In-Vitro Inhibition of Staphylococcal Pathogenesis by Witch-Hazel and Green Tea Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Determination of Total Phenolic Content of WH and GT
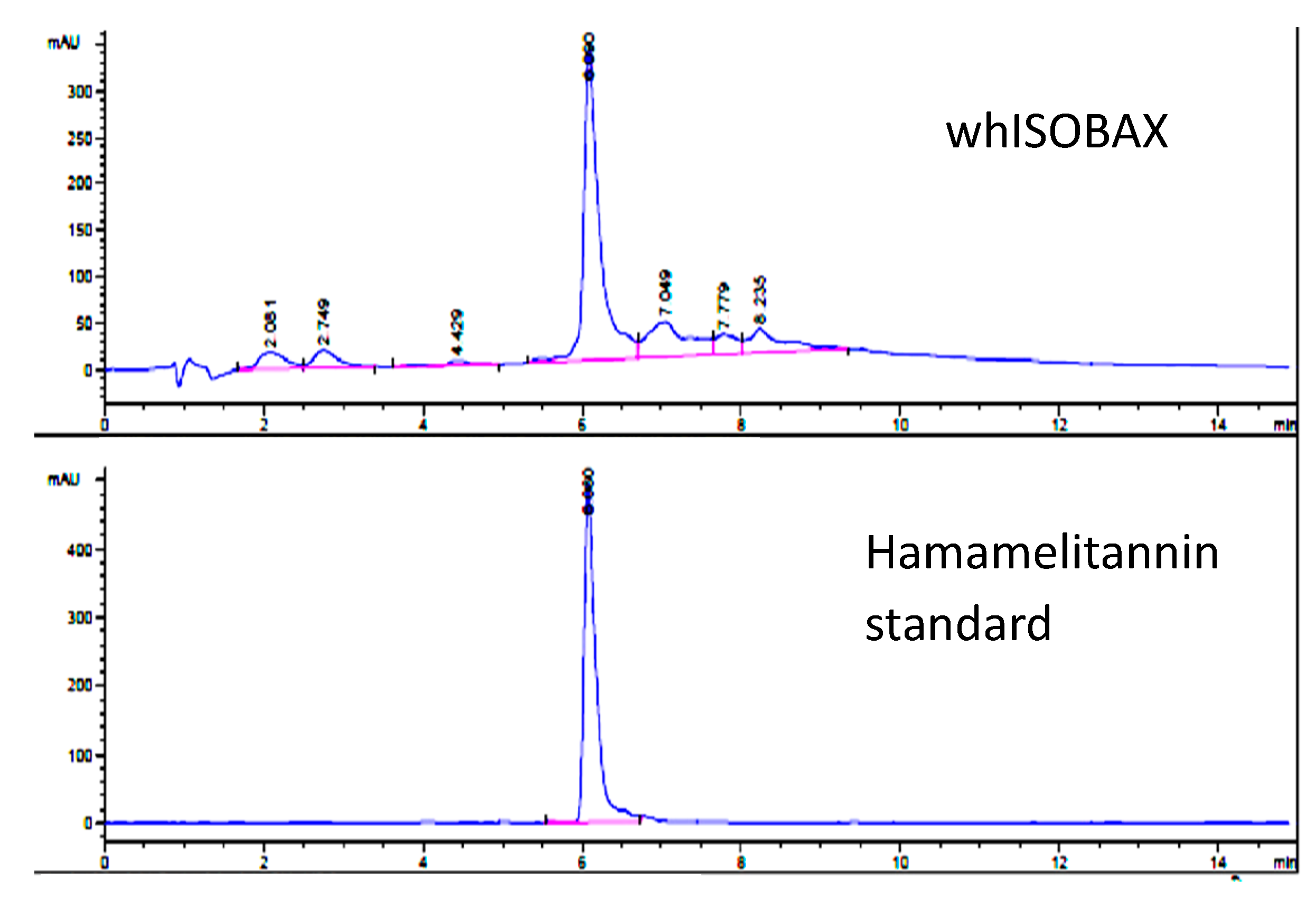
2.2. Determination of HAMA Content in WH by HPLC
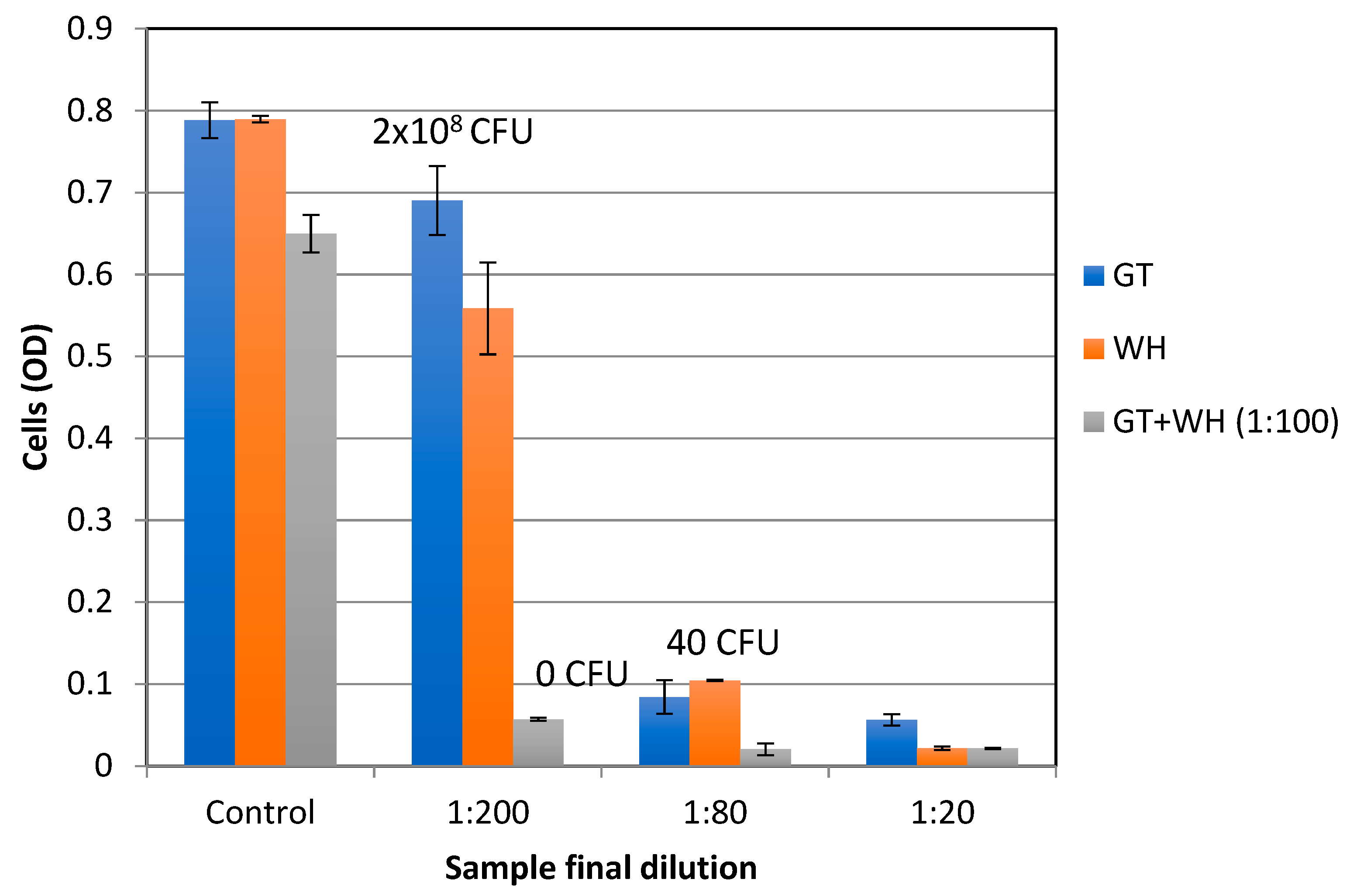
2.3. Antibacterial Activity Against Planktonic Cells
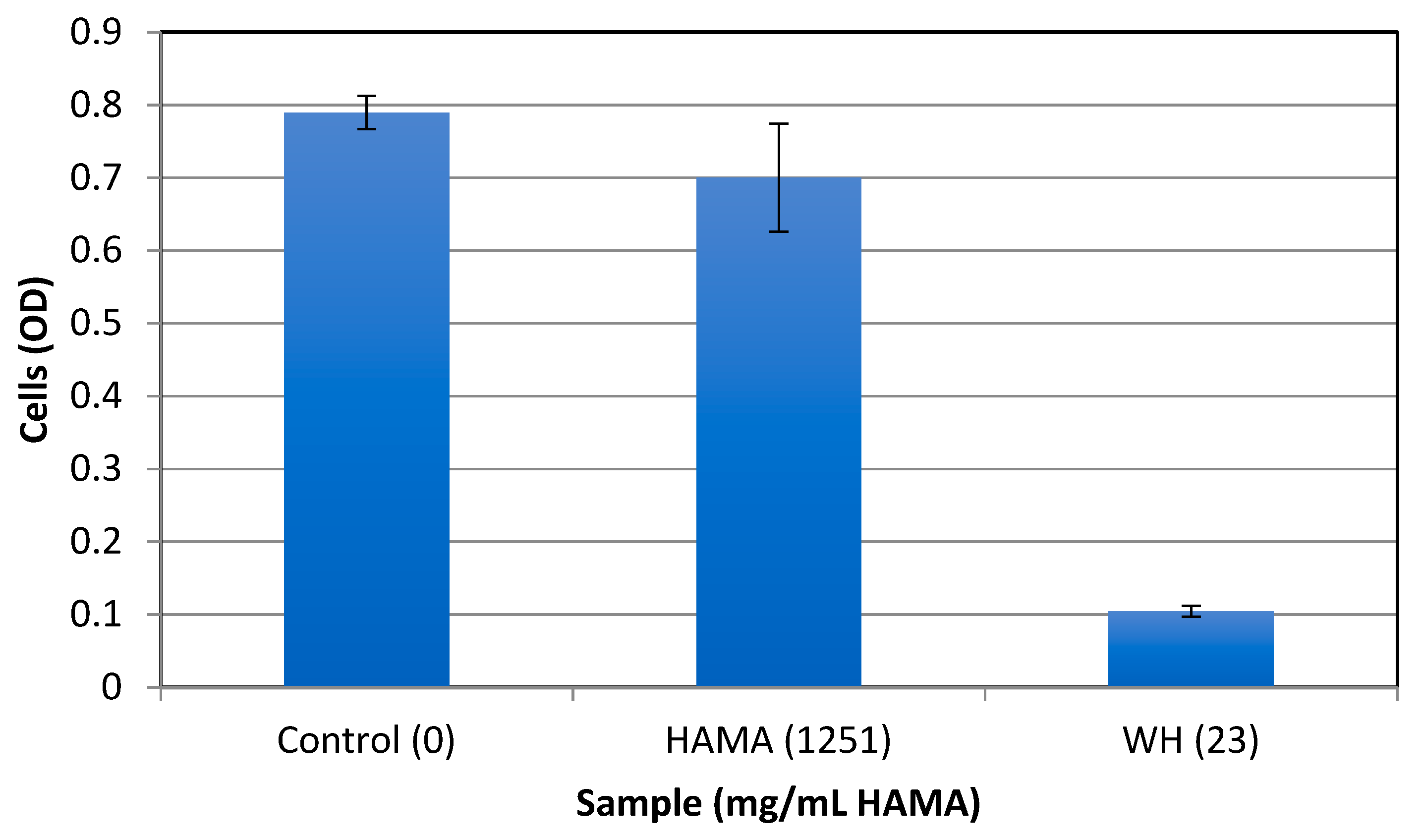
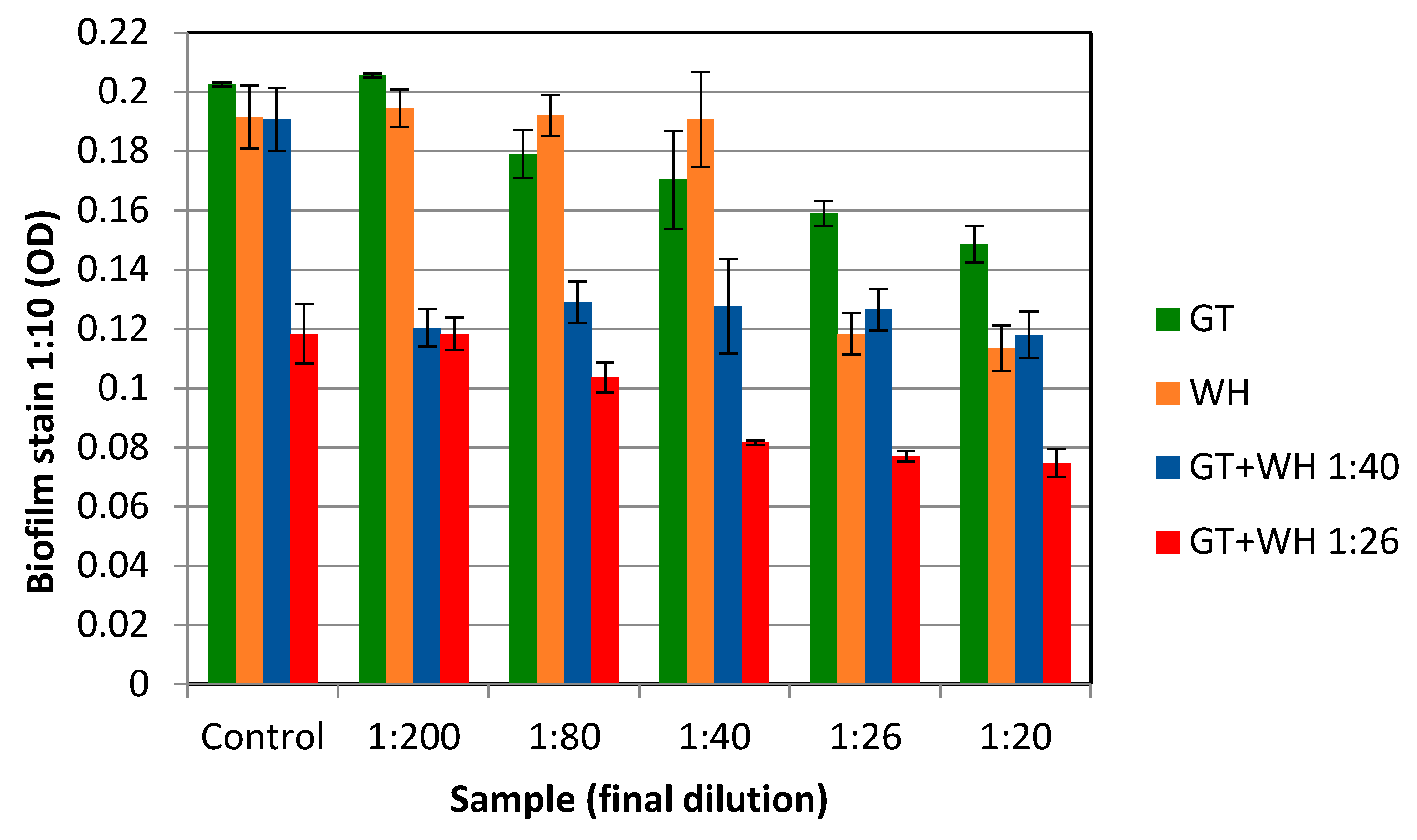
2.4. The Effect of WH and GT on Staphylococcal Pathogenesis (Biofilm Formation and Toxin Production)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteria
4.2. Test Formulations
4.3. Total Phenolic Content Determination for whISOBAX
4.4. Hamamelitannin Content in WH (HPLC Determination)
4.5. Antibacterial Testing on Planktonic Cells
4.6. Antibacterial Testing on Biofilm Cells
4.7. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin A (SEA) Production
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Practical Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delorme, T.; Dang, D.; Garcia, A.; Nasr, P. Genotypic and phenotypic variations in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from outpatient, inpatient and nursing homes. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Frees, D.; Ingmer, H. Antibiotic Resistance and the MRSA Problem. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.A.; Swogger, E.; Wolcott, R.; Pulcini, E.; Secor, P.; Sestrich, J.; Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S. Biofilms in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2008, 16, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis--the ’accidental’ pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, N.; Goldkorn, T.; Nhan, R.T.; Dang, L.B.; Scott, S.; Ridgley, R.M.; Rasooly, A.; Wright, S.C.; Larrick, J.W.; Rasooly, R.; et al. Autoinducer of virulence as a target for vaccine and therapy against Staphylococcus aureus. Science 1998, 280, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, Y.; Parsek, M.R. Quorum sensing and microbial biofilms. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 322, 67–84. [Google Scholar]
- Nadell, C.D.; Xavier, J.B.; Levin, S.A.; Foster, K.R. The evolution of quorum sensing in bacterial biofilms. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, N.; Goldkorn, T.; Gov, Y.; Hirshberg, M.; Koyfman, N.; Matthews, H.R.; Nhan, R.T.; Singh, B.; Uziel, O. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis via target of RNAIII-activating Protein (TRAP). J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, M.D.; Balaban, N. TRAP plays a role in stress response in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2009, 32, 592–599. [Google Scholar]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushniak, B.D. Antibiotic resistance: A public health crisis. Public Health Rep. 2014, 129, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossolini, G.M.; Arena, F.; Pecile, P.; Pollini, S. Update on the antibiotic resistance crisis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S. Antimicrobial Tolerance in Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, F.; Feng, L.; Li, J. Inhibition of quorum sensing, biofilm, and spoilage potential in Shewanella baltica by green tea polyphenols. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillo, A.; Papa, R.; Ricciardelli, A.; Sannino, F.; Ziaco, M.; Tilotta, M.; Selan, L.; Marino, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Long-Chain Fatty Aldehyde from Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 against Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.Y.; Dykes, G.A.; Choo, W.S. Biofilm formation by staphylococci in health-related environments and recent reports on their control using natural compounds. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; De Martino, L.; Coppola, R.; De Feo, V. Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.M. Plant products as antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 564–582. [Google Scholar]
- Sirk, T.W.; Brown, E.F.; Friedman, M.; Sum, A.K. Molecular binding of catechins to biomembranes: Relationship to biological activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6720–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackman, G.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Quorum sensing inhibitors increase the susceptibility of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, B.; Eberl, L.; Feucht, W.; Polster, J. Influence of polyphenols on bacterial biofilm formation and quorum-sensing. Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung C 2003, 58, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Brackman, G.; Breyne, K.; De Rycke, R.; Vermote, A.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Meyer, E.; Van Calenbergh, S.; Coenye, T. The Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Hamamelitannin Increases Antibiotic Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms by Affecting Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis and eDNA Release. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobrado, L.; Azevedo, M.M.; Silva-Dias, A.; Ramos, J.P.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A.G. Cerium, chitosan and hamamelitannin as novel biofilm inhibitors? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobrado, L.; Silva-Dias, A.; Azevedo, M.M.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A.G. In vivo antibiofilm effect of cerium, chitosan and hamamelitannin against usual agents of catheter-related bloodstream infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, M.D.; Adikesavan, N.V.; Cirioni, O.; Giacometti, A.; Silvestri, C.; Scalise, G.; Ghiselli, R.; Saba, V.; Orlando, F.; Shoham, M.; et al. Discovery of a quorum-sensing inhibitor of drug-resistant staphylococcal infections by structure-based virtual screening. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, A.; Brackman, G.; Risseeuw, M.D.P.; Coenye, T.; Van Calenbergh, S. Novel hamamelitannin analogues for the treatment of biofilm related MRSA infections-A scaffold hopping approach. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, J.; Muthu, M.; Paul, D.; Kim, D.H.; Chun, S. Bactericidal activity of green tea extracts: The importance of catechin containing nano particles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Anderson, D.; Racicot, K.; Pilkenton, S.J.; Apostolidis, E. Evaluation of Phenolic Phytochemical Enriched Commercial Plant Extracts on the In Vitro Inhibition of alpha-Glucosidase. Front. Nutr. 2017, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Bolwell, P.G.; Bramley, P.M.; Pridham, J.B. The relative antioxidant activities of plant-derived polyphenolic flavonoids. Free Radic. Res. 1995, 22, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton, P.D.; Shah, S.; Anderson, J.C.; Hara, Y.; Hamilton-Miller, J.M.; Taylor, P.W. Modulation of beta-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by catechins and gallates. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Wang, W.; Bai, F.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Sun, T.; He, Y. Antimicrobial effect and membrane-active mechanism of tea polyphenols against Serratia marcescens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Provan, G.J.; Helliwell, K. Determination of hamamelitannin, catechins and gallic acid in witch hazel bark, twig and leaf by HPLC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 33, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Morroni, G.; (Department of Biomedical Sciences and Public Health, Marche Polytechnic University, Ancona, Italy). Personal communication, 2019.
- Kuang, H.; Wang, W.; Xu, L.; Ma, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. Monoclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 1598–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I. Broad-spectrum quorum sensing and biofilm inhibition by green tea against gram-negative pathogenic bacteria: Deciphering the role of phytocompounds through molecular modelling. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirioni, O.; Giacometti, A.; Ghiselli, R.; Dell’Acqua, G.; Orlando, F.; Mocchegiani, F.; Silvestri, C.; Licci, A.; Saba, V.; Scalise, G.; et al. RNAIII-inhibiting peptide significantly reduces bacterial load and enhances the effect of antibiotics in the treatment of central venous catheter-associated Staphylococcus aureus infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsilinakos, A.; Artini, M.; Papa, R.; Sabatino, M.; Bozovic, M.; Garzoli, S.; Vrenna, G.; Buzzi, R.; Manfredini, S.; Selan, L.; et