Abstract
Polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) is a 3′–5′-exoribnuclease that is found in most bacteria and in some eukaryotic organelles. The enzyme plays a key role in RNA decay in these systems. PNPase structure and function have been studied extensively in Escherichia coli, but there are several important aspects of PNPase function in Streptomyces that differ from what is observed in E. coli and other bacterial genera. This review highlights several of those differences: (1) the organization and expression of the PNPase gene in Streptomyces; (2) the possible function of PNPase as an RNA 3′-polyribonucleotide polymerase in Streptomyces; (3) the function of PNPase as both an exoribonuclease and as an RNA 3′-polyribonucleotide polymerase in Streptomyces; (4) the function of (p)ppGpp as a PNPase effector in Streptomyces. The review concludes with a consideration of a number of unanswered questions regarding the function of Streptomyces PNPase, which can be examined experimentally.
1. Introduction
Polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase, EC 2.7.7.8) was the first enzyme shown to synthesize polyribonucleotides [1], and for some time, it was thought to be the bacterial RNA polymerase. The enzyme was subsequently characterized in Escherichia coli and other bacteria, and was shown to catalyze the following reaction:
where N is any of the four bases found in RNA [2,3]. As written, the reaction depicts the phosphorolytic degradation of RNA chains, and this activity appears to reflect the major function of PNPase in vivo. The reaction is reversible, however, and PNPase will synthesize polyribonucleotide chains, using nucleoside diphosphates (NDPs), rather than triphosphates, as substrates. The polymerizing activity of PNPase played an important role in the synthesis of polyribonucleotides used to unravel the genetic code [4,5].
(p5′N3′OH)X + Pi ⇆ (p5′N3′OH)X−1 + pp5′N
PNPase is found in all bacteria examined to date, except Mycoplasma, and is also present in eukaryotic organelles [6]. The enzyme has not been identified in Archaea [7]. In E. coli, PNPase and RNase II are the major 3′-exonucleases involved in RNA degradation [8]. In addition to its degradative function, PNPase plays a role in the bacterial response to environmental stresses, such as cold shock [9,10,11], is involved in biofilm formation [12,13] and virulence determination [14,15], and the activity of the enzyme is modulated by a number of small molecule effectors, at least in vitro [16,17,18,19].
Streptomyces are Gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacteria, notable for their ability to form spores and for their capacity to produce antibiotics [20,21]. Nearly 70% of all antibiotics used in clinical and veterinary medicine worldwide are synthesized as natural products by members of the genus [22]. Of particular relevance to this review, a number of biochemical and genetic features of Streptomyces PNPase distinguish it from its counterparts in other bacteria. In what follows, the functions of PNPase in Streptomyces will be explored. The reader is referred to several excellent reviews as sources of additional information on PNPase from E. coli and other bacteria [2,3,23,24].
2. Organization and Expression of the PNPase Gene in Streptomyces
In E. coli, and other organisms that have been studied, the PNPase gene, pnp, is a part of an operon that also includes rpsO, the gene for ribosomal protein S15 [9,25,26]. That operon is transcribed from two promoters in E. coli, designated PrpsO and Ppnp [25,27]. PrpsO is situated upstream of the rpsO gene, and Ppnp is located in the intergenic region between the two genes. Transcription from PrpsO ends at a rho-independent terminator and produces the rpsO transcript, but transcription through this terminator occurs with significant frequency and produces a readthrough transcript, containing both rpsO and pnp. Transcription from the intergenic promoter, Ppnp, produces a transcript containing pnp only [25,27]. In addition to the rpsO terminator, the rpsO–pnp intergenic region contains a second stem–loop that functions as a processing site for the double strand specific endoribonuclease, RNase III. RNase III processing plays an important role in pnp expression [25,28,29,30].
Our interest in the mechanisms of RNA decay in Streptomyces led to an examination of the transcriptional organization of the rpsO–pnp operon in Streptomyces coelicolor, the paradigm for biological studies in the genus. To our surprise, primer extension analysis of RNAs isolated from a parental strain of S. coelicolor and from an RNase III null mutant revealed not two, but four extension products, suggesting the presence of four promoters within the rpsO–pnp operon [31]. A visual inspection of 162 putative Streptomyces promoters from Strohl [32] and Yamazaki et al. [33], and a group of synthetic promoters generated by Seghezzi et al. [34], indicated that all four of the 5′-ends identified by primer extension in our studies were preceded by sequences similar to the −10 and −35 regions of characterized streptomycete promoters. Promoter probe cloning of DNA fragments containing these putative promoter sequences verified that the rpsO–pnp operon of S. coelicolor is transcribed from four promoters, two situated upstream of rpsO (PrpsOA and PrpsOB) and two situated in the intergenic region, upstream of pnp (PpnpA and PpnpB, Figure 1).
