Abstract
Zinc oxide (ZnO) and porous anodic aluminum oxide (PAAO) are technologically important materials, rich with features that are of interest in optical applications, for example, in light-emitting and sensing devices. Here, we present synthesis method of aligned ZnO nanorods (NR) with 40 nm diameter and variable length in 150 to 500 nm range obtained by atomic layer deposition (ALD) of ZnO in pores of continuously variable thickness PAAO. The relative intensity of yellow (1.99 eV), green (2.35 eV), and blue (2.82 eV) photoluminescence (PL) components originating from the different types of defects, varied with non-monotonic dependency on the composite film thickness with a Fabry–Pérot like modulation. The intensity variation of any individual PL component correlated well with anti-reflective properties of ZnO NR–PAAO composite film at the peak wavelength of the particular PL component. This provides a route for selective enhancement or suppression of color components of hybrid fluorescent emitters by tuning only geometric parameters, with potential use in imaging and other optical devices. As an application example we tested the composite film for sensing of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using a widely accessible fluorescence microscopy setup. The intensity of the yellow and green PL components reduced in response to increased VEGF concentrations, whereas blue component remained invariant.
1. Introduction
Arrays of aligned nanorods (NR), including nanowires, nanotubes, or nanopillars, with well-defined morphology that is necessary for modeling and engineering of nanomaterials with desired optical properties [1]. Aligned ZnO NR with diameters below 100 nm and length in the sub-micrometer range can be produced using different methods, including hydrothermal growth [2,3], pulsed laser deposition [4], electrochemical deposition [5], radio frequency magnetron sputtering [6], and others [7]. The placement of individual NR in an array can be controlled by lithographic patterning the ZnO seed film [8] or masking the seed layer [9] prior ZnO growth. A viable route to lithography-free ZnO NR array production involves use self-organized templates such as porous anodic aluminum oxide (PAAO) membranes [5,10,11,12,13,14]. PAAO, also called nanoporous anodic alumina (NAA), is a well-known highly ordered material that can be obtained with various pore diameters, most commonly arranged in hexagonal arrays. Pore to pore distances can be selected by the choice of electrolyte solution and anodizing voltage [15]. It is a very universal template for hosting many different materials. In our previous works, PAAO was used to produce nanowires of germanium [16], antimony sulfide [17], gold [18], arrays of metal and diamond nanoparticles [19,20,21], as well as different types of nanostructured metal-insulator-metal systems [22,23]. Recently ZnO NR arrays in PAAO templates were produced using atomic layer deposition (ALD) [24,25,26,27,28], a technique that is capable to uniformly coat surfaces with a nearly arbitrary topology, including pores with high aspect ratio [29].
One of the key properties of ZnO nanostructures is strong photoluminescence (PL) that can be observed at room temperature (RT) and typically consists of a ultraviolet (UV) band near 3.37 eV (380 nm) corresponding to exciton recombination and a broad visible band containing several components that are associated with defects and impurities [1]. Similarly PL can be observed in PAAO [30], but in comparison to ZnO it is relatively weak [31].
Several studies have demonstrated PL dependence on ZnO NR geometry [1,4,25,27,32,33]. However, systematic evaluation of morphology effects on PL has been difficult, due to different processes required to produce various shapes and sizes of ZnO nanostructures, which may significantly impact the optical properties due to variations of defect or impurity concentration. For example, reduction of visible PL was observed after annealing of ZnO NR in air and attributed to decrease of number of oxygen vacancies [31]. Furthermore, studies that use the same process with systematic parameter variation require production of many samples, which can be time consuming and difficult to reproduce. As a result, important phenomena may be overlooked in analysis of undersampled data sets. In particular, thin film interference in luminescent layers [34] is often ignored.
In this work, we demonstrate a method to produce aligned ZnO NR embedded in PAAO with virtually continuous length variation and fixed diameter. PAAO with controlled thickness gradient [35] was filled with ZnO using ALD [36]. The subcomponents of visible PL from ZnO NR–PAAO composite film on aluminum substrate varied with periodicity depending on NR length (PAAO thickness), indicating that thin-film interference effects must be taken into account when analyzing PL of NR arrays. This observation can be generalized to other luminescent films, for example, electroluminescent materials [37], when the film thickness is in the range of the wavelength of light.
With the continuous variation of the film thickness, we can analyze the morphology influence on the PL with a fine resolution over large thickness interval. There are many articles where PL change with film thickness was observed; however, due to the limited number of samples, the relation may appear random or aliased. Here, by analyzing the PL signal at different wavelengths and continuous film thickness variation, we show that basic interference causes significant modulation of the intensity of the measured PL components. The interference can also result in apparent spectral shift of observable peak energies of the PL components, which often causes ambiguity in interpretation of PL data. In our case, the PL intensity showed clear negative correlation with the coefficient of reflection at the same wavelength as the center of the particular subcomponent. This is similar to observations on Si-ZnO core–shell nanowires [36], where samples with low reflectivity had highest PL intensity. However, the results are opposite to observations in porous silicon layers [38], where positive correlation between the reflectivity and PL was reported.