al. Machine Learning Analyses on Data including Essential Oil Chemical Composition and In Vitro Experimental Antibiofilm Activities against Staphylococcus Species. Molecules 2019, 24, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Final Dilution of Tested Extracts | GT Phenolic Content (mg/mL GAE) | WH Phenolic Content (mg/mL GAE) |
|---|---|---|
| 1:2000 | 0.005 | 0.006 |
| 1:800 | 0.012 | 0.015 |
| 1:400 | 0.025 | 0.031 |
| 1:200 | 0.050 | 0.063 |
| 1:80 | 0.125 | 0.157 |
| 1:40 | 0.250 | 0.315 |
| 1:26 | 0.375 | 0.471 |
| 1:20 | 0.500 | 0.630 |
| 1:16 | 0.625 | 0.790 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasooly, R.; Molnar, A.; Choi, H.-Y.; Do, P.; Racicot, K.; Apostolidis, E. In-Vitro Inhibition of Staphylococcal Pathogenesis by Witch-Hazel and Green Tea Extracts. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040244
Rasooly R, Molnar A, Choi H-Y, Do P, Racicot K, Apostolidis E. In-Vitro Inhibition of Staphylococcal Pathogenesis by Witch-Hazel and Green Tea Extracts. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(4):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040244
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasooly, Reuven, Adel Molnar, Hwang-Yong Choi, Paula Do, Kenneth Racicot, and Emmanouil Apostolidis. 2019. "In-Vitro Inhibition of Staphylococcal Pathogenesis by Witch-Hazel and Green Tea Extracts" Antibiotics 8, no. 4: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040244
APA StyleRasooly, R., Molnar, A., Choi, H.-Y., Do, P., Racicot, K., & Apostolidis, E. (2019). In-Vitro Inhibition of Staphylococcal Pathogenesis by Witch-Hazel and Green Tea Extracts. Antibiotics, 8(4), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040244