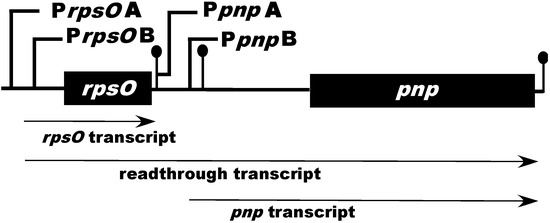
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the Streptomyces coelicolor rpsO–pnp operon. PrpsOA, B and PpnpA, B represent the upstream and intergenic promoters found in S. coelicolor, respectively. The ball-and-stick structures immediately following rpsO and pnp represent rho-independent transcription terminators. The ball-and-stick structure just upstream of pnp represents the intergenic hairpin which is cleaved by RNase III. The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Of particular interest in this analysis was the observation that the four promoters were temporally regulated. That is, the activity of the four promoters varied with time after inoculation of liquid cultures and the variations were promoter-specific, as shown in Figure 2. In terms of maximal activity, PpnpB was most active followed by PrpsOB, PpnpA, and PrpsOA.
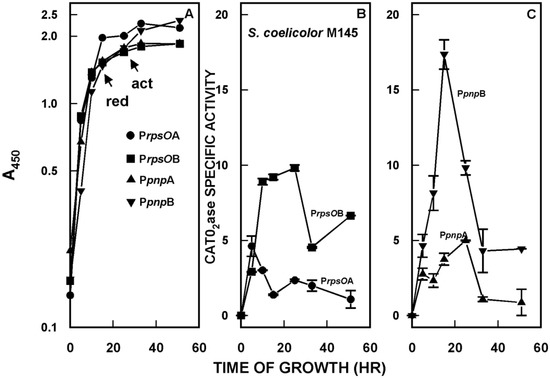
Figure 2.
(A) Growth of the S. coelicolor strains containing promoter probe constructs. Growth was measured as the increase in optical density at 450 nm. The arrows in the figure indicate the onset of the production of two of the secondary metabolites synthesized by S. coelicolor, undecylprodigiosin (red) and actinorhodin (act). (B) Catechol dioxygenase (CATO2ase) activity of mycelial extracts of S. coelicolor derivatives containing the putative rpsOA and rpsOB promoters, cloned in the promoter probe vector pIPP2 [35]. Mycelium was harvested at the indicated times, disrupted by sonication, and following centrifugation, supernatants were assayed for catechol dioxygenase, as described previously [31,35]. The catechol dioxygenase gene is the reporter in the promoter probe vector [35]. (C) CATO2ase activities of extracts of strains containing the putative pnpA and pnpB promoters. The results shown are the averages of duplicate assays from two independent experiments ± SEM. This figure is reprinted from Gene, 536, Patricia Bralley, Marcha L. Gatewood, George H. Jones, Transcription of the rpsO–pnp operon of Streptomyces coelicolor involves four temporally regulated, stress responsive promoters. 177–185, Copyright (2014), with permission from Elsevier [31].
A major mechanism for the modulation of promoter activity in bacterial systems involves the use of alternative sigma factors by RNA polymerase. The S. coelicolor genome encodes over sixty alternative sigma factors, many of which play roles in differentiation and responses to stress (reviewed in [36]). It was of considerable interest to determine whether the four rpsO–pnp promoters might require alternative sigma factors for transcription in S. coelicolor.
To this end, we obtained null mutants for a number of sigma factors, including σB, σH, and σL [36], and their corresponding parental strains. We transferred the rpsO–pnp promoter probe constructs to each strain and measured promoter activity. The results obtained for the σH and σL mutants were quite similar to those for the parental strain of S. coelicolor, that is, the same pattern of temporal regulation was observed in both of these sigma factor mutants as in the parental strain (cf. Figure 2). In marked contrast, the PrpsOA, PrpsOB, and PpnpB promoters were completely inactive in the σB mutant. PpnpA, however, was as active in the σB mutant as in the parental strain, and showed a similar pattern of temporal expression [31]. This result indicates that PrpsOA and B and PpnpB are dependent on σB for activity, and suggests that these promoters are transcribed by an RNA polymerase holoenzyme containing σB.
PNPase is a cold shock protein in many bacteria, and it has been shown that cold shock leads to an increase in PNPase levels in E. coli and other organisms [9,10,11]. It was of interest to determine whether PNPase levels increased in cold shock in S. coelicolor, and whether any such increase reflected changes in the activity of the rpsO–pnp promoters. As shown in Figure 3C, PNPase activity increased significantly (two-fold) in S. coelicolor over three hours of cold shock at 10 °C. This increase in activity was accompanied by an increase in the activities of all four of the rpsO–pnp promoters (Figure 3A,B) as compared with their activities at the normal growth temperature, 30 °C.
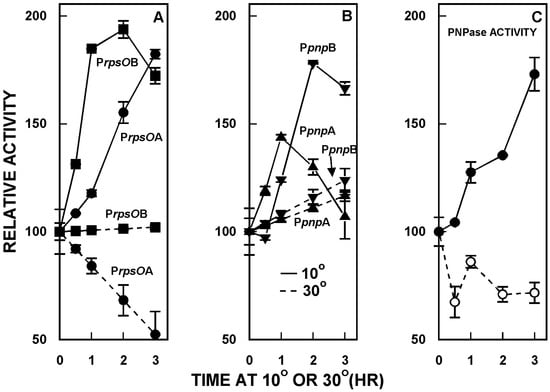
Figure 3.
