Impacting Droplet Can Mitigate Dust from PDMS Micro-Post Array Surfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Numerical Methods
3.1. Initial and Boundary Conditions
3.2. Numerical Implementation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Surface Texture and Hydrophobic State of Micro-Post Arrays
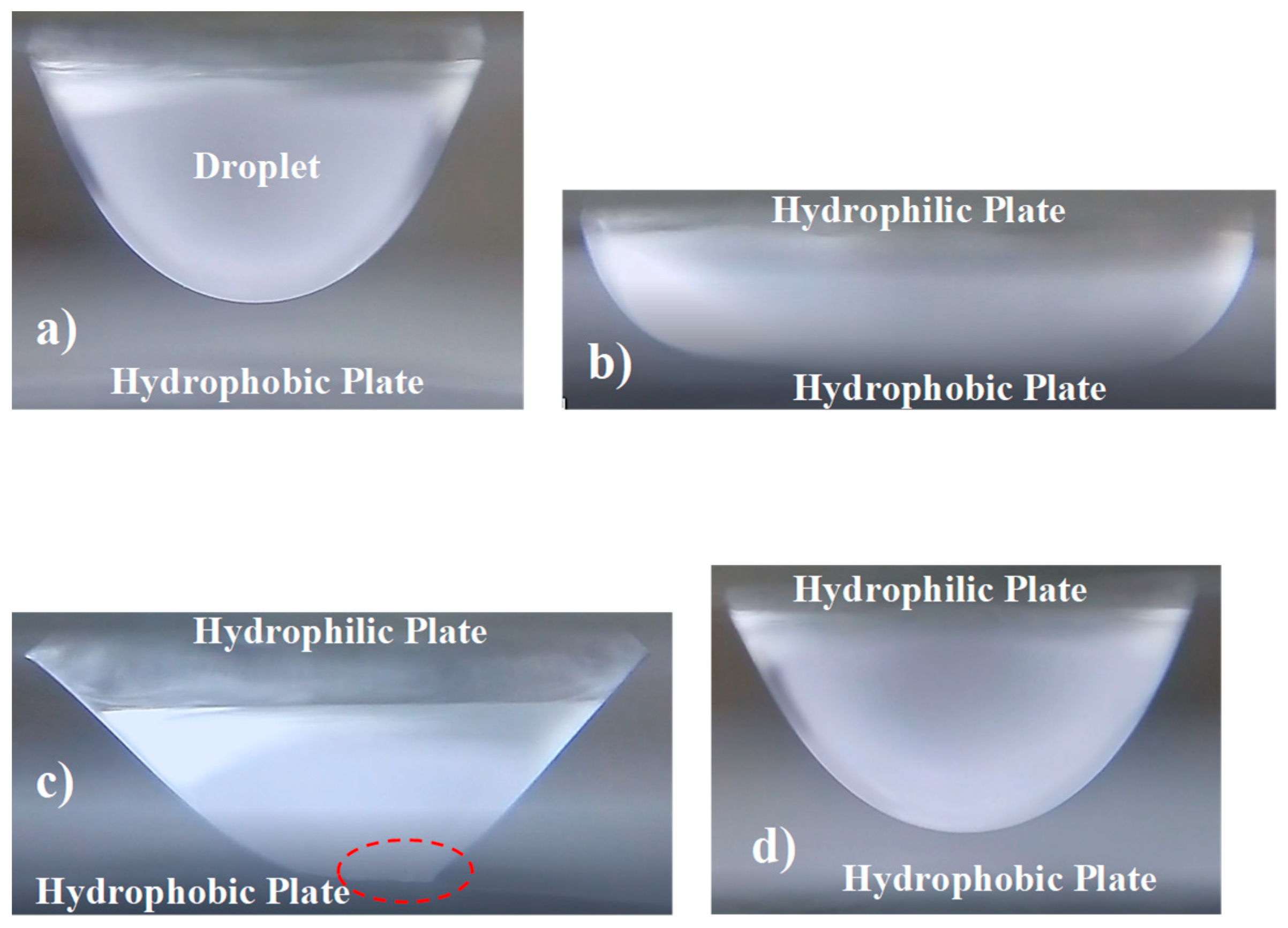
4.2. Dynamics of Droplet on Impacted Surface
4.3. Removal of Dust by Impacting Droplet
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Mathematical Formulations of Two-Phase Field Model
Appendix B. Formulation of Penetration Height of Impacting Droplet over Micro-Post Array Surfaces

References
- Khojasteh, D.; Kazerooni, N.M.; Marengo, M. A review of liquid droplet impacting onto solid spherical particles: A physical pathway to encapsulation mechanisms. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 71, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, N.; Wijayanti, W.; Fahmi, R. Pressure Effect in Droplet Combustion of Blended Fuel on Ethanol and Kemiri Sunan (Reutealis Trisperma (Blanco) Airy Shaw) Biodiesel. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Malang, Indonesia, 23–25 October 2018; IOP Publishing: Malang, Indonesia, 2019; Volume 494, p. 12052. [Google Scholar]
- Havaić, T.; Đumbir, A.-M.; Gretić, M.; Matijašić, G.; Žižek, K. Droplet impact phenomena in fluidized bed coating process with a wurster insert. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4546230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilbas, B.S.; Abubakar, A.A.; Ali, H.; Al-Sharafi, A.; Sahin, A.Z.; Sunar, M.; Al-Qahtani, H. Impacting water droplets can alleviate dust from slanted hydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2021, 37, 4355–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-Y.; Tsai, C.-H.D. Universal plasma jet for droplet manipulation on a pdms surface towards wall-less scaffolds. Polymers 2021, 13, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quetzeri-Santiago, M.A.; Castrejón-Pita, A.A.; Castrejón-Pita, J.R. The effect of surface roughness on the contact line and splashing dynamics of impacting droplets. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.-P.; Fan, D.; Bai, X.-Z.; Cui, C.-X.; Chen, J.; Li, R.-L.; Liu, P.-F.; Qu, L.