Recently, ZnO nanostructures have been proposed for biosensing using different readout schemes, including photocurrent measurements [39,40,41], combination of ellipsometry and the surface plasmon resonance [42], UV photoluminescence [43], and others. Different physical mechanisms of molecule interaction with ZnO for biosensing have been described, for example, charge transfer, and hydrophobic and electrostatic interaction between the biomolecule and ZnO surface [44]. Sensing can be based on reduction of PL intensity which is typically is observed in the UV band [43]. For testing the applicability of the obtained ZnO NR–PAAO composites for fluorescent biosensing, we observed changes of visible PL in response to exposure to various concentrations of human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is a glycosylated protein and initiates angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. VEGF is secreted by tumor cells and can serve as the cancer biomarker. Elevated levels of VEGF in human body fluids (blood serum and tears) can be associated with many other diseases, for example, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetic retinopathy, and others [45,46,47,48]. In our study, we use hybrid ZnO NR–PAAO film for detection of secreted homodimer isoform VEGF165. The advantage of present detection scheme is that it can be implemented using a commonly available fluorescence microscopy setup.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ZnO NR–PAAO Hybrid Film
PAAO templates were produced from high purity (99.999%) bulk aluminum sheet (GoodFellow) using a modified two-step anodization protocol in 0.3 M oxalic acid electrolyte at constant 40 V voltage [20,49] with the key difference that during the second anodization step the sample was gradually withdrawn from the electrolyte solution, which terminated the pore growth at different time moments [35]. At a 4.6 mm/min withdraw rate, continuously variable thickness (from approximately 100 nm to above 500 nm) PAAO membranes were produced on the same sample (typically 9 mm wide and 18 mm long). The thickness gradient was produced in the direction of the longer dimension, referred as the x-coordinate. The hexagonal pore arrangement with nearest neighbor center-to-center distance 100 nm and pore diameter 40–50 nm was confirmed using scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi 4800, Tokyo, Japan). Full details on variable thickness PAAO synthesis can be found in [35].
The ZnO layer was deposited on variable-thickness PAAO template via atomic layer deposition (ALD) at low temperature (100 °C) using home-built setup [50]. Briefly, diethyl zinc (DEZ CAS: 557-20-0, purity > 95%, Strem Chemicals, Bischheim, France) and deionized water were used as precursors in a cycle consisting of 0.2 s pulse of DEZ, 40 s exposure, and 60 s purge with argon, followed by 2 s pulse of H2O, 40 s exposure to DEZ, and 60 s purge with argon. 175 cycles were used to achieve 35 nm ZnO thickness. For reference measurements samples with a fixed PAAO thickness, an electropolished Al sample without PAAO and a silicon wafer chip (Ted Pella, Inc. 16007, Redding, CA, USA) were coated with ZnO in the same ALD batch.
PL spectra were recorded using a fiber-coupled spectrometer (Ocean Optics USB4000, Largo, FL, USA) attached to a microscope (Olympus IX 71, Tokyo, Japan) with a 10× objective lens (CPLNFLN 10XPH, NA 0.3), Hg lamp light source (U-LH100HG, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and fluorescence filter set (U-MWU2, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). For reflectivity measurements the same optical system was used with a halogen lamp (U-LH100-3, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) light source and neutral density filter set (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). A programmable motorized microscope table (PRIOR) was used to record PL and reflection spectra from the same set of spots with different ZnO NR in PAAO composite film thicknesses. The spot size was 40 µm in diameter using an optical fiber with a 200 µm core (Thorlabs M25L02) 10× objective lens and a 0.5× ocular adapter.
Crystallographic properties of samples were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD, PANalytical X’Pert-PRO diffractometer, Eindhoven, The Netherlands).
2.2. Functionalization for Biosensing
Recombinant VEGF165 expressed in HEK 293 cells was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany, processed according to manufacturer’s recommendations. Before measurements it was diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to required concentration. The anti-VEGF165 DNA aptamer SL2-B (5′-CAATTGGGCCCGTCCGTATGGTGGGT-3′) [51] with 3′-thiol-modifier-C6 was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck), reduced with DL-dithiothreitol (DTT) and purified using NAP-10 (Cytiva) columns according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. (3-Aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES, Sigma-Aldrich) was used for silanization of ZnO/PAAO/Al surfaces. The samples were dipped in APTES solution (5% APTES solution in toluene) and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. After that, samples were washed with toluene and isopropanol, and dried. The silanized samples were dipped in 1 mM 3-maleimidobenzoic acid N-hydroxysuccinimide solution in a 1:9 (v/v) mixture of dimethyl sulfoxide and PBS for 1 h [52]. After that, samples were rinsed with PBS, immersed in 10 µM solution of 3′ thiolated DNA aptamer SL2-B, and incubated overnight (16 h). After functionalization of ZnO surface with aptamer, samples were washed with PBS. To avoid nonspecific protein–ZnO surface interactions, the sample was dipped in 1% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) blocking solution in PBS for 30 min. After the surface blocking treatment, samples were washed with PBS and immediately used for photoluminescence measurements.
