City or Suburb, Resistance Flows: Wastewater-Borne ESKAPE and AMR Genes in Malaysian Hospitals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Situ Physical Parameters of Wastewater Testing
2.2. Prevalence and Distribution of Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Bacteria
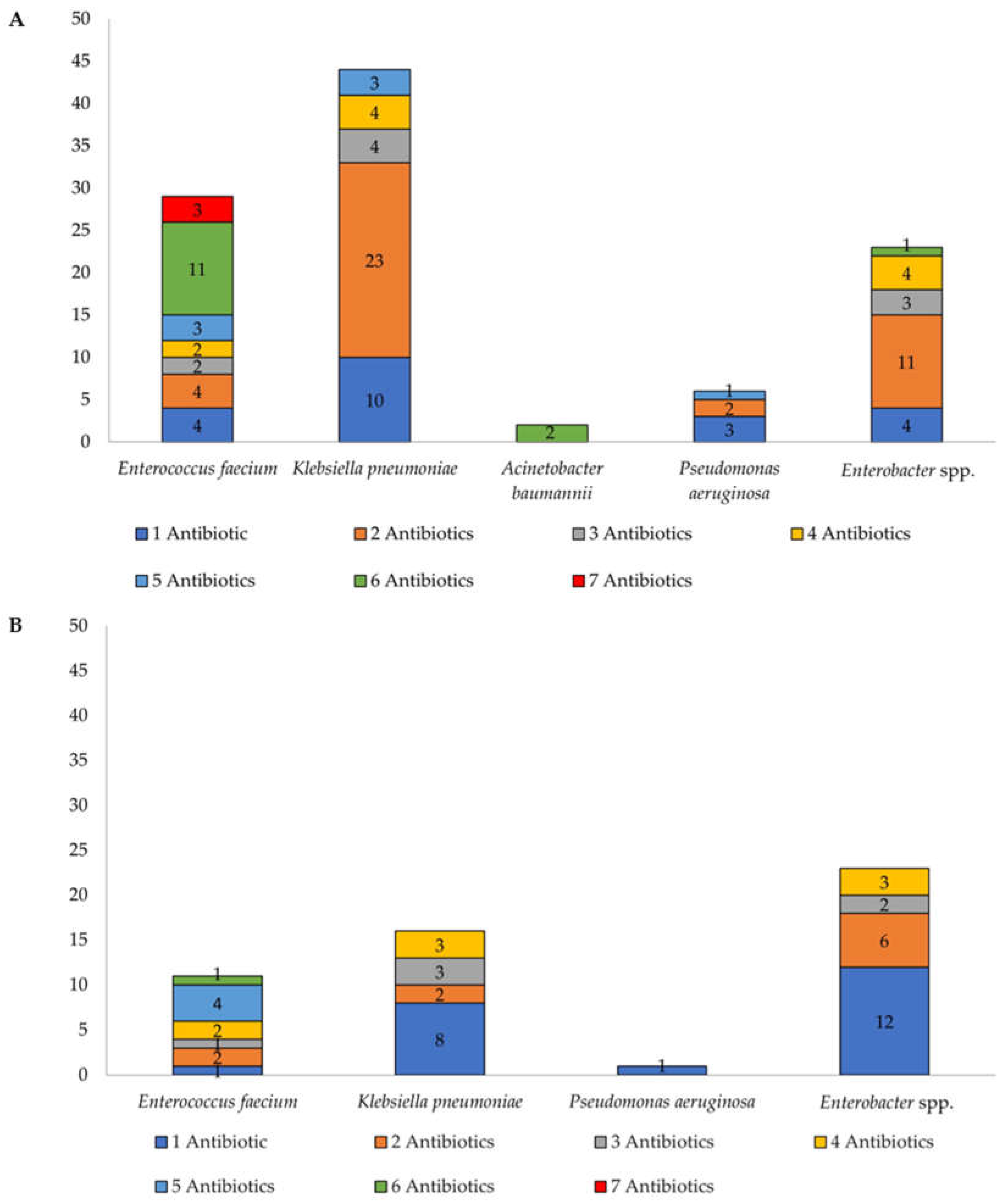
2.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profiles and Multidrug Resistance Trends
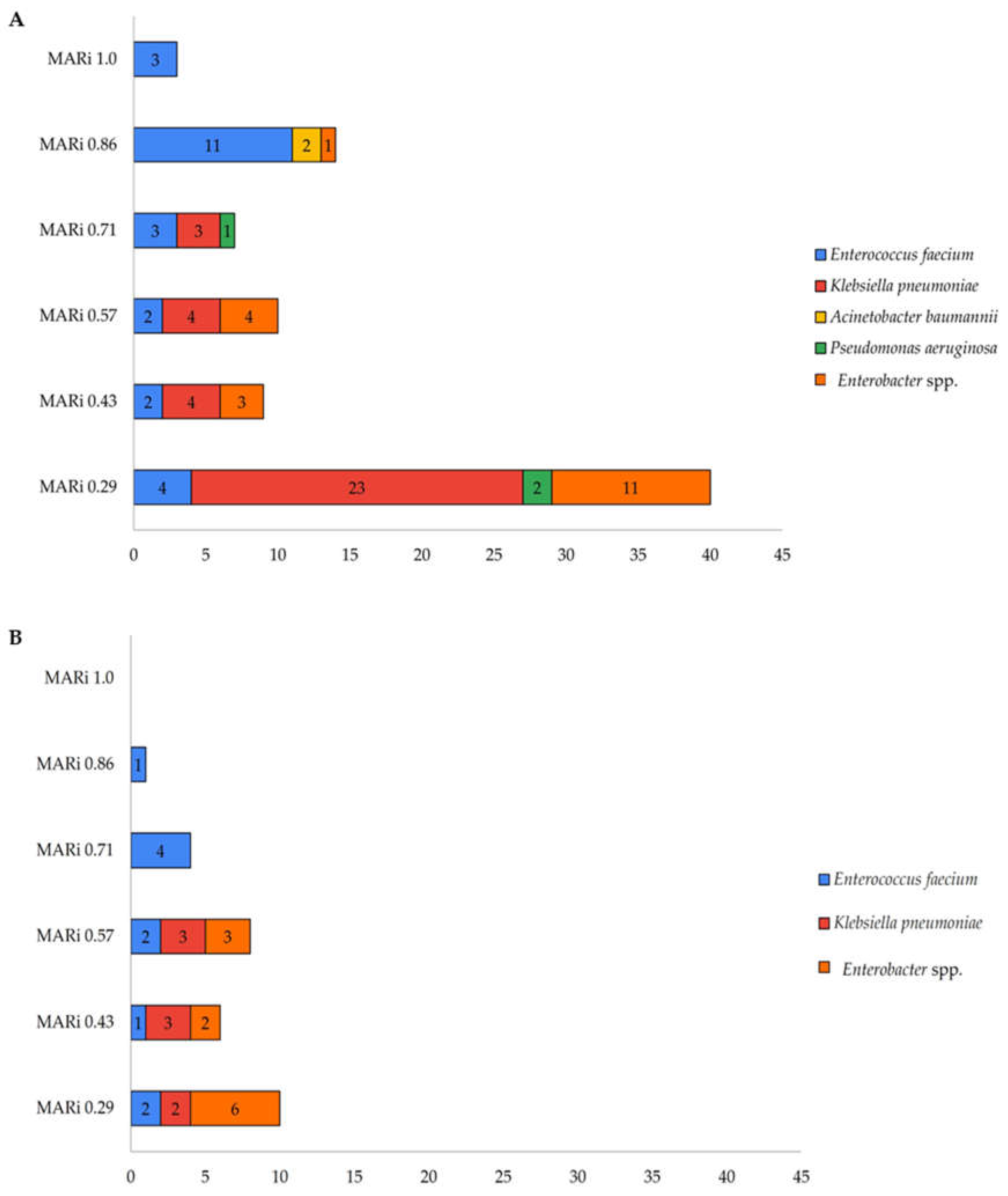
Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Index (MARi)
2.4. Detection and Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs)
2.5. Quantification and Antibiotic Residues Levels in Hospital Effluents
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Hospital Wastewater Sampling
4.2. Bacteria Isolation and Identification
4.3. Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
4.4. Antibiotic Resistance Gene Screening
4.5. Quantification of Antibiotic Residues
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| ARB | Antimicrobial resistant bacteria |
| ARGs MDR | Antimicrobial resistant genes Multidrug-resistant |
| HAIs | Hospital-acquired infections |
| ESKAPE | Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp. |
| CLSI | Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute |
| EUCAST | European Committee of Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| qPCR | quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| BLASTn | Basic Local Alignment Seacrh Tool Nucleotide |
| LCMS | Liquid Chromatography-mass Spectrometry |
References
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwu, E.E.; Awoderu, O.B.; Enwuru, C.A.; Afocha, E.E.; Lawal, R.G.; Ahmed, R.A.; Olanrewaju, I.; Onwuamah, C.K.; Audu, R.A.; Ogunsola, F.T. High prevalence of resistance to third-generation cephalosporins detected among clinical isolates from sentinel healthcare facilities in Lagos, Nigeria. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregova, G.; Kmet, V. Antibiotic resistance and virulence of Escherichia coli strains isolated from animal rendering plant. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutinel, M.; Fick, J.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C.-F. Investigating the effects of municipal and hospital wastewaters on horizontal gene transfer. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin-Reisman, I.; Brauner, A.; Ronin, I.; Balaban, N.Q. Epistasis between antibiotic tolerance, persistence, and resistance mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14734–14739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metersky, M.L.; Kalil, A.C. New guidelines for nosocomial pneumonia. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2017, 23, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, S.; Robertson, C.; Pan, J.; Kennedy, S.; Haahr, L.; Manoukian, S.; Mason, H.; Kavanagh, K.; Graves, N.; Dancer, S.J.; et al. Impact of healthcare-associated infection on length of stay. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 114, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Carmeli, Y.; Cosgrove, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global incidence in hospital-associated infections resistant to antibiotics: An analysis of point prevalence surveys from 99 countries. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Yadav, B.; Tyagi, R.D. 4-Microbiology of hospital wastewater. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Tyagi, R.D., Sellamuthu, B., Tiwari, B., Yan, S., Drogui, P., Zhang, X., Pandey, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 103–148. [Google Scholar]
- Petrovich, M.L.; Zilberman, A.; Kaplan, A.; Eliraz, G.R.; Wang, Y.; Langenfeld, K.; Duhaime, M.; Wigginton, K.; Poretsky, R.; Avisar, D.; et al. Microbial and Viral Communities and Their Antibiotic Resistance Genes Throughout a Hospital Wastewater Treatment System. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, Z.A.; Bakon, S.K.; Jamilan, M.A.J.; Daud, N.; Ciric, L.; Ahmad, N.; Muhamad, N.A. Prevalence of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic-Resistant Genes and the Quantification of Antibiotics in Drinking Water Treatment Plants of Malaysia: Protocol for a Cross-sectional Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2022, 11, e37663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, M.T.H.; Jones, E.R.; Flörke, M.; Franssen, W.H.P.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Yearsley, J.R. Global water scarcity including surface water quality and expansions of clean water technologies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 024020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.; Stone, W.; Botes, M.; Feil, E.J.; Wolfaardt, G.M. Wastewater Treatment Works: A Last Line of Defense for Preventing Antibiotic Resistance Entry Into the Environment. Front. Water 2022, 4, 883282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, Z.A.; Bakon, S.K.; Mohamad Jamil, N. From Rivers to Tap: The Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance in Drinking Water Systems. In Antimicrobial Resistance—New Insights; Mustafa, G., Thoms-Rodriguez, C.-A., Mullings, J., Akpaka, P.E., Roye-Green, K.J., McIntosh-Morgan, V., Arif, R., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Heuer, H.; Krögerrecklenfort, E.; Wellington, E.M.; Egan, S.; van Elsas, J.D.; van Overbeek, L.; Collard, J.M.; Guillaume, G.; Karagouni, A.D.; Nikolakopoulou, T.L.; et al. Gentamicin resistance genes in environmental bacteria: Prevalence and transfer. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 42, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.K.M.; Ghaly, T.M.; Gillings, M.R. A survey of sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics in the environment. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashbolt, N.J.; Amézquita, A.; Backhaus, T.; Borriello, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Collignon, P.; Coors, A.; Finley, R.; Gaze, W.H.; Heberer, T.; et al. Human Health Risk Assessment (HHRA) for environmental development and transfer of antibiotic resistance. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of Resistant Bacteria at Very Low Antibiotic Concentrations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakon, S.K.; Mohamad, Z.A. Flushed and Forgotten: Antimicrobial Resistance from Wastewater Perspective. In Antimicrobial Resistance—New Insights; Mustafa, G., Thoms-Rodriguez, C.-A., Mullings, J., Akpaka, P.E., Roye-Green, K.J., McIntosh-Morgan, V., Arif, R., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sinthuchai, D.; Boontanon, S.K.; Boontanon, N.; Polprasert, C. Evaluation of removal efficiency of human antibiotics in wastewater treatment plants in Bangkok, Thailand. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.R.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Wanders, N.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; van Beek, L.P.H.; van Vliet, M.T.H. Current wastewater treatment targets are insufficient to protect surface water quality. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Anselmo, A. Advanced treatment of urban wastewater by UV radiation: Effect on antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant E. coli strains. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Fischer, M.A.; Neumann, B.; Kiesewetter, K.; Hoffmann, I.; Werner, G.; Pfeifer, Y.; Lübbert, C. Carbapenemase-producing Gram-negative bacteria in hospital wastewater, wastewater treatment plants and surface waters in a metropolitan area in Germany, 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, A.R.; Ferro, G.; Vredenburg, J.; Yanık, M.; Vieira, L.; Rizzo, L.; Lameiras, C.; Manaia, C.M. Vancomycin resistant enterococci: From the hospital effluent to the urban wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450–451, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, I.; Hernández Leal, L.; Waar, K.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Schmitt, H.; García-Cobos, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae species complex: From wastewater to the environment. One Health 2024, 19, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.; Sib, E.; Gajdiss, M.; Klanke, U.; Lenz-Plet, F.; Barabasch, V.; Albert, C.; Schallenberg, A.; Timm, C.; Zacharias, N.; et al. Dissemination of multi-resistant Gram-negative bacteria into German wastewater and surface waters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, T.; Cloutier, M.; Schop, R.; Lowerison, M.W.; Khan, I.U.H. Comparative assessment of growth media and incubation conditions for enhanced recovery and isolation of Acinetobacter baumannii from aquatic matrices. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 176, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarde-López, M.; Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Godoy-Lozano, E.E.; Carrillo-Quiroz, B.A.; Cornejo-Juárez, P.; Sassoé-González, A.; Ponce-de-León, A.; Saturno-Hernández, P.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M. Presence and Persistence of ESKAPEE Bacteria before and after Hospital Wastewater Treatment. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhang, J.; Ruan, Z. In vivo Emergence of Colistin Resistance in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Mediated by Premature Termination of the mgrB Gene Regulator. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannatelli, A.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Giani, T.; Pilato, V.D.; Arena, F.; Ambretti, S.; Gaibani, P.; Rossolini, G.M. In Vivo Emergence of Colistin Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Producing KPC-Type Carbapenemases Mediated by Insertional Inactivation of the PhoQ/PhoP mgrB Regulator. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5521–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M Campos, J.C.d.; Antunes, L.C.M.; Ferreira, R.B.R. Global Priority Pathogens: Virulence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Prospective Treatment Options. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 649–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutuku, C.; Melegh, S.; Kovacs, K.; Urban, P.; Virág, E.; Heninger, R.; Herczeg, R.; Sonnevend, Á.; Gyenesei, A.; Fekete, C.; et al. Characterization of β-Lactamases and Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms in Enterobacterales from Hospital Effluents and Wastewater Treatment Plant. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.; Morris, C.; Morris, D.; Cormican, M.; Cummins, E. The effect of hospital effluent on antimicrobial resistant E. coli within a municipal wastewater system. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.M.; Bhanupriya, B.; Shewade, D.G.; Harish, B.N. Relationship between Antimicrobial Consumption and the Incidence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, Dc08–Dc12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, S.; Rahman, S.U.; Muhammad, F.; Mohsin, M. Association between antimicrobial consumption and resistance rate of Escherichia coli in hospital settings. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowy, E.; Luczkiewicz, A. Drug-resistant and hospital-associated Enterococcus faecium from wastewater, riverine estuary and anthropogenically impacted marine catchment basin. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, W.P.M.; Baker-Austin, C.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Ryan, J.J.; Micallef, C.; Maskell, D.J.; Pearce, G.P. Overexpression of antibiotic resistance genes in hospital effluents over time. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J. How covid-19 is accelerating the threat of antimicrobial resistance. BMJ 2020, 369, m1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Horcajada, J.P.; Oliver, A.; Garbajosa, P.R.; Vila, J. Inappropriate use of antibiotics in hospitals: The complex relationship between antibiotic use and antimicrobial resistance. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2013, 31, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Söderquist, B.; Jass, J. Prevalence and Diversity of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Swedish Aquatic Environments Impacted by Household and Hospital Wastewater. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, D.; Komatsu, M.; Nakamura, A.; Suzuki, S.; Oka, M.; Masuo, K.; Hamanaka, E.; Sato, M.; Maeda, K.; Nakamura, F. Nosocomial infections caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus in a Japanese general hospital and molecular genetic analysis. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 1689–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Ortiz, A.; Flores-Treviño, S.; Bocanegra-Ibarias, P. Prevalence of difficult-to-treat resistance in ESKAPE pathogens in a third level hospital in Mexico. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2025, 7, 100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakon, S.K.; Mohamad, Z.A.; Jamilan, M.A.; Hashim, H.; Kuman, M.Y.; Shaharudin, R.; Ahmad, N.; Muhamad, N.A. Prevalence of Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria and Level of Antibiotic Residues in Hospital Effluents in Selangor, Malaysia: Protocol for a Cross-sectional Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2023, 12, e39022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Hospital A | Hospital B | Hospital C | Hospital D | Hospital E (Suburban) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.99 ± 0.03 | 7.46 ± 0.11 | 7.51 ± 0.04 | 7.42 ± 0.09 | 7.14 ± 0.19 |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 532.67 ± 4.16 | 373.33 ± 0.58 | 331.00 ± 0 | 596.33 ± 0.58 | 633.33 ± 4.73 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 50.27 ± 1.27 | 78.63 ± 1.57 | 8.55 ± 1.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 30.07 ± 0.65 |
| Free Chlorine (mg/L) | 0.2 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.006 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Total Chlorine (mg/L) | 0.22 ± 0.006 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| Temperature (°C) | 27.33 ± 0.61 | 26.83 ± 0.21 | 28.60 ± 0.00 | 25.87 ± 0.64 | 30.30 ± 0.26 |
| Pathogen | Hospital A | Hospital B | Hospital C | Hospital D | Total (Hospital A–D) | Hospital E (Suburban) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus faecium | 8.97 (7/78) | 5.15 (5/97) | 16.95 (10/59) | 10.77 (7/65) | 9.70 (29/299) | 7.60 (11/145) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 19.23 (15/78) | 25.77 (25/97) | 3.39 (2/59) | 10.77 (7/65) | 16.39 (49/299) | 11.03 (16/145) |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.62 (3/65) | 1.00 (3/299) | 0 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1.28 (1/78) | 2.06 (2/97) | 3.39 (2/59) | 1.54 (1/65) | 2.00 (6/299) | 0.70 (1/145) |
| Enterobacter spp. | 3.85 (3/78) | 7.22 (7/97) | 6.8 (4/59) | 15.38 (10/65) | 8.03 (24/299) | 15.86 (23/145) |
| Antibiotic Resistant Genes (ARGs) | Enterococcus faecium | Staphylococcus aureus | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Acinetobacter baumannii | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Enterobacter spp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VanA | 10.3 (3/29) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| BlaTEM | ND | ND | 38.8 (19/49) | 33.3 (1/3) | 16.7 (1/6) | 12.5 (3/24) |
