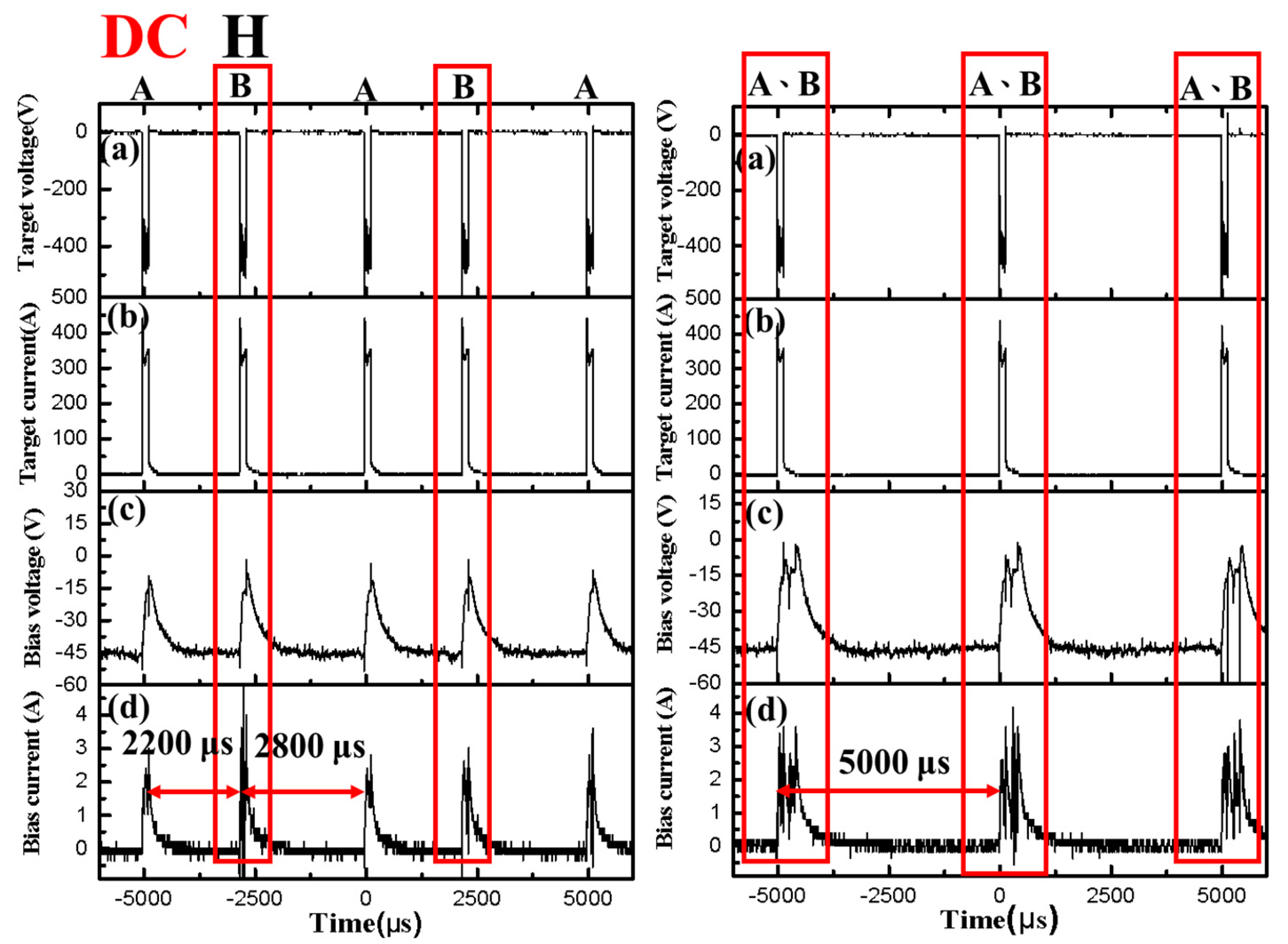
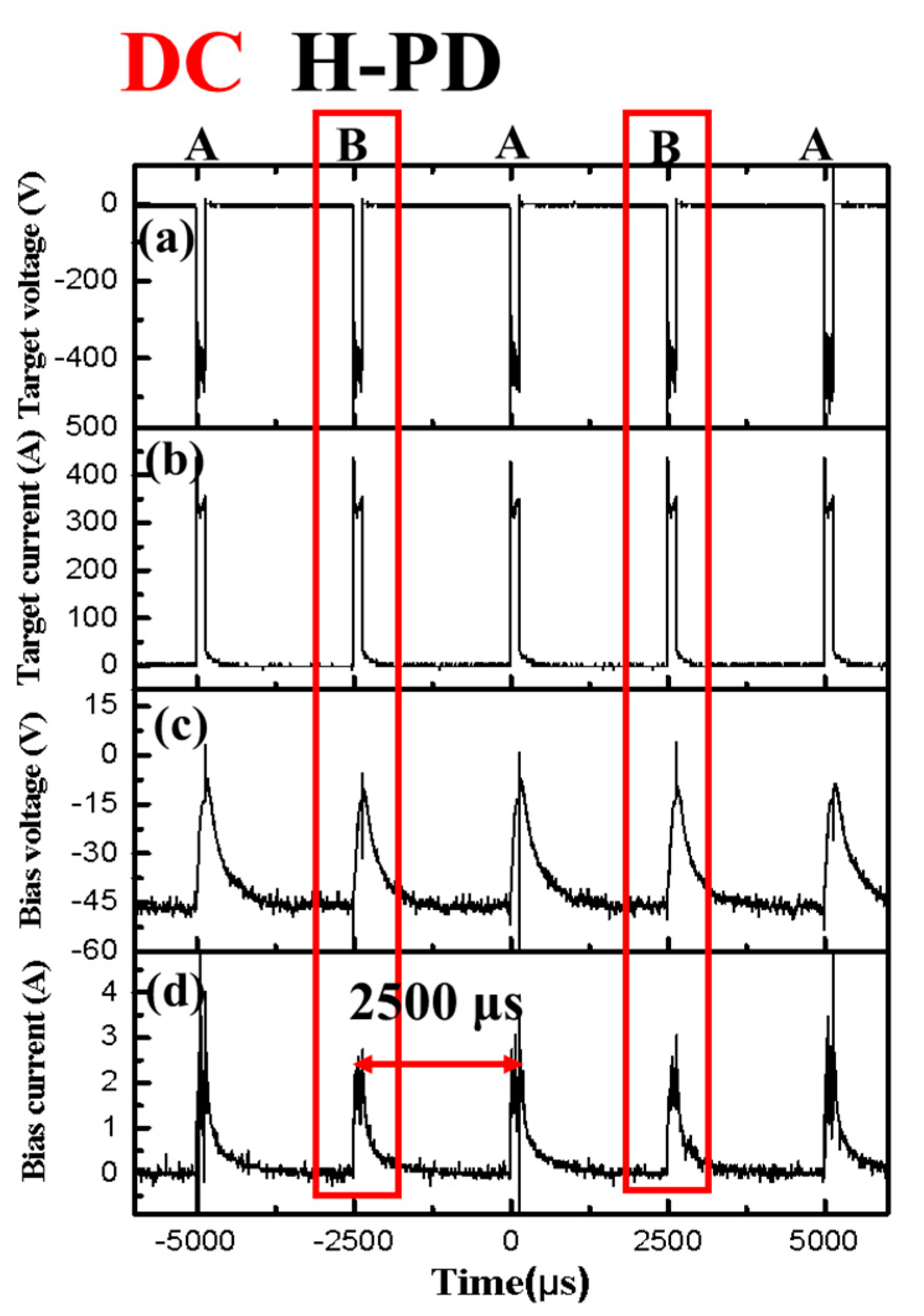
- The Ib waveforms revealed that the output interval affected the Ib value. The Ib increased when the time interval was changed from random to regular (DC or pulsed-DC). Furthermore, FF setting can be used to reduce Vb.