Cold shock responses of S. coelicolor. Derivatives containing the rpsO–pnp promoter probe constructs were grown and 30 °C, and half of each culture was then shifted to 10 °C. Mycelium was harvested at the indicated times, disrupted by sonication, and following centrifugation, supernatants were assayed for promoter activity, as described [31,35]. Panel C shows the results of PNPase polymerization assays. In Panels A and B, PNPase promoter activities are expressed relative to the activity measured at 30 °C at zero time, immediately before the shift to 10 °C. The results shown are the averages of duplicate assays from two independent experiments ± SEM. In the first experiment, PNPase levels were measured in S. coelicolor containing PrpsOA and in the second, PNPase levels were measured in the derivative containing PpnpB. This figure is reprinted from Gene, 536, Patricia Bralley, Marcha L. Gatewood, George H. Jones, Transcription of the rpsO-pnp operon of Streptomyces coelicolor involves four temporally regulated, stress responsive promoters. 177–185, Copyright (2014), with permission from Elsevier [31].
Thus, PNPase is a cold shock protein in Streptomyces, and the cold shock response involves changes in the activities of the promoters responsible for transcription of the rpsO–pnp operon [31].
3. PNPase Function as an RNA 3′-Polyribonucleotide Polymerase in Streptomyces
As is the case in eukaryotes, bacterial RNAs have oligo- and polyribonucleotide tails at their 3′-ends, and these tails are added post-transcriptionally (reviewed in [37]). In E. coli, the primary enzyme responsible for the synthesis of these tails is poly(A) polymerase I (PAP I), and the tails are composed primarily of A residues [38]. In bacteria, poly(A) tails function to facilitate RNA degradation as the major 3′-exoribonucleases, viz. RNase II and PNPase in E. coli, digest these tails processively in vitro and in vivo [8,39].
It was shown some years ago by Mohanty and Kushner that an E. coli mutant lacking PAP I still added tails to the 3′-ends of its RNAs. However, these tails were not composed exclusively of A residues; the tails contained G, C, and U residues as well, i.e., they were heteropolymeric [40]. Mohanty and Kushner demonstrated that the enzyme responsible for the synthesis of these heteropolymeric tails was none other than PNPase [40]. Thus, even in the absence of PAP I, PNPase can add 3′-tails to facilitate the degradation of cellular RNAs.
Streptomyces do not contain PAP I. Yet the 3′-ends of streptomycete RNAs do possess tails. Moreover, the tails are heteropolymeric in composition, like those synthesized by PNPase in E. coli in the absence of PAP I [41,42]. These observations, and the report that PNPase functions as the RNA 3′-polyribonucleotide polymerase in plant chloroplasts and in cyanobacteria [43,44], led to the hypothesis that PNPase played the same role in Streptomyces [45]. The straightforward way to test this hypothesis would be to create a pnp null mutant, e.g., in S. coelicolor, and to determine whether the mutant was still capable of adding 3′-tails to its RNAs. However, attempts to disrupt pnp in S. coelicolor and in the sister species, Streptomyces antibioticus, were only successful when a second copy of pnp was added to the genome. In other words, gene disruption attempts revealed that, unlike the situation in E. coli and in the Bacilli, pnp is an essential gene in Streptomyces [42].
A model for the function of PNPase as an RNA 3′-polyribonucleotide polymerase is presented in detail below.
4. Function of PNPase as Both an Exoribonuclease and as an RNA 3′-Polyribonucleotide Polymerase
PNPase activity is highly processive and the enzyme is impeded by stem–loop structures [46]. Streptomycete genomes are GC rich, so that enzymes involved in RNA decay may have evolved to degrade the RNAs derived from these genomes efficiently. A possible strategy for facilitating this degradation was suggested by the observation that PNPase appears to utilize its polymerizing activity to add 3′-tails to streptomycete RNAs [42,45]. It seemed possible that the enzyme might add such tails during phosphorolysis to create single stranded 3′-ends that would then function as the substrates for that phosphorolysis. If this were the case, it might be expected that nucleoside diphosphates, the substrates for polymerization, would stimulate phosphorolysis. To test this hypothesis, two model PNPase substrates were constructed from the sequence of the rpsO–pnp operon of S. coelicolor. Both substrates contained the rpsO–pnp terminator and the intergenic hairpin. Thus, both model substrates contained secondary structure that would be expected to impede phosphorolysis by PNPase. One substrate, designated 5601, also possessed a single stranded 3′-tail, 33 bases in length, while the other substrate, 5650, terminated at the base of the intergenic hairpin, and did not have a single stranded tail [47].
