Abstract
Studies on biofilm-related infections are gaining prominence owing to their involvement in most clinical infections and seriously threatening global public health. A biofilm is a natural form of bacterial growth ubiquitous in ecological niches, considered to be a generic survival mechanism adopted by both pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms and entailing heterogeneous cell development within the matrix. In the ecological niche, quorum sensing is a communication channel that is crucial to developing biofilms. Biofilm formation leads to increased resistance to unfavourable ecological effects, comprising resistance to antibiotics and antimicrobial agents. Biofilms are frequently combated with modern conventional medicines such as antibiotics, but at present, they are considered inadequate for the treatment of multi-drug resistance; therefore, it is vital to discover some new antimicrobial agents that can prevent the production and growth of biofilm, in addition to minimizing the side effects of such therapies. In the search for some alternative and safe therapies, natural plant-derived phytomedicines are gaining popularity among the research community. Phytomedicines are natural agents derived from natural plants. These plant-derived agents may include flavonoids, terpenoids, lectins, alkaloids, polypeptides, polyacetylenes, phenolics, and essential oils. Since they are natural agents, they cause minimal side effects, so could be administered with dose flexibility. It is vital to discover some new antimicrobial agents that can control the production and growth of biofilms. This review summarizes and analyzes the efficacy characteristics and corresponding mechanisms of natural-product-based antibiofilm agents, i.e., phytochemicals, biosurfactants, antimicrobial peptides, and their sources, along with their mechanism, quorum sensing signalling pathways, disrupting extracellular matrix adhesion. The review also provides some other strategies to inhibit biofilm-related illness. The prepared list of newly discovered natural antibiofilm agents could help in devising novel strategies for biofilm-associated infections.
1. Introduction
Bacterial infections threaten public health worldwide, and the severity of the crisis has intensified due to the appearance and proliferation of drug-resistant bacterial species [1]. The majority of the microbes defend themselves by diverse survival mechanisms, including morphogenesis, proteolytic approaches, demographic heterogeneity, etc., to overcome environmental stress conditions. One of the prominent growth states for microorganisms that exist in 90% or more of bacteria strains is biofilm. Biofilms are considered heterogeneous assemblages of surface-associated microbes compressed in a matrix composed of different polysaccharides, proteins, and DNA. Quorum sensing, an inter and intra-bacterial communication channel, plays a significant role in biofilm development with its extracellular surrounding matrix. Contrary to their planktonic compartments, bacteria residing in biofilm exhibit vulnerable adaptive antibiotic resistance, leading to hindrance in biofilm-associated ill-treatment and chronic infections globally [2,3]. The matrix functions as a physical barrier to medications and provides microorganisms a safe ecological niche for their survival. Many microorganisms, such as P. aeruginosa, C. albicans, S. epidermidis, and M. tuberculosis Mycoplasma, pose intense health crises due to antimicrobial medication resistance and immune responses [4].
Consequently, new approaches to combating microbial biofilm formation should be devised. Research suggests that novel approaches to combating biofilm formation and quorum sensing have been widely developed and report that natural drugs show potency in combating drug resistance and antibiofilm illness [5]. Herbal therapies have been used for ages by various human societies; moreover, these natural products play a crucial role in the prophylaxis of infectious diseases. Some Chinese plants, for instance, have frequently been considered in the treatment of bacterial infection, e.g., Scutellara, Tussilago, etc., [6]. Published articles have shown that different plant extracts regulate biofilm formation and QS inhibition. This article briefly discusses the mechanisms underlying biofilm formation and the fate of quorum sensing along with recent events in the identification of natural products derived from plants that act as antibiofilm agents. The current standard practice for treating bacterial infections is antibiotic therapy. Other strategies include phage therapy, inhibitors of the quorum sensing system, antibodies therapy, antimicrobial peptides therapeutics, smart stimuli-responsive materials, and nanotechnology. These recently identified natural antibiofilm compounds are interesting candidates that may offer fresh approaches to treating infections brought on by biofilm-associated bacteria and pathogenic bacteria.
The application of natural plant-derived ingredients in the field of antimicrobial therapy has emerged as a suitable alternative to combat the growing issues of antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation [7]. These are present in different parts of plants such as the leaf, flowers, stem, root bark, or fruits, which act through different pathways to restrict and inhibit the microbial growth. Some common mechanisms through which they show their effects are: (i) disruption of the microbial cell wall and membrane, (ii) leakage of cellular components as a result of structural alteration, (iii) interference with protein synthesis, (iv) dissipation of ATP, and (v) obstruction in the bacterial quorum sensing. Another benefit of using phyto-constituents as antibacterial and antimicrobial agents are their ease of availability, low cost, and negligible side effects on the body. Thus, sustainable herbal antimicrobial therapy requires further isolation of active plant constituents that could be used as novel antimicrobial agents. Some of the essential phyto-constituents that have already been utilized as antibacterial agents are piperine, dictamnine, berberine, reserpine, conessine, matrine, caffeine, ajoene, baicalein, silybin, quercetin, chrysoplenetin, gallic acid, naringenin, toxifolin, limonene, nerolidol, linalool, etc. [8]. These ingredients follow different pathways, the details of which have been mentioned in the text.
2. Biofilm
Biofilm is a congregation of microorganisms where planktonic cells cling to a surface [9]. These aggregated colonies are usually sheathed in a self-produced extracellular polymeric substance (EPS), a matrix cell sometimes known as slime (though not all slime consider biofilm), a polymeric aggregation comprised primarily of various proteins, extracellular saccharides, and DNAs [10,11]. Considering the composition of the EPS matrix, biofilm may evolve into a variety of distinct forms, including filamentous streamers and microcolonies that resemble mushrooms [12]. It has been established that the morphology of biofilms in microcolonies is regulated by fluid flow, nutritional makeup, and the messenger molecules called quoromones. N-Acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) are utilized for bacterial communication. [13,14]. Biofilms can evolve on non-living and living surfaces and are frequently seen in the natural world and in healthcare facilities. In contrast to planktonic cells, single cells of the same organism that grow in biofilms show different physiological properties [15]. Research has shown that the microbial cells in the biofilms hold the ability to mutate, which is the leading cause of developing resistance to antibiotics used in eroding the biofilm [16,17]. Each and every component plays a critical role in biofilm structure; that is, Pel and psl polysaccharide helps provide a solid surface for biofilm, whereas the alginate provides the surface adhesion. In case of starvation, eDNA functions as a nutrient source [18,19].
2.1. Stages of Biofilm Formation
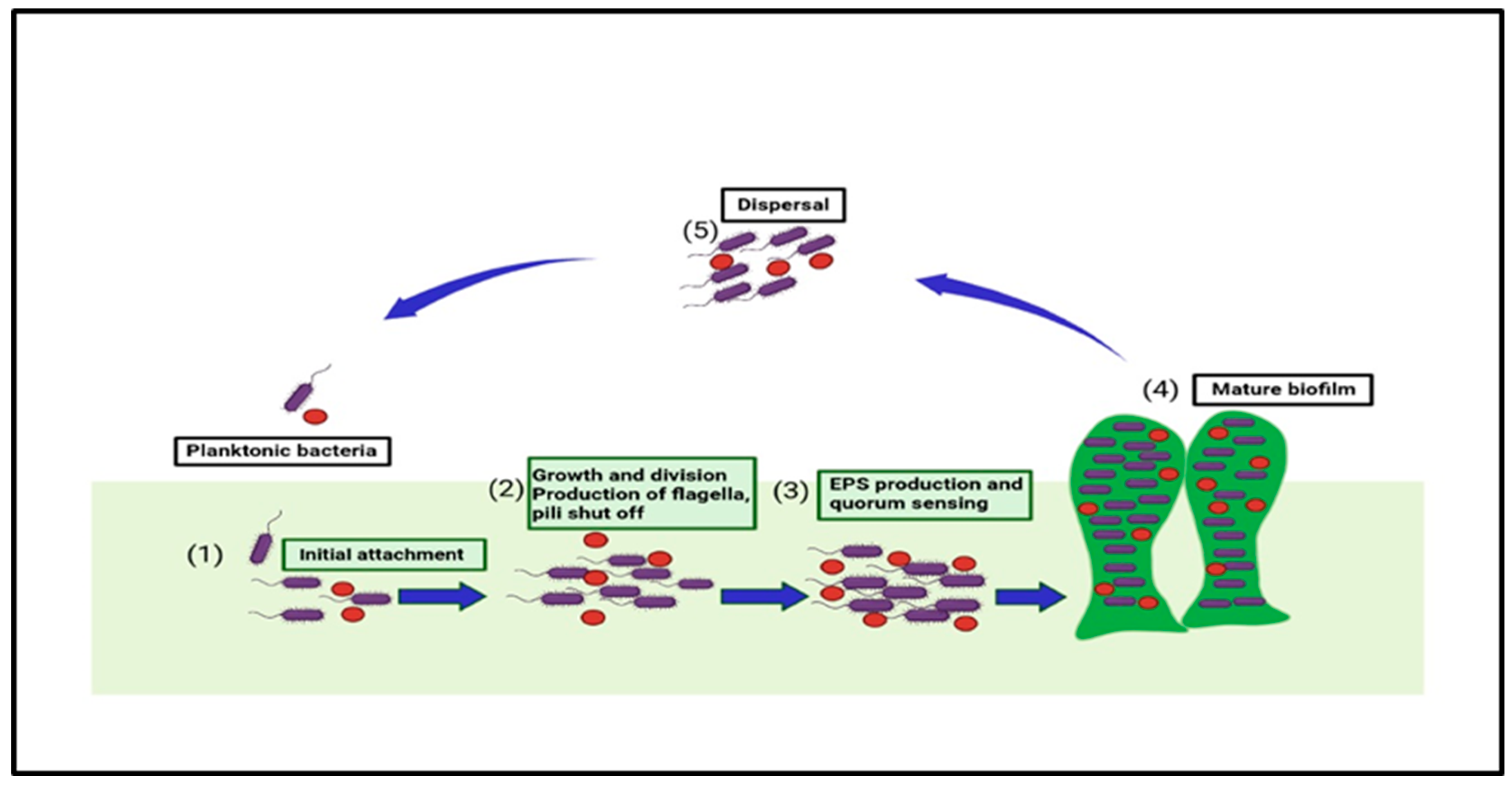
There are five steps found in forming biofilm, as shown in Figure 1. They start from the initial stage of attachment of planktonic microorganisms to a surface. The initial stage (reversible) is defined as a set of physiochemical factors that specify how the bacteria’s cell surfaces interact with the prepared surface [20]. The secondary stage consists of the specific adhesion with the surface; the bacteria in this stage undergo both phenotypic and genotypic changes. The third stage is maturation, wherein the irreversibly attached bacteria communicate with the nearby organic and inorganic molecules [21]. Microcolonization of the bacteria can be defined as the fourth stage in which the association also becomes stable, and the bacteria start the step of intercommunication among different bacteria [22,23]. The final fifth stage is dispersion, where factors such as fluid dynamic and shear stress cause microbial dispersal from the older biofilm; thus, either shedding the daughter cells and causing the microorganisms to move to the newer locations or leading to the formation of other biofilms [24,25].
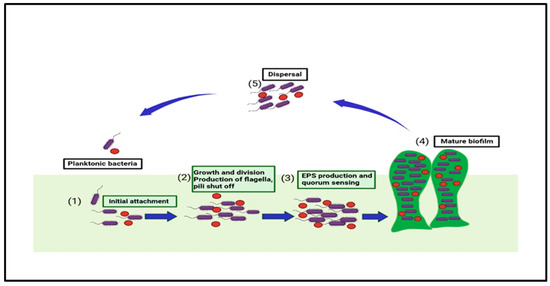
Figure 1.
This figure shows the five stages in biofilm formation and the associated factors that take part in biofilm development and quorum sensing.
