Characterization of Phage vB_SalM_SPJ41 and the Reduction of Risk of Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enterica Contamination in Two Ready-to-Eat Foods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Phage SPJ41 and Its Morphology
2.2. Lysis Profiles of Phage SPJ41
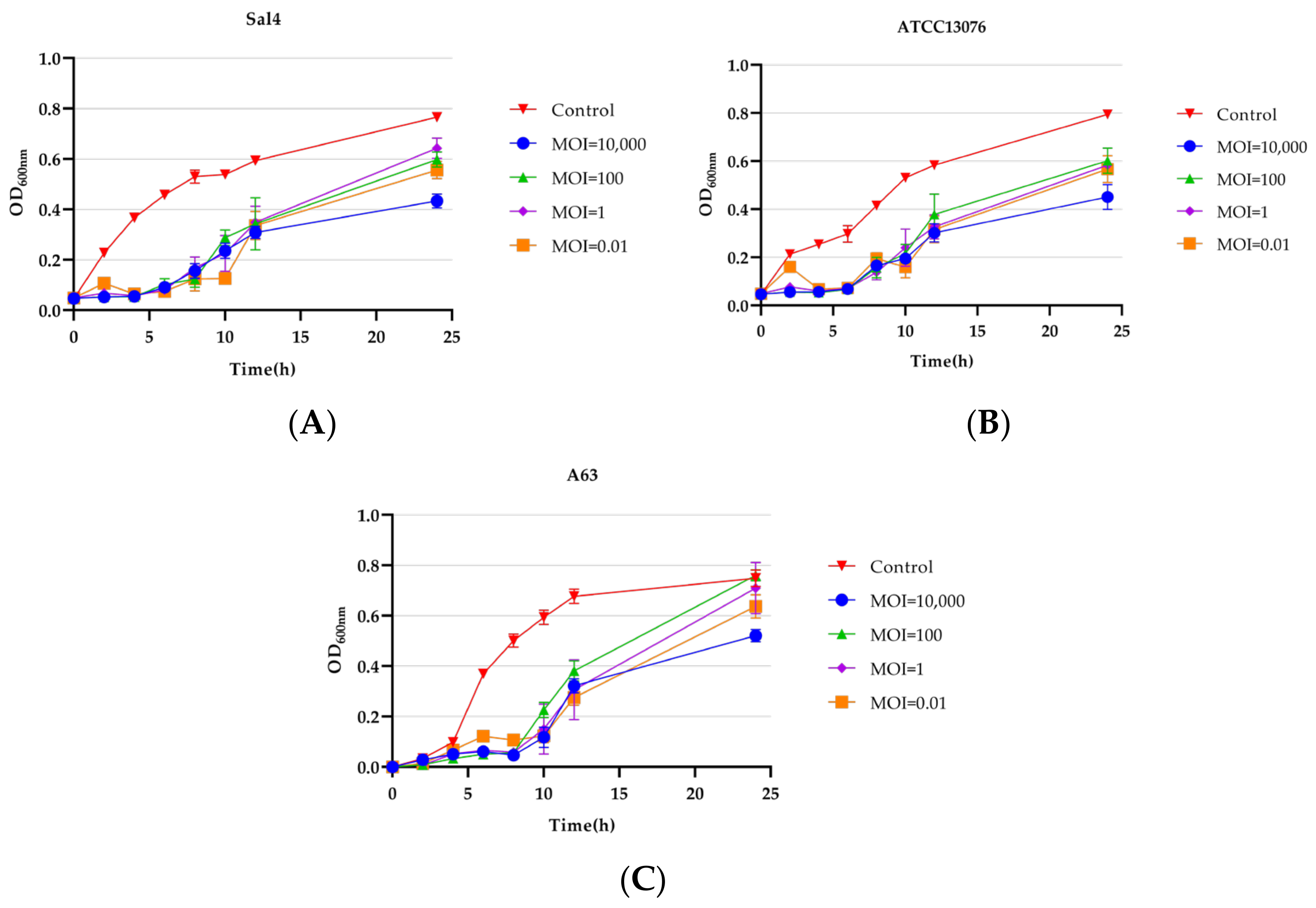
2.3. Optimal MOI and Replication Kinetic
2.4. Stability of SPJ41 at Different pH Values and Temperatures
2.5. Genomic Characterization of SPJ41
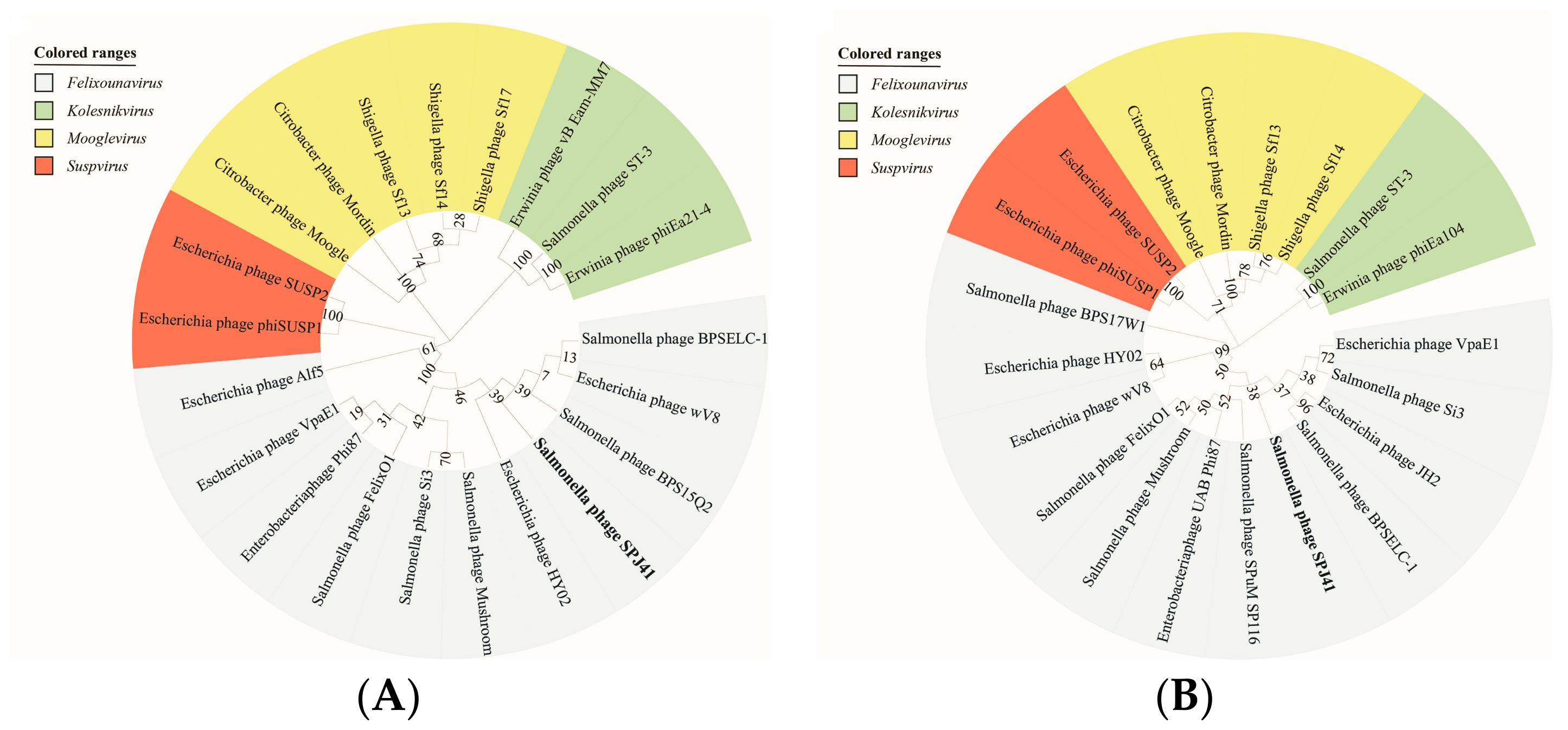
2.6. Classification and Genome Comparison of Lytic Phage SPJ41
2.7. Inhibition Curves of Phage SPJ41 on Salmonella
2.8. Inhibition and Disruption of Biofilms by SPJ41 Phage Treatment
2.9. Phage SPJ41 Biological Control of Salmonella in Two Ready-to-Eat Foods
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteria Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Bacteriophage Isolation and Purification
4.3. Determination of Phage Host Range
4.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) of SPJ41
4.5. Optimal Multiplicity of Infection (MOI) Determination
4.6. Replication Kinetic Curve of Phage SPJ41
4.7. pH and Temperature Stability of Phage SPJ41
4.8. Phage SPJ41 Genome Sequencing, Annotation, and Comparison
4.9. Inhibition Curve of Bacteriophage SPJ41 against Salmonella
4.10. Effect of Phage SPJ41 against Salmonella Biofilms
4.11. Effect of Phage SPJ41 against Salmonella in Food Samples
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jajere, S.M. A review of Salmonella enterica with particular focus on the pathogenicity and virulence factors, host specificity and antimicrobial resistance including multidrug resistance. Vet. World 2019, 12, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, G.L.; Papa, M.I. Salmonella spp. Infection—A continuous threat worldwide. Germs 2021, 11, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chang, Y. Anti-Salmonella polyvinyl alcohol coating containing a virulent phage PBSE191 and its application on chicken eggshell. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.N.; Wang, L.X. The microbial safety of fish and fish products: Recent advances in understanding its significance, contamination sources, and control strategies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 738–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Alam, M.U.; Luies, S.K.; Kamal, A.; Ferdous, S.; Lin, A.D.; Sharior, F.; Khan, R.; Rahman, Z.; Parvez, S.M.; et al. Contamination of Fresh Produce with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Associated Risks to Human Health: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, Y.; Kavvas, E.; Lachance, J.C.; Yurkovich, J.T.; Nuccio, S.P.; Fang, X.; Catoiu, E.; Raffatellu, M.; Palsson, B.O.; Monk, J.M. Genome-scale metabolic reconstructions of multiple Salmonella strains reveal serovar-specific metabolic traits. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, G.B.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic nontyphoidal Salmonella: An alarming trend? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, D.F.; Lincopan, N.