3. Results and Discussion
SEM analysis of scratches made at regular intervals in the ZnO NR–PAAO hybrid film on Al substrate (Figure 1) revealed that pores at different locations were equally filled with ZnO independently from pore depth. The pore diameter and consequently NR diameter remains constant, approximately 40 nm. The ZnO NR appear to have granular structure and an empty core. The integrity of nanorods was checked on a separate fixed-thickness sample by selective dissolution of Al substrate in a mixture of 0.37 M CuCl2/1 M HCl solution and 10 wt % FeCl3 in volume ratio 1:3 [20]. Subsequently, the PAAO matrix was dissolved by a carbonate buffered NaOH solution (pH 10) for 11 min at 60 °C temperature [53]. As can be seen in Figure 2a, the nanorods are intact and continuous, have equal length, and form a freestanding array with ordering, replicating PAAO pore geometry.
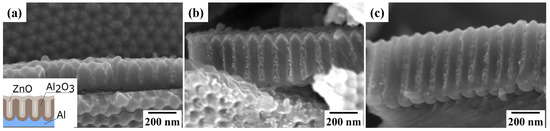
Figure 1.
(a–c) Cross section SEM images of variable-thickness ZnO NR–PAAO hybrid film from the same sample at different positions (x coordinates). The inset shows a schematic of the sample morphology.
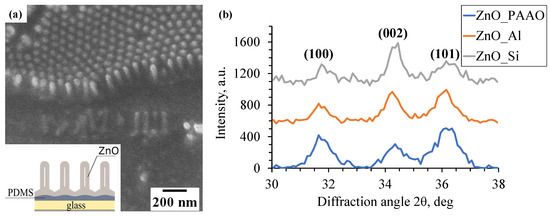
Figure 2.
(a) SEM image of free standing ZnO NR array obtained by transferring ZnO NR–PAAO hybrid film to a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-coated glass slide and selective removal of Al substrate and PAAO matrix. The inset shows a schematic of the sample morphology. (b) XRD spectra of ZnO thin film on Si, electropolished Al and PAAO/Al substrates.
XRD spectra (Figure 2b) of the ZnO layer on Si, electropolished Al, and Al with PAAO show the diffraction peaks at 2 = 31.77°, 34.38°, 36.18°, corresponding to (100), (002), and (101) reflection planes of hexagonal wurtzite structure of ZnO [54,55,56]. The average crystallite size D of the ZnO layer on different substrates was calculated using the Scherrer equation: , where k, , , and are crystallite shape factor (), full width of half maximum, diffraction angle, and X-ray wavelength ( = 0.154 nm), respectively [57]. The obtained crystallite size values of ZnO/Si, ZnO/Al and ZnO/PAAO/Al were 12.5 ± 3.5, 11 ± 2 and 8.0 ± 0.8 nm.
For nondestructive and much faster measurement of composite layer thickness, reflectance spectra were recorded from different spots and fitted to a multilayer model, based on propagation and matching matrices at each interface [58] with realistic complex refractive index values taken from spectroscopic ellipsometry measurements [22] and tabulated materials data.
We found that the following layer stack gave satisfactory fit for thickness determination: (i) aluminum substrate had values by Rakić et al. [59]; (ii) a fixed 40 nm thickness barrier layer was described by effective values from Bruggeman model [60] with 20% Al and 80% Al2O3 [61]; (iii) for porous PAAO/ZnO/void layer with thickness to be determined by fitting, a fixed effective value was used; (iv) and, finally, for the 35 nm ZnO layer we used a refractive index value of 1.95 [42]. Typical fitted reflectance spectra along with measured data are shown in Figure 3a,b. The total film thickness obtained by fitting the above model to the reflectance measurements agreed well with the cross-section measurements by SEM (Figure 3c). The optical approach had the advantage that layer thickness and consequently ZnO NR length could be measured continuously and rapidly across entire sample without dissection. The hybrid layer thickness varied linearly depending on lateral sample coordinate (Figure 3d) with minor jumps due to crystallographic grain structure of the aluminum substrate [35].
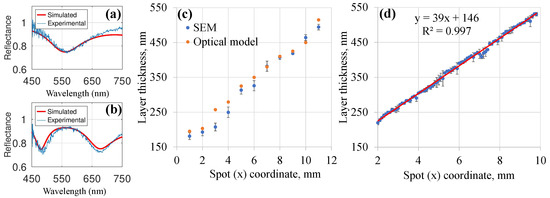
Figure 3.