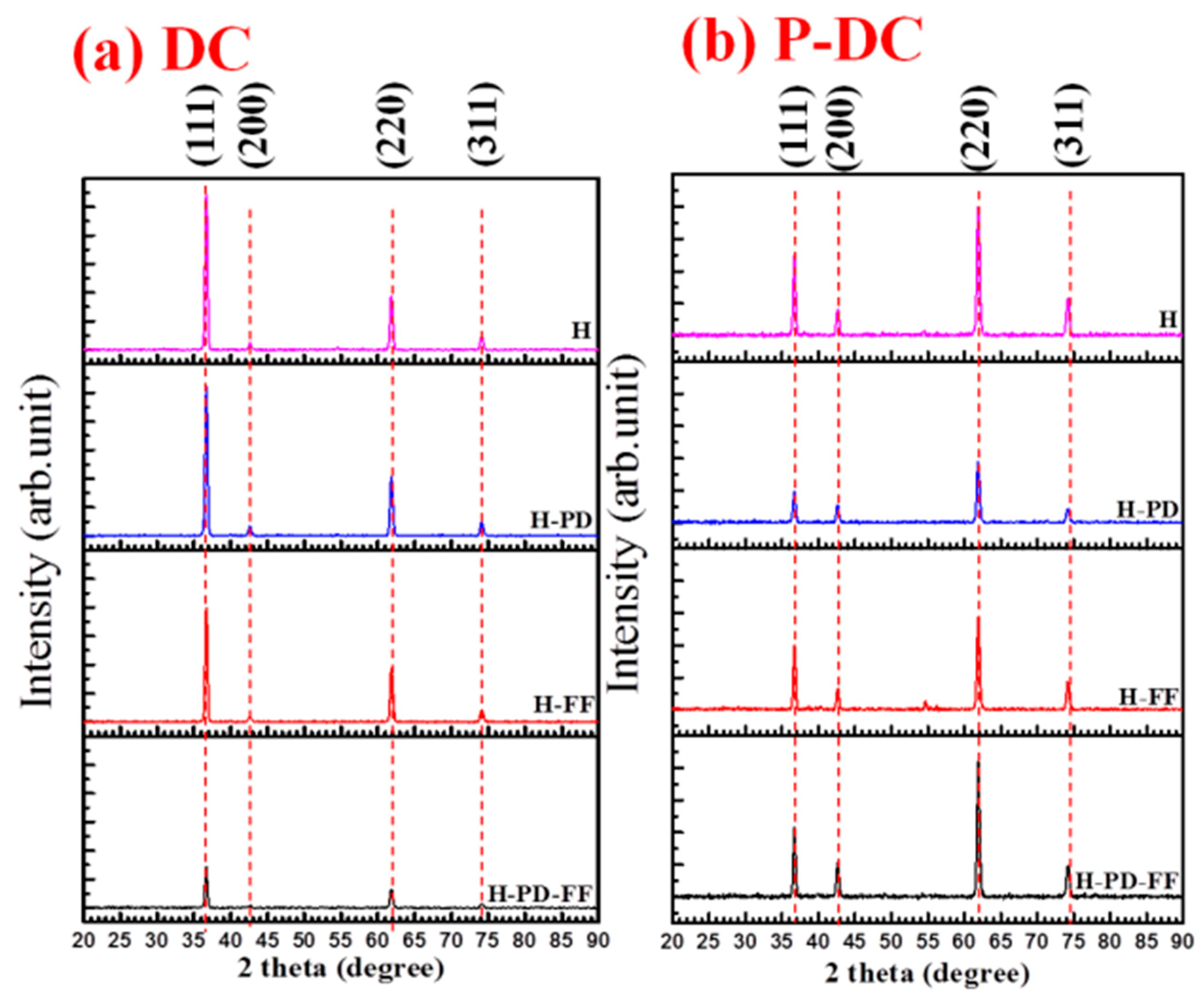
- XRD analysis revealed that TiN exhibited a strong (111) preferred orientation under DC mode and a strong (220) preferred orientation under pulsed-DC mode. This can be attributed to higher substrate current and ion bombardment energy, which also increased the deposition rate and final thickness of TiN.