2.2. Mechanism of Biofilm Formation
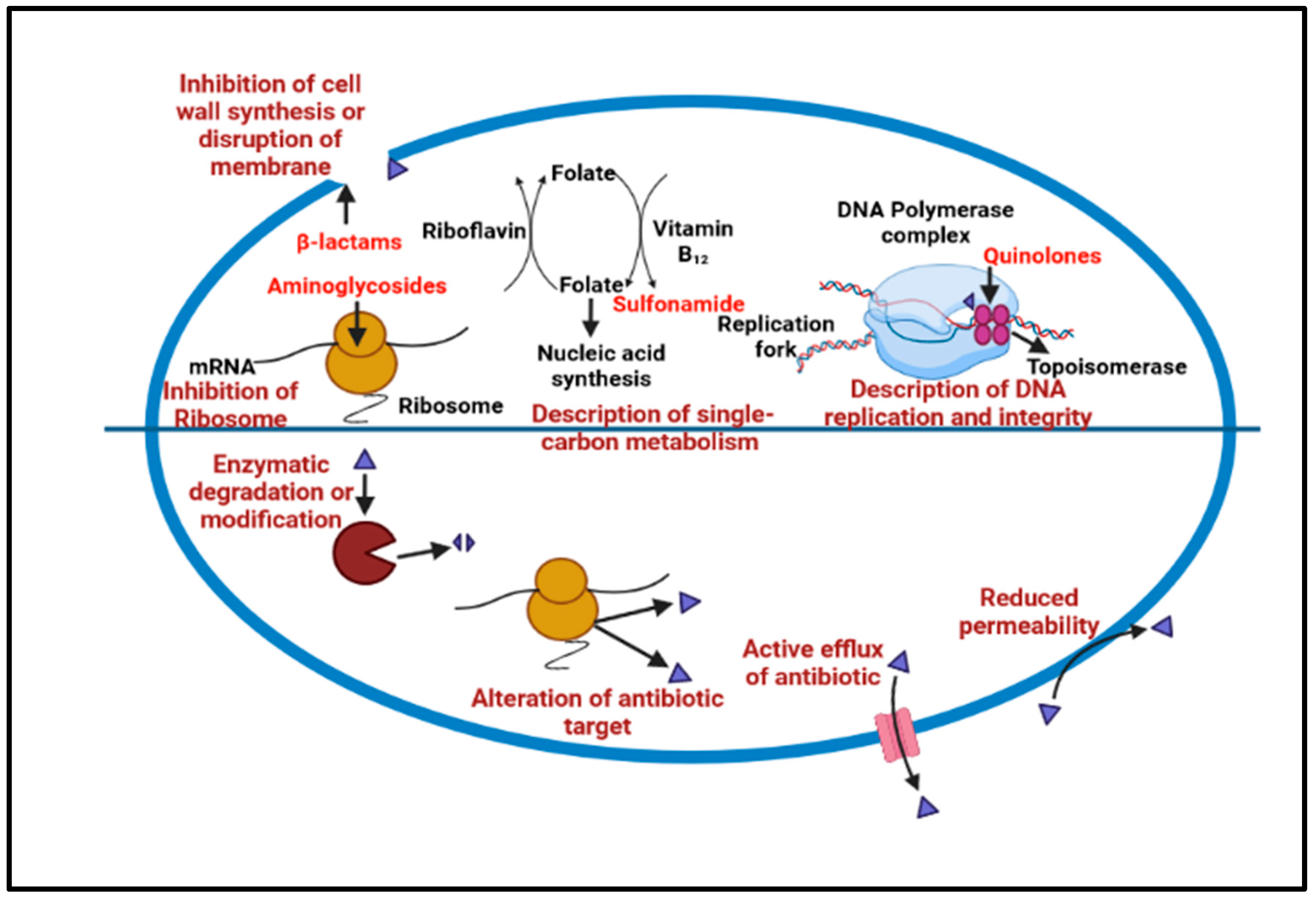
The microbial cells in the biofilm are composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) with a larger molecular weight, causing resistance to many acids as well as metals; as well as this, the other causes of this resistance are a genetic adaptation, cell growth, and metabolic changes [26]. The mechanisms of biofilm tolerance can be explained as the synthesis of EPS, prompting physical tolerance, leading to difficulty in antimicrobial diffusion inside the matrix. The second type of tolerance caused is passive tolerance, which is basically due to the enzymes of the biofilm matrix that cause the antimicrobial agents’ neutralization [27]. The third one is physiological tolerance, in which the deeper layers of the biofilm have metabolically dormant cells that demonstrate adaptive stress responses that modulate biofilm resistance to different antimicrobials [28]. During biofilm maturation, the microbial cells inside the EPS begin to communicate and secrete specific proteins, which are responsible for efflux pump development. Finally, free planktonic cell dispersal from the produced biofilm encourages the creation of additional biofilms in the periphery [29]. Many naturally obtained biofilm-resistant drugs target various stages of biofilm production and inhibit growth. Specific strategies could be targeted to degrade the cells in the matrix to halt the biofilm mechanism that inhibits QS, preventing efflux pump expression, and inhibiting matrix formation and surface modification, as shown in Figure 2.
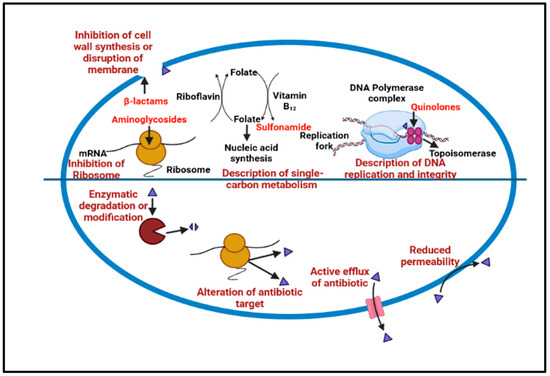
Figure 2.
Show the common antibiotic resistance mechanism that leads to biofilm development.
2.3. Quorum Sensing and Its Association with Biofilm Development
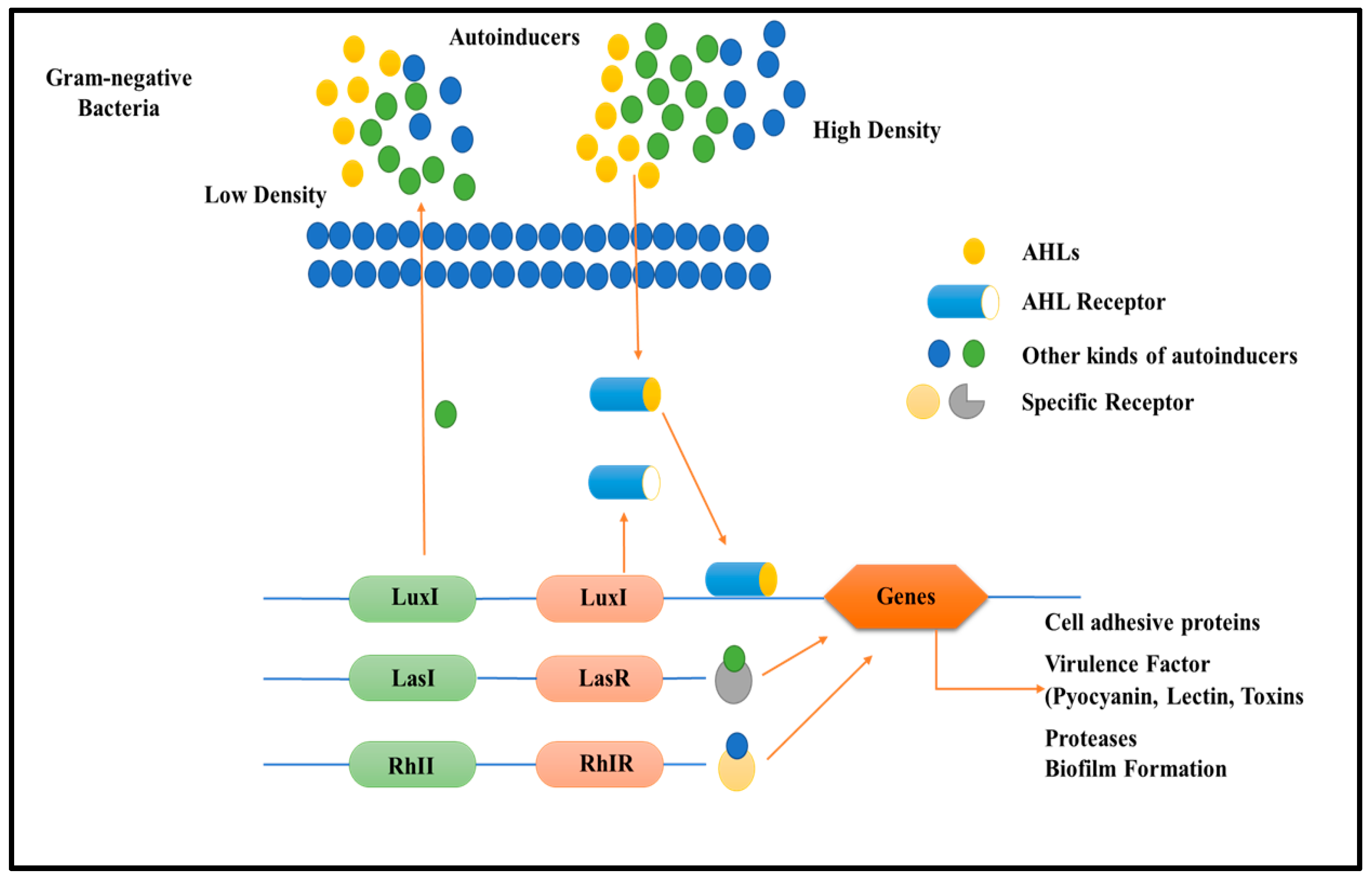
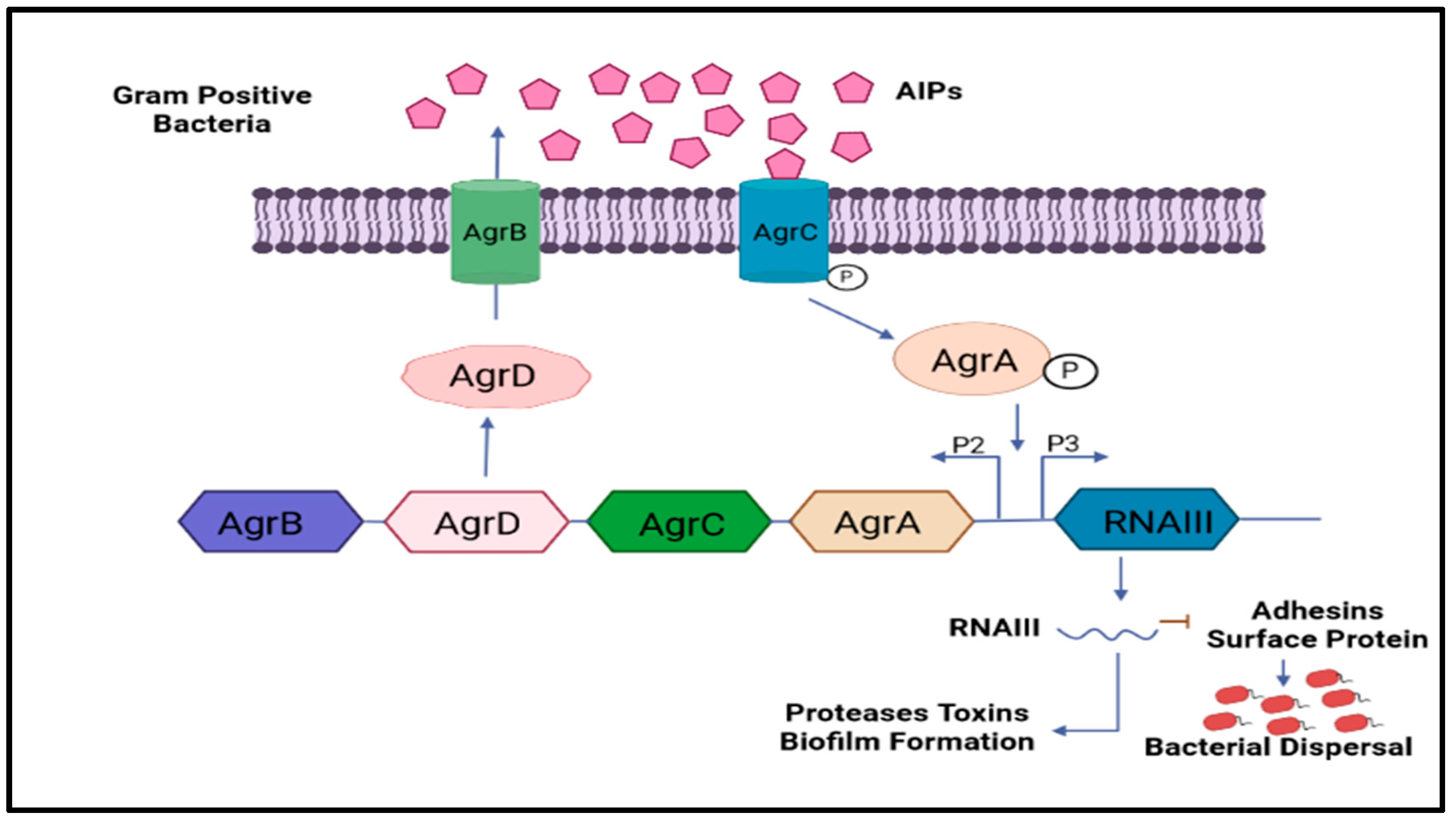
Multi-drug resistance is mainly caused by the rigid development of biofilm, which is a complex structure developed in four to five different stages, starting with the irreversible attachment (initial) of planktonic bacteria, the second step is colony formation, the third one is bacterial growth, the fourth is extracellular matrix generation, and, finally, the biofilm’s maturation leading to the final reversible detachment of cells from the older formed biofilm [30,31], see Figure 1. The exopolysaccharide or (EPS) is composed of so many essential nutrients among which Aap protein associated with the cell surface contains the G-5 domain, accountable for cell adhesion; during infection in Gram-negative time bacteria (Figure 3), Sortase A (SrtA), a transpeptidase, induces extracellular localization and biofilm generation and can bind cell surface proteins [32,33]. Thus, it can be concluded that inhibitors against this adhesion can potentiate the antibiofilm activity [34]. The communication among the cells is dependent on a chemical signal molecule termed as quorum sensing (QS) [35]. The QS mechanism varies between bacteria, as evidenced by the production of signalling molecules in Gram-negative bacteria N-acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) as described in Figure 3, whereas in Gram-positive bacteria, the signalling molecule is peptides (autoinducer 2), which are described in Figure 4. Thus, similar to the adhesion inhibitors discussed above, some other enzyme shows the enzymatic degradation of QS signals caused by different enzymes such as lactonase, various acylase, and paraoxonase oxidoreductase, and the enzyme may provide a promising strategy for regulating biofilm development. As a result, the inhibition of QS and biofilm development has been reported in numerous studies [36,37,38]. It has been observed that many of the natural QSIs show a remarkable degradation of biofilm when combined with antibiotics [39], for example, usnic acid, which is a derived metabolite of lichen origin, and interfere with QS resulting in a changed morphology of S. aureus as well as of P. aeruginosa [36,40]. The biofilm has a specific relevance in terms of the QS system for a specific gene expression as well as communication among the cells; pyocyanin is a QS-mediated product helpful in the maturation of biofilm by interacting with eDNA released after the cell lysis and causing a viscous solution and thus aggregation of the cells and the production of an established mature biofilm [41,42]. In most of the microbes, the quorum signalling system, viz, rhl, iqs, pqs, and las. P. aeruginosa las and rhl are QS, is an expression for virulence genes. The las and rhl are further divisions in which LasR, acts as a transcriptional activator protein and is associated with AHL synthase LasI, which controls the production autoinducer, N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone [43,44]. Likewise, the N-butyryl-l-homoserine lactone (AHL) of the Rhl system, which RhlI produces, is composed of the transcriptional activator RhlR [45].
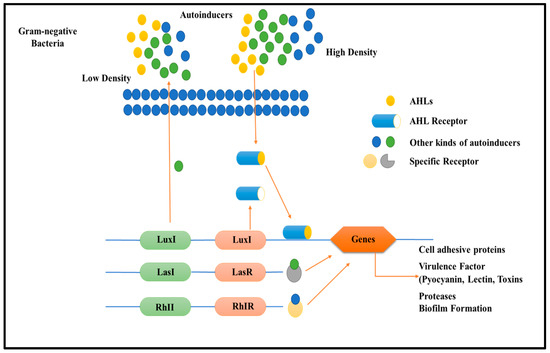
Figure 3.
