Evaluation of Properties and Mechanisms of Waste Plastic/Rubber-Modified Asphalt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. WPRMA Preparation
2.3. Laboratory Experimentation and Testing
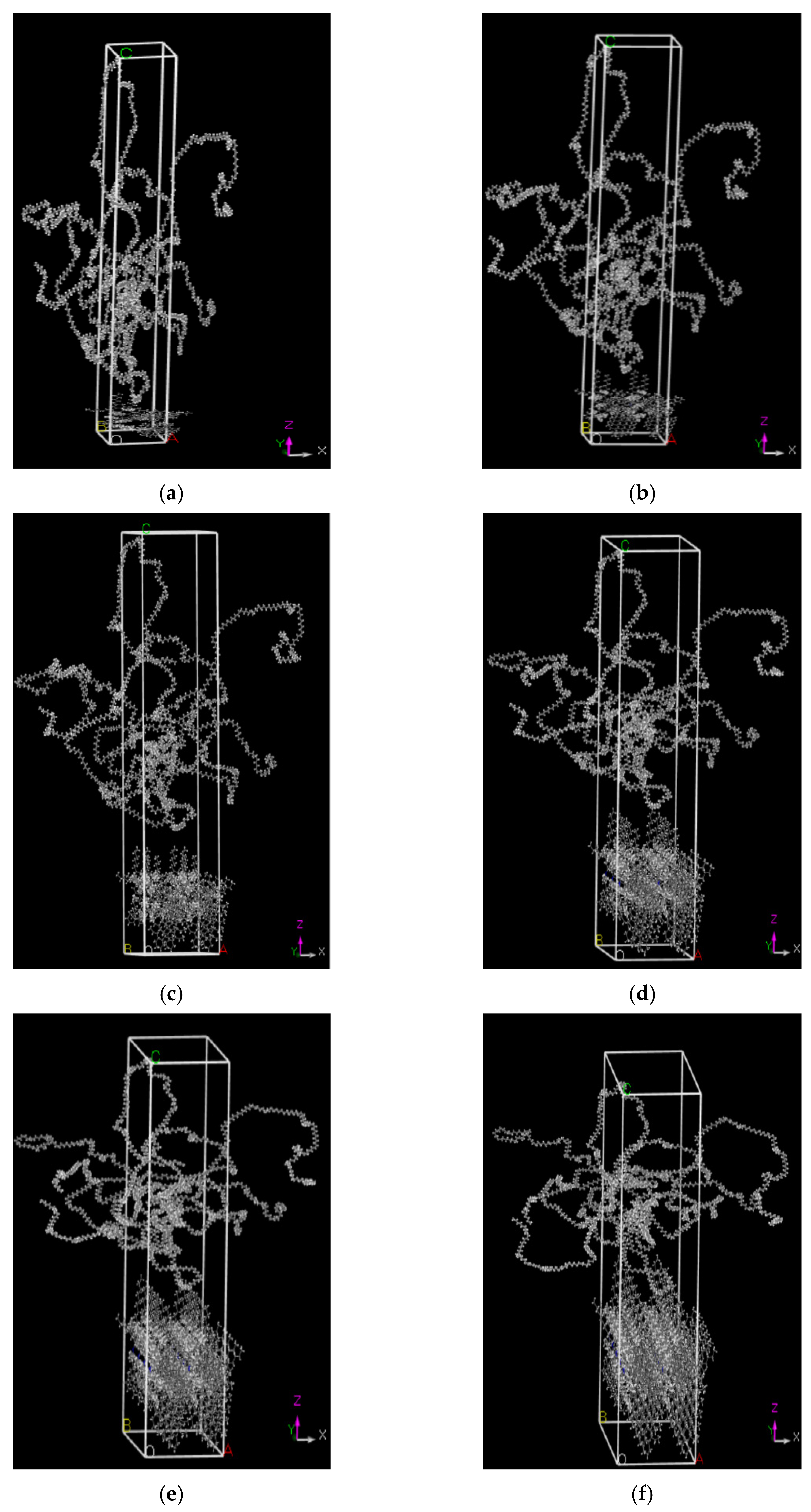
2.4. Molecular Dynamic Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
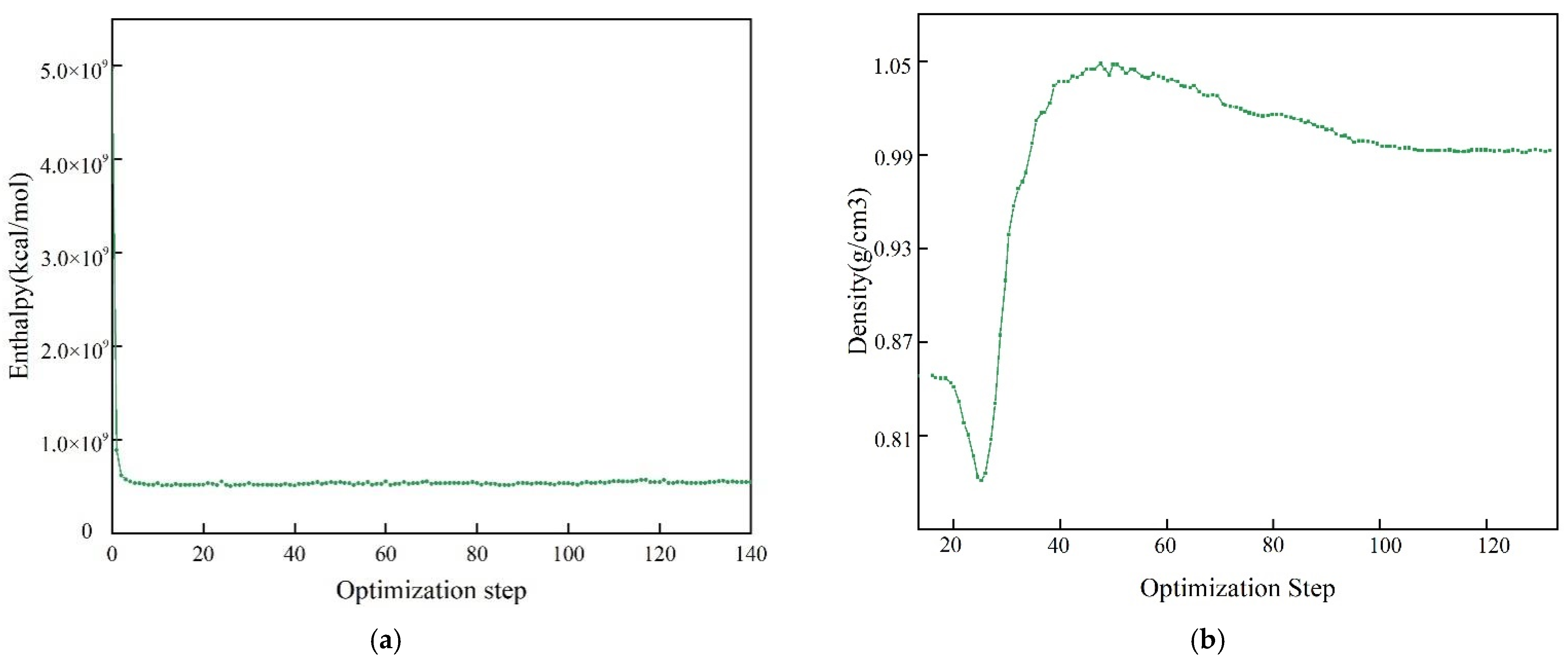
3.1. Assessment of Reliability of Molecular Simulation Results
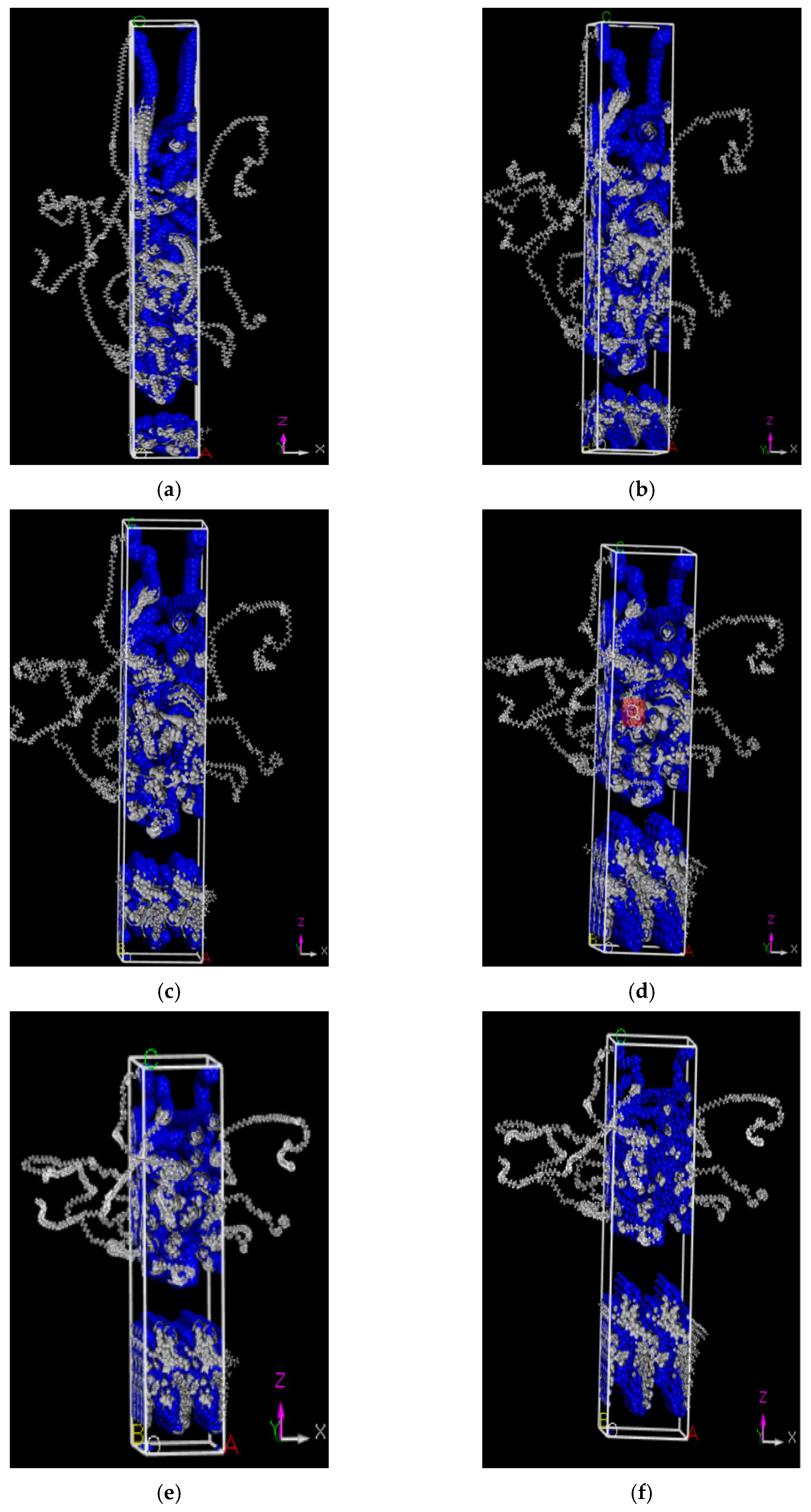
3.2. Assessment of WPRMA Properties via Molecular Simulations
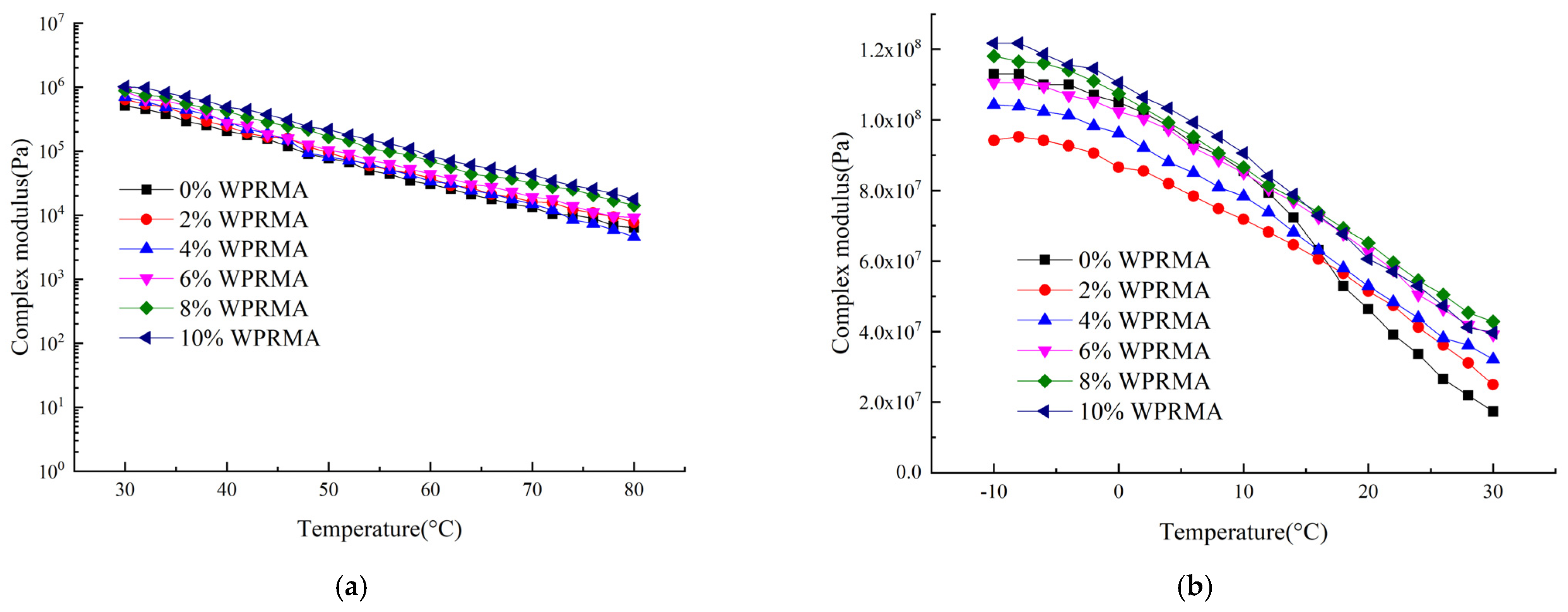
3.3. Assessment of WPRMA Rheological Properties and Storage Stability via Tests
3.4. Interaction Mechanism of WPRMA
4. Conclusions
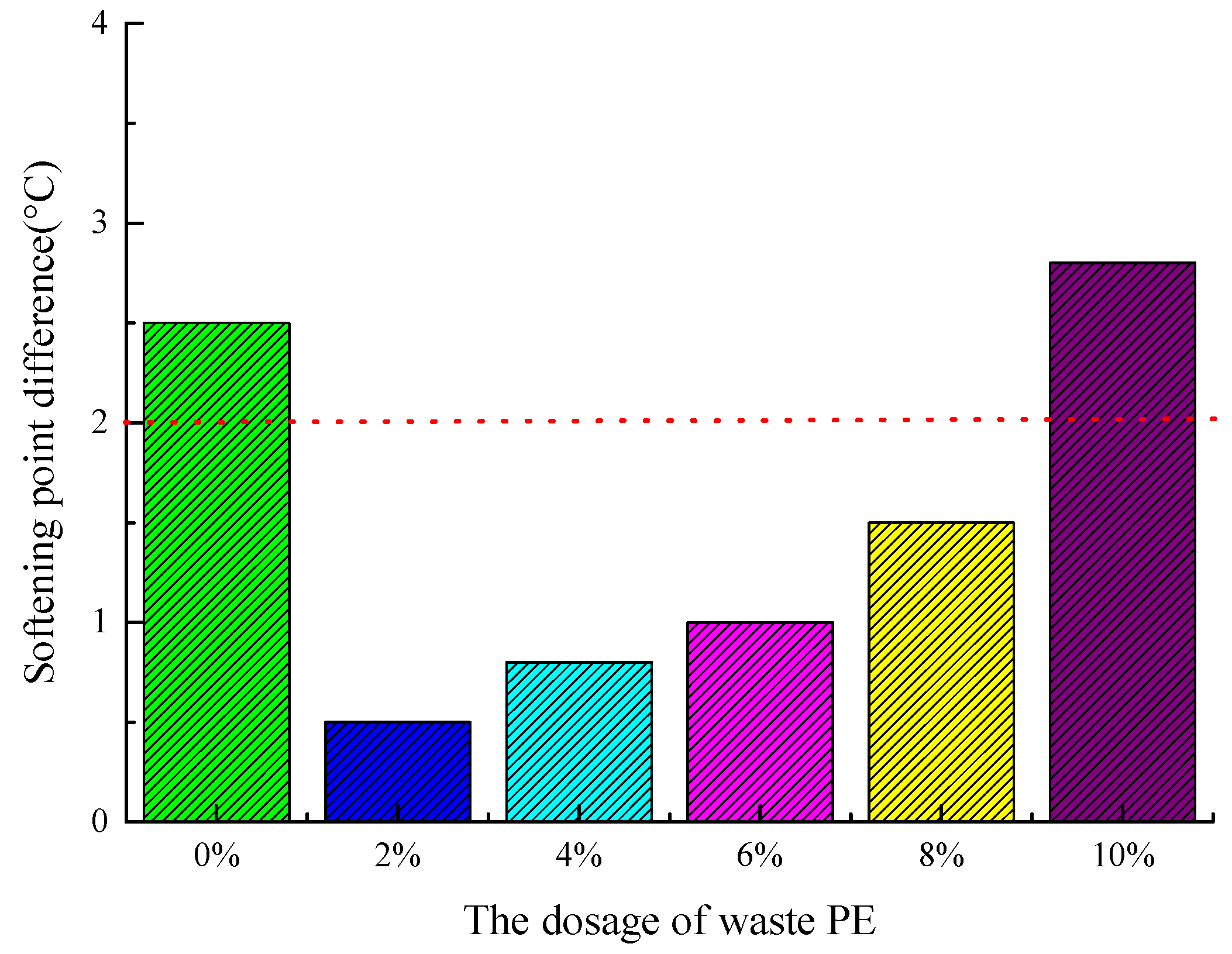
- The inclusion of waste PE in the mix can inhibit the movement of WPRMA and diminish its self-healing properties. However, the inclusion of waste PE can increase the viscosity and enhance the adhesive properties of WPRMA. Furthermore, waste PE can enhance the high-temperature properties of WPRMA, but high temperatures can diminish the viscoelastic properties of WPRMA due to the presence of fill in waste PE.