- The highest hardness values achieved in the current study (23.2 GPa) were obtained in PD and FF modes under DC bias. This can be attributed to a high (111) texture coefficient and high residual stress. The value of hardness and residual stress are inversely proportional to Vb. This can be attributed to the variation of Vb being smaller than the texture coefficient.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ichimura, H.; Rodrigo, A. The correlation of scratch adhesion with composite hardness for TiN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 126, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, H.; Rodriguez, F.; Rodrigo, A. The composite and film hardness of TiN coatings prepared by cathodic arc evaporation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 127, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, D.; Patscheider, J. A complete and self-consistent evaluation of XPS spectra of TiN. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2012, 185, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.Q.; Noda, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Ohsawa, T.; Komiyama, H. Initial growth and texture formation during reactive magnetron sputtering of TiN on Si(111). J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2002, 20, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyomsoan, S.; Grant, W.; Olson, D.; Mishra, B.; Niyomsoan, S.; Grant, W.; Olson, D.; Mishra, B. Variation of color in titanium and zirconium nitride decorative thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2002, 415, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, B.; Kornmann, M.; Amiguet, J. Hard decorative TiN coatings by ion plating. Thin Solid Film. 1977, 45, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.; Pilkington, A.; Dowey, S. Studies on the effect of arc current mode and substrate rotation configuration on the structure and corrosion behavior of PVD TiN coatings. Coatings 2017, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, S.; Acharya, R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Paul, S. Effect of substrate bias voltage on structural and mechanical properties of pulsed DC magnetron sputtered TiN–MoSx composite coatings. Vacuum 2010, 84, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; Braucke, T.V.; Liu, Z.; Arnell, R.; Doyle, E. Pulsed DC titanium nitride coatings for improved tribological performance and tool life. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattemann, M.; Helmersson, U.; Greene, J. Fully dense, non-faceted 111-textured high power impulse magnetron sput-tering TiN films grown in the absence of substrate heating and bias. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 518, 5978–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-L.; Ho, C.-T.; Chen, P.-H.; Chen, W.-C.; Wang, D.-Y.; Wu, W.