Diagram describes quorum sensing signalling mechanism in Gram-negative bacteria relation and biofilm development role. Gram-negative bacteria frequently created (AHLs) during communication, which activated the relevant cytoplasmic receptors to modify the expression of the targeted genes. Luxl/luxR transcriptional factors of QS in Gram-negative bacteria.
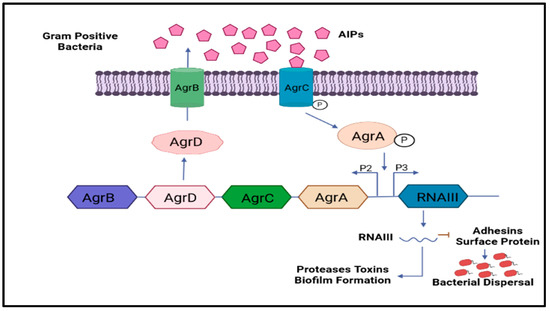
Figure 4.
Shows the involvement of Gram-positive bacteria’s classical QS signalling molecules and their role in biofilm development. The common QS signalling system is Agr.
As a result of the ongoing drug resistance, it is essential to search for alternative antimicrobial medications. It has been observed that the las and rhl QS systems use either a direct or indirect method to regulate their expression of environmental changes. Quorum quenching is one of these, and it impairs microbial quorum sensing. It minimises the virulence factors’ synthesis and biofilm formation. Only a few quorum quenching (QQ) methods use structurally similar QS receptor autoinducers (AI). They are natural or synthetic chemicals. Most of the QQ molecules that have been discovered are enzymes that can degrade signalling molecules, preventing the creation of biofilms [31,46]. Thus it can be concluded that quorum sensing inhibitors, whether from a natural or synthetic origin, when combined with antibiotics, can help erode biofilms [47,48,49].
3. Natural Product as Antibiofilm Agent
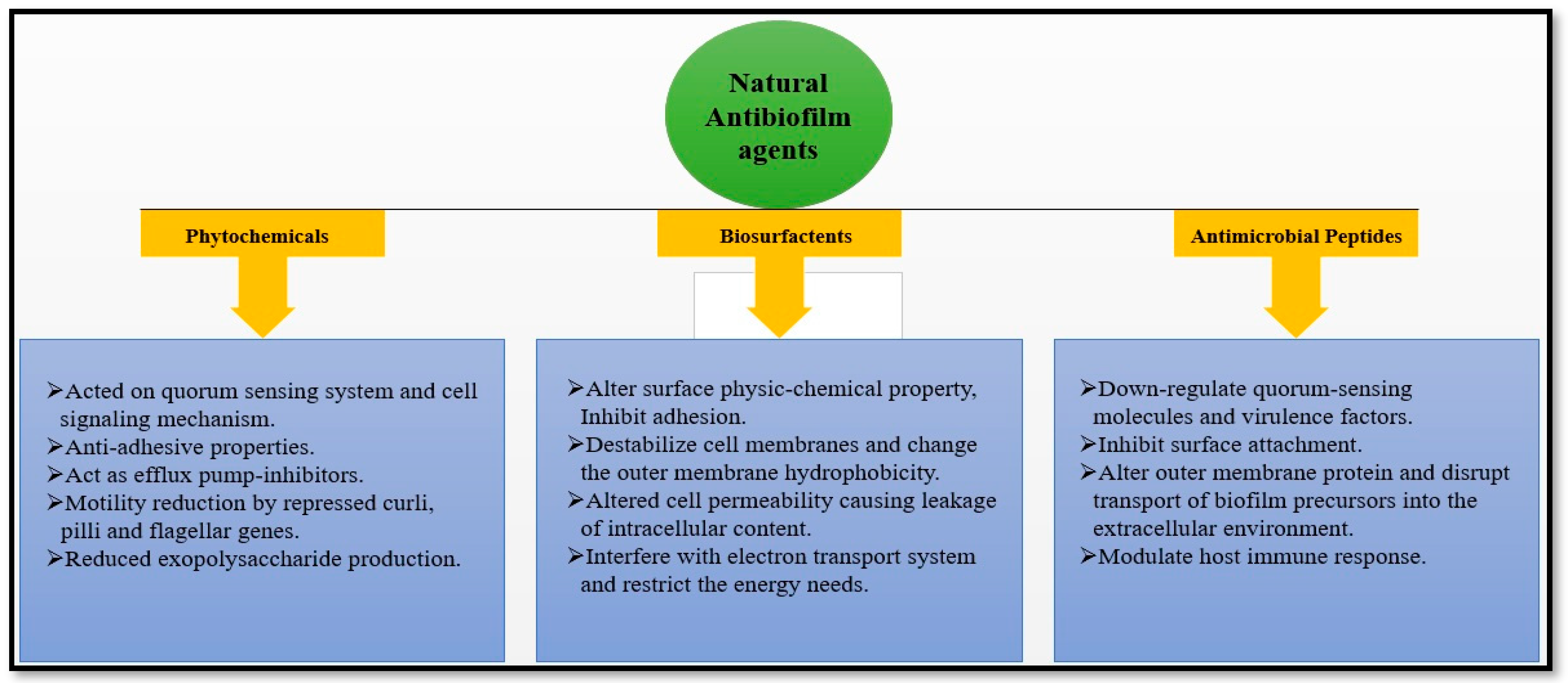
Natural medicines have been used for centuries. Various plant-derived natural compounds exhibit in vitro antimicrobial and antibiofilm properties [50]. Numerous plant-derived molecules or medicinal herbs, and natural compounds show remarkable prophylaxis effects for bacterial biofilm infections, and their mechanisms of action in antibiofilm activity have been identified [7,51]. The development of biofilm is a very complex process. The factors responsible for the antibiofilm activity of natural drugs prevent polymer matrix development, inhibit cell adhesion and attachment, prevent the formation of extracellular matrix (ECM), and limit the virulence factors’ production, thus leading to the development of the QS system, and the biofilm is restrained. Targeting one or both of the initial two stages crucial for developing biofilms seems to be the best action to prevent their creation [52]. Antibiofilm activity of the natural product is divided into three subcategories based on their mode of action, as shown in Figure 5 and Table 1; the potential antibiofilm activity of a few natural antimicrobial drugs is shown.
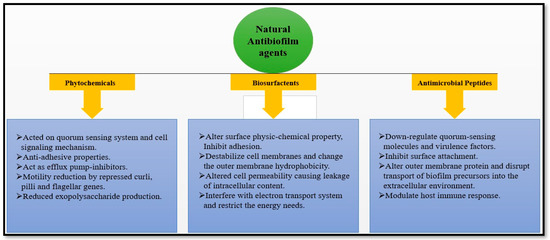
Figure 5.
Natural antibiofilm agents based on their mode of action.
3.1. Phytochemicals
Plants produce substances that may not be essential for their primary metabolism but exhibit their potential to adapt to harsh abiotic and biotic environmental conditions. Extensive research was conducted on various plant extracts and their active ingredients to get rid of the Propionibacterium acne biofilm [53,54]. Studies showed that these extracts (Dolichos lablab, Polygonum cuspidatum, Malus pumila, Rhodiola crenulata, and Epimedium brevicornum) have significant antibiofilm activity [55]. The research also revealed that P. cuspidatum and E. brevicornum extracts with icartin and resveratrol as active components demonstrated considerable antibiofilm activity below their minimal inhibitory concentrations [56]. After being tested, Melia dubia bark extracts effectively regulate E. coli biofilm development [57,58,59] Extract from the caper bush (Capparis spinosa) effectively reduced the growth of biofilms and the production of EPS in S. marcescens, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and P. mirabilis [60,61]. Southeast Asian native herb Lagerstroemia speciosa significantly reduced biofilm growth in P. aeruginosa PAO1 [62,63]. The aqueous extracts of Brazilian xeric show antibiofilm activity and serve as an in vitro screening of S. epidermidis [64]. According to the study, biofilm development was significantly decreased by extracts of Bauhinia acuruana, Chamaecrista desvauxii, and Pityrocarpa moniliformis. Moreover, Senna macranthera and Commiphora leptophloes fruit extracts were said to diminish biofilms by 67.3% and 66.7%, respectively [65]. Using qualitative and quantitative methods, a study on the growth of M. smegmatis biofilm revealed the role of various herbs, spices, and plants, including Vaccinium oxycoccus, Azadirachta indica, Juglans regia, and Hippophae rhamnoides. The extract of A. indica was shown to be the most effective on M. smegmatis biofilms [66,67].
Natural substances with strong antibiofilm characteristics fall roughly into eight types, flavonoids, terpenoids, lectins, alkaloids, polypeptides, polyacetylenes and phenolics, and essential oils [68]. There are seven subclasses of phenols, and condensed tannins, which mainly show antibiofilm activity [64]. These compounds act on biofilms using different mechanisms, including substrate restriction, cell wall rupture, acting on adhesion groups and cellular membranes, protein binding, and DNA association, leading to blocking viral fusion [69,70]. According to a published research article, antibiofilm capabilities of Indian-originated herbs, Bischofia javanica, Syzygium Roxb, Rathakr. Mazz, and Cinnamomum glaucescens (Nees) showed positive results. Extract of Holigarna caustica (Dennst.), extract of gum Arabic tree Acacia nilotica (L.), Anacardiaceae family, extract of jack of orange jasmine Murraya paniculata (L.), and fruit extract of Buddha Coconut Pterygota alata, act on S. aureus against their biofilm development [71]. Salvia officinalis L., a medicinal herb from Algeria that contains 12-Methoxy-trans-carnosic acid and abietane diterpenoid, also known as carnosol, demonstrated antibiofilm efficacy against Candida [72]. Phytochemicals generally act on the inducers molecule such as AHL and may act on some other autoinducer and type 2 receptors, to stop the functioning of the QS signalling system [73]. Garlic extracts exhibited a significant inhibitory role in the QS signalling compound of P. aeruginosa biofilm and other species’ biofilms such as Vibrio spp. [6,74]. Emodin is a potent inhibitor and facilitates the protein degradation of transcription factors involved in quorum sensing [75].
Numerous researchers have shown that quorum quenchers and antibiotics combination might be considered as the best non-traditional antibiofilm agents [46]. Furthermore, phytochemicals are essential for suppressing the genes that lead to biofilms forming and preventing bacterial adhesions [76]. Biofilms in their early phases can be disturbed by the fluid dynamic properties of the planktonic cell, an electrostatic force of attraction, and properties of sedimentation that encourage attachment to diverse surfaces [34]. Phytocompounds have the ability to stop the availability of essential nutrients required for bacterial attachment and growth. The Psidium guajava L. extracts in ethanol and acetone, as well as extracts from several Eugenia species, have been shown to have antiadhesive effects on C. albicans [77]. Syzygium aromaticum (S. aromaticum) extract shows antibacterial activity in dental caries against various strains of streptococci [78]
Norbgugaine significantly impacted P. aeruginosa biofilm by inhibiting cell motility caused by an inability to adhere to the surface [79]. Adiantum philippense L. crude extract has the potential to reduce the number of exopolysaccharides in biofilms [76]. They discovered that crude extract of Adiantum philippense L. blocks the generation of EPS, targets adhesin proteins, and deforms already-formed biofilms to prevent biofilm growth in the initial stages. In terms of different phytocompounds, numerous studies have discovered that polyphenols, particularly those such as 7-epiclusianone (tetraprenyl benzophenone derivative), casbane parent hydride of casbene, and tannic acid, a type of polyphenol, inhibit surface attachment [76,80,81]. Enterobacteriaceae’s curli, an amyloid fibre expressed on the EPS surface, encourages the formation of biofilms, cell aggregation, and target attachment [82,83] They revealed that the flagellar operon flhDC was suppressed by the citrus sterol-sitosterol glucoside, which prevented the production of biofilms and cell motility in E. coli O157:H7. Curlicide derivative (Aβ-peptide) and pilicide phytocompounds are used as new therapeutic approaches to prevent Enterobacteriaceae biofilms [84]. Pyridones interfere with curli, leading to expression modification and biogenesis of the CsgA. (Curli, pilli) genes are regulated by phytochemicals from Malaysian plants, including phloretin, ginkgolic acid, and phytocompounds [84,85,86].
Garlic extract has been shown to inhibit QS in the research of Bjarnsholt. It was found that the administration of garlic extract for a lung infection (mouse model) reduces the drug resistance of tobramycin and the neutrophils (PMN) phagocytosis of P. aeruginosa [87]. Garlic extract diminishes QS signals, and virulent factors of P. aeruginosa are reported in the UTI model [88]. Six clinical bacterial isolates showed resistance to the biofilm-forming activities of garlic extracts [89,90]. Plant extracts from Coptis chinensis and C. trilobus may prevent germs from adhering to fibronectin-coated surfaces. They show the effects at the adhesion stage by inhibiting sortase (an enzyme of biofilm development) and enhanced the covalent attachment of surface proteins in Gram-positive bacteria [91,92]. The polyphenols found in cranberries prevent the growth of biofilms and the colonisation of pathogens [93,94]. Cranberry components exhibited promising effects for the deterrence and cure of oral infections, such as dental caries and periodontitis, by impacting binding proteins (glucan); the enzymes acted by splitting down the ECM, energy production, hydrophobicity of the biofilm, and degradation activities [95]. According to studies, Ginkgo biloba extract significantly reduced the development of fimbriae and biofilm in Escherichia coli O157:H7; this agreed with the inhibited curli and prophage genes [96,97]. E. coli’s ability to swim was found to be impaired by cinnamaldehyde, which also allegedly affects biofilm formation and structure [98]. Citrus limonoids are distinct secondary triterpenoid metabolites.