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Landgraf, M. Current insights on high priority antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enterica in food and foodstuffs: A review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 26, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzitey, F. Antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica isolated from cabbage and lettuce samples in Tamale metropolis of Ghana. Int. J. Food Contam. 2018, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeLièvre, V.; Besnard, A.; Schlusselhuber, M.; Desmasures, N.; Dalmasso, M. Phages for biocontrol in foods: What opportunities for Salmonella sp. control along the dairy food chain? Food Microbiol. 2019, 78, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaadi, A.; Imam, M.; Alghamdi, A.A.; Alghoribi, M.F. Towards promising antimicrobial alternatives: The future of bacteriophage research and development in Saudi Arabia. J. Infect. Public Health 2022, 15, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattana, P.; Kitiya, V. Combined effects of Salmonella phage cocktail and organic acid for controlling Salmonella Enteritidis in chicken meat. Food Control 2022, 133, 108653. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ma, W.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. A broad-spectrum phage controls multidrug-resistant Salmonella in liquid eggs. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ding, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Characterization of a novel Siphoviridae Salmonella bacteriophage T156 and its microencapsulation application in food matrix. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Yang, X.; Euler, C.W.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Hossen, M.I.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J. Application of a novel phage ZPAH7 for controlling multidrug-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila on lettuce and reducing biofilms. Food Control 2021, 122, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, I.R. A review of current methods using bacteriophages in live animals, food and animal products intended for human consumption. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 130, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, H.W. Frequency of morphological phage descriptions in 1995. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoliunas, E.; Vilkaityte, M.; Kaliniene, L.; Zajanckauskaite, A.; Kaupinis, A.; Staniulis, J.; Valius, M.; Meskys, R.; Truncaite, L. Incomplete LPS Core-Specific Felix01-Like Virus vB_EcoM_VpaE1. Viruses 2015, 7, 6163–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Tu, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhang, A. Characterization and whole-genome sequencing of broad-host-range Salmonella-specific bacteriophages for bio-control. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 143, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.M.; Sullivan, M.B.; Knezevic, P.; van Zyl, L.J.; Sarkar, B.L.; Dutilh, B.E.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Łobocka, M.; Tong, Y.; Brister, J.R.; et al. Taxonomy of prokaryotic viruses: 2018-2019 update from the ICTV Bacterial and Archaeal Viruses Subcommittee. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodea, G.E.; González-Villalobos, E.; Medina-Contreras, O.; Castelán-Sánchez, H.G.; Aguilar-Rodea, P.; Velázquez-Guadarrama, N.; Hernández-Chiñas, U.; Eslava-Campos, C.A.; Balcázar, J.L.; Molina-López, J. Genomic characterization of two bacteriophages (vB_EcoS-phiEc3 and vB_EcoS-phiEc4) belonging to the genus Kagunavirus with lytic activity against uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 165, 105494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Pinto, G.; Oliveira, A.; Noben, J.-P.; Hendrix, H.; Lavigne, R.; Łobocka, M.; Kropinski, A.M.; Azeredo, J. Characterization and genomic analyses of two newly isolated Morganella phages define distant members among Tevenvirinae and Autographivirinae subfamilies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chegini, Z.; Khoshbayan, A.; Vesal, S.; Moradabadi, A.; Hashemi, A.; Shariati, A. Bacteriophage therapy for inhibition of multi drug-resistant uropathogenic bacteria: A narrative review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whichard, J.M.; Weigt, L.A.; Borris, D.J.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Kapur, V.; Pierson, F.W.; Lingohr, E.J.; She, Y.-M.; Kropinski, A.M.; et al. Complete Genomic Sequence of Bacteriophage Felix O1. Viruses 2010, 2, 710–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Drab, M.; Mąkosa, M.; Zembala, M.; Barbasz, J.; Dąbrowska, K.; Boratyński, J. Aggregation/dispersion transitions of T4 phage triggered by environmental ion availability. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Shahin, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, S.; Stefan, S.; Wang, R. Morphologic and genomic characterization of a broad host range Salmonella enterica serovar Pullorum lytic phage vB_SPuM_SP116. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 136, 103659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.; Suissa, M.; Chiswell, D.; Azriel, A.; Berman, B.; Shahar, D.; Reznick, S.; Sharf, R.; Wyse, J.; Bar-On, T.; et al. A bacteriophage reagent for Salmonella: Molecular studies on Felix 01. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 74, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Wu, S.; et al. Occurrence, serovars and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella spp. in retail ready-to-eat food products in some Chinese provinces. LWT 2022, 154, 112699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T. Selection for bacteriophage latent period length by bacterial density: A theoretical examination. Microb. Ecol. 1989, 18, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.R.; LaBossiere, B.; Switt, A.I.M.; Delaquis, P.; Goodridge, L.; Levesque, R.C.; Danyluk, M.D.; Wang, S.Y. Characterization of Four Novel Bacteriophages Isolated from British Columbia for Control of Non-typhoidal Salmonella in Vitro and on Sprouting Alfalfa Seeds. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binetti, A.G.; Quiberoni, A.; Reinheimer, J.A. Phage adsorption to Streptococcus thermophilus. Influence of environmental factors and characterization of cell-receptors. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron-Montenegro, R.; Garcia, R.; Duenas, F.; Rivera, D.