The phosphorolysis of these two substrates was studied in the absence and presence of a mixture of all four nucleoside diphosphates (NDPs) with the interesting result, predicted by our hypothesis, that the NDPs, normally the substrates for the polymerizing activity of PNPase, did stimulate RNA degradation by phosphorolysis. Figure 4 shows the results of phosphorolysis of the 5650 transcript (labeled RP3 in the figure).
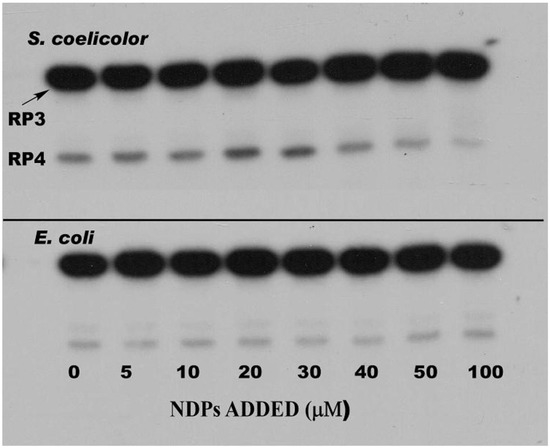
Figure 4.
Effects of nucleoside diphosphates on the phosphorolysis of the 5650 transcript. Phosphorolysis reactions were performed as described in [47], and reaction products were separated by gel electrophoresis. The top panel shows the results obtained with S. coelicolor PNPase and the bottom panel results using E. coli PNPase. Reactions were conducted in the presence of increasing concentrations of a mixture of ADP, CDP, UDP, and GDP (nucleoside diphosphates (NDPs)) as indicated. RP3 is the 5650 transcript, and RP4 represents the product obtained by complete digestion of the intergenic hairpin in RP3 by PNPase. Note that as PNPase is highly processive [48], no intermediates with mobilities between those of RP3 and RP4 were observed. Copyright © American Society for Microbiology (J. Bacteriol. 190, 2008, 98–106, DOI:10.1128/JB.00327-07) [47].
Analysis of the results shown in Figure 4 revealed that NDPs at 20–30 µM in phosphorolysis mixtures stimulated that reaction by 2–3 fold as compared with controls, but only when the structured RNA, 5650 (RP3) was used as the substrate [47]. NDPs had no effect on the phosphorolysis of the 5601 substrate, possessing the single stranded tail. Kinetic analyses showed that NDPs affected the Km for phosphorolysis. Thus, the Km value for phosphorolysis of the 5650 substrate in the absence of NDPs was 3.1 µM. This value decreased to 0.65 µM in the presence of all four NDPs at 20 µM. This latter Km was almost identical to that obtained in the absence of NDPs for the 5601 substrate, which has a single stranded 3′-tail (0.62 µM). NDPs did not further decrease the Km for the 5601 substrate. It is noteworthy as well, that NDPs had no effect on the phosphorolysis of either substrate by E. coli PNPase, and that the E. coli enzyme was intrinsically less active with the structured substrate than was its counterpart from S. coelicolor [47].
Our model for the explanation of the foregoing observations is shown in Figure 5 [49].
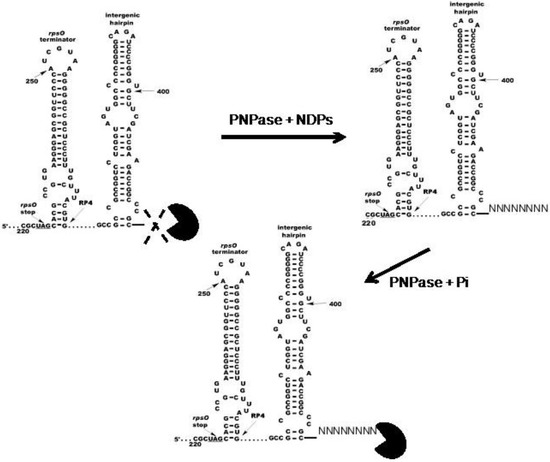
Figure 5.
Model for the effects of NDPs on the activity S. coelicolor PNPase. The model posits that S. coelicolor PNPase (PacMan symbol) is able to phosphorolyze 5650 and other structured substrates to a limited extent in the absence of NDPs, as indicated by the dashed X. In the presence of NDPs, PNPase synthesizes unstructured 3′-tails in vivo, and these tails then provide an anchor for the enzyme, thus facilitating the digestion of structured substrates. Copyright © American Society for Microbiology (J. Bacteriol. 195, 2013, 5151–5159, DOI:10.1128/JB.00936-13) [49].
We posit that the stem–loops of structured substrates, like 5650, block PNPase action. The addition of short 3′-tails during phosphorolysis, or the presence of naturally occurring tails on substrates like 5601, allows for the breathing of stems and thus permits PNPase, which might otherwise stall at the stem–loops in structured substrates, to continue phosphorolysis through those structures. As indicated above, this mechanism may represent an evolutionary adaptation occasioned by the high GC content of streptomycete genomes and their transcripts.
It must be noted, however, that the evidence for the function of PNPase as a 3′-polyribonucleotide polymerase in Streptomyces is indirect. In vivo evidence for this function remains to be uncovered.