The purified limonoids demonstrate their capacity to obstruct Vibrio harve’s cell–cell communication and biofilm development. Bacterial cell–cell signalling is effectively modified by isolimonic acid [98,99], ichangin block biofilm, and the type III system. Additionally, it disrupts the AI-3, which triggers the signalling pathway according to QseBC and QseA dependence [100]. Hordenine’s anti-QS potential is a signalling molecule competitor inhibitor and novel for foodborne infections. Hordenine successfully decreased the QS-related gene expression in P. aeruginosa PAO1 [101,102,103]. Hordenine-conjugated AuNPs showed improved antibiofilm properties on P. aeruginosa PAO1 [104]. It has been discovered that different gene levels (LasI, LasR, RhlI, and RhlR) for QS signalling are significantly lowered by the presence of the plant polyphenol quercetin [105]. Quercetin potently inhibits P. aeruginosa pathogenicity and biofilm formation [106]. It is a potent SrtA antagonist that could significantly prevent the formation of S. pneumoniae biofilms, causing the inhibition of sialic acid expression [107]. Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis antibiofilm activities of quercetin in biofilm production, and biofilm-related infections were also explored, and the results indicated quercetin’s potential for application in human health bacterial infection and anticaries therapy [108,109]. Natural antibiofilm agents’ screening has expanded in scope over time. Other antibiofilm substances, such as those made from herbs, are, in addition to those mentioned [110], medicinal plants, phenolic compounds [111], green tea [112], mushrooms [113], licorice root [114], Polish propolis [115], Allium sativum [116], Psidium cattleianum leaf [116], Solidago virgaurea [117], Roselle calyx [118], and Juglans regia L. [119].
3.1.1. Essential Oils
Essential oils (EOs) are aromatic compounds that plants produce; they are nonbiocidal and show promise as a treatment for bacterial biofilm illness and increased drug resistance in vitro [120,121]. In the case of S. epidermidis strains, EOs primarily function as biofilm inhibitors. Results have demonstrated that they can destabilise biofilms at deficient concentrations without compromising bacterial viability due to their effectiveness against P. aeruginosa. The effectiveness of cumin oil in contradiction of the biofilm production by pneumonia strains was investigated [122]. This study showed that this EO decreased biofilm growth and improved the antibiotic ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness. The research reveals that cinnamon oil is effective against the biofilm of S. mutans and Lactobacillus plantarum [123,124]. Cinnamon oil effectiveness was reported in S. epidermidis biofilm [125]. The Enteropathogenic E. coli attachment stage in biofilm is suppressed by Cinnamomum oil [126]. The essential oil derived from oregano showed disruptive biofilm properties of staphylococci and E. coli species [127]. Oregano EO exerts antibacterial potency on different species of Staphylococcus and E. coli planktonics, and prevents biofilm formation [127,128]. Recently, studies have been conducted on the antibiofilm properties of vegetable oil (Brazil nut oil) on dentifrice biofilm [129]. It was claimed that using commercially available dentifrice with vegetable oil could help prevent and treat dental caries and periodontal disease because of its antibacterial properties. With regards to tea tree oil, the tea tree EO (TTO) and ciprofloxacin (CIP) combination and their antibacterial activity were evaluated on P. aeruginosa. The result revealed that the synergistic effect of the combination reduces the biofilm biomass by 70%. According to reports, EOs (thymol, cinnamon oils and oregano) were found to be effective against the biofilm-forming strains of Acinetobacter, Sphingomonas, and Stenotrophomonas at sublethal concentrations [130,131].
3.1.2. Andrographis paniculata (Andrographolide)
Andrographis paniculata (A. paniculata), commonly found in China, belong to the Acanthaceae family [132]. It has proven successful in treating bacterial infections and has a sizable impact on P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and E. coli biofilm generation [133,134] and decreases the synthesis of extracellular pathogenic factors in P. aeruginosa regulated by the QS system, such as anthocyanins and elastase. Andrographolide (AG) is the active metabolite of A. paniculata; AG inhibits biofilm formation by inhibiting the QS system by regulating SarA factor, which is responsible for biofilm development in S. aureus [135]. E. coli adhesion can be reduced by AG as the amount of PIA/PNAG declines because this also affects the ability to produce biofilms [136].
3.1.3. Polygonum cuspidatum (Emodin)
Polygonum cuspidatum’s constituents are anthraquinone, emodin, etc. [137]. One goal of caries prevention is to control dental plaque. Since biofilm formation in the dental cavity starts with the salivary membrane and planktonic bacteria adhering to the surface of teeth, reduced planktonic bacterial loads may help regulate biofilm development [138].
3.1.4. Curcuma longa (Curcumin)
Curcuma longa of the Zingiberaceae family produces sesquiterpenes, turpentine, and fatty acids that disrupt antibiofilm activity, impairing the bacterial cell membrane’s normal barrier function, and is crucial for the growth and metabolism of bacteria [139]. It modulates various QS-dependent pathogenic factors, such as Vibrio spp. swarming, alginate synthesis, and mobility [140,141]. It works by blocking the growth of EPS and decreasing the flagellum effect, which restricts bacteria from swimming and the development of biofilms [140,142].
3.1.5. Allium sativum (Allicin)
Ajoene exhibits QS inhibitory activity in Allium sativum, where organic sulphide is the main antibacterial component and decreases the rhlA gene in P. aeruginosa, lowering the concentration of rhamnolipids encrypted by rhlA. Garlic extract inhibits the biofilm formation in L. monocytogenes and P. aeruginosa [116], and garlic checks the virulence factors and QS signal generation in P. aeruginosa [88].


Table 1.
The potential antibiofilm activity of a few natural antimicrobials drugs.
Table 1.
The potential antibiofilm activity of a few natural antimicrobials drugs.
| Plant Extract/Compounds | Botanical Source | Species | Mechanism | Antibiofilm Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-homoserine lactone (Garlic extract) | Allium sativum L. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Acted on transcriptional pathway (LuxR and LasR) | Reduced synthesis of QS signals and decreased pathogenicity. | [61] |
| Carvacrol (terpenoid) | Origanum vulgare L. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Inhibition of lasI, which affects AHL production. | It acts by post-translational inhibition enzyme and interrupts the QS signaling mechanism | [143] |
| Polyphenols (cranberry) | Vaccinium oxycoccos | Cariogenic and periodontopathogenic bacteria | Glucan-binding proteins, enzymes used in biofilm formation | Impaired biofilm development by coaggregation, degradation of ECM, glucose synthesis, bacterial hydrophobicity, and photolytic activities. | [65] |
| Ajoene | Allium sativum L. | P. aeruginosa, S.aureus | Impedes RNA regulatory molecules (rsmY, rsmZ, and rnaIII) and reduces rhamnolipid synthesis | Limits the QS signalling RNA regulatory molecules | [144,145] |
| Emodin (anthraquinone) | Origanum vulgare L. | Staphylococcus aureus | Reduces eDNA production, and impairs gene regulator (cidA, icaA, dltB, sortase and AagrA) | It regulates eDNA, and inhibition of gene expression, which is essential in biofilm formation (cidA, icaA, dltB, agrA, sortaseA, and sarA). | [146] |
| Allicin | Allium sativum L. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Inhibits EPS production, regulating the pathogenic factors. | Inhibits EPS production, reduces bacterial adherence at the primary stages of biofilm generation, and acts on the QS system by altering the expression of virulence factors. | [147] |
| Hordenine | Hordeum vulgare L. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Impaired AHL production, gene regulation rhlR, rhlI, lasI, and lasR genes. | Limits the generation of AHL resulting in bacterial biofilm generation | [101] |
| Vitexin (flavonoid) | Vitex species | P. aeruginosa | Inhibit EPS, by acting on LasA, Las B, and Lux R | Reduces the production of proteolysis enzyme, and surface protein as well as EPS and components linked with QS. Attenuates LasA, Las B, and Lux R | [148] |
| Patriniae | Patrinia scabiosifolia | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Acts on biofilm-associated genes | Decreased exopolysaccharide synthesis and prevented biofilm development | [67] |
| Ginkgolic acids (Leaf extract) | Ginkgo biloba | E. coli O157:H7 | Acted on Curli and prophage genes | Prevented biofilms’ production on non-living surfaces such as nylon, polystyrene, and glass | [149] |
| Phloretin (Natural phenol) | Annurca apples | S. aureus RN4220 and SA1199B | Efflux protein genes | Production of an antibiofilm at low concentrations | [58] |
| Cinnamaldehyde (Phenylpropanoid) | Cinnamomum ceylanicum | E. coli and Vibrio spp. | DNA-binding ability of LuxR | Inhibits biofilm development by regulating structure, flagella of bacteria, and stress responses | [121] |
| Phloretin (Natural phenol) | Annurca apples | E. coli O157:H7 | It acted on Curli genes (csgA and csgB), toxin genes (stx(1)), autoinducer-2 importer genes (DE3), | Inhibited biofilm formation and fimbria production | [58] |
| Emodin (Anthroquinone) | Polygonum cuspidatum Siebold & Zucc.Rheumpalmatum L. | Candida spec. like C. albicans, C.krusei, etc. | Acts on cellular kinase signalling and CK2 | Inhibits biofilm development by acting on cellular kinase signalling. Disrupts planktonic cells by inhibiting the growth of hyphae. | [131] |
| Pulverulentone A (Skeels leaves) | Callistemon citrinu | Methicillin-resistant S. aureus | Inhibits staphyloxanthin production | It decreases staphyloxanthin synthesis, and the cell membrane is impaired, preventing biofilm growth. | [150] |
| Tannic acid | not defined | E. coli BW25113 | Prevents the generation of polysaccharides in the matrix. | Impeding generation of saccharide in ECM. Regulates SOS cell to cell response and declines to kill bacteria in pgaA mutant biofilms. | [151] |
| Aloe-emodin | Rheum officinale Baill. | Staphylococcus aureus | Inhibit extracellular proteins of the matrix | Limits ECM extracellular polysaccharide and protein adhesion | [152] |
| 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural | Musa acuminata Colla. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Prevents the synthesis of EPS, cell protein | Prevents the synthesis of EPS, and extracellular proteins, limits hydrophobicity, regulates expression of pathogenic genes that QS controls | [153] |
| Isolimonic acid and ichangin | Citrus species | Enterohaemorrhagic, E. coli, Vibrio harveyi | Inhibits gene regulator for flagella flagellar (flhC and flhD), luxO expression | Diminishes adherence, reduces the expression of ler (transcriptional regulator of LEE), a gene involved in making the flagellum. Suppresses master regulator’s expression (flhC and flhD) and controls luxO expression, effectively modifying bacterial cell–cell signalling. | [154] |
| Chelerythrine | Bocconia cordata willd. | Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus | Acts on hyphae formation, eDNA, regulation, inhibit saccharide, and protein levels | Hinders the development of hyphae, decreases the quantities of eDNA, polysaccharides, and proteins to reduce the production of biofilms. | [155] |
| Quercetin | different sources | Streptococcus Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa | SrtA, LasI, LasR, RhlI and RhlR | It acts by blocking SrtA, gene which checks the sialic acid generation and inhibit biofilm formation | [74,75,76,77] |
| Methanolic fraction of Zingiber officinale | Zingiber officinale | S. mutans | Impairs protein generation factor F-ATPase, surface protein antigen SpaP | It regulates surface protein by impairing antigen SpaP, showing effect on cell surface hydrophobicity in S. mutans | [64] |
| Methanolic caper bush extract | Capparis spinosa L. | S. marcescens, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and P. mirabilis | Synthesis of EPS producing enzyme | Effectively reduced the growth of biofilms and the production of EPS | [64] |
| Emodin | Rheum palmatum | Pseudomonas and Vibrio spp. | Transcription factors in QS | Potent inhibitor and facilitates degradation of transcription factors involved in quorum sensing | [156] |
| Guava alcoholic extract | Psidium guajava L | C. albicans | Inhibits cell motility enzyme. | Inhibits primary-stage adhesion due to a lack of motility, impacted on biofilm development | [66] |
| 12-Methoxy-trans-carnosic acid and carnosol | Salvia officinalis L | Candida | QS sensor disruption (AHL), autoinducers, and type 2 receptors | Inhibits biofilm formation using quorum sensing system from functioning by QS disruption sensor inducers (AHL), autoinducers, and type 2 receptors | [64,65] |
| Norbgugaine | Arisarum vulgare | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Acts on cell motility proteins | Inhibits a primary attachment caused by cell motility, showed significant impact on biofilm formation | [52] |
| Curlicide and pilicide | not defined | Enterobacteriaceae | Acts on the flagellar operon flhDC enzyme | Inhibits the cell motility by blocking flagellar operon flhDC enzyme production biofilm development | [57] |
3.2. Biosurfactants
Biosurfactants (BS) impede the capacity of cells to attach to surfaces by affecting the hydrophilic nature of the cell membrane, perforating membranes, and limiting the electron transport chain, thus decreasing the energy need of cells [157]. Medical implants such as urinal catheters and bone implants can be coated with biosurfactants to prevent biofilms from harmful organisms without synthetic medications [158]. Staphylococcus aureus was tested for how biosurfactants from Lactobacillus Plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici affected the expression of biofilm-related genes and quorum sensing signalling molecules [146,159]. As claimed from the study, biosurfactants control gene expression related to biofilms, such as dltB, icaA, cidA, etc., which control the development of S. aureus biofilm [158]. At 50 mg/mL, Pediococcus acidilactici biosurfactant inhibits gene production such as (AI-2) signalling factor and staphylococcal accessory regulatory-sar A [158]. According to earlier research, BS-loaded liposomes made from Lactobacillus were more efficient than free BS, preventing the development and removal of S. aureus (MRSA) biofilms [160,161]. According to earlier research, BS-loaded liposomes produced from Lactobacillus were more efficacious than plain BS at preventing the development and removal of S. aureus (MRSA) biofilms. Table 2 summarizes some biosurfactants with their effect on biofilm development.

Table 2.
List of biosurfactants with their effect on biofilm development.
