Assessment and Assay Comparison for Detection of Antimicrobial Residues in Freshwater Aquaculture Fish in Erbil Governorate, Iraq
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Assessment of ARs by QFDA
2.2. Assessment of ARs by DDA
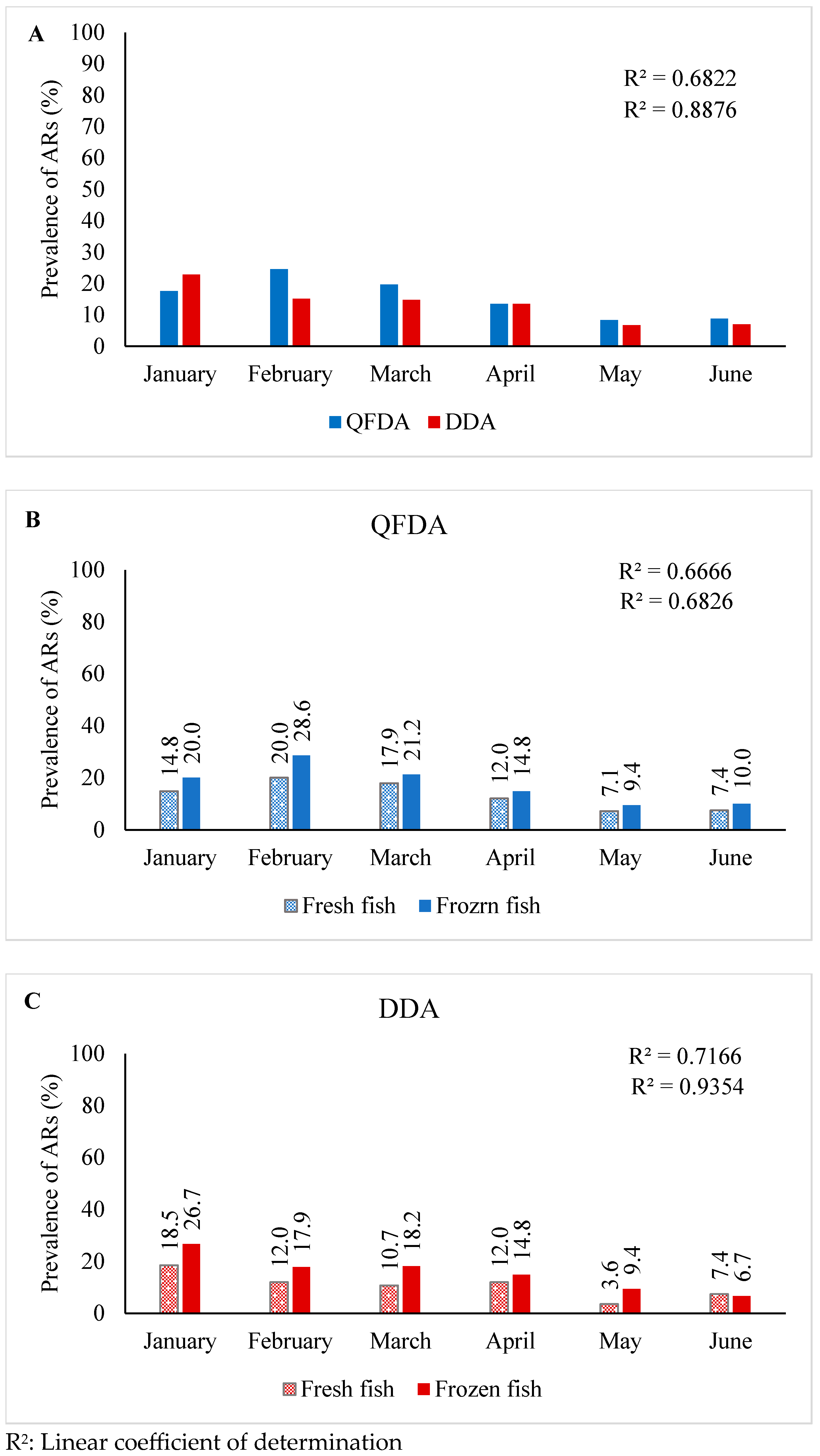
2.3. Temporal Variations of ARs in Fish
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Fish Sampling
3.2. Source and Type of Frozen Fish
3.3. Inspection of Fresh Fish
3.4. Detection of Antimicrobial Residues
3.4.1. Qualitative Field Disk Assay (QFDA)
Preparation of Spore Suspension
Preparation of Test Plates
Qualitative Field Disk Assay (QFDA)
3.4.2. Disk Diffusion Assay (DDA)
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schulz, P.; Pajdak-Czaus, J.; Siwicki, A.K. In vivo bacteriophages’ application for the prevention and therapy of aquaculture animals– chosen aspects. Animals 2022, 12, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Laurent, F.; Topp, E.; Billet, L.; Batisson, I.; Malandain, C.; Besse-Hoggan, P.; Morin, S.; Artigas, J.; Bonnineau, C.; Kergoat, L.; et al. Environmental risk assessment of antibiotics in agroecosystems: Ecotoxicological effects on aquatic microbial communities and dissemination of antimicrobial resistances and antibiotic biodegradation potential along the soil-water continuum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18930–18937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serwecińska, L. Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A risk to the environment and to public health. Water 2020, 12, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, L.; Weis, J.S.; Cabello, F.; Pizarro, J.; Bostick, K. Chemical use in salmon aquaculture: A review of current practices and possible environmental effects. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, E.M.; Okocha, R.C.; Adesina, B.T.; Ehigie, J.O.; Alabi, O.O.; Bolanle, A.M.; Matekwe, N.; Falana, B.M.; Tiamiyu, A.M.; Olatoye, I.O.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance in fish and poultry: Public health implications for animal source food production in Nigeria, Egypt, and South Africa. Front. Antibiot. 2022, 1, 1043302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okocha, R.C.; Olatoye, I.O.; Adedeji, O.B. Food safety impacts of antimicrobial use and their residues in aquaculture. Public Health Rev. 2018, 39, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Report of a joint, FAO/OIE/WHO. In Proceedings of the Expert Consultation on Antimicrobial Use in Aquaculture and Antimicrobial Resistance, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 13–16 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.; Ahmad, F.; Yaqub, B.; Ramzan, A.; Imran, A.; Afzaal, M.; Mirza, S.A.; Mazhar, I.; Younus, M.; Akram, Q.; et al. Current trends of antimicrobials used in food animals and aquaculture. Antibiot. Antimicrob. Resist. Genes Environ. 2020, 1, 39–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañada-Cañada, F.; Muñoz de la Peña, A.; Espinosa-Mansilla, A. Analysis of antibiotics in fish samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 987–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, L.M.; Nobile, M.; Ceriani, F.; Malandra, R.; Arioli, F.; Panseri, S. Risk characterisation from the presence of environmental contaminants and antibiotic residues in wild and farmed salmon from different FAO zones. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.K.; Chu, J.; Do, N.T.; Brose, F.; Degand, G.; Delahaut, P.; De Pauw, E.; Douny, C.; Van Nguyen, K.; Vu, T.D. Monitoring antibiotic use and residue in freshwater aquaculture for domestic use in Vietnam. EcoHealth 2015, 12, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Lively, J.A. Determination of sulfite antimicrobial residue in imported shrimp to the USA. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, G.D.T.M.; Szpunar, J.; Lobinski, R.; Edirisinghe, E.M.R.K.B. Determination of multi-class antibiotics residues in farmed fish and shrimp from Sri Lanka by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Fishes 2023, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Asely, M.M.; Elbab, G.F.F.; Shaltout, F.A.E. Antibiotic residues in commercially available freshwater and marine fish: A risk assessment. Egypt. J. Aqua Biol. Fish. 2024, 28, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, Z.; Nie, X.; Yang, Y.; Pan, D.; Leung, A.O. Residues of Fluoroquinolones in Marine Aquaculture Environment of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2012, 34, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, S.H.; Andrade, G.; Garcia, F.; Pilarski, F. Antibiotic residues and resistant bacteria in aquaculture. Pharm. Chem. J. 2018, 5, 127–147. [Google Scholar]
- Rafati, L.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Mokhtari, M.; Sohrabi, A.; Shirazi, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Momtaz, S.M. The analysis of oxytetracycline residue in tissues of cultured rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Health Scope 2018, 7, e57495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornber, K.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.; Hinchliffe, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Bass, D.; Tyler, C.R. Evaluating antimicrobial resistance in the global shrimp industry. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 966–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankpal, U.T.; Pius, H.; Khan, M.; Shukoor, M.I.; Maliakal, P.; Lee, C.M.; Abdelrahim, M.; Connelly, S.F.; Basha, R. Environmental factors in causing human cancers: Emphasis on tumorigenesis. Tumor Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2012, 33, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amangelsin, Y.; Semenova, Y.; Dadar, M.; Aljofan, M.; Bjørklund, G. The impact of tetracycline pollution on the aquatic environment and removal strategies. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. A review of antibiotics, antibiotic resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: Occurrence, contamination, and transmission. Toxics 2023, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanekamp, J.C. Chloramphenicol in Shrimp: Europe as Food Safety Utopia «Global Aquaculture Advocate». 2002, pp. 1–12. Available online: https://www.globalseafood.org/advocate/chloramphenicol-in-shrimp-europe-as-food-safety-utopia/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Polzer, J.; Hackenberg, R.; Stachel, C.; Gowik, P. Determination of chloramphenicol residues in Crustaceans: Preparation and evaluation of a proficiency test in Germany. Food Addit. Contam. 2006, 23, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, B.; Cakli, S. Screening for antibiotic residues in the trout by the Four Plate test, Premi test and ELISA test. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, Z.; Shahbazi, Y.; Ahmadi, F. Comparative screening of chloramphenicol residue in chicken tissues using four plate test and Premi® test methods. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 24, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, M.M.L.; Hogenboom, A.C.; Brinkman, U.A.T. Analytical strategies for the screening of veterinary drugs and their residues in edible products. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1995, 667, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almashhadany, D.A. Detecting antibiotic residues among sheep milk using YCT, DDA, and acidification method in Erbil city, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Bull. UASVM Anim Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 77, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.J.; Mata, L.; García-Gonzalo, D.; Antón, A.; Razquin, P.; Condón, S.; Pagán, R. optimization and validation of a new microbial inhibition test for the detection of antimicrobial residues in living animals intended for human consumption. Foods 2021, 10, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikkemaat, M.G. Microbial screening methods for detection of antibiotic residues in slaughter animals. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, L.; Sanz, D.; Razquin, P. Validation of the Explorer® 2.0 test coupled to e-Reader® for the screening of antimicrobials in muscle from different animal species. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stead, S.; Sharman, M.; Tarbin, J.A.; Gibson, E.; Richmond, S.; Stark, J.; Geijp, E. Meeting maximum residue limits: An improved screening technique for the rapid detection of antimicrobial residues in animal food products. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, R.; Monette, C.E.; Bracero, S. Methods for field measurement of antibiotic concentrations: Limitations and outlook. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OEC. The Observatory of Economic Complexity. Non-Fillet Frozen Fish in Iraq. 2021. Available online: https://oec.world/en/profile/bilateral-product/non-fillet-frozen-fish/reporter/irq#historical-data (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Almashhadany, D.A.; Nahla, A.A.; Zaki, A.M.; Mohammad, V.S. Detection of antibiotic residues among poultry in Erbil City and impact of thermal processing on remnants. Res. J. Life Sci. Bioinform. Pharm. Chem. Sci. 2018, 3, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. β-Lactam Antibiotics in milk (Bacillus subtilis Qualitative Field Disk Assay). In Officials Method of Analysis, Association of Official Analytical Chemists; International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mangsi, A.S.; Khaskheli, M.; Soomro, A.H.; Shah, M.G. Antibiotic residues detection in raw beef sold for human consumption in Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Res. Appl. Nat. Soc. Sci. 2014, 2, 2321–2351. [Google Scholar]
- Tajik, H.; Malekinejad, H.; Razavi-Rouhani, S.M.; Pajouhi, M.R.; Mahmoudi, R.A.; Haghnazari, A. Chloramphenicol residues in chicken liver, kidney and muscle: A comparison among the antibacterial residues monitoring methods of Four Plate Test, ELISA and HPLC. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2464–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnasri, H.A.; Adil, M.; Samah, A. Screening of antibiotic residues in poultry liver, kidney and muscle in Khartoum State, Sudan. J. Appl. Ind. Sci. 2014, 3, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Felis, E.; Kalka, J.; Sochacki, A.; Kowalska, K.; Bajkacz, S.; Harnisz, M.; Korzeniewska, E. Antimicrobial pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment-occurrence and environmental implications. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 866, 172813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, S.; Koudande, O.; Sanders, P.; Laurentie, M.; Mensah, G.A.; Abiola, F.A. Antimicrobial residues in foods of animal origin in Africa: Public health risks. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2014, 33, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almashhadany, D.A. Detection of antibiotic residues among raw beef in Erbil City (Iraq) and impact of temperature on antibiotic remains. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2019, 8, 7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almashhadany, D.A. Screening of antibiotic residues in raw milk of cows and buffalos by diffusion assays. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2021, 10, 9034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.; Resen, A.K.; AL-Niaeem, K.S. Effects of antibiotic residues on some health parameters of Planiliza abu H. in Shatt Al-Arab, Southern Iraq. Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 20, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovee, T.; Pikkemaat, M. Bioactivity-based screening of antibiotics and hormones. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8035–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, S.E.P.; Dakpogan, H.; Aboh, A.B.; Sika, K.C.; Abléto, M.; Adjahoutonon, K.Y.K.B.; Koudandé, O.D.; Sanders, P.; Mensah, G.A. Occurrence of antibiotic residues in raw fish Clarias gariepinus and Oreochromis niloticus from intensive rearing system in Benin. Veterinaria 2019, 68, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yipel, M.; Kurekci, C.; Tekeli, I.O.; Metli, M.; Sakin, F. Determination of selected antibiotics in farmed fish species using, LC-MS/MS. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 3829–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ren, L.; Yu, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; He, G.; Jiang, Q. Antibiotic residues in meat, milk and aquatic products in Shanghai and human exposure assessment. Food Control 2017, 80, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, F.; Almugbel, R.; Maher, H.M.; Alodaib, F.M.; Alzoman, N.Z. Determination of tetracycline, oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline residues in seafood products of Saudi Arabia using high performance liquid chromatography–Photo diode array detection. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukhtyn, M.; Malimon, Z.; Salata, V.; Rogalskyy, I.; Gutyj, B.; Kladnytska, L.; Kravcheniuk, K.; Horiuk, Y. The effects of antimicrobial residues on microbiological content and the antibiotic resistance in frozen fish. World’s Vet. J. 2022, 4, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, F.; Ghanem, K.; Al-Sisi, M. Occurrence and human health risks of pesticides and antibiotics in Nile tilapia along the Rosetta Nile branch, Egypt. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, B.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Characterization of pharmaceutically active compounds in Beijing, China: Occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and its environmental implication. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pękala-Safińska, A. Contemporary Threats of bacterial infections in freshwater fish. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, D.T. Bacterial zoonoses of fishes: A review and appraisal of evidence for linkages between fish and human infections. Vet. J. 2015, 15, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, R.M.; Maleno, F.D.; Figueras, M.J.; Pujol-Bajador, I.; Fernández-Bravo, A. Potential pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp. recovered in river water, soil, and vegetation from a natural recreational area. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnuraj, M.R.; Kandeepan, G.; Rao, K.H.; Chand, S.; Kumbhar, V. Occurrence, public health hazards and detection methods of antibiotic residues in foods of animal origin: A comprehensive review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1235458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almashhadany, D.A.; Mohammed, H.I.; Muslat, T.A.M.; Rashid, R.F.; Hassan, R.R.; Hassan, A.O. Antimicrobial residues in meat and meat products. In Health Risks of Food Additives—Recent Developments and Trends in Food Sector; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Methods | Fish | Number of Samples | ARs Inhibition Zone (mm) Degrees | Total Number of Positive (% **) | Statistical Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absence (0–≤1) | Weak * (>1–<2) | Moderate (>2–<3) | High (≥3) | 95% CI | p-Value | ||||
| QFDA | Fresh | 160 | 128 | 11 | 13 | 8 | 21 (13.1) | 8.3–19.4 | 0.295 |
| Frozen | 180 | 122 | 27 | 19 | 12 | 31 (17.2) | 12.0–23.6 | ||
| Total | 340 | 288 | 38 | 32 | 20 | 52 (15.3) | 11.6–19.6 | ||
| DDA | Fresh | 160 | 118 | 25 | 12 | 5 | 17 (10.6) | 6.3–16.5 | 0.175 |
| Frozen | 180 | 118 | 34 | 17 | 11 | 28 (15.6) | 10.6–21.7 | ||
| Total | 340 | 236 | 59 | 29 | 16 | 45 (13.2) | 9.8–17.3 | ||
| Method | Month | Fresh Fish | Frozen Fish | Total Samples of Both Fish Types | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Samples | Number of Positive (%) | Number of Samples | Number of Positive (%) | Total Number | Total Positive (%) | ||
| QFDA | January | 27 | 4 (14.8) | 30 | 6 (20) | 57 | 10 (17.5) |
| February | 25 | 5 (20) | 28 | 8 (28.6) | 53 | 13 (24.5) | |
| March | 28 | 5 (17.9) | 33 | 7 (21.2) | 61 | 12 (19.7) | |
| April | 25 | 3 (12) | 27 | 4 (14.8) | 52 | 7 (13.5) | |
| May | 28 | 2 (7.1) | 32 | 3 (9.4) | 60 | 5 (8.3) | |
| June | 27 | 2 (7.4) | 30 | 3 (10) | 57 | 5 (8.8) | |
| Total | 160 | 21 (13.1) | 180 | 31 (17.2) | 340 | 52 (15.3) | |
| DDA | January | 27 | 5 (18.5) | 30 | 8 (26.7) | 57 | 13 (22.8) |
| February | 25 | 3 (12) | 28 | 5 (17.9) | 53 | 8 (15.0) | |
| March | 28 | 3 (10.7) | 33 | 6 (18.2) | 61 | 9 (14.7) | |
| April | 25 | 3 (12) | 27 | 4 (14.8) | 52 | 7 (13.4) | |
| May | 28 | 1 (3.6) | 32 | 3 (9.4) | 60 | 4 (6.6) | |
| June | 27 | 2 (7.4) | 30 | 2 (6.7) | 57 | 4 (7.0) | |
| Total | 160 | 17 (10.6) | 180 | 28 (15.6) | 340 | 45 (13.2) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almashhadany, D.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Rashid, R.F.; Abdulmawjood, A.; Khan, I.U.H. Assessment and Assay Comparison for Detection of Antimicrobial Residues in Freshwater Aquaculture Fish in Erbil Governorate, Iraq. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13030225
Almashhadany DA, Hassan AA, Rashid RF, Abdulmawjood A, Khan IUH. Assessment and Assay Comparison for Detection of Antimicrobial Residues in Freshwater Aquaculture Fish in Erbil Governorate, Iraq. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(3):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13030225
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmashhadany, Dhary Alewy, Abdulwahed Ahmed Hassan, Rzgar Farooq Rashid, Amir Abdulmawjood, and Izhar U. H. Khan. 2024. "Assessment and Assay Comparison for Detection of Antimicrobial Residues in Freshwater Aquaculture Fish in Erbil Governorate, Iraq" Antibiotics 13, no. 3: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13030225
APA StyleAlmashhadany, D. A., Hassan, A. A., Rashid, R. F., Abdulmawjood, A., & Khan, I. U. H. (2024). Assessment and Assay Comparison for Detection of Antimicrobial Residues in Freshwater Aquaculture Fish in Erbil Governorate, Iraq. Antibiotics, 13(3), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13030225