(a,b) Measured and calculated reflectance spectra at different layer thicknesses, 260 and 520 nm, of ZnO NR–PAAO hybrid film on Al substrate. (c) Comparison of hybrid film thickness measurements at different sample positions (x coordinate) obtained by SEM and fitting the reflectance spectra (optical model). (d) Hybrid film thickness profile obtained using reflectance measurements.
Under the UV illumination from a Hg lamp, the PL from the ZnO NR–PAAO hybrid film was observed with various colors, that changed depending on the film thickness (Figure 4a–c). The “political map” like patterns in the microscopy images were caused by regions of different PAAO film thicknesses that originate in variations of PAAO growth rate on different crystallographic grain orientations in the Al substrate [22]. Although decomposition of PL spectra in Gaussian components is a common practice and could reproduce experimental data with a pleasing accuracy (Figure 4d–f), the peak positions of individual Gaussians only approximately matched the known PL bands associated with the emission from various ZnO defects [62]. Furthermore, the peak positions and the relative intensities changed depending on the ZnO NR–PAAO hybrid film thickness. One may expect that in the absence of interference effects the PL signal would simply scale with the amount of material in the detection volume, as the composition of the hybrid film is the same across entire sample. However, PL intensity at specific wavelengths showed undulating dependency on film thickness as will be discussed shortly. Note that PAAO also contributes to PL emission in approximately the same wavelength range, however, in comparison to ZnO a much weaker PAAO photoluminescence intensity was reported from similar structures [31].
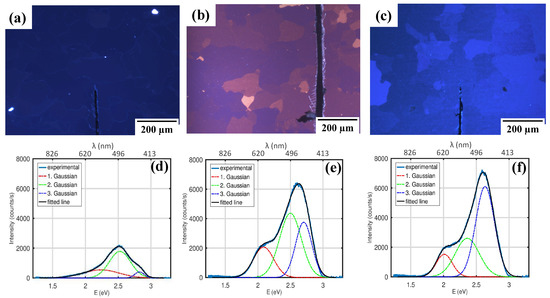
Figure 4.
(a–c) PL microscopy images of ZnO NR–PAAO hybrid film on Al substrate from regions with different thickness (a) 190 nm, (b) 300 nm, and (c) 500 nm. (d–f) Corresponding PL spectra with decomposition in Gaussian components.
For reference and comparison, PL spectra were also measured from 35 nm ZnO layers that was obtained by ALD on electropolished Al surface, Si surface as well as 230 nm thick PAAO layer on Al substrate with empty pores (Figure 5). As 35 nm ZnO thickness is much smaller than the wavelength of the visible light, the PL spectra can be assumed to be free from interference effects. Gaussian components of PL from ZnO on Al (Figure 5a) had center positions at 1.99, 2.35, and 2.82 eV, which corresponded well to known yellow (2.0 eV), green (2.48 eV), and blue (2.78 eV) PL components, respectively, associated with different types of oxygen vacancies [63]. Other possible origins of yellow and green PL, including Zn vacancies [64] have been considered. The same components could be identified in PL from 35 nm thick ZnO on Si (Figure 5b). PL spectrum from an empty 230 nm thick PAAO (Figure 5c) looks similar to the thin ZnO but is somewhat blue-shifted. Previously reported PL from PAAO samples, that were produced using the same 0.3 M oxalic acid protocol at 40 V anodization voltage [65] but excited using a different light source, contained only two Gaussian components centered at 2.64 eV (470 nm) and 2.80 eV (443 nm) that were identified as emission by oxygen vacancies and oxalic impurities. We note that there are ambiguities in the reports in experimental PL studies of PAAO [66] but further analysis is beyond the scope of present article.
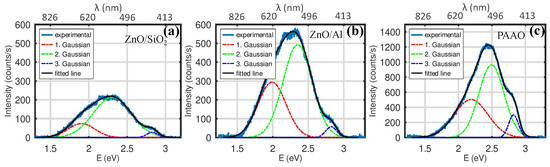
Figure 5.
PL spectra of 35 nm ZnO on (a) electrochemically polished Al and (b) Si wafer. (c) PL spectrum of 230 nm PAAO on Al without ZnO.
In order to demonstrate the significance of interference, we plotted the PL signal at specific wavelengths that correspond to center positions of identified yellow, green, and blue components of ZnO as a function of film thickness (Figure 6). In the same graph, we plot the calculated and measured coefficient of reflection at the same wavelengths. The periodic variation in reflectance was caused by basic thin-film interference as confirmed by model calculations using the same multilayer stack as was used for the composite film thickness measurements.