The lipopeptide component of the anionic bacteria Acinetobacter junii is found to self-assemble and create vesicles filled with biosurfactant sheets. A lipidic biosurfactant of the fungus Beauveria bassiana is essential for M. canis to function as a biofilm inhibitory agent in ex vivo settings [162]. It impacted membrane permeability and started to break down the integrity of the cell membrane. Cyclical metal complexes were discovered to be highly efficient against infections brought on by C. albicans biofilms [163]. Surfactin does not have the same antiadhesive and antibiofilm properties as Pseudomonas aeruginosa MN1 rhamnolipids [164]. The glycolipid produced by Burkholderia sp. WYAT7 showed ant biofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus [165] as an endophyte of Artemisia nilagirica (Clarke) Pamp [166]. Burkholderia cepacia is resistant to biofilm formation Burkholderia pnomenusa MS5 [167]. According to reports, rhamnolipids and sophorolipids may be effective inhibitors of the biofilms developed by all classes of microorganisms [168]. Several studies have demonstrated that when exposed to cell-associated biosurfactants from Lactobacillus acidophilus, S. aureus, and Proteus vulgaris cannot develop biofilms on (PDMS)-based implants [169]. Biosurfactants from L. rhamnosus promote cell lysis by upsetting the structure of the membrane, making them an effective antibiofilm agent for diverse microbial biofilms on silicone implants, such as voice prostheses in laryngectomy situations [170]. Caprylic acid, which prevents the growth of biofilms from P. aeruginosa, E. coli, and B. subtilis, can significantly increase the antibiofilm efficacy of biosurfactants [171]. Fluconazole and (AmB) work together to prevent the growth of a biofilm and the existing biofilm of Candida albicans [172]. Surfactants such as sodium dodecyl sulfate caused P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm’s inhibition. [173].
3.3. Antimicrobial Peptides
Broad-acting antimicrobial medications (AMPs) are commonly used against bacterial and fungal biofilms. Infections caused by S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, Acinetobacter, and Enterobacter spp. (ESKAPE) as well as non-ESKAPE microorganisms are interrupted by these peptides acting on medical specimens such as valves, stents, and dentures [174,175]. Antimicrobial AMPs can block various biofilm formation molecular pathways [176]. The several AMPs in amphibian skin are efficient against different microbes that cause biofilms. AMP Japonicin-2LF, which inhibits MRSA biofilms by permeabilizing membranes, is a derived secretion from the skin of Limnonectes fujianensis, a frog from Fujian. Both sessile and planktonic pathogens are eliminated from biofilms by the detergent-like behaviour of Japonicin-2LF. Esculentin-1a, also known as Esc, is an AMP obtained from frog skin; its Esc contains D-amino acids (1–21). By disrupting membranes, -1c inhibited the biofilms of P. aeruginosa [172]. Three processes work together to prevent P. aeruginosa from forming biofilms. The fleN gene, which determines the flagella number in P. aeruginosa, is first downregulated, which prevents flagella-mediated swimming. Second, it inhibits P. aeruginosa twitching motility, which is crucial for microcolony formation and colonization during biofilm growth. It reduces type IV pili synthesis genes’ mRNA levels at a low concentration. Third, it prohibits the lasB gene, which codes for the virulence factor elastase LasB, and the lasI gene, which codes for the QS protein (AHL) synthase. It also carries out its function by electrostatically binding to the negatively charged bacterial cytoplasmic membrane, causing the creation of pores as a result of the solubilization of the membrane, which results in its destruction [177]. Due to their unique qualities of limitless sequence space and ability to produce antimicrobial action, these AMPs become the perfect candidate for overcoming microbial resistance. Additionally, some low molecular weight AMPs that penetrate the cellular structure act by becoming bound to the microbial genetic material, triggering the ROS-dependent pathway for their antimicrobial effect. The AMPs are mainly classified as defensins and bacteriocins. The defensins are the class of AMPs and peptides obtained from natural sources. This class of AMPs is also known as HDPs (host defence peptides), which act as broad-spectrum antibiotics and perform their action by electrostatic interaction at the microbial membrane, causing membrane destruction and causing a bactericidal effect [178,179]. On the other hand, bacteriocins are peptides obtained from bacteria, which are synthesized in the ribosomes. The first class of bacteriocins were discovered in 1925, after which a number of different forms of bacteriocins were discovered [180]. Although functionally they also perform antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities very similar to that of defensin, they are different from defensin in that this cationic amphiphilic molecule, in addition to becoming attached to the bacterial cell, causes the destruction of the phospholipid membrane, and hence obtains access to the DNA component and organelles of the cell, causing direct interference with the protein synthesis process. Thus, both forms of AMPs have proven to be valuable weapons in dealing with resistant microbes, which usually avoid killing via biofilm formation.
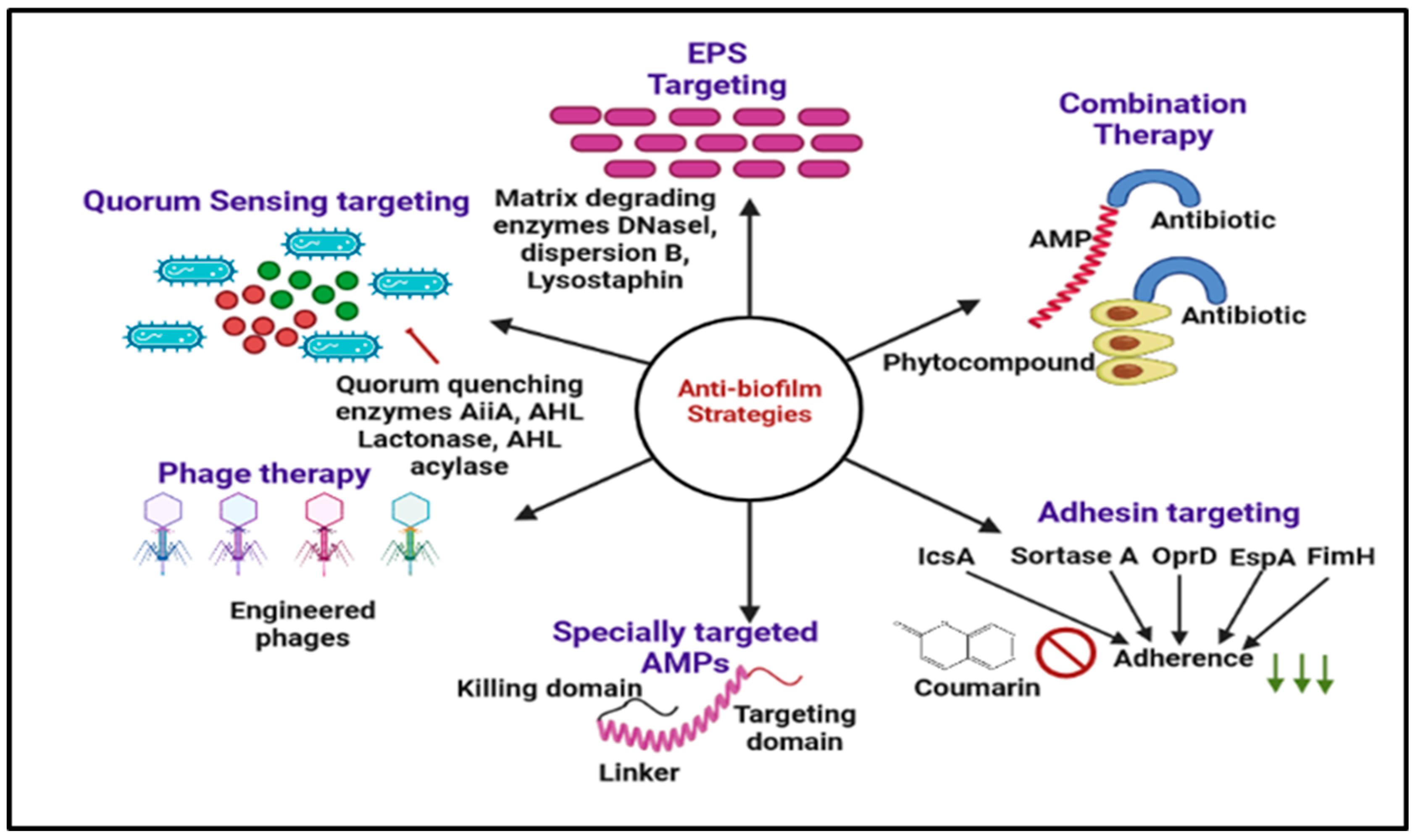
4. Other Ways to Inhibit Biofilm Resistance
The increasing case of ‘the non-effectiveness’ of antibiotics while dealing with common microbial infections has opened the door for in-depth study and research on the cause of microbial resistance and dealing with the strategies to combat such resistance. The search for new alternatives to the current conventional therapies should be able to act as broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents while keeping minimal side effects [181]. Some novel methods for combating resistance are the application of chitosan and its derivatives, antimicrobial peptide use of metallic nanoparticles and (QACs) [182], stimuli-responsive materials, and the application of Phage therapy. The details of these new methods are discussed below [183] and summarized in Figure 6.
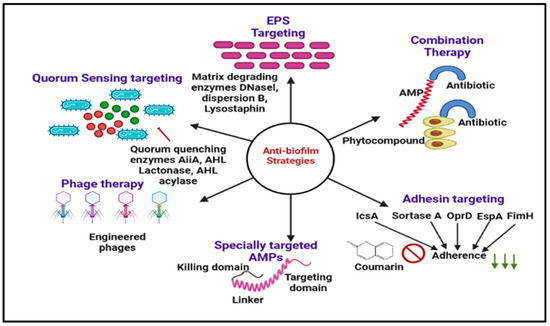
Figure 6.
Graphical illustration of the different antibiofilm approaches discussed in this review. EPS targeting (DNaseI, dispersion B, lysostaphin), Phage therapy, nanotechnology, chitosan and derivatives, and antimicrobial peptides.
4.1. Use of Chitosan and Its Derivatives
Chitosan is obtained from its natural precursor, chitin, which is commonly found in organisms such as algae, crustaceans, insects, and fungus, etc. When Chitosan undergoes the process of deacetylation either enzymatically or under the effect of an alkaline solution, chitosan formation takes place. Since, chitosan is obtained naturally, it is known for its biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, non-immunogenicity, and ease of availability. Owing to its various beneficial properties, several studies from the literature have reported its use as an antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer agent [184]. Chitosan, being a positively charged agent, has been used in various drug delivery systems either as the main component or applied as a coating material to impart a positive charge to the particles. The positive charge on the chitosan has been utilized for electrostatic interaction between surfaces that are either negatively charged and/or have been altered to induce a negative charge on the surface. The prime reason behind using chitosan as an antibiofilm agent is the cellular component of biofilms such as (lipids, exopolysaccharides, and e-DNA), and external components that constitute bacterial membranes such as (lipopolysaccharides or teichoic acids) are all anionic in nature. Thus, positively charged polymeric agents such as chitosan are electrostatically bound to the component at the membrane and disrupt the cellular structure of microbes, leading to the destabilization and leakage of the bacterial membrane. This causes leakage of the internal cellular components, such as proteins and electrolytes, through pore formation, thus completing the bacteriostatic and bactericidal effect [185]. Usually, the science of nanotechnology has been applied in the formulation of chitosan nanoparticles, which have been used for antimicrobial and antibiofilm therapy. With the chitosan nanoparticles being small in size, they can penetrate deep inside the biofilm membrane, thus causing the lysis, disruption, and disaggregation of the biofilm [186,187]. A different group of researchers worked with Chitosan either as a single agent or in combination with other herbal or synthetic molecules with promising antimicrobial effects.
In one such study, Hongbin et al. developed a system of minocycline-loaded chitosan and alginate, which reportedly destroyed adherent and planktonic bacterial colonies [188]. Subhaswaraj et al. formulated cinnamaldehyde-loaded chitosan NPs, which showed effective inhibition of P. aeruginosa-led biofilm formation effecting QS function and altering mortality [189]. In another study, Jinhong et al. designed a system in which chitosan and heparin were deposited in alternate manners on poly (ethylene terephthalate) film to carry out an antibacterial effect. A critical outcome of this study was that the system was found to be antiadhesive; hence could be used in implants [190]. Another form of chitosan, quaternized chitosan (QCS), known as HACC (hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan), is antibacterial in nature. It has been widely used in coating implants, tissue engineering, and wound healing. Peng et al. conducted their research and suggested that 18% of substituted HACC showed firm antibacterial activity, keeping toxicity to the minimum [49].
4.2. Phage Therapy
Phage is the virus that specifically invades and multiplies in bacterial cells. This inherent quality of the virus has been exploited to solve the issue of drug resistance in bacteria due to the biofilm formation. These phages have been explored as they only attack bacterial cells leaving behind healthy host cells and micro flora untouched [191,192]. Since phage therapy involves the steps of virus attachment to the host and transfer of the genetic material into the bacteria, this property was utilized to destroy the extracellular biofilm matrix to cause the bacterial elimination [191]. As the research progressed further, the cocktail of bacteriophage and antibiotics was explored with many studies showing a positive synergistic effect on disrupting biofilms [193]. The group, Gu et al., worked on the step-by-step technique for the combined delivery of phages to eradicate Klebsiella pneumonia by administering three phages (GH-K1, GH-K2, and GH-K3). The findings showed that when combined phages were delivered, they produced a stronger response against Klebsiella pneumonia than individual phages in the murine K7 strain model. They used data to prove their hypothesis that the lowest effective dose of the combined phage level was significantly lower than that of a single phage. Although this idea looks very effective for combating biofilm resistance, much effort still needs to be applied to formulate bacteriophage into some dosage forms. Needs for standardization, optimization, and guarantees of safety and efficacy are some of the questions that need to be addressed before such therapies can be used as a generalized treatment method for the larger population.
