Determination of the Complex Dielectric Function of Ion-Implanted Amorphous Germanium by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry
Abstract
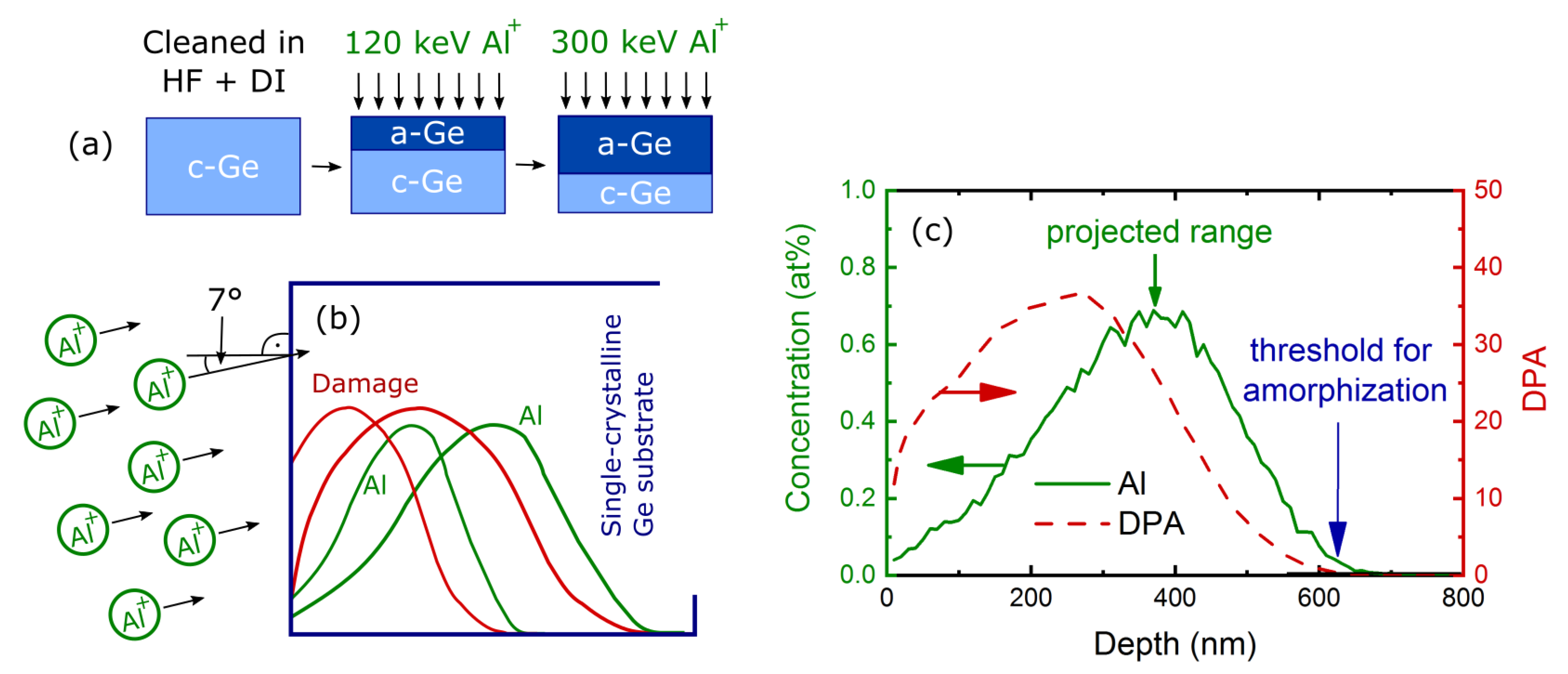
1. Introduction
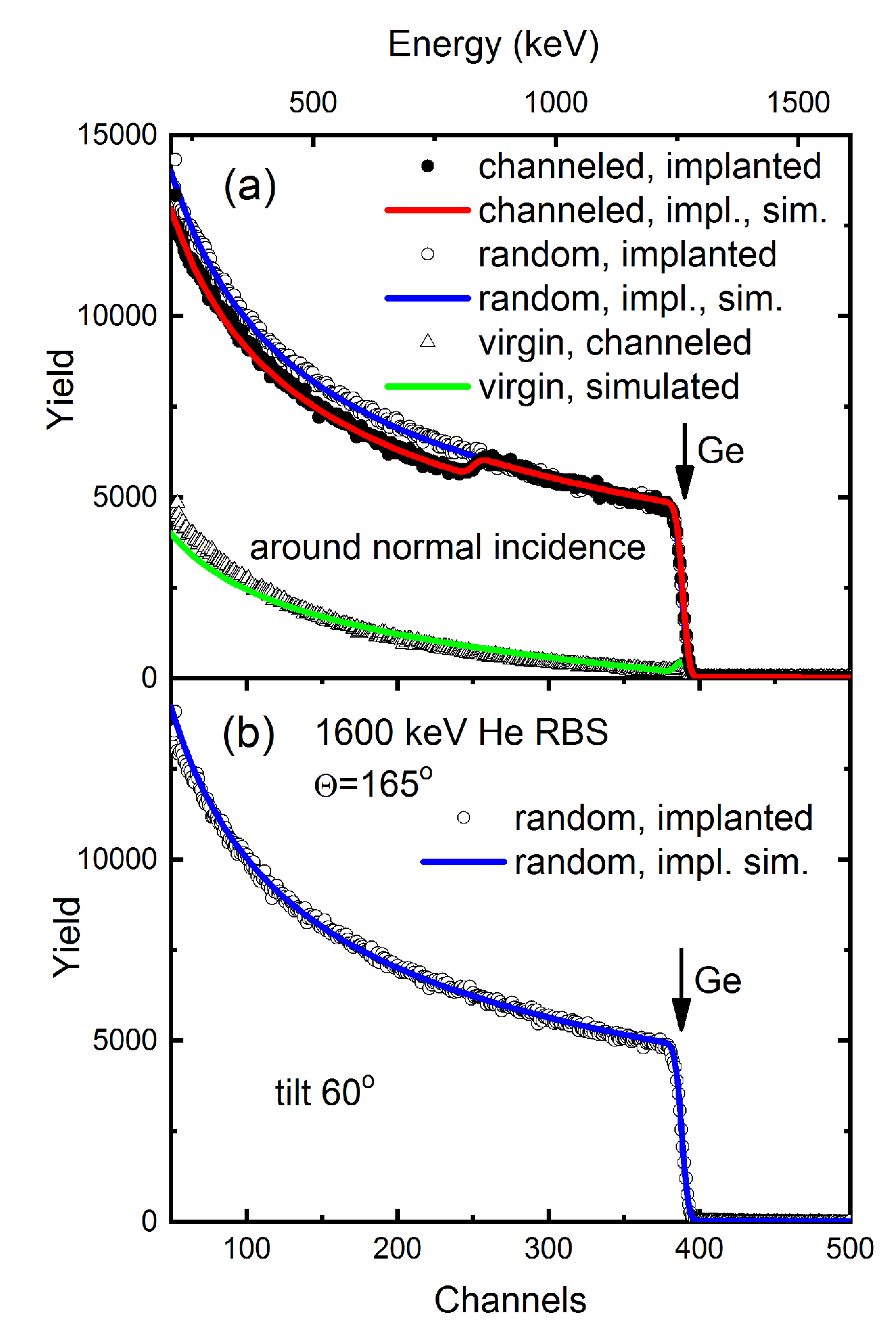
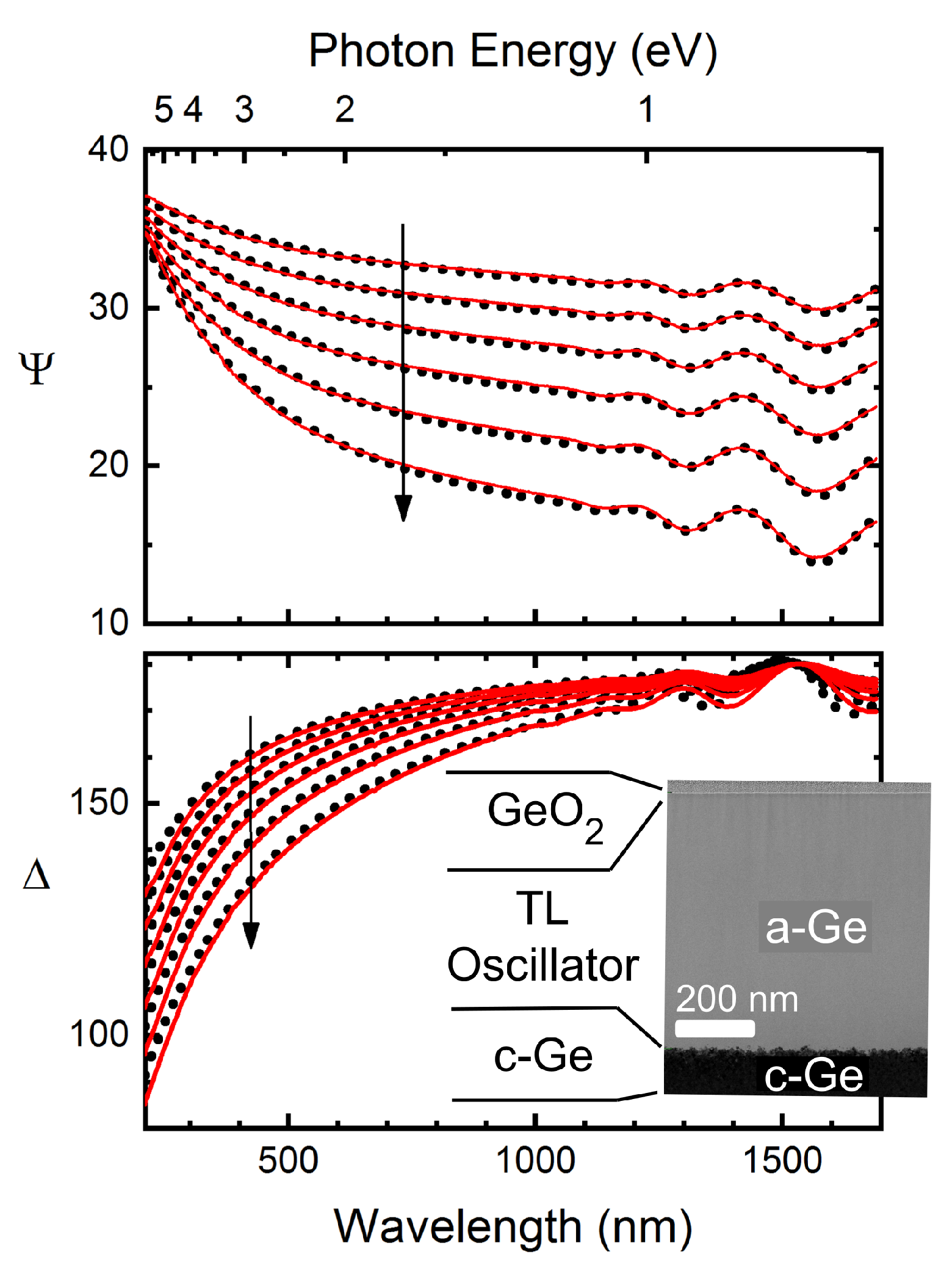
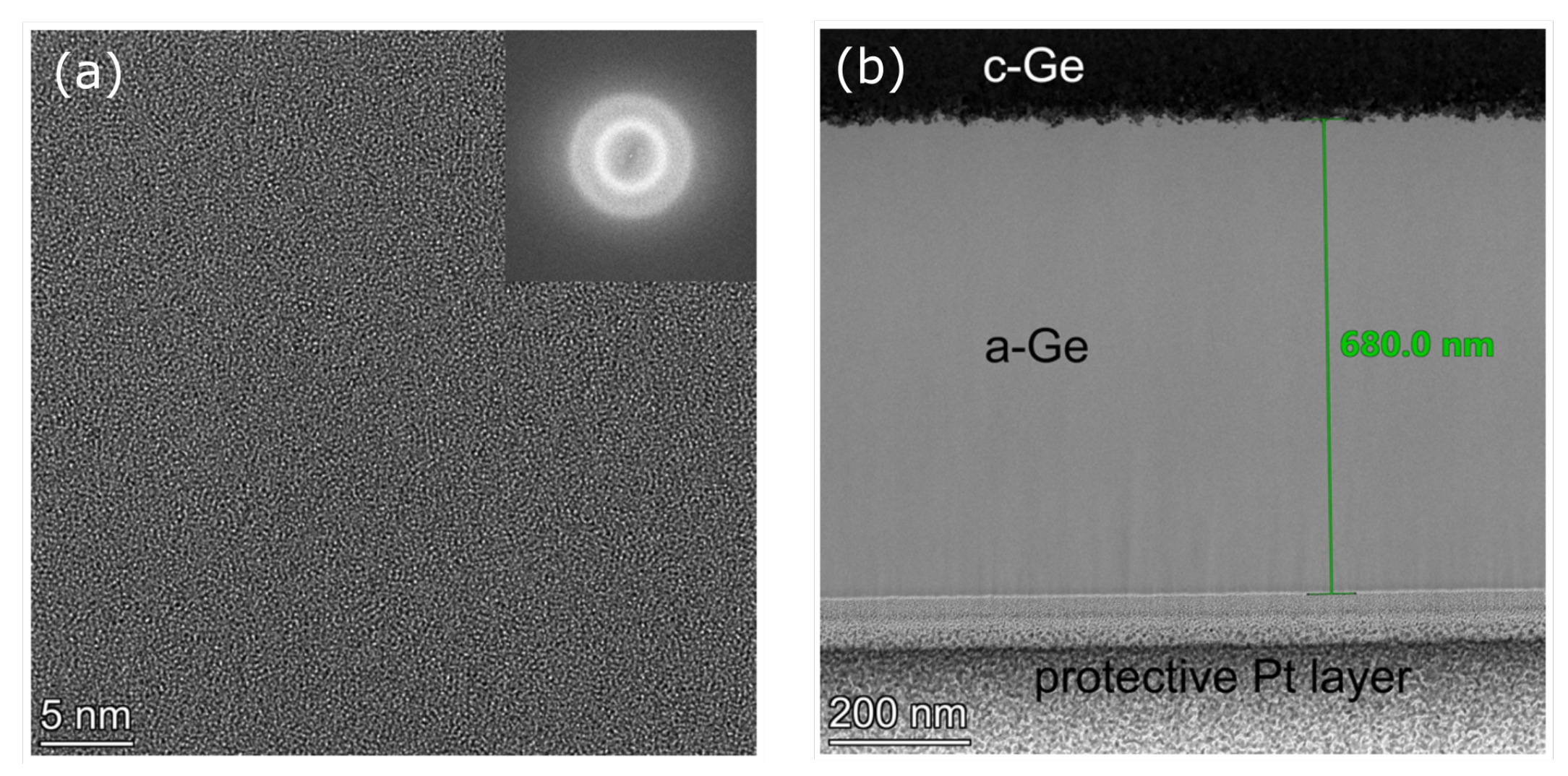
2. Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CL model | Cody-Lorentz model |
| DI | Deionized Water |
| DPA | Displacements per Atoms |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| RBS | Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry |
| SE | Spectroscopic Ellipsometry |
| SRIM | Stopping and Range of Atoms in Matter |
| TL model | Tauc-Lorentz model |
| XTEM | Cross-sectional Transmission Electron Microscopy |
References
- Lohner, T.; Kalas, B.; Petrik, P.; Zolnai, Z.; Serényi, M.; Sáfrán, G. Refractive Index Variation of Magnetron-Sputtered a-Si1-xGex by ’One-Sample Concept’ Combinatory. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalas, B.; Zolnai, Z.; Safran, G.; Serenyi, M.; Agocs, E.; Lohner, T.; Nemeth, A.; Fried, M.; Petrik, P. Micro-combinatorial sampling of the optical properties of hydrogenated amorphous Si1-xGex for the entire range of compositions towards a database for optoelectronics. Sci. Rep. 2020. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino, S.; Miritello, M.; Crupi, I.; Nicotra, G.; Simone, F.; Spinella, C.; Terrasi, A.; Mirabella, S. Room-temperature efficient light detection by amorphous Ge quantum wells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leem, J.W.; Yu, J.S. Design and fabrication of amorphous germanium thin film-based single-material distributed Bragg reflectors operating near 2.2 μm for long wavelength applications. JOSA B 2013, 30, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colace, L.; Balbi, M.; Masini, G.; Assanto, G.; Luan, H.C.; Kimerling, L.C. Ge on Si p-i-n photodiodes operating at 10Gbit/s. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carletti, L.; Sinobad, M.; Ma, P.; Yu, Y.; Allioux, D.; Orobtchouk, R.; Brun, M.; Ortiz, S.; Labeye, P.; Hartmann, J.M.; et al. Mid-infrared nonlinear optical response of Si-Ge waveguides with ultra-short optical pulses. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 32202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, J. Silicon-based semiconductor heterostructures: Column IV bandgap engineering. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry: Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Castriota, M.; Politano, G.G.; Vena, C.; De Santo, M.P.; Desiderio, G.; Davoli, M.; Cazzanelli, E.; Versace, C. Variable Angle Spectroscopic Ellipsometry investigation of CVD-grown monolayer graphene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, A.; Kozma, P.; Hülber, T.; Kurunczi, S.; Horvath, R.; Petrik, P.; Muskotál, A.; Vonderviszt, F.; Hos, C.; Fried, M.; et al. In Situ Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Study of Protein Immobilization on Different Substrates Using Liquid Cells. Sens. Lett. 2010, 8, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, L.; Böntgen, T.; Lorbeer, J.; Bundesmann, C.; Schmidt-Grund, R.; Grundmann, M. An extended Drude model for the in-situ spectroscopic ellipsometry analysis of ZnO thin layers and surface modifications. Thin Solid Films 2014, 571, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahasneh, A.; Al Attar, H.; Shahin, I. Spectroscopic ellipsometry of single and multilayer amorphous germanium/aluminum thin film systems. Opt. Commun. 