-Y. Synergetic effect for improved deposition of titanium nitride films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, A. A review comparing cathodic arcs and high power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 257, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, A. Discharge physics of high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulitsch, J.; Schenkel, M.; Zufraß, T.; Mayrhofer, P.; Münz, W.-D. Structure and properties of high power impulse magnetron sputtering and DC magnetron sputtering CrN and TiN films deposited in an industrial scale unit. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 518, 5558–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmkhah, H.; Attarzadeh, F.; Fattah-Alhosseini, A.; Kim, K.H. Microstructural and electrochemical comparison between TiN coatings deposited through HIPIMS and DCMS techniques. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnus, F.; Ingason, A.S.; Olafsson, S.; Gudmundsson, J.T. Nucleation and resistivity of ultrathin TiN films grown by high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2012, 33, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Seyfi, P.; Farhadizadeh, A.; Ghomi, H. The experimental approach into the influence of external inductance on the discharge characteristic of HiPIMS. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2019, 13, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubička, Z.; Gudmundsson, J.T.; Larsson, P.; Lundin, D. Hardware and power management for high power impulse magnetron sputtering. High Power Impulse Magn. Sputtering 2020, 49–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, D.; Ghosh, A.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Paul, S. Effect of target frequency, bias voltage and bias frequency on micro-structure and mechanical properties of pulsed DC CFUBM sputtered TiN coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3684–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruvenket, S.; Rao, G.M. Effect of ion bombardment and substrate orientation on structure and properties of titanium nitride films deposited by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2002, 20, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cooke, K.; Hampshire, J.; Southall, W.; Teer, D. Industrial application of pulsed DC bias power supplies in closed field unbalanced magnetron sputter ion plating. Surf. Eng. 2004, 20, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, W.; Fessmann, J.; Kampschulte, G.; Ebberink, J. Improved control of TiN coating properties using cathodic arc evaporation with a pulsed bias. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1991, 49, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoney, G.G. The tension of metallic films deposited by electrolysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1909, 82, 172–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Y.X.; Lin, J.; Tong, S.; Che, H.L.; Sproul, W.D.; Lei, M.K. Wear and corrosion resistance of CrN/TiN superlattice coatings deposited by a combined deep oscillation magnetron sputtering and pulsed dc magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Kan, J.; Liu, Z. The structure and toughness of TiN coatings prepared by modulated pulsed power magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2016, 125, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, H.; Xiao, W.; Deng, H.; Zou, S.; Ren, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhou, X. Substrate bias effects on mechanical properties and high temperature oxidation performance of sputtered TiN-coated Zr-4. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 524, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; He, J.; Hon, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of surface layer obtained by plasma nitriding and/or TiN coating on high speed steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1994, 64, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurkmans, T.; Lewis, D.; Paritong, H.; Brooks, J.; Münz, W. Influence of ion bombardment on structure and properties of unbalanced magnetron grown CrNx coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 114, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Kuo, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-J.; Chang, L.-C.; Liu, K.-T. Effects of substrate bias frequencies on the characteristics of chromium nitride coatings deposited by pulsed DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 203, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Jung, D.; Na, H.; Joo, J.; Lee, J. The properties of (Ti,Al)N coatings deposited by inductively coupled plasma assisted d.c. magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 142–144, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Hon, M. Texture formation in titanium nitride films prepared by chemical vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 8047–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungcrantz, H.; Odén, M.; Hultman, L.; Greene, J.; Sundgren, J.E. Nanoindentation studies of single-crystal (001)-,(011)-, and (111)-oriented TiN layers on MgO. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 80, 6725–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-C.; Zheng, Y.-Z.; Chen, Y.-I. Mechanical properties of Zr–Si–N films fabricated through HiPIMS/RFMS co-sputtering. Coatings 2018, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ke, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, A. Influence of substrate negative bias on structure and properties of TiN coatings prepared by hybrid HIPIMS method. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Rajendran, N. Effect of nitrides on the corrosion behaviour of 316L SS bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC). Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Zhu, L.; Dong, C.; Xiao, K. Corrosion and interfacial contact resistance of 316L stainless steel coated with magnetron sputtered ZrN and TiN in the simulated cathodic environment of a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 363, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