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Bacterial biofilms are widespread and play a crucial role in antibiotic resistance. Therapy of biofilm-associated infections is nowadays a problematic task for healthcare professionals. There is the urge to develop novel antimicrobial techniques to overcome problems associated with bacterial resistance. As revealed in this review, a vast library of natural resources is available to examine antibiofilm compounds. A number of researches have shown the inhibitory effects of natural drugs on the formation and growth of bacterial biofilms, revealing their potential as substitute treatments for bacterial illnesses. Their possible regulation mechanism was primarily caused by the inhibition of the QS system at different phases of biofilm development. Many plant extracts have also shown potential antibiofilm activity; there molecular structures are not identified, indicating more clinical trials need to be performed. This review also focuses on the quorum quenching (QQ) molecules and natural extracellular polymeric substance inhibitory enzymes and their mechanism of action on biofilm. Most of the natural drugs’ mechanisms are still unknown. More research in this area can overcome drug resistance. Clinical investigations that are now underway mostly concentrate on the external use of oral biofilms formed in dental plaque, periodontitis, and gingivitis. A promising therapy approach for biofilm infections is the combination of antibiotic drugs and herbal antibiofilm drugs for effective remedies. It is vital to conduct in vivo research to assess the dependability of the combined medications because most investigations on these drugs are now conducted in vitro. Based on fingerprint efficacy, QC modelling, and PK-PD (pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic) correlation in in vivo investigations, the formation of combined pharmaceutical therapies will be aided by the ability to show the mechanisms of the combined medications.
Author Contributions
A.S. (Athar Shamim), M.A.M., A.S. (Ayesha Siddiqui) writing—original draft preparation; A.S. (Athar Shamim), M.A. and S.M.K., writing—review and editing; P.P.N., A.A.F.A. and M.S.K. resources; V.K. and A.S. (Ayesha Siddiqui), data curation; A.A. and Z.I., project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by King Khalid University, grant number (RGP 2/218/43).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are included in this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia (RGP 2/218/43).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Falagas, M.E.; Bliziotis, I.A.; Kasiakou, S.K.; Samonis, G.; Athanassopoulou, P.; Michalopoulos, A. Outcome of Infections Due to Pandrug-Resistant (PDR) Gram-Negative Bacteria. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masák, J.; Čejková, A.; Schreiberová, O.; Řezanka, T. Pseudomonas Biofilms: Possibilities of Their Control. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 89, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H.; Lee, J.H. Antibiofilm Agents: A New Perspective for Antimicrobial Strategy. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D. Understanding Biofilm Resistance to Antibacterial Agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Vanitha, J. Immunomodulatory and Antimicrobial Effects of Some Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herbs: A Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Hu, W.; Tian, Z.; Yuan, D.; Yi, G.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Zhu, J.; Li, M. Developing Natural Products as Potential Anti-Biofilm Agents. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzo, F.; Scognamiglio, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Buommino, E.; D’abrosca, B. Plant Derived Natural Products against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Staphylococcus Aureus: Antibiofilm Activity and Molecular Mechanisms. Molecules 2020, 25, 5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khameneh, B.; Eskin, N.A.M.; Iranshahy, M.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S. Phytochemicals: A Promising Weapon in the Arsenal against Antibiotic-resistant Bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.C.; Kundukad, B.; Seviour, T.; Van der Maarel, J.R.C.; Yang, L.; Rice, S.A.; Doyle, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Dynamic Remodeling of Microbial Biofilms by Functionally Distinct Exopolysaccharides. MBio 2014, 5, e01536-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Microbial Biofilms: From Ecology to Molecular Genetics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.C.; Macedo, A.P.; Melo, L.D.R.; Santos, S.B.; Hermann, P.R.S.; Silva-Lovato, C.H.; Paranhos, H.F.O.; Andrade, D.; Watanabe, E. Bacteriophage Cocktail-Mediated Inhibition of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm on Endotracheal Tube Surface. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, D.; Bachofen, R.; Brandl, H. Effect of Medium Composition, Flow Rate, and Signaling Compounds on the Formation of Soluble Extracellular Materials by Biofilms of Chromobacterium Violaceum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.G.; Parsek, M.R.; Pearson, J.P.; Iglewski, B.H.; Costerton, J.W.; Greenberg, E.P. The Involvement of Cell-to-Cell Signals in the Development of a Bacterial Biofilm. Science 1998, 280, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, B.; Riedel, K.; Köthe, M.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Eberl, L. Genetic Analysis of Functions Involved in the Late Stages of Biofilm Development in Burkholderia Cepacia H111. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. Biofilm Quantification and Comparative Analysis of MIC (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration) & MBIC (Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration) Value for Different Antibiotics against E. Coli. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 198–224. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, P.S.; Costerton, J.W. Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria in Biofilms. Lancet 2001, 358, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mil-Homens, D.; Martins, M.; Barbosa, J.; Serafim, G.; Sarmento, M.J.; Pires, R.F.; Rodrigues, V.; Bonifácio, V.D.B.; Pinto, S.N. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Isolates: In Vivo Virulence Assessment in Galleria Mellonella and Potential Therapeutics by Polycationic Oligoethyleneimine. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Yu, S.; Wozniak, D.J.; Ma, L.Z. The Exopolysaccharide Psl-EDNA Interaction Enables the Formation of a Biofilm Skeleton in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, E.; Doudet, L.; Allart-simon, I.; Colin, M.; Gangloff, S.C.; Gérard, S.; Reffuveille, F. Synergy between Indoloquinolines and Ciprofloxacin: An Antibiofilm Strategy against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.F.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Qin, L.; Tay, J.H. The Influence of Cell and Substratum Surface Hydrophobicities on Microbial Attachment. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 110, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, B.; Cerf, O. Biofilms and Their Consequences, with Particular Reference to Hygiene in the Food Industry. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1993, 75, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.; Flint, S.; Brooks, J. Bacterial Cell Attachment, the Beginning of a Biofilm. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 34, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyżek, P.; Grande, R.; Migdał, P.; Paluch, E.; Gościniak, G. Biofilm Formation as a Complex Result of Virulence and Adaptive Responses of Helicobacter Pylori. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiers, A.J.; Bohannon, J.; Gehrig, S.M.; Rainey, P.B. Biofilm Formation at the Air-Liquid Interface by the Pseudomonas Fluorescens SBW25 Wrinkly Spreader Requires an Acetylated Form of Cellulose. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinas, S.; Charalampogiannis, N.; Euverink, G.J.W. A Brief Recap of Microbial Adhesion and Biofilms. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branda, S.S.; Vik, Å.; Friedman, L.; Kolter, R. Biofilms: The Matrix Revisited. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, C.A.; Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Stoodley, P. Survival Strategies of Infectious Biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, A.; Maisonneuve, E.; Gerdes, K. Mechanisms of Bacterial Persistence during Stress and Antibiotic Exposure. Science 2016, 354, aaf4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.; Condinho, M.; Carvalho, B.; Arraiano, C.M.; Pobre, V.; Pinto, S.N. The Two Weapons against Bacterial Biofilms: Detection and Treatment. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; Coppola, R. Quorum Sensing and Phytochemicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12607–12619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Chamkhi, I.; Balahbib, A.; Rebezov, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Wilairatana, P.; Mubarak, M.S.; Benali, T.; El Omari, N. Mechanisms, Anti-Quorum-Sensing Actions, and Clinical Trials of Medicinal Plant Bioactive Compounds against Bacteria: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Liu, G.; Ton-That, H.; Schneewind, O. Staphylococcus Aureus Sortase, an Enzyme That Anchors Surface Proteins to the Cell Wall. Science 1999, 285, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Tian, X. Quorum Sensing and Bacterial Social Interactions in Biofilms. Sensors 2012, 12, 2519–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Tiwari, M.; Donelli, G.; Tiwari, V. Strategies for Combating Bacterial Biofilms: A Focus on Anti-Biofilm Agents and Their Mechanisms of Action. Virulence 2018, 9, 522–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annous, B.A.; Fratamico, P.M.; Smith, J.L. Scientific Status Summary: Quorum Sensing in Biofilms: Why Bacteria Behave the Way They Do. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, R24–R37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francolini, I.; Norris, P.; Piozzi, A.; Donelli, G.; Stoodley, P. Usnic Acid, a Natural Antimicrobial Agent Able to Inhibit Bacterial Biofilm Formation on Polymer Surfaces. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4360–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saqr, A.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.S.; Shaldam, M.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abbas, H.A. A Novel Use of Allopurinol as a Quorum-Sensing Inhibitor in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topa, S.H.; Palombo, E.A.; Kingshott, P.; Blackall, L.L. Activity of Cinnamaldehyde on Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Susceptibility to Antibiotics in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackman, G.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors Increase the Susceptibility of Bacterial Biofilms to Antibiotics in Vitro and in Vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, O.; Desouky, S.E.; El-Sherbiny, G.M.; Abu-Elghait, M. Correlation between Phenotypic Virulence Traits and Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Clinical Isolates. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 162, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradali, M.F.; Ghods, S.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Lifestyle: A Paradigm for Adaptation, Survival, and Persistence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, D.; Zhao, H.; Gong, S.G.; Lévesque, C.M. A DNA-Damage Inducible Gene Promotes the Formation of Antibiotic Persisters in Response to the Quorum Sensing Signaling Peptide in Streptococcus Mutans. Genes 2022, 13, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kievit, T.R. Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, K.; Charlesworth, J.C.; LeBard, R.; Visscher, P.T.; Burns, B.P. Quorum Sensing in Extreme Environments. Life 2013, 3, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, A.; Foglino, M.; Tanaka, K.; Williams, P.; Lazdunski, A. A Hierarchical Quorum-Sensing Cascade in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Links the Transcriptional Activators LasR and RhIR (VsmR) to Expression of the Stationary-Phase Sigma Factor RpoS. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 21, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch, E.; Rewak-Soroczyńska, J.; Jędrusik, I.; Mazurkiewicz, E.; Jermakow, K. Prevention of Biofilm Formation by Quorum Quenching. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algburi, A.; Comito, N.; Kashtanov, D.; Dicks, L.M.T.; Chikindas, M.L. Control of Biofilm Formation: Antibiotics and beyond. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02508-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Núñez, J.L.; Pérez-López, M.; Espinosa, N.; Campos-Hernández, N.; García-Contreras, R.; Díaz-Guerrero, M.; Cortes-López, H.; Vázquez-Sánchez, M.; Quezada, H.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.; et al. Anti-Virulence Properties of Plant Species: Correlation between in Vitro Activity and Efficacy in a Murine Model of Bacterial Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.X.; Wang, L.; Du, L.; Guo, S.R.; Wang, X.Q.; Tang, T.T. Adjustment of the Antibacterial Activity and Biocompatibility of Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride Chitosan by Varying the Degree of Substitution of Quaternary Ammonium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoor, S.; Nazim, F.; Rizwan-ul-Hasan, S.; Ahmed, K.; Khan, S.; Ali, S.N.; Abidi, S.H. Analysis of the Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Natural Compounds and Their Analogues against Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates. Molecules 2022, 27, 6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, C.; Chan, A.N.; Wright, G.D. The Antibiotic Resistome: A Guide for the Discovery of Natural Products as Antimicrobial Agents. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 3464–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowe, S.D.; Richards, J.J.; Tucker, A.T.; Thompson, R.; Melander, C.; Cavanagh, J. Anti-Biofilm Compounds Derived from Marine Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2010–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenye, T.; Brackman, G.; Rigole, P.; De Witte, E.; Honraet, K.; Rossel, B.; Nelis, H.J. Eradication of Propionibacterium Acnes Biofilms by Plant Extracts and Putative Identification of Icariin, Resveratrol and Salidroside as Active Compounds. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castronovo, L.M.; Vassallo, A.; Mengoni, A.; Miceli, E.; Bogani, P.; Firenzuoli, F.; Fani, R.; Maggini, V. Medicinal Plants and Their Bacterial Microbiota: A Review on Antimicrobial Compounds Production for Plant and Human Health. Pathogens 2021, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, A.; Abreu, A.C.; Dias, C.; Saavedra, M.J.; Borges, F.; Simões, M. New Perspectives on the Use of Phytochemicals as an Emergent Strategy to Control Bacterial Infections Including Biofilms. Molecules 2016, 21, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Biswas, K.; Jena, S.K.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Mohanta, T.K. Corrigendum: Anti-Biofilm and Antibacterial Activities of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by the Reducing Activity of Phytoconstituents Present in the Indian Medicinal Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Albuquerque, A.; Sampaio, F.; Keyson, D. Nanomaterials with Antimicrobial Properties: Applications in Health Sciences. 2013. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Nanomaterials-with-Antimicrobial-Properties%3A-in-Santos-Albuquerque/327a696eea04046991a26546bcccb1504e2b9297 (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Abraham, W.R. Controlling Pathogenic Gram-Negative Bacteria by Interfering with Their Biofilm Formation. Drug Des. Rev. 2005, 2, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandiran, V.; Shanmugam, K.; Anupama, K.; Thomas, S.; Princy, A. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Plant-Derived SdiA-Selective Ligands as Potential Antivirulent Agents against Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 48, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac Abraham, S.V.P.; Palani, A.; Ramaswamy, B.R.; Shunmugiah, K.P.; Arumugam, V.R. Antiquorum Sensing and Antibiofilm Potential of Capparis Spinosa. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izano, E.A.; Sadovskaya, I.; Vinogradov, E.; Mulks, M.H.; Velliyagounder, K.; Ragunath, C.; Kher, W.B.; Ramasubbu, N.; Jabbouri, S.; Perry, M.B.; et al. Poly-N-Acetylglucosamine Mediates Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in Actinobacillus Pleuropneumoniae. Microb. Pathog. 