-B. Sorting liquid droplets by surface tension using devices with quasi-superamphiphobic coatings. Polymers 2020, 12, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malijevský, A. Does surface roughness amplify wetting? J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 184703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, G.; Yilbas, B.S.; Said, S.A.M.; Al-Aqeeli, N.; Matin, A. Chemo-mechanical characteristics of mud formed from environmental dust particles in humid ambient air. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abubakar, A.A.; Yilbas, B.S.; Al-Qahtani, H.; Alzaydi, A. Environmental dust repelling from hydrophilic/hydrophobic surfaces under sonic excitations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14346. [Google Scholar]
- Ragulskis, K.; Bubulis, A.; Mažeika, D.; Janutienė, R.K.; Ragulskis, L.M.; Bartkus, A. Vibrational method of cleaning of surfaces from homogeneous waste materials. J. Vibroeng. 2017, 19, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Yakubu, M.; Yilbas, B.S.; Abubakr, A.A.; Al-Qahtani, H. Droplet rolling and spinning in V-shaped hydrophobic surfaces for environmental dust mitigation. Molecules 2020, 25, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaszczur, M.; Teneta, J.; Styszko, K.; Hassan, Q.; Burzyńska, P.; Marcinek, E.; Łopian, N. The field experiments and model of the natural dust deposition effects on photovoltaic module efficiency. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8402–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghazi, S.; Sayigh, A.; Ip, K. Dust effect on flat surfaces—A review paper. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.Y.D.; Zhang, Z.; Cristobal, G.; Chin, W.S. One-pot synthesis of surface functionalized spherical silica particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 460, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heib, F.; Schmitt, M. Statistical contact angle analyses with the high-precision drop shape analysis (HPDSA) approach: Basic principles and applications. Coatings 2016, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tracker Program. Available online: https://physlets.org/tracker (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Bhattacharya, S.; Charonko, J.J.; Vlachos, P.P. Particle image velocimetry (PIV) uncertainty quantification using moment of correlation (MC) plane. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2018, 29, 115301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Xiong, X.; Xiao, H.; Wan, K. Effects of Contact Angle on the Dynamics of Water Droplet Impingement. In Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 7–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- COMSOL Inc. COMSOL Multiphysics; COMSOL Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Herring, M.L.; Mardel, J.I.; Fox, B.L. The effect of material selection and manufacturing process on the surface finish of carbon fibre composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 210, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, E.W. The dynamics of capillary flow. Phys. Rev. 1921, 17, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, G.; Lee, M.; Senthil, K.; Yong, K. Impact dynamics of water droplets on chemically modified WOx nanowire arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 153101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, O.G. Waterdrop collisions with solid surfaces. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1955, 54, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharafi, A.; Yilbas, B.S.; Ali, H.; Sahin, A.Z. Flow Field inside a sessile droplet on a hydrophobic surface in relation to self-cleaning applications of dust particles. ASME J. Heat Transfer 2017, 139, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, O.A.; Xiao, J.; Rodrigo, C.S.; Mercadé-Prieto, R.; Sempere, J.; Chen, X.D. Detailed numerical analysis of evaporation of a micrometer water droplet suspended on a glass filament. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 165, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Weibel, J.A.; Garimella, S.V. Numerical simulation of evaporating two-phase flow in a high-aspect-ratio microchannel with bends. J. Heat Transfer 2017, 139, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asibor, J.O.; Ighodaro, O. Steady state analysis of nanofuel droplet evaporation. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Tatekura, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Sanada, T. Pressure generated at the instant of impact between a liquid droplet and solid surface. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 181101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
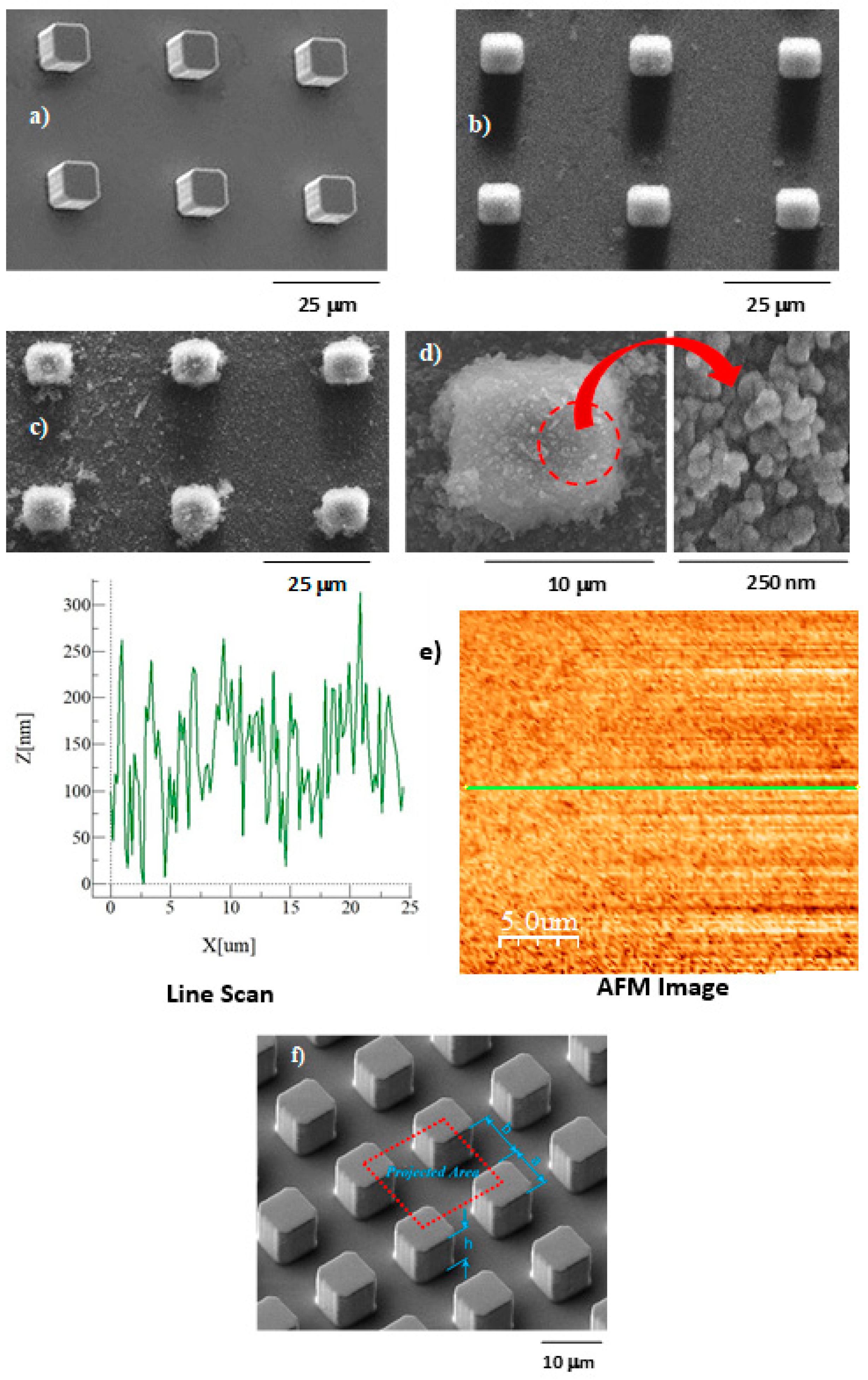















| Property | Name | Air | Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 6 × 10−6 T2 − 0.0036 T + 2.1483 | 838.5 + 1.4 T−0.003 T2 + 3.7 × 10−7 T3 | |
