Rifabutin Suppresses Inducible Clarithromycin Resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus by Blocking Induction of whiB7 and erm41
Abstract
1. Introduction
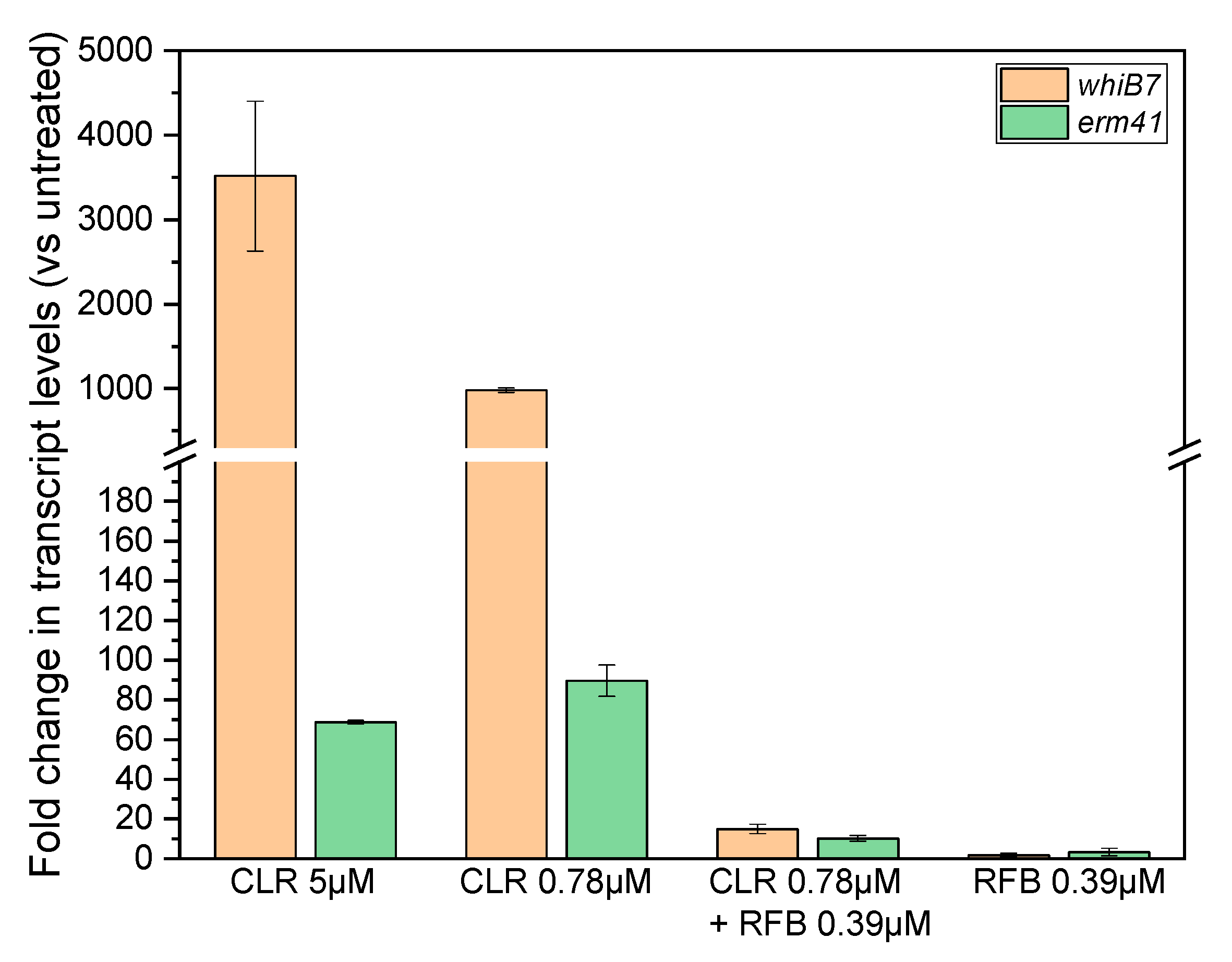
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffith, D.E.; Aksamit, T.; Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Catanzaro, A.; Daley, C.; Gordin, F.; Holland, S.M.; Horsburgh, R.; Huitt, G.; Iademarco, M.F.; et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 367–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, C.S.; Banks, J.; Capstick, T.; Fisher, A.J.; Gorsuch, T.; Laurenson, I.F.; Leitch, A.; Loebinger, M.R.; Milburn, H.J.; Nightingale, M.; et al. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease (NTM-PD). Thorax 2017, 72, ii1–ii64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopeman, R.C.; Harrison, J.; Desai, M.; Cox, J.A.G. Mycobacterium abscessus: Environmental Bacterium Turned Clinical Nightmare. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.J.; Jeong, B.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeon, K.; Park, K.U.; Jhun, B.W.; Lee, H.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Huh, H.J.; et al. Mycobacterial Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes in Mycobacterium abscessus Lung Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Mao, Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Chu, H. Clinical Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Antibiotics Used to Treat Mycobacterium abscessus Pulmonary Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, K.A.; Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Wallace, R.J., Jr. A novel gene, erm(41), confers inducible macrolide resistance to clinical isolates of Mycobacterium abscessus but is absent from Mycobacterium chelonae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst-Hess, K.; Rudra, P.; Ghosh, P. Mycobacterium abscessus WhiB7 Regulates a Species-Specific Repertoire of Genes To Confer Extreme Antibiotic Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryjma, M.; Burian, J.; Kuchinski, K.; Thompson, C.J. Antagonism between Front-Line Antibiotics Clarithromycin and Amikacin in the Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus Infections is Mediated by the whiB7 Gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.; Gutierrez, A.V.; Kremer, L. Dissecting erm(41)-mediated macrolide inducible resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortoli, E.; Kohl, T.A.; Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Trovato, A.; Leao, S.C.; Garcia, M.J.; Vasireddy, S.; Turenne, C.Y.; Griffith, D.E.; Philley, J.V.; et al. Emended description of Mycobacterium abscessus, Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus and Mycobacteriumabscessus subsp. bolletii and designation of Mycobacteriumabscessus subsp. massiliense comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4471–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, S.; Veziris, N.; Roux, A.L.; Brossier, F.; Gaillard, J.L.; Jarlier, V.; Cambau, E. Assessment of clarithromycin susceptibility in strains belonging to the Mycobacterium abscessus group by erm(41) and rrl sequencing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, F.P.; Castelberg, C.; Quiblier, C.; Bottger, E.C.; Somoskovi, A. Erm(41)-dependent inducible resistance to azithromycin and clarithromycin in clinical isolates of Mycobacterium abscessus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Sheng, W.H.; Hung, C.C.; Yu, C.J.; Lee, L.N.; Hsueh, P.R. Mycobacterium abscessus Complex Infections in Humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Vasireddy, S.; Vasireddy, R.; Iakhiaeva, E.; Howard, S.T.; Nash, K.; Parodi, N.; Strong, A.; Gee, M.; Smith, T.; et al. Utility of sequencing the erm(41) gene in isolates of Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus with low and intermediate clarithromycin MICs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1211–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.L.; Aziz, D.B.; Dartois, V.; Dick, T. NTM drug discovery: Status, gaps and the way forward. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1502–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, D.B.; Low, J.L.; Wu, M.L.; Gengenbacher, M.; Teo, J.W.P.; Dartois, V.; Dick, T. Rifabutin Is Active against Mycobacterium abscessus Complex. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, T.; Shin, S.J.; Koh, W.J.; Dartois, V.; Gengenbacher, M. Rifabutin is active against Mycobacterium abscessus in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryjma, M.; Burian, J.; Thompson, C.J. Rifabutin Acts in Synergy and Is Bactericidal with Frontline Mycobacterium abscessus Antibiotics Clarithromycin and Tigecycline, Suggesting a Potent Treatment Combination. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Tsai, Y.T.; Chang, S.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Wu, U.I.; Sheng, W.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, S.C. In Vitro Synergism of Rifabutin with Clarithromycin, Imipenem, and Tigecycline against the Mycobacterium abscessus Complex. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, U.S.; Dartois, V.; Dick, T. Repositioning rifamycins for Mycobacterium abscessus lung disease. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Rominski, A.; Sander, P. The Role of Antibiotic-Target-Modifying and Antibiotic-Modifying Enzymes in Mycobacterium abscessus Drug Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildkraut, J.A.; Pennings, L.J.; Ruth, M.M.; de Brouwer, A.P.; Wertheim, H.F.; Hoefsloot, W.; de Jong, A.; van Ingen, J. The differential effect of clarithromycin and azithromycin on induction of macrolide resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus. Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.E.; Shin, S.J.; Won, C.J.; Min, K.N.; Oh, T.; Hahn, M.Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.H.; Daley, C.L.; Kim, S.; et al. Macrolide treatment for Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium massiliense infection and inducible resistance. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, D.B.; Teo, J.W.P.; Dartois, V.; Dick, T. Teicoplanin - Tigecycline Combination Shows Synergy Against Mycobacterium abscessus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.H.; Yu, C.M.; Yu, V.L.; Chow, J.W. Synergy assessed by checkerboard. A critical analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1993, 16, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isolate Code | M. Abscessus Subspecies | Erm41 Sequevar | Erm41 Status | CLR Susceptibility | CLR + RFB | FICI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 19977 | abscessus | T28 | Functional | Resistant | S | 0.26 |
| Bamboo | abscessus | C28 | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 0.56 |
| M9 | abscessus | T28 | Functional | Resistant | S | 0.39 |
| M199 | abscessus | T28 | Functional | Resistant | S | 0.39 |
| M337 | abscessus | T28 | Functional | Resistant | S | 0.39 |
| M421 | abscessus | T28 | Functional | Resistant | S | 0.49 |
| M422 | abscessus | T28 | Functional | Resistant | S | 0.39 |
| CCUG 50184-T | bolletii | T28 | Functional | Resistant | S | 0.32 |
| M232 | bolletii | T28 | Functional | Resistant | S | 0.21 |
| M506 | bolletii | C28 | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 0.77 |
| CCUG 48898-T | massiliense | deletion | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 0.77 |
| M111 | massiliense | deletion | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 0.78 |
| M353 | massiliense | deletion | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 0.65 |
| M357 | massiliense | deletion | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 1.05 |
| M414 | massiliense | deletion | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 0.86 |
| M444 | massiliense | deletion | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 0.85 |
| M505 | massiliense | deletion | Non-functional | Sensitive | I | 1.17 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aziz, D.B.; Go, M.L.; Dick, T. Rifabutin Suppresses Inducible Clarithromycin Resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus by Blocking Induction of whiB7 and erm41. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020072
Aziz DB, Go ML, Dick T. Rifabutin Suppresses Inducible Clarithromycin Resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus by Blocking Induction of whiB7 and erm41. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(2):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020072
Chicago/Turabian StyleAziz, Dinah Binte, Mei Lin Go, and Thomas Dick. 2020. "Rifabutin Suppresses Inducible Clarithromycin Resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus by Blocking Induction of whiB7 and erm41" Antibiotics 9, no. 2: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020072
APA StyleAziz, D. B., Go, M. L., & Dick, T. (2020). Rifabutin Suppresses Inducible Clarithromycin Resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus by Blocking Induction of whiB7 and erm41. Antibiotics, 9(2), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020072