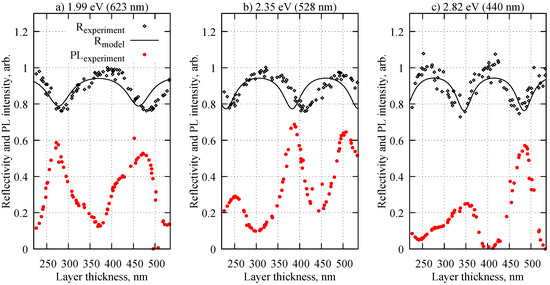
Figure 6.
Coefficient of reflection and PL intensity (not to scale) depending on ZnO NR–PAAO hybrid film thickness recorded at specific wavelengths that correspond to (a) yellow, (b) green, and (c) blue components in reference spectrum of 35 nm ZnO on Al surface (see main text).
The PL intensity showed opposite behavior to reflectance, the PL maxima occur at nearly the same layer thicknesses as reflectance minima. The correlation coefficients between all three PL components and measured reflectance were negative, −0.52 at 1.99 eV, −0.16 at 2.35 eV, and −0.70 at 2.82 eV. This is a strong indication that both signals are modulated by the same physical process, namely, interference. Indeed, the PL dependency on layer thickness is very similar to calculated and measured interference-dependent cathodluminescence in wedged SiO2 films. The deviations from a perfect match may be caused by partial overlapping of ZnO PL bands and additional PL from the PAAO matrix. Interestingly, similar experiments in porous silicon layers [38] on Si substrate resulted in positive correlation between PL and reflectance, which is opposite to our observations. This discrepancy motivates further research, but likely can be explained by different phase flips of electromagnetic wave reflection from different interfaces in multilayer systems. Detailed simulations would be required, but one possible explanation could be the difference in substrates (Al and Si) used in both experiments. Aluminum in the visible wavelength range has a negative real part of the dielectric permittivity [59], but silicon has a positive one [67]. This in turn leads to different boundary conditions and may result in different required film thicknesses for constructive and destructive interference.
Finally, we tested the obtained hybrid films for detection of cancer biomarker VEGF165. Figure 7a shows typical PL spectra obtained from a single spot (40 µm diameter) of a 300 nm thick hybrid film exposed to different concentrations of VEGF165. A response can be observed as change in PL intensity and shift of PL band to shorter wavelengths. Most notably the reduction of intensity can be detected for regions corresponding to yellow (2.1 eV) and green (2.48 eV) PL components. However, the blue (2.78 eV) component remained invariant to VEGF165 presence. Note that the blue PL of ZnO coincides with that of PAAO and originates from defects in the volume of hybrid film. Figure 7b shows variation of the intensity of the green PL component depending on protein concentration at different spots on the same sample. Despite considerable scatter, the correlation between PL intensity and protein concentration is obvious when detected PL is subtracted from the reference signal (Figure 7c). This proof of concept experiment demonstrates that with further improvements a visible fluorescence microscopy setup, accessible in most research facilities, can be used for detection of low concentrations of biomarkers using hybrid ZnO NR–PAAO film.
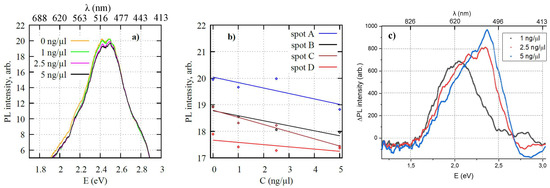
Figure 7.
(a) Typical PL spectra of hybrid film after exposure to different concentrations C of VEGF165 and (b) green PL (2.48 eV) intensity depending on concentrations of VEGF165 recorded at different spots on the same sample. The Pearson correlation coefficients r of between C and PL intensity in spots A, B, C, and D was −0.73, −0.97, −0.96, and −0.79, respectively. (c) Difference between PL spectra of functionalized and BSA-treated sample before and after exposure to different concentrations of VEGF.
4. Conclusions
Continuously variable-length ZnO NR arrays were produced on the same sample by low-temperature ALD using PAAO template with controlled thickness gradient for the first time. The PL signal from ZnO NR–PAAO film did not increase monotonously with film thickness, but showed a periodic intensity modulation attributed to interference effects in luminescent film [34]. The thin-film interference can alter the intensity and apparent peak wavelengths of different PL components. This effect can be easily overlooked when analysis of PL from luminescent films is done based on a limited number of thickness values. Continuous tuning of the film thickness (NR length) enables selective enhancement or suppression of individual PL components by changing only single geometric parameter. This may be useful for development of PL based light emitting or sensing devices.