| Dynamic viscosity | 1.77 × 10−8 T + 12.536 × 10−6 | 1.38 – 0.021 T + 1.36 × 10−4 T2 – 4.65 × 10−7 T3 | |
| Surface tension | - | −0.0206 T + 13.41 | |
| Re-initialization parameter | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| Interfacial thickness | - | 10 − 50 | |
| Contact angle | - | 130° ± 4° for b = 0 µm | |
| 138° ± 4° for b = 10 µm | |||
| 146° ± 4° for b = 25 µm | |||
| 152° ± 4° for b = 50 µm | |||
| Specific heat capacity | 0.0004 T2 − 0.1704 T + 1023 | 0.0112 T2 – 7.0516 T + 5294.5 | |
| Thermal conductivity | 5.75 × 10−5 (1 − 2.1 × 10−6 T2 – 3.17 × 10−3 T + 1) | −8.354 × 10−6 T2 + 6.53 × 10−3 T − 0.5981 | |
| Diffusion coefficient | - | 0.0018 T − 0.2913 | |
| b (μm) | Spacing between micro-posts | 0, 10, 25, 50 | |
| a (μm) | Square micro-post width | 10 | |
| h (μm) | Micro-post height | 10 | |
| We | Area Ratio = Cleaned Area/Droplet Cross-Sectional Area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b = 0 µm | b = 10 µm | b = 25 µm | b = 50 µm | |
| 7.2 | 3.507106 | 2.79177 | 2.236873 | 1.856246 |
| 10.8 | 4.248223 | 3.571959 | 2.793005 | 2.135425 |
| 14.4 | 4.420782 | 3.795227 | 3.061624 | 2.571364 |
| 18.0 | 5.450434 | 4.660953 | 4.135096 | 3.103018 |
| 21.0 | 6.470626 | 5.211640 | 4.171407 | 3.519041 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abubakar, A.A.; Yilbas, B.S.; Yakubu, M.; Al-Qahtani, H.; Hassan, G.; Adukwu, J.E. Impacting Droplet Can Mitigate Dust from PDMS Micro-Post Array Surfaces. Coatings 2021, 11, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111377
Abubakar AA, Yilbas BS, Yakubu M, Al-Qahtani H, Hassan G, Adukwu JE. Impacting Droplet Can Mitigate Dust from PDMS Micro-Post Array Surfaces. Coatings. 2021; 11(11):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111377
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbubakar, Abba Abdulhamid, Bekir Sami Yilbas, Mubarak Yakubu, Hussain Al-Qahtani, Ghassan Hassan, and Johnny Ebaika Adukwu. 2021. "Impacting Droplet Can Mitigate Dust from PDMS Micro-Post Array Surfaces" Coatings 11, no. 11: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111377
APA StyleAbubakar, A. A., Yilbas, B. S., Yakubu, M., Al-Qahtani, H., Hassan, G., & Adukwu, J. E. (2021). Impacting Droplet Can Mitigate Dust from PDMS Micro-Post Array Surfaces. Coatings, 11(11), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111377