| ermB | 69.0 (20/29) | ND | 18.4 (9/49) | ND | ND | 16.7 (4/24) |
| tetA | ND | ND | 38.8 (19/49) | ND | 16.7 (1/6) | 8.3 (2/24) |
| Sul1 | ND | ND | 34.7 (17/49) | ND | 16.7 (1/6) | 58.3 (14/24) |
| BlaNDM-1 | 3.5 (1/29) | ND | 14.3 (7/49) | ND | 33.3 (2/6) | 4.2 (1/24) |
| Antibiotic Resistant Genes (ARGs) | Enterococcus faecium | Staphylococcus aureus | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Acinetobacter baumannii | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Enterobacter spp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VanA | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 13.0 (3/23) |
| BlaTEM | ND | ND | 43.8 (7/16) | ND | ND | 8.7 (2/23) |
| ermB | 45.5 (5/11) | ND | 12.5 (2/16) | ND | ND | 13.0 (3/23) |
| tetA | ND | ND | 31.3 (5/16) | ND | ND | 26.1 (6/23) |
| Sul1 | ND | ND | 50.0 (8/16) | ND | 100 (1/1) | 52.2 (12/23) |
| BlaNDM-1 | 9.1 (1/11) | ND | 18.8 (3/16) | ND | ND | ND |
| Antibiotics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Source (Wastewater) | CT (µg/L) (1000–5000 µg/L; R2 = 0.9803; DL 2990 µg/L) | VA (µg/L) (100–500 µg/L; R2 = 0.9860; DL 61 µg/L) | MEM (µg/L) (0.10–0.50 µg/L; R2 = 0.9940; DL 0.05 µg/L) | CIP (µg/L) (1.0–5.0 µg/L; R2 = 0.9953; DL 0.3 µg/L) | CRO (µg/L) (5.0–25.0 µg/L; R2 = 0.9692; DL 2.1 µg/L) | TZ (µg/L) 0.50–2.50 µg/L; R2 = 0.9992; DL 0.16 µg/L) | P (µg/L) (0.10–0.50 µg/L; R2 = 0.9917; DL 0.02 µg/L) |
| Hospital A | ND | 0.091 ± 0.128 * | ND | 0.019 ± 0.003 * | ND | ND | ND |
| Hospital B | ND | 0.193 ± 0.273 * | ND | 0.627 ± 0.003 | ND | ND | ND |
| Hospital C | ND | 0 ± 0.520 * | ND | 0.041 ± 0.001 * | ND | ND | ND |
| Hospital D | ND | ND | ND | 0.080 ± 0.014 * | ND | ND | ND |
| Hospital E | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.393 ± 0.005 | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakon, S.K.; Zakaria, N.F.S.; Jamilan, M.A.; Hashim, H.; Mohamad, Z.A. City or Suburb, Resistance Flows: Wastewater-Borne ESKAPE and AMR Genes in Malaysian Hospitals. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111058
Bakon SK, Zakaria NFS, Jamilan MA, Hashim H, Mohamad ZA. City or Suburb, Resistance Flows: Wastewater-Borne ESKAPE and AMR Genes in Malaysian Hospitals. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111058
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakon, Sophia Karen, Nur Fatihah Sholehah Zakaria, Mohd Azerulazree Jamilan, Hazimah Hashim, and Zuraifah Asrah Mohamad. 2025. "City or Suburb, Resistance Flows: Wastewater-Borne ESKAPE and AMR Genes in Malaysian Hospitals" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111058
APA StyleBakon, S. K., Zakaria, N. F. S., Jamilan, M. A., Hashim, H., & Mohamad, Z. A. (2025). City or Suburb, Resistance Flows: Wastewater-Borne ESKAPE and AMR Genes in Malaysian Hospitals. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111058