5. (p)ppGpp as a PNPase Effector
Highly phosphorylated guanine nucleotides, (p)ppGpp, guanosine pentaphosphate, and guanosine tetraphosphate, are alarmones that play a number of roles in the regulation of bacterial metabolism (reviewed in [50,51]). (p)ppGpp is synthesized by the product of the relA gene in E. coli [52], and that gene is found in S. coelicolor [53,54], S. antibioticus [55], and other streptomycetes [56]. In Streptomyces, ppGpp plays an important role in the regulation of antibiotic synthesis [53,54,55,56].
PNPase from S. antibioticus was shown to synthesize pppGpp in vitro [57,58]. While this activity may be an in vitro artifact, as no other PNPases are known to possess it, the observation suggested a possible relationship between (p)ppGpp and RNA decay in Streptomyces. To begin to examine this relationship, the effects of (p)ppGpp on polymerization and phosphorolysis by S. coelicolor, S. antibioticus, and E. coli PNPases were measured in the absence and presence of (p)ppGpp [59]. As shown in Figure 6, both guanosine penta- and tetraphosphates inhibited the activity of S. coelicolor PNPase, in both phosphorolysis and polymerization, though ppGpp was a more potent inhibitor than pppGpp.
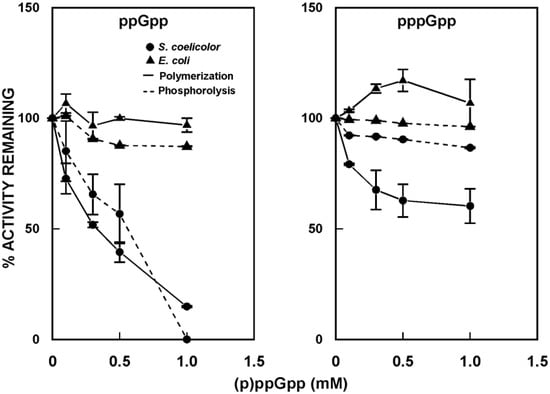
Figure 6.
Effects of (p)ppGpp on the activity of PNPase. Polymerization and phosphorolysis reactions were performed in the absence and presence of guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) or guanosine pentaphosphate (pppGpp), using purified PNPase from S. coelicolor and E. coli [59]. Results are expressed relative to the activities measured in the absence of (p)ppGpp, set arbitrarily to 100%.
Essentially identical results were obtained for S. antibioticus PNPase (not shown). By contrast, neither ppGpp nor pppGpp were effective inhibitors of the activity of E. coli PNPase. Indeed, at concentrations up to 1 mM, pppGpp actually stimulated the polymerizing activity of the E. coli enzyme.
In the same study, the effects of (p)ppGpp on the stability of bulk mRNA in S. coelicolor were examined [59]. It was initially observed that the half-life of bulk mRNA increased by 1.8-fold in stationary phase cultures as compared with exponential phase. That this increase might be related to the effects of (p)ppGpp was suggested by studies with an S. coelicolor relA mutant, and a strain containing an inducible relA gene. While the half-life of bulk mRNA was longer in the relA mutant than in the parental strain (e.g., 8.9 min vs 3.2 min in exponential phase), the half-life decreased slightly in the relA mutant in stationary phase (to 7.2 min). In the strain containing an inducible relA gene, producing increased levels of (p)ppGpp, induction occasioned a ca. two-fold increase in the half-life of bulk mRNA, from 6.6 to 11.8 min. Taken together, these observations suggest that (p)ppGpp may stabilize mRNAs in stationary phase S. coelicolor cells, as compared with cells growing exponentially.
Why and how might this stabilization occur? It is well established that although levels of RNA and protein synthesis decrease dramatically as Streptomyces cultures move from the exponential to the stationary phase of growth, a basal level of synthesis is maintained throughout stationary phase [60,61]. This basal level of macromolecular synthesis is presumably required to produce enzymes and other proteins involved in the synthesis of the secondary metabolites these organisms produce in stationary phase. Stabilization of the transcripts for these proteins would represent one strategy the organisms could employ to ensure the persistence of macromolecular synthesis to support secondary metabolite production. It is known that (p)ppGpp is present in significant amounts, even in stationary phase streptomycete cultures [62,63]. Thus, the inhibition of PNPase by (p)ppGpp might represent a strategy used by Streptomyces to stabilize essential mRNAs during stationary phase. It would be interesting to determine whether (p)ppGpp inhibits the activity of other exo- and endonucleases and while such analyses have yet to be performed, it is noteworthy that ppGpp inhibits PNPase from another actinomycete, Nonomuraea sp. [64].
6. Conclusions and Unanswered Questions
It is apparent from the brief analysis above that PNPase is a multitalented enzyme that plays a critical role in the metabolic activities of bacterial cells. Despite the wealth of information that has been accumulated about PNPase, a number of important biological questions remain unanswered, particularly as they relate to the functions of Streptomyces PNPase.