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Erickson, S.; Moreno-Switt, A.I. Comparative Analysis of Felixounavirus Genomes Including Two New Members of the Genus That Infect Salmonella Infantis. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, D.; Torrents, E.; Poole, A.M.; Sjöberg, B.-M. RNRdb, a curated database of the universal enzyme family ribonucleotide reductase, reveals a high level of misannotation in sequences deposited to Genbank. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.; Young, R. Phage Lysis: Multiple Genes for Multiple Barriers. Adv. Virus Res. 2019, 103, 33–70. [Google Scholar]
- Savalia, D.; Westblade, L.F.; Goel, M.; Florens, L.; Kemp, P.; Akulenko, N.; Pavlova, O.; Padovan, J.C.; Chait, B.T.; Washburn, M.P.; et al. Genomic and Proteomic Analysis of phiEco32, a Novel Escherichia coli Bacteriophage. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, A.A. Studies of a Receptor for Felix 0-1 Phage in Salmonella Minnesota. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1967, 48, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, E.; Park, H.; Jeon, B.; Ryu, S. Characterization of the lytic phage MSP1 for the inhibition of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars Thompson and its biofilm. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 385, 110010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Islam, M.S.; Yan, T.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, L.; Connerton, I.F.; Deng, K.; Li, J. Application of a novel phage vB_SalS-LPSTLL for the biological control of Salmonella in foods. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yao, L.; Li, F.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Y. Biocontrol of Salmonella Typhimurium in Raw Salmon Fillets and Scallop Adductors by Using Bacteriophage SLMP1. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, W.; Sun, X. Characterization of vB_VpaP_MGD2, a newly isolated bacteriophage with biocontrol potential against multidrug-resistant Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Virk, S.M.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Willias, S.P.; Morsy, M.K.; Abdelnabby, H.E.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Isolation, Characterization, and Application of Bacteriophage LPSE1 Against Salmonella enterica in Ready to Eat (RTE). Foods Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Abdelhamid, A.G.; Xu, Y.; Yousef, A.E. Characterization of broad-host lytic Salmonella phages isolated from livestock farms and application against Salmonella Enteritidis in liquid whole egg. LWT 2021, 144, 111269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coil, D.; Jospin, G.; Darling, A.E. A5-miseq: An updated pipeline to assemble microbial genomes from Illumina MiSeq data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, J.D.; Cohen, F.E. Pairwise sequence alignment below the twilight zone. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortright, K.E.; Chan, B.K.; Koff, J.L.; Turner, P.E. Phage Therapy: A Renewed Approach to Combat Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P.; Wishart, D.S. Circular genome visualization and exploration using CGView. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Heredia, A.; García, S.; Merino-Mascorro, J.; Feng, P.; Heredia, N. Natural plant products inhibits growth and alters the swarming motility, biofilm formation, and expression of virulence genes in enteroaggregative and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Food Microbiol. 2016, 59, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Liao, Z.; Lei, H.; Fang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Q. Antibacterial activity of food-grade chitosan against Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Strains | Source | Drug Resistance d | Lytic e |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmonella Enteritidis | |||
| ATCC13076 | ATCC a | ERY | +++ |
| A184 | Customs b | AMP, CFZ, FEP, TET, DOX, CIP, OFX, SMZ, ERY, AZM, KAN | ++ |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | |||
| Sal4 | Customs | AMP, ERY | +++ |
| A18 | Customs | AMP, DOX, SMZ, ERY, GEN | |
| Salmonella Shubra | |||
| Sal6 | Customs | AMP, TET, CHL, SMZ, ERY | ++ |
| Salmonella Derby | |||
| Sal18 | Customs | AMP, DOX, SMZ, ERY | + |
| A63 | Customs | AMP, CFZ, TET, DOX, CHL, CIP, OFX, SMZ, ERY, AZM, GEN, KAN | ++ |
| A64 | Customs | AMP, TET, DOX, CIP, OFX, SMZ, ERY, AZM, KAN, GEN | ++ |
| A174 | Customs | AMP, TET, DOX, SMZ, ERY | +++ |
| A176 | Customs | AMP, TET, DOX, SMZ, ERY | +++ |
| Salmonella Nchanga | |||
| A91 | Customs | AMP, TET, DOX, CHL, SMZ, ERY, AZM, GEN | + |
| A92 | Customs | AMP, TET, DOX, CHL, SMZ, ERY, AZM, GEN | + |
| Listeria monocytogenes | |||
| ATCC19115 | ATCC | − | |
| ATCC19116 | ATCC | − | |
| CMCC25926 | CMCC c | − | |
| Escherichia coli | |||
| ATCC25922 | ATCC | − | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | |||
| ATCC29213 | ATCC | − | |
| CMCC26003 | CMCC | − | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Tao, Z.; Lan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X. Characterization of Phage vB_SalM_SPJ41 and the Reduction of Risk of Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enterica Contamination in Two Ready-to-Eat Foods. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020364
Li T, Chen H, Zhao J, Tao Z, Lan W, Zhao Y, Sun X. Characterization of Phage vB_SalM_SPJ41 and the Reduction of Risk of Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enterica Contamination in Two Ready-to-Eat Foods. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(2):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020364
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tengteng, Hong Chen, Jiayi Zhao, Zhenxiang Tao, Weiqing Lan, Yong Zhao, and Xiaohong Sun. 2023. "Characterization of Phage vB_SalM_SPJ41 and the Reduction of Risk of Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enterica Contamination in Two Ready-to-Eat Foods" Antibiotics 12, no. 2: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020364
APA StyleLi, T., Chen, H., Zhao, J., Tao, Z., Lan, W., Zhao, Y., & Sun, X. (2023). Characterization of Phage vB_SalM_SPJ41 and the Reduction of Risk of Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enterica Contamination in Two Ready-to-Eat Foods. Antibiotics, 12(2), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020364