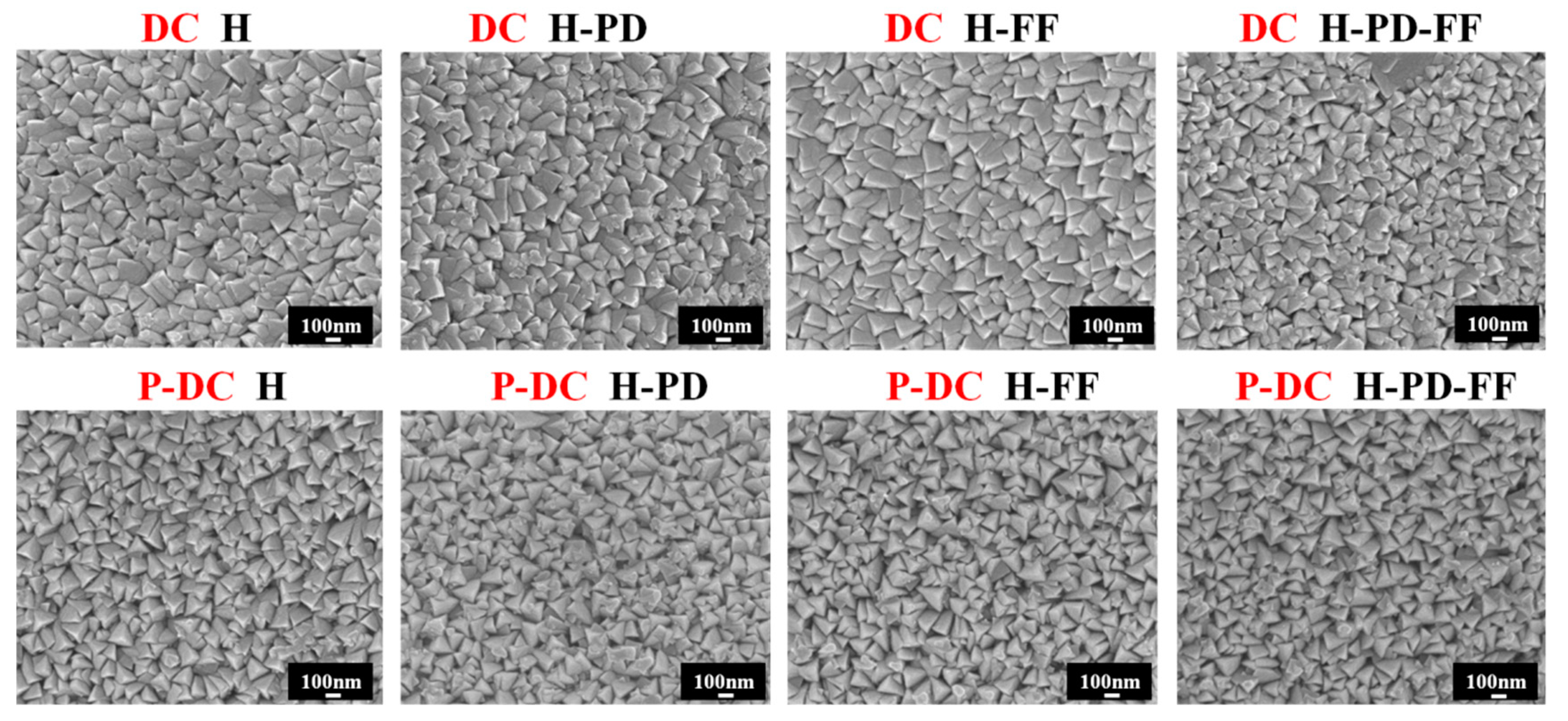
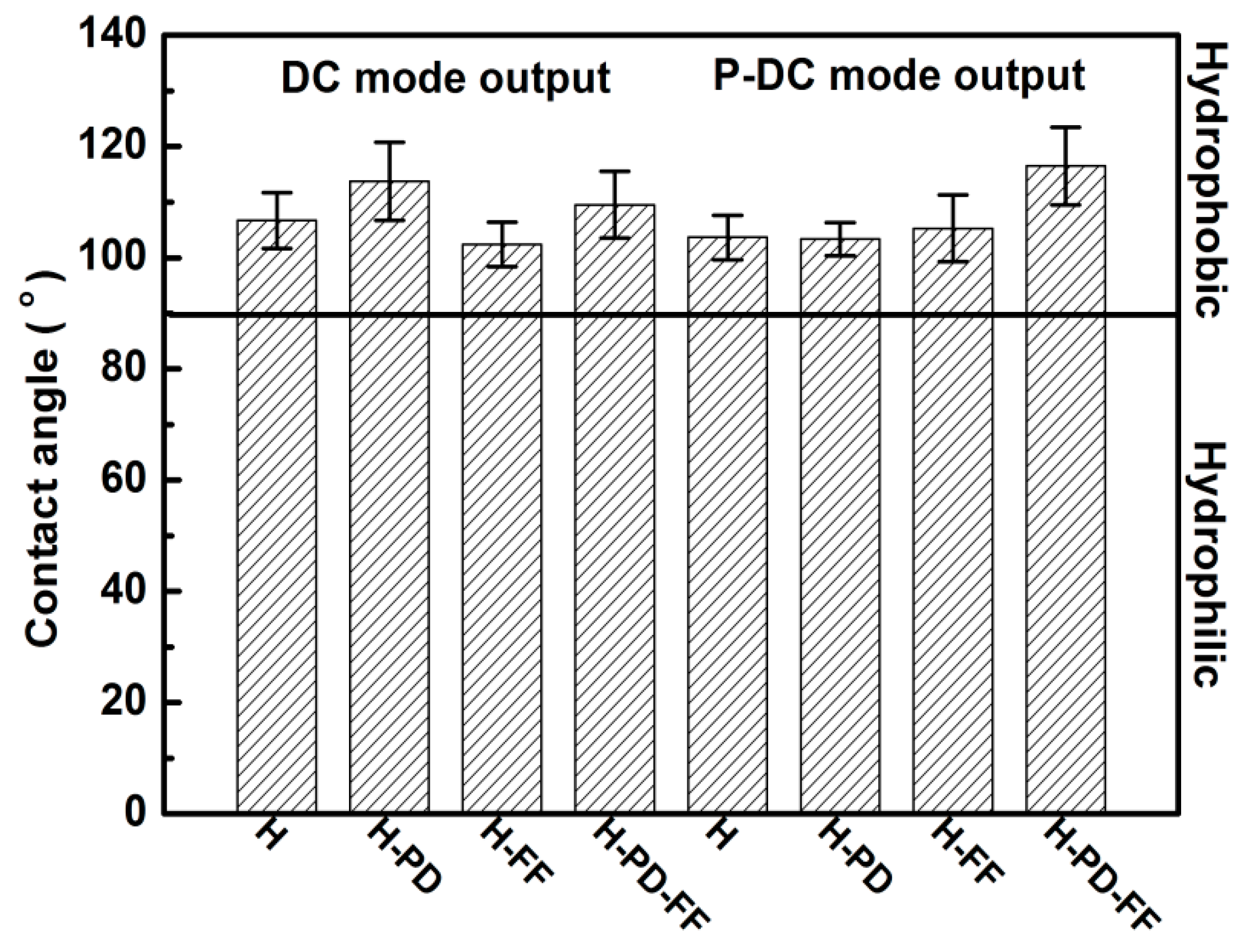
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Target to substrate distance (mm) | 150 |
| Working pressure (Pa) | 0.4 |
| N2/Ar flow ratio (%) | 9 |
| Deposition time of TiN coating (min) | 180 |
| Duty cycle (%) | 3 |
| Pulse frequency (Hz) | 200 |
| Pulse on-time/off-time (μs) | 150/4850 |
| Bias voltage mode | DC, pulsed-DC |
| Sample Name | Peak Power (W) | Peak Power Density (W/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| DC H | 181,662 | 454 |
| DC H-PD | 179,142 | 448 |
| DC H-FF | 181,770 | 454 |
| DC H-PD-FF | 179,580 | 449 |
| P-DC H | 181,770 | 454 |
| P-DC H-PD | 181,770 | 454 |
| P-DC H-FF | 178,808 | 447 |
| P-DC H-PD-FF | 182,208 | 455 |
| Sample Name | Interval Time (2500 μs) | Ib (A) | Vb (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC H | × | 0.56 | −30.8 |
| DC H-PD | ○ | 0.60 | −31.1 |
| DC H-FF | × | 0.64 | −32.5 |
| DC H-PD-FF | ○ | 0.67 | −32.6 |
| P-DC H | × | 0.71 | −32.8 |
| P-DC H-PD | ○ | 0.73 | −32.9 |
| P-DC H-FF | × | 0.80 | −33.7 |
| P-DC H-PD-FF | ○ | 0.84 | −34.9 |
| Sample Name | Hardness (GPa) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Texture Coefficient | Residual Stress (GPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (111) | (220) | ||||
| DC H | 23.2 ± 0.7 | 371 ± 6.7 | 1.78 | 1.15 | −0.68 |
| DC H-PD | 23.2 ± 0.3 | 380 ± 11.5 | 1.67 | 1.24 | −0.58 |
| DC H-FF | 22.7 ± 1.1 | 385 ± 14.5 | 1.58 | 1.35 | −0.57 |
| DC H-PD-FF | 22.8 ± 1.0 | 367 ± 9.6 | 1.58 | 1.37 | −0.46 |
| P-DC H | 19.1 ± 0.7 | 318 ± 4.6 | 0.70 | 2.11 | −0.26 |
| P-DC H-PD | 18.5 ± 0.7 | 321 ± 13.7 | 0.58 | 2.15 | −0.20 |
| P-DC H-FF | 19.0 ± 1.0 | 315 ± 9.4 | 0.76 | 2.04 | −0.20 |
| P-DC H-PD-FF | 19.3 ± 0.7 | 327 ± 6.5 | 0.59 | 2.17 | −0.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Yang, F.-C.; Tang, J.-F. The Effect of Match between High Power Impulse and Bias Voltage: TiN Coating Deposited by High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings 2021, 11, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070822
Chang C-L, Lin C-Y, Yang F-C, Tang J-F. The Effect of Match between High Power Impulse and Bias Voltage: TiN Coating Deposited by High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings. 2021; 11(7):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070822
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Chi-Lung, Ching-Yen Lin, Fu-Chi Yang, and Jian-Fu Tang. 2021. "The Effect of Match between High Power Impulse and Bias Voltage: TiN Coating Deposited by High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering" Coatings 11, no. 7: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070822
APA StyleChang, C.-L., Lin, C.-Y., Yang, F.-C., & Tang, J.-F. (2021). The Effect of Match between High Power Impulse and Bias Voltage: TiN Coating Deposited by High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings, 11(7), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070822