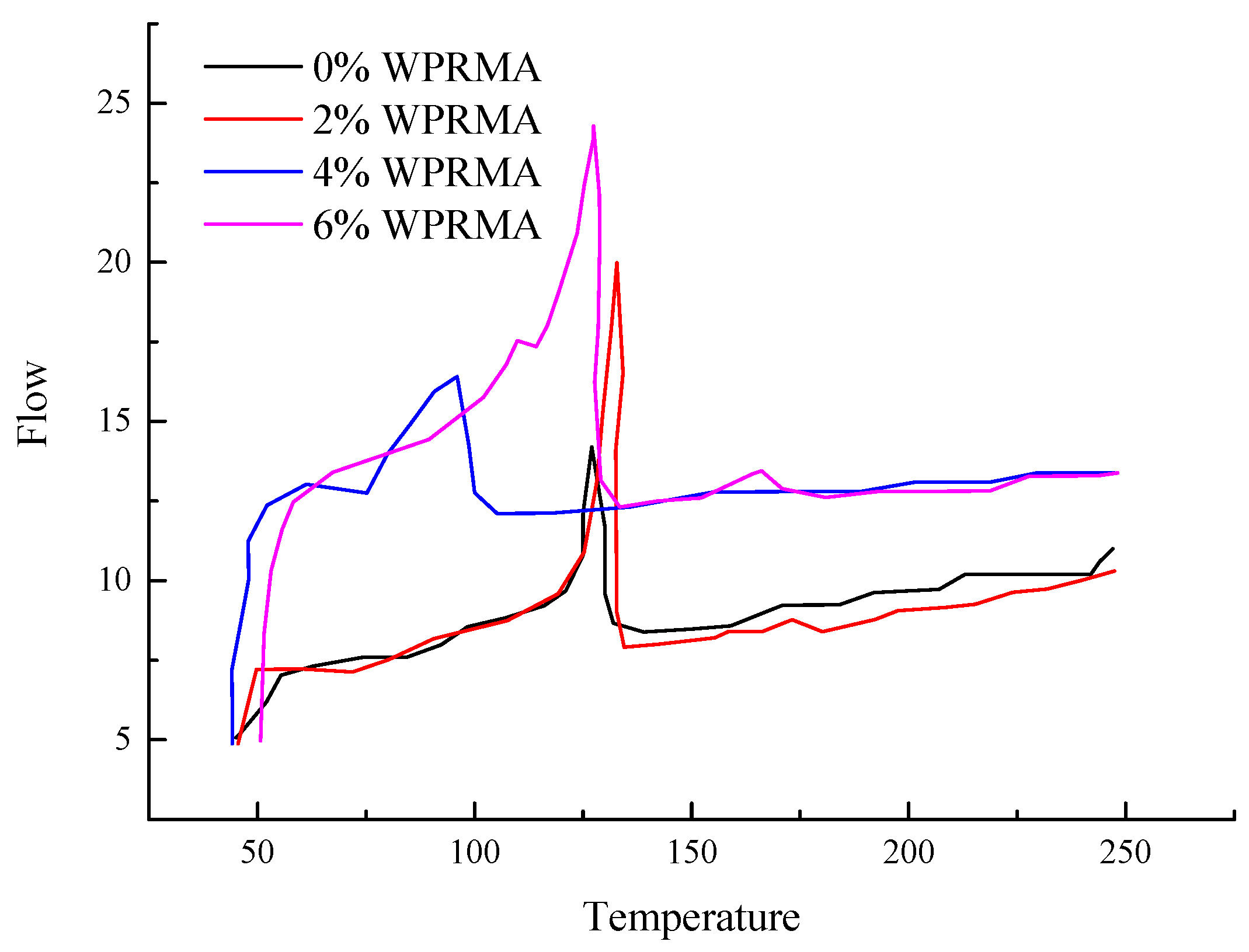
- The inclusion of waste PE in the mix can increase the free volume of WPRMA and promote its mobility properties. During the degradation process of WPRMA, first the waste PE degrades, then the asphalt, and finally the rubber powder. The dosage of the waste PE can significantly affect the degradation of WPRMA because waste PE and rubber powder are synergetic.
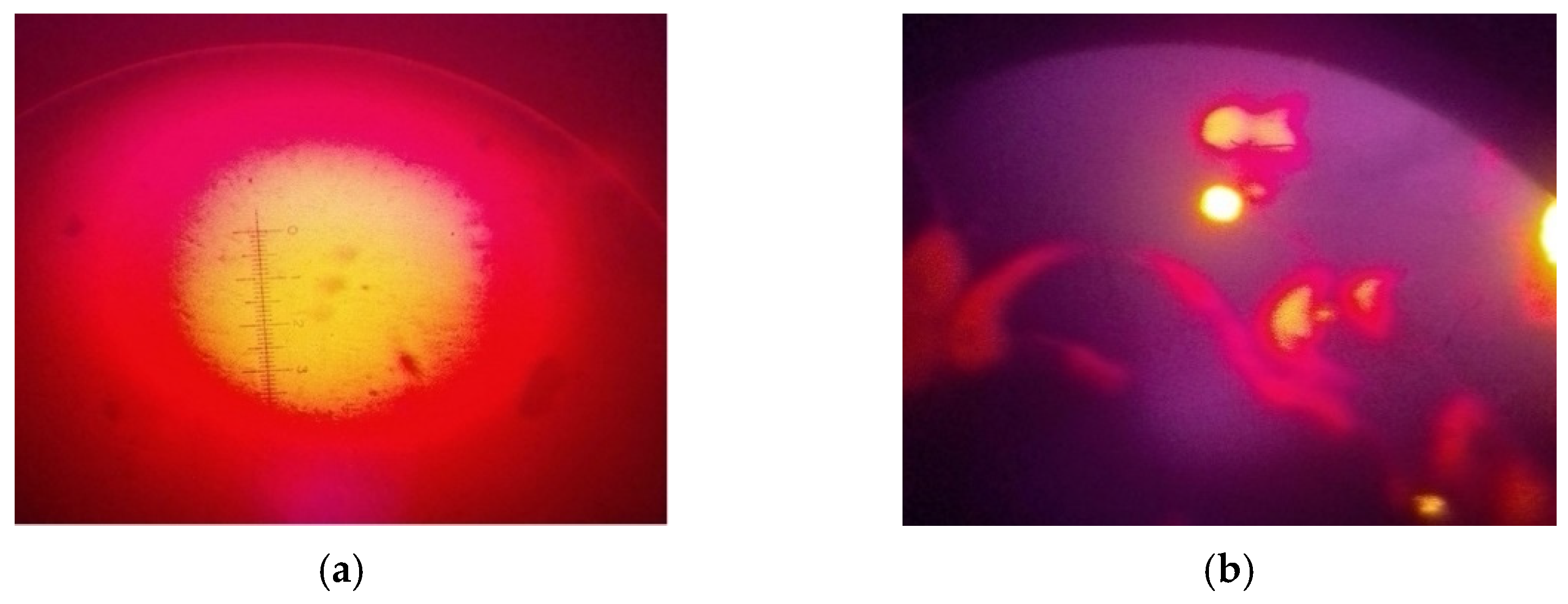
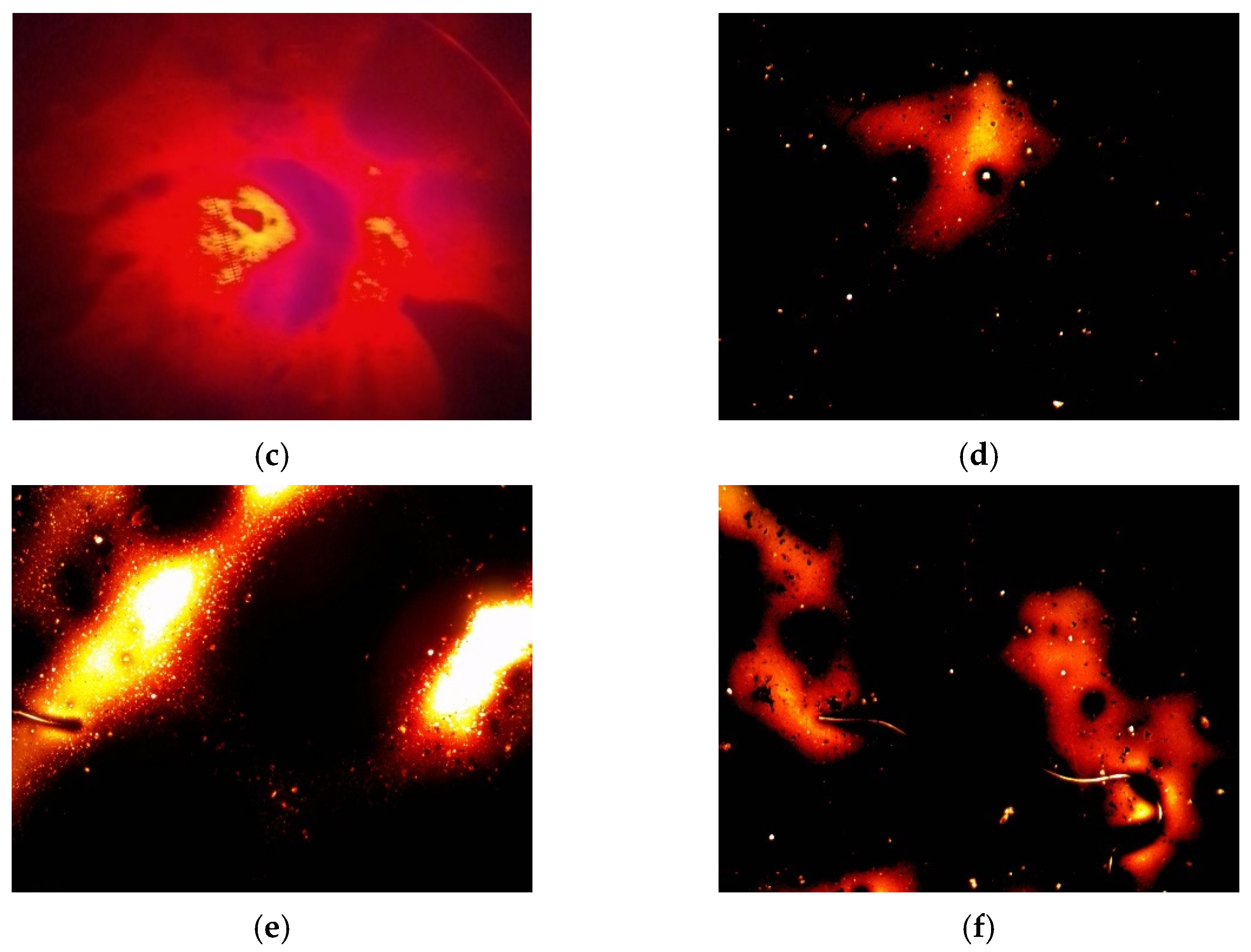
- The micro-morphology of WPRMA in terms of change regularly indicates a granular shape, movement phase, networks, and a separation phase. Temperature is the factor that directly promotes the melting and decomposition of the functional groups in WPRMA. Therefore, temperature must be strictly controlled during the mixture production process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Emmerich, L.; Wu, J.; Vana, P.; Zhang, K. Hydroplastic polymers as eco-friendly hydrosetting plastics. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 7, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritz, S.; Andrew, P. Plastics recycling with a difference. Science 2018, 360, 380–381. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Buzoglu, K.; Tang, C. Alternative plastics. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, Y.; Kumar, V.; Smadar, P.; Yang, Y.; Leed, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Song, H.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwonf, E.E.; Jeon, Y.J. Production of bioplastic through food waste valorization. Environ. Int. 2019, 119, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; Mahari, W.; Ok, Y.; Penga, W.; Chong, C.T.; Ma, N.L.; Chase, H.A.; Liew, Z.; Yusup, S.; Kwon, E.E.; et al. Microwave vacuum pyrolysis of waste plastic and used cooking oil for simultaneous waste reduction and sustainable energy conversion: Recovery of cleaner liquid fuel and techno-economic analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xian, Z.; Jin, X.; Liang, S.; Chen, Z.; Pan, B.; Wu, B.; Ok, Y.S.; Gu, C. Photo-Aging of polyvinyl chloride microplastic in the presence of natural organic acids. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, F.; Wang, J. Low temperature performance characteristics of polyethylene modified asphalts—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coralie, J.; Haritz, S. Dynamic polymer network points the way to truly recyclable plastics. Nature 2019, 568, 467–468. [Google Scholar]
- Jitsangiam, P.; Nusit, K.; Phenrat, T.; Kumlai, S.; Pra-Ai, S. An examination of natural rubber modified asphalt: Effects of rubber latex contents based on macro- and micro-observation analyses. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 289, 123158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Lyu, L. Preparation and performance evaluation of swine manure bio-oil modified rubber asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Jinyang, H.; Guo, H.; Yang, B. Performance of modified asphalt of rubber powder through tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 121032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Yang, C.; Li, A.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z. Flue gas composition of waste rubber modified asphalt (WRMA) and effect of deodorants on hazardous constituents and WRMA. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Lin, P. Investigating the role of swelling-degradation degree of crumb rubber on CR/SBS modified porous asphalt binder and mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Yang, X.; Shen, A.; Wu, H.; Lyu, Z.; Li, B. Mechanical properties and reaction mechanism of microwave-activated crumb rubber-modified asphalt before and after thermal aging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 267, 120773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, W.; Liang, L.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, F. Performance evaluation of warm-mixed crumb rubber modified asphalt based on rheological characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, G.M.; Faxina, A.L. High-temperature rheological properties of asphalt binders modified with recycled low-density polyethylene and crumb rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Sun, C.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Ren, S. Utilization of wax residue as compatibilizer for asphalt with ground tire rubber/recycled polyethylene blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Xu, H.; You, L. Rheological properties of asphalts modified by waste tire rubber and reclaimed low density polyethylene. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 83, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibreil, H.; Cheng, P. Effects of high-density polyethylene and crumb rubber powder as modifiers on properties of hot mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 142, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghrafy, Y.; Alla, E.; El-Badawy, S. Rheological