2003, 220, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaglehole, D.; Zavetova, M. The fundamental absorption of amorphous Ge, Si and GeSi alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1970, 4, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafla-Yuan, H.; Rancourt, J.; Cumbo, M. Ellipsometric study of thermally evaporated germanium thin film. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 6360–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, S. Optical Constants of Crystalline and Amorphous Semiconductors: Numerical Data and Graphical Information; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.; Xu, Y.; Nagata, S.; Narumi, K.; Naramoto, H. Structure and optical properties of germanium implanted with carbon ions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B: Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2003, 206, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspnes, D.; Studna, A. An investigation of ion-bombarded and annealed 111 surfaces of Ge by spectroscopic ellipsometry. Surf. Sci. 1980, 96, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, J.; Zandvliet, H.; van Silfhout, A. Low energy ion bombardment on c-Ge surfaces. Vacuum 1990, 41, 1690–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellison, G.E.; Modine, F.A. Erratum: “Parameterization of the optical functions of amorphous materials in the interband region” [Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 371 (1996)]. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlauto, A.S.; Ferreira, G.M.; Pearce, J.M.; Wronski, C.R.; Collins, R.W.; Deng, X.; Ganguly, G. Analytical model for the optical functions of amorphous semiconductors from the near-infrared to ultraviolet: Applications in thin film photovoltaics. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 2424–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlund, K.; Djurabekova, F.; Hobler, G. Large fraction of crystal directions leads to ion channeling. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 214109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.; Koffel, S.; Pichler, P.; Bauer, A.; Amon, B.; Claverie, A.; Benassayag, G.; Scheiblin, P.; Frey, L.; Ryssel, H. Honeycomb voids due to ion implantation in germanium. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 2323–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.F.; Ziegler, M.; Biersack, J. SRIM – The stopping and range of ions in matter (2010). Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B: Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2010, 268, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtcher, R. Energy dependence of amorphization of Ge by Kr ions. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 1993, 279, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pászti, F.; Manuaba, A.; Hajdu, C.; Melo, A.; Da Silva, M. Current measurement on MeV energy ion beams. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 1990, 47, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kótai, E. Computer methods for analysis and simulation of RBS and ERDA spectra. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. B 1994, 85, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollam Co. Inc. Available online: http://www.jawoollam.com (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- (Ge Tabulated from UNL (Multiple Data Sets Fit)—Data in the Woollam Software Library). Available online: /WVASE32new/mat/Ge.mat (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Fried, M.; Lohner, T.; Aarnink, W.; Hanekamp, L.; Van Silfhout, A. Determination of complex dielectric functions of ion implanted and implanted-annealed amorphous silicon by spectroscopic ellipsometry. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 71, 5260–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspnes, D.E.; Studna, A.A. Dielectric functions and optical parameters of Si, Ge, GaP, GaAs, GaSb, InP, InAs, and InSb from 1.5 to 6.0 eV. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 985–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: The dielectric function data determined for the amorphous Ge layer created by implantation of Al ions can be downloaded from https://seafile.it.energia.mta.hu/f/32291c1f099541ba855d/?dl=1. |
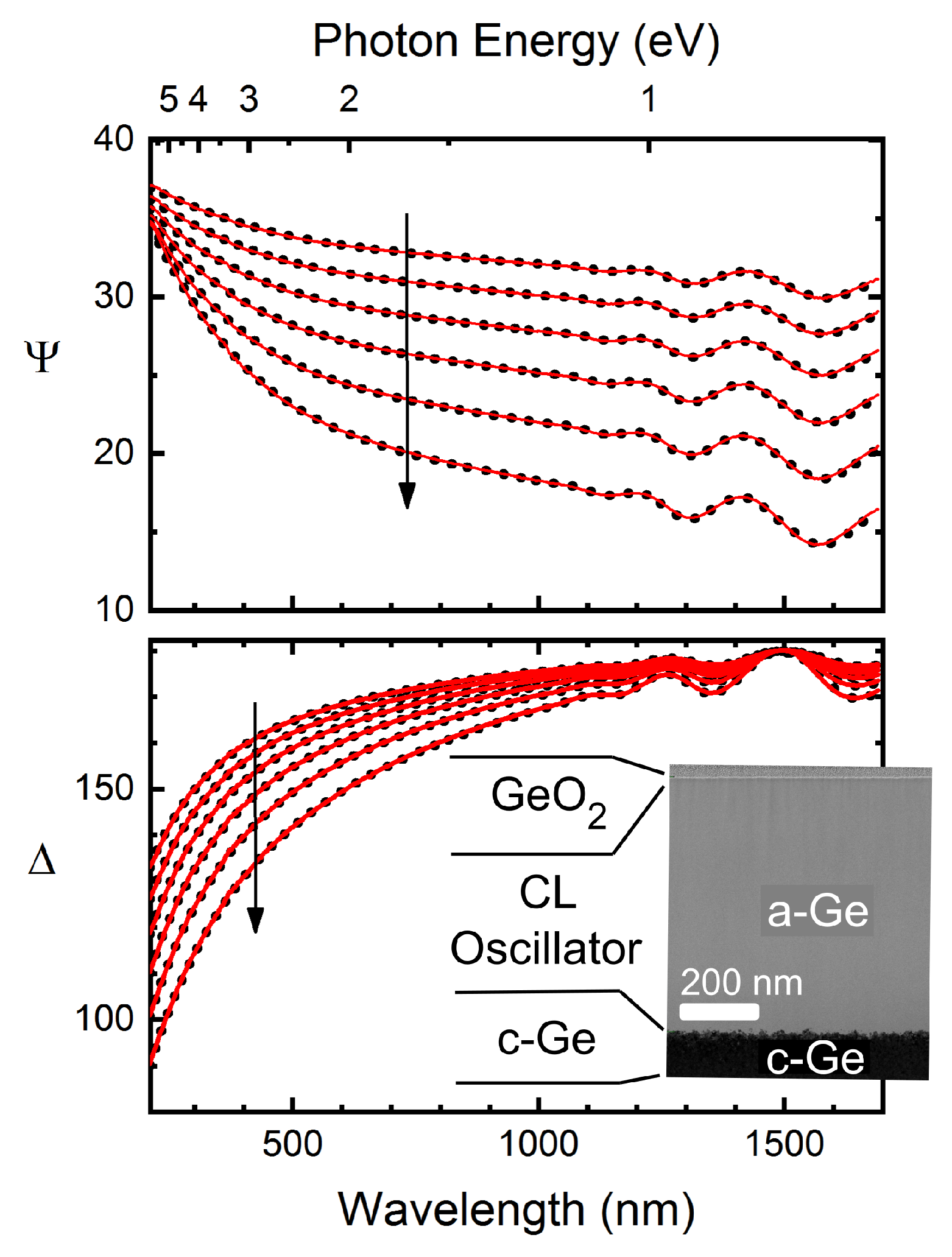
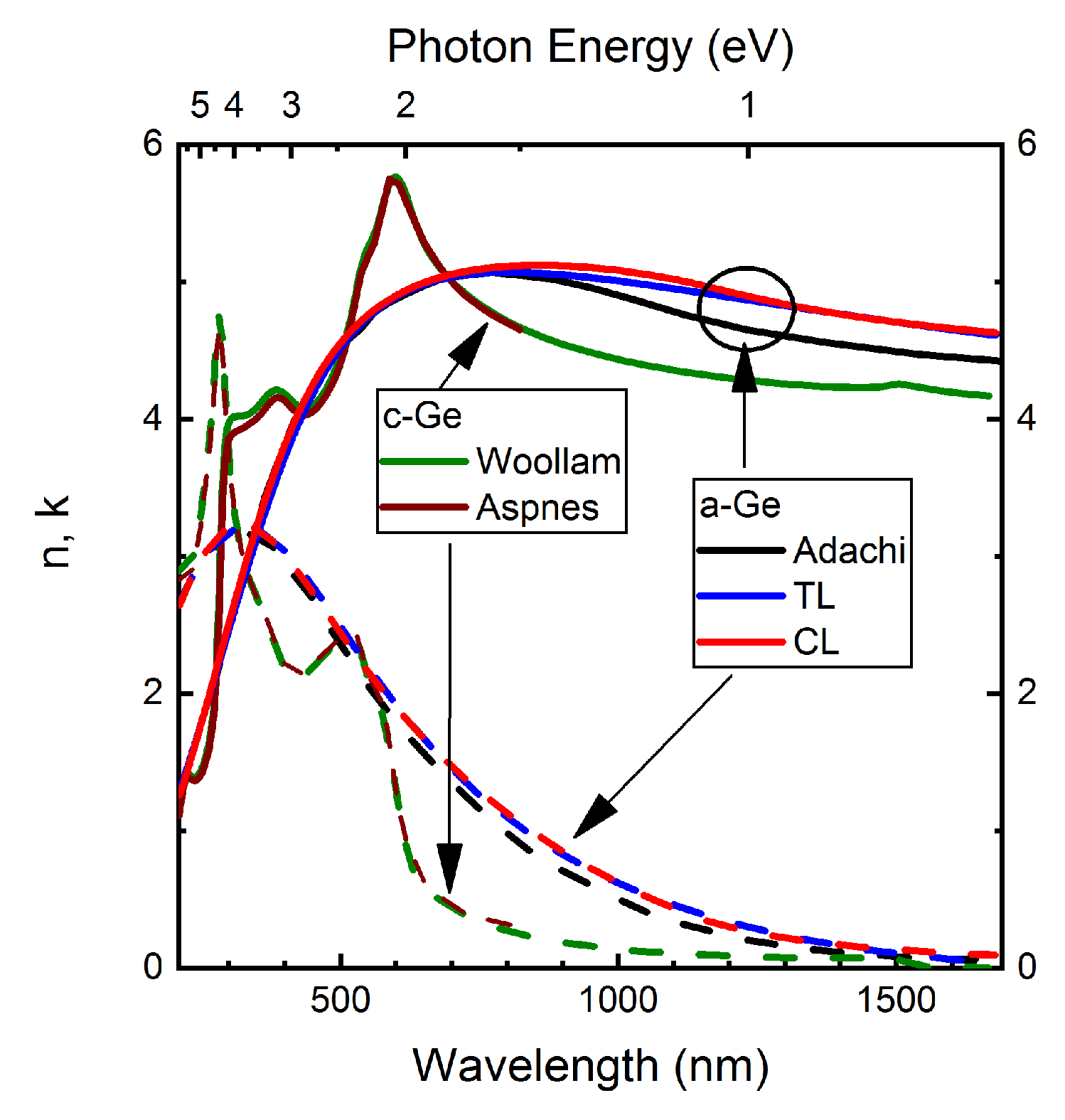
| Parameter | TL Model | CL Model |
|---|---|---|
| Oxide thickness (nm) | 1.61 ± 0.03 | 1.74 ± 0.01 |
| a-Ge layer thickness (nm) | 679.4 ± 0.3 | 678.9 ± 0.1 |
| Amplitude | 142.4 ± 0.4 | 92.7 ± 0.2 |
| Energy position (eV) | 3.042 ± 0.004 | 3.355 ± 0.002 |
| Broadening (eV) | 3.95 ± 0.01 | 4.08 ± 0.01 |
| Band gap (eV) | 0.622 ± 0.001 | 0.689 ± 0.002 |
| Offset | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.01 |
| Ep (eV) | 0.561 ± 0.004 | |
| Et (eV) | 0.39 ± 0.05 | |
| Eu (eV) | 0.189 ± 0.001 | |
| Mean Square Error | 23.2 | 9.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lohner, T.; Szilágyi, E.; Zolnai, Z.; Németh, A.; Fogarassy, Z.; Illés, L.; Kótai, E.; Petrik, P.; Fried, M. Determination of the Complex Dielectric Function of Ion-Implanted Amorphous Germanium by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry. Coatings 2020, 10, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050480
Lohner T, Szilágyi E, Zolnai Z, Németh A, Fogarassy Z, Illés L, Kótai E, Petrik P, Fried M. Determination of the Complex Dielectric Function of Ion-Implanted Amorphous Germanium by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry. Coatings. 2020; 10(5):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050480
Chicago/Turabian StyleLohner, Tivadar, Edit Szilágyi, Zsolt Zolnai, Attila Németh, Zsolt Fogarassy, Levente Illés, Endre Kótai, Peter Petrik, and Miklós Fried. 2020. "Determination of the Complex Dielectric Function of Ion-Implanted Amorphous Germanium by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry" Coatings 10, no. 5: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050480
APA StyleLohner, T., Szilágyi, E., Zolnai, Z., Németh, A., Fogarassy, Z., Illés, L., Kótai, E., Petrik, P., & Fried, M. (2020). Determination of the Complex Dielectric Function of Ion-Implanted Amorphous Germanium by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry. Coatings, 10(5), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050480