2007, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Singh, H.B.; Singh, A.; Singh, B.R.; Mishra, A.; Nautiyal, C.S. Lagerstroemia Speciosa Fruit Extract Modulates Quorum Sensing-Controlled Virulence Factor Production and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Microbiology 2012, 158, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K.; Parsek, M.R.; Greenberg, E.P.; Welsh, M.J. A Component of Innate Immunity Prevents Bacterial Biofilm Development. Nature 2002, 417, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trentin, D.D.S.; Giordani, R.B.; Zimmer, K.R.; Da Silva, A.G.; Da Silva, M.V.; Correia, M.T.D.S.; Baumvol, I.J.R.; MacEdo, A.J. Potential of Medicinal Plants from the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region (Caatinga) against Staphylococcus Epidermidis Planktonic and Biofilm Lifestyles. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeltawab, S.S.; Abu Haimed, T.S.; Bahammam, H.A.; Arab, W.T.; Abou Neel, E.A.; Bahammam, L.A. Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Action of Salvadora Persica Extract as Intracanal Medication (In Vitro and Ex Vivo Experiment). Materials 2022, 15, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidi, S.H.; Ahmed, K.; Sherwani, S.K.; Bibi, N.U.; Kazmi, S. Detection of Mycobacterium Smegmatis Biofilm and Its Control by Natural Agents. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 801–812. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, C.A.K.; Arnason, J.T. Mini Review of Phytochemicals and Plant Taxa with Activity as Microbial Biofilm and Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Molecules 2016, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.Y.; Dykes, G.A.; Choo, W.S. Biofilm Formation by Staphylococci in Health-Related Environments and Recent Reports on Their Control Using Natural Compounds. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.M. Plant Products as Antimicrobial Agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadelkareem, A.M.; Al-Shammari, E.; Elkhalifa, A.O.; Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Mahmood, D.; Azad, Z.R.A.A.; Patel, M.; Mehmood, K.; Danciu, C.; et al. Anti-Adhesion and Antibiofilm Activity of Eruca Sativa Miller Extract Targeting Cell Adhesion Proteins of Food-Borne Bacteria as a Potential Mechanism: Combined In Vitro-In Silico Approach. Plants 2022, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Das, R.; Lavigne, R.; Luyten, W. Indian Medicinal Plant Extracts to Control Multidrug-Resistant S. Aureus, Including in Biofilms. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 128, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkoub, N.; Panda, S.K.; Yang, M.R.; Lu, J.G.; Jiang, Z.H.; Nasri, H.; Luyten, W. Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Anti-Candida Biofilm Compounds from Methanol Extracts of the Aerial Parts of Salvia Officinalis (Annaba, Algeria). Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ćirić, A.D.; Petrović, J.D.; Glamočlija, J.M.; Smiljković, M.S.; Nikolić, M.M.; Stojković, D.S.; Soković, M.D. Natural Products as Biofilm Formation Antagonists and Regulators of Quorum Sensing Functions: A Comprehensive Review Update and Future Trends. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 120, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, G.; Bayston, R.; Costerton, W.B.; Shirtliff, M.E. The First European Congress on Microbial Biofilms: EUROBIOFILMS 2009, Rome, Italy, 2–5 September 2009. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Yin, B.; Qian, L.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, S. Screening for Novel Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors to Interfere with the Formation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Patel, M.; Deshpande, S.; Alreshidi, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Reddy, M.N.; Emira, N.; De Feo, V. Effect of Adiantum Philippense Extract on Biofilm Formation, Adhesion with Its Antibacterial Activities Against Foodborne Pathogens, and Characterization of Bioactive Metabolites: An in Vitro-in Silico Approach. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardi, J.d.C.O.; Freires, I.A.; Lazarini, J.G.; Infante, J.; de Alencar, S.M.; Rosalen, P.L. Unexplored Endemic Fruit Species from Brazil: Antibiofilm Properties, Insights into Mode of Action, and Systemic Toxicity of Four Eugenia Spp. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-sherbiny, G.M.; Moghannemm, S.A.; Sharaf, M.H. Antibacterial, antibiofilm, antioxidants and phytochemical profiling of Syzygium aromaticum extract. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Majik, M.S.; Naik, D.; Bhat, C.; Tilve, S.; Tilvi, S.; D’Souza, L. Synthesis of (R)-Norbgugaine and Its Potential as Quorum Sensing Inhibitor against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2353–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, R.M.; Branco-de-Almeida, L.S.; Franco, E.M.; Yatsuda, R.; dos Santos, M.H.; de Alencar, S.M.; Koo, H.; Rosalen, P.L. Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans Biofilm Accumulation and Development of Dental Caries in Vivo by 7-Epiclusianone and Fluoride. Biofouling 2010, 26, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, V.A.; Dos Santos, H.S.; Arruda, F.V.S.; Bandeira, P.N.; Albuquerque, M.R.J.R.; Pereira, M.O.; Henriques, M.; Cavada, B.S.; Teixeira, E.H. Casbane Diterpene as a Promising Natural Antimicrobial Agent against Biofilm-Associated Infections. Molecules 2011, 16, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, S.A.; Puligedda, R.D.; Szabo, P.; Nicastro, L.K.; Miller, A.L.; Qiu, C.; Gallucci, S.; Relkin, N.R.; Buttaro, B.A.; Dessain, S.K.; et al. Salmonella Typhimurium Biofilm Disruption by a Human Antibody That Binds a Pan-Amyloid Epitope on Curli. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.; Ilatovskiy, A.V.; Stewart, A.G.; Coleman, J.L.J.; McRobb, F.M.; Riek, R.P.; Graham, R.M.; Abagyan, R.; Kufareva, I.; Smith, N.J. Retraction Note: Orphan Receptor Ligand Discovery by Pickpocketing Pharmacological Neighbors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja Yahya, M.F.Z. Anti-Biofilm Potential and Mode of Action of Malaysian Plant Species: A Review. Sci. Lett. 2020, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Regmi, S.C.; Kim, J.A.; Cho, M.H.; Yun, H.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J. Apple Flavonoid Phloretin Inhibits Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Biofilm Formation and Ameliorates Colon Inflammation in Rats. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4819–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedler, E.; Uhlén, P. Frequency Decoding of Calcium Oscillations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Christophersen, L.; Calum, H.; Hentzer, M.; Hougen, H.P.; Rygaard, J.; Moser, C.; Eberl, L.; et al. Garlic Blocks Quorum Sensing and Promotes Rapid Clearing of Pulmonary Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infections. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3873–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjai, K.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S. Garlic Blocks Quorum Sensing and Attenuates the Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 58, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, T.; Hansen, T.H.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Skindersø, M.E.; Givskov, M.; Nielsen, J. Rational Design and Synthesis of New Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors Derived from Acylated Homoserine Lactones and Natural Products from Garlic. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.; Luís, Â.; Gradillas, A.; García, A.; Restolho, J.; Fernández, N.; Domingues, F.; Gallardo, E.; Duarte, A.P. Ayahuasca Beverages: Phytochemical Analysis and Biological Properties. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Chang, I.M.; Oh, K.B. Inhibition of the Bacterial Surface Protein Anchoring Transpeptidase Sortase by Medicinal Plants. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2751–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Kar, A.; Bhowmik, R.; Karmakar, S.; Tripathy, S.; Matsabisa, M.G.; Mukherjee, P.K. Quality Related Safety Evaluation of a South African Traditional Formulation (PHELA®) as Novel Anti-Biofilm Candidate. Molecules 2022, 27, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrecque, J.; Bodet, C.; Chandad, F.; Grenier, D. Effects of a High-Molecular-Weight Cranberry Fraction on Growth, Biofilm Formation and Adherence of Porphyromonas Gingivalis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, S.; Gregoire, S.; Singh, A.P.; Vorsa, N.; Schaich, K.; Bowen, W.H.; Koo, H. Inhibitory Effects of Cranberry Polyphenols on Formation and Acidogenicity of Streptococcus mutans Biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 257, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodet, C.; Grenier, D.; Chandad, F.; Ofek, I.; Steinberg, D.; Weiss, E.I. Potential Oral Health Benefits of Cranberry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Wu, Q.; Dang, M.; Bai, D.; Guo, Q.; Shen, L.; Duan, K. Inhibition of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm Formation by Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herb Herba Patriniae. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9584703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Ryu, S.Y.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. Ginkgolic Acids and Ginkg o Biloba Extract Inhibit Escherichia Coli O157: H7 and Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilm Formation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 174, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, T.; Cao, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X. Effects of Ginkgoneolic Acid on the Growth, Acidogenicity, Adherence, and Biofilm of Streptococcus Mutans in Vitro. Folia Microbiol. 2013, 58, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Dey, A.; Pandit, S.; Sarkar, T.; Pati, S.; Kari, Z.A.; Ishak, A.R.; Edinur, H.A.; et al. Phytocompound Mediated Blockage of Quorum Sensing Cascade in ESKAPE Pathogens. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, A.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Pillai, S.D.; Patil, B.S. Isolimonic Acid Interferes with Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Biofilm and TTSS in QseBC and QseA Dependent Fashion. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.W.; Luo, H.Z.; Jiang, H.; Jian, T.K.; Chen, Z.Q.; Jia, A.Q. Hordenine: A Novel Quorum Sensing Inhibitor and Antibiofilm Agent against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.W.; Hou, B.; Liu, G.Y.; Jiang, H.; Sun, B.; Wang, Z.N.; Shi, R.F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, R.; Jia, A.Q. Attenuation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm by Hordenine: A Combinatorial Study with Aminoglycoside Antibiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9745–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macé, S.; Truelstrup Hansen, L.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Anti-Bacterial Activity of Phenolic Compounds against Streptococcus Pyogenes. Medicines 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumari, J.; Meena, H.; Gangatharan, M.; Busi, S. Green Synthesis of Anisotropic Gold Nanoparticles Using Hordenine and Their Antibiofilm Efficacy against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, F.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Quercetin Is an Effective Inhibitor of Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczak, A.; Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M. Antibacterial Activity of Some Flavonoids and Organic Acids Widely Distributed in Plants. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Song, M.; Pan, J.; Shen, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Deng, X. Quercetin Impairs Streptococcus Pneumoniae Biofilm Formation by Inhibiting Sortase a Activity. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 6228–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Nikitkova, A.; Abdelsalam, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, J. Activity of Quercetin and Kaemferol against Streptococcus Mutans Biofilm. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 98, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, S.; Sharma, D.; Bisht, D.; Khan, A.U. Identification of Factors Involved in Enterococcus Faecalis Biofilm under Quercetin Stress. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.W.K.; Hägg, U.; Samaranayake, L.; Yuen, M.K.Z.; Seneviratne, C.J.; Kao, R. Antimicrobial Activity of Chinese Medicine Herbs against Common Bacteria in Oral Biofilm. A Pilot Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagani, S.; Chelikani, R.; Kim, D.S. Effects of Phenol and Natural Phenolic Compounds on Biofilm Formation by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Biofouling 2009, 25, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, D.P.; Salvia, A.C.R.D.; De Araújo, R.M.; Di Nicolõ, R.; Koga Ito, C.Y.; De Araujo, M.A.M. Effect of Green Tea Extract and Mouthwash without Alcohol on Candida Albicans Biofilm on Acrylic Resin. Gerodontology 2015, 32, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, A.; Kikuchi, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Yoshida, Y. The Inhibitory Effects of Mushroom Extracts on Sucrose-Dependent Oral Biofilm Formation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.J.; Cho, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.N.; Lim, Y.K.; Kook, J.K. The Antimicrobial Effects of Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice Root Extract on Streptococcus Mutans UA159 in Both Planktonic and Biofilm Cultures. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtyczka, R.D.; Kȩpa, M.; Idzik, D.; Kubina, R.; Kabała-Dzik, A.; Dziedzic, A.; Wa̧sik, T.J. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Polish Propolis against Biofilm Forming Staphylococcus Epidermidis Strains. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 590703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsenipour, Z. The Effects of Allium Sativum Extracts on Biofilm Formation and Activities of Six Pathogenic Bacteria. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e18971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, M.; Medioni, E.; Prêcheur, I. Inhibition of Candida Albicans Yeast-Hyphal Transition and Biofilm Formation by Solidago Virgaurea Water Extracts. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistyani, H.; Fujita, M.; Miyakawa, H.; Nakazawa, F. Effect of Roselle Calyx Extract on in Vitro Viability and Biofilm Formation Ability of Oral Pathogenic Bacteria. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatabadi, S.; Moghadam, H.N.; Mahdavi-Ourtakand, M. Evaluating the Anti-Biofilm and Antibacterial Effects of Juglans regia L. Extracts against Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.A.; Carson, C.F.; Riley, T.V. Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils and Other Plant Extracts. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 86, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekes, E.B.; Vidács, A.; Takó, M.; Petkovits, T.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Horváth, G.; Balázs, V.L.; Krisch, J. Anti-Biofilm Effect of Selected Essential Oils and Main Components on Mono- and Polymicrobic Bacterial Cultures. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, S.; Sattari, M.; Bigdeli, M. Effect of Cumin (Cuminum Cyminum) Seed Essential Oil on Biofilm Formation and Plasmid Integrity of Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2010, 6, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filoche, S.K.; Soma, K.; Sissons, C.H. Antimicrobial Effects of Essential Oils in Combination with Chlorhexidine Digluconate. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 20, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, M.; Hidalgo, W.; Stashenko, E.; Torres, R.; Ortiz, C. Essential Oils of Aromatic Plants with Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities against Pathogenic Bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuryastuti, T.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J.; Iravati, S.; Aman, A.T.; Krom, B.P. Effect of Cinnamon Oil on IcaA Expression and Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6850–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.M.M.; Brugnera, D.F.; do Nascimento, J.A.; Batista, N.N.; Piccoli, R.H. Cinnamon Essential Oil and Cinnamaldehyde in the Control of Bacterial Biofilms Formed on Stainless Steel Surfaces. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 234, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge Oral, N.; Vatansever, L.; Duman Aydin, B.; Sezer, C.; Güven, A.; Gülmez, M.; Başer, K.H.C.; Kürkçuoǧlu, M. Effect of Oregano Essential Oil on Biofilms Formed by Staphylococci and Escherichia Coli. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2010, 16, S23–S29. [Google Scholar]