First, why is the rpsO–pnp operon of S. coelicolor transcribed from four promoters? The answer to this question may relate to the fact that the operon contains a ribosomal protein gene, as well as the gene for PNPase. It is possible that the promoters are not only critical to the regulation of pnp expression, but that they also play and important role in ribosome biogenesis via their regulation of the levels of the rpsO transcript. Mutation of the four promoter sequences may provide insight into these possibilities.
Second, what is the significance, if there is any, to the fact that the S. coelicolor rpsO–pnp operon produces six transcripts (two rpsO transcripts from PrpsOA and B, two readthrough transcripts from the same two promoters, and two pnp transcripts from PpnpA and B)? It should be noted that Northern blot analysis of the transcripts derived from the S. coelicolor rpsO–pnp operon did not reveal the presence of six separate transcripts [65]. It is possible that the different transcripts are not sufficiently different in size to have been resolved on the Northern blotting gels. Another intriguing possibility is that the longer transcripts, obtained from the upstream promoter in each case, might be processed at their 5′-ends by RNase J, which possesses 5′–3′-exoribonuclease activity. RNase J has recently been characterized in S. coelicolor [66,67].
Third, as described above, PNPase is a cold shock protein in Streptomyces. It is relevant to ask whether PNPase responds to other environmental stresses, such as heat, oxidative stress, metal ion stress, etc. It would be of interest, in particular, to examine the effects of various types of stress on the activities of the rpsO–pnp promoters. Mutational analyses again might reveal important aspects of promoter function in stress conditions in Streptomyces.
Fourth, a number of small effector molecules modulate the activity of E. coli PNPase, e.g., ATP, citrate, and cyclic-diGMP [16,17,18,19]. It has been proposed that these effectors connect RNA decay to other metabolic pathways in bacterial cells. It would be interesting to determine whether these effectors also affect the activity of Streptomyces PNPase. It is noteworthy, in this regard, that in silico molecular docking studies suggest that citrate, which inhibits the activity of E. coli PNPase, will bind to PNPase from S. antibioticus [18].
Finally, in E. coli and other organisms, PNPase is part of a larger macromolecular complex generally referred to as the degradosome ([68,69]. In E. coli, the components of the degradosome are organized around a scaffold provided by the single strand specific endoribonuclease, RNase E [70]. RNase E is present in S. coelicolor, and has been shown to interact with PNPase in vivo [71]. However, unlike the situation in E. coli, the identities of other proteins that might be involved in the degradative machine are unknown in Streptomyces.
It is fervently hoped that the foregoing and other important questions related to PNPase structure and function will continue to attract interest and experimentation to provide answers to them.
Acknowledgments
Much of the research described in this report was supported by grants MCB-0133520 and MCB-0817177 from the U. S. National Science Foundation to the author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Grunberg-Manago, M.; Ochoa, S. Enzymatic synthesis and breakdown of polynucleotides: Polynucleotide phosphorylase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 3165–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godefroy-Colburn, T.; Grunberg-Manago, M. Polynucleotide phosphorylase. Enzymes 1972, 7, 533–574. [Google Scholar]
- Littauer, U.Z.; Soreq, H. Polynucleotide phosphorylase. Enzymes 1982, 15, 517–553. [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel, P.; Speyer, J.F.; Ochoa, S. Synthetic polynucleotides and the amino acid code. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1962, 47, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaei, J.H.; Jones, O.W.; Martin, R.G.; Nirenberg, M. Characteristics and composition of RNA coding units. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1962, 48, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Deutscher, M. Exoribonuclease superfamilies: Structural analysis and phylogenetic distribution. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2001, 29, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin-Chao, S.; Chiou, N.T.; Schuster, G. The PNPase, exosome and RNA helicases as the building components of evolutionarily-conserved RNA degradation machines. J. Biomed. Sci. 2007, 14, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, W.P.; Kushner, S.R. Polynucleotide phosphorylase and ribonuclease II are required for cell viability and mRNA turnover in Escherichia coli k-12. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, D.J.; Dowds, B.C. The gene coding for polynucleotide phosphorylase in Photorhabdus sp. Strain k122 is induced at low temperatures. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 3775–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goverde, R.L.J.; Huis in’t Veld, J.H.J.; Kusters, J.G.; Mooi, F.R. The psychrotropic bacterium Yersinia enterocolitica requires expression of pnp, the gene for polynucleotide phosphorylase, for growth at low termperature (5 °C). Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangrossi, S.; Briani, F.; Ghisotti, D.; Regonesi, M.E.; Tortora, P.; Deho, G. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of polynucleotide phosphorylase during cold acclimation in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carzaniga, T.; Antoniani, D.; Deho, G.; Briani, F.; Landini, P. The RNA processing enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylase negatively controls biofilm formation by repressing poly-N-acetylglucosamine (PNAG) production in Escherichia coli C. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pobre, V.; Arraiano, C.M. Next generation sequencing analysis reveals that the ribonucleases RNAse II, RNAse R and PNPase affect bacterial motility and biofilm formation in E. coli. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenzweig, J.A.; Chopra, A.K. The exoribonuclease polynucleotide phosphorylase influences the virulence and stress responses of Yersiniae and many other pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engman, J.; Negrea, A.; Sigurlasdottir, S.; Georg, M.; Eriksson, J.; Eriksson, O.S.; Kuwae, A.; Sjolinder, H.; Jonsson, A.B. Neisseria meningitidis polynucleotide phosphorylase affects aggregation, adhesion, and virulence. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Favero, M.; Mazzantini, E.; Briani, F.; Zangrossi, S.; Tortora, P.; Deho, G. Regulation of Escherichia coli polynucleotide phosphorylase by ATP. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27355–27359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurmohamed, S.; Vincent, H.A.; Titman, C.M.; Chandran, V.; Pears, M.R.; Du, D.; Griffin, J.L.; Callaghan, A.J.; Luisi, B.F. Polynucleotide phosphorylase activity may be modulated by metabolites in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 14315–14323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuckerman, J.R.; Gonzalez, G.; Gilles-Gonzalez, M.A. Cyclic di-GMP activation of polynucleotide phosphorylase signal-dependent RNA processing. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 407, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, C.M.; Butt, L.E.; Bufton, J.C.; Lourenco, D.C.; Gowers, D.M.; Pickford, A.R.; Cox, P.A.; Vincent, H.A.; Callaghan, A.J. Inhibition of homologous phosphorolytic ribonucleases by citrate may represent an evolutionarily conserved communicative link between RNA degradation and central metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Chater, K.F.; Chandra, G.; Niu, G.; Tan, H. Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 112–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, G.; Chater, K.F. Developmental biology of Streptomyces from the perspective of 100 actinobacterial genome sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 345–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdy, J. Recent advances in and prospects of antibiotic research. Process. Biochem. 1980, 15, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Littauer, U.Z. From polynucleotide phosphorylase to neurobiology. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38889–38897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Briani, F.; Carzaniga, T.; Deho, G. Regulation and functions of bacterial PNPase. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2016, 7, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Régnier, P.; Portier, C. Initiation, attenuation and RNase III processing of transcripts from the Escherichia coli operon encoding ribosomal protein S15 and polynucleotide phosphorylase. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 187, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttinger, A.; Hahn, J.; Dubnau, D. Polynucleotide phosphorylase is necessary for competence development in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portier, C.; Regnier, P. Expression of the rpsO and pnp genes: Structural analysis of a DNA fragment carrying their control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 6091–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Le Meur, M.; Portier, C. E. coli polynucleotide phosphorylase expression is autoregulated through an RNase III-dependent mechanism. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robert-Le Meur, M.; Portier, C. Polynucleotide phosphorylase of Escherichia coli induces degradation of its RNase III processed messenger by preventing its translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jarrige, A.-C.; Mathy, N.; Portier, C. Pnpase autocontrols its expression by degrading a double-stranded structure in the pnp mRNA leader. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6845–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bralley, P.; Gatewood, M.L.; Jones, G.H. Transcription of the rpsO-pnp operon of Streptomyces coelicolor involves four temporally regulated, stress responsive promoters. Gene 2014, 536, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohl, W.R. Compilation and analysis of DNA sequences associated with apparent streptomycete promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Ohnishi, Y.; Horinouchi, S. Transcriptional switch on of ssgA by a-factor, which is essential for spore septum formation in Streptomyces griseus. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seghezzi, N.; Amar, P.; Koebmann, B.; Jensen, P.R.; Virolle, M.J. The construction of a library of synthetic promoters revealed some specific features of strong Streptomyces promoters. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.H. Integrative, xyle-based promoter probe vectors for use in Streptomyces. Plasmid 2011, 65, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W. Connecting metabolic pathways: Sigma factors in Streptomyces spp. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, B.K.; Kushner, S.R. Bacterial/archaeal/organellar polyadenylation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2011, 2, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.J.; Sarkar, N. Identification of the gene for an Escherichia coli poly(A) polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10380–10384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.J.; Kalapos, M.P.; Sarkar, N. Polyadenylated mrna in Escherichia coli: Modulation of poly(A) RNA levels by polynucleotide phosphorylase and ribonuclease II. Biochimie 1997, 79, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.K.; Kushner, S.R. Polynucleotide phosphorylase functions both as a 3′-5′ exonuclease and a poly(A) polymerase in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11966–11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bralley, P.; Jones, G.H. cDNA cloning confirms the polyadenylation of RNA decay intermediates in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 2002, 148, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bralley, P.; Gust, B.; Chang, S.A.; Chater, K.F.; Jones, G.H. RNA 3′-tail synthesis in streptomyces: In vitro and in vivo activities of RNase PH, the SCO3896 gene product and pnpase. Microbiology 2006, 152, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehudai-Resheff, S.; Hirsh, M.; Schuster, G. Polynucleotide phosphorylase functions as both an exonuclease and a poly(A) polymerase in spinach chloroplasts. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 5408–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rott, R.; Zipor, G.; Portnoy, V.; Liveanu, V.; Schuster, G. RNA polyadenylation and degradation in cyanobacteria are similar to the chloroplast but different from E. coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 15771–15777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohlberg, B.; Huang, J.; Cohen, S.N. The Streptomyces coelicolor polynucleotide phosphorylase homologue, and not the putative poly(A) polymerase can polyadenylate RNA. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 7273–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spickler, C.; Mackie, G.A. Action of RNase II and polynucleotide phosphorylase against RNAs containing stem-loops of defined structure. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.A.; Cozad, M.; Mackie, G.A.; Jones, G.H. Kinetics of polynucleotide phosphorylase: Comparison of enzymes from Streptomyces and Escherichia coli and effects of nucleoside diphosphates. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Symmons, M.; Jones, G.H.; Luisi, B. A duplicated fold is the structural basis for polynucleotide phosphorylase catalytic activity, processivity and regulation. Structure 2000, 8, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.H.; Mackie, G.A. Streptomyces coelicolor polynucleotide phosphorylase can polymerize nucleoside diphosphates under phosphorolysis conditions, with implications for the degradation of structured rnas. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 5151–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Potrykus, K.; Cashel, M. (p)ppgpp: Still magical? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivatsan, A.; Wang, J.D. Control of bacterial transcription, translation and replication by (p)ppgpp. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, F.S.; Kjelgaard, N.O. Analysis of the relA gene product of Escherichia coli. Eur. J. Biochem. 1977, 76, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraburtty, R.; White, J.; Takano, E.; Bibb, M.J. Cloning and characterization and disruption of a (p)ppgpp synthetase gene (relA) of Streptomyces coelicolor a3(2). Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraburtty, R.; Bibb, M.J. The ppgpp synthetase gene (relA) of Streptomyces coelicolor a3(2) plays a conditional role in antibiotic production and morphological differentiation. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5854–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyt, S.; Jones, G.H. RelA is required for actinomycin production in Streptomyces antibioticus. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3824–3829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Ryu, Y.G.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, S.K.; Saito, N.; Ochi, K.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.J. Two relA/spoT homologous genes are involved in the morphological and physiological differentiation of Streptomyces clavuligerus. Microbiology 2004, 150, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jones, G.H. Purification and properties of atp:Gtp 3′-pyrophosphotransferase (guanosine pentaphosphate synthetase) from Streptomyces antibioticus. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jones, G.H. Activation of ATP-GTP 3′-pyrophosphotransferase (guanosine pentaphosphate synthetase) in Streptomyces antibioticus. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatewood, M.L.; Jones, G.H. (p)ppgpp inhibits polynucleotide phosphorylase from Streptomyces but not from Escherichia coli and increases the stability of bulk mRNA in Streptomyces coelicolor. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 4275–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.H. RNA synthesis in Streptomyces antibioticus: In vitro effects of actinomycin and transcriptional inhibitors from 48-h cells. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 3331–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liras, P.; Villanueva, J.R.; Martin, J.F. Sequential expression of macromolecule biosynthesis and candicidin formation in Streptomyces griseus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1977, 102, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.S.; Ochi, K.; Jones, G.H. Pleiotropic effects of a relC mutation in Streptomyces antibioticus. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 2297–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesketh, A.; Sun, J.; Bibb, M.J. Induction of ppGpp synthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) grown under conditions of nutritional sufficiency elicits actII-ORF4 transcription and actinorhodin biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siculella, L.; Damiano, F.; di Summa, R.; Tredici, S.M.; Alduina, R.; Gnoni, G.V.; Alifano, P. Guanosine 5′-diphosphate 3′-diphosphate (ppgpp) as a negative modulator of polynucleotide phosphorylase activity in a ‘rare’ actinomycete. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatewood, M.L.; Bralley, P.; Jones, G.H. RNase III-dependent expression of the rpsO-pnp Operon of Streptomyces coelicolor. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 4371–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bralley, P.; Aseem, M.; Jones, G.H. SCO5745, a bifunctional RNase J Ortholog, affects antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.Y.; Bralley, P.; Jones, G.H.; Luisi, B.F. Linkage of catalysis and 5′ end recognition in ribonuclease RNase J. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8066–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Py, B.; Causton, C.F.; Mudd, E.A.; Higgins, C.F. A protein complex that mediates mRNA degradation in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 14, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait-Bara, S.; Carpousis, A.J. RNA degradosomes in bacteria and chloroplasts: Classification, distribution and evolution of RNase E homologs. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 97, 1021–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanzo, N.E.; Li, Y.S.; Py, B.; Blum, E.; Higgins, C.F.; Raynal, L.C.; Krisch, H.M.; Carpousis, A.J. Ribonuclease E organizes the protein interactions in the Escherichia coli degradosome. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2770–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Cohen, S.N. A Streptomyces coelicolor functional orthologue of Escherichia coli RNAse e shows shuffling of catalytic and PNPase-binding domains. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).