properties and aging performance of sulfur extended asphalt modified with recycled polyethylene waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 273, 121771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Moghaddam, T.B.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Adhikari, S.; Wang, F.; Fan, Z. Nano-scale analysis of moisture diffusion in asphalt-aggregate interface using molecular simulations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wu, S.; Wei, M.; Xie, J. Multi-Scale performance evaluation and correlation analysis of blended asphalt and recycled asphalt mixtures incorporating high RAP content. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Fan, Z. Evaluation of thermo-mechanical properties of graphene/carbon-nanotubes modified asphalt with molecular simulation. Mol. Simul. 2017, 43, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Z. Comparison of rheological properties and compatibility of asphalt modified with various polyethylene. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Han, C.; Otto, F.; Zhang, F. Evaluation of Properties and Mechanisms of Waste Plastic/Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Coatings 2021, 11, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111365
Zhang X, Han C, Otto F, Zhang F. Evaluation of Properties and Mechanisms of Waste Plastic/Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Coatings. 2021; 11(11):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111365
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaorui, Chao Han, Frédéric Otto, and Fan Zhang. 2021. "Evaluation of Properties and Mechanisms of Waste Plastic/Rubber-Modified Asphalt" Coatings 11, no. 11: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111365
APA StyleZhang, X., Han, C., Otto, F., & Zhang, F. (2021). Evaluation of Properties and Mechanisms of Waste Plastic/Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Coatings, 11(11), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111365