- Gherasim, O.; Popescu, R.C.; Grumezescu, V.; Mogoșanu, G.D.; Mogoantă, L.; Iordache, F.; Holban, A.M.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Oprea, O.C.; et al. MAPLE Coatings Embedded with Essential Oil-conjugated Magnetite for Anti-biofilm Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filogônio, C.d.F.B.; Soares, R.V.; Horta, M.C.R.; Penido, C.V.d.S.R.; Cruz, R.d.A. Effect of Vegetable Oil (Brazil Nut Oil) and Mineral Oil (Liquid Petrolatum) on Dental Biofilm Control. Braz. Oral Res. 2011, 25, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanski, S.; Lipski, A. Essential Oils Show Specific Inhibiting Effects on Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Food Control 2013, 36, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, A.; Sblano, S.; Salvagno, L.; Carocci, A.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Corbo, F.; Fracchiolla, G. Anti-Biofilm Inhibitory Synergistic Effects of Combinations of Essential Oils and Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielian, E.S.; Shukarian, A.K.; Goukasova, G.I.; Chandanian, G.L.; Panossian, A.G.; Wikman, G.; Wagner, H. A Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Andrographis Paniculata Fixed Combination Kan Jang in the Treatment of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Including Sinusitis. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, M.; Moulick, S.; Bhattacharya, K.K.; Parai, D.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mukherjee, S.K. Attenuation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Quorum Sensing, Virulence and Biofilm Formation by Extracts of Andrographis Paniculata. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Bao, M.; Liu, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, C.; He, X.; Yi, J.; et al. Effect of Andrographolide and Its Analogs on Bacterial Infection: A Review. Pharmacology 2020, 105, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.B.; Mulks, M.H. Biofilm Formation Is Prevalent among Field Isolates of Actinobacillus Pleuropneumoniae. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 108, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzzaman, W.M.I.W.M.; Fekeri, M.F.M.; Nasir, N.A.M.; Hamidi, N.A.S.M.; Baharom, M.Z.; Adnan, A.; Shaifudin, M.S.; Abdullah, W.R.W.; Wan Nik, W.M.N.; Suhailin, F.H.; et al. Anticorrosive and Microbial Inhibition Performance of a Coating Loaded with Andrographis Paniculata on Stainless Steel in Seawater. Molecules 2021, 26, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Xuan, L.; Xu, Y.; Bai, D.; Zhong, D. Constituents from Polygonum Cuspidatum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczkowska-Walendowska, M.; Szymańska, E.; Winnicka, K.; Szwajgier, D.; Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Ruchała, M.A.; Simon, M.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Cyclodextrin as Functional Carrier in Development of Mucoadhesive Tablets Containing Polygoni Cuspidati Extract with Potential for Dental Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm-Stecher, B.F.; Johnson, E.A. Sensitization of Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli to Antibiotics by the Sesquiterpenoids Nerolidol, Farnesol, Bisabolol, and Apritone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3357–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packiavathy, I.A.S.V.; Sasikumar, P.; Pandian, S.K.; Veera Ravi, A. Prevention of Quorum-Sensing-Mediated Biofilm Development and Virulence Factors Production in Vibrio Spp. by Curcumin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 10177–10187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packiavathy, I.A.S.V.; Priya, S.; Pandian, S.K.; Ravi, A.V. Inhibition of Biofilm Development of Uropathogens by Curcumin—An Anti-Quorum Sensing Agent from Curcuma Longa. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.I.; Priya, A.; Balasubramaniam, B.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Sivasankar, C.; Selvaraj, A.; Valliammai, A.; Jothi, R.; Pandian, S. Biomedical Applications and Bioavailability of Curcumin—An Updated Overview. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Rodriguez, M.R.; Bernal-Mercado, A.T.; Gutierrez-Pacheco, M.M.; Vazquez-Armenta, F.J.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A.; Martinez-Tellez, M.A.; Nazzaro, F.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F. Virulence of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Exposed to Carvacrol: Alterations of the Quorum Sensing at Enzymatic and Gene Levels. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 13, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; Van Gennip, M.; Phipps, R.K.; Shanmugham, M.S.; Christensen, L.D.; Alhede, M.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Friedrich, K.; Uthe, F.; et al. Ajoene, a Sulfur-Rich Molecule from Garlic, Inhibits Genes Controlled by Quorum Sensing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; Warming, A.N.; Vejborg, R.M.; Moscoso, J.A.; Stegger, M.; Lorenzen, F.; Rybtke, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Petersen, R.; Andersen, P.S.; et al. A Broad Range Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Working through SRNA Inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Gu, S.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Wen, S.; Ge, J. The Effect of Emodin on Staphylococcus Aureus Strains in Planktonic Form and Biofilm Formation in Vitro. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Dai, Q.; Xiong, J.; Sheng, H.; Qiu, J.; Jiang, L.; Peng, J.; He, X.; et al. Allicin Inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence by Suppressing the rhl and pqs Quorum-Sensing Systems. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.C.; Sandhu, P.; Gupta, P.; Rudrapaul, P.; De, U.C.; Tribedi, P.; Akhter, Y.; Bhattacharjee, S. Attenuation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm Formation by Vitexin: A Combinatorial Study with Azithromycin and Gentamicin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahrioui, A.; Ortiz, S.; Azuama, O.C.; Bouffartigues, E.; Benalia, N.; Tortuel, D.; Maillot, O.; Chemat, S.; Kritsanida, M.; Feuilloley, M.; et al. Membrane-Interactive Compounds from Pistacia lentiscus L. Thwart Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabeldine, A.M.; Ashour, R.M.; Okba, M.M.; Saber, F.R. Callistemon Citrinus Bioactive Metabolites as New Inhibitors of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilm Formation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 254, 112669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, Z.; Tyulenev, A.; Muzyka, N.; Smirnova, G.; Oktyabrsky, O. Tannic and Gallic Acids Alter Redox-Parameters of the Medium and Modulate Biofilm Formation. AIMS Microbiol. 2019, 5, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Cao, F.; Ming, D.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhong, X.; Mu, D.; Li, B.; Zhong, L.; Cao, J.; et al. Aloe-Emodin Inhibits Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms and Extracellular Protein Production at the Initial Adhesion Stage of Biofilm Development. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6671–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, K.; Ramanathan, T. Musa Acuminata and Its Bioactive Metabolite 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Mitigates Quorum Sensing (Las and Rhl) Mediated Biofilm and Virulence Production of Nosocomial Pathogen Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Gong, H.; Xiao, H.; Petersen, R.B.; Zheng, L.; Huang, K. Inhibiting Toxic Aggregation of Amyloidogenic Proteins: A Therapeutic Strategy for Protein Misfolding Diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4860–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Fu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Efficacy of Chelerythrine against Mono-and Dual-Species Biofilms of Candida Albicans and Staphylococcus Aureus and Its Properties of Inducing Hypha-to-Yeast Transition of C. Albicans. J. Fungi. 2020, 6, 45, Retraction in 18 April 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeczko, M.; Masłyk, M.; Kubiński, K.; Golczyk, H. Emodin, a Natural Inhibitor of Protein Kinase CK2, Suppresses Growth, Hyphal Development, and Biofilm Formation of Candida Albicans. Yeast 2017, 34, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satputea, S.K.; Banpurkar, A.G.; Banat, I.M.; Sangshetti, J.N.; Patil, R.H.; Gade, W.N. Multiple Roles of Biosurfactants in Biofilms. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 1429–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gu, S.; Cui, X.; Shi, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, H.; Ge, J. Antimicrobial, Anti-Adhesive and Anti-Biofilm Potential of Biosurfactants Isolated from Pediococcus Acidilactici and Lactobacillus Plantarum against Staphylococcus Aureus CMCC26003. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Hamadou, W.S.; Ashraf, S.A.; Hassan, M.I.; Snoussi, M.; Badraoui, R.; Jamal, A.; Bardakci, F.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; et al. Functional and Structural Characterization of Pediococcus Pentosaceus-Derived Biosurfactant and Its Biomedical Potential against Bacterial Adhesion, Quorum Sensing, and Biofilm Formation. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, B.; Costantini, P.E.; Fedi, S.; Cappelletti, M.; Abruzzo, A.; Parolin, C.; Foschi, C.; Frisco, G.; Calonghi, N.; Cerchiara, T.; et al. Liposomes Containing Biosurfactants Isolated from Lactobacillus Gasseri Exert Antibiofilm Activity against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Strains. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, E.; Marchetti, A.; Ceresa, C.; Piccoli, F.; Anesi, A.; Nollo, G.; Caola, I.; Bosetti, M.; Fracchia, L.; Ghensi, P.; et al. Counter-Acting Candida Albicans-Staphylococcus Aureus Mixed Biofilm on Titanium Implants Using Microbial Biosurfactants. Polymers 2021, 13, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Al-Omar, M.S.; Mohammed, H.A.; Emam, T.M. In Vitro and Ex Vivo Antibiofilm Activity of a Lipopeptide Biosurfactant Produced by the Entomopathogenic Beauveria Bassiana Strain against Microsporum Canis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janek, T.; Drzymała, K.; Dobrowolski, A. In Vitro Efficacy of the Lipopeptide Biosurfactant Surfactin-C15 and Its Complexes with Divalent Counterions to Inhibit Candida Albicans Biofilm and Hyphal Formation. Biofouling 2020, 36, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, S.; Tofighi, Z.; Babaee, T.; Shamsi, M.; Rahimzadeh, G.; Rezvanifar, H.; Saeidi, E.; Amiri, M.M.; Ashtiani, Y.S.; Samadi, N. Evaluation of Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Biogenic Surfactants Derived from Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaji, N.; Ncib, K.; Bahia, W.; Ghorbel, M.; Leban, N.; Bouali, N.; Bechambi, O.; Mzoughi, R.; Mahdhi, A. Control of Multidrug-Resistant Pathogenic Staphylococci Associated with Vaginal Infection Using Biosurfactants Derived from Potential Probiotic Bacillus Strain. Fermentation 2022, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashitha, A.; Radhakrishnan, E.K.; Jyothis, M. Characterization of Biosurfactant Produced by the Endophyte Burkholderia Sp. WYAT7 and Evaluation of Its Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Potentials. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 313, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, L.P.; Castellane, T.C.L.; Polachini, T.C.; de Macedo Lemos, E.G.; Alves, L.M.C. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Pandoraea Shows Emulsifying and Anti-Biofilm Activities. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharahi, J.Y.; Azimi, T.; Shariati, A.; Safari, H.; Tehrani, M.K.; Hashemi, A. Advanced Strategies for Combating Bacterial Biofilms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14689–14708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpute, S.K.; Mone, N.S.; Das, P.; Banat, I.M.; Banpurkar, A.G. Inhibition of Pathogenic Bacterial Biofilms on PDMS Based Implants by L. acidophilus Derived Biosurfactant. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, N.; Shirzad, H.; Elahi, S.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Rahimian, G.; Shafigh, M.; Rashidii, R.; Sarafnejad, A.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Faridani, R.; et al. Downregulated Regulatory T Cell Function Is Associated with Increased Peptic Ulcer in Helicobacter Pylori-Infection. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz De Rienzo, M.A.; Stevenson, P.S.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Effect of Biosurfactants on Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms in a BioFlux Channel. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5773–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, F.; Alfatah, M.; Ganesan, K.; Bhattacharyya, M.S. Inhibitory Effect of Sophorolipid on Candida Albicans Biofilm Formation and Hyphal Growth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.V.G.; Nagakubo, T.; Toyofuku, M.; Nomura, N.; Utada, A.S. Synergy between Sophorolipid Biosurfactant and SDS Increases the Efficiency of P. Aeruginosa Biofilm Disruption. Langmuir 2020, 36, 6411–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.; Kumar, M. Anti-Biofilm Peptides: A New Class of Quorum Quenchers and Their Prospective Therapeutic Applications. In Biotechnological Applications of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9789811090264. [Google Scholar]
- Chalasani, A.G.; Roy, U.; Nema, S. Purification and Characterisation of a Novel Antistaphylococcal Peptide (ASP-1) from Bacillus sp. URID 12.1. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrour, H.; Ferrer-Espada, R.; Dandache, I.; Bárcena-Varela, S.; Sánchez-Gómez, S.; Chokr, A.; Martínez-de-Tejada, G. AMPs as Anti-Biofilm Agents for Human Therapy and Prophylaxis. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ageitos, J.M.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Calo-Mata, P.; Villa, T.G. Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): Ancient Compounds That Represent Novel Weapons in the Fight against Bacteria. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 133, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookherjee, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Davidson, D.J. Antimicrobial Host Defence Peptides: Functions and Clinical Potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, B.S.; Hanafiah, A.; Nachimuthu, R.; Muthupandian, S.; Md Nesran, Z.N.; Patil, S. The Role of Antimicrobial Peptides as Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Agents in Tackling the Silent Pandemic of Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecules 2022, 27, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascales, E.; Buchanan, S.K.; Duché, D.; Kleanthous, C.; Lloubès, R.; Postle, K.; Riley, M.; Slatin, S.; Cavard, D. Colicin Biology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 158–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrynyshyn, A.; Simões, M.; Borges, A. Biofilms in Surgical Site Infections: Recent Advances and Novel Prevention and Eradication Strategies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Somma, A.; Moretta, A.; Canè, C.; Cirillo, A.; Duilio, A. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Peptides. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y. Alternatives to Conventional Antibiotic Therapy: Potential Therapeutic Strategies of Combating Antimicrobial-Resistance and Biofilm-Related Infections. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 1103–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, I.; Özogul, F.; Regenstein, J.M. Industrial Applications of Crustacean By-Products (Chitin, Chitosan, and Chitooligosaccharides): A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; Von Bargen, K.; Haas, A.; Sahl, H.G. Insights into the Mode of Action of Chitosan as an Antibacterial Compound. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Deng, Y.; Yeh, C.K.; Sun, Y. Quaternized Chitosans Bind onto Preexisting Biofilms and Eradicate Pre-Attached Microorganisms. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 8518–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paz, L.E.C.; Resin, A.; Howard, K.A.; Sutherland, D.S.; Wejse, P.L. Antimicrobial Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticles on Streptococcus Mutans Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3892–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Cen, L.; Zhang, X.; Gao, P. ScienceDirect Loaded Chitosan / Alginate Multilayer on Titanium Substrates to Inhibit Biofilm Formation. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhaswaraj, P.; Barik, S.; Macha, C.; Chiranjeevi, P.V.; Siddhardha, B. Anti Quorum Sensing and Anti Biofilm Efficacy of Cinnamaldehyde Encapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa PAO1. LWT 2018, 97, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Ji, J.; Yuan, W.; Shen, J. Construction of Anti-Adhesive and Antibacterial Multilayer Films via Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Heparin and Chitosan. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6684–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkhilaishvili, T.; Winkler, T.; Müller, M.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. Bacteriophages as Adjuvant to Antibiotics for the Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00924-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Han, W.; Lei, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Y.; Song, J.; Lu, R.; et al. A Method for Generation Phage Cocktail with Great Therapeutic Potential. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, W.N.; Concepcion-Acevedo, J.; Park, T.; Andleeb, S.; Bull, J.J.; Levin, B.R. Synergy and Order Effects of Antibiotics and Phages in Killing Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).