We have tested the applicability of hybrid ZnO NR–PAAO film on Al as luminescent substrate for biosensing. VEGF was used as a test molecule to determine PL sensitivity to biomarkers that are relevant for cancer diagnostics. The variations of the green PL component showed good correlation with the concentration of VEGF. The advantage of presented biosensor is that it can be implemented using standard fluorescence microscopy components.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.E., J.P. and U.M.; methodology, U.M., J.P., R.P., D.J., O.G. and M.B.; software, A.D., R.P. and J.P.; validation, U.M., A.D. and J.P.; investigation, A.D., D.J., R.P., U.M. and O.G.; resources, D.E. and I.M.; data curation, A.D., U.M. and J.P.; writing—original draft preparation, U.M. and J.P.; writing—review and editing, D.E., M.B., I.M. and J.P.; visualization, A.D., U.M. and J.P.; supervision, D.E. and I.M.; project administration, D.E. and J.P.; funding acquisition, D.E. and J.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Latvian fundamental and applied research program FLPP within project LZP-2020/1-0200 “Nanostructured multilayer hybrid coatings for interferometric and optoelectronic sensors” and European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No: 778157, “Novel 1D photonic metal oxide nanostructures for early stage cancer detection—CanBioSe”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Galina Makarenkova and Līga Avotiņa for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Djurišić, A.B.; Leung, Y.H. Optical properties of ZnO nanostructures. Small 2006, 2, 944–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.X.; Sun, X.W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Lee, Y.C.; Tan, O.K.; Vayssieres, L. Hydrothermally grown oriented ZnO nanorod arrays for gas sensing applications. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4995–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Liao, C.H.; Chueh, Y.L.; Lai, C.C.; Chen, L.Y.; Chu, A.K.; Kuo, C.T.; Wang, H.C. High performance Cu2O/ZnO core-shell nanorod arrays synthesized using a nanoimprint GaN template by the hydrothermal growth technique. Opt. Mater. Express 2014, 4, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fuge, G.M.; Ashfold, M.N. Growth of aligned ZnO nanorod arrays by catalyst-free pulsed laser deposition methods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 396, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.J.; Zhang, L.D.; Li, G.H.; Shen, W.Z. Fabrication and optical properties of large-scale uniform zinc oxide nanowire arrays by one-step electrochemical deposition technique. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 363, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, P.S.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Jeganathan, K. Investigations on the growth and optical properties of one dimensional ZnO nanostructures grown by radio frequency magnetron sputter deposition. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 3811–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willander, M.; Nur, O.; Zhao, Q.X.; Yang, L.L.; Lorenz, M.; Cao, B.Q.; Zúñiga Pérez, J.; Czekalla, C.; Zimmermann, G.; Grundmann, M.; et al. Zinc oxide nanorod based photonic devices: Recent progress in growth, light emitting diodes and lasers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 332001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wei, Y.; Kirkham, M.; Liu, J.; Mai, W.; Davidovic, D.; Snyder, R.L.; Wang, Z.L. Patterned growth of vertically aligned ZnO nanowire arrays on inorganic substrates at low temperature without catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14958–14959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, W.; Guo, R.; Yuan, D.; Das, S.; Wang, Z.L. Wafer-scale High-throughput ordered growth of vertically aligned ZnO nanowire arrays. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3414–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chik, H.; Liang, J.; Cloutier, S.G.; Kouklin, N.; Xu, J.M. Periodic array of uniform ZnO nanorods by second-order self-assembly. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 3376–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Xu, B.; Jie, J.; Han, X.; Li, G.; Li, Q.; Hou, J.G. Non-aqueous cathodic electrodeposition of large-scale uniform ZnO nanowire arrays embedded in anodic alumina membrane. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Hou, J.G. Synthesis and characterization of aligned ZnO nanorods on porous aluminum oxide template. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 11976–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.J.; Lee, W.; Scholz, R.; Dadgar, A.; Krost, A.; Nielsch, K.; Zacharias, M. Arrays of vertically aligned and hexagonally arranged ZnO nanowires: A new template-directed approach. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zapien, J.; Yao, Y.; Meng, X.; Lee, C.; Fan, S.; Lifshitz, Y.; Lee, S. High-density, ordered ultraviolet light-emitting ZnO nanowire arrays. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulka, G.D. Highly ordered anodic porous alumina formation by self-organized anodizing. In Nanostructured Materials in Electrochemistry; Wiley–VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, B.; Prikulis, J.; Grigorjeva, L.; Millers, D.; Daly, B.; Holmes, J.D.; Erts, D. Photoconductivity of germanium nanowire arrays incorporated in anodic aluminum oxide. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 61, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasulaneca, L.; Meija, R.; Livshits, A.I.; Prikulis, J.; Biswas, S.; Holmes, J.D.; Erts, D. Determination of Young’s modulus of Sb2S3 nanowires by in situ resonance and bending methods. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baitimirova, M.; Pastare, A.; Katkevics, J.; Viksna, A.; Prikulis, J.; Erts, D. Gold nanowire synthesis by semi-immersed nanoporous anodic aluminium oxide templates in potassium dicyanoaurate–hexacyanoferrate electrolyte. Micro Nano Lett. 2014, 9, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikulis, J.; Malinovskis, U.; Poplausks, R.; Apsite, I.; Bergs, G.; Erts, D. Optical scattering by dense disordered metal nanoparticle arrays. Plasmonics 2014, 9, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinovskis, U.; Poplausks, R.; Apsite, I.; Meija, R.; Prikulis, J.; Lombardi, F.; Erts, D. Ultrathin anodic aluminum oxide membranes for production of dense sub-20 nm nanoparticle arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 8685–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinovskis, U.; Berzins, A.; Gahbauer, F.; Ferber, R.; Kitenbergs, G.; Muiznieks, I.; Erts, D.; Prikulis, J. Colloidal nanoparticle sorting and ordering on anodic alumina patterned surfaces using templated capillary force assembly. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 326, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikulis, J.; Tamulevičius, T.; Poplausks, R.; Bergs, G.; Apsite, I.; Malinovskis, U.; Actins, A.; Erts, D. Optical properties of thin metal films with nanohole arrays on porous alumina–aluminum structures. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68143–68150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinovskis, U.; Poplausks, R.; Erts, D.; Ramser, K.; Tamulevičius, S.; Tamulevičienė, A.; Gu, Y.; Prikulis, J. High-density plasmonic nanoparticle arrays deposited on nanoporous anodic alumina templates for optical sensor applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.J.; Wang, S.M.; Liang, S.W.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, C.; Shieh, J.M. Low-temperature growth of ZnO nanorods in anodic aluminum oxide on Si substrate by atomic layer deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 033104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.H.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.M.; Chen, C. Fabrication and characteristics of self-aligned ZnO nanotube and nanorod arrays on Si substrates by atomic layer deposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, K236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Son, J.; Rhee, J.S. Vertical ZnO nanorod array as an effective hydrogen gas sensor. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norek, M.; Zaleszczyk, W.; Łuka, G.; Budner, B.; Zasada, D. Tailoring UV emission from a regular array of ZnO nanotubes by the geometrical parameters of the array and Al2O3 coating. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5693–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.L.; Xie, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Q.-H.; Ding, S.J.; Zhang, D.W. Tailoring the luminescence of anodized aluminum oxide with atomic layer deposited ZnO thin films. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 15th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Rome, Italy, 27–30 July 2015; Volume 1, pp. 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tynell, T.; Karppinen, M. Atomic layer deposition of ZnO: A review. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Zhang, L.D. Wavelength dependent photoluminescence of anodic alumina membranes. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 8663–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Meng, G.W.; Zhang, L.D.; Phillipp, F. Ordered semiconductor ZnO nanowire arrays and their photoluminescence properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 2011–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, I.; Qamhieh, N.; Mahmoud, S.T. Synthesis and length dependent photoluminescence property of zinc oxide nanorods. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 3552–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Jangir, L.K.; Rathore, K.S.; Kumar, M.; Awasthi, K. Morphology-dependent structural and optical properties of ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, R.T.; McKnight, S.W.; Palik, E.D.; Lukosz, W. Interference effects in luminescence studies of thin films. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poplausks, R.; Jevdokimovs, D.; Malinovskis, U.; Erts, D.; Prikulis, J. Variable thickness porous anodic alumina/metal film bilayers for optimization of plasmonic scattering by nanoholes on mirror. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5783–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graniel, O.; Fedorenko, V.; Viter, R.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Nowaczyk, G.; Weber, M.; Załȩski, K.; Jurga, S.; Smyntyna, V.; Miele, P.; et al. Optical properties of ZnO deposited by atomic layer deposition (ALD) on Si nanowires. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 236–237, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- So, S.K.; Choi, W.K.; Leung, L.M.; Neyts, K. Interference effects in bilayer organic light-emitting diodes. App. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 1939–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Khan, F.; Singh, S.; Singh, P. Correlation between reflectivity and photoluminescent properties of porous silicon films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, F.; Li, H.; Guo, R.; Han, Y.; Ai, S. Photoelectrochemical biosensor for histone acetyltransferase detection based on ZnO quantum dots inhibited photoactivity of BiOI nanoflower. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.C.; Weng, Y.H.; Lu, M.Y.; Jen, C.P.; Fedorov, V.E.; Chen, W.C.; Wu, M.T.; Kuo, C.T.; Wang, H.C. Nano-structure ZnO/Cu2O photoelectrochemical and self-powered biosensor for esophageal cancer cell detection. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Huang, S.; Lu, X.X.; Gao, X.; Song, S.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.Q.; Guan, E.H. Highly sensitive and selective dopamine biosensor using Au nanoparticles-ZnO nanocone arrays/graphene foam electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balevicius, Z.; Paulauskas, A.; Plikusiene, I.; Mikoliunaite, L.; Bechelany, M.; Popov, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Towards the application of Al2O3/ZnO nanolaminates in immunosensors: Total internal reflection spectroscopic ellipsometry based evaluation of BSA immobilization. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 8778–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viter, R.; Savchuk, M.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Pietralik, Z.; Starodub, N.; Shpyrka, N.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Analytical, thermodynamical and kinetic characteristics of photoluminescence immunosensor for the determination of Ochratoxin A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshchenko, A.; Bechelany, M.; Viter, R.; Khranovskyy, V.; Smyntyna, V.; Starodub, N.; Yakimova, R. Optical biosensors based on ZnO nanostructures: Advantages and perspectives. A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, C.; Stringer, S. The splice variants of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and their receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Girsh, J.; Fang-ju Jou, A.; Ho, J.-a.A.; Hug, T.; Dernedde, J.; Willner, I. Optical aptasensors for the analysis of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6192–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.J.; Zunaina, E.; Norfadzillah, A.J.; Raja-Norliza, R.O.; Julieana, M.; Ab-Hamid, S.A.; Mahaneem, M. Evaluation of vascular endothelial growth factor levels in tears and serum among diabetic patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahdary, M. Aptamers in nanostructure-based electrochemical biosensors for cardiac biomarkers and cancer biomarkers: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 152, 112018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Satoh, M. Fabrication of gold nanodot array using anodic porous alumina as an evaporation mask. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 35, L126–L129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Chaaya, A.; Viter, R.; Bechelany, M.; Alute, Z.; Erts, D.; Zalesskaya, A.; Kovalevskis, K.; Rouessac, V.; Smyntyna, V.; Miele, P. Evolution of microstructure and related optical properties of ZnO grown by atomic layer deposition. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, H.; Yung, L.Y.L. Probing high affinity sequences of DNA aptamer against VEGF165. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakatsuka, N.; Yang, K.A.; Abendroth, J.M.; Cheung, K.M.; Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, B.; Rim, Y.S.; Yang, Y.; et al. Aptamer–field–effect transistors overcome Debye length limitations for small-molecule sensing. Science 2018, 362, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.G.; Li, Y.V.; Saint John, D.B.; Jackson, T.N. pH-Controlled Selective Etching of Al2O3 over ZnO. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7028–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaaya, A.A.; Viter, R.; Baleviciute, I.; Bechelany, M.; Ramanavicius, A.; Gertnere, Z.; Erts, D.; Smyntyna, V.; Miele, P. Tuning optical properties of al2O3/ZnO nanolaminates synthesized by atomic layer deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 3811–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viter, R.; Chaaya, A.A.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Nowaczyk, G.; Kovalevskis, K.; Erts, D.; Miele, P.; Smyntyna, V.; Bechelany, M. Tuning of ZnO 1D nanostructures by atomic layer deposition and electrospinning for optical gas sensor applications. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baitimirova, M.; Viter, R.; Andzane, J.; van der Lee, A.; Voiry, D.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Coy, E.; Mikoliunaite, L.; Tumenas, S.; Załȩski, K.; et al. Tuning of structural and optical properties of graphene/ZnO nanolaminates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 23716–23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, U.; Gibson, N. The Scherrer equation versus the ‘Debye-Scherrer equation’. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfanidis, S.J. Electromagnetic Waves and Antennas; Rutgers University: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rakić, A.D.; Djurišić, A.B.; Elazar, J.M.; Majewski, M.L. Optical properties of metallic films for vertical-cavity optoelectronic devices. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruggeman, D.A.G. Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Substanzen. I. Dielektrizitätskonstanten und Leitfähigkeiten der Mischkörper aus isotropen Substanzen. Ann. Phys. 1935, 416, 636–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitson, I.H.; Dodge, M.J. Refractive index and birefringence of synthetic sapphire. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1972, 62, 1405. [Google Scholar]
- Galdámez-Martinez, A.; Santana, G.; Güell, F.; Martínez-Alanis, P.R.; Dutt, A. Photoluminescence of ZnO nanowires: A review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.M.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhou, Y.B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.M.; Yu, D.P. Surface effects on photoluminescence of single ZnO nanowires. Phys. Lett. A 2008, 372, 4505–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.W.; Norton, D.P.; Pearton, S.J. Origin of green luminescence in ZnO thin film grown by molecular-beam epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 073502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, C.; Chao, C.; Chen, T. The investigation of photoluminescence centers in porous alumina membranes. Appl. Phys. A 2006, 84, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal Khan, G.; Singh, A.K.; Mandal, K. Structure dependent photoluminescence of nanoporous amorphous anodic aluminium oxide membranes: Role of F+ center defects. J. Lumin. 2013, 134, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspnes, D.E.; Studna, A.A. Dielectric functions and optical parameters of Si, Ge, GaP, GaAs, GaSb, InP, InAs, and InSb from 1.5 to 6.0 